Academic Team Science Laws
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
law of mass action
this law states that reaction rate is proportional to the product of the reactant concentrations
beer lamberts law
this law states that the concentration of a substance is directly proportional to its ability to absorb specific light wavelengths
bergmanns rule
this ecological trend says that body size is larger in colder climates (near poles) to conserve body temperature
dulong petit law
this empirical law states that the molar heat capacity of solids is 3 times ideal gas constant. it doesnt work at very low temperatures.
ehrenfests theorem
this law states that the expectation values of displacement and momentum obey time evolution equations
gibbs duhem equation
this equation is used to determine the partial molar volume of one part of a binary mixture from measurements of the partial molar volume of the second part
vant hoff equation
this equation is used to estimate the new value for an equilibrium constant when there is a change in temperature
law of definite proportions
a given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. AKA PROUSTS LAW
combined gas law
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2, relates pressure (atm), volume (L), and temperature (K) to each other after a change.
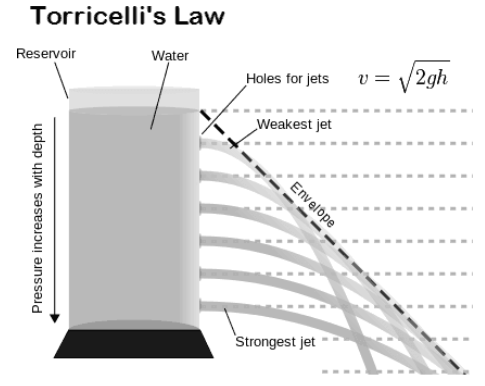
torricellis law
this law is derived from bernoulli's principle and relates the velocity of an ideal liquid to the height of the fluid above the opening
hess law
this law says enthalpy change of reaction = sum of all enthalpy changes for each step of the reaction. AKA law of constant heat summation
first law of thermodynamics
this law states that change in internal energy = added heat - work done. conserves energy. U=Q+-V
second law of thermodynamics
energy flows from hot to cold objects unless energy is used. (work done). entropy only increases.
third law of thermodynamics
entropy of a perfectly organized crystal at absolute zero is zero. absolute zero is unreachable.
zeroth law of thermodynamics
If two thermodynamic systems are each in equilibrium with a third, they are in equilibrium with each other. (if A=C and B=C then A=B=C)
coulombs law
this law states that electric force between charged objects depends on the distance between the objects and the magnitude of the charges.
gauss law
this law states that the total electric flux summed over any closed surface = net charge enclosed by the surface divided by permittivity of free space.
rayleigh jeans law
this law dealing with blackbodies has inconsistencies that suggest a UV catastrophe (perfect blackbodies emit infinite energy)
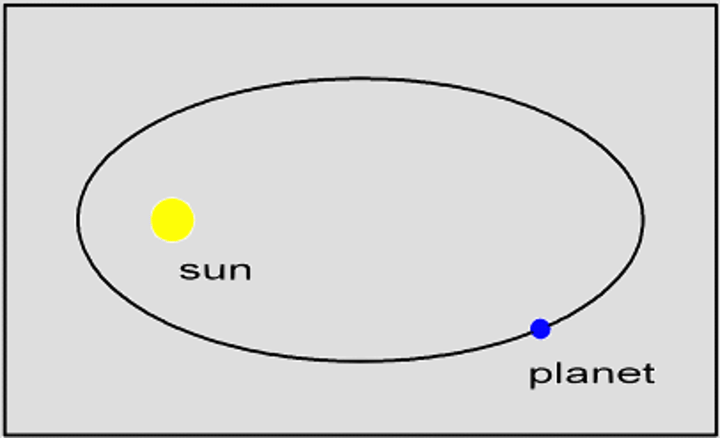
keplers first law
this law states that the orbits of the planets are ellipses, with the sun at one focus
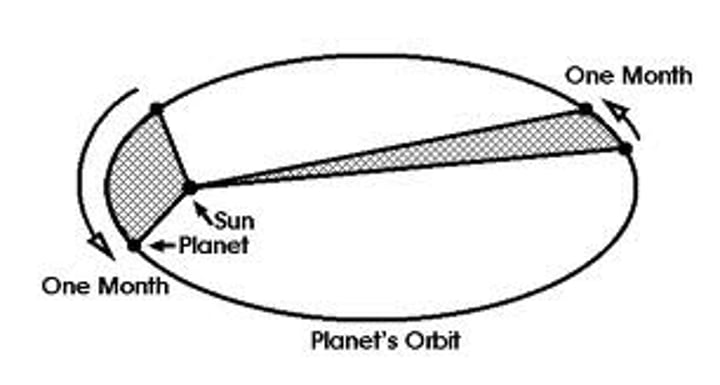
keplers second law
this law states that as a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times
keplers third law
this law states that distant planets orbit the sun at slower average speeds. AKA law of harmonics.

