CH 9: Muscular System -- Histology and Physiology
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
General functions of muscular system (7)
Movement
Maintain posture
Respiration
Production of HEAT
Communication
Constrict of organs
Contract heart
Skeletal muscle tissue
Characteristic: STRIATIONS, Multinucleate, VOLUNTARY
Function: regulate body temp + control breathing
Location: ATTACH TO BONES
There’s a lot of striations (very thick)
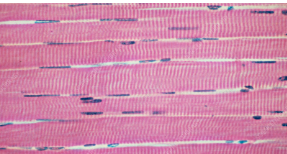
Cardiac Muscular Tissue
Characteristics: INTERCALATED DISCS, INVOLUNTARY, THIN STRIATIONS, Uninucleate
Function: PUMP HEART
Location: HEART
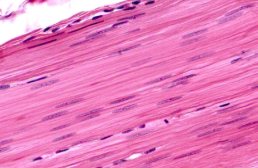
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Characteristic: INVOLUNTARY, NO striations, uninucleate,
Function: CONSTRICT BLOOD VESSELS/ORGANS
Location: INTERNAL ORGANS (digestive tract)
NO STRIATIONS
NOT WAVY unlike dense regular connective tissue
General Properties of Muscle Tissue
Contractility: Muscles can SHORTEN WITH FORCE
Excitability: Muscles can RESPOND TO STIMULI
Extensibility: Muscles can be STRETCHED BEYOND NORMAL
Elasticity: Muscles can GO BACK TO ORIGINAL LENGTH after being stretched a lot
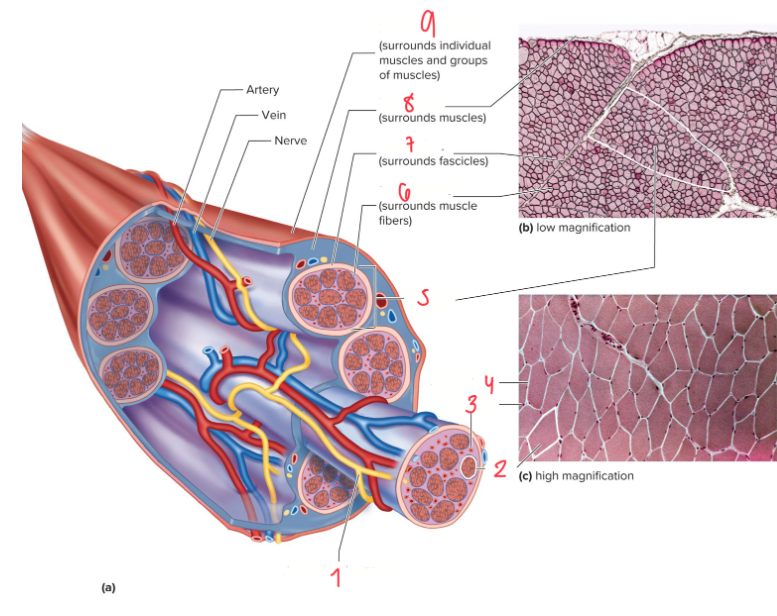
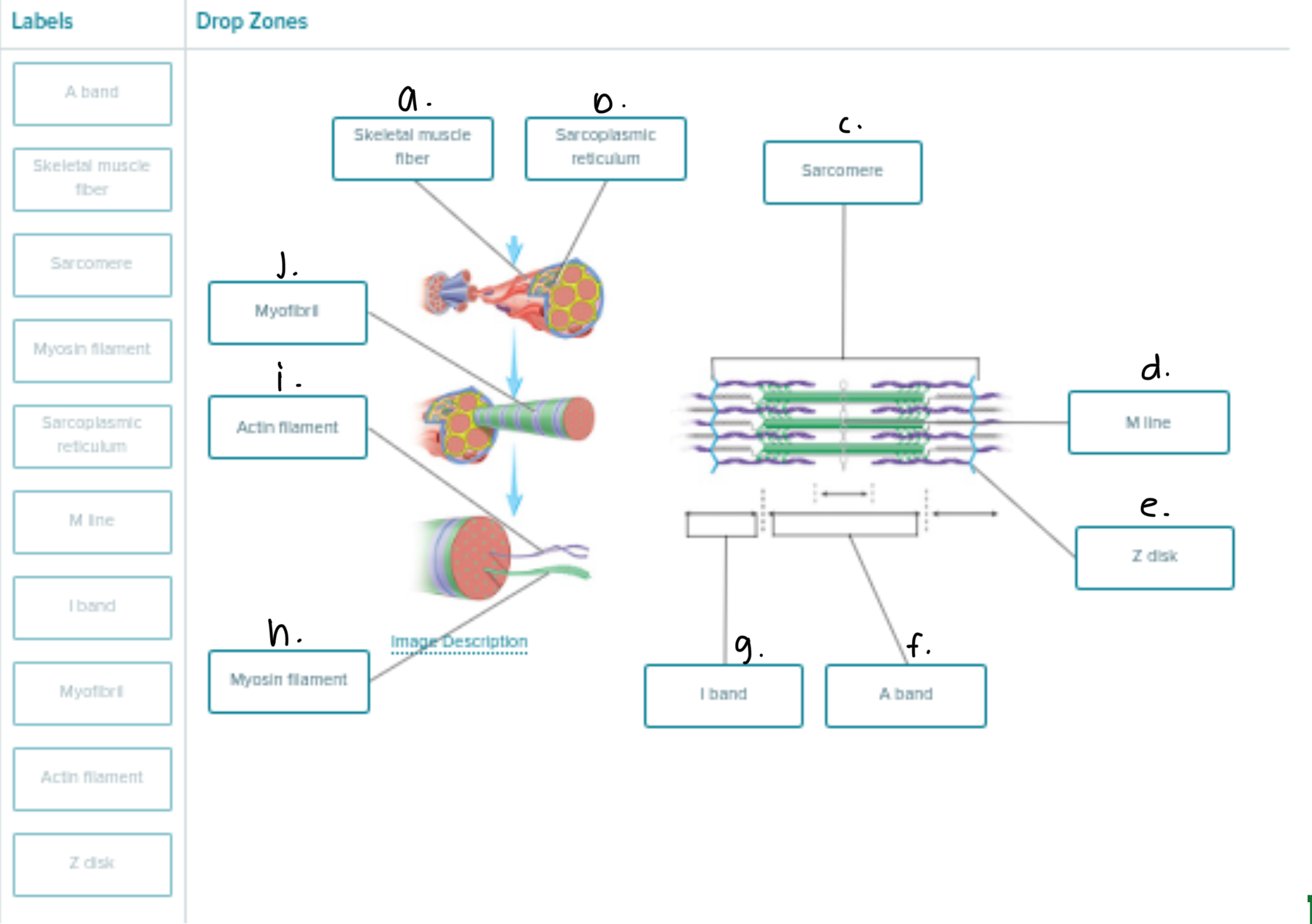
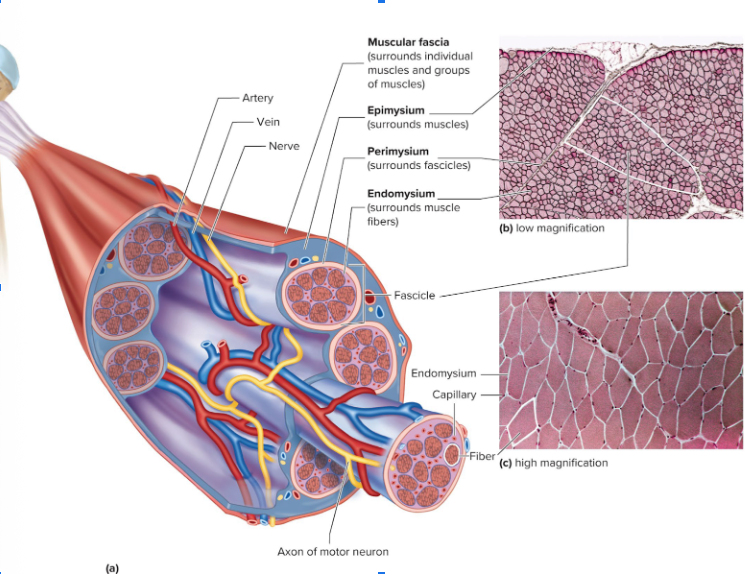
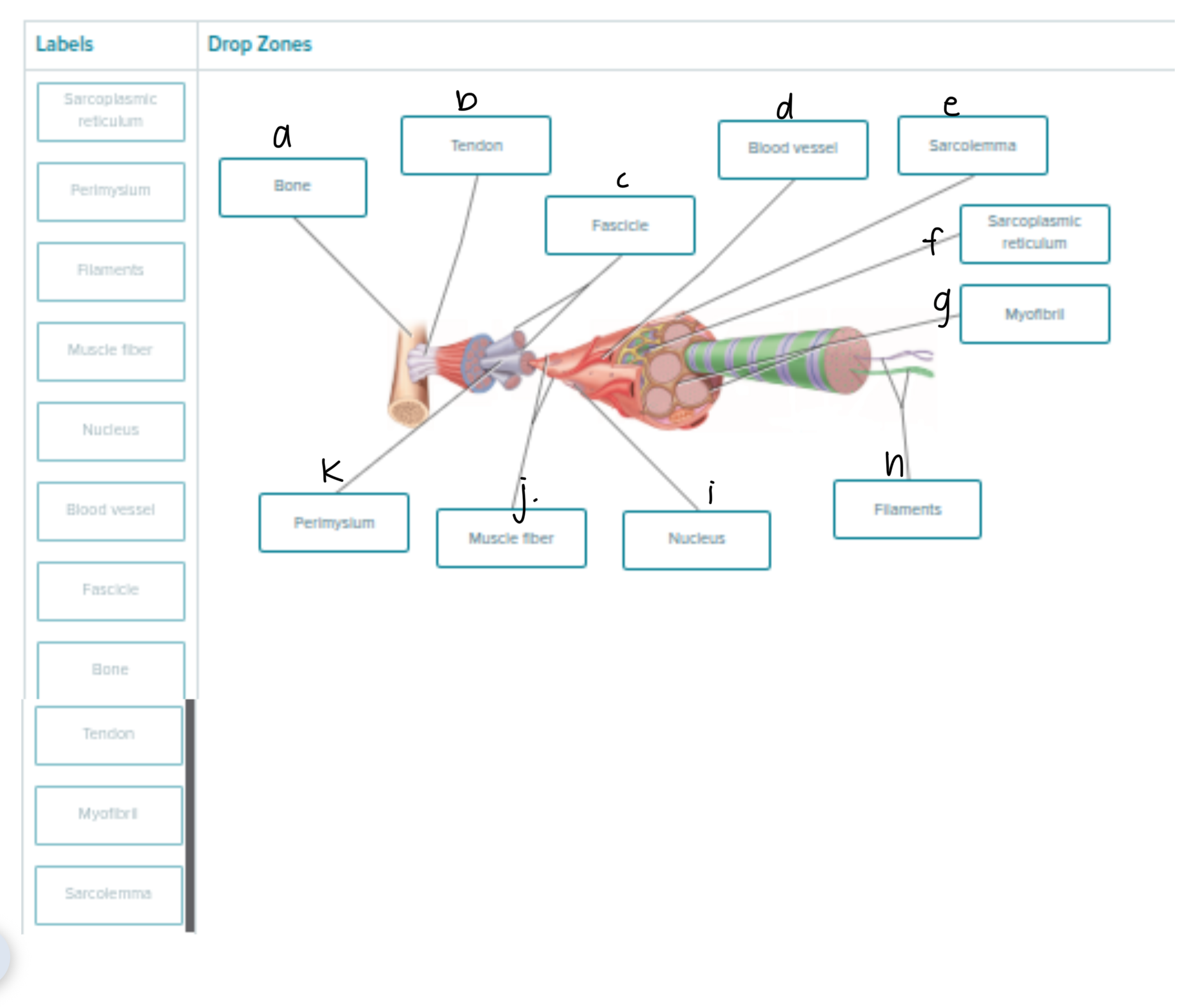
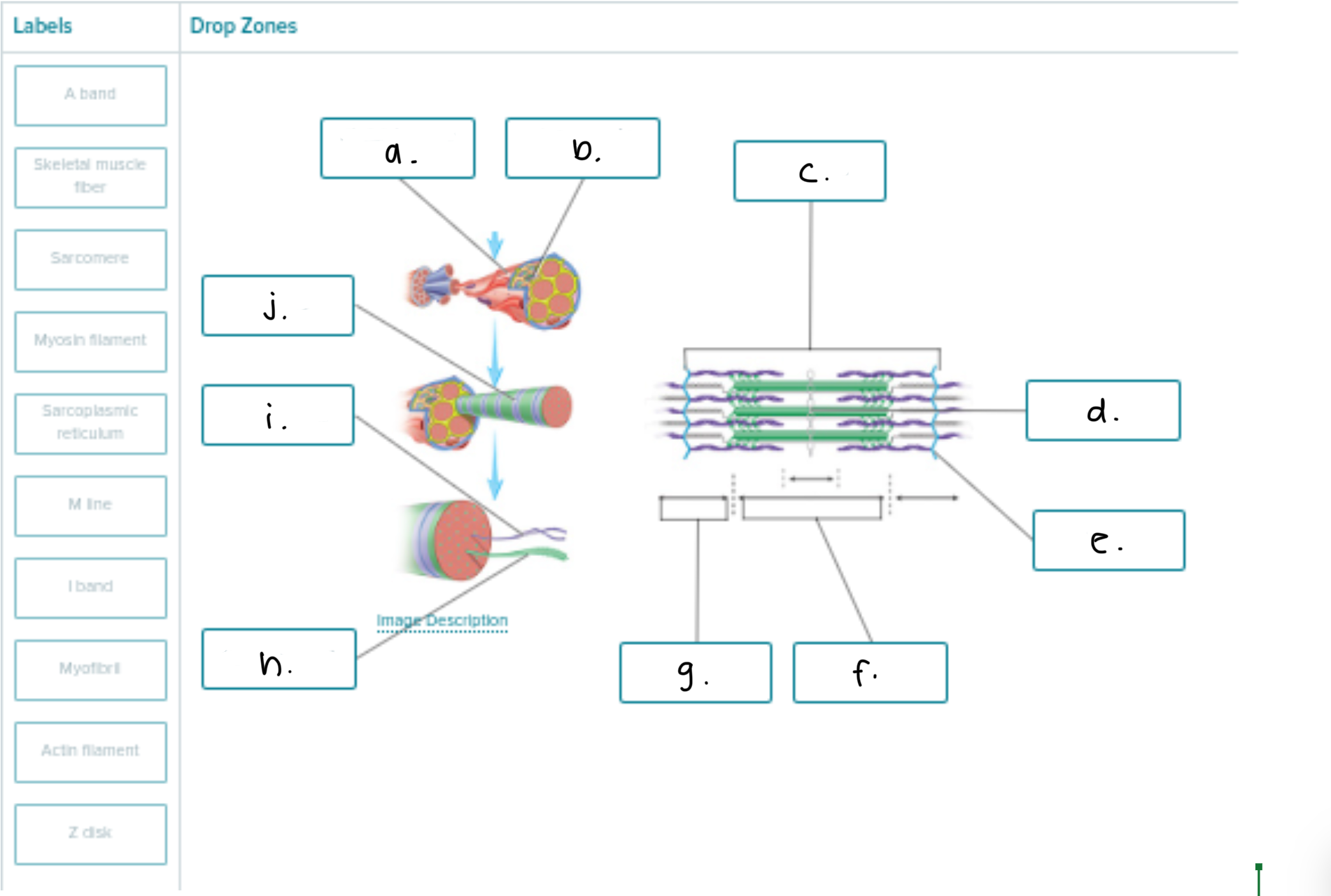
