exam 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/324
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
325 Terms
1
New cards
organ
structure with discrete boundaries that is composed of 2 or more tissue types
2
New cards
histology
\-microscope anatomy
\-the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs
\-the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs
3
New cards
tissue
a group of similar cells and cell products working together to perform a specific role in an organ
4
New cards
how do tissues differ from each other
\-types and functions of their cells
\-characteristics of the matrix
\-relative amount of space occupied by cells vs matrix
\-characteristics of the matrix
\-relative amount of space occupied by cells vs matrix
5
New cards
matrix
\-extracellular material
\-composed of fibrous proteins & ground substance
\-composed of fibrous proteins & ground substance
6
New cards
ectoderm
\-outer
\-gives rise to epidermis and nervous sysytem
\-gives rise to epidermis and nervous sysytem
7
New cards
endoderm
\-inner
\-gives rise to mucous membrane lining digestive and respiratory tracts, digestive glands, among other things
\-gives rise to mucous membrane lining digestive and respiratory tracts, digestive glands, among other things
8
New cards
mesoderm
\-middle
\-becomes gelatinous tissue called mesenchyme
\-whispy collagem fibers and fibroblasts in gel matrix
\-gives rise to cartilage, bone, blood, and muslce
\-becomes gelatinous tissue called mesenchyme
\-whispy collagem fibers and fibroblasts in gel matrix
\-gives rise to cartilage, bone, blood, and muslce
9
New cards
longitudinal section
tissue cut on its long axis
10
New cards
cross section
\-transverse section
\-tissue cut perpendicular to long axis of organ
\-tissue cut perpendicular to long axis of organ
11
New cards
oblique section
tissue cut at angle between cross and longitudinal sections
12
New cards
smear
tissue is rubbed across a slide
13
New cards
spread
some membranes and cobwebby tissues are laid out on a slide
14
New cards
epithelial tissue
\-sheets of closely adhering cells, one or more cells thick
\-covers body surfaces and lines body cavities
\-upper surface usually exposed to the environment or an internal space in the body
\-constitutes most glands
\-avasular
\-almost no matrix
\-covers body surfaces and lines body cavities
\-upper surface usually exposed to the environment or an internal space in the body
\-constitutes most glands
\-avasular
\-almost no matrix
15
New cards
epithelial tissue functions
\-protect depper tissues from injury and infection
\-produce and release chemical secretions
\-excrete waste
\-absorb chemicals including nutrients
\-selectively filter substances
\-sense stimuli
\-produce and release chemical secretions
\-excrete waste
\-absorb chemicals including nutrients
\-selectively filter substances
\-sense stimuli
16
New cards
basement membrane
\-layer between an epithelium and underlying connective tissue
\-collagen, reticular proteins, glycoproteins, other proteins (carbohydrate complexes)
\-anchors the epithelium to the connective tissue below it
\-collagen, reticular proteins, glycoproteins, other proteins (carbohydrate complexes)
\-anchors the epithelium to the connective tissue below it
17
New cards
basal surface
surface of epithelial cell facing the basement membrane
18
New cards
apical surface
surface of epithelial cell that faces away from the basement membrane
19
New cards
simple epithelia
\-contain one layer of cells
\-named by shape of cells
\-all cells touch basement membrane
\-named by shape of cells
\-all cells touch basement membrane
20
New cards
stratified epithelia
\-contain more than one layer
\-named by shape of apical cells
\-some cells rest on top of other and don’t touch basement membrane
\-named by shape of apical cells
\-some cells rest on top of other and don’t touch basement membrane
