Extended Response PPQs
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Describe how the structure of glycogen is related to its function
coiled so compact
Polymer of glucose so easily hydrolysed
branched so more ends for hydrolysis
glucose polymer so provides energy for respiratory substrate energy release
insoluble so does not affect water potential of the cell
Describe how the structures of starch and cellulose molecules are related to their functions
Starch:
Helical/coiled so compact
Large/ insoluble so does not affect water potential of the cell
Branched so glucose is easily released for respiration
Large so cannot leave cell
Cellulose:
Long, straight chain of beta glucose
joined by hydrogen bonding
forms microfibrils
provides strength
Describe how the structure of a protein depends on the amino acids it contains
determined by the position R group/interactions (bonding)
Primary structure is the order and sequences of amino acids
Secondary structure is the folding into alpha helix or beta pleated sheet with hydrogen bonding
Tertiary structure formed by further folding into 3D shapes with hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions
Quaternary structure is folding of one or more polypeptide chain
Creates active site in enzymes
Compare and contrast the structure AND properties of triglycerides and phospholipids
Both contain ester bonds
Both contain glycerol
Fatty acids on both may be saturated or unsaturated
Both insoluble in water
Both contain C, H, O but phospholipids also contain P
Triglycerides has 3 fatty acids and phospholipid has 2 with a phosphate group
Triglycerides are fully hydrophobic and phospholipids have hydrophilic and hydrophobic region
Phospholipids form monolayer in water but triglycerides don’t
Explain why maltase:
only breaks down maltose
allows this reaction to take place at normal body temperature
Tertiary structure/ 3D shape of an enzyme
Active site is specific to maltose
Induced fit model (substrate mostly complimentary to active site but active site changes shape to fit substrate)
Enzyme is a catalyst
Forming enzyme-substrate complexes
Describe competitive and non-competitive inhibition of an enzyme
Inhibitors prevent formation of enzyme-substrate complexes
Competitive:
Inhibitor similar shape to substrate
Binds in active site
Can be overcome by more substrate
Non-competitive:
Inhibitor binds to allosteric site of enzyme
Changes the shape of the active site
Cannot be overcome by adding more substrate
Describe the role of the enzymes of the digestive system in the complete breakdown of starch
Amylase
Starch to maltose
Maltase
Maltose to glucose
Hydrolysis
Glycosidic bond
Describe the structure of DNA
Polymer of nucleotides
Each nucleotide formed from deoxyribose, phosphate and nitrogenous base
Phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides
Double helix held by hydrogen bonds
Between adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine
Contrast how optical and transmission microscopes work AND contrast limitations of each
TEM use electrons and optical use light
TEM allows greater resolution
Smaller organelles can be observed
TEM view only dead and optical can view live specimens
TEM does not show colour and optical can
TEM requires thinner specimens
TEM requires a more complex staining process
TEM focuses on using magnets and optical uses lenses
Contrast the structure of a bacteria cell and the structure of a human cell
Bacteria cell much smaller than human cell
Bacteria cell has a cell wall but a human does not
Bacteria cells does not have a nucleus but a human cell does
Bacteria lack membrane-bound organelles but human ell has membrane-bound organelles
Bacterial ribosomes 70s whilst human cells have 80s
Bacterial DNA is circular but human DNA is linear
Bacterial DNA not bound to histone proteins whilst human DNA is
Name and describe 5 ways substances can move across cell surface membrane into cell
Simple diffusion of small non-polar molecules down a concentration gradient
Facilitated diffusion down a concentrate gradient via proteins (channel/carrier)
Osmosis of water down a water potential gradient
Active transport against a concentration gradient via protein carrier using ATP
Co-transport of 2 different substances using a carrier protein
Explain how the transport of Na+ is involved in the absorption of glucose by epithelial cells
Na+ leave epithelial cells and enter blood
By active transport via Na+ / K+ pump
Na+ conc. in cell lower than lumen
Na+ enter via facilitated diffusion
