Lecture 28 Cytoskeleton 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
monomers that make up microtubules and actin filaments bind to and hydrolyze ____
nucleotides
critical concentration Cc
rate of subunit addition is equal to the rate of subunit loss
konC
number of subunits that add to the polymer is proportional to the concentration of the free subunit
koff
number of subunits that leave polymer at a constant rate
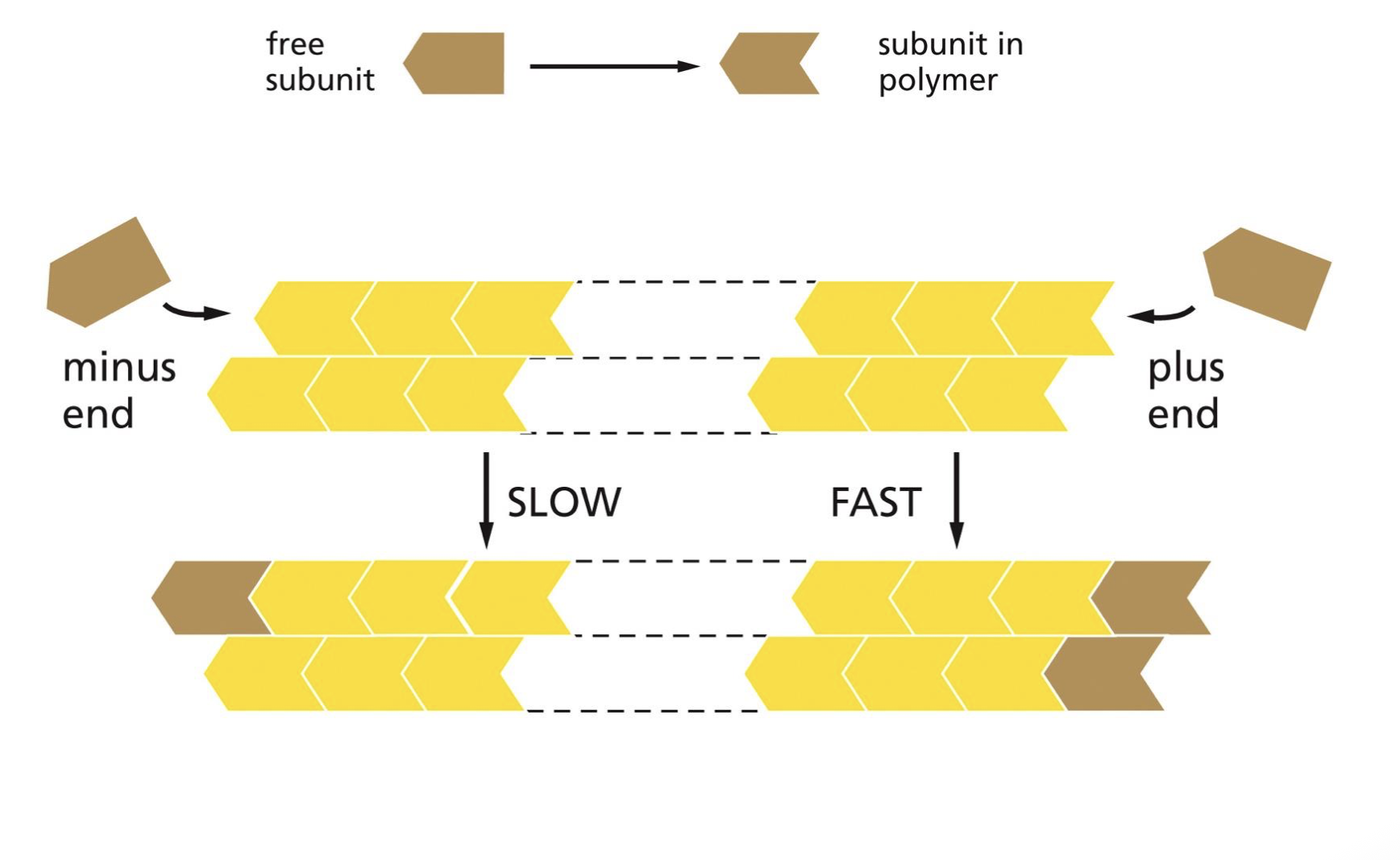