21
New cards
goblet cells
wineglass-shaped mucus-secreting cells in simple columnar and pseudostratified epithelia
22
New cards
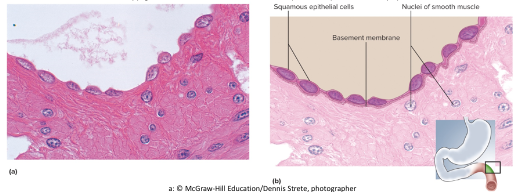
simple squamous epithelium
\-sinlge row of thin cells
\-permits rapid diffusion or transport of substances
\-secretes serous fluid
\-locations: alveoli, glomeruli, endothelium, and serosa
\-permits rapid diffusion or transport of substances
\-secretes serous fluid
\-locations: alveoli, glomeruli, endothelium, and serosa
23
New cards
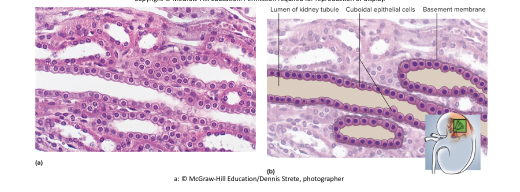
simple cuboidal epithelium
\-single layer of square or round cells
\-absorption and secretion, mucus production and movement
\-locations: liver, thyroid, mammary and salivary glands, bronchioles, and kidney tubules
\-absorption and secretion, mucus production and movement
\-locations: liver, thyroid, mammary and salivary glands, bronchioles, and kidney tubules
24
New cards
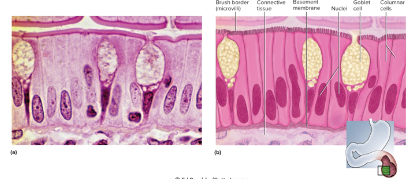
simple columnar epithelium
\-single row of tall, narrow cells
\-oval nuclei in basal half of cell
\-brush border of microvilli, ciliated in some organs, may possess goblet cells
\-absorption and secretion of mucus
\-locations: lining of GI tract, uterus, kidney, and uterine tubes
\-oval nuclei in basal half of cell
\-brush border of microvilli, ciliated in some organs, may possess goblet cells
\-absorption and secretion of mucus
\-locations: lining of GI tract, uterus, kidney, and uterine tubes
25
New cards
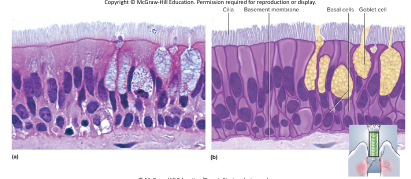
pseudostratified epithelium
\-looks multilayered, but all cells touch basement membrane
\-nuclei at several layers
\-has cilia and goblet cells
\-secretes and propels mucus
\-locations: respiratory tract and portions of male urethra
\-nuclei at several layers
\-has cilia and goblet cells
\-secretes and propels mucus
\-locations: respiratory tract and portions of male urethra
26
New cards
stratified epithelia
\-deepest layers undergo continuous mitosis
\-daughter cells push toward the surface and become flatter as they migrate upward
\-finally die and flake off (exfoliation or desquamation)
\-daughter cells push toward the surface and become flatter as they migrate upward
\-finally die and flake off (exfoliation or desquamation)
27
New cards
keratinized
\-found on skin surface
\-abrasion resistant
\-abrasion resistant
28
New cards
nonkeratinized
lacks surface layer of dead cells
29
New cards
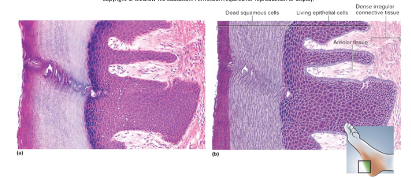
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
\-multiple cell layers; cells become flat and scaly toward surface
\-resists abrasion; retards water loss through skin; resists penetration by pathogenic organisms
\-locations: epidermis, palms and soles heavily keratinized
\-resists abrasion; retards water loss through skin; resists penetration by pathogenic organisms
\-locations: epidermis, palms and soles heavily keratinized
30
New cards
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
\-same as keratinized epithelium w/o surface layer of deal cells
\-resists abrasion and penetration of pathogens
\-locations: tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, and vagina
\-resists abrasion and penetration of pathogens
\-locations: tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, and vagina
31
New cards
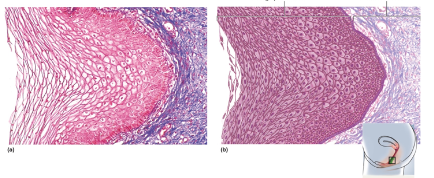
stratified cuboidal epithelium
\-2 or more cell layers; surface cells square or round
\-secretes sweat, produces sperm, produces ovarian hormones
\-locations: sweat gland ducts, ovarian follicles, and seminiferous tubules
\-secretes sweat, produces sperm, produces ovarian hormones
\-locations: sweat gland ducts, ovarian follicles, and seminiferous tubules
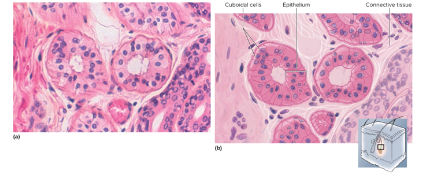
32
New cards
transitional epithelium
\-multilayered epithelium with surface cells that change from round to flat when stretched
