Anatomy & Physiology Exam 1 (MSU VMT)
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
enamel
the hardest substance in the body
what is the second hardest substance in the body?
bone
osteoblast
cells that produce bone
ossification
osteoblast harden the matrix through a process called
osteocyte
once ossification has occurred, osteoblasts are then called this,
also maintain the bone tissue
functions of bone
1. support
2.protection
3.leverage
4.storage
5. blood cell formation
hematopoesis
blood cell formation
Periosteum
the outer surface of the bone are covered with a membrane known as ...
cancellous bone
spaces are filled with marrow
spongy bone
compact bone
dense, hard, strong
shafts of long bone
osteogenic cell
develops into osteoblast
osteoclast
functions in resorption, the breakdown of bone matrix
Volkmann's canals
channels in the bone matrix which join to blood vessels
haversian cannals
brings nutrients to the osteocytes and connected to volkmanns canals
nutrient foramina
large holes in bones where things like large blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves enter
what can look like crack like type fractures in radiographs
nutrient foramina, volkmanns canal and haversian canals
endochondral bone formation
-body lays down a cartilage template that is gradually replaced by bone
primary growth center
the long bones start developing in the diaphysis of the cartilage
secondary growth center
the epiphyses ends of the bone are the...
epiphyseal plates
plates of cartilage , allows the long bones to lengthen as the animal grows
intramembranous bone formation
happens only in certain bones of the skull
creates the flat bones of the cranium that surround the brain, occurs in primitive connective tissue
red bone marrow
makes up the majority of the marrow in young animals but only a little left in older animals (long bones, sternum, pelvic bones)
makes red blood cells
yellow bone marrow
consists of mostly adipose tissue,
most common marrow in adult animals
does not have the ability to produce red blood cells but does have ability to revert back to red bone marrow if needed
mandible
the only moveable joint in the skull
sutures
immovable joints of the skull
hyoid apparataus
located high in the neck
supports the base of tongue, pharynx, and larynx, helps animal swallow
only can be seen in x-rays
invertebral discs
separates vertebrae and absorbs shock
spinous process
located dorsally on vertebrae
transverse process
located laterally on vertebrae
articular process
located on the ends pf vertebrae and acts as joints
cervical vertebra
neck vertebra, 7 on domesticated animals
atlas
c1 vertebra
yes joint
axis
c2
no joint
has the dens
thoracic vertebra
number varies between animals, very tall spinous process, comes after cervical vertebrae
lumbar vertebrae
number varies between species,
largest bone in spinal column
long transverse and spinous processes
must support the weight of the abdomen
sacral vertebra
vertebra fused to make a single structure called the sacrum
forms a joint with the pelvis called the sacroiliac joint
coccygeal vertebrae
bones of the tail
number varies on species
towards end of tail, they become simple rods
floating ribs
ribs that are unattached
manubrium
first part of sternum
xiphoid process
last part of sternum
costal cartilage
connects ribs to sternum
costalchondral junction
where the ribs and costal cartilage meet
acromion
expanded portion of the distal end of the spine
glenoid cavity
the concave articular surface
brachium
upper arm
greater tubercle
largest process opposite the head of the humerus
trochlea
the medial distal condyle is called --- and it articulates with the ulna
capitulum
distal condyle is called --- and it articulates with the radius
olecrannon fossa
The Posterior depression of the humerus (located at the distal end)
antebrachium
lower arm
olecrannon process
forms the point of the elbow
trochlear notch
a half moon shaped surface that wraps around the humeral condyle to make the elbow joint secure
anconeal process
proximal end of the trochlear notch and tucks in the olecrannon fossa
radius
main weight bearing bone of antebrachium
shaft is very straight in cats, bowed in dogs, horses, and swine
Carpal
proximal row are radial, ulnar, and accessory
ungual process
process that surrounded by the claw
pelvic symphyses
the two halves of the pelvis are joined by a cartilinagious joint
obturator foramen
two large holes on either side of pelvis for vessels to run through but to also lighten the pelvis
illium
cranial most portion of pelvis
forms sacroiliac joint
ischium
caudal most aspect of pelvis, projecting portion is called ischial tuberosity (pins)
pubis
smallest part of pelvis, forms the cranial portion of the pelvic floor
acetabulum
large socket in the pelvic bone for the head of the femur
trochlea
a smooth, grooved articular process for patella to ride
greater trochanter
larger process near head of femur
patella
knee cap
largest sesamoid bone
fabellae
2 small sesamoid bones located in proximal tendons of calf muscle behind knee
not present in cattle and horses
will only see in radiographs
tibial tuberosity
the point that faces forward on the proximal in of the tibia
tibial crest
ridge on the front of the tibia
fibula
thin
does not support any weight but serves as muscle attachment site
phalanges
typically animals only have II-IV
os cordis
is a bone in the heart of cattle and sheep that helps support the valves of the heart
os penis
is a bone found in the penis of dogs, beavers, racoons, and walruses that surrounds the penile, portion of the urethra
os rostri
is a bone in the nose of swine used for rooting
joint
the junction between two bones is known as --- pr articulation point
synovial joints
consists of joint capsule, ligaments, synovial membranes, synovial fluid, articular cartilage, and menisci
synovial fluid
provides lubrication to the joint
atlanto-occipital joint
The location where the atlas articulates with the occipital condyles.