lenz law
this law says that induced magnetic current flows in the opposite direction of the original current (flux change)
raoults law
this law states that the vapor pressure of a solution is directly proportional to the mole fraction of solvent present
henrys law
this law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas on the surface of the liquid
sieverts law
This law states that the solubility of a gas in a metal is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas on the surface of the metal
pascals law
this law states that pressure exerted by a confined fluid acts equally in all directions.
stokes law
this law states that when any object rises or falls through a fluid it will experience a viscous drag
fouriers law
AKA law of heat conduction, this law state that heat transfers from hot to cold matter to reach equilibrium.
laplaces law
this law states that the larger the vessel radius, the larger the wall tension needed to withstand any fluid pressure
wiens law
this law states that hotter objects emit photons with a shorter wavelength. applies to blackbodies
stefan boltzmann law
this law states that an object emits energy at a rate proportional to the fourth power of its temperature, in Kelvin.
bernoulli principle
this law states that as the speed of a fluid/gas increases, its pressure decreases.
daltons law
this law states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases = the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases
poiseuilles law
this law calculates the rate of flow of a fluid through a confined vessel (laminar flow)
grahams law
this law states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to its molar mass's square root
boyles law
this law inversely relates pressure and volume of gas
charles law
this law directly relates volume and temperature of gas
gay lussacs law
this law directly relates pressure and temperature of gas. AKA amontons law
avogadros law
this law directly relates moles of gas with volume
vant hoffs law
this law states that osmotic potential is negative and proportional to the concentration of solute particles
darcys law
this law states that groundwater discharge depends on the hydraulic gradient, hydraulic conductivity, and cross-sectional area of an aquifer.
law of segregation
this mendelian law states that homologous chromosomes separate allele pairs in meiosis.
law of independent assortment
this mendelian law states that alleles of 2+ genes get sorted into gametes individually without the influence of another allele. has to do with punnet squares and f1, f2
le chateliers principle
this law states that when stress is applied in dynamic equilibrium, the system adjusts in the direction with less moles to relieve it.
law of universal gravitation
this law states that every object in the universe attracts every other object. G = 6.67*10^-11
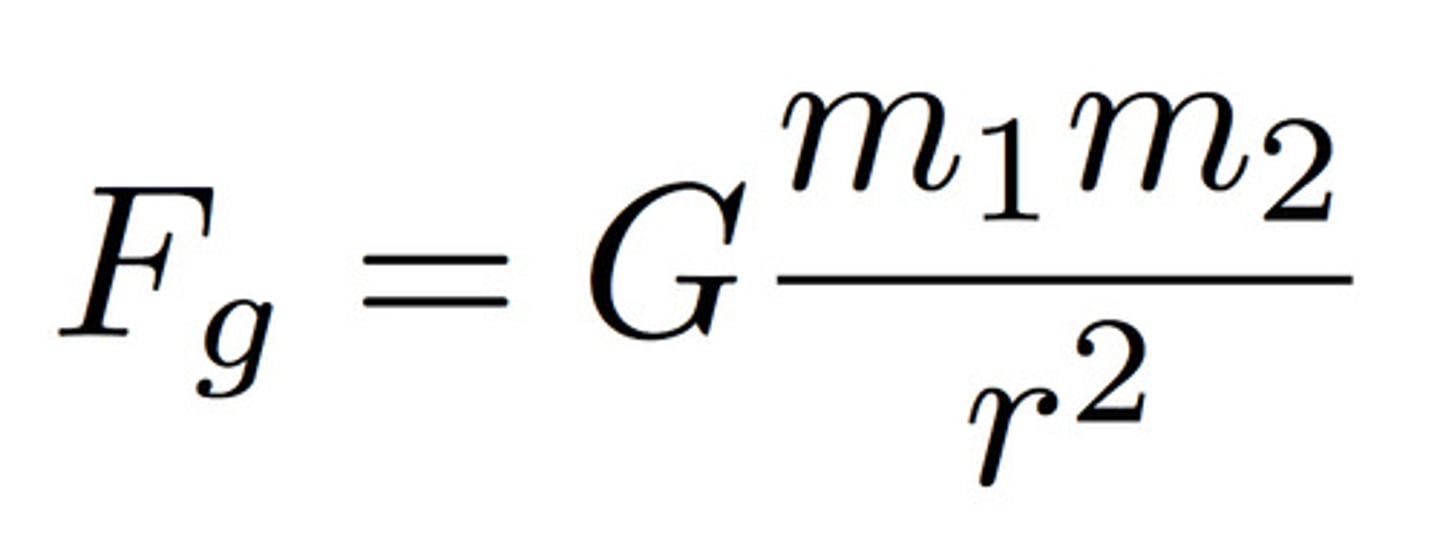
biot savart law
this physical law describes the equation of the magnetic field generated by an electric current. equivalent of coulombs law but for magnetic fields instead of electric currents
amperes law
this law describes how a changing electric current corresponds to an induced magnetic field
faradays law
this law describes how a changing magnetic field corresponds to an induced current
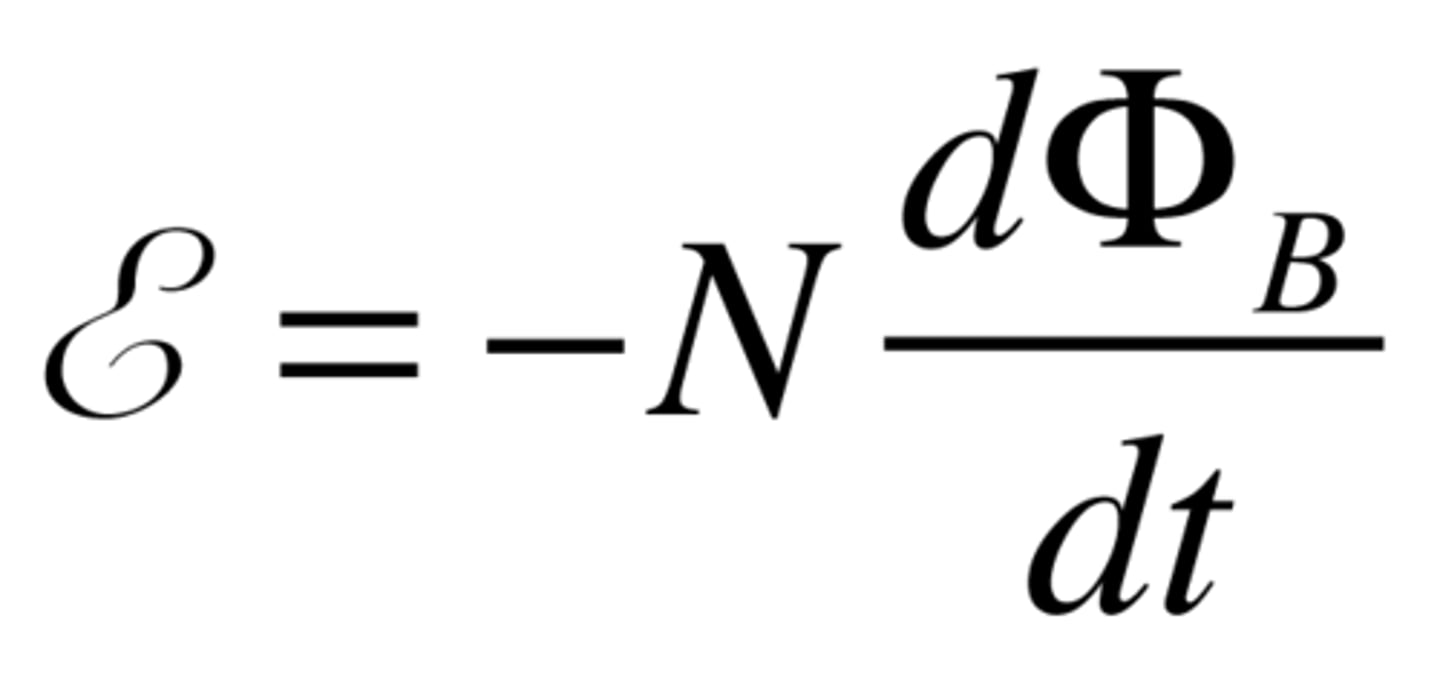
pascals principle
this law explains how pressure moves through an enclosed static fluid without losing force. ex. Heimlich maneuver.