the fast growing end of a filament is called ___ and the slow growing end call ___
plus end ; minus end
the different rates of the plus and minus end is due to what
different conformation as it enters the polymer
actin binds and hydrolyzes ___
tubular binds and hydrolyzes __
ATP
GTP
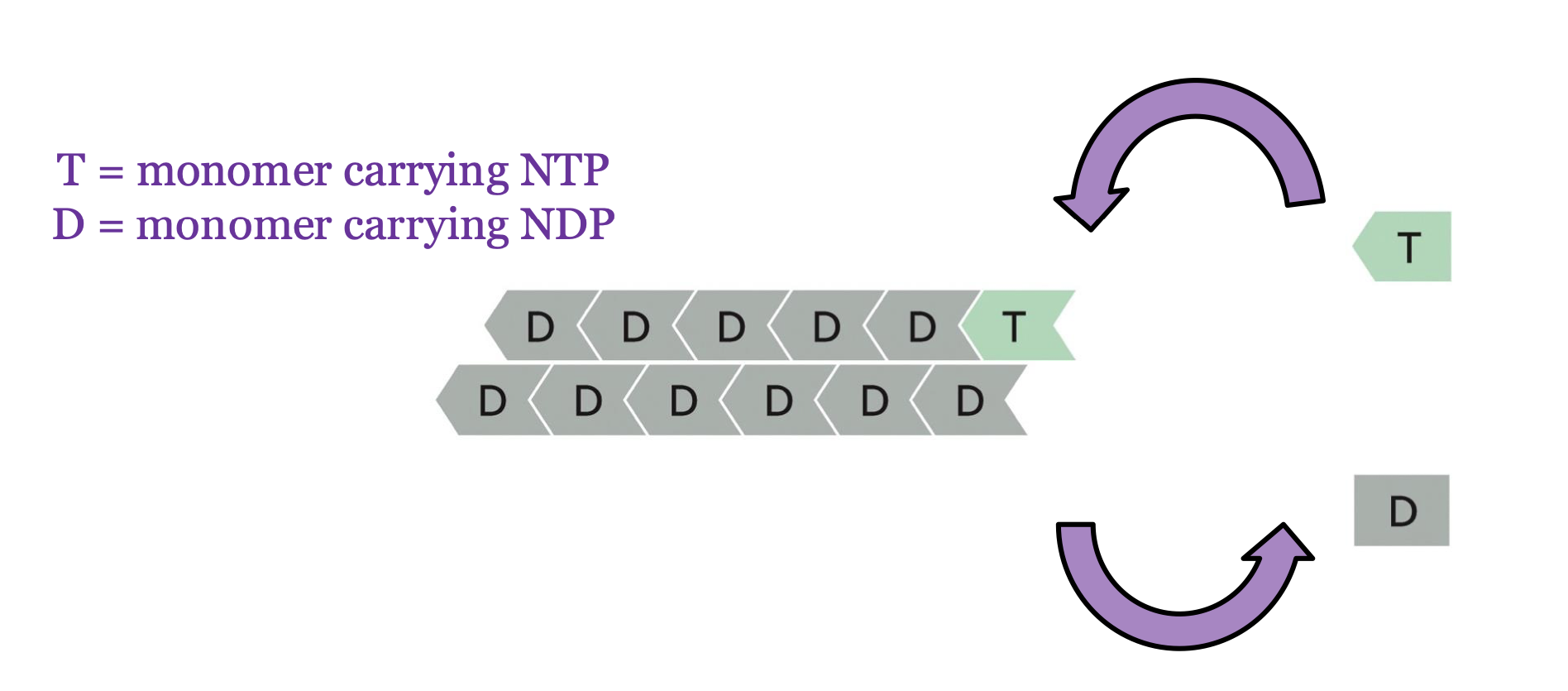
hydrolysis of the bound nucleotide reduces the binding affinity of the subunit for the neighboring subunits, making it more likely ___
to dissociate