Glucose absorbed with Na+ against concentration gradient, glucose absorbed down an electrochemical gradient
Describe the behaviour of chromosomes during mitosis and explain how this results in two genetically identical cells
Chromosomes shorten and thicken
Two identical chromatids due to replication
Chromosomes more to equator
Attach to individual spindle fibres
Spindle fibres contract/ centromere divides
Sister chromatids more to opposite poles of the cell
Each pole receives identical copies of each chromosome
Nuclear envelopes forms around each group of chromosomes
Describe how phagocytic white blood cells destroy bacteria
Phagocyte attracted to bacteria by chemicals/ recognise bacteria as foreign
Engulf bacteria
Bacteria in vesicle
Lysosome fuses with vesicle producing phagolysosome
Bacteria digested by lysozymes
Describe how vaccination can lead to protection against bacterial meningitis
Antigen binds to surface protein on specific B cell
B cell divides by mitosis during clonal expansion
This is stimulated by cytokines/ T cells
Plasma B cells produce antibodies
Some B cells become memory B cells
Memory B cells produce antibodies faster
Describe the difference between active and passive immunity
Active involves memory cells, passive does not
Active involves production of antibodies by plasma cells
Passive involves antibody introduced into body from outside
Active, long term, because antibody produced in response to antigen
Passive, short term, because antibody is broken down
Active can take time to develop, passive fast acting
Describe how the structure of the insect gas exchange system:
Provides cells with sufficient oxygen
limits water loss
Spiracles, tracheae, tracheoles
Spiracles allow diffusion of oxygen through tracheae and tracheoles
Tracheoles highly branches so large surface area for gas exchange
Tracheole walls thing so short diffusion distance
Tracheole walls are permeable to oxygen
Chitin exoskeleton so reduce water loss
Spiracles close so less water loss
Hairs around spiracles reduce water loss
Describe how humans breathe in and out
Breathing in:
Diaphragm muscle contracts and flattens
External intercostal muscles contract and ribs pulled up
Volume increases and pressure decreases in thoracic cavity below atmospheric pressure
Breathing out:
Diaphragm muscle relaxes and raises
External intercostal muscles relax and ribcage moves in
Volume decrease and pressure increases in thoracic cavity above atmospheric pressure
Explain how ventilation mechanism of a fish and structure of its gill result in the efficient uptake of oxygen from water
Gill filaments/ lamellae, large surface area
Large no. of capillaries, to maintain concentration gradient
thin epithelium, short diffusion pathway
pressure changes, to maintain concentration gradient
counter current flow, concentration gradient maintained across the whole length of the lamella
Describe the processes involved in absorption and transport of digested lipid molecules from ileum to lymph
micelles contain bile salts and fatty acids/ monoglycerides
bring monoglycerides to the cell lining
Monoglycerides absorbed by diffusion
Triglycerides reformed in cells
Vesicles move to the cell membrane
Explain how the heart muscle and valves maintain a one-way flow of blood from left atrium to aorta
Atrium has higher pressure than ventricle due to contraction causing atrioventricular valves to open
Ventricle has higher pressure than atrium due to contraction causing atrioventricular valves to close
Ventricle has higher pressure than aorta causing semi-lunar valve to open
Higher pressure in aorta than ventricle as heart relaxes causing semi-lunar valve to close
Atrial/ventricular contraction causes increase in pressure
Explain how tissue fluid is formed and how it may be returned to circulatory system
High hydrostatic pressure of blood at arterial end
Water/ soluble molecules pass out
Proteins/ large molecules remain
Lowers the water potential in the blood
Water moves back into venous end of capillary by osmosis
Lymph system collects any excess tissue fluid which returns to blood
Describe the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem
Water lost from leaf because of transpiration/ evaporation of water
Lowers water potential of mesophyll
Water pulled up from xylem creating tension
Cohesion of water molecules by hydrogen bonds
Forming continuous column of water
Adhesion of water to walls of xylem
Describe the process involved in the transport of sugars in plant stems
At source, sucrose is actively transported into phloem/sieve tube element
