cs paper 2
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what is the internet, go from internet to web page. and what is a url
internet: globally connected network system
internet-www-website-webpage
URL (Uniform Resource Locator): address you type into a browser to visit a website or search something online
accessing a website
every website is stored on a server, you send a request to that server when accessing
Browser → asks DNS server → gets IP → contacts web server → gets webpage
what is a DNS
DNS (Domain Name Server): translates human readable domain names into machine readable IP addresses, used when accessing a website
like a phonebook
what is a protocol and the types
protocol: a set of rules that govern how data i transmitted ex.HTTP,TCP/IP
format, time, sequencing
important for communication, packet switching
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
used for transmitting information on the WWW, used used anytime you request a webpage
requests response between server and client
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
secure version of HTTP
data is encrypted using SSL which is established at the IP step
TCP/IP
Makes sure the messages are broken into smaller packets and reassembled correctly
TCP/IP vs HTTP
TCP/IP: how the data travels (ex. roads, vehicles)
HTTP: what the message says (ex. language, what you want)
What are ports
doors that allow programs to send and receive data over a network-reach the right service
important for running multiple networks on a device
HTTP sends a request to the web using a port number
static vs dynamic web pages
static: fixed content, same for every visitor, no server side processing (HTML) ex. about us, menu
dynamic: dynamic content, changes for every visitor, server side processing (PHP, java) ex. instagram, amazon, facebook
client-side scripting vs server-side scripting
Client-side scripting: can run in your browser, adds interactive behavior (HTML, CSS)
Server-side scripting: runs on a server, handles user login, databases (PHP, Python).
XML (extensive markup language)
like HTML, but it’s used to structure data so computers can read and share it easily
both human and machine language
web browser vs search engine
web browser: application used to access and display www content ex. chrome, safari
search engine: a program that enables searching information with keywords, phrases, uses algorithms to search through data
search engine process
Crawling: search engine crawler scans the web, following links, collecting content
Organizing: Content is organized and stored in an index (page info, title, URL)
Ranking: Algorithm retrieves the most relevant pages and ranks them
Deliver results: Based on ranking, relevance, authority, freshness, user experience
Metatags: HTML tags that give info about a webpage and help search engines understand content, stored in the head section
Search engine algorithm types
Page Rank (google’s alogirthm) “General importance”
based on how many pages link to it
each page given a score between 0 and 1
fewer outlinks means higher value
HITS (hyperlink induced algorithm) “hub or authority”
every page gets 2 scores:
Authority (experts): number and quality of incoming links
good authority if many good hubs link to it
Hub (recommenders): number of outgoing links
good hub if if it links to many good authorities
types/layers of webs
Surface Web 0.5%
content accessible by standard engine, and is publicly available
Deep Web 99.5%
private databases hidden behind logins or firewalls
Dark Web 0.01%
Intentionally hidden, usually illegal
Requires specialized software like TOR
what is SEO and types
SEO-search engine optimization: improving a website so it appears higher on search engine results
white hat SEO: ethical ways to optimize results
keyword optimization
content creation
link building
black hat SEO: unethical techniques
cloaking
link farming
hidden texts
Computing types
computing: use of computers to perform calculations, process data, run programs
Grid computing: a network of connected computers solving complex tasks over a network in different geographical locations
PROS: can solve complex problems faster, easy collaboration
CONS: Security risks due to sharing data, complex set up, relies on network connectivity
Mobile computing: use of portable devices
PROS: portability, cost, connectivity
CONS: limited screen size, battery life, security risks
Ubiquitous computing: concept of integrating computer technology into daily lives
ex. mobile devices, smart homes, brainchips
PROS: convenience, improvement of quality of life
CONS: privacy concerns, security risks, technological dependency
P2P computing: decentralized network where each computer acts as both a server and a client
PROS: effective sharing, cost effective, enhanced privacy, fault tolerance
CONS: lack of control, scalability/lack of resources
Cloud computing: use of remote servers, computing over the internet
PROS: flexibility, scalability, cost effective
CONS: security concerns, downtime, dependency on 3rd party
Interoperability and standards
different systems, devices, applications working together
Standardization: interoperability relies on standardized protocols, formats, interface
standards: guidelines making sure everyone builds systems the same way
open standards: publicly available specifications ex. HTML, bluetooth, TCP/IP
benefits: interoperability, innovation, longevity
Flexibility: Interoperability systems are designed to be flexible, allowing a range of systems
ISO and creative commons license
ISO (international organization for standardization): creates standards internationally
creative commons license: work is publicly available, but authors still have control over how its used, like a copyright
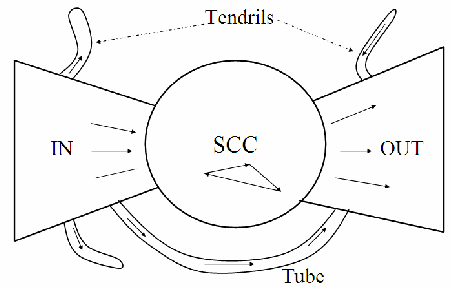
graph theory
used to represent how websites are connected
directed graph (web graph):
core (SCC): central, most densely connected part of the web, small number of highly interconnected pages (ex. reddit, google, facebook)
In components: pages that have links to the core, none from the core (ex. a blog linking google)
out components: pages the core links out to (ex. news site linked on reddit)
Tendrils: connect to the in and out groups but not directly to the core (ex. small blog linking a news site, but no big sites link back to it)
Tubes: pages that link the in and out section, like a shortcut (ex. blog linking booking site and is also linked from other blogs)
Diameter: longest shortest path between 2 pages, worst case scenario how many links it takes
Ambient and collective intelligence
ambient: technology built into the environment, use of sensors, networks ex. smart home
collective: a group of individuals pooling their knowledge to solve tasks, decisions ex. wikipedia, google traffic
power law distribution and ontology, folksonomy
power law distribution: small number of pages have a disproportionately number of links
it’s why the web graph is highly centralized around a few core hubs
Inequality
ontology: organize and categorize knowledge for computers
ex. medicine: so computers can organize and understand data
folksonomy: tagging done by regular people
models natural behavior
ex. social media, #