DTM
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
Stage 1
Low population
No growth
High birth rate-no knowledge of family planning
High death rate-High infant and child mortality.
poor access to medical care
Low life expectancy- poor nutrition and disease.

Stage 2
Rapidly growing population
High birth rate-Lack of contraception
Falling death rate- have access to improved medical care and more children survive because of national vaccination programmes.
More access to food, and less people die from infectious disease.
Education is still low, many girls are left out of school and marry young.

Stage 3
High growing population
population growth begins to slow down -due to improved education
Falling birth rate-slows down due to improved education
Low death rate
Higher life expectancy-medical provision and nutrition have continued to improve.
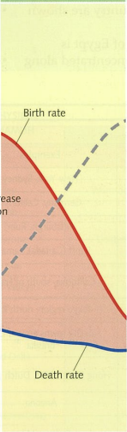
Stage 4
High population
Low birth rate
Low death rate
High life expectancy -excellent health care
Family size is small as people prefer fewer children-due to work pressures and more leisure time.
Women have full careers and marriage and children is put back to a much later age.
Some fluctuation in birth rate due to generational differences.

Stage 5
Falling population
Low death rate
Low birth rate - Increasingly people choose not to have children.
Death rate > birth rate
Increasing death rates=population size begins to fall.-ageing population
