Agri 22 Exam bruh
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Advantages of Poultry over Other Livestock Species
• No cultural restrictions
• Has socio-cultural importance
• Shorter production cycle
• Shorter generation interval
• Higher reproduction rate
• Lower production cost / minimal inputs
• Convenience of preparation
Intensive
(i.e. use of sophisticated housing system)
Extensive
(i.e. free-ranging)
Commercial Poultry Farm
Operations
• Broiler
• Layer
• Breeder
• Hatchery
• Native chicken and duck
• Game fowl
Supporting Industries
• Feed milling companies
• Transport services
• Equipment suppliers
• Veterinary suppliers
• Processing plants
• Packaging industries
• Marketing and distribution
Broiler Farms
Central Luzon
Layer Farms
CALABARZON
Native Chicken
Western Visayas
Duck Farms
Central Luzon
China
is the
top producer
of duck meat
in the world
13.93 million birds
As of Dec 2024, the
total duck population
recorded was
Poultry
domesticated birds kept for eggs or meat
Subgroup Archaeopteryx
ancient winged creature
Gallus gallus (red)

Gallus lafayetti (Ceylonese)

Gallus varius (Green)

Gallus sonneratii (Grey)

Peafowl
Pheasant
Guinea Fowl

Swan

Goose

Galliformes

Anseriformes
Mallard
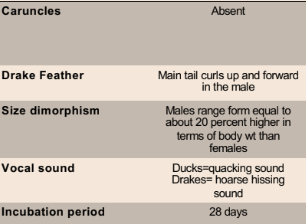
Muscovy

EGG Class
Comparatively small
body size
Normally lays large
white-shelled eggs
Very active
Non-sitters
Leghorn, Minorcas,
Anconas, Mikawa,
Lohmann
MEAT Class
Large body size
Slow movement
Poorer egg layers
Generally lay brown
shelled eggs
Brahmas, Cochin,
Langshans, Cornish,
White Rocks, Cobb,
Ross, Hubbard
GENERAL
PURPOSE Class
Medium sized good layers
Young ones are fast growers
Not so nervous as egg class but
more active than meat class
New Hampshire, Rhode Island
Red, Plymouth Rock, Lancaster,
Nagoya, Cantonese
FANCY Class
Beautiful plumage or form
Rare unusual appearance
Raised as ornamentals or pets
Frizzle, Bantams, Long tailed
General purpose class