Label the following 1-9
Axon of Motor Neuron
Fiber — 1 MUSCLE FIBER that’s SHAPED LIKE A CYLINDER
Capillary
Endomysium (and 6 is included too)
Fascicle — GROUPS OF MUSCLE FIBERS; more than 1 fascicle = muscle organ
Endomysium
Perimysium
Epimysium
Muscular Fascia
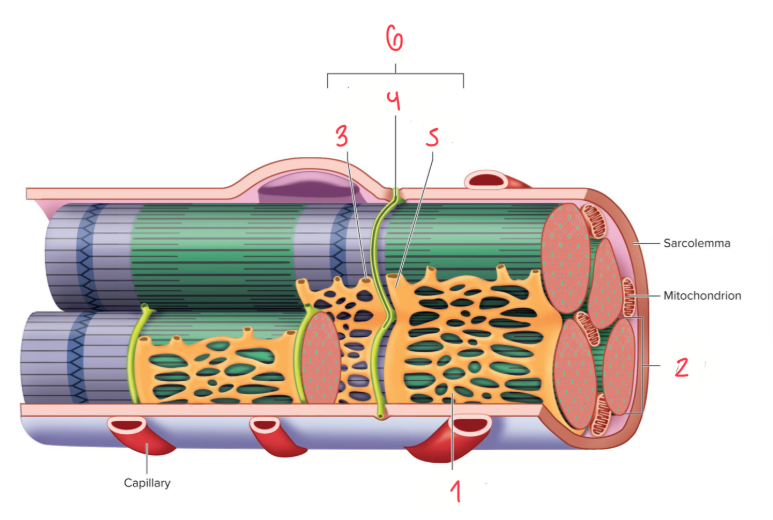
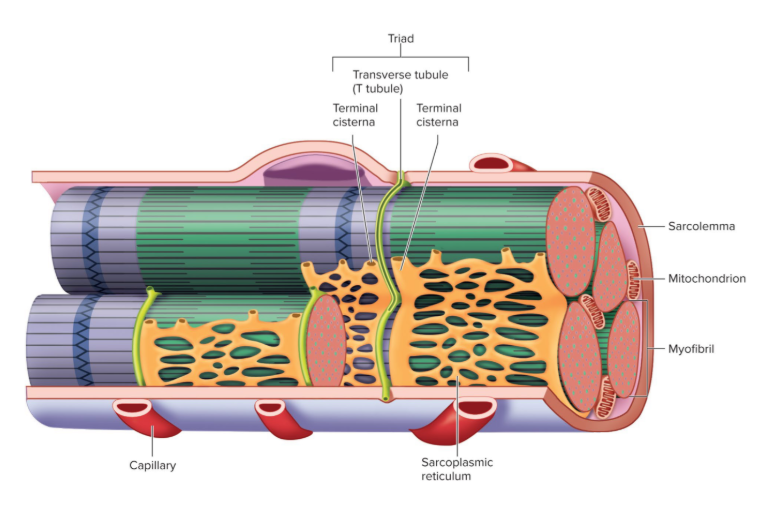
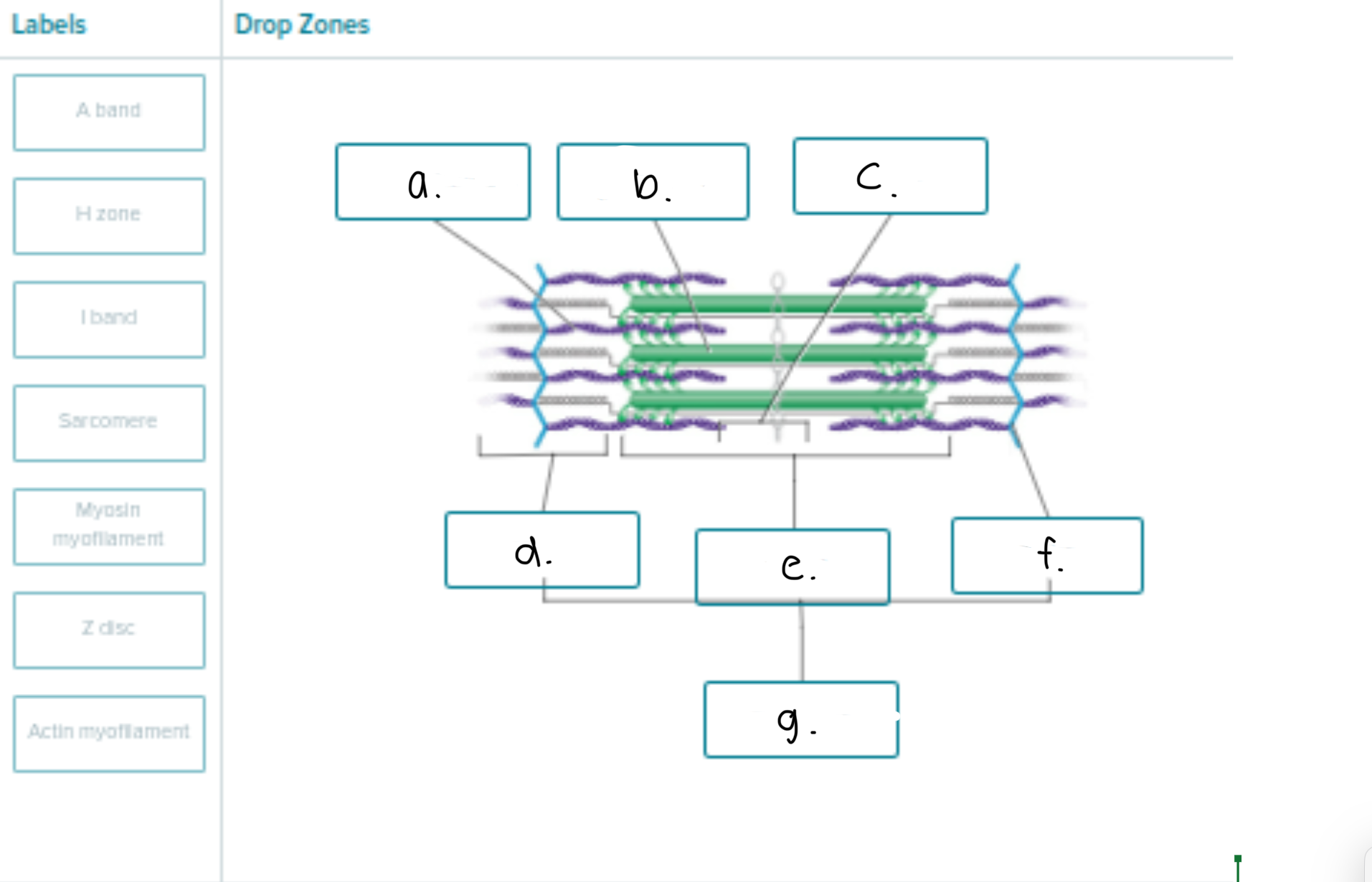
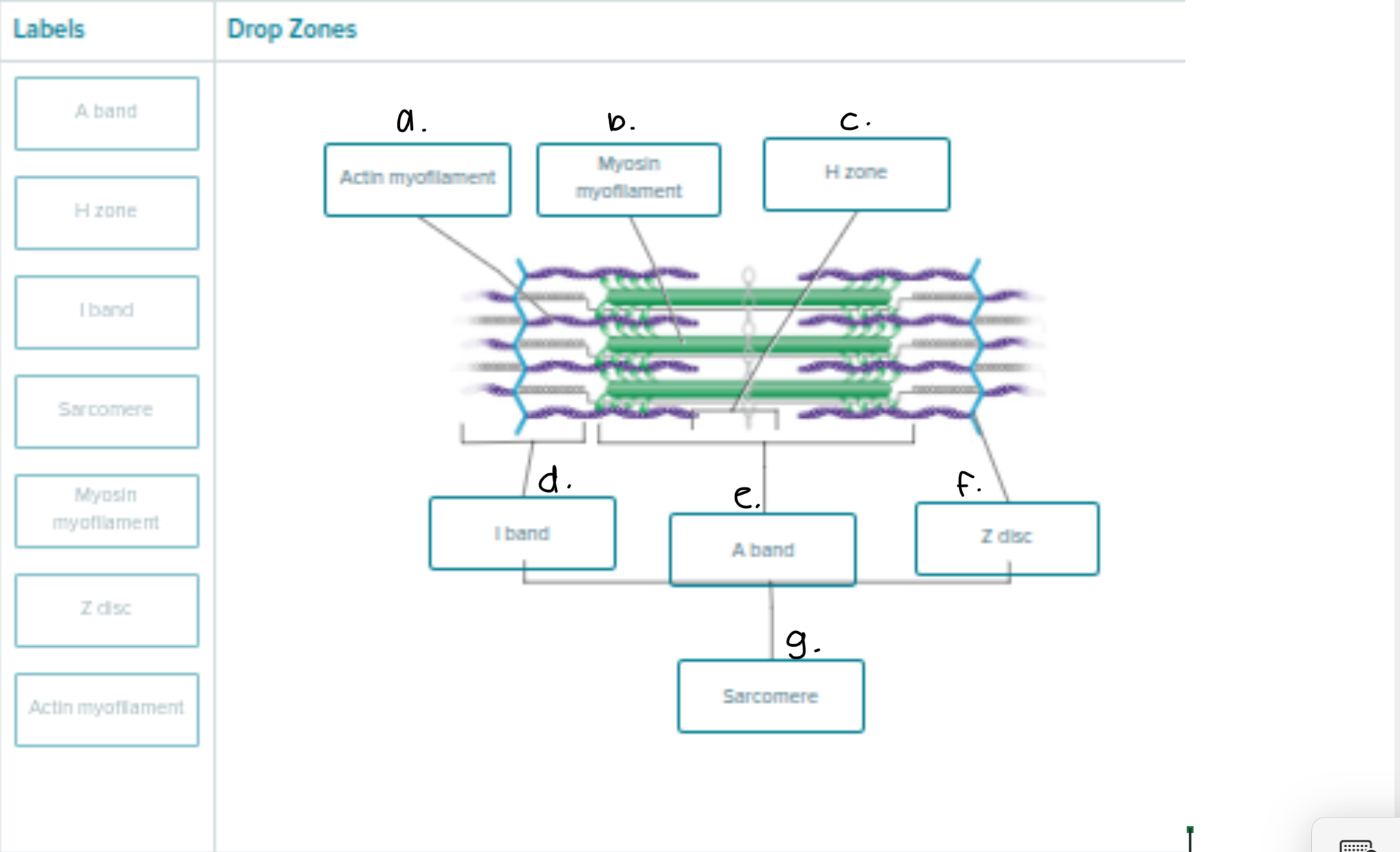
Label following 1-6