T form adds to the filaments and the D form leaves
lag phase corresponds to
time taken for nucleation
growth phase occurs when
subunits add to the exposed ends of the growing filaments, causing elongation
equilibrium phase (steady state) occurs when
the growth of the polymer due to monomer addition is precisely balanced to the shrinkage due to disassembly back to monomers
three major families of cytoskeleton filaments
microtubules
actin
intermediate filaments
which filament is the largest and most rigid
microtubules
rupture when stretched
polar
which filament is the smaller, more flexible structure
actin / microfilaments
polar
which filament is made of rope like fibers and allow cell to distribute tensile forces to prevent rupturing
intermediate filaments
coil coil tetramer aka strong as balls
non polar
2 kinds of intermediate filaments
cytoplasmic
keratin filaments in epithelial cells
Nuclear lamins
in all animals cells
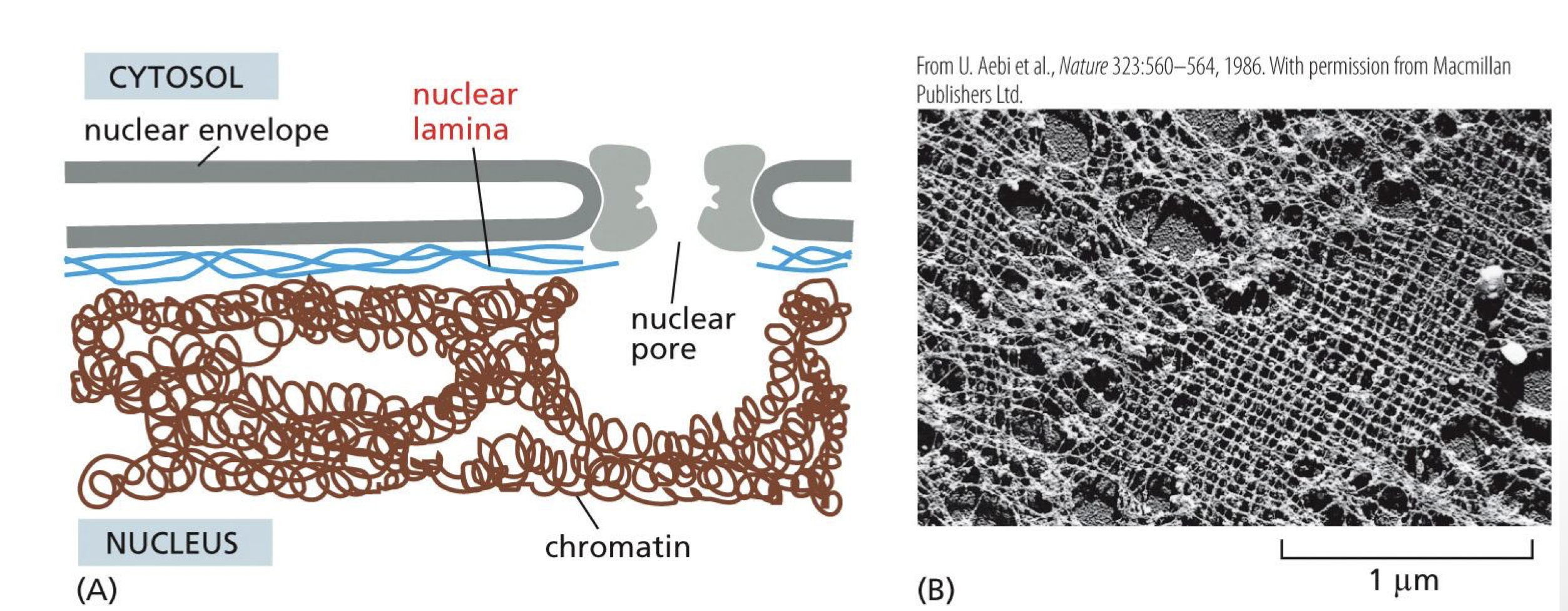
what is the purpose of nuclear lamina
support and strength nuclear envelope to protect our DNA
what promotes nuclear envelope disassembly during mitosis
phosphorylation of the nuclear lamina (nuclear intermediate filaments)
can reform due to nuclear import proteins being imported after every cycle of cell division
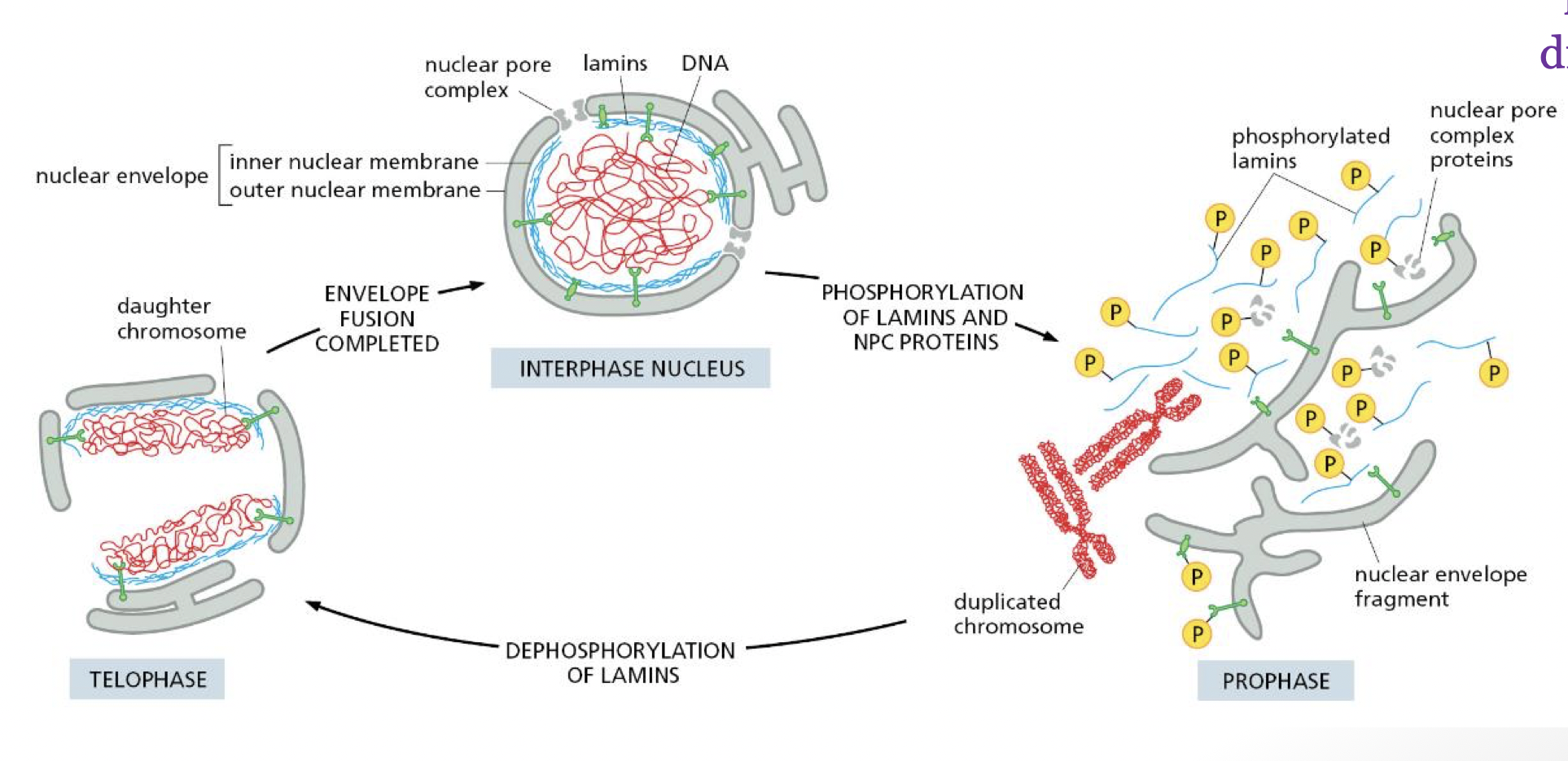
what is progeria
a disease the results from deformed nuclear lamina where the nuclear envelope