\-allows for filling of urinary tract
\-locations: ureter and bladder
\-allows for filling of urinary tract
\-locations: ureter and bladder
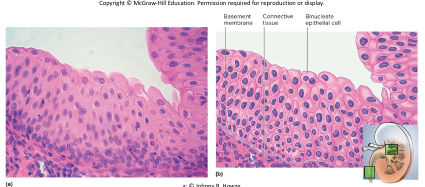
33
New cards
cell junctions
\-connections between 2 cells
\-most cells are anchored to each other or their matrix
\-cells communicate with each other, resist mechanical stress, and control what moves through the gaps between them
\-most cells are anchored to each other or their matrix
\-cells communicate with each other, resist mechanical stress, and control what moves through the gaps between them
34
New cards
tight junction
\-linkage between 2 adjacent cells by transmembrane cell-adhesion proteins
\-in epithelia, they form a zone that completely encircles each cell near its apical pole
\-seals off intercellular space, making it difficult for substance to pass between cells
\-water proof velcro
\-in epithelia, they form a zone that completely encircles each cell near its apical pole
\-seals off intercellular space, making it difficult for substance to pass between cells
\-water proof velcro
35
New cards
desmosomes
\-patch that holds cells together (like a clothing snap)
\-keeps cells from pulling appart--resist mechanical stress
\-hook-like, J-shaped proteins arise from cytoskeleton
\-anchor cytoskeleton to membrane plaque
\-transmembrane proteins from each cell joined by cell adhesion proteins
\-allow for liquid to move, is more flexible
\-loose
\-keeps cells from pulling appart--resist mechanical stress
\-hook-like, J-shaped proteins arise from cytoskeleton
\-anchor cytoskeleton to membrane plaque
\-transmembrane proteins from each cell joined by cell adhesion proteins
\-allow for liquid to move, is more flexible
\-loose
36
New cards
hemidesmosomes
\-half desmosomes that anchor basal cells of an epithelium to underlying basement membrance
\-epithelium can’t easily peel away from underlying tissues
\-epithelium can’t easily peel away from underlying tissues
37
New cards
gap (communicating) junction
\-formed by ring-like connexons
\-connexon consists of 6 transmembrane proteins arranged like segments of an orange around water-filled pore
\-ions, nutrients, and other small solutes pass between cells
\-located in cardiac and smooth muscle, embryonic tissue, lens and cornea
\-cytoplasm can flow
\-connexon consists of 6 transmembrane proteins arranged like segments of an orange around water-filled pore
\-ions, nutrients, and other small solutes pass between cells
\-located in cardiac and smooth muscle, embryonic tissue, lens and cornea
\-cytoplasm can flow
38
New cards
gland
\-cell or organ that secretes substances for use elsewhere in the body or releases them for elimination from the body
\-usually composed of epithelial tissue in a connective tissue framework and capsule
\-usually composed of epithelial tissue in a connective tissue framework and capsule
39
New cards
secretion
product useful to the body
40
New cards
excretion
waste product
41
New cards
endocrine glands
have no ducts; secrete hormones directly into blood
42
New cards
hormones
\-chemical messengers that stimulate cells elsewhere in the body
\-ex: thyroid, adrenal, and pituitary glands
\-ex: thyroid, adrenal, and pituitary glands
43
New cards
exocrine glands
\-maintain their contact with surface of epithelium by way of a duct
\-surface can be external (ex: sweat & tear glands) or internal (ex: pancreas & salivary glands)
\-leave the body
\-surface can be external (ex: sweat & tear glands) or internal (ex: pancreas & salivary glands)
\-leave the body
44
New cards
unicellular glands
\-found in an epithelium that is predominantly nonsecretory
\-can be exocrine or endocrine
\-ex: mucus-secreting goblet cells in tracea or endocrine cells of stomach
\-can be exocrine or endocrine
\-ex: mucus-secreting goblet cells in tracea or endocrine cells of stomach
45
New cards
capsule