kirchoffs law of radiation
this law states that the ratio of emissive power to the coefficient of absorption is constant for all substances at a given temperature and = emissive power of perfect blackbody at that temperature
tennis racket theorem
this law states that rigidbodies with 3 moments of inertia have unstable rotations about the intermediate axis
snells law
this law states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant.
huygens principle
this law states that every point on any wave front can be regarded as a new point source of secondary waves.
braggs law
this law states that when xrays are incident on a crystal surface, its angle of incidence will reflect back with the same angle
dobereiners law of triads
the mean of the atomic masses of the 1st and 3rd elements in a triad equals the atomic mass of the 2nd element in the triad.
kirchoffs loop rule
this rule states that the voltage gains/drops in a circuit loop are equal
kirchoffs junction rule
this rule states that the currents coming in and out of a junction are equal
rule of 70
this rule is used to find the time it takes to double a variable by dividing the namesake number by the growth rate.
gauss law of magnetism
this law states that the magnetic flux across a closed surface is 0. this means that magnetic monopoles cant exist.
ficks law
this law states that the diffusion of a gas across a membrane is proportional to the diffusion gradient and area, and inversely proportional to the diffusion distance
allens rule
this ecological trend says that animal appendages are longer in warmer areas (near the equator)
glogers rule
this ecological trend says that animal coloration gets darker in warmer more humid areas (near the equator)
gauses principle
this ecological rule says that no two species can occupy the same niche at the same time
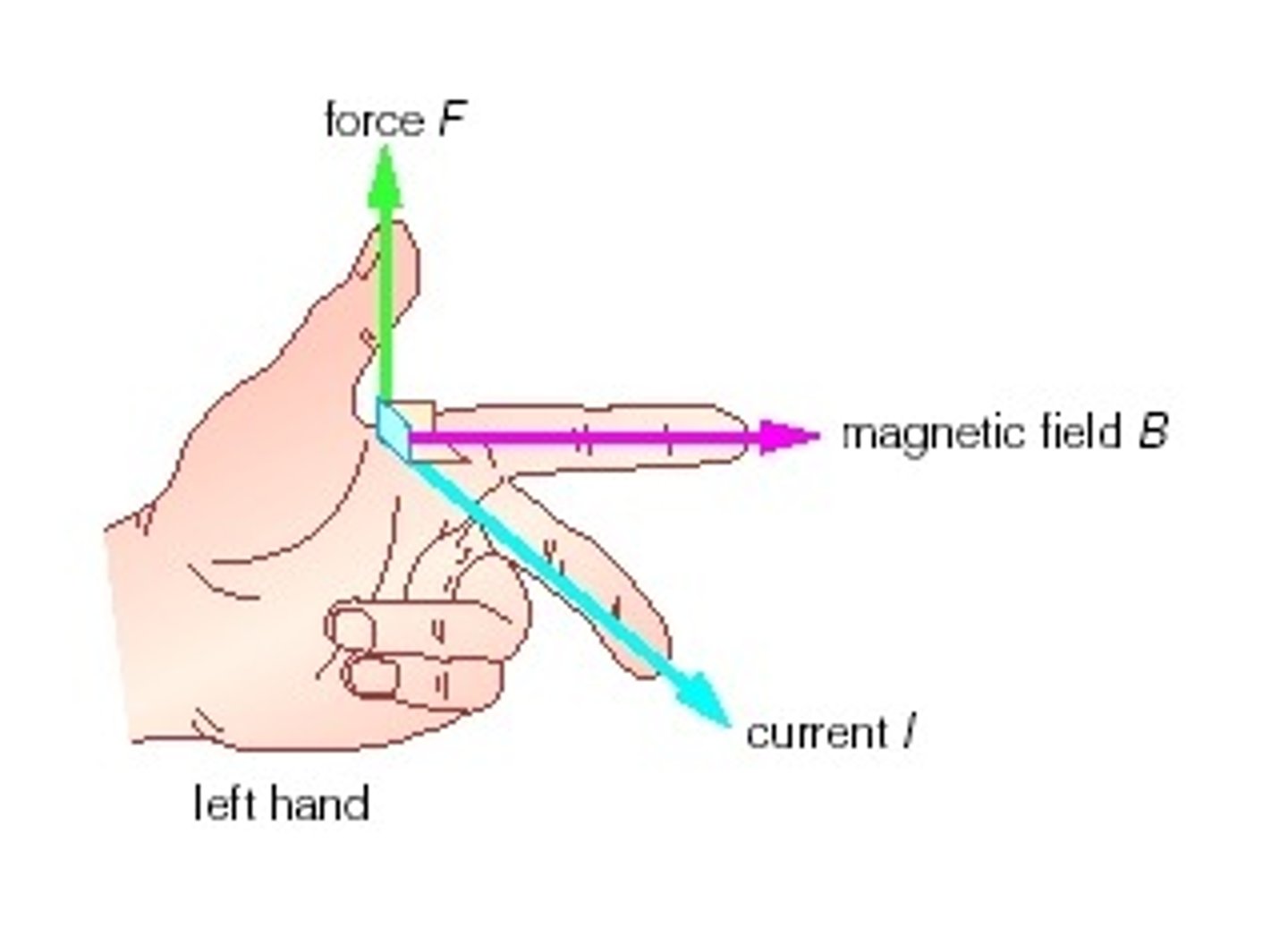
right hand rule
in this RIGHT HAND mnemonic, make perpendicular axes with thumb, pointer, and middle fingers. orient middle finger in direction of magnetic field. orient pointer finger in direction of positive particle. thumb will point in new direction of particle. negative particles will move in opposite direction of thumb.
OR
for electric currents, make 'thumbs up' and orient thumb in direction of current. finger coils point in direction of induced magnetic field.
einstein velocity addition
this rule states that the relative velocity of any two objects never exceeds the velocity of light
mitserlich law
this law predicts which chemical compounds have the same crystal structures
fermats principle
this law states that light follows the path of least time
kopp neumann law
chemically-similar bodies of analogous atomic constitution have approximately the same atomic heat
the big slurp
this theory says that the universe exists in a false vacuum and that it could become a true vacuum at any moment
