Integumentary System - Skin & Nails Review (CHP 5)
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary related to the integumentary system, including differences between thick and thin skin, nail anatomy, and skin functions like thermal regulation and protection.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
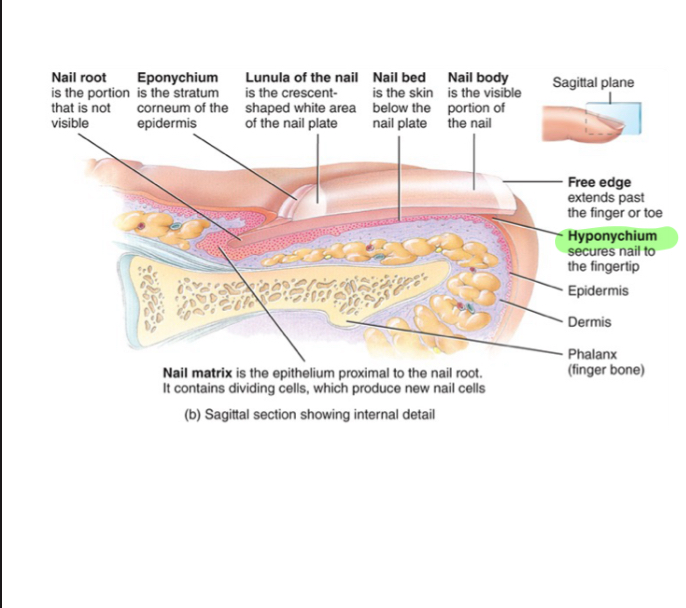
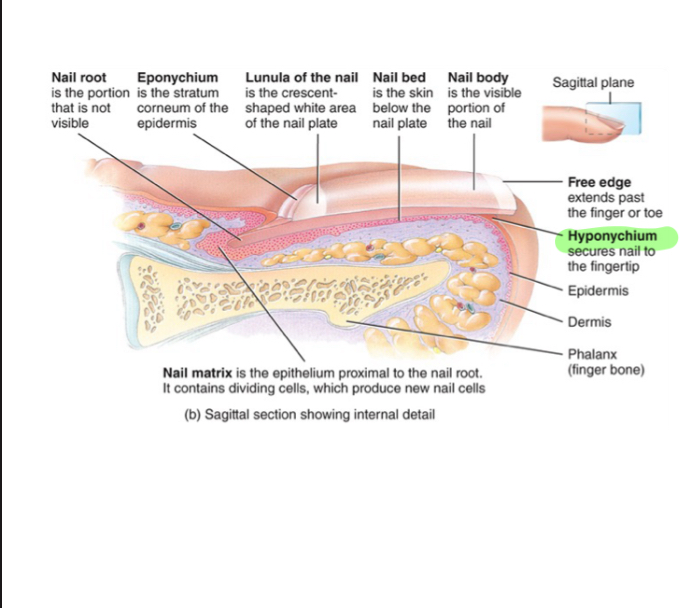
Hyponychium
The skin that holds down the nail, securing it to the fingertip.
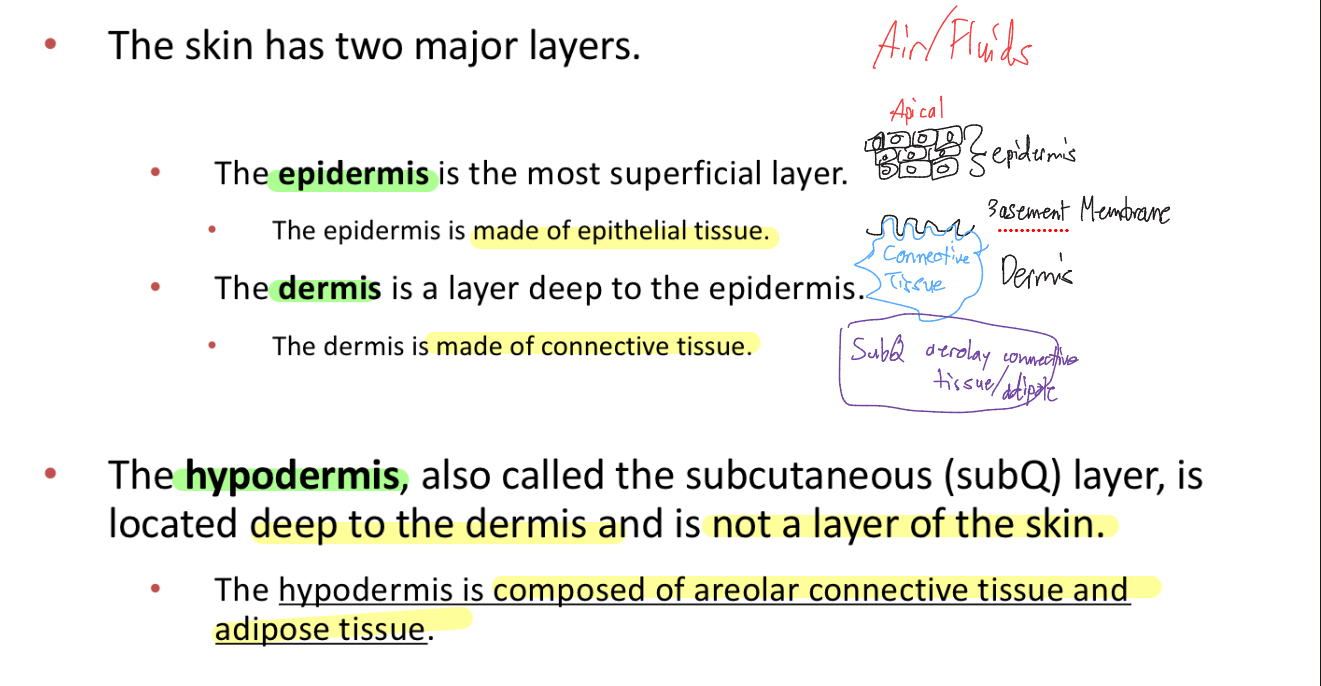
3 Layers of Skin
-Epidermis: superficial, made of epethelial tissue
-Dermis: deep to epidermis, made of connective tissue
-Hypodermis/Subq: deep to dermis, not a layer of skin, made of areolar connective and adipose tissue
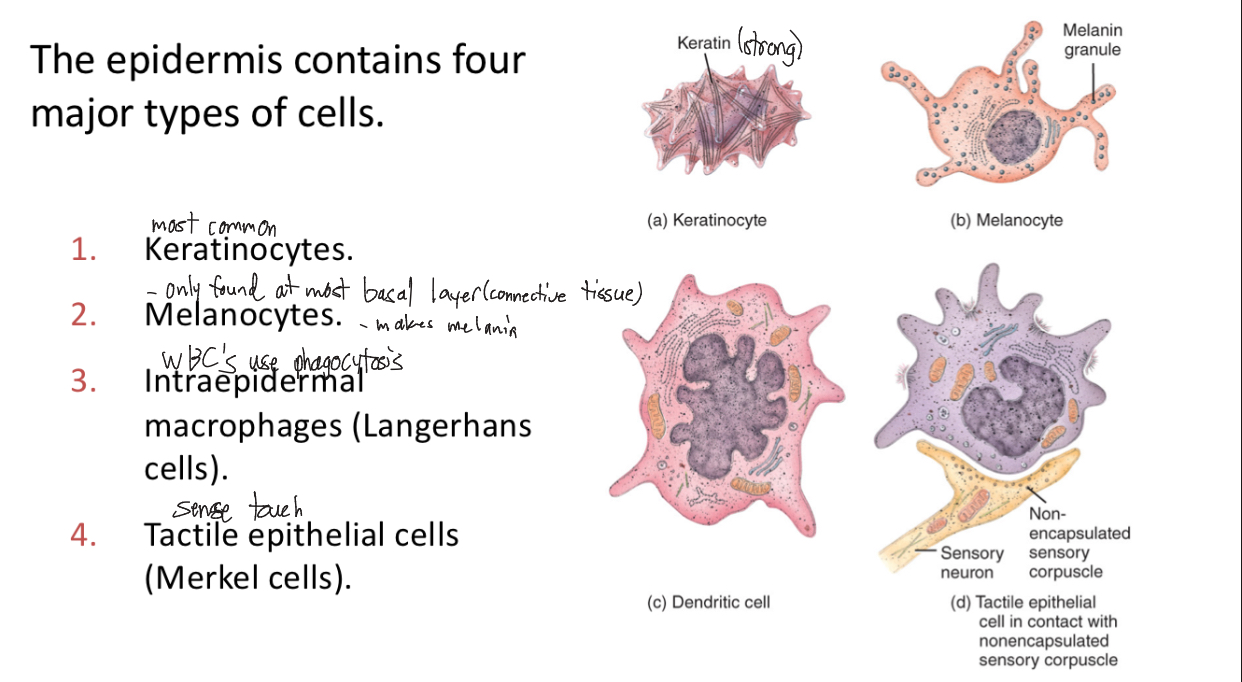
4 Cells in Epidermis
