biological molecules
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Symbol and role of calcium
Ca 2+ involved in muscle contraction and impulse transmission
Symbol and role of sodium
Na+ involved in
Co-transport
Reabsorption of water in kidneys
Regulating water potential
Nerve impulse transmission
Symbol and role of potassium ions
Involved in
Stomatal opening
Nerve impulse transmission
Symbol and role of hydrogen ions
H+
Involved in chemiosmosis
Regulating ph
translocation
Symbol and role of ammonium ions
NH4 +
Involved in
Nitrgen cycle where bacteria convert ammonium ions into nitrate ions
Symbol and role of nitrate ions
NO3-
Mineral ion absorbed by plants to form amino acids
Symbol and role of hydrogencarbonate
HCO3-
Involved in
Transport of carbon dioxide in blood
Symbol and role of chloride ions
Cl-
Involved in
Transport of co2 round blood as they balance positive charges
Symbol and role of phospate
Po4 3-
Involved in
Formation of phopolipids for cell membranes
Nucleic acid
Atp formation
Symbol and role of hydroxide ions
OH-
Involved in
Catalysis of reactions
Regulating pH
What type of molecule is water and why
Water is polar due to unevenly distributed charges
Bonds in water
Hydrogen bonds formed between oxygen (negative) and hydrogen (positive)
Properties of water
Solvent
Transport medium
Coolant
Provides habitat
Water as a solvent
As water is polar it will attract other polar molecules
Hydrogen attracts negative and oxygen attracts negative
Water as a transport medium
Water molecules are cohesive meaning as water moves up a xylem it makes a continou column
Water as a coolant
Water has a high specific heat capacity meaning lots of energy is needed to raise temperature of water due to hydrogen bonds
Water as a habitat
Due to high shc aNd latent heat water wont change temperatures easily (allows for enzymes to not denature)
Due to cohesion water has surface tension which allows small invertebrates to lie on surface away from predators
Ice is less dense than liquid meaning ice floats insulating water
What is a monomer
Smaller units that can create larger molecules
What is a polymer
Made from lots of monomers bonded togheter
What polymes does glucose form
Starch, cellulose, glycogen
What monomer is starch cellulose and glycogen are out of
glucose
What polymer does amino acids form
Protein
What monomer is protein made out of
Amino acid
What polymer does nucleotides form
DNA and RNA
What monomer is DNA and RNA formed from
nucleotides
Examples of monosaccarides
Glucose
Ribose
Fructose
Galactose
Examples of disaccarides
Sucrose
Maltose
lactose
Examples of polysaccarides
Starch
Cellulose
glycogen
Structure and formula of alpha glucose
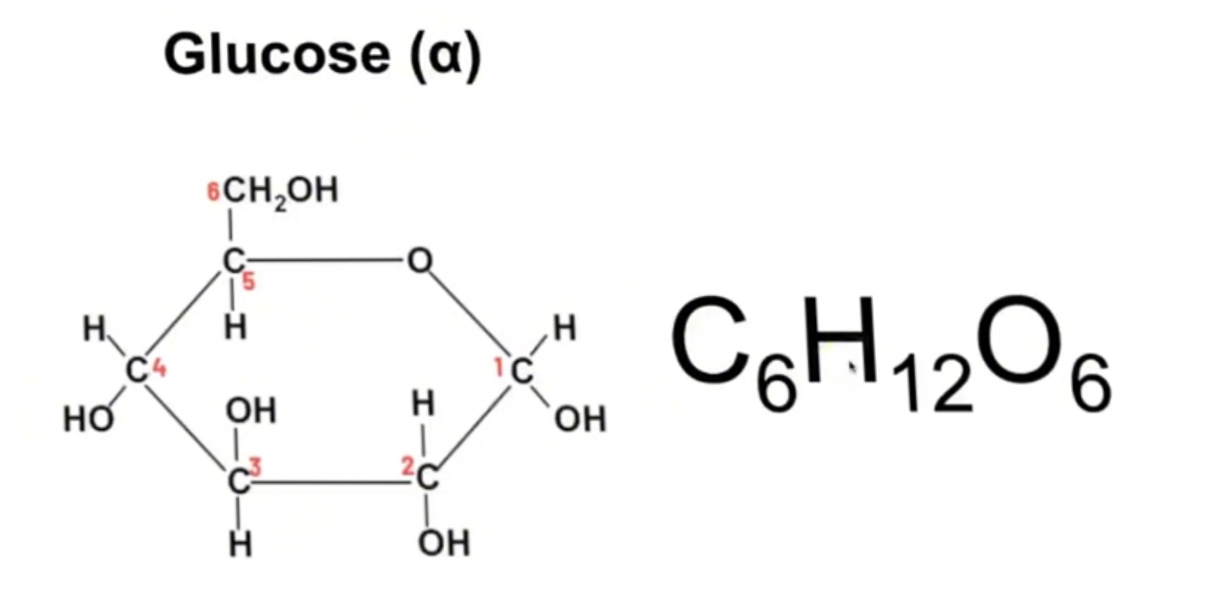
What is an isomer
Same molecular formula but different structure
Difference between alpha and beta glucose
Beta glucose has hydrogen on the bottom
What type of sugar is ribose
Pentose as it has 5 carbons
Definition of disaccharides
Made of two monosaccharides
Type of bond in disaccarides and how it is formed
Glycosidic bond
Formed via a condensation reaction
How is maltose made
Alpha glucose + alpha glucose
Alpha glucose + alpha glucose =