lamm equation
this equation describes the sedimentation and diffusion of a solute under ultracentrifugation in traditional sector-shaped cells.
haldanes rule
If in the offspring of two different animal species one sex is absent, rare, or sterile, that sex is the heterogametic (XY) sex
michaelis menten equation
this model of enzyme kinetics proposes a steady state equilibrium between enzyme-substrate complex and products
thevenins theorem
this theorem says that any network of voltage or current sources and resistors can be reduced to a single voltage source in series with a single resistor.
poyntings rule
this law states that the rate of energy transfer per unit volume from a region of space equals the rate of work done plus divergence
boltzmann equation
this equation describes the statistical behavior of a fluid not in thermodynamic equilibrium
newtons law of cooling
this law states that the rate of cooling of an object is proportional to the temperature difference between the object and its surroundings.
kirchoffs principle
this law states that current in a circuit will seek out the path of least resistance.
babinets principle
this law states that the diffraction pattern from an opaque body is identical to one from a hole of the same size and shape except for the overall forward beam intensity
renschs rule
this ecological trend says that sexual size dimorphism increases with size when males are larger and decreases with size when females are larger
moselys law
this law states that the square root of the X-ray frequency emitted by an element is directly proportional to its atomic number.
law of octaves
this law states that the same properties appear every eighth element when the elements are listed in order of their atomic masses
markovnikov rule
the hydrogen atom is attached to the carbon atom with the MOST number of hydrogen substituents
antimarkovnikov rule
the hydrogen atom is attached to the carbon atom with the LEAST number of hydrogen substituents
hammonds postulate
this law states that a transition state in a chemical reaction resembles the structure of the nearest stable species (reactant, intermediate or product)
zeitsev rule
in elimination reactions where an alkene is formed from the removal of a halide and a hydrogen from an alkane, the reaction prefers a more highly substituted alkene
huckels rule
this law states that if a cyclic, planar molecule has 4n+2 pi electrons, it is considered aromatic
madelung rule
this rule determines the order electrons fill sublevels based on energy levels. aufbau principle was based off of this rule. differs from Aufbau Principle by considering sublevel energies. =n+l
slaters rules
set of rules used to determine the effective nuclear charge (positive charge experienced by electron) experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom.