PT7130- Lab Values
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
Most current
In hospital, check _______________________ lab values to determine whether patient is appropriate for PT.
Hold therapy
Delay PT to afternoon or next day d/t patient medical stability (i.e., patient will tolerate PT better s/p blood transfusion).
Tolerance; mobility
Abnormalities in electrolytes and fluids, hematology, ABG's, enzymes, and vitals can impair activity _______________________, cognition, and functional _______________________.
Current
Lab values assist in determining _______________________ patient presentation and clinical observation during examination and treatment.
Guide
Lab values ______________________ intervention appropriatness, intensity, and duration, safety, and effectiveness.
↓
↓ hemoglobin, ____________________ exercise tolerance
Lower
IV rehydration will dilute lab values, so they may appear _______________________ than they are.
MRI
(-) CT scan does not immediately rule out an embolic stroke, so ________________________ may be ordered. → Rules our hemorrhagic stroke
Liver dysfunction
↑ ALT (alanine aminotransferase) or AST (aspartate aminotransferase) indicates _______________________.
14-18 g/dL
Normal hemoglobin values for men.
12-16 g/dL
Normal hemoglobin values for women.
42-52%
Normal hematocrit values for men.
36-48%
Normal hematocrit values for women.
3
Hematocrit is ____________________x hemoglobin.
5,000-10,000/mm³
Normal WBC values.
150,000-400,000/mm³
Normal platelet values.
WBC
Light green in image.
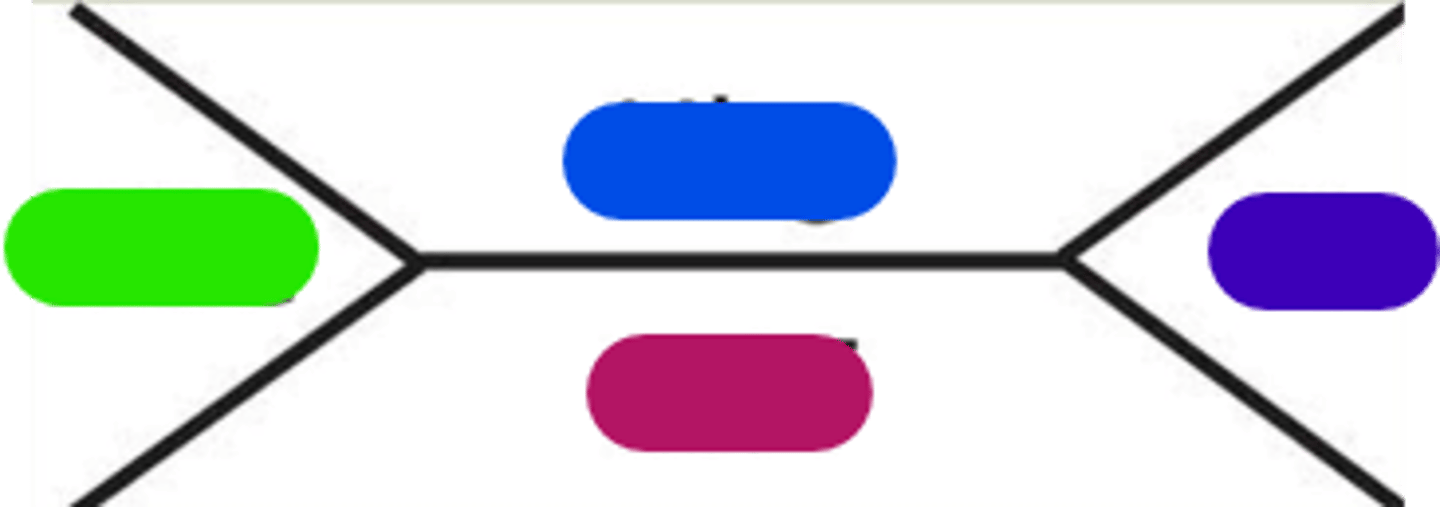
Hemoglobin
Blue in image.
Platelets
Purple in image.
Hematocrit
Burgundy in image.
Symptoms based; signs and symptoms
PT Implications Hematology Value:
__________________________ approach when determining appropriateness for activity, monitor symptoms, collaborate with the interprofessional team. → _________________________ may carry more weight than an isolated lab value in clinical decision making.
Therapy as indicated
Hemoglobin >10 g/dL:
_____________________________
Cardiopulmonary reserve; perfusion; orthostatic hypotension; intolerance
Hemoglobin 8-10 g/dL:
- Anticipate poor _______________________/limited endurance.
- Monitor vitals closely (especially SpO2 for tissue _______________________, may present with __________________________ and tachycardia).
