Acoustics and Psychoacoustics
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
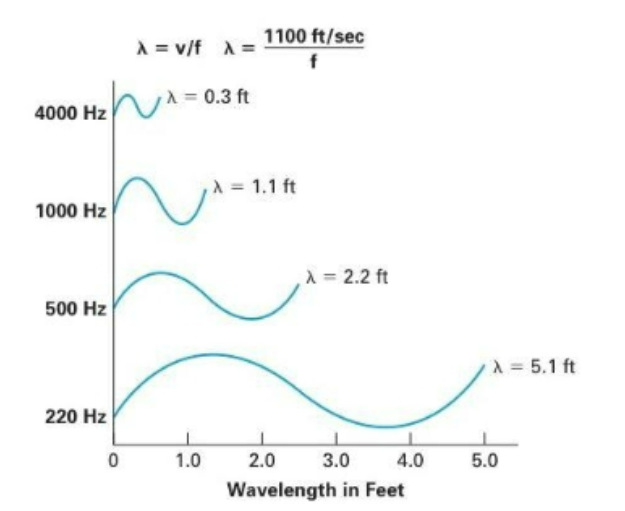
Figure 2.6: Low to high frequencies wavelength
Octave
An increase of an octave is a doubling of frequency
Terminology includes
harmonics, subharmonics, resonant frequencies
Resonance
the natural rate of vibration of a mass.
This frequency is the frequency at which the mass most easily is set into vibration and at which the magnitude of vibration is greatest and decays most slowly
Resonant frequency
The following scenario is an example of what?:
when a drinking glass is shattered by a particular musical note, it is affected by its resonant frequency. If that amplitude of the frequency becomes great enough, the glass will distort and shatter
resonant frequency
Which wave is analyzed in terms of its sinusoidal components?
Complex wave
Fourier analysis
Analyzing a complex wave in terms of its sinusoidal components
Fundamental Frequency
The lowest frequency within a complex wave
Periodic sounds
complex sounds that repeat over time
Aperiodic sounds
vary randomly over time and do not have fundamental frequencies
_ sounds are perceived as nosie
aperiodic