A&P: Chapter 10 (Part 1)
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/53
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
Functions of Nervous System
1.) Sensory Input
2.) Integration
3.) Control of muscles and glands
4.) Homeostasis
5.)Mental Activity
2.) Integration
3.) Control of muscles and glands
4.) Homeostasis
5.)Mental Activity
2
New cards
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord.
3
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
Sensory receptors and nerves
4
New cards
Sensory Division
(Afferent Division) Sends action potentials from sensory receptors to CNS.
5
New cards
Motor Division
(Efferent Division) Sends action potentials from CNS to muscles, organs, or glands.
6
New cards
Somatic Motor
Sends action potentials from CNS to skeletal muscles (voluntary).
7
New cards
Autonomic NS
Sends action potentials from CNS to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands (involuntary).
8
New cards
Sympathetic Division
Active during physical activity, "fight or flight" NS during emergencies.
9
New cards
Parasympathetic Division
Active during resting, regulates some digestion and other "vegetative" functions.
10
New cards
Enteric Division
Located in digestive tract, runs most of digestion independent of the CNS.
11
New cards
Neuron
(Nerve cells) Cells that actually receive and transmit action potentials.
12
New cards
Neuroglia
(Glial Cells) Cells that support the neurons. They do NOT transmit and receive APs, they have functions to help the neurons transmit and receive APs.
13
New cards
Yes
Can you label this picture?
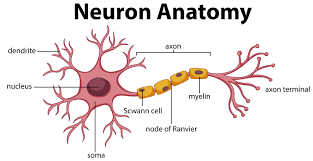
14
New cards
Soma
Main cell body
15
New cards
Trigger Zone
Beginning of axon and place where a new action potential originates.
16
New cards
Dendrites
Extensions of the cell membrane which have dendrite spines.
17
New cards
Dendrite Spines
Allow axons from other cells to form synapses.
18
New cards
Axon
Long tail of cell, often called the nerve fiber.
19
New cards
Synapse
Any connection point between an axon and another cell.
20
New cards
Presynaptic Terminal
An ending of an axon at the synapse.
21
New cards
Bipolar
1 dendrite & 1 axon
Found in retina of eye and in nasal cavity.
Found in retina of eye and in nasal cavity.
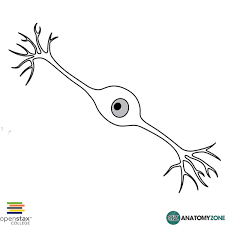
22
New cards
Unipolar
Has axon but the other end is not actually dendrites.
Often has a receptor instead of the dendrite, most sensory neurons are like this.
Often has a receptor instead of the dendrite, most sensory neurons are like this.
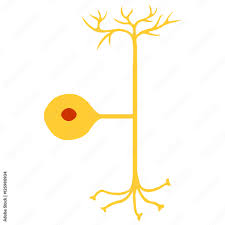
23
New cards
Multipolar
Many dendrites and 1 axon.
Most CNS and motor neurons are like this.
Most CNS and motor neurons are like this.
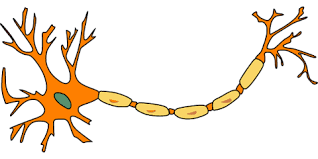
24
New cards
Types of CNS Glial Cells
1.) Astrocytes
2.) Ependymal Cells
3.) Microglial
4.) Oligodendrocytes
2.) Ependymal Cells
3.) Microglial
4.) Oligodendrocytes
25
New cards
Types of PNS Glial Cells
1.) Schwann Cells
2.) Satellite Cells
2.) Satellite Cells
26
New cards
Astrocytes
Forms link between blood vessel & neuron, can dilate or contract nearby blood vessels, help form synapses, regulate amount of ions available (needed for APs), and produces lactic acid for "back up energy" when glucose is low for neurons.
27
New cards
Reactive Astrocytes
Production of many astrocytes after a CNS injury. They wall of injury sites and limits inflammation, and limits regeneration of the damaged axons.
28
New cards
Ependymal Cells
Line ventricles of brain and spinal cord, (with blood vessels) form choroid plexus.
29
New cards
Choroid Plexus
Produces cerebrospinal fluid.
30
New cards
Microglia
The CNS's version of white blood cells, breaks down dead cells and invading microoganisms.
31
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
Wrap around axons and form myelin sheaths, only in the CNS.
32
New cards
Schwann Cells
Form myelin sheaths of PNS.
33
New cards
Satellite Cells
Surround soma (cell body), also helps gen nutrients to cell and absorb poisons away from it.
34
New cards
Functions of Myelin
1.) Insulates the signal (prevents signal from jumping to nearby axons).
2.) Encourages faster action potential propagation.
2.) Encourages faster action potential propagation.
35
New cards
surrounded
Myelinated and unmyelinated axons are different based on how they are ____________ by Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes.
36
New cards
Myelinated Axons
Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes wrap around axon.
37
New cards
Unmyelinated Axons
Axons are "buried" within Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes but are not individually wrapped.
38
New cards
Action Potential
The electrical signal of the body.
39
New cards
Ligand-gated ion channels
Opens only for a specific ligand (molecule).
40
New cards
Voltage-gated ion channels
Opens only when a specific membrane potential is reached.
41
New cards
Leak channels
Always open and slowly leak one type of ion.
42
New cards
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Uses energy (ATP) to force K+ inside the cell and force Na+ outside the cell.
43
New cards
Resting Membrane Potential
The membrane potential in a normal or unstimulated cell.
44
New cards
Membrane Potential
Difference in charges between the sides of the membrane.
45
New cards
Polarized
When one side of the membrane is + and the other is -, the membrane is said to be _________.
46
New cards
-70 mV
The resting membrane potential of neurons.
47
New cards
Items Affecting Membrane Potential
1.) Ions
2.) Depolarization
3.)Hyperpolarization
2.) Depolarization
3.)Hyperpolarization
48
New cards
Ions Affecting Membrane Potential
Na+, K+, Ca+2, Cl-
49
New cards
Depolarization
Decrease in the membrane potential, charges difference is becoming closer to 0 mV.
50
New cards
Hyperpolarization
Increase in the membrane potential, charge difference is becoming further from 0 mV.
51
New cards
Graded Potential
Any change in the resting membrane potential, or any stimulus that can affect an ion pump or channel.
Ex.) ligand binding to receptor, voltage change, mechanically opening a gate, temperature change, pH change
Ex.) ligand binding to receptor, voltage change, mechanically opening a gate, temperature change, pH change
52
New cards
Summation
The adding up effect of multiple graded potentials.
53
New cards
proportional
Graded potential strength is ___________ to the stimulus.
54
New cards
Threshold
The level of voltage that must be reached for the change in membrane potential to spread to nearby parts of the cell membrane.