maltose
beta glucose + galactose =
lactose
What two monosaccarides form lactose
Beta Glucose + galactose
What two onosaccardies form sucrose
Glucose + fructose
Glucose + fructose =
sucrose
What is a condensaton reaction
Joining two molecules togheter by removing water
What is a hydrolysis reaction
Splitting apart molecules through the addition of a water molecu
What monomer is starch made from
Alpha glucose
What 2 polymers make up starch
Amylose and amylopectin
What are the bonds in starch
1-4 glycosidic bond in amylose
1-6 glycosidic bond in amylopectin
What is the function of starch
Store of glucose
Where is starch found
Plant cells
What is the structure of starch
Amylose which is an unbranched helix
and
amylopectin which is a branched moelcule
How does structure of starch lead to the function
Helix can compact a lot of glucose in small space
Branched structure allows for rapid hydrolysis back to glucose
It is insoluble- wont affect water potential
What is the monomer in cellulose
Beta glucose
Bonds found in cellulose
1-4 glycosidic bonds
Function of cellulose
Structure strength for cell wall
Where
Structure of cellulose
Forms long straight chain
Chains are held parallel by many hydrogen bonds which form fibrils
How does structure lead t function
Many hydrogen bonds provide collecive strength
Insoluble meaning it won affect water potential
Monomer in glycogen
Alpha glucose
Bons between monomers
1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Function of glycogen
Store of glucose
Loation of glycogen
Animals - mainly in muscle and liver cells
Structure of glycogen
A highly branched molecule
How does structure lead to function
Branched structure means higher surface area for quick hydrolysis
Insoluble-wont affect water potential
What are lipids
They are macromolecules but not polymers
Lipids and solubility
They are non polar meaning they are insoluble in water this means they are hydrophobic
What are lipids made of
Fatty acids and glycerol
Bonds between glycerol and fatty acids
Ester bonds are formed between glycerol and a fatty acid where water is removed
What is a saturated fatty acid
The hydrocarbon chain has only single bonds between carbons
What is unsaturated fatty acid
The hydrocarbon chain has at least one double bond between carbons
Properties of triglycerides-energy
Can transfer energy due to many carbon hydrogen bonds compared to carbon atoms
Properties of tryglycerides - water
Due to lots of hydrogen and oxygen atoms they can act as a metabolic water source when oxidised
Properties of tryglycerides- insolubility
They are non polar meaning they are hydrophobic meaning they wont affect water potential and osmosis
Lipids - storage
They are low n mass meaning a lot can be stored in animals
What is a phospholipid made of
Made of glycerol molecule, two fatty acids and a phophate group bonded to glycerol
Properties of phospholipids
Hydrophillic head of phospholipid can atarct with water as it is charged and it reepels other fats
The fatty acid chain is not charged meaning it il repel water but mix with other fats
Phospholipid bilayer and how it works
It has two charged regions meaning it is charged