atlanto-axial joint
articulation between the atlas and axis
nuchal ligament
elastic connective tissue that connects the upper cervical vertebra or skull to spinous processes of the thoracic vertebra
-helps support the head
canine nuchal ligament
extends from spinous process of the axis to spinous process of the first thoracic vertebra
feline nuchal ligament
absent in felines
bovine and equine nuchal ligament
arises from the skull and inserts on spinous processes of thoracic vertebra at the level of withers
skeletal muscle
cranial/spinal nerves
striated
have red, white, and intermediate muscle
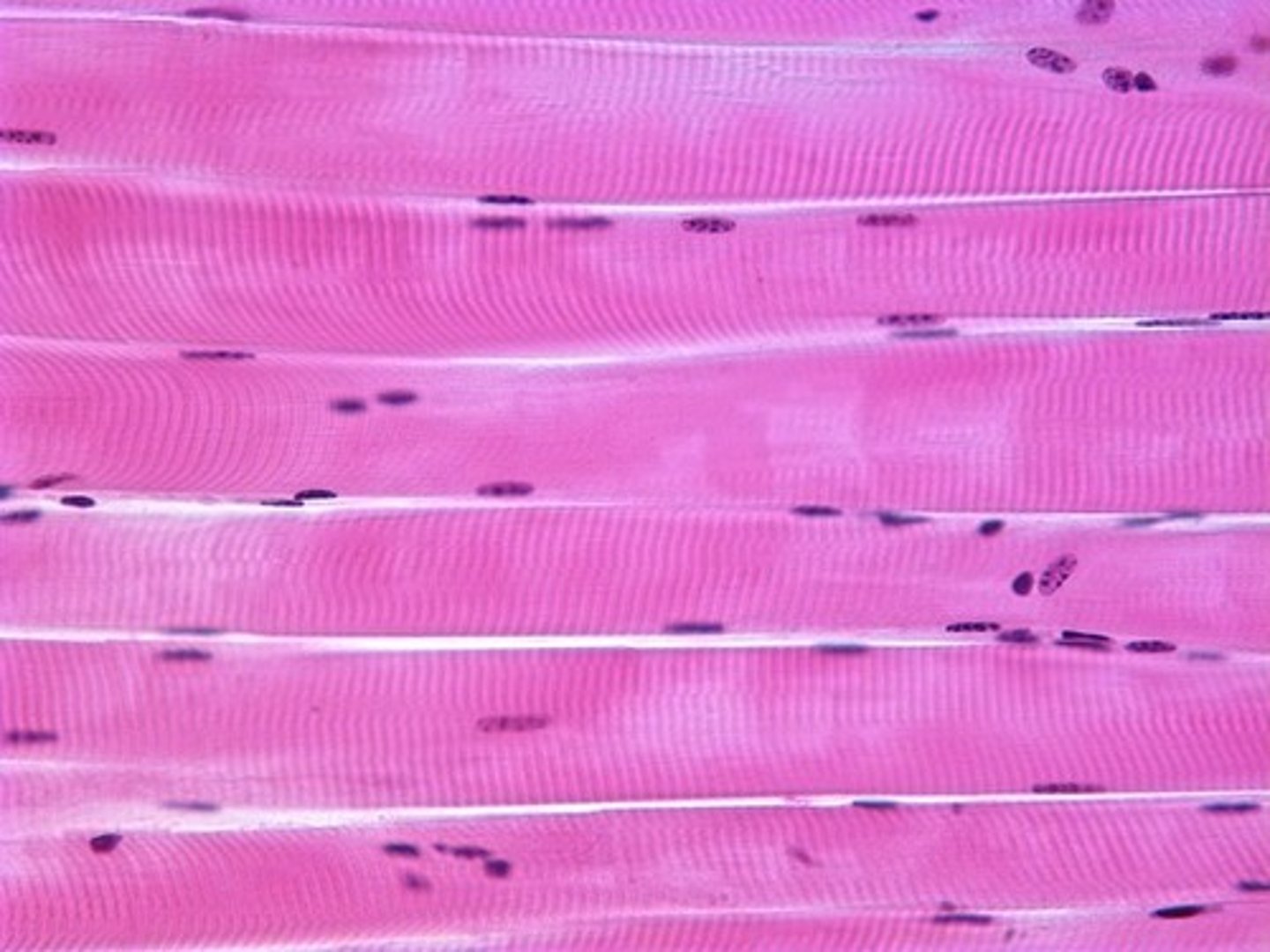
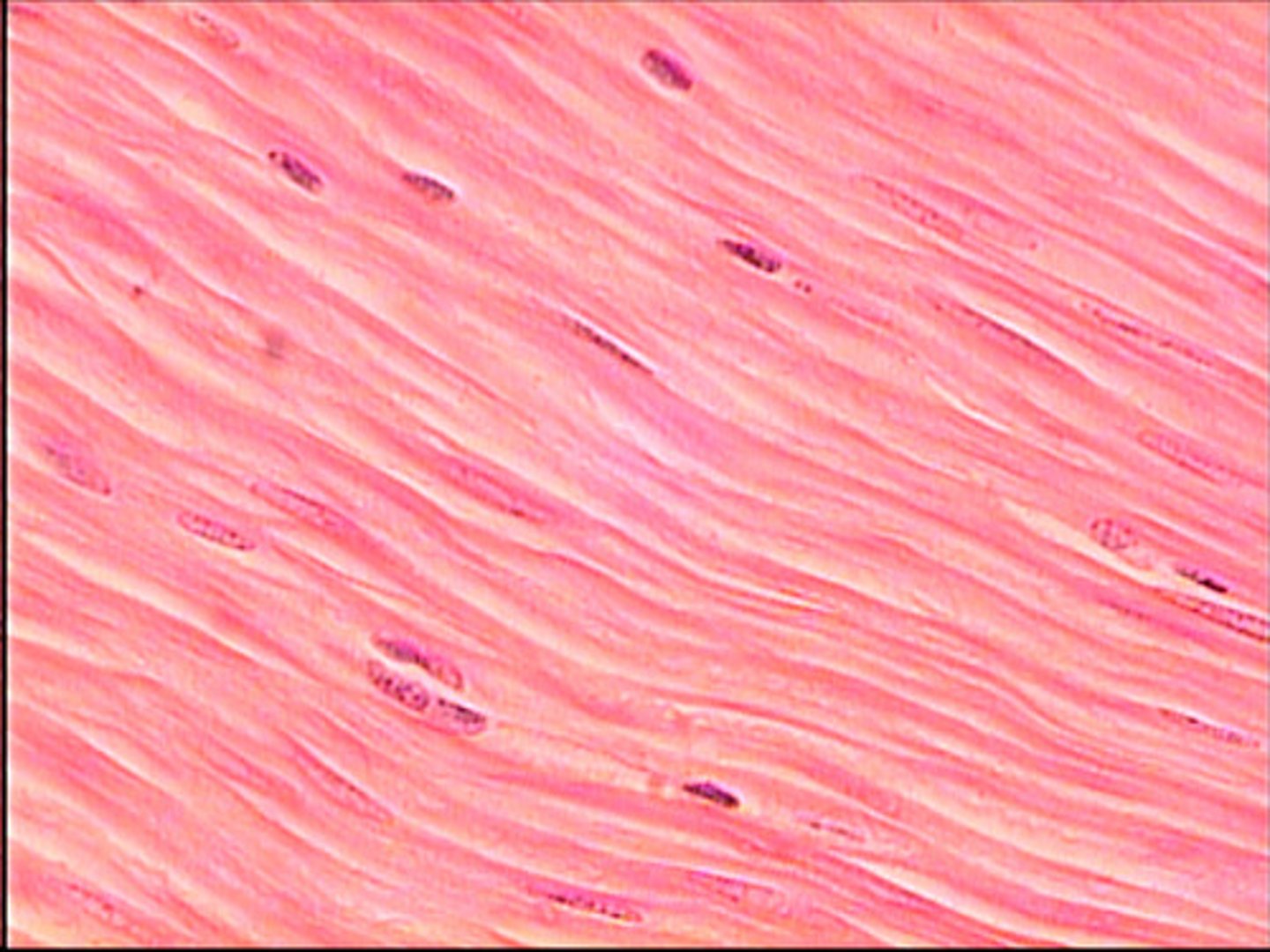
smooth muscle
no striations
autonomic nervous system
