Sinus Rhythm Criteria
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
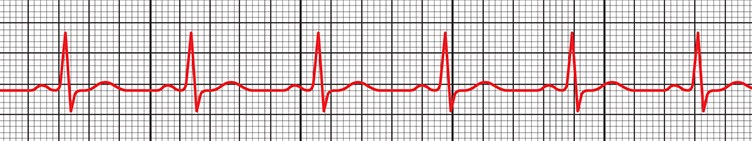
What rhythm is this?
Sinus Rhythm (the normal, regular rhythm of the heart initiated by the sinoatrial (SA) node with a rate of 60-100 bpm)
What is the criteria for a normal sinus rhythm?
• Preceded by a P wave
• Has a QRS complex
• Has a T wave
• The intervals are within normal ranges
• The heart rate is within 60 – 100/min
• P waves and QRS complexes are similar
• Distance of one R to the next is the same
• Regular rhythm
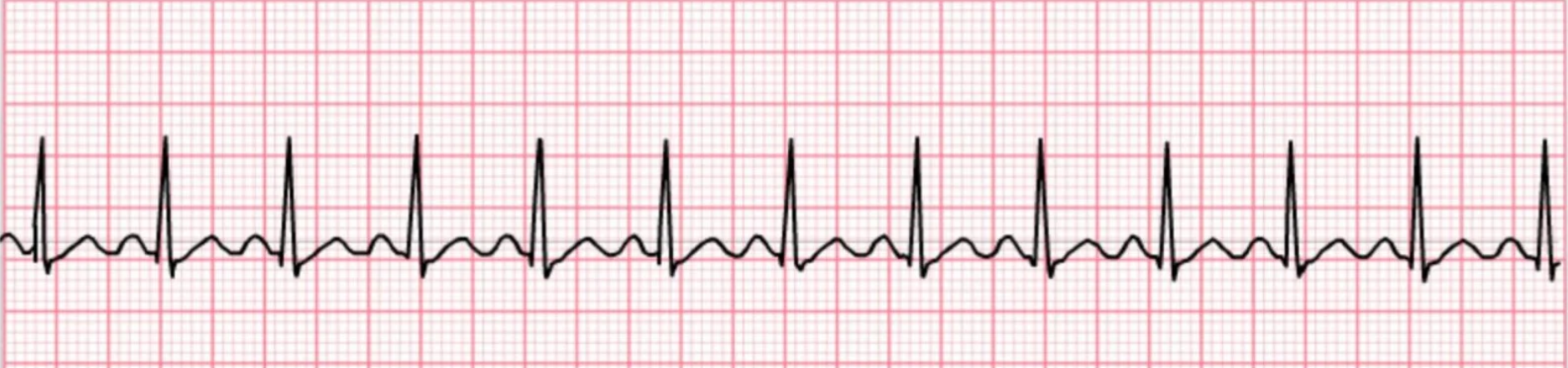
What rhythm is this?
Sinus Tachycardia (sinus rhythm with a heart rate greater than 100 bpm)
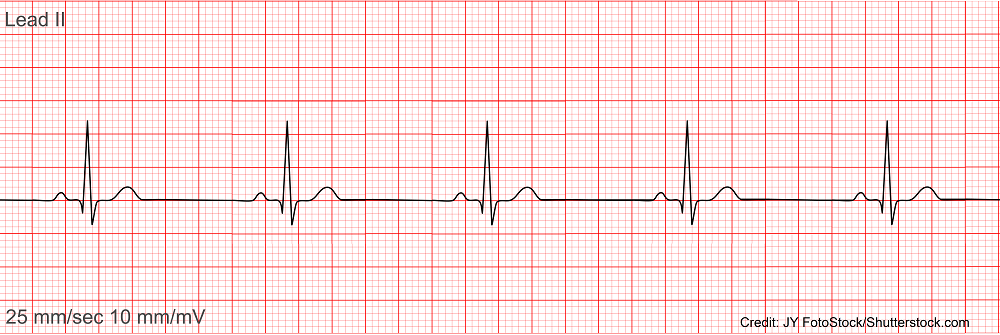
What rhythm is this?
Sinus Bradycardia (sinus rhythm with a heart rate less than 60 bpm)
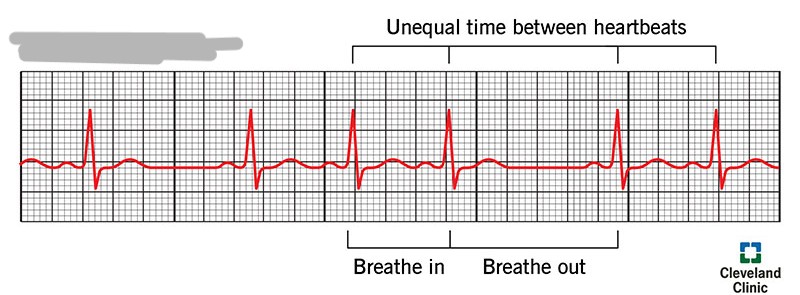
What rhythm is this?