does not have enough support which leads to impaired cell division, increase cell death
result → premature aging
how does mutant keratin lead to epidermolysis bullosa
normal keratin filaments create a structural network that provides resilience to mechanical stress.
if mutant and pressure is applied to the skin, it can redistribute that force and then skin blisters
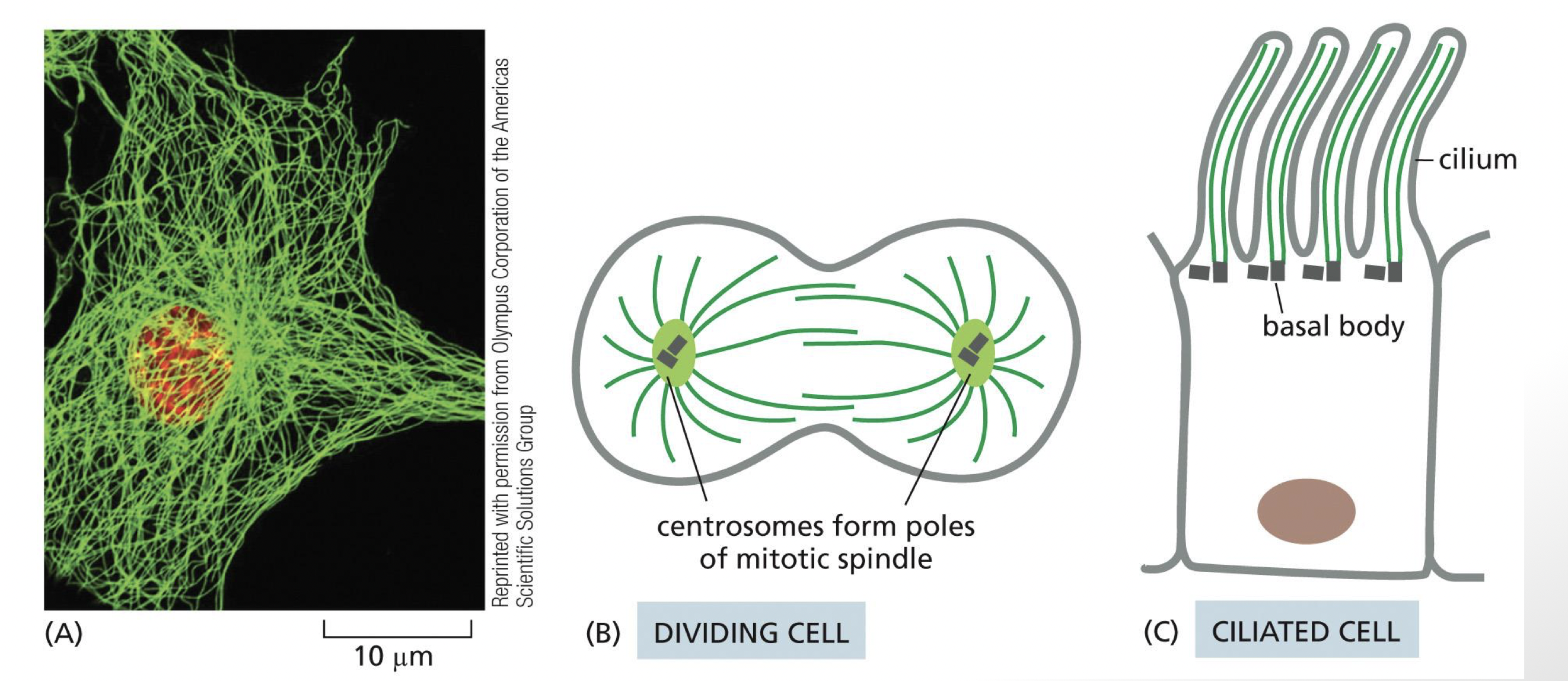
what is the microtubule organizing center
