Geometrical Qualities of the Radiographic Image LECTURE (copy)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What are the 3 components of Recognizability
Sharpness (spatial resolution)
Magnification (size distortion)
Shape Distortion
What are some other names for Sharpness
Spatial resolution
Detail
Should spatial resolution be maximized or minimized?
MAXIMIZED
What is the most important component of the recognizability of an image
Sharpness
What is the ARRT definition for spatial resolution
The sharpness of the structural edges recorded in the image
What is another definition for sharpness
Abruptness with which the particular edges stop
What is Umbra
The sharp area of a radiographic image
How is Umbra casted
cast from a point source of light
(no blur; perfectly sharp edges)
Umbra is referred to as
“pure”, “complete”, or “true” dark shadow
What is Penumbra
The unsharpness or blurring that surrounds the edge of a radiographic image
How is Penumbra casted
Cast from an area source of light (disk source)
What is the partial shadow cast around pure shadow called