Sinus Arrhythmia (sinus rhythm with slight irregularity in the rate, often related to breathing)
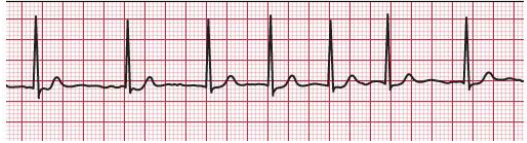
What rhythm is this?
Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib) (QRS, T, flat, QRS,,) (an irregularly irregular heart rhythm characterized by the absence of distinct P waves and erratic atrial electrical activity)
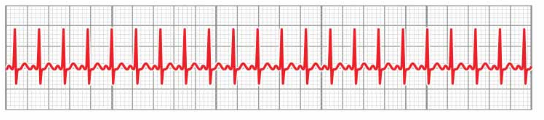
What rhythm is this?
Atrial Flutter (A-Flutter) (a rapid, regular atrial rhythm caused by a reentrant circuit, producing sawtooth-shaped flutter waves, typically with an atrial rate of 250–350 bpm)
What are the waves called in between the atrial flutter?
Sawtooth flutter waves (especially visible in leads II, III, and aVF)
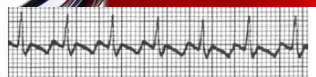
What rhythm is this?
Atrial Flutter with 2:1 AV Conduction
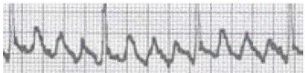
What rhythm is this?
Atrial Flutter with 3:1 AV Conduction
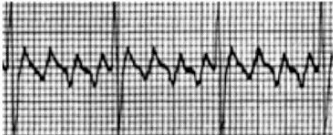
What rhythm is this?
Atrial Flutter with 4:1 AV Conduction
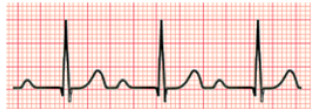
What rhythm is this?
1st Degree AV Block (a delay in AV conduction characterized by a prolonged PR interval > 0.20 seconds (1 block) with every P wave followed by a normal QRS complex)
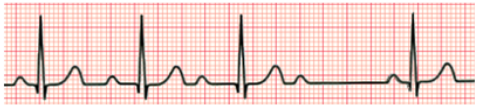
What rhythm is this?
2nd Degree AV Block Type I (Mobitz I / Wenckebach) (PR interval gradually lengthens until a QRS complex is dropped)
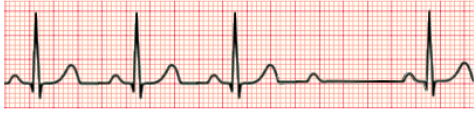
What rhythm is this?
2nd Degree AV Block Type II (Mobitz II) (PR interval stays the same, but QRS complexes are suddenly dropped)
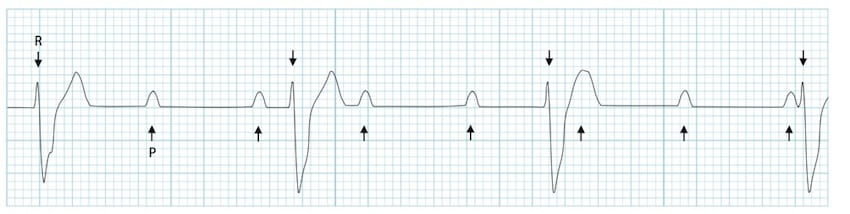
What rhythm is this?
3rd Degree AV Block (AV dissociation) (No relationship between P waves and QRS complexes)
Why is 3rd degree AV block also called AV dissociation?
there is no relationship between atrial and ventricular events
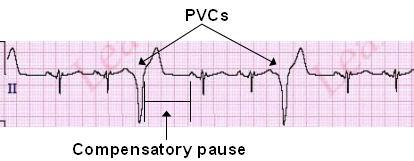
What is a Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC)
extra, abnormal heartbeats that originate in the ventricles, the heart's lower chambers, and disrupt the normal rhythm.