- Examine for pallor, tachycardia, exercise ________________________
May be; blood transfusion
Hemoglobin <7-8 g/dL:
- Therapy _______________________ contraindicated
- Symptoms based approach
- ________________________ probable
- Monitor as described above
Death; likely
Hemoglobin <5-7 g/dL:
- Heart failure and _____________________
- Blood transfusion ______________________
- PT higher likelihood of being contraindicated
Blockage; ischemia
Hemoglobin 20 g/dL:
Increased blood viscosity → Capillary ______________________ and tissue ________________________
Cancer; 300 mL
Low Hemoglobin Considerations:
- Chronic conditions (i.e., CKD, __________________)
- Post-op surgery (~___________________ blood loss = 1.5 unit drop Hg)
- Fluid dilution
Hemodilution
↓ Hg d/t fluid intake.
Hematocrit
Proportion of blood that are RBC; expressed as a percentage.
Light ROM, isometrics
Hematocrit <25%.
Light exercise, SxS based approached
Hematocrit >25%.
>30-35%
Ambulation, resistance as tolerated.
Anemia
Acute blood loss, destruction, or decreased production of RBCs.
Paleness; fatigued; dyspnea; rapid, shallow
Signs and Symptoms of Anemia:
- ______________________ of skin
- Weak
- Listless
- Easily _______________________
- _______________________ on exertion
- ________________________ pulse
Transfusion; vitals; pacing
Indications for Anemia:
- Risk vs. benefit
- Need/timing of ______________________
- Frequent ______________________ monitoring
- Activity _____________________
- Close monitoring
Polycythemia
Myeloproliferative disorders (cancer), hypoxia at tissue level, higher altitudes, heavy tobacco smoking, chronic lung disease, congenital heart defects → Hypoxemia is stimulus.
Blurred; decreased; sensation
Signs and Symptoms of Polycythemia:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- _______________________ vision
- ______________________ mental acuity
- Altered ________________________ in hands/feet (blocked capillaries)
CVA and thrombosis
Polycythemia has increased risk for ________________________ → Pay attention to signs and symptoms of stroke, PE, DVT.
Leukocytosis
WBC > 10,000/mm³
Infection; inflammation; necrosis
Causes of Leukocytosis:
- ______________________
- Leukemia
- PNA
- Neoplasms
- _____________________
- Tissue ______________________
Fever; sore; fatigue
Signs and Symptoms of Leukocytosis:
- ______________________
- Chills
- ______________________ throat
- _______________________
Leukocytopenia
WBC < 5,000/mm³
Bone marrow; autoimmune
Causes of Leukocytopenia:
- _________________________ failure
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
- HIV
- ________________________ disease
Stiff; sore; fever; ulcers
Signs and Symptoms of Leukocytopenia:
- _____________________ neck
- _____________________ throat
- _____________________/chills
- Headache
- Mouth ____________________
- Frequent infections
Neutropenia
WBC < 1500/mm³
Reverse isolation; mask; flowers
Neutropenia:
- __________________________
- Neutropenic precautions
- Increased risk for infection
- Pt should wear a mask outside of room
- Therapist should wear ________________________
- If therapist sick, do not treat patient
- No fresh fruit/______________________
Platelets
Cytoplasmic fragments of megakaryocytes in bone marrow; function in hemostasis and initiating clotting mechanism.
Thrombocytosis
>400,000/mm³ platelets
Infection; myeloproliferative
Causes of Thrombocytosis:
- __________________________
- Inflammation
- Genetic _______________________ conditions
Thrombosis; bleeding
Risks associated with Thrombocytosis:
- Increased ________________________ formation
- Paradoxical increased risk for _________________________
Weakness; chest; tingling
Signs and Symptoms of Thrombocytosis:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- _______________________
- _______________________ pain
- ________________________ hands/feet
Thrombocytopenia
<150,000/mm³ platelets
Suppression; cytotoxic
Causes of Thrombocytopenia:
- Bone marrow ____________________________
- Leukemia
- _________________________ drugs
Bleeding; resistive; valsalva
Risks associated with Thrombocytopenia:
- Increased risk for ___________________________
- Avoid bumps, bruising
- Avoid ________________________ exercises d/t risk of intramuscular bleeding
- Avoid ________________________
Oral; petechiae
Signs and Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia:
- Bruising
- Epistaxis
- Hematuria
- _______________________ bleeding
- ________________________
AROM; walking
Thrombocytopenia: 20,000-50,000/mm³
- ________________________ exercise with or without resistance
- _________________________ ad lib
Without; spontaneous; prolonged
Thrombocytopenia: <20,000/mm³
- Ther ex ______________________ resistance
- Risk of ________________________ bleeding
- Petechia (small hemorrhage, local, spots)
- Ecchymosis
- ________________________ bleeding time
CNS, GI, or respiratory tract; contraindicated
Thrombocytopenia:
<10,000/mm³ and/or temp >100.5°F
- Risk for spontaneous ______________________________ bleeding
- PT __________________________
Blood transfusions
Replete blood volume, maintain O2 delivery to tissues, maintain proper coagulation. → Typically takes 3-4 hours per unit.
OOB; 15 minutes
Blood Transfusions:
Depending on condition of patient, may defer ________________________ activity. → No contra-indications to therapy, except for the first __________________________ of transfusion.