centrosome containing structure organizes the microtubules
describe the minus and plus ends of a microtubule
minus end contain alpha subunit
plus ends contains beta subunit
microtubules grow from minus to plus end
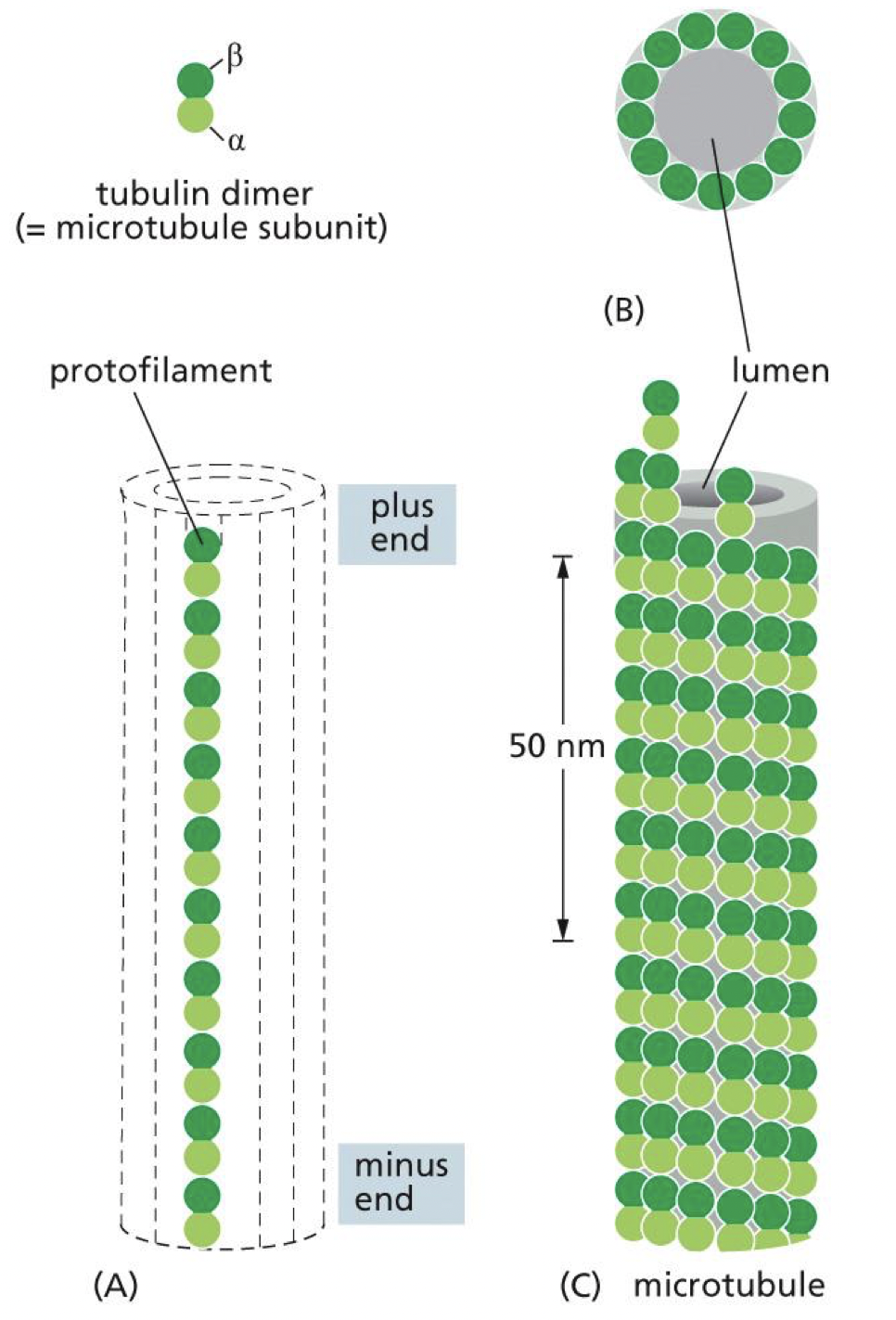
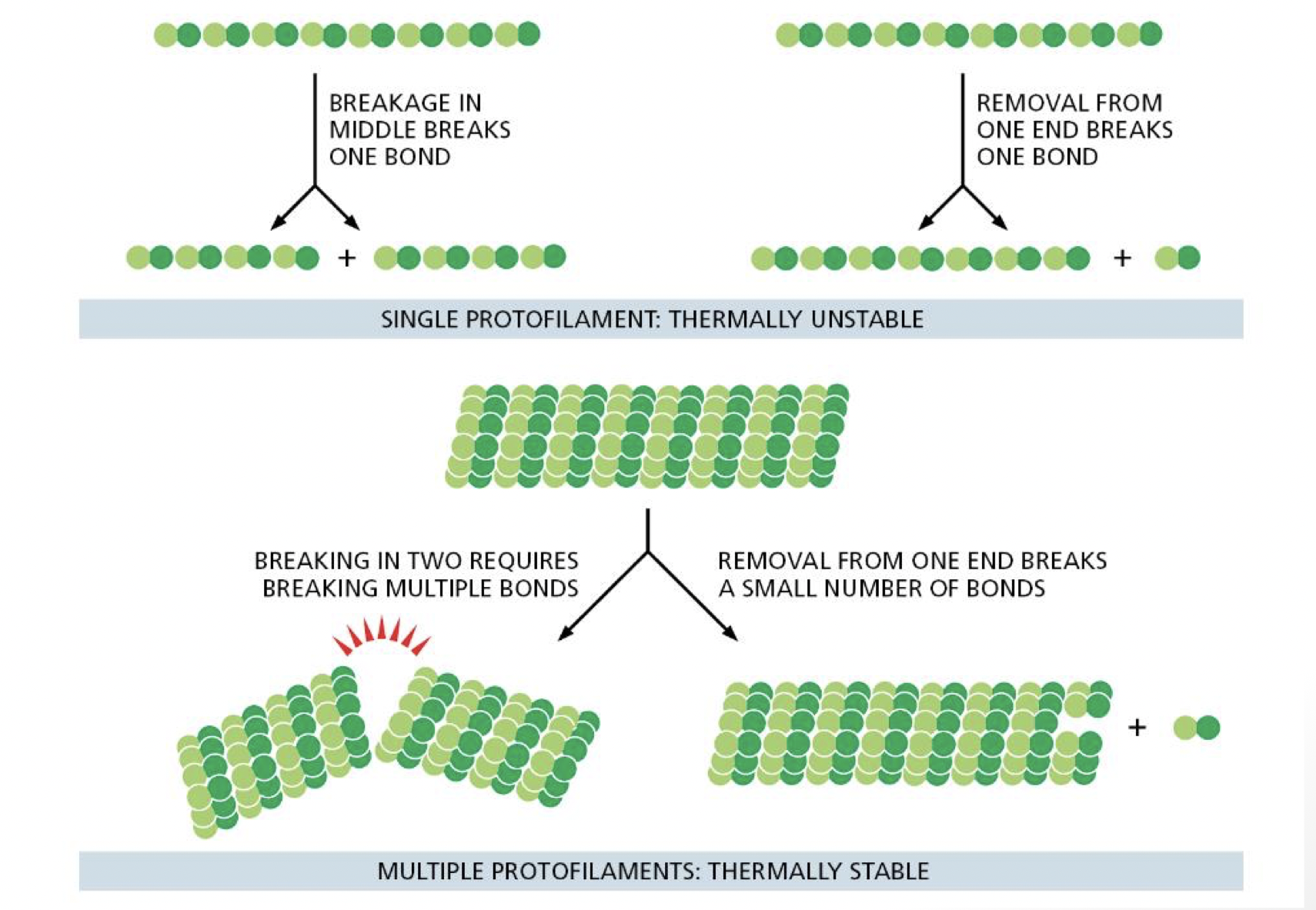
why do microtubules have 13 protofilaments
allows microtubules to be thermally stable and still be dynamic
in microtubules, which tubular subunit never hydrolyzes GTP
alpha subunit