\-connective tissue covering of exocrine gland
\-boundary
\-boundary
46
New cards
septa or trabeculae
\-extensions of capsule that divide interior of gland into compartments (lobes and lobules)
\-either stratified squamous or dense regular connective tissue
\-either stratified squamous or dense regular connective tissue
47
New cards
stroma
\-connective tissue framework of the gland
\-supports and organizes glandular tissue
\-framework
\-supports and organizes glandular tissue
\-framework
48
New cards
parenchyma
\-cells that perform the tasks of synthesis and secretion
\-typically cuboidal or simple columnar epithelium
\-secretion
\-typically cuboidal or simple columnar epithelium
\-secretion
49
New cards
classification of glands
\-duct shape
\-gland shape
\-gland shape
50
New cards
duct shape
\-simple (unbranched, one tube)
\-compound (branched, multiple tubes that come together)
\-compound (branched, multiple tubes that come together)
51
New cards
tubular
narrow secretory portion
52
New cards
acinar
secretory cells form dilated sac (acinus or alveolus)
53
New cards
tubuloacinar
both tubular and acinar portions
54
New cards
serous glands
\-produce thin, watery secretions
\-ex: sweat, milk, tears, digestive juices
\-ex: sweat, milk, tears, digestive juices
55
New cards
mucous glands
\-produce glycoprotein, mucin, which absorbs water to form mucus
\-goblet cells: unicellular mucous glands
\-goblet cells: unicellular mucous glands
56
New cards
mixed glands
contain both serous and mucous cell types and produce a mixture of the two types of secretions
57
New cards
apocrine secretion
\-lipid droplet covered by membrane and cytoplasm buds from cell surface
\-mode of milk fat secretion by mammary gland cells
\-mode of milk fat secretion by mammary gland cells
58
New cards
merocrine secretion
\-used by eccrine glands
\-uses vesicles that release their secretion by exocytosis
\-ex: tear glands, pancreas, gastric glands, serous glands
\-uses vesicles that release their secretion by exocytosis
\-ex: tear glands, pancreas, gastric glands, serous glands
59
New cards
holocrine secretion
\-cells accumulate a product until they disintegrate
\-secrete a mixture of cell fragments and synthesized substances
\-ex: oil glands of scalp and skin, and glands of eyelids
\-high solid content/viscosity
\-secrete a mixture of cell fragments and synthesized substances
\-ex: oil glands of scalp and skin, and glands of eyelids
\-high solid content/viscosity
60
New cards
membranes
may be only epithelial, only connective or a mix of epithelial, connective, and muscluar tissues
61
New cards
connective tissue membranes
dura mater, synovial membranes, periosteum
62
New cards
epithelial tissue membranes
anterior surface of cornea and lens of eye
63
New cards
cutaneous membrane
\-the skin
\-the largest membrane in the body
\-stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) resting on a layer of connective tissue (dermis)
\-relatively dry layer serves protective function
\-compound membrane (multiple tissue types)
\-the largest membrane in the body
\-stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) resting on a layer of connective tissue (dermis)
\-relatively dry layer serves protective function
\-compound membrane (multiple tissue types)
64
New cards
mucous membrane (mucosa)
\-lines passages that open to the external environment
\-ex: digestive tract
\-sublayers: epithelium, lamina propria (areolar tissue), muscularis mucosa (smooth muscle)
\-absorptive, secretory, and protective functions
\-often have mucus producing goblet cells
\-ex: digestive tract
\-sublayers: epithelium, lamina propria (areolar tissue), muscularis mucosa (smooth muscle)
\-absorptive, secretory, and protective functions
\-often have mucus producing goblet cells
65
New cards
serous membrane (serosa)
\-internal membrane
\-simple squamous epithelium resting on a layer of areolar tissue