Transfusion-Related Immunomodulation (TRIM) reactions; circulatory overload
During first 15 minutes minutes of transfusion, observe for signs and symptoms of _________________________ and _________________________ (i.e., CHF exacerbation).
Tachycardia; dyspnea; distended
Signs and Symptoms of Transfusion-Related Immunomodulation (TRIM) Reactions:
- HR: ______________________
- Cough
- Breathing: ________________________
- Crackles
- Headache
- HTN
- _______________________ neck veins
- Fever
- Rash
- Hypotension
Use extreme caution with mobility, fall risk, etc.
Monitor vitals
Jehova's Witnesses
What religion objects to blood transfusions?
Erythropoietin; salvage; normovolaemic haemodilution
Alternatives to Blood Transfusion:
- ___________________________
- Aprotinin
- Cell _______________________
- Tranexamic acid
- Novoseven
- Acute ___________________________
Prothrombin Time (PT)
Examines the function of the extrinsic system in clotting cascade.
Bleeding; clotting
↑ PT, ↑ risk of ________________________. ↓ PT, ↑ risk fo _______________________.
11-13.5 seconds
Normal Prothrombin Time (PT).
International Normalization Ratio (INR)
Used to correct for differences in lab reagents used for test PT time; calculated from PT value.
0.9-1.1
Normal International Normalization Ratio (INR).
Bleeding
↑ INR, ↑ risk of ______________________.
Coumadin (Warfarin)
What drug(s) is/are used for extrinsic system (PT and INR)?
Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT)
Examines the function of the intrinsic system and common pathways in clotting cascade.
60-70 seconds
Normal Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT).
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT)
Same as PTT however an activator is used → results available in < 1 hour.
30-40 seconds
Normal Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT).
Heparin, Lovenox
What drug(s) is/are used for intrinsic system (PTT and aPTT)?
A-fib
If you have _______________________, you are going to be put on a blood thinner for the rest of your life.
2-3
If patient is on anti-coagulant, INR therapeutic range is __________________________.
Regular; therapeutic range
INR <4.0:
- Perform eval and _________________________ exercise regime
- Do not advance or increase intensity until _________________________ is reached
Resistive; 11
INR 4-5:
- Avoid ______________________ exercise
- Light exercise RPE <___________________
Held; vitamin K; fresh frozen plasma; no
Typically, if INR is >5-6:
- Coumadin is __________________________
- Administration of _________________________ or _________________________
- Perform eval for discharge planning/determine level of function
- _______________________ treatment
Avoid; consult
INR 5-9:
- _______________________ excessive physical activity
- Bed rest
- May do eval only for discharge planning or to determine current level of function
- _______________________ with team
Heart rate; O2 saturation; exertion
Guidlines for Therapy for Patient on Anti-Coagulant:
Monitor blood pressure, ________________________, ________________________, blood counts, physical appearance, level of _______________________, and safety.
Subtherapeutic levels
Coagulation level below goal. INR < 2-3
Clotting
Subtherapeutic INR levels, at risk for ________________________ (forming embolisms).
Supratherapeutic levels
Coagulation level above goal.
Bleeding
Supratherapeutic INR levels, at risk for ___________________________. → Can be reversed with Vit K or Fresh Frozen Plasma.
D-Dimer
Produced by action of plasmin on X-linked fibrin and their presence in the blood confirms that clotting has occurred. → By itself, does not indicate blood clot, but can be used /c signs and symptoms.
0.5 mg/L
Normal D-Dimer value.
Fibrin
D-Dimer is a measurement of _________________________ degradation.
DVT, PE
High levels of D-Dimer associated with ______________________.
Doppler ultrasound
Scan for DVT?
Chest scan, V/Q scan
Scan for PE?
Unlikely; weeks; does not; reduces
Mobilization with Acute DVT:
- Highly _____________________ to mobilize blood clot → More likely to cause another blood clot through immobility!
- Superficial vs. deep venous thrombosis
- Explain risks vs. benefits
- Can remain in LE for ______________________
- Anticoagulation therapy → _______________________ remove existing clot, blood thinner _______________________ risk of another clot
- Education on SxS: PE, DVT, CVA, MI
Chest; breathing; cyanosis
Signs and Symptoms of PE:
- Sudden ___________________ pain
- Cough
- Difficulty ______________________
- Anxiety
- LOC
- Increased RR
- ______________________ of skin
- Lightheadedness
Pumps; TED hose
DVT Prophylaxis:
- Early mobilization
- Ankle ______________________
- ________________________
- Sequential compression devices
- Pharmacological intervention
60%; 2/3; 1/3
Fluid Distribution:
- _____________________ of body weight is made up of water
- Intracellular compartment = ____________________ water in body
- Extracellular compartment = ______________________ water in body → Interstitial spaces (tissue spaces), plasma (vascular compartment), trans-cellular compartment (3rd spaces)
Extracellular
Are lab values intracellular or extracellular?
Ascites
Fluid between the skin and viscera.
Pericardial effusion
Fluid in pericardial space.