Fancy class

Brooding
Early period of growth of poultry
species when supplemental heat must
be provided (Austic and Nesheim, 1990)
Nursery period for the chicks
Hover/heater
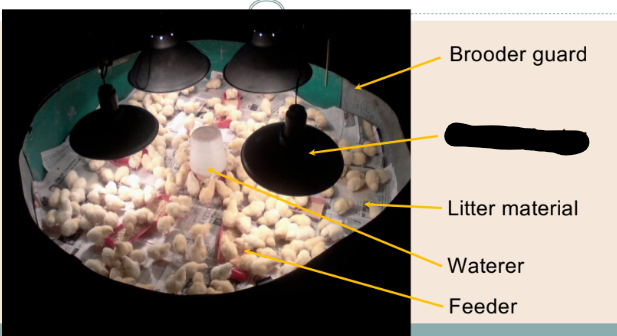
31-32C (1st week)
Reduced by 2C per week
Maintained at 21-24C at the end of brooding
Ideal temperature:
22%
3100
Provide booster feeds immediately after arrival (__%CP & ___kcal/kg ME) for one week
Overcrowding
results of
o Stunted growth
o Poor flock uniformity
o Cannibalism
Precision Beak Trimming
Removal of the portion of the beak to prevent cannibalism
Cannibalism
o Toe, vent, head or tail picking, or feather pulling
Practiced only for breeders
and layers NOT for broilers
Rate of feathering
Slow feathering – longer brooding
Fast feathering – shorter brooding
Season of the year
Summer – shorter brooding
Rainy – longer brooding
Goal during preparation for lay
Acceleration of body weight
Attain sexual maturity with good body conformation
Goal during the maintenance phase
Control the growth (except for broiler)
Quantitative
Types of feed restriction:
(reduction in amount)
Qualitative
Types of feed restriction:
(feed dilution)
4.5 birds/m2
Floor space allowance
Light
Management During Growing
Photoperiod or daylength should be restricted during
this period
Should not exceed 12 hours
Stimulates the development of the reproductive system
of the fowl
Too early sexual maturity
Production of too small eggs
Short production cycle
High incidence of prolapse
Characteristics of healthy pullets
free from physical and genetic deformities
alert and active
has ideal bodyweight
well-developed comb and wattles
clean and tidy feathers
strong straight legs
has deep yellow pigmented beaks and shanks
Transition Phase (Growing to Laying)
Transfer pullets at least one month before laying (15-18
weeks)
Transfer birds at night or early morning
Transfer only healthy pullets
Management Practices
Growing: Pre-Lay Phase
Plan transport in advance and organize it well to ensure optimal comfort for the birds.
Monitor the body weight before and after transfer to
guarantee that the flock is developing correctly.
Closely monitor water consumption during the week after arrival at the laying house.
No vaccinations during transfer where possible.
Management Practices
Laying
After transfer
During the first two days:
-observing behavior
-monitoring water and feed consumption
At the same time the birds will identify with this
person.
Management Practices
Growing: Pre-Lay Phase
Pre-Lay Diet
Reinforce the mineralisation of medullary bone, layer calcium storage, before the beginning of the lay prevent demineralisation of early sexual mature birds
RESULT: Good eggshell quality during LAYING
Increasing calcium content of the diet
Calcium content of the diet is essential for the production of egg-
shell. If calcium in the diet is not enough, the birds will tend to
withdraw it from the medullary bones or the birds will lay soft-
shelled or shell-less eggs
Body weight
Photoperiod
Two main factors that stimulate the onset of
laying in the flock:
Water Requirement
Rule of Thumb: Water intake should be 1.5 to
2 higher than feed intake
25-26
A hen would ideally lay eggs every __-__ hours from 7am to 4pm.
Egg collection must be done 3-4 times a day especially during the peak season in order to maintain the quality of the eggs.
Egg Collection
If eggs stored in higher temperature, lower
humidity leads to rapid loss of weight and
impairs the quality of the egg
Large
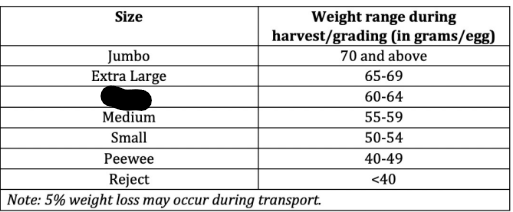
Culling
Removal of unprofitable/unproductive birds from the
flock
• Sick Birds
• Non-laying
• Poor producers
Purchase of day-old chicks
Ready-to-lay-pullets
(RTLP)
Two starting points for layer production
Auto Sexing

Vent sexing
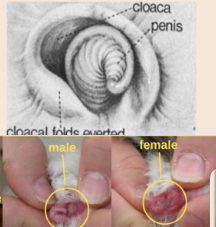
Feather sexing

Molting and Recycling
Periodic shedding and replacement of feathers
Involves reproductive quiescence, which is incomplete, hen tends to
lay eggs at a lower rate
Practice Sex Separate Feeding (SSF)
o Different nutrient requirement
o How to implement?
1. Install feeders of males higher
2. Use feeder for females with narrower grills
3. Insert plastic nose bar in males
All-in-all-out System
-Day-old broiler chicks are raised only in one particular batch or
age group at any given time.
Multiple-batch system
-Day-old broiler chicks are purchased in batches at weekly or bi-
weekly intervals and reared at the same time in the same farm.
28-35 days
Rearing period
14 days
Cleaning time
Gain in Weight

Feed Conversion ratio (FCR)

Mortality rate (depletion rate)

Tunnel-ventilated housing system

Conventional housing system