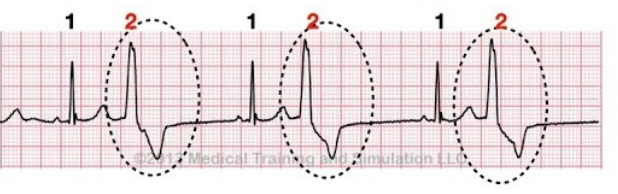
What rhythm is this?
Bigeminy (one, two, PVC (every beat)
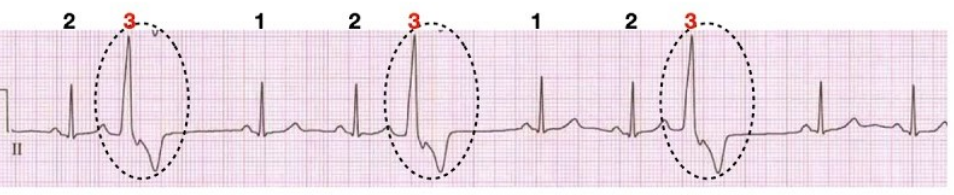
What rhythm is this?
Trigeminy (one, two, three, PVC (every 2 beat)
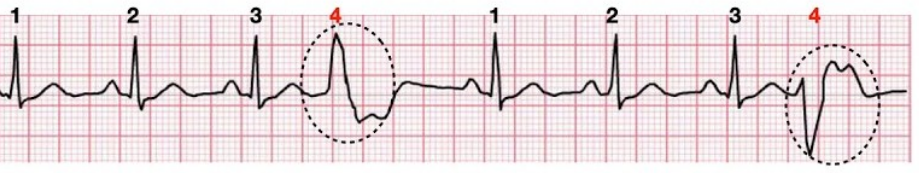
What rhythm is this?
Quadrigeminy (one, two, three, four, PVC in every 3 beat)
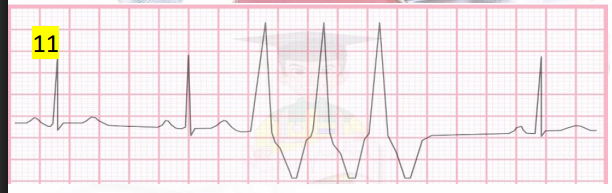
What rhythm is this?
PVC in salvo (3 consecutive PVC)
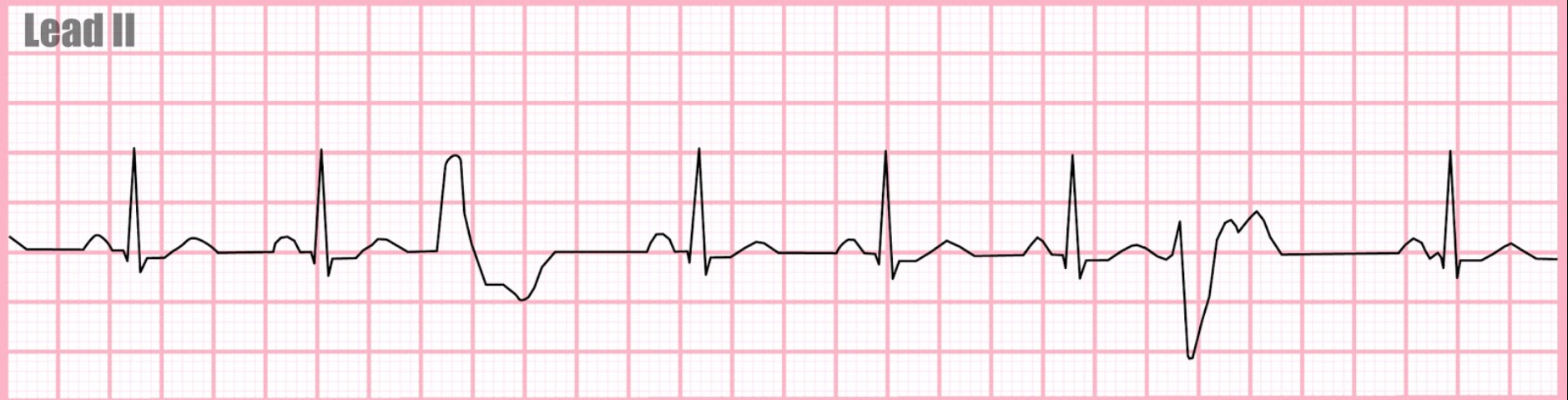
What rhythm is this?
Multifocal (PVC in various forms)
Whats the type of PVC if its less that 5 per min?
Infrequent PVCs
Whats the type of PVC if its 5 or more per min?
Frequent PVCs
What is it called if PVCs occurr singly?
Isolated PVCs (Beats)
What is it called if PVCs occurring in groups of two or more?