In water heads are exposed while tails are not
This makes a membrane structure which makes up plasma membrane in cells
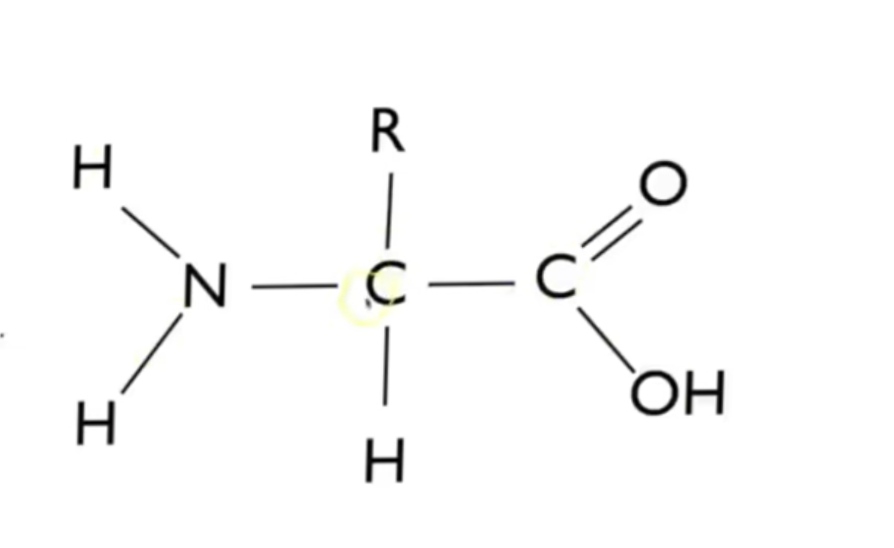
Structure of amino acids
4 stages of protein structure
Primary-the sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain
Secondary structure- sequence of amino acids causes parts of protein molecule to bend into alpha helix or beta pleated sheets. Hydrogen bonds hold the secondary structure
Tertiary structure - second structure is bent and folded to form 3d shape
-hydrophobic/phillic interactions
-hydrogen bonds
-Ionic bonds
-Disulfide bonds
Quaternary - a protein made up of more than one polypeptide chain
Fibrous proteins
-Polypeptide chains form long twisted strands
-stable structure
-Insoluble in water
-strength gives structural function
Globular protein
Spherical shape
Relatively unstable
Metabolic function
Examples of fibrous proteins
Collagen
Keratin
Elastin
Examples of globular protein
Haemoglobin
Enzymes
Insulin
Test for starch
-Add iodine
Positive= orange to blue black
Test for reducing sugar
-add Benedict solution and heat for 5 minutes at 80c
Positive= blue to red
Non reducing sugars
-add HCl and boil
-add alkali to neutralise
-add Benedict and heat for 5 minutes at 80
-blue to red
Test for proteins
-add biuret solution
Blue to purple
Test for lipids
Dissolve in Ethanol
Pour on top of distilled water
White emulsion
Purines structure and names
2 carbon ring structure
Adenine and guanine
Pyramidene structure and exanple
1 carbon ring
Cytosine thymine uracil
Bond in nucleotides
Condensation reaction to form phosphodiester bonds between pentose sugar and phosphate
Atp structure and function
Contains 3 phosphate ions
Essential for metabolism
-Immeadite source of energy
-Adenine , ribose, 3 inorganic phosphate groups
Function and structure of dna
Codes for sequence of amino acid
Polymer formed from double helix made of two antiparallel strands
How DNA structure links to function
-Stable structure due to sugar phosphate backbone and double helix
DNA precipitation
Break cell membranes with detergent
-filter to remove large debris
-add salt to break hydrogen bonds
-add protease
Add cold ethanol to precipate out the DNA
Types of rna
mRNA
Trna
Rrna
Mrna
Copy of one gene from DNA
Created in nucleus leaves via pores to ribosome
Every 3 bases (codon one amino acid)
Trna
Single stranded
Brings amino acid to ribosome
Determined by anticodon on trna
Semi conservative DNA replication
One strand is conserved and one new strand is created
Stages of DNA replication
DNA helicase breaks hydrogen bonds causing double helix to unwind
Both strands act as a template
Free DNA nucleotides align opposite their complementary base on the on template strand. Hydrogen bonds form
DNA polymerase joins sugar phosphate backbone
The genetic code
Degenerate amino acids r coded by more than one triplet base
Universal:same triplet of bases codes for same amino acids in all organisms
Transcription
DNA sequence for one gene is copied into mrna
Translation
mRNA joins with ribosome and corresponding trna molecule brings amino acid on codon it codes for