Keratinocytes (most common 85%, strong, basal layer)
Melanocytes (makes melanin, 8%)
Dendritic Cells (immune response, 5%)
Merkel/Tactile Epithelial Cells (sense touch)
5 Layer of Skin (Deep to Superficial)
-Stratnum basale, spinosum, granulosum, lucidom (only in thick skin), corneum
-BSGLC
Stratnum Basale
Deepest layer, makes keratinocytes, mitosis, has melanocytes
-one cell layer thick
-keratinocytes, stem cells, melanocytes, TE cells
Stratnum Spinosum
Thickest, held by desmosomes
Makes keratin, receiving melanin
Survive on resources provided by vessels in dermis
Stratnum Granulosm
-release contents of lamellar granules
-dying cells (apoptosis)
-lipids inside lamellar granules creates water resistance in epidermis
Stratnum Lucidum
-only in thick skin, clear flat dead cells
Stratnum Corneum
-most superficial layer
-layer of dead cells that shed off, replaced by cells from below, surrounded by lipids (water repellant)
Papillary Region of Dermis
-superficial portion of dermis, has thin collagen n elastic fibers, dermal papillae (bumps), capillaries that supply episdermis
-inc. surface area btw epidermis n dermis
-20%
Reticular Region of Dermis
-deeper portion of dermis, thick collagen n coarse elastic fibers, spaces between contain fat cells, oil n sweat glands (overall very strong n stretchy)
-80%
Shaft (Hair)
-visible, above skin surface
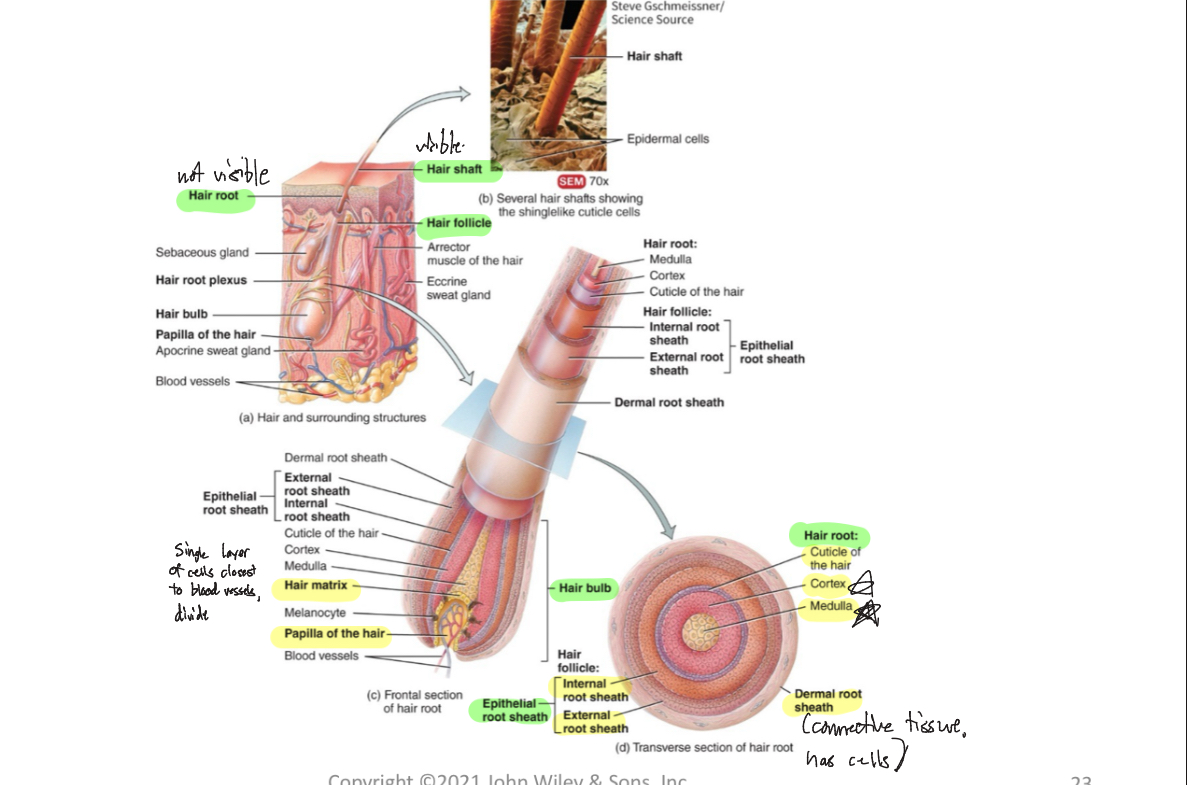
Root (Hair)
-not visible, below skin surface, penetrates into dermis
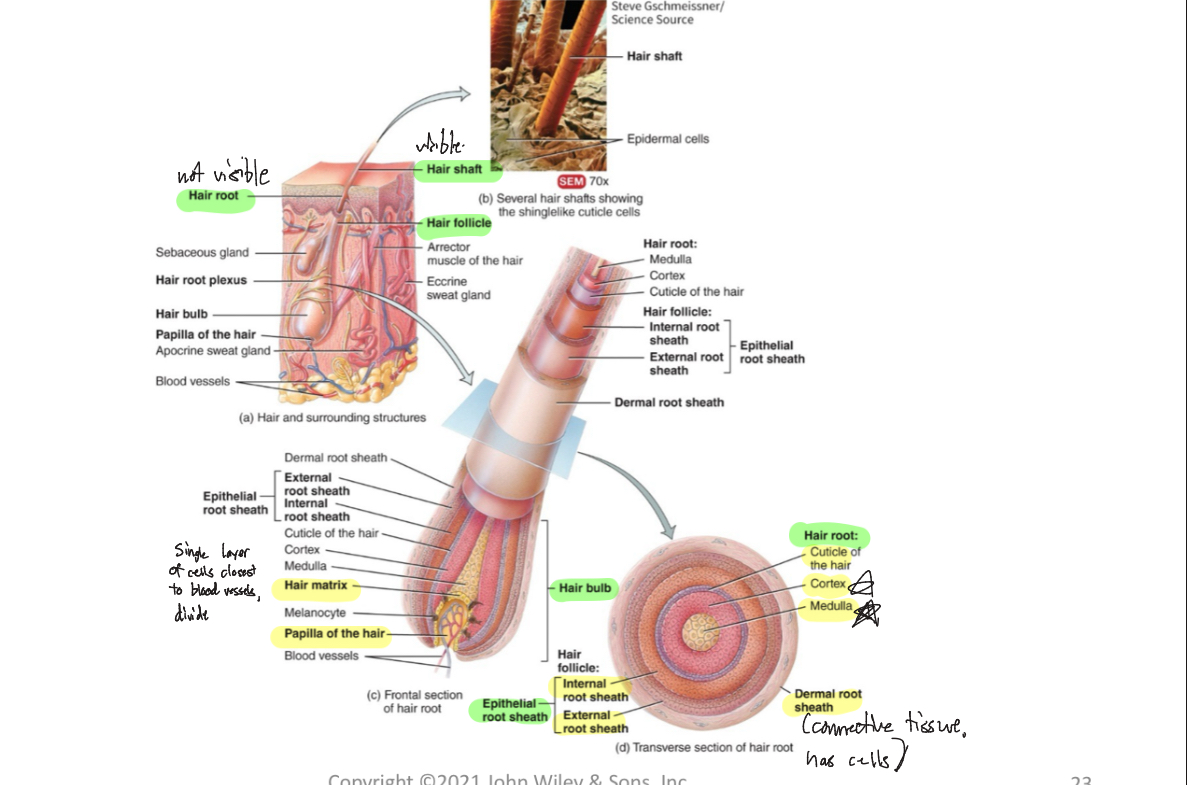
Follicle (Hair)
-structure surrounding hair root
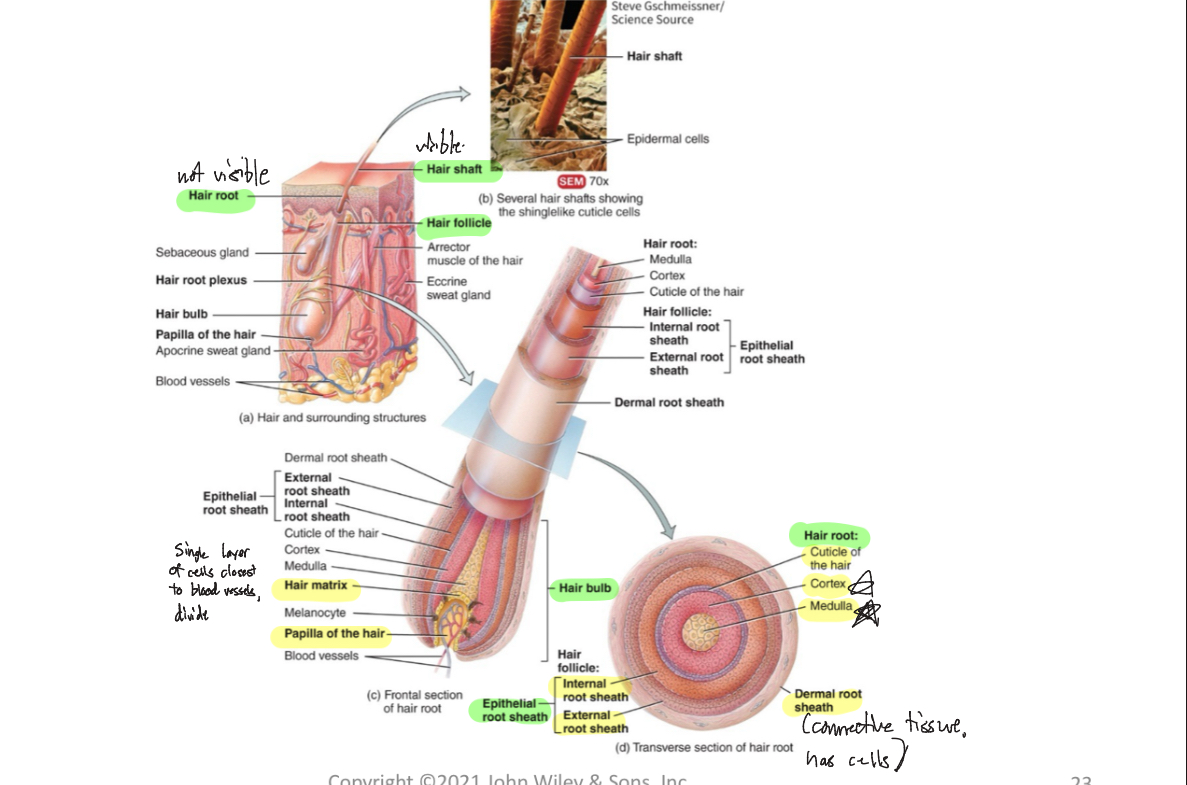
Dermal root sheath (Hair)
-envelops hair follicle, adds support
