(AnaPhy) Topic 6: Skeletal system
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Axial and Appendicular
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Collagen
Is a fibrous protein that provides flexibility but resists pulling or compression.
Matrix ground substance
contains proteoglycans which are water trapping proteins that help cartilage to be smooth and resilient.
Components of Skeletal System
Bones
Cartilages
Tendons
Ligaments
Organic material of Bone Matrix
35%
primarily collagen and proteoglycans.
Inorganic material of Bone Matrix
65%
primarily a calcium phosphate crystal called hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2.
Osteoblasts
are responsible for the formation of bone and the repair and remodeling of bone.
Produce collagen and proteoglycans
Also secrete high concentrations of Ca2+ and phosphate ions, forming crystals called hydroxyapatite.
Ossification
also known as osteogenesis, is the process of bone formation.
It's how your bones develop from childhood to adulthood, and how they repair themselves after a fracture.
Osteocytes
Cells that maintain bone matrix and form from osteoblast after bone matrix has surrounded it
Account for 90–95% of bone cells and are very long-lived.
Osteoclasts
Are bone-destroying cells.
They contribute to bone repair and remodeling by removing existing bone, called bone reabsorption
Spongy bone
has less bone matrix and more space
consists of interconnecting rods or plates of bone called trabeculae
Compact bone
which has more bone matrix and less space.
Also known as cortical bone, is the solid, outer layer surrounding each bone.
Its functional unit is an osteon. It is composed of concentric rings of matrix surrounding a central canal.
Lacunae
Spaces within the hard bone matrix. Each houses an osteocyte, which is a mature bone cell.
Lamellae
are concentric rings of bone matrix which surround the central canal.
Canaliculi
Lacunae connected by a network of tiny "canals" or tunnels. They are microscopic channels that radiate outward from the lacunae.
Axial Skeleton
Has 80 bones
Components:
Skul
Vertebral Column
Thoracic Cage
Appendicular Skeleton
Has 126 bones
The limbs and their attachments: consists of the bones of your limbs (arms and legs) and the girdles that connect them to the axial skeleton.
Components:
Pectoral Girdle
Upper Limbs
Pelvic Girdle
Lower Limbs
206 bones
Amount of bones in average adult
270-300
Amount of bones in infants
Long bones
Bones are longer than they are wide; examples are upper and lower limb bones.
Diaphysis
This is the long, cylindrical shaft of the bone.
It's the main structural part, providing strength and support.
It's made up of compact bone, which is dense and strong.
Contains the medullary cavity, which houses bone marrow
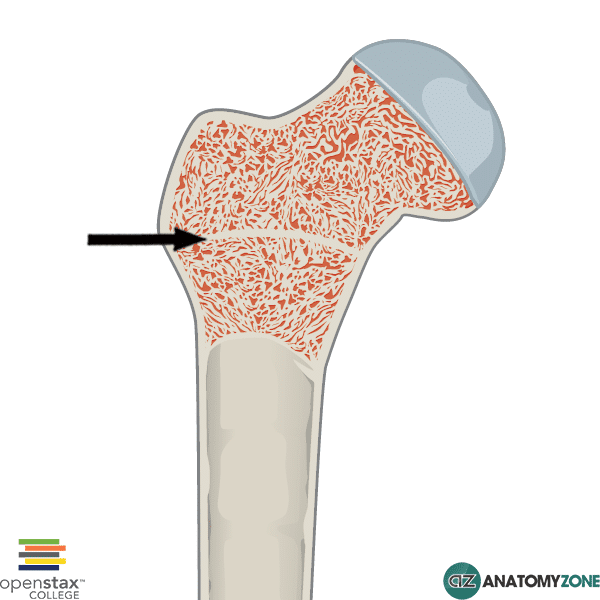
Epiphyses
These are the enlarged ends of the bone.
They're primarily made up of spongy bone, which is lighter than compact bone and contains spaces.
Are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth, slippery tissue that reduces friction and absorbs shock within joints.
Epiphyseal line
When bone stops growing in length, it becomes ossified
Short bones
Are approximately as wide as they are long; examples are the bones of the wrist and ankle.
Flat bones
Have a relatively thin, flattened shape; examples are bones of the skull and sternum.
To protect body organs, such as the brain
Irregular bones
include the vertebrae and facial bones, which have shapes that do not fit readily into the other three categories.
Sesamoid bones
Small, round or oval bones embedded within tendons.
Unlike most bones that connect to other bones at joints, sesamoid bones are connected to muscles by tendons.
Their name comes from the Arabic word "sesamum," meaning sesame seed
Bone Marrow
Cavities in spongy bone and the medullary cavity in the diaphysis are filled with soft tissue
Red and yellow
Red Bone Marrow
Primary function: Produces blood cells
Composition: Contains hematopoietic stem cells, which can differentiate into various blood cell types.
Location: Primarily found in flat bones (skull, sternum, ribs, vertebrae, pelvis) and the spongy ends of long bones.
Prevalence: Predominant in infants and children, gradually decreasing with age
Yellow Bone Marrow
Primary function: Stores fat.
Composition: Mainly consists of fat cells (adipocytes) and some mesenchymal stem cells, which can differentiate into cartilage, bone, or fat cells.
Location: Primarily found in the medullary cavity (the hollow shaft) of long bones.
Prevalence: Increases with age, replacing red bone marrow in many areas.
Periosteum
is the tough, fibrous membrane that covers the outside surface of bones. Think of it as the bone's outer "skin."
Outer fibrous layer: Made of dense irregular connective tissue, providing strength and attachment points for tendons and ligaments.
Inner cellular layer: Contains cells responsible for bone growth, repair, and remodeling (osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoprogenitor cells).
Endosteum
is a thinner membrane that lines the inside surfaces of bones, including the medullary cavity and the Haversian canals.
It's a single layer of cells, including osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoprogenitor cells.
Intramembranous ossification
Starts within embryonic connective tissue membranes.
A direct process where mesenchymal tissue converts directly into bone. It doesn't involve a cartilage intermediate. This process is crucial for the development of specific bones, particularly those of the skull and clavicle.
Endochondral ossification
Starts with a cartilage model
an indirect process where bone replaces a pre-existing cartilage model. This process is essential for the formation of most of the bones in your body, allowing for growth and development of the skeleton.
Ossification centers
crucial starting points where bone tissue is initially laid down, leading to the formation of a complete bone. They're essential for both the development of the skeleton in the embryo and the growth and remodeling of bones throughout life.
Appositional growth
As osteoblasts deposit new bone matrix on the surface of bones between the periosteum and the existing bone matrix, the bone increases in width, or diameter.
Bone growth occurs by the deposition of new bone lamellae onto existing bone or other connective tissue.
Bone Repair
Bone causes bleeding and a hematoma forms.
A callus forms which is a bone cartilage network between and around the bone fragments.
Woven, spongy bone replaces the callus.
Compact bone replaces the spongy bone.
Bone Remodeling
removal of existing bone by osteoclasts and deposition of new bone by osteoblasts
occurs in all bones
responsible for changes in bone shape, bone repair, adjustment of bone to stress, and calcium ion regulation
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
is a key hormone that maintains calcium homeostasis in the body. It increases blood calcium levels by acting on bones, kidneys, and intestines, and it also plays a role in phosphate regulation and vitamin D metabolism.
Stimulates reabsorption of Ca2+ from urine in the kidney, reducing the amount of Ca2+ excreted in the urine.
Indirectly increases Ca2+ uptake from the small intestine through the activation of calcitriol.
Calcitonin
is a hormone produced by the C-cells (parafollicular cells) of the thyroid gland. It plays a role in calcium regulation, though its importance is not as clearly understood as that of parathyroid hormone (PTH).
a hormone that can help lower blood calcium levels, primarily by inhibiting bone resorption.
Foramen
Hole
Fossa
Depression
Process
Projection
Condyle
Smooth, rounded end
Meatus or canal
Canal-like passageway
Tubercle or tuberosity
Lump of bone
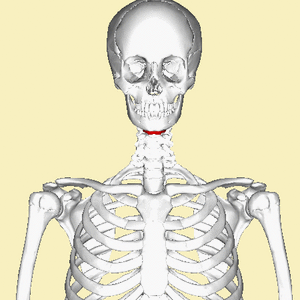
Hyoid Bone
is an unpaired, U-shaped bone that is not part of the skull and has no direct bony attachment to the skull or any other bones.
provides an attachment for some tongue muscles, and it is an attachment point for important neck muscles that elevate the larynx.