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Myofibril
Terminal Cisterna
T Tubule
Terminal cisterna
Triad (the t tubule in the middle and terminal cisterna in both sides of the t-tubule)
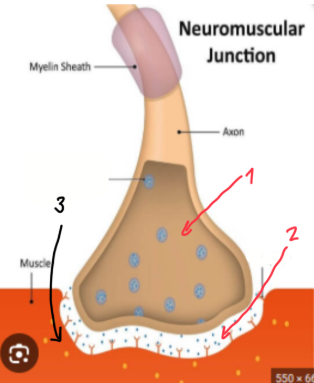
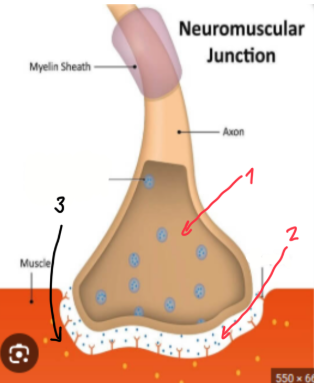
Neuromuscular junction (AKA synapse)
Presynaptic terminal — where ACTION POTENTIAL ENDS in which RELEASES NEUROTRANSMITTERS into the synaptic cleft
When the neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft, it binds to the receptors within there which triggers the opening of ligand-gated Na+ ion channels, ultimately causing depolarization
Synaptic cleft — this is the SPACE between PRE AND POSTSYNAPTIC
Postsynaptic membrane — this is the RECEIVING END that CONTAINS RECEPTORS the NEUROTRANSMITTERS WOULD BIND TO
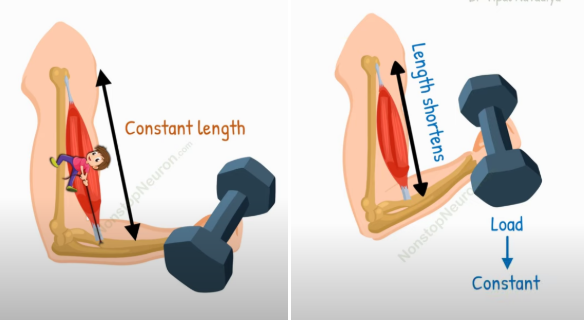
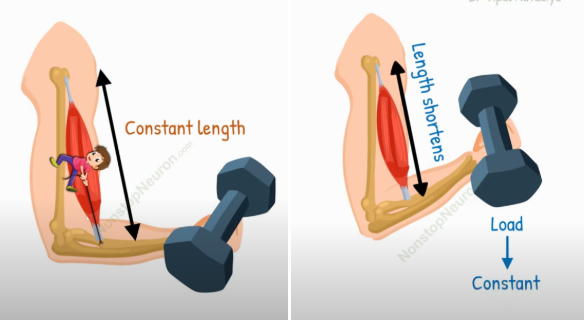
Isometric VS isotonic Muscle contraction
Isometric contraction: the LENGTH stays SAME, but there’s FORCE CREATED because it’s holding something
this helps with MAINTAINING POSTURE
e.g: holding a dumbell upright
NO MOVEMENT INVOLVED
Isotonic contraction: the LENGTH CHANGES BECAUSE OF MOVEMENT, but the RESISTANCE (LOAD) stays the SAME
MOVEMENT INVOLVED
e.g: doing a bicep curl
The muscle changes because there’s movement, but the weight of the resistance stays the same
Process of process of crossbridge cycle (6 steps)