\-produces serous fluid that arises from blood
\-covers organs and lines walls of body cavities
\-double membrane w/ watery sloution
\-simple squamous epithelium resting on a layer of areolar tissue
\-produces serous fluid that arises from blood
\-covers organs and lines walls of body cavities
\-double membrane w/ watery sloution
66
New cards
endothelium
lines blood vessels and heart
67
New cards
mesothelium
lines body cavities (pericardium, peritoneum, and pleura)
68
New cards
viseral layer
against organ
69
New cards
parietal layer
against cavity
70
New cards
tissue growth
increasing the number of cells or size of existing cells
71
New cards
hyperplasia
growth through cell multiplication
72
New cards
hypertrophy
\-enlargement of preexisting cells
\-muscle growth through exercise
\-accumulation of body fat
\-muscle growth through exercise
\-accumulation of body fat
73
New cards
neoplasia
\-development of a tumor (neoplasm)
\-benign or malignant
\-composed of abnormal, nonfunctional tissue
\-benign or malignant
\-composed of abnormal, nonfunctional tissue
74
New cards
diferentiation
\-development of more specialized form and function by inspecialized tissue
\-ex: embryonic mesenchyme becoming cartilage and bone
\-ex: embryonic mesenchyme becoming cartilage and bone
75
New cards
metaplasia
\-changing from one type of mature tissue to another
\-Simple cuboidal tissue of vagina before puberty changes to stratified squamous after puberty
\-Pseudostratified columnar epithelium of bronchi of smokers to stratified squamous epithelium
\-Simple cuboidal tissue of vagina before puberty changes to stratified squamous after puberty
\-Pseudostratified columnar epithelium of bronchi of smokers to stratified squamous epithelium
76
New cards
stem cells
\-undifferentiated cells that are not yet performing any specialized function
\-Have potential to differentiate into one or more types of mature functional cells
\-in deepest layer of epidermis (stratum basale)
\-Have potential to differentiate into one or more types of mature functional cells
\-in deepest layer of epidermis (stratum basale)
77
New cards
Developmental plasticity
ability of a stem cell to give rise to a diversity of mature cell types
78
New cards
totipotent
\-have potential to develop into any type of fully differentiated human cell including accessory organs of pregnancy
\-source: cells of very early embryo
\-source: cells of very early embryo
79
New cards
pluripotent
\-can develop into any type of cell in the embryo (but not accessory organs of pregnancy)
\-source: cells of the inner cell mass of embryos (blastocyst)
\-source: cells of the inner cell mass of embryos (blastocyst)
80
New cards
Adult stem cells
\-undifferentiated cells found in mature organs
\-some are multipotent and some are unipotent
\-some are multipotent and some are unipotent
81
New cards
multipotent
able to develop into two or more cell lines (ex: bone marrow stem cells)
82
New cards
unipotent
produce only one cell type (ex: cells giving rise to sperm)
83
New cards
induced pluripotent stem cell (iPS Cell)
\-start as a multipotent stem cell, reprogrammed to mimic a pluripotent stem cell
\-bypasses ethical considerations of pluripotent stem cells
\-performs like pluripotent stem cells
\-possibility of genetically 100% compatible organ transplants feasible
\-bypasses ethical considerations of pluripotent stem cells
\-performs like pluripotent stem cells
\-possibility of genetically 100% compatible organ transplants feasible
84
New cards
regeneration
\-replacement of dead or damaged cells by the same type of cell as before
\-restores normal function
\-ex: repair of minor skin or liver injuries
\-restores normal function
\-ex: repair of minor skin or liver injuries
85
New cards
fibrosis
\-replacement of damaged cells with scar tissue
\-Scar holds organs together, but does not restore function