Frontal bone
Anterior part of cranium, the ‘forehead”
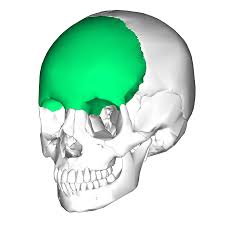
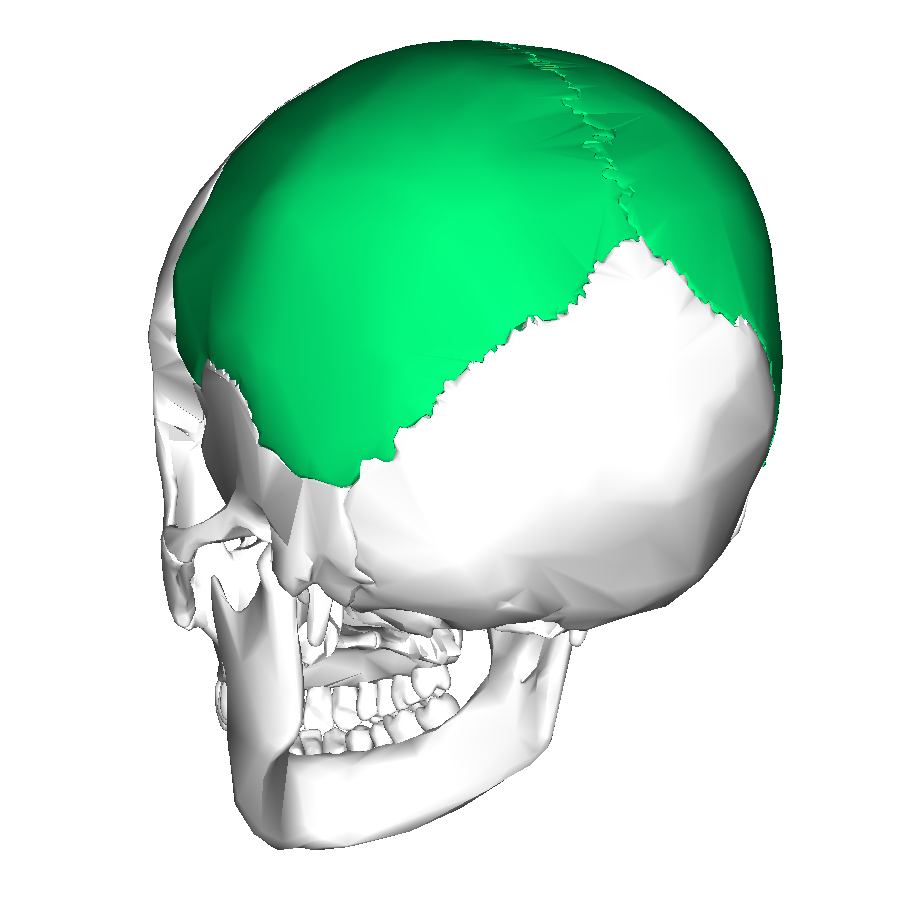
Parietal bones
Sides and roof of cranium
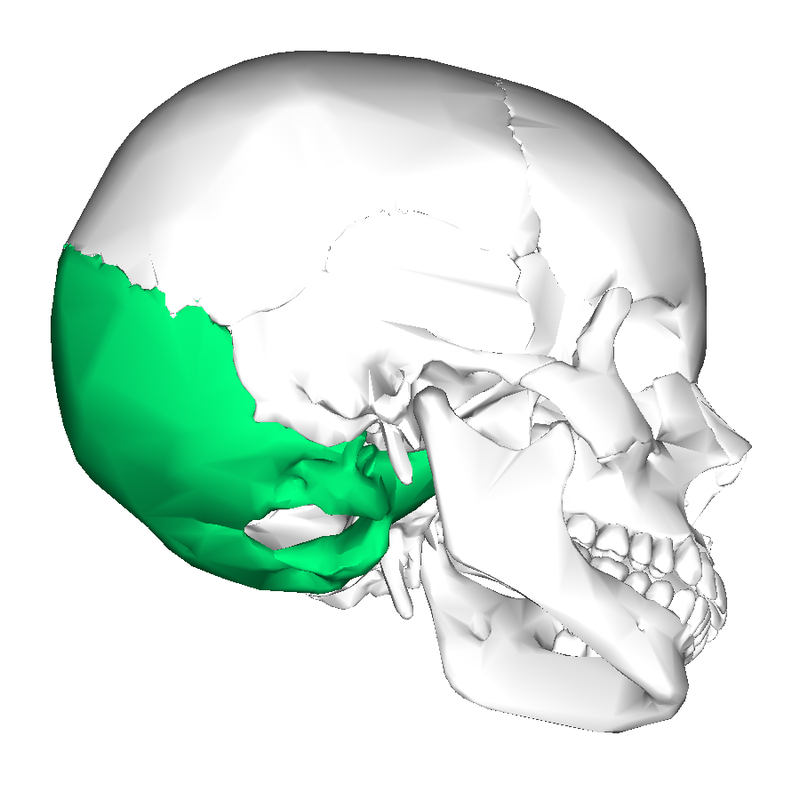
Occipital bones
Posterior portion and floor of cranium
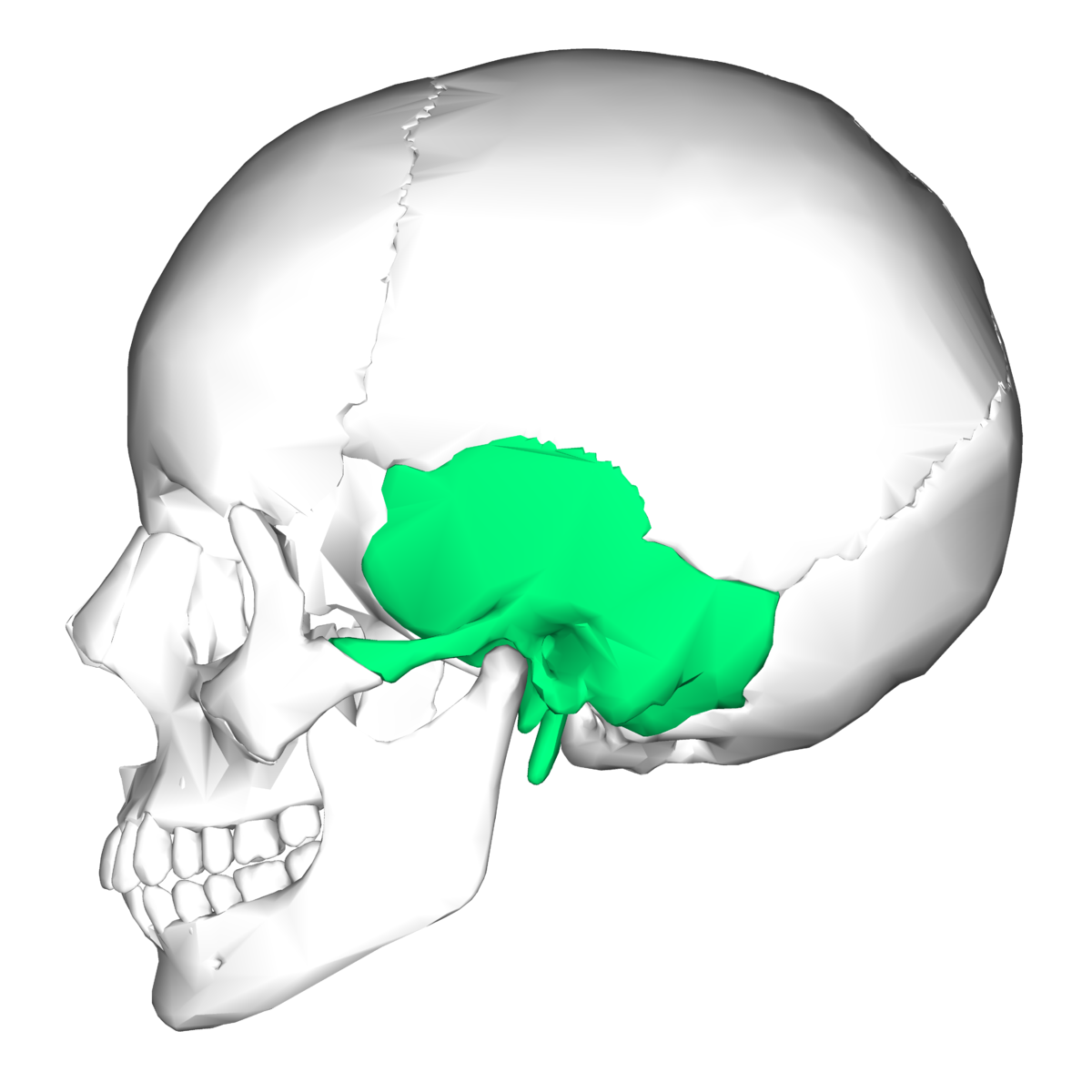
Temporal bones
Inferior to parietal bones on each side of the cranium
Temporomandibular joint
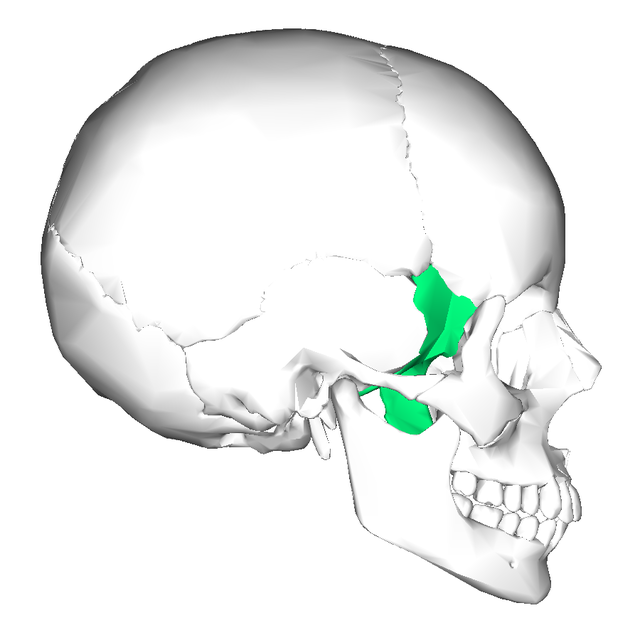
Sphenoid bone
Forms part of cranium floor, lateral posterior portions of eye orbits, lateral portions of cranium anterior to temporal bones
Sella turcica
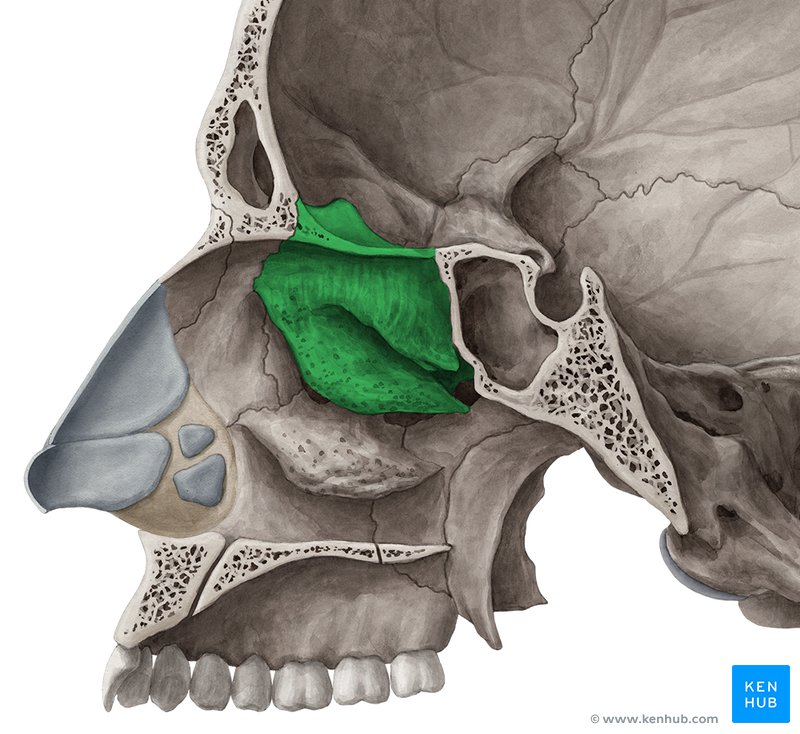
Ethmoid bone