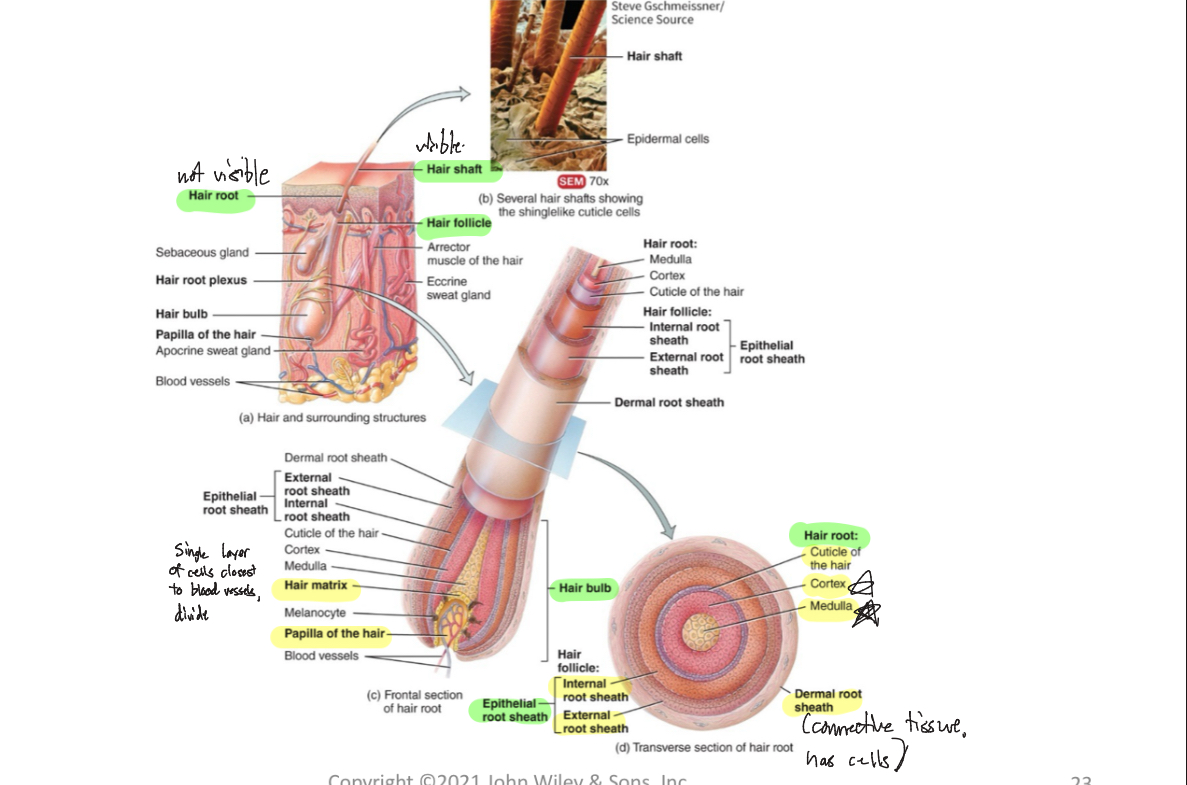
Hair bulb
-deepest part of hair follicle, contains dermal papilla
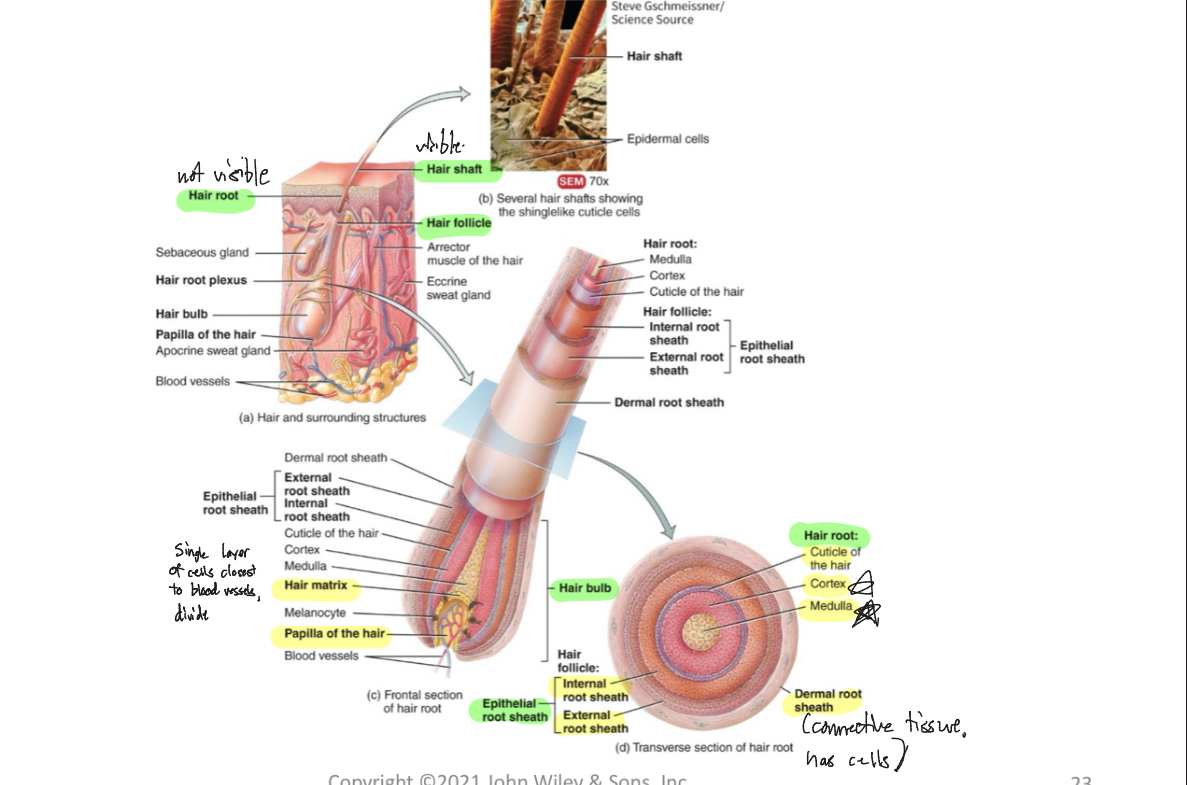
2 Types of Hairs + Functions
terminal hairs (long, coarse, heavy pigment)
Velus hairs (short, fine, pale)
prevents heat loss, decrease sunburn, touch receptors
3 Types of Skin Glands
Sebaceous (oil) glands: connected to hair follicles (not in thick skin)
Sudoriferous (sweat) glands: eccrine (most common) + apocrine (mainly in hairy skin areas)
Ceruminous glands: sweat glands in ear canal
Sebaceous Glands
-in lips, glans penis
-secretes sebum in dermis
-terminates excretory duct in hair follicle
-prevents hairs from drying out
-active during puberty
Eccrine Sweat Glands
-in forehead, palms, soles
-secretes perspiration in reticular dermis
-regulates body temp, waste removal