By companion cells
Lowers water potential in phloem and water enters by osmosis
Leads to high hydrostatic pressure
Mass flow to wards sink
At sink, sugars are removed/ unloaded
Describe how mRNA is formed by transcription in eukaryotes
Hydrogen bonds break
One DNA strand acts as a template
RNA nucleotides align by complimentary base pairing
Uracil base pairs with Adenine
RNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides together
By phosphodiester bonds
Pre-mRNA is spliced/ introns are removed
Describe how a polypeptide is formed by translation of mRNA
mRNA attaches to ribosomes
Anticodons bind to complimentary mRNA codons
tRNA brings a specific amino acid
Amino acids join by peptide bonds
With the use of ATP
tRNA released
Ribosom moves along mRNA to form the polypeptide
Describe how meiosis causes variation and explain advantage of variation to the species
Crossing over of non-sister chromatids
Independent segregation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I
Independent segregation of homologous chromatids in meiosis II
Different adaptations
Some survive
To reproduce
Can pass on gene/allele
Allows for changing environment
Explain how a high density of species can occur in one area
No interbreeding/ gene pools are separate/ geographical isolation
Mutation
Different selection pressures (food/ niches/ habitats etc)
Adapted organisms survive and breed
Increases in allele frequencies
Describe how you could estimate the size of a population of sundews in a small marsh
Use tape measures to form a grid
Use a random number generator to generate co-ordinates
Place quadrate at co-ords and count number of sundews in quadrat
Repeat many times for a large sample and calculate mean
mean no. of sundews per quadrat x area of the marsh
Describe how you could use the mark-release-capture method to estimate number of lizards on an island
Capture sample, mark and release
Methods of marking does not harm lizard or make it more visible to predators
Leave sufficient time for lizards before collecting a second sample
Population = (no. in first sample x no. in second sample) / no. marked in second sample
Describe how a scientist should collect and process data from seeds to investigate whether there is a difference in seed size between these two populations of trees.
Use random samples of seeds
Use large sample so representative of the whole population
Measuring mass of seed
Calculate a mean and standard deviation for each population
Use student t-test
Analyse whether differences are significant between the means of the two populations
Describe the light-dependent reaction
Chlorophyll absorbs light energy
Electrons become excited and are removed from chlorophyll
Electrons move along electron transport chain releasing energy
Energy used to join ADP and Pi to form ATP
Photolysis of water produces protons, electrons and oxygen
NADP reduced to NADPH by gaining electrons
How is CO2 converted into organic substances during the light-independent reaction
CO2 combines with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
Produces 2 x glycerate 3-phosphate (GP)
GP reduced to triose phosphate TP
Using NADPH
Using energy from ATP
5/6 TP regenerated into RuBP, 1/6 TP converter into glucose
Describe how ATP is made in the mitochondria
ATP produced in the Krebs cycle
Krebs/ Link reaction produce NADH and FADH
Electrons release from NADH and FADH
Electrons pass along electron transport chain through series of redox reactions
Energy is released
ADP + Pi
H+ move into intermembrane space
ATP synthase
Describe and explain how succession occurs
Colonisation by a pioneer species
Change in environment
Enable other species to colonise and survive
Change in biodiversity
Conditions become less hostile
Climax community
Explain how nitrate may cause death of fish in fresh water
Algal bloom blocks light
No photosynthesis so aquatic plants die
Saprobionts
Aerobically respire and use oxygen in respiration
SO less oxygen available for fish to respire
Explain how farming practices increase the productivity of agricultural crops
Fertilisers and ions are added to the soil
Nitrates and Phosphates used by the plant to make ATP and DNA for growth
Selective breeding/ GMO crops
Ploughing decreases denitrification
Crop rotation as left over nitrates from last harvest can be used by new crops
Describe how the action of microorganisms in the soil produce a source of nitrates for crop plants
DNA/ amino acids into ammonia
BY saprobionts
Ammonia into nitrite
Nitrite into Nitrate