involuntary
visceral structures- intestines, sweat/salivary glands
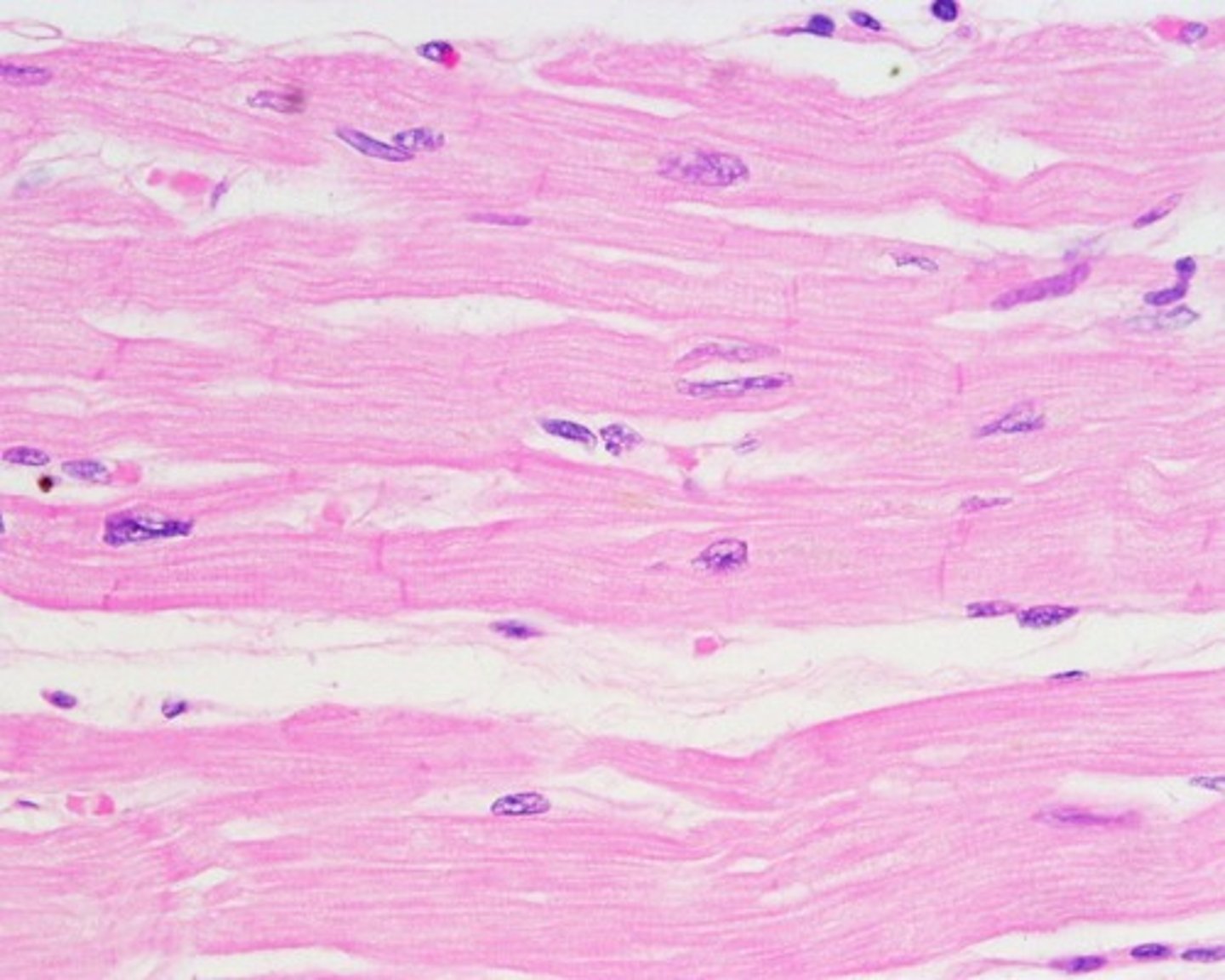
cardiac muscle
autonomic nervous system
striations
intercalated disks (make their own action potential)
functions of muscles
1. locomotion
2. movement
connective tissue order
endomysium, perimysium, epimysium, epimysium
endomysium
muscle fibers sarcolemma
perimysium
muscle fascicles
Epimysium
continuous with tendon or aponeurosis
skeletal muscle order
myofilaments, myofibrils, muscle fiber, muscle fiber bundle, muscle
Actin
A globular protein that links into chains, two of which twist helically about each other, forming microfilaments in muscle and other contractile elements in cells.
myosin
A protein present in muscle fibers that aids in contraction and makes up the majority of muscle fiber
Sarcotubular system
made up sarcoplasmic reticulum, t tubule
why is the sarcoplasmic system important
storage of calcium
Acetylcholine (Ach)
a neurotransmitter involved in learning, memory and muscle movement, released at synaptic gap
functions of integumentary system
-prevents disiccation, reduces threat of injury, maintains normal body temperature, excretes water, salt, and organic wastes, receives and conveys sensory information, synthesizes vitamin D; stores nutrients
layers of skin
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
keratinocytes
produce keratin - a tough fibrous protein that provides protection.
melanocytes
produce melanin pigment