-termination of excretory duct on epidermis surface
-active soon after birth
Apocrine Sweat Glands
-in skin of armpit, groin, areolae
-secretes perspiration in reticular dermis
-stimulated during stress and arrousal
-termination of excretory duct in hair follicles
-starts in puberty
Ceruminous Gland
-in ear canal
-secretes cerumen (earwax) in subq layer, contains secretions of oil n wax glands
-ducts open to surface or into sebaceous ducts
Free Edge (Nail)
Extends past finger/toe
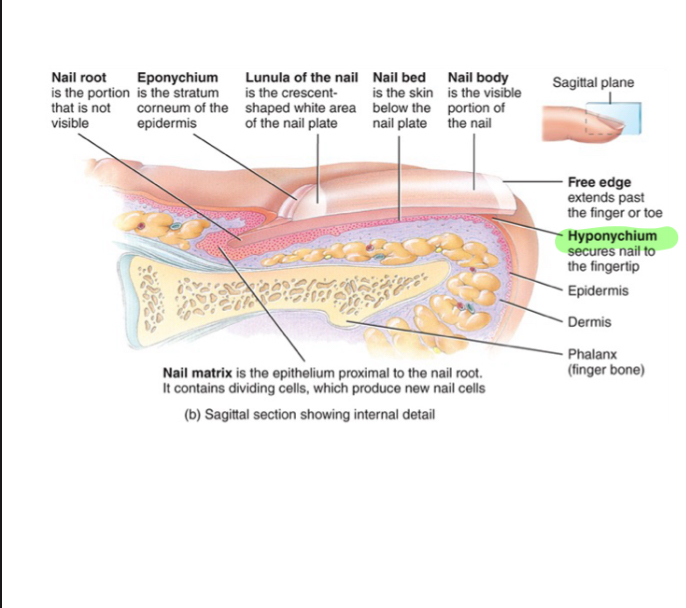
Nail body (Nail)
-like stratnum corneum of epidermis, but harder keratin and no shedding
-Nail bed is below nail body
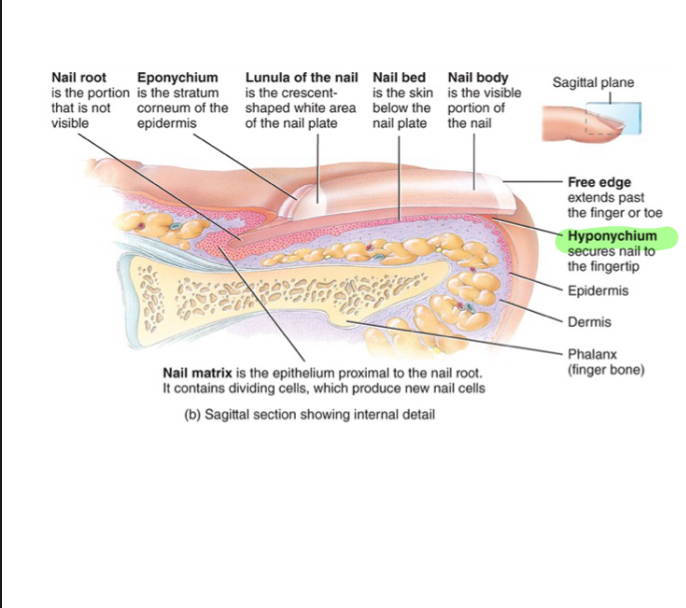
Lunule (Nail)
Crescent shaped white area of nail body
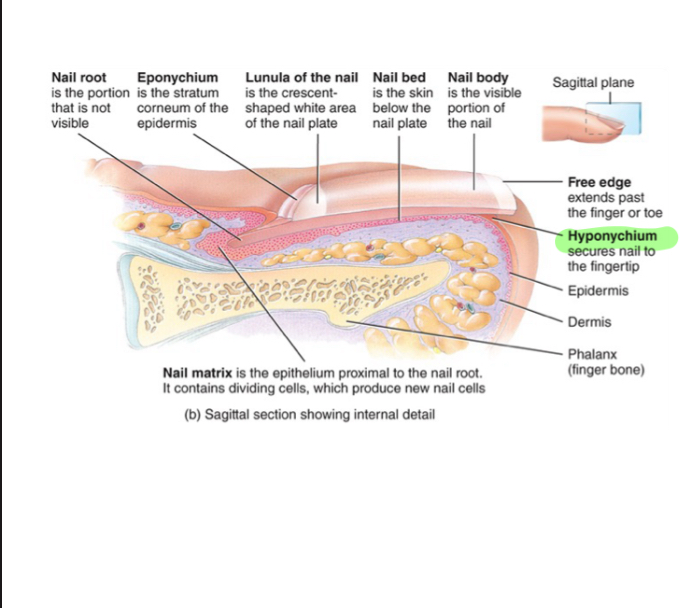
Eponychium (Nail)