Anterior portion of cranium, including medial surface of eye orbit and roof of nasal cavity
Nasal conchae
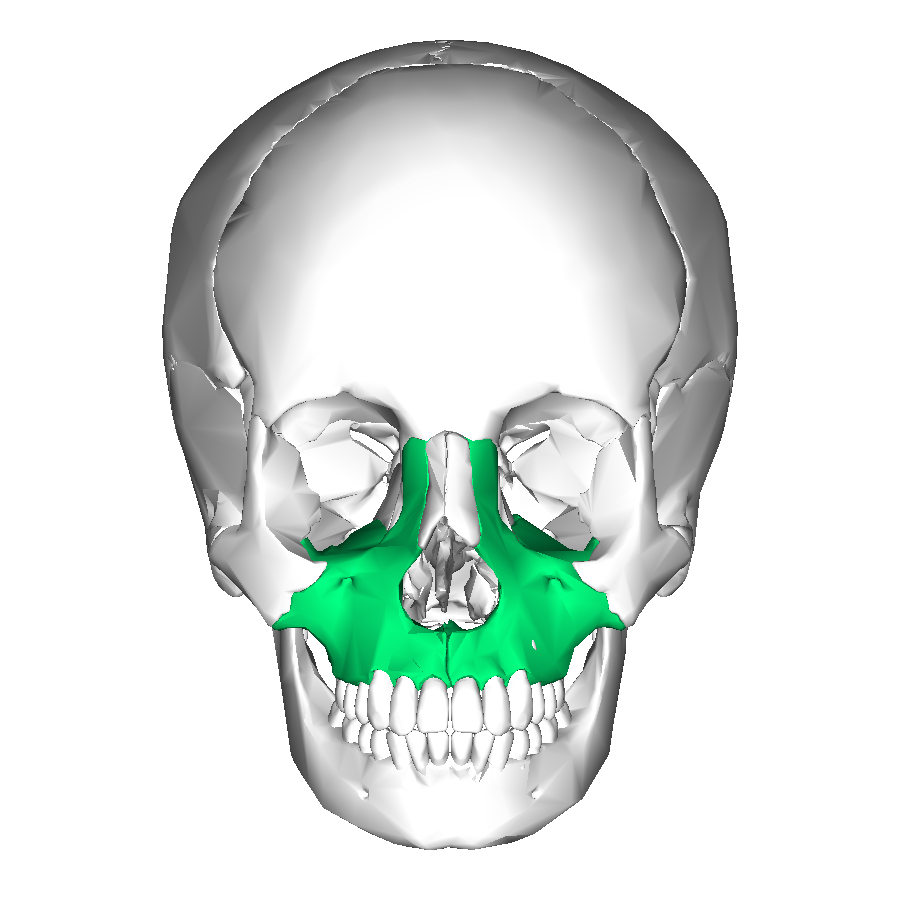
Maxillae
Forms the upper jaw, anterior portion of hard palate, part of lateral walls of nasal cavity, floors of eye orbits
Maxillary sinus
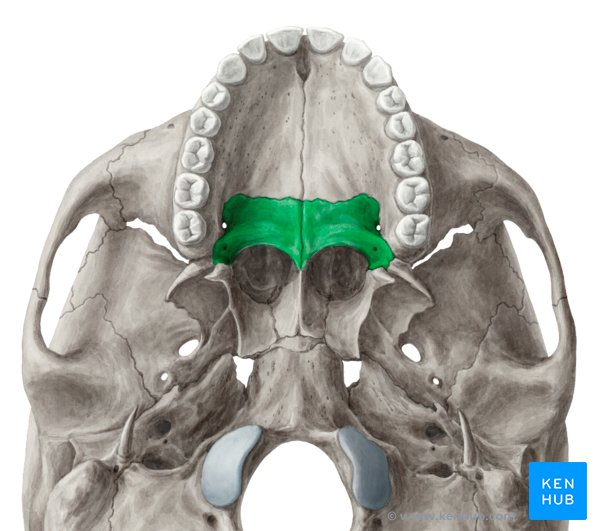
Palatine bones
Form posterior portion of hard palate, lateral wall of nasal cavity
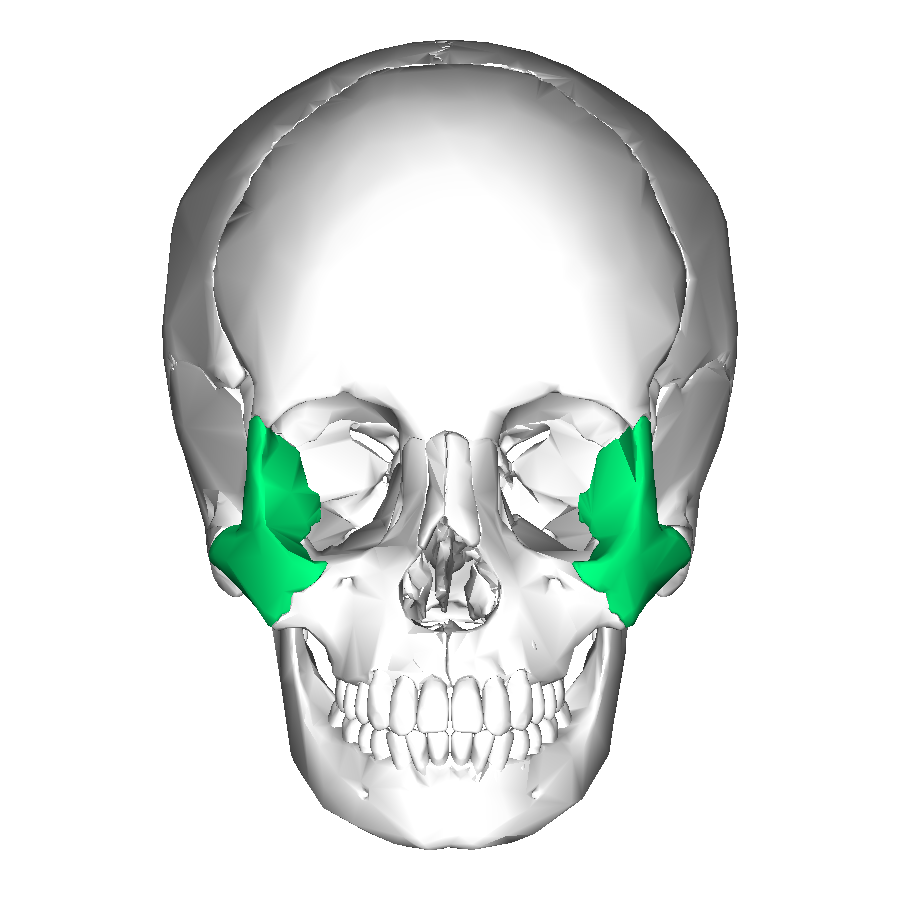
Zygomatic bones
Cheek bones
Also form floor and lateral wall of each eye orbit
Lacrimal bones
Medial surfaces of eye orbits
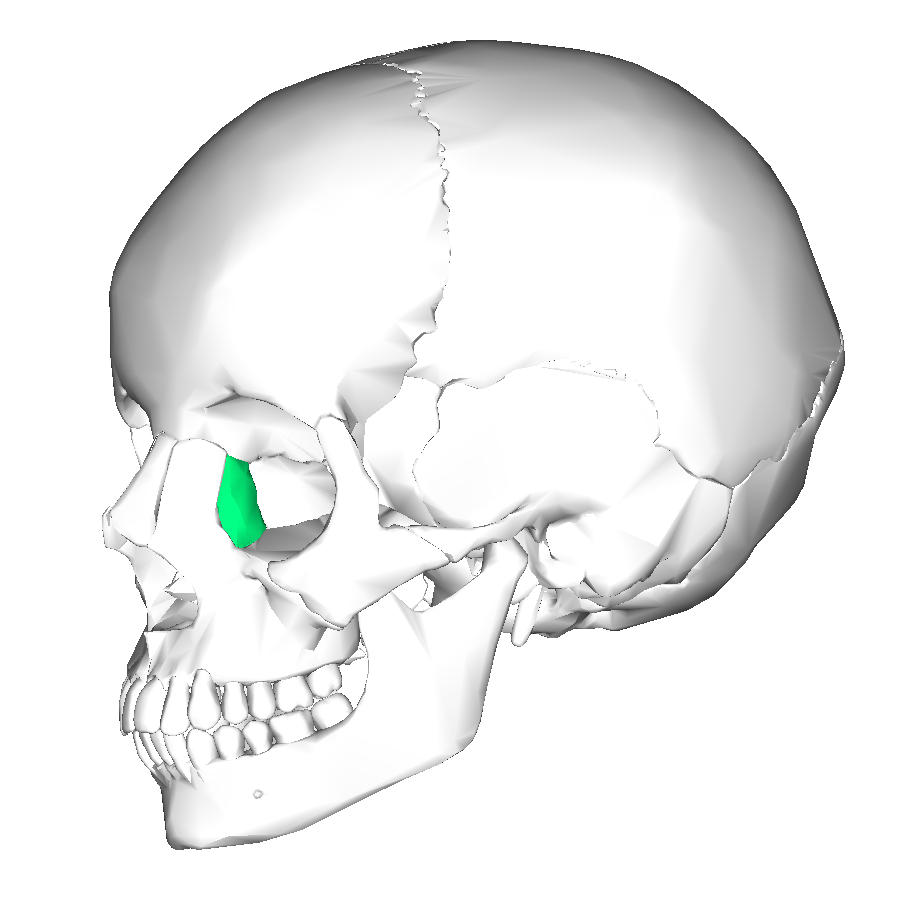
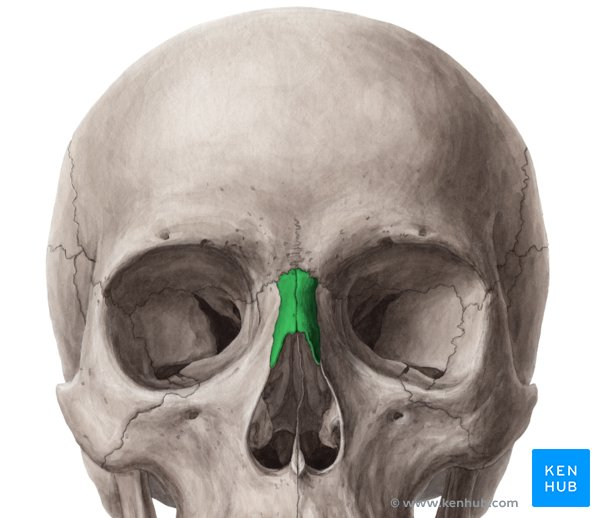