\-ex: repair of severe cuts and burns, scarring of lungs in tuberculosis
\-Scar holds organs together, but does not restore function
\-ex: repair of severe cuts and burns, scarring of lungs in tuberculosis
86
New cards
stages in healing of a skin wound 1
1)healing of a cut in the skin:
\-severed vessels bleed into cut
\-mast cells and damaged cells release histamine
\-histamine dilates blood vessels and makes capillaries more permeable
2)blood plasma seeps into the wound carrying antibodies & clotting proteins
\-severed vessels bleed into cut
\-mast cells and damaged cells release histamine
\-histamine dilates blood vessels and makes capillaries more permeable
2)blood plasma seeps into the wound carrying antibodies & clotting proteins
87
New cards
stages in healing of a skin wound 2
3)blood clot forms
\-knits edges of cut together
\-inhibits spread of pathogens
4)forms scab that temporarily seals wound and blocks infection
5)macrophages phagocytize and digest tissue debris
\-knits edges of cut together
\-inhibits spread of pathogens
4)forms scab that temporarily seals wound and blocks infection
5)macrophages phagocytize and digest tissue debris
88
New cards
stages in healing of a skin wound 3
6)new capillaries sprout from nearby vessels
7)deeper portions of clot become infiltrated by capillaries and fibroblasts
\-transform into soft mass called granulation tissue -macrophages remove the blood clot
\-fibroblasts deposit new collagen
\-begins 3–4 days after injury and lasts up to 2 weeks
7)deeper portions of clot become infiltrated by capillaries and fibroblasts
\-transform into soft mass called granulation tissue -macrophages remove the blood clot
\-fibroblasts deposit new collagen
\-begins 3–4 days after injury and lasts up to 2 weeks
89
New cards
stages in healing of a skin wound 4
8)epithelial cells around wound multiply and migrate beneath scab (tissue regenerates)
9)underlying connective tissue undergoes fibrosis
\-scar tissue may or may not show through epithelium
10)remodeling (maturation) phase begins several weeks after injury and may last up to 2 years
9)underlying connective tissue undergoes fibrosis
\-scar tissue may or may not show through epithelium
10)remodeling (maturation) phase begins several weeks after injury and may last up to 2 years
90
New cards
atrophy
\-shrinkage of a tissue through loss in cell size or number
\-senile atrophy through normal aging
\-disuse atrophy from lack of use
\-senile atrophy through normal aging
\-disuse atrophy from lack of use
91
New cards
necrosis
pathological tissue death due to trauma, toxins, or infections
92
New cards
infarction
sudden death of tissue when blood supply is cut off
93
New cards
gangrene
tissue necrosis due to insufficient blood supply (usually involves infection)
94
New cards
Decubitus ulcer (bed sore or pressure sore)
form of dry gangrene where continual pressure on skin of immobilized patient cuts off blood flow
95
New cards
Dry gangrene
common complication of diabetes
96
New cards
Wet gangrene
liquefaction of internal organs with infection
97
New cards
Gas gangrene
usually from infection of soil bacterium that results in hydrogen bubbles in tissues
98
New cards
Apoptosis
\-programmed cell death
\-normal death of cells that have completed their function and best serve the body by dying and getting out of the way
\-phagocytized by macrophages and other cells
\-billions of cells die by apoptosis
\-every cell has a built-in “suicide program”
\-normal death of cells that have completed their function and best serve the body by dying and getting out of the way
\-phagocytized by macrophages and other cells
\-billions of cells die by apoptosis
\-every cell has a built-in “suicide program”
99
New cards
Extracellular suicide
signal binds receptor protein in the plasma membrane called Fas
100
New cards
Fas activates enzymes
endonuclease chops up DNA and protease destroys proteins