Also known as the cuticle, it is the stratum corneum that holds down the nail to the nail plate at the proximal end.
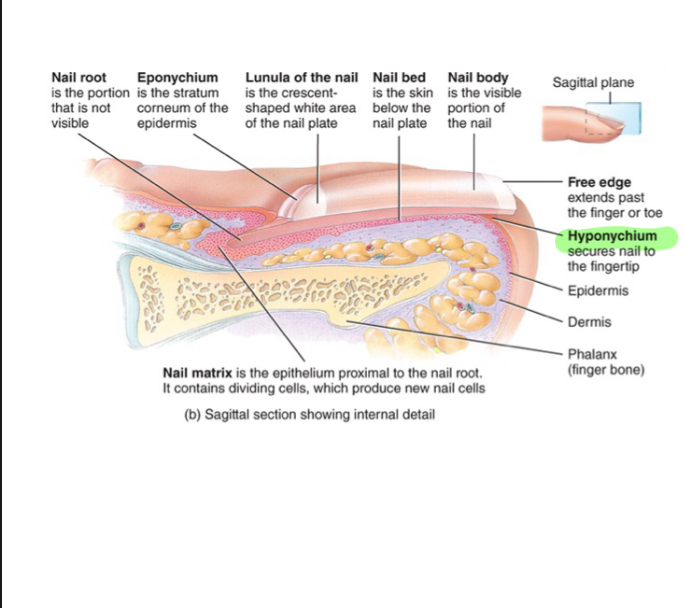
Nail root
-not visible portion of nail
-has plexus (nerve ending) detects hair movement
Arrector pili
-smooth muscle in dermis
-contracts with cold, fear, emotions (erect hair)
Nail matrix
-epithelium proximal to nail root, cells divide mitotically to make new nail cells
Thick (hairless) Skin
Skin type that covers palms, palmar surfaces of fingers, and soles
Thin (hairy) Skin
Skin type that covers all body regions BUT palms, palmar surfaces, surfaces of fingers, and soles
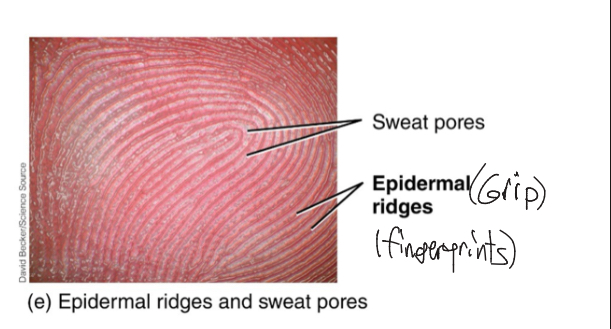
Epidermal Ridges
Structures that form fingerprints, present in thick skin and absent in thin skin.
Hair Follicles + 3 Layers
Structures responsible for hair growth, present in thin skin and absent in thick skin (e.g., palms).
-internal root sheath (epi. Tissue)
-external root sheath (epi. Tissue)
-dermal root sheath (CT)
Sebaceous Glands (Oil Glands)
Glands that produce sebum, connected to hair follicles, present in thin skin and absent in thick skin.
Sudoriferous Glands (Sweat Glands)
Glands responsible for producing sweat; more numerous in thick skin (e.g., palms) for thermal regulation.
Theromoregulation of Skin
-sweat (from eccrine glands)
Evaporation of sweat takes energy, thus cools us down
-blood vessels in dermis dilate/contract to confrol flow
Protection of Skin
-keratin, lipids, sebum, acidic sweat (prevent bacteria grotwth)
-Melanin (UV protection)
Macrophages (eat up microbes)
Sensory Receptors (Skin)
Nerves that detect touch, temperature, and pain, found more densely in thick skin (palms, soles).