GTP in beta is hydrolyzed/exchanged to control whether or not we will add or lose subunits
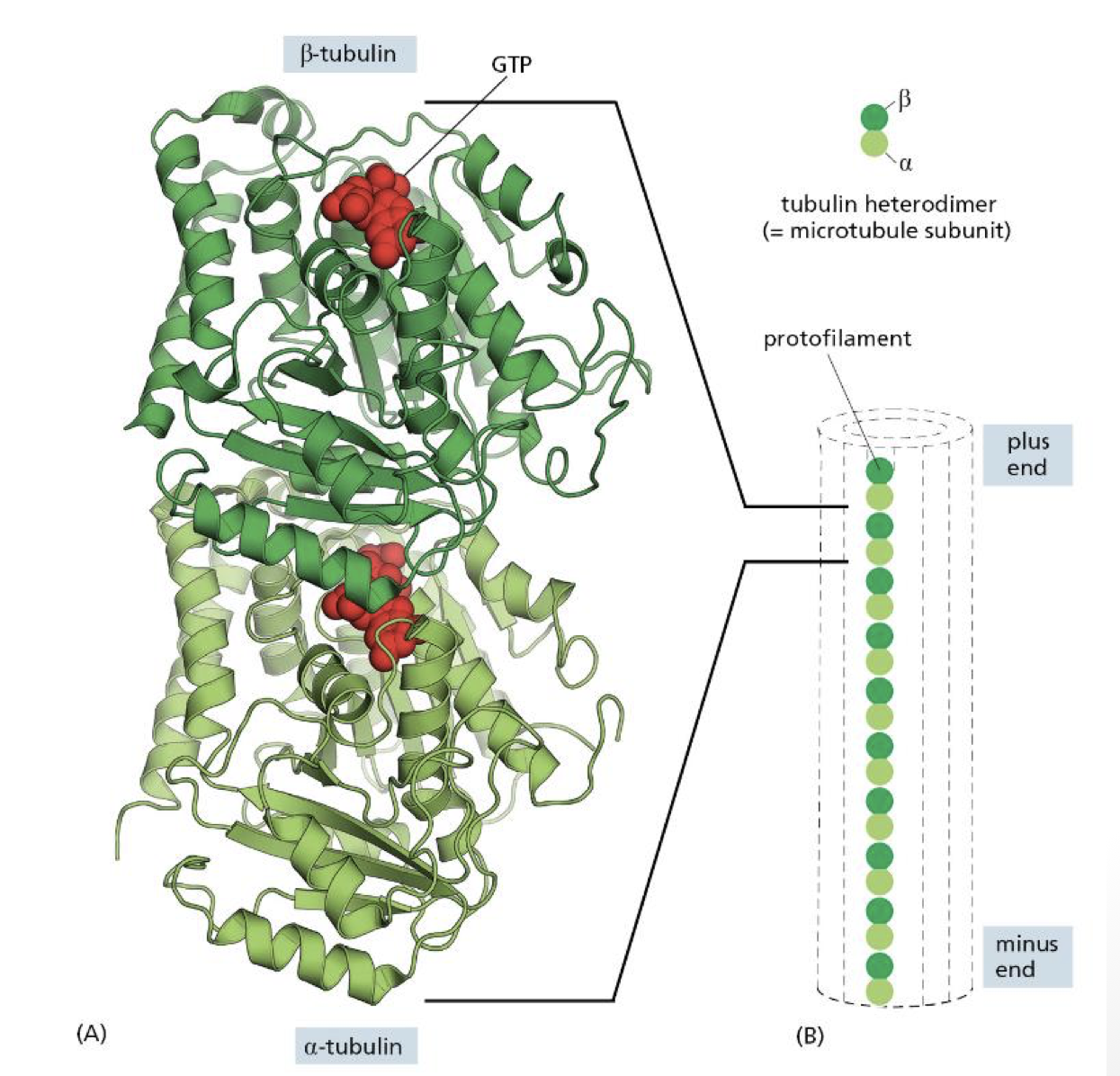
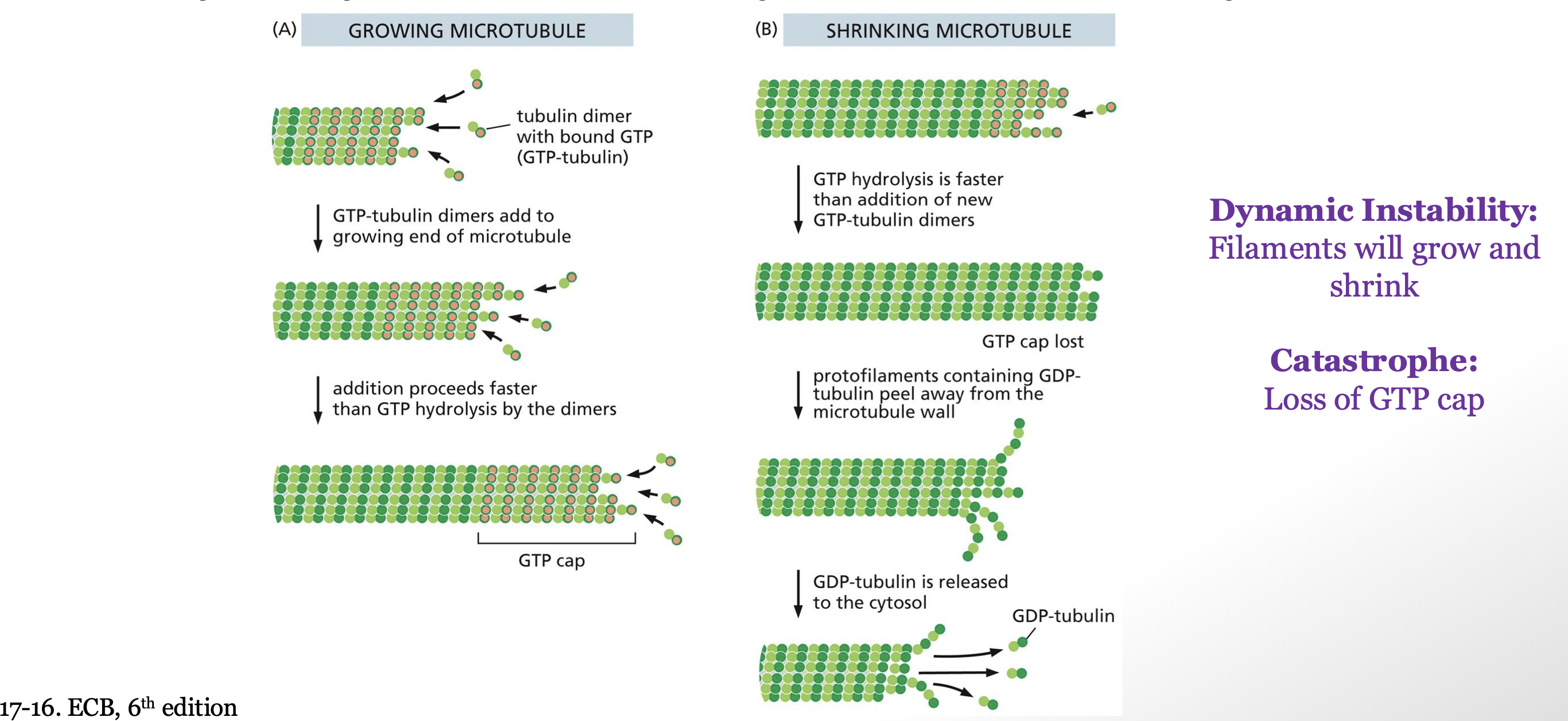
describe how GTP hydrolysis controls dynamic instability
GTP tubulin enters polymer and hydrolyzes GTP to GDP
when GDP bound it has lower affinity for polymer
Polymer only grows when GTP tubulin is added faster than it is hydrolyzed
GTP cap forms to protect end (think of the wax thing that protects the end of shoe laces)