By nitrifying bacteria
Nitrogen to ammonia
By nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Describe the sequence of events involved in transmission across a cholinergic synapse
Action potential arrives at presynaptic membrane
Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enter
Vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release acetylcholine
Acetylcholine diffuses across synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the post synaptic membrane
Na+ enter and cause a new action potential in the post synaptic membrane
Describe how the cardiac cycle is controlled by the SAN and the AVN
SAN initiates a heartbeat
SAN sends impulses across atria causing atria contraction
AVN delays
Allowing atria to empty before ventricles contract
Sends impulses down bundle of His and Purkyne tissue
Causing the ventricles to contract from base up
Explain how a rise in blood pressure results in a decrease in the rate of a heartbeat
Baroreceptors
Send impulses to medulla
via parasympathetic neurone
to SAN
release of acetylcholine decreases impulse form SAN
Leads to decrease of impulses to AVN
Describe the roles of Ca2+ and ATP in the contraction of a myofibril
Ca2+ diffuse into the myofibrils from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Causes movement of tropomyosin on actin
Exposes the binding site on the actin
Myosin heads attach to binding sites on the actin
Hydrolysis of ATP on mysosin heads causes heads to bend
Pulling actin molecules
Attachments of new ATP molecule to each myosin head causes the heads to detach from actin sites
Describe how ultrafiltration produces glomerular filtrate
High hydrostatic pressure
Small molecules e.g water
Pass through basement membrane and the basement membrane acts as a filter
Proteins that are too large remain and are not filtered out
Through pores in capillaries
How does having a long loop of Henle and large amounts of ADH benefit organisms in desert conditions
In general:
More water reabsorbed from filtrate
By osmosis
from collecting duct
Due to longer loop of Henle
For loop of Henle:
Sodium and chloride ions absorbed from filtrate in ascending limp
Gradient established in medulla
For ADH:
Acts on collecting duct and distal convoluted tubule
Makes cells more permeable by adding more aquaporins in plasma membranes
Explain the role of the loop of Henle in the absorption of water from the filtrate
In ascending limp, Na+ actively removed
Ascending limo impermeable to water
In descending limp, Na+ diffuse in
Descending limb permeable to water
Low water potential in medullaThe longer the loop, the lower the water potential in medulla
Water leaves collecting duct/ DCT
By osmosis down a water potential gradient
How can two species of palm tree arise by sympatric speciation
Occurs in the same habitat
Mutations can cause different flowering times
Reproductive isolation so gene pools remain separate
Change in frequency of alleles as different alleles are passed on
Disruptive natural selection
Eventually species cannot interbreed to produce fertile offspring
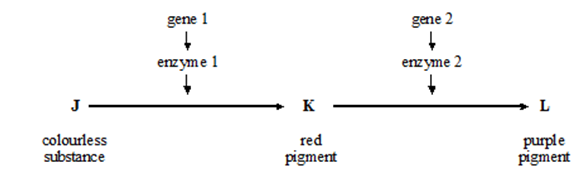
Gene 1: Aa Gene 2: Bb
Explain how the two genes are incvolved in producing white, red or purple flowers
Alleles A makes enzyme converting colourless to red
Allele a produces a non-functional enzyme
Allele B makes enzyme converting red to purple
Allele b produces a non-functional protein
White flowers result from a genotype aa
colourless produces white
Red flowers when A_bb only
Purple flowers when A_B_ enzymes 1 & 2
Describe how bacteria may be produces which have the resistance gene in their plasmids from oat plants
Cut desired gene from DNA of oat plant/ use mRNA from oat which code for resistance/ make artificial DNA with correct sequence of bases
Using restriction endonucleases/ and use reverse transcriptase to form desired DNA/ using DNA polymerase
Cut plasmids open
With the same restriction endonuclease
Leaves sticky ends
Use DNA ligase to join
Return plasmid to bacteria cell
Describe how PCR is carried out
DNA heated to 95°C
Strands separate
Cooled to 55°C
Primers bind
Nucleotides attach
By complimentary base pairing
Increase temperate to 72°C
DNA polymerase joins nucleotides together
Cycle repeated
Describe how a gene could be removed from cells of an amaranth plant and inserted into cells of a potato plant
Cute gene using restriction endonucleases
At recognition site
Leaves sticky ends
Use the same enzyme to cut
Plasmid/ potato DNA
Fixed by ligase
Vector e.g. virus to inject DNA
remove plant cell wall