Group Beats / Bursts / Salvos
What is it called if 2 PVC’s in a row?
Paired PVCs (Couplet)
What is it called if its three or more PVCs in a row?
Ventricular Tachycardia
What is it called if PVCs alternating with the QRS complexes of the underlying rhythm?
Ventricular Bigeminy (Basically: one, PVC, one, PVC)
What is it called if its PVCs following every two or three QRS complexes of the underlying rhythm?
Ventricular Trigeminy / Ventricular Quadrigeminy
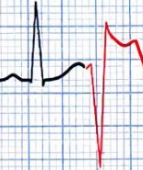
What rhythm is this called?
R-on-T Phenomenon (A PVC occurring during the downslope of the preceding T wave (vulnerable period of ventricular repolarization)
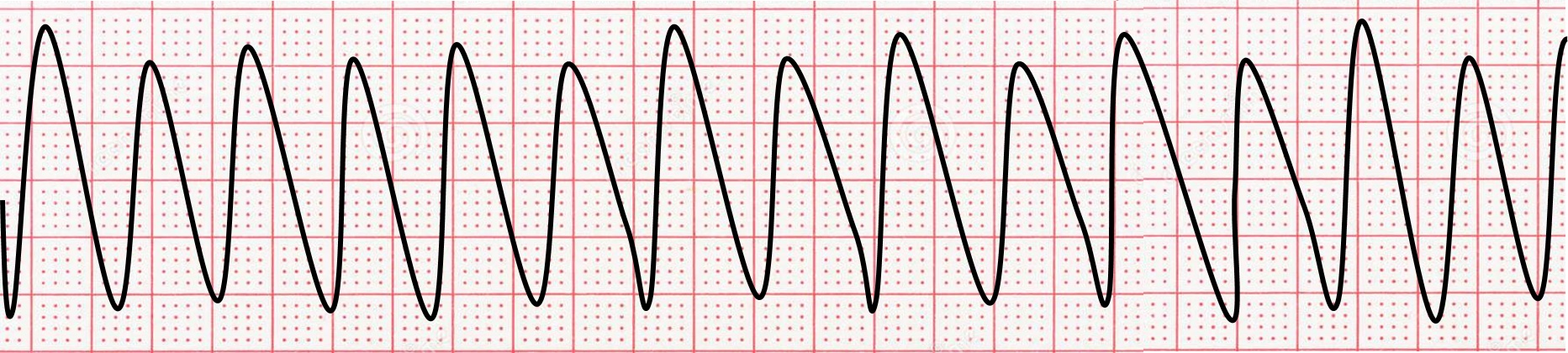
What rhythm is this called?
Ventricular Tachycardia (VTAC) (No visible P wave & Ventricular rate 100-220 b/min)
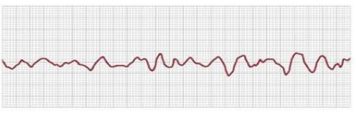
What rhythm is this called?
Ventricular Fibrillation (V-fib, sawtooth pattern, no visible P wave and QRS complex, chaotic pattern, no cardiac output, a medical emergency)
Why is Ventricular fibrillation a medical emergency?
The heart does not pump blood/ no cardiac output
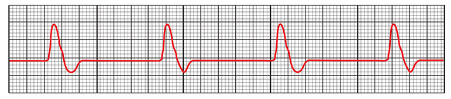
What rhythm is this called?
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) (is a condition where your heart stops. The electrical activity in your heart doesn't generate a heartbeat but it is still shown in the monitor)
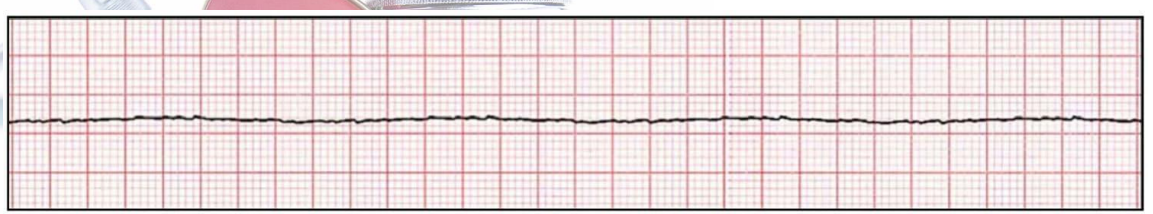
What rhythm is this called?
Asystole (cardiac arrest with no electrical activity)
How to treat asystole?
treat with high quality CPR and 1mg Epinephrine given every 3-5 mins
What will you do if you found out that the tracing of your patient is Asystole?
Check pulse & Start high quality chest compression/CPR