The Myosin binding site is BLOCKED because of tropomyosin
1 ATP in the myosin (golf club looking thing) goes through HYDROLYSIS and turns into 1 ADP + inorganic phosphate.
Binding site still becomes BLOCKED
Ca+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum and BINDS TO TROPONIN, CHANGING ITS SHAPE
Tropomyosin that’s attached to the troponin gets DISPLACED because the troponin changed shape
The binding site becomes FREE, allowing myosin head to bind to actin filament
Muscle Twitch
CONTRACTION of 1 MUSCLE FIBER
SMALL MUSCLE CONTRACTION
Summation
ADDING EFFECT of repeated muscle twitches that CAUSE STRONG AND LONG MUSCLE CONTRACTION
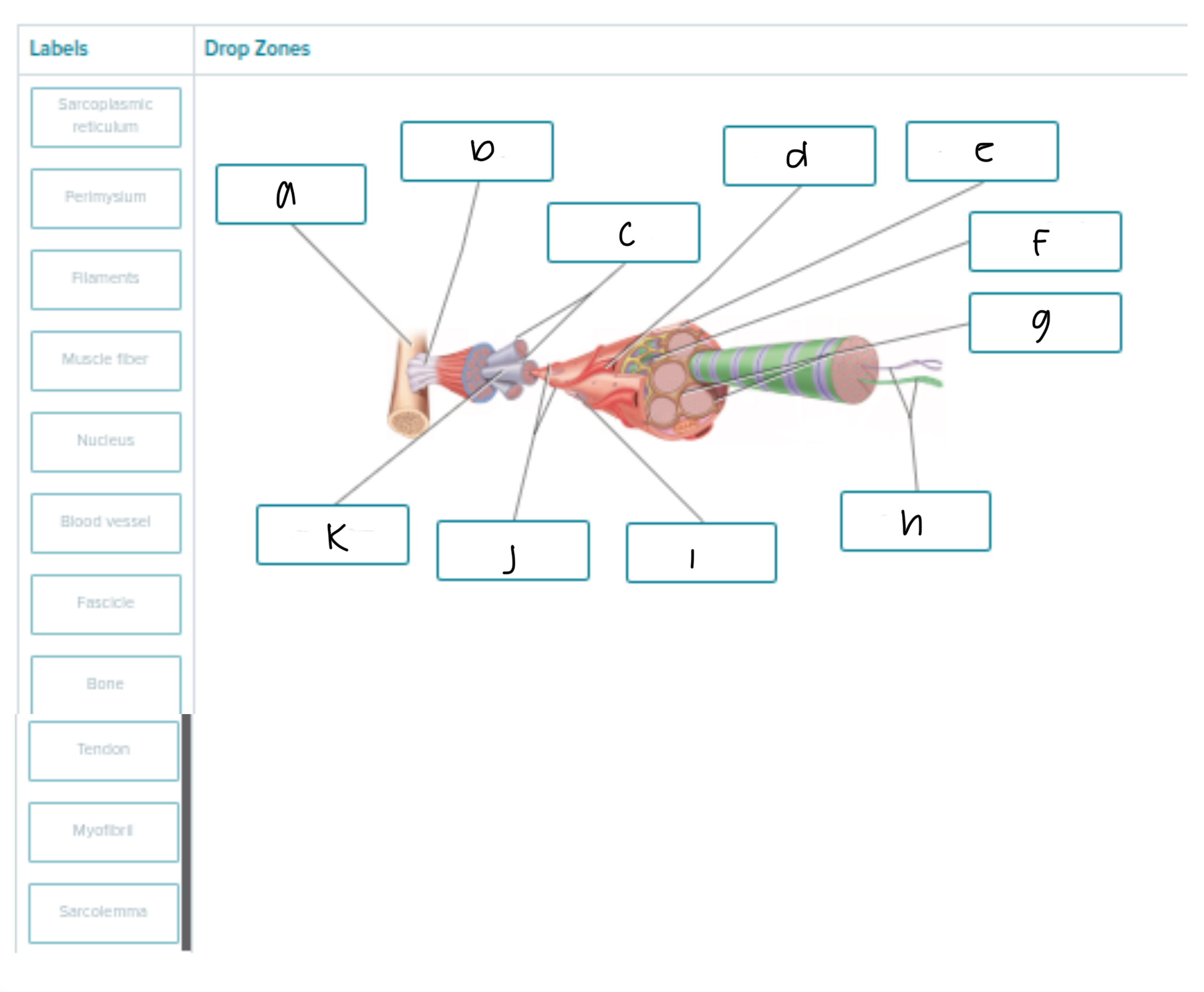
Fill in the blank
Fill in the blank
Fill in the blank