Nasal bones
Form bridge of nose
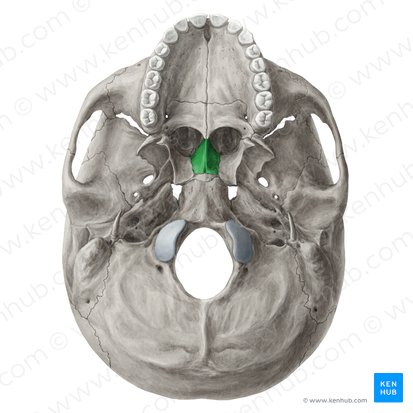
Vomer
In midline of nasal cavity
Forms nasal septum with the ethmoid bone
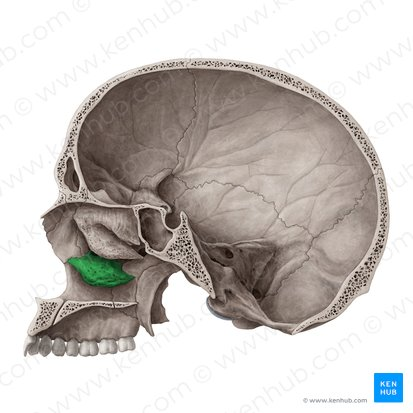
Inferior nasal conchae
Attached to lateral walls of nasal cavity
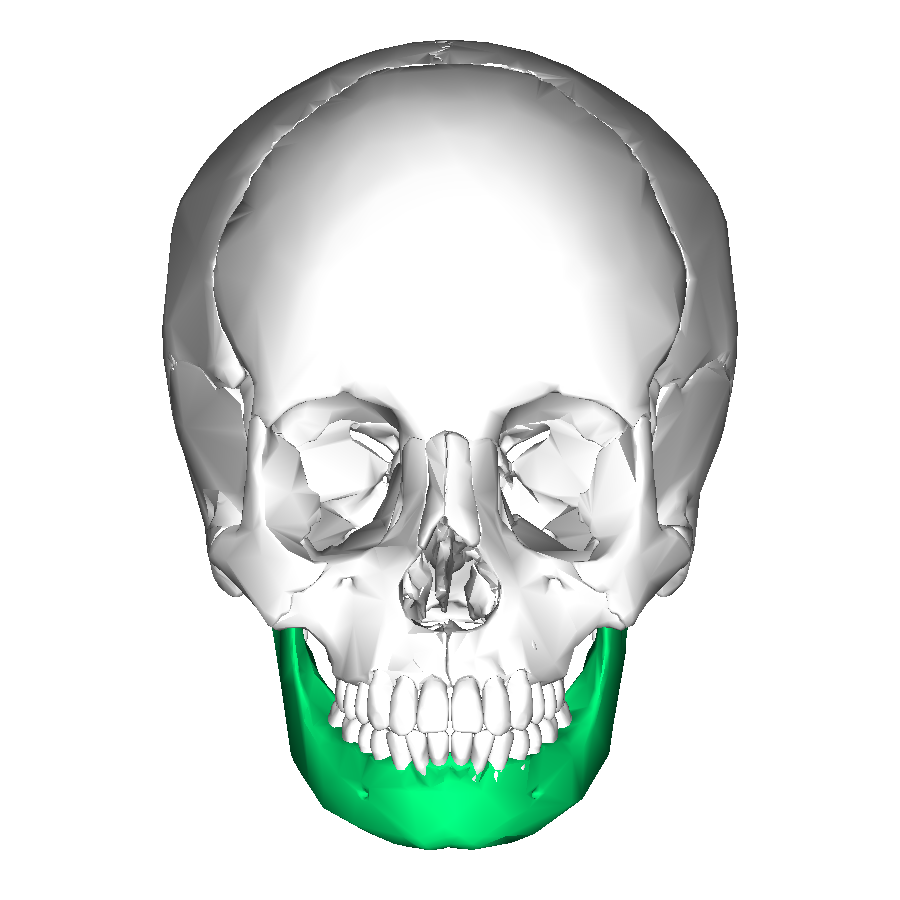
Mandible
Lower jawbone
Only movable skull bone
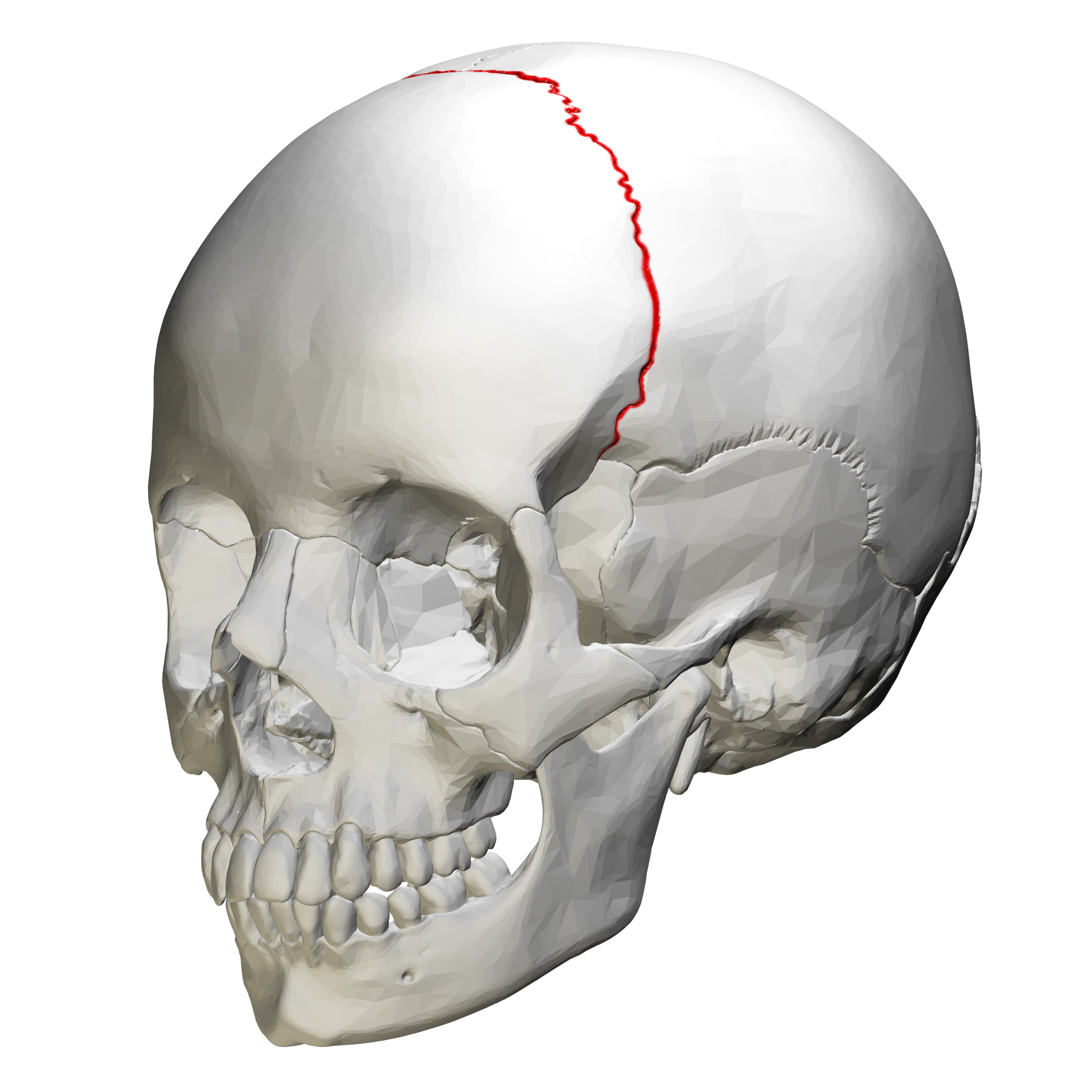
Coronal suture
This suture runs across your forehead, from ear to ear.
It connects the frontal bone (forehead) to the parietal bones.
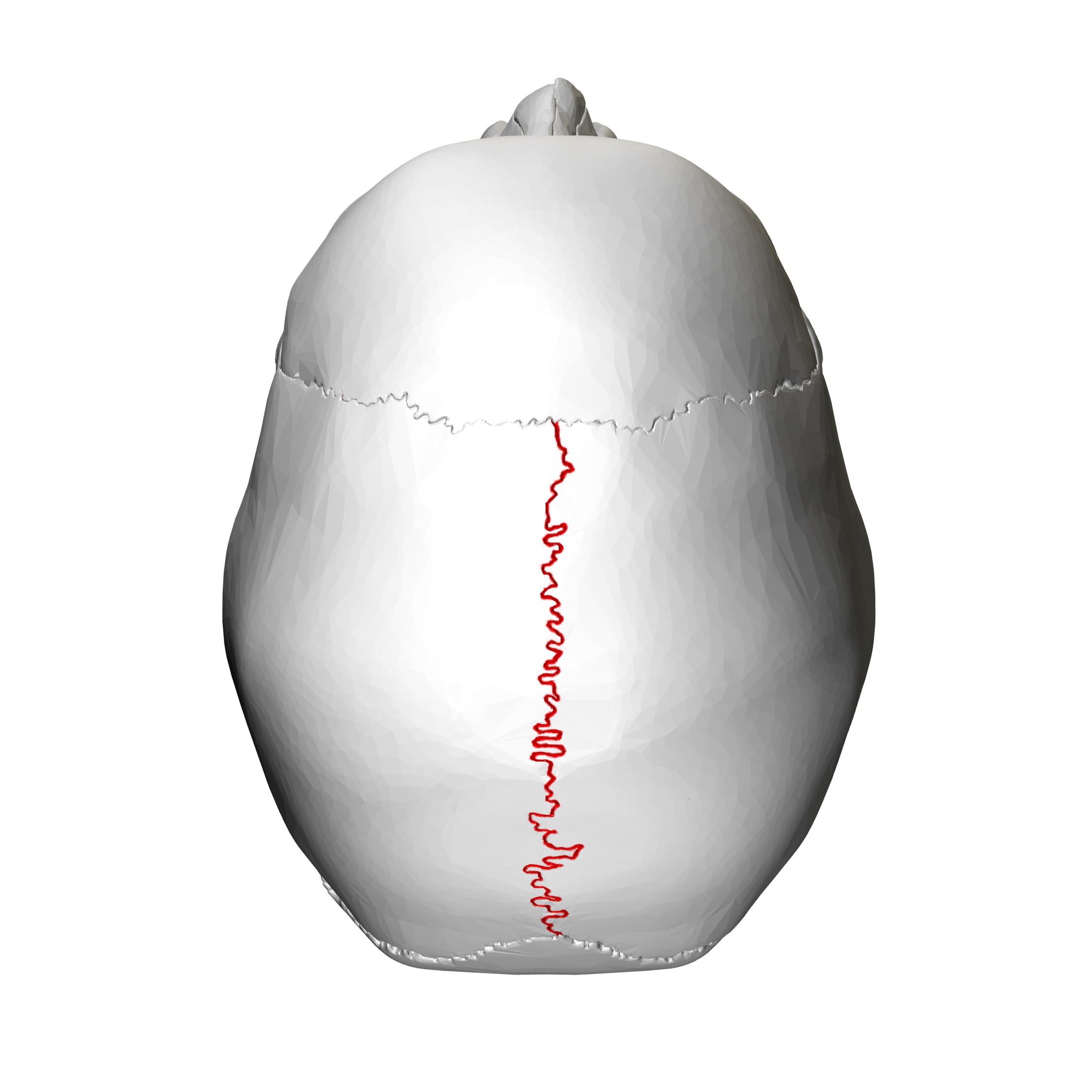
Sagittal Suture
This suture runs along the top of your head, from front to back.