Excretion n Absorption of Skin
-eliminate cellular waste
-passage of materials from outside into body cells
Vitamin D Synthesis in Skin
-enzymes in liver and kidneys make calcitrol (most active form of Vitamin D)
-Vitamin D helps absorb Ca + P, enhances phagocytic activity
4 Steps of Deep Wound Healing
-injury that extends into dermis and subq layer
Inflammatory: injured tissue secretes signaling molec’s, attracts phagocytes that ingest bacteria n debris, blood clot forms
Migratory: clot becomes a scab (prevents infections), epithelial cells migrate beneath scab to bridge wound
Proliferative: epithelial cell growth beneath scab, vessels grow more
Maturation: scab falls off, collagen fibers more organized
Eccrine Sweat Glands
A type of sudoriferous gland that secretes watery sweat for cooling the body through evaporation when warm.
Vasodilation (Dermis)
The widening of blood vessels in the dermis when the body is WARM, increasing blood flow to the surface to release heat.
Vasoconstriction (Dermis)
The narrowing of blood vessels in the dermis when the body is COLD, decreasing blood flow to the surface to conserve heat.
Reservoir for Blood (Skin Function)
The ability of the dermis to hold a significant and variable amount of blood within its extensive network of blood vessels.
Keratin (Skin Protection)
Strong proteins, produced by cells in the stratum spinosum and filling cells in the stratum lucidum and corneum, providing physical protection against abrasion.
Lamellar Granules
Structures found in the stratum granulosum that produce lipids, making the skin waterproof and preventing dehydration.
3 Major Types of Skin Cancer
-excessive exposure to UV light most common cause
-Basal cell carcinoma (78%), squamos cell carcinoma (20%), malignant melanoma (2%, worst kind)
Warning of Malignant Melanoma (ABCDE)
A - Asymmetry
B - Border is irregular
C- color is uneven
D - diameter is 6>mm
E - evolving, chanigning in shape n size
Burns
Tissue damage from heat, electricity, etc, denatures proteins in skin cells
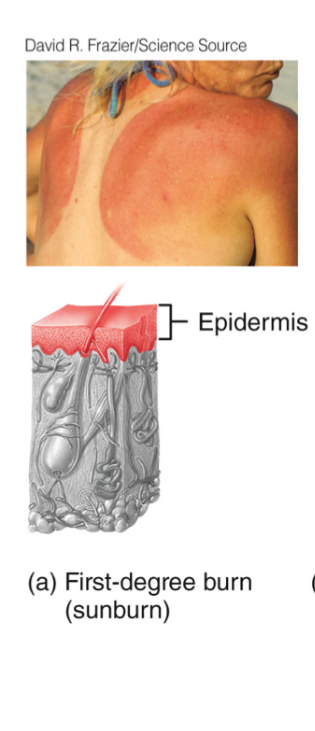
1st Degree Burn
-only epidermis, redness n mild pain, 3-6d of healing
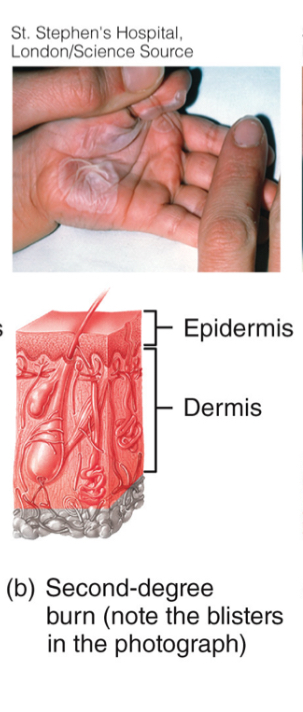
2nd Degree Burn
-epidermis + part of dermis
-some skin functions lost, redness, blisters, swelling
3rd Degree Burn
-all 3 layers
-most skin functions lost, marked swelling, numbness, skin cant heal
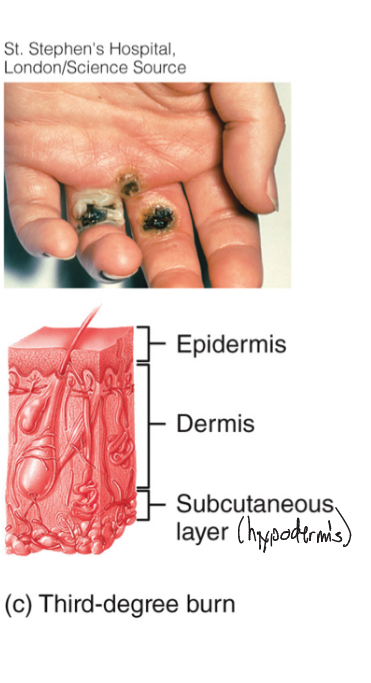
Effects of Burn
-large loss of water, plasma, causes shock + inflammation
-bacterial infection (barrier loss)
-blood circulation reduced (fluid loss)
-urine production decreased (fluid loss)
-diminished immune response (highly taxed)