It connects the two parietal bones, which form the sides and top of your skull.
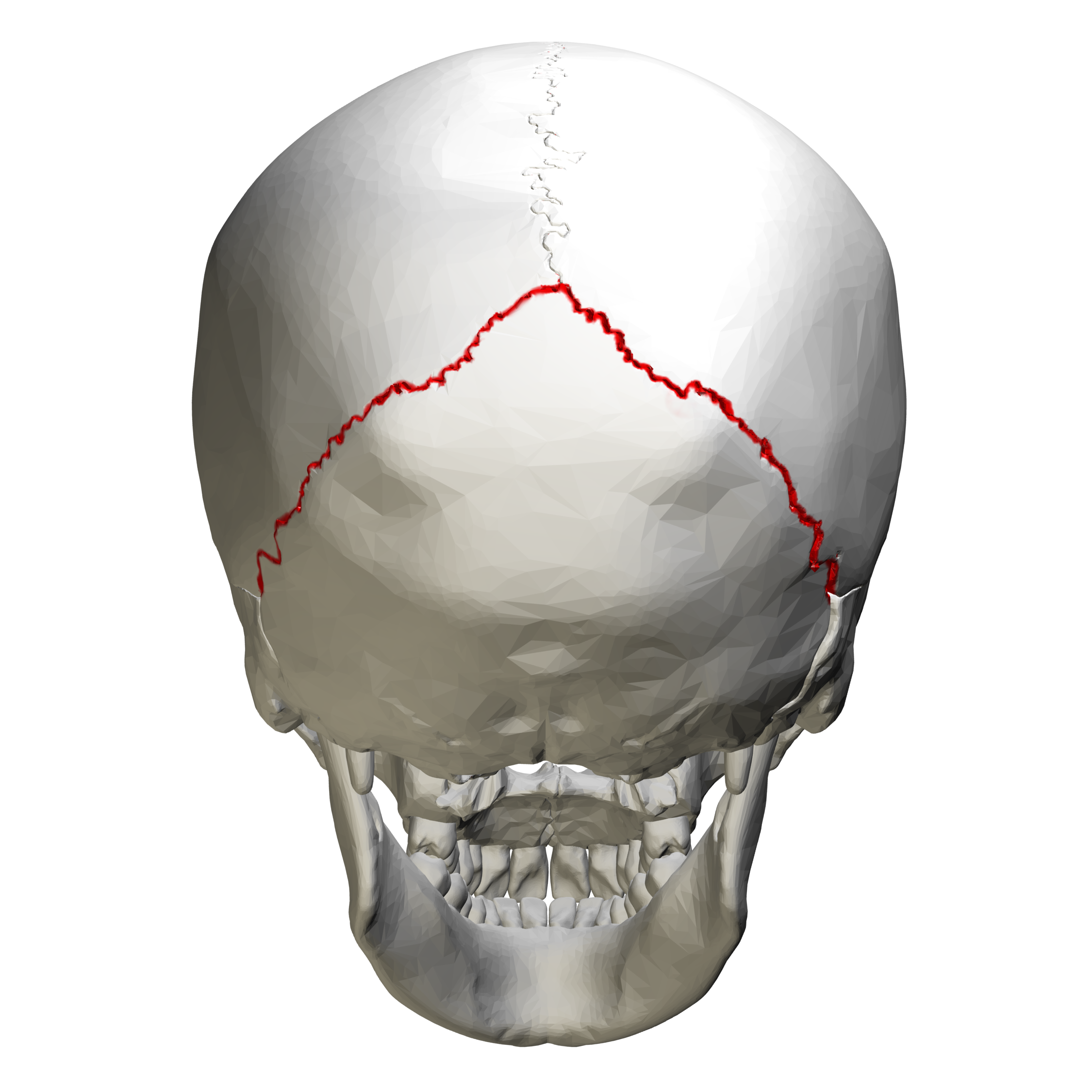
Lambdoid Suture
This suture is located at the back of your skull.
It connects the parietal bones to the occipital bone (back of the skull).
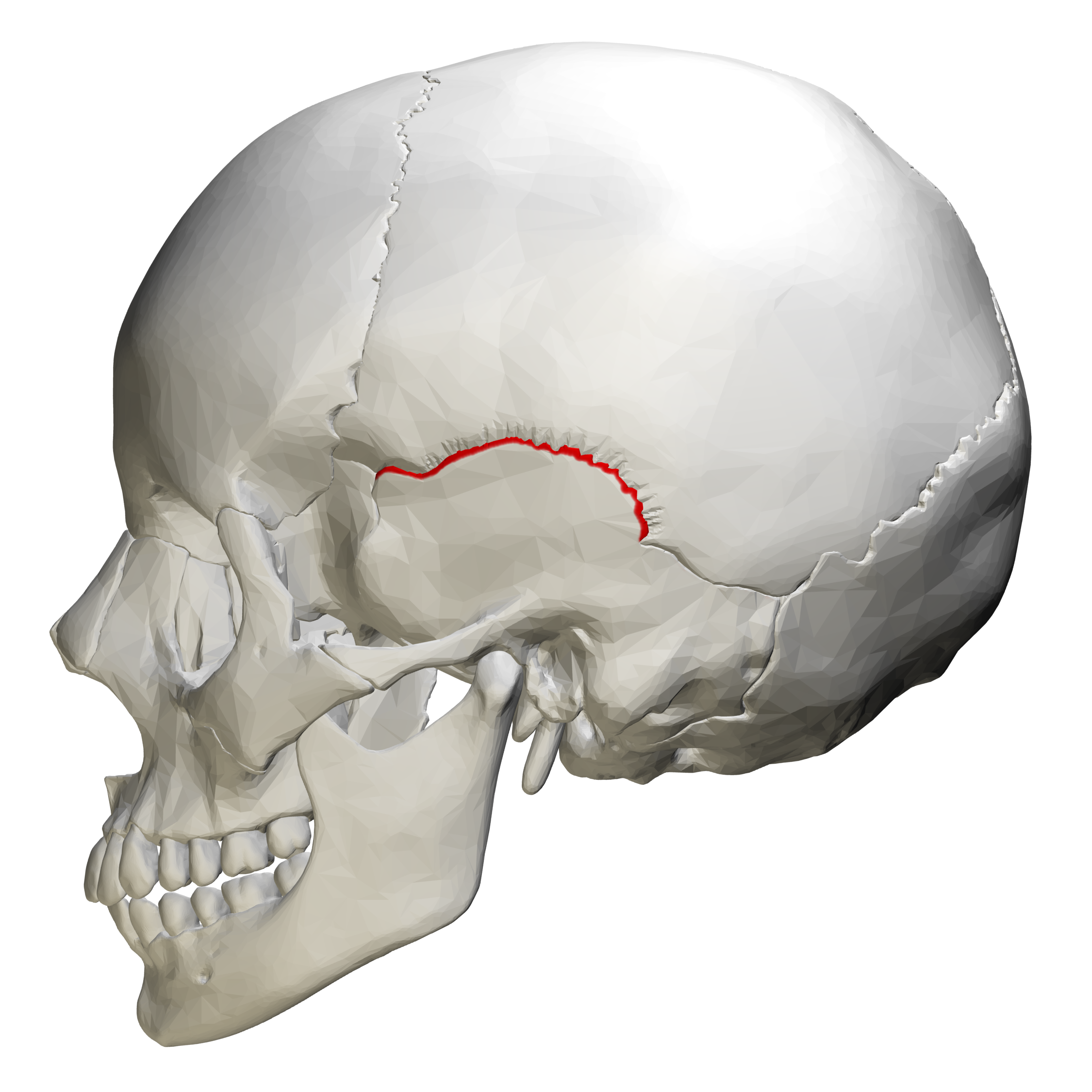
Squamous suture
is found on the side of your skull. It connects the temporal bone to the parietal bone.
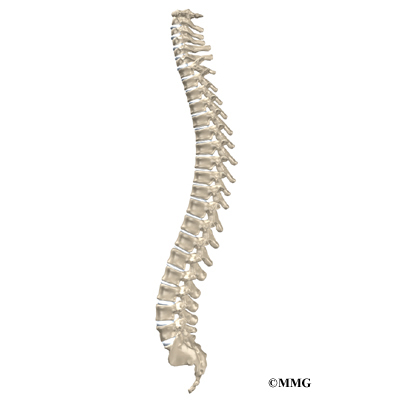
Vertebral Column
or spine, is the central axis of the skeleton, extending from the base of the skull to slightly past the end of the pelvis.
In adults, it usually consists of 26 individual bones, grouped into five regions.
The adult vertebral column has four major curvatures: cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacrococcygeal
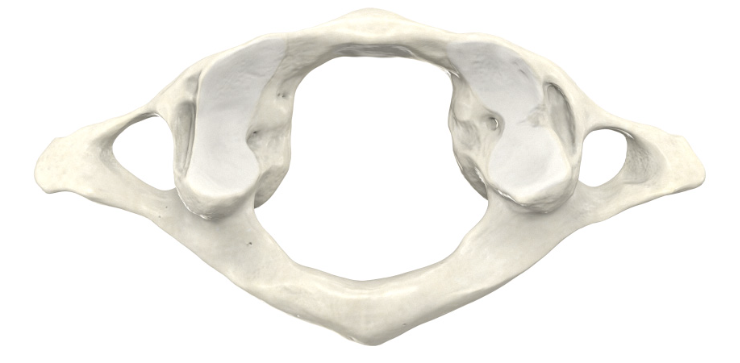
First Cervical Vertebra (C1) - Atlas
The "ring" that supports the skull
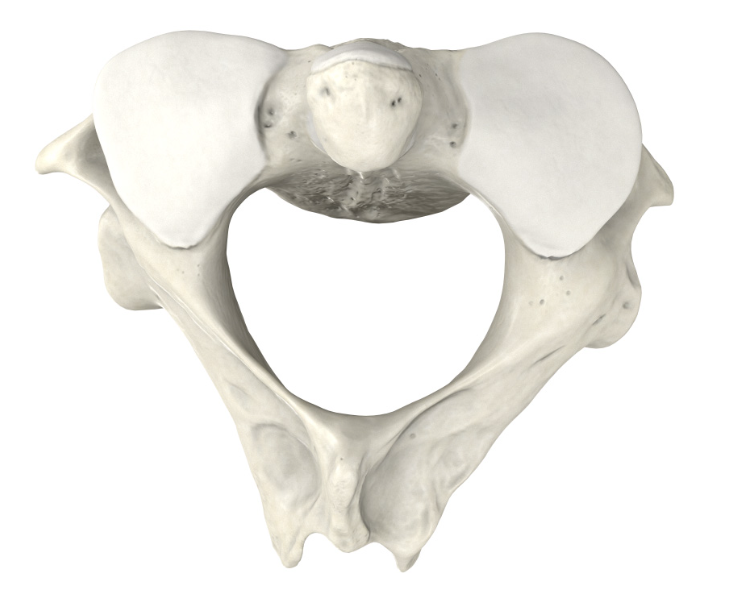
Second Cervical Vertebra (C2) - Axis
The "pivot" that allows the atlas (and thus the skull) to rotate.
Cervical Vertebra
Bones of your neck, forming the upper part of your spine
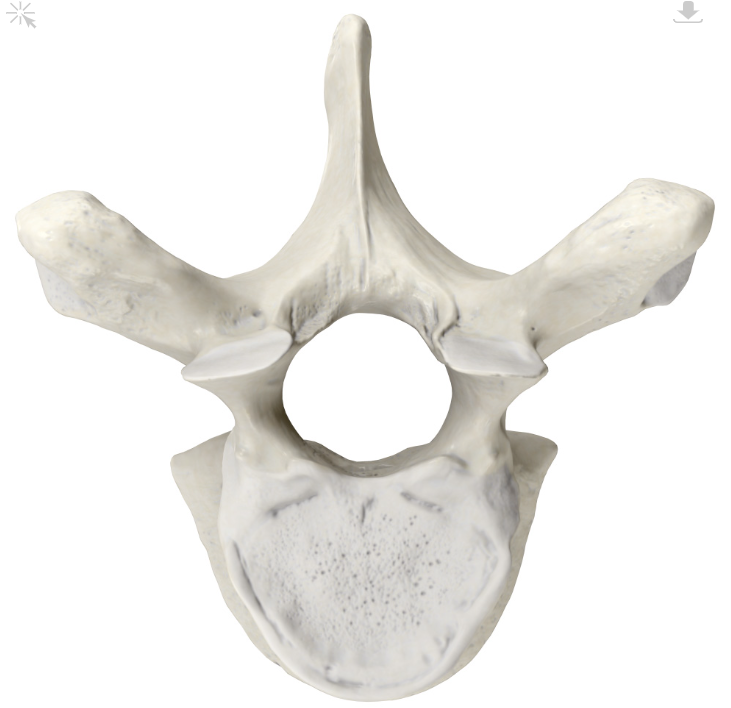
Lumbar Vertebra
Bones of your lower back, located between the thoracic vertebrae
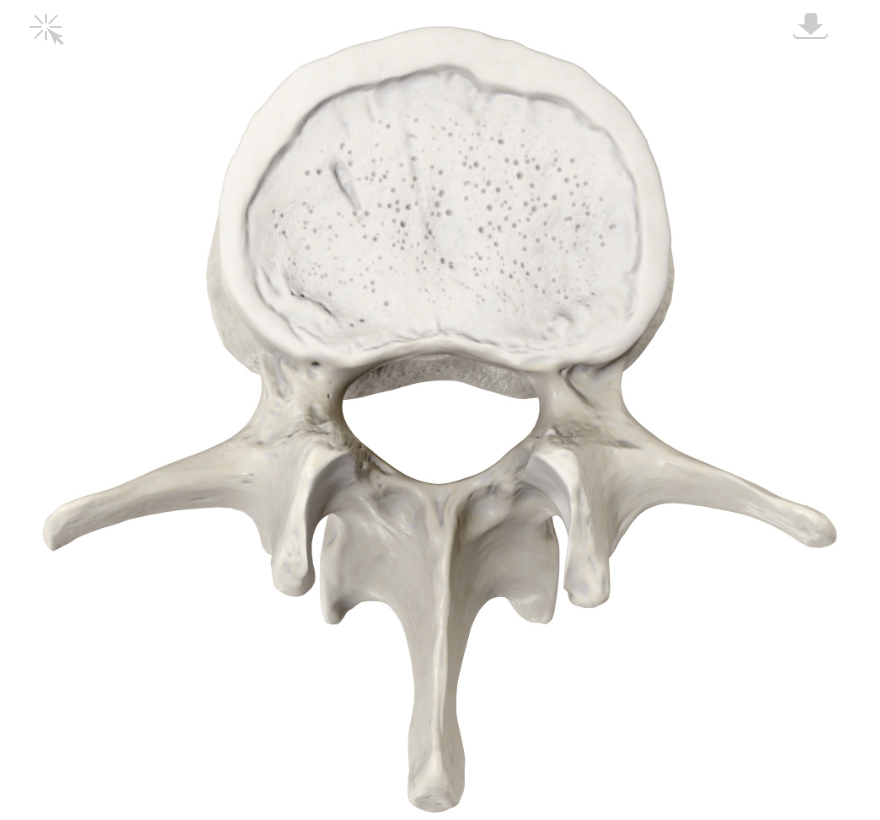
Thoracic vertebrae
12 bones that make up the middle part of your spine
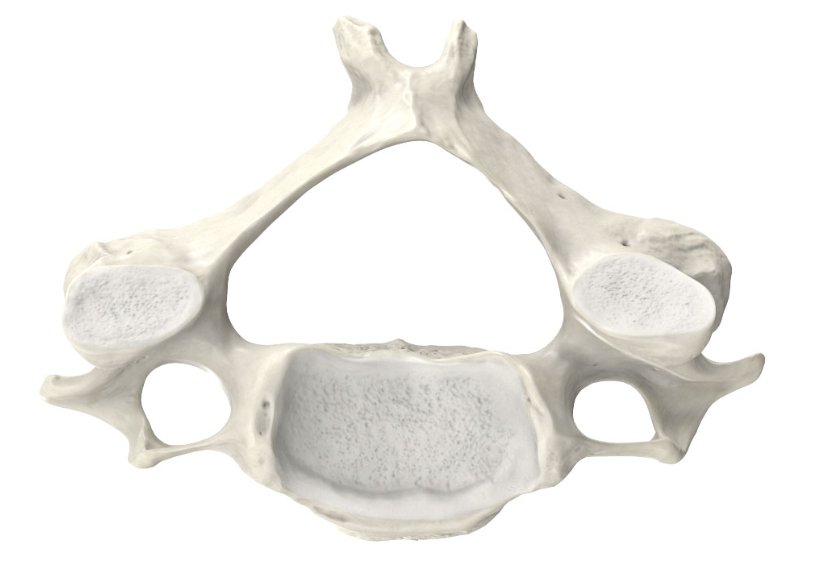
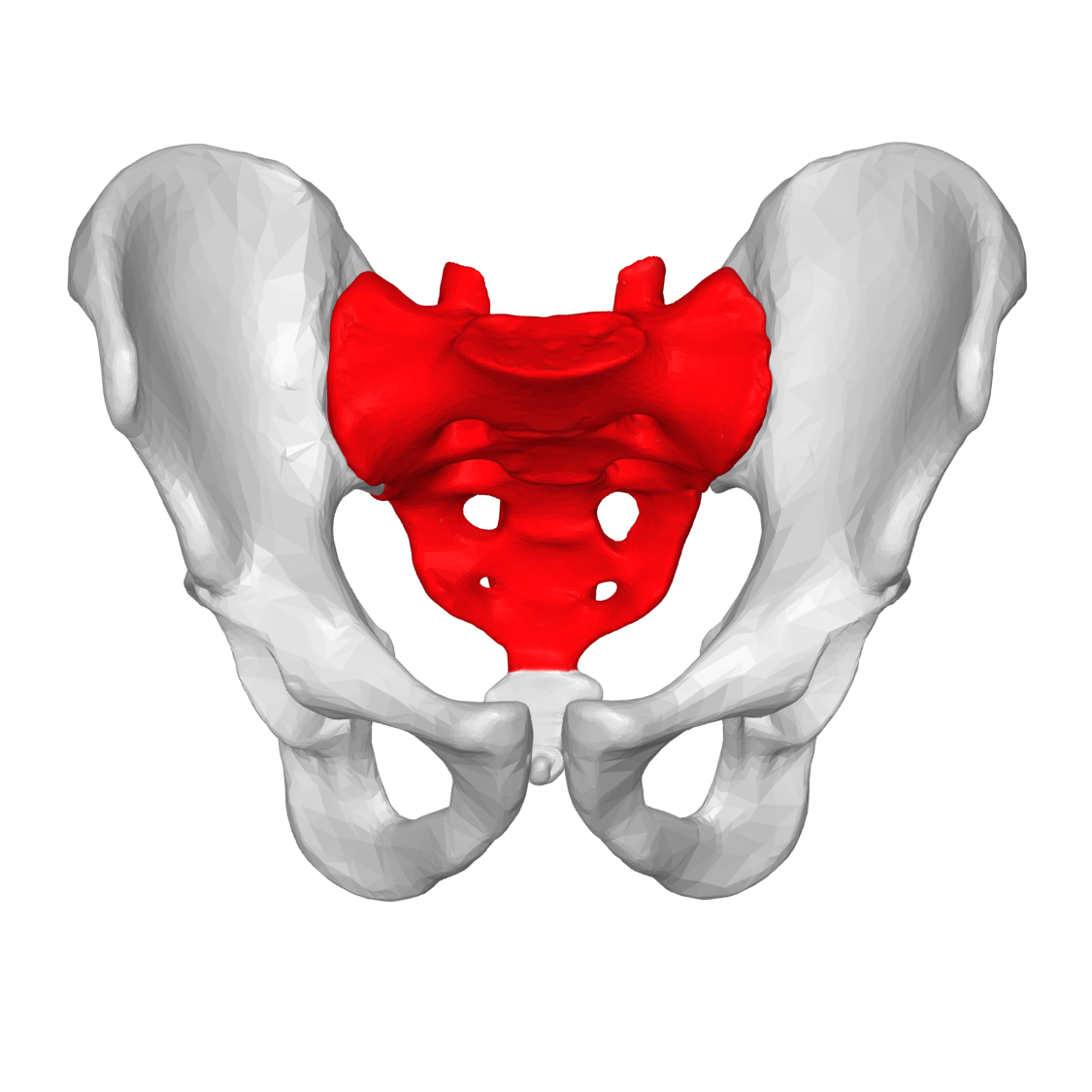
Sacrum
Triangular bone at the base of your spine,
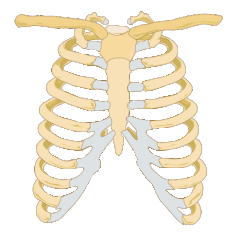
Thoracic cage / Rib cage
is a bony and cartilaginous structure that surrounds and protects the organs of the chest cavity, including the heart and lungs.
It plays a vital role in breathing and providing support for the upper body.
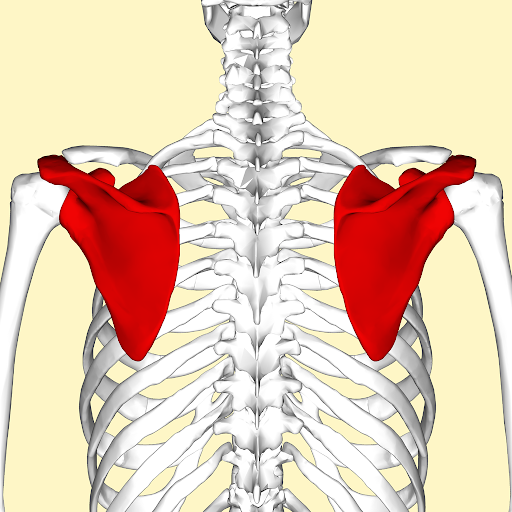
Scapula / Shoulder blade
flat, triangular bone located in the upper back.
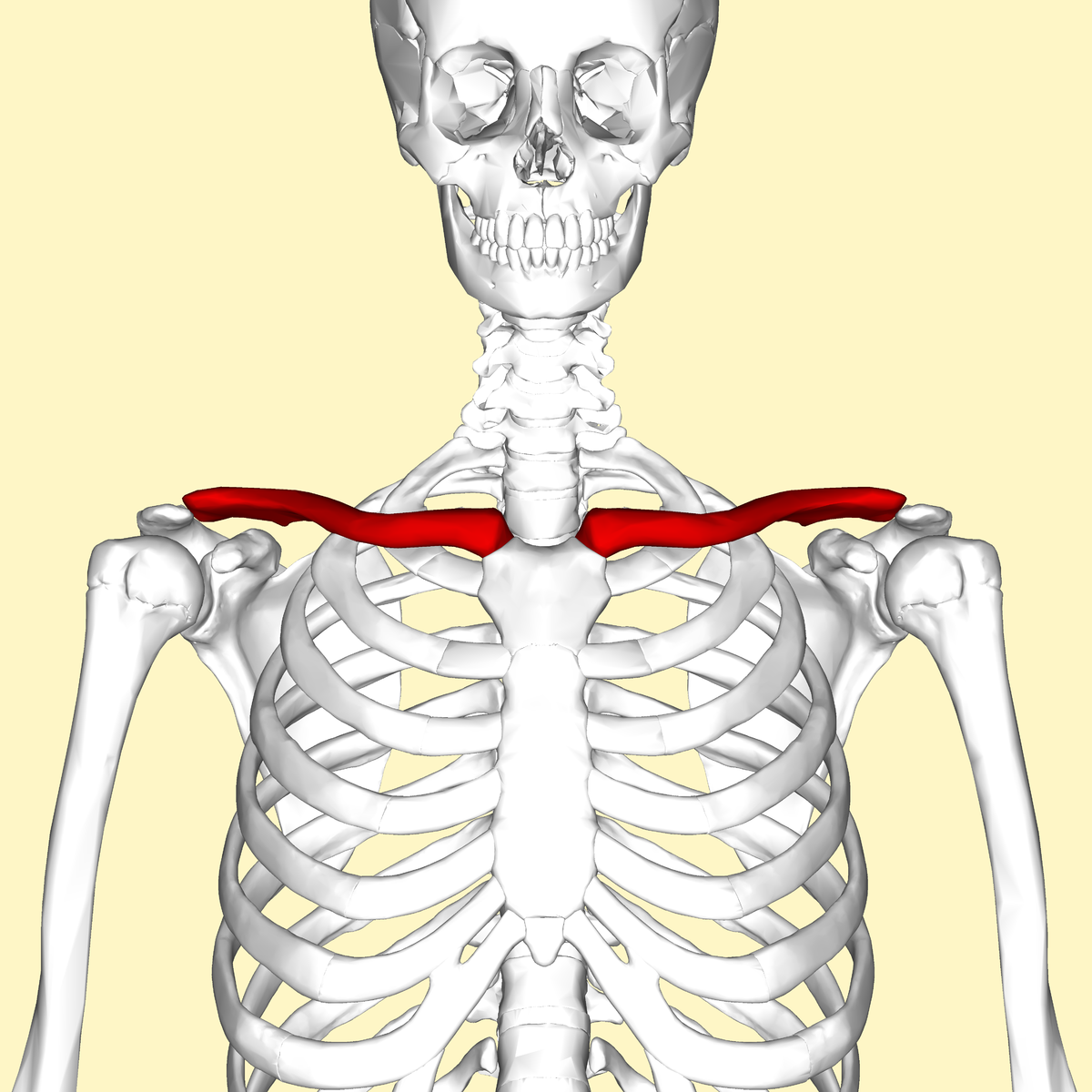
Clavicle / Collarbone
a long, slender bone that connects the arm to the body.
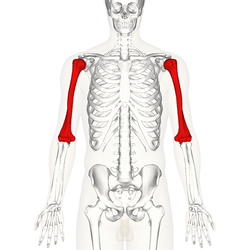
Humerus
long bone in your upper arm, connecting your shoulder to your elbow.
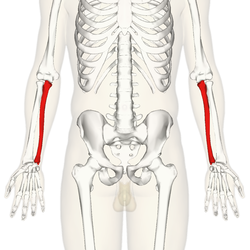
Ulna
Location: Medial (pinky finger side) bone of the forearm.
Shape: Longer of the two bones, with a prominent "hook" at its proximal (upper) end called the olecranon process.
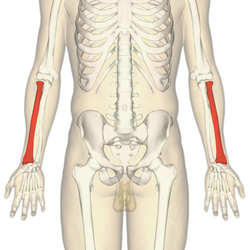
Radius
Location: Lateral (thumb side) bone of the forearm.
Shape: Shorter and thicker
Articulations (joints)
classified structurally as fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial, according to the major connective tissue type that binds the bones together and whether a fluid-filled joint capsule is present.
where two bones come together.
Fibrous joint
united by fibrous connective tissue
subclasses are sutures, syndesmosis, and gomphoses
Cartilaginous
united by means of cartilage
subclasses are synchondrosis and symphysis
Synovial
joined by a fluid cavity
Most joints of the appendicular skeleton
Synarthrosis
non-movable joint
Example – skull bone articulations
Amphiarthrosis
slightly movable joint
Example - between vertebrae
Diarthrosis
freely movable joint
Example - knee, elbow, and wrist articulations
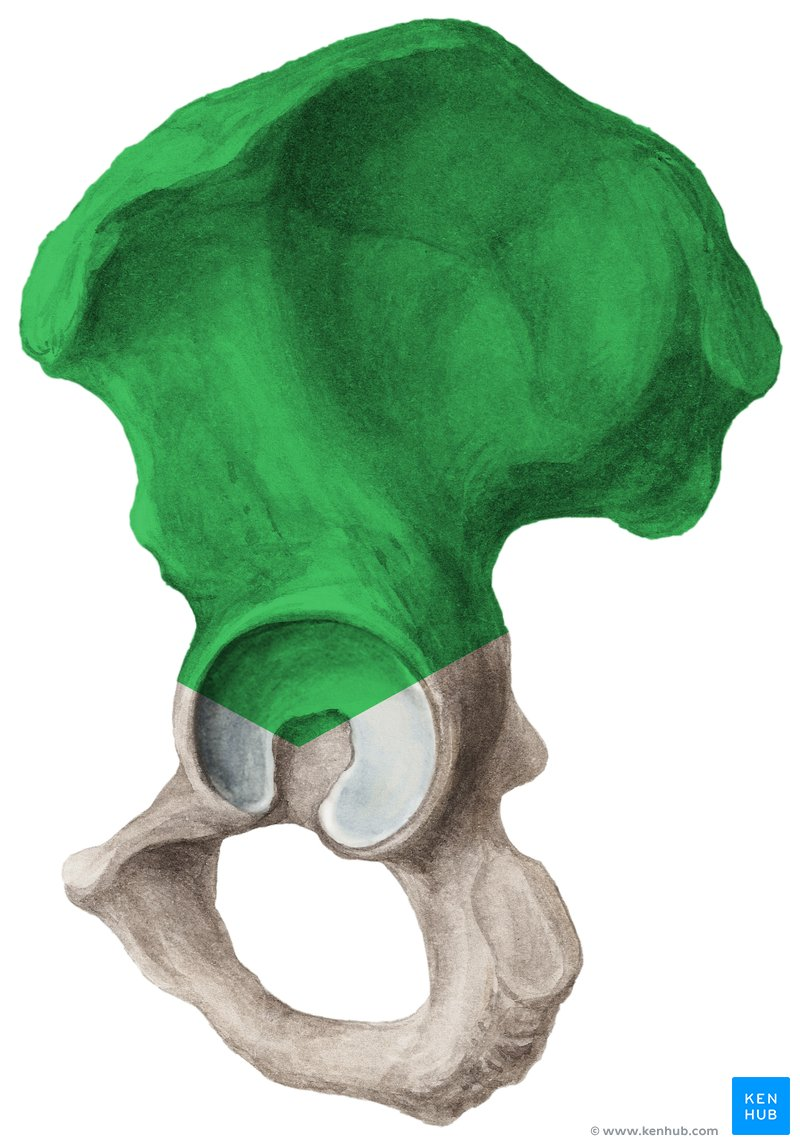
Ilium
the largest and uppermost of the three bones that make up the hip bone
Pubis
contributes to the formation of the pelvic girdle
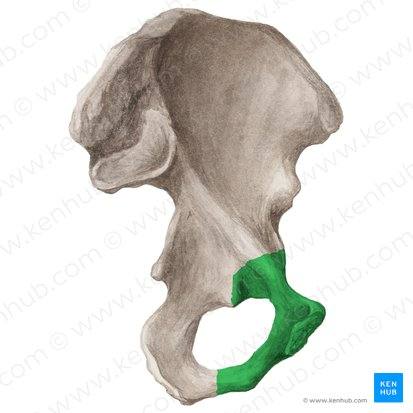
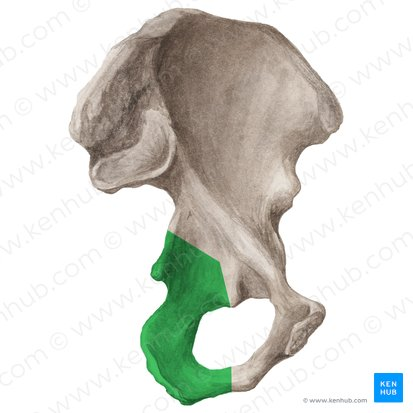
Ischium
bone you sit on
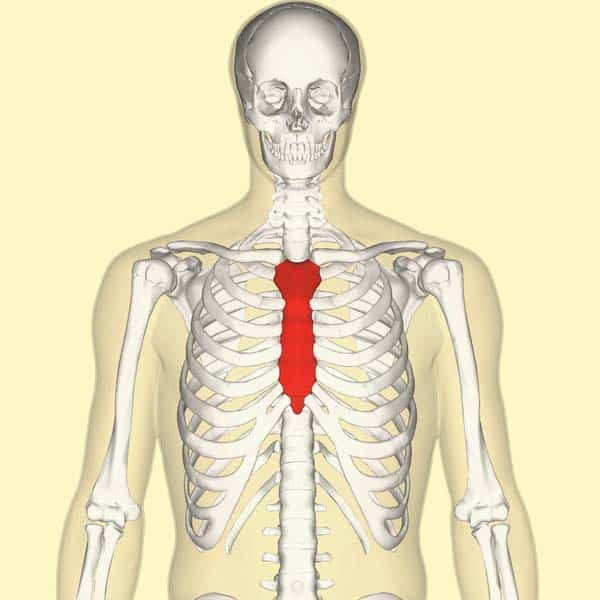
Sternum / breastbone
is a long, flat bone located in the center of the chest.
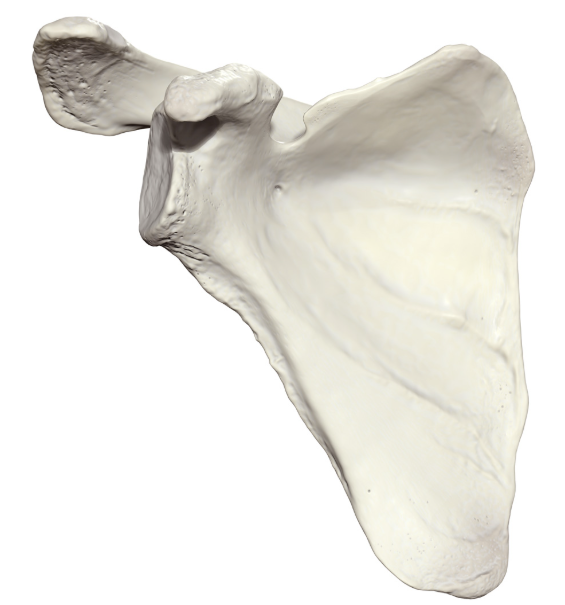
Scapula: Anterior view
Subscapular fossa
Superior boarder
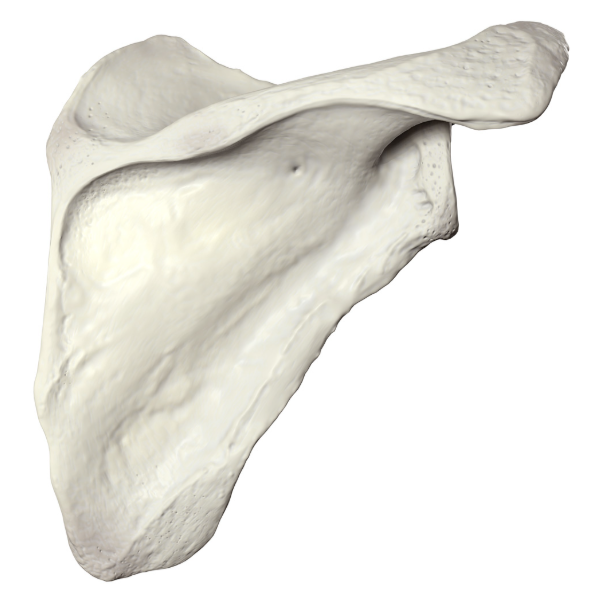
Scapula: Posterior view
Spine of scapula can be seen
Infraspinous fossa
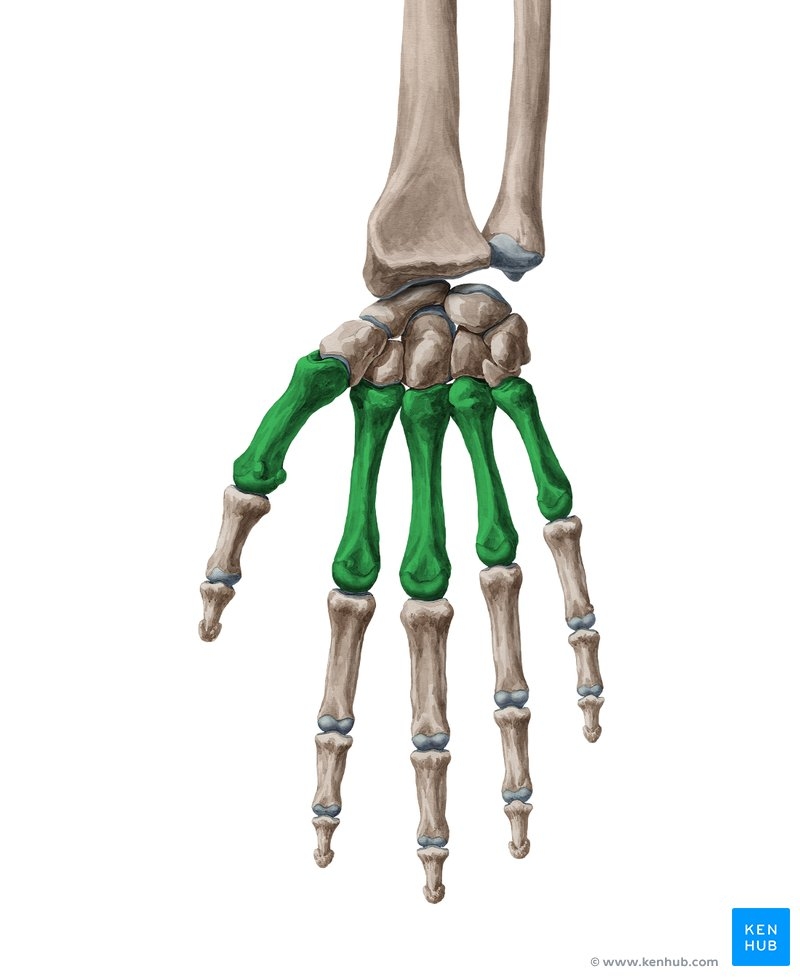
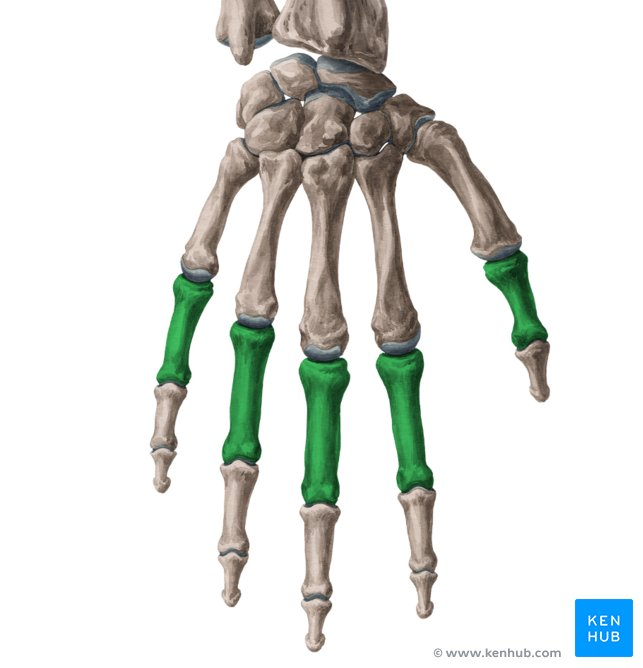
Phalanges
These are the bones of the fingers
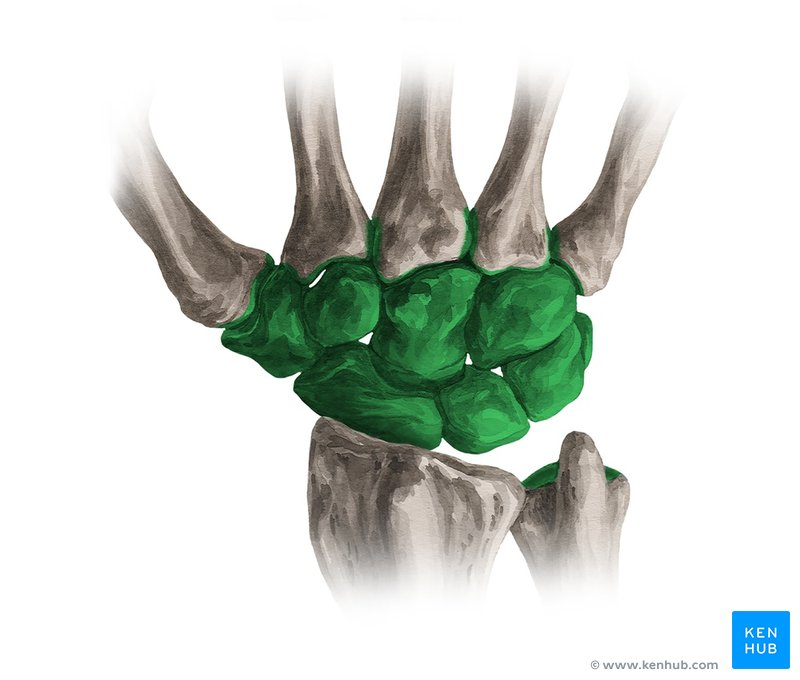
Carpal
These are the eight small bones that make up the wrist
Metacarpal
These are the five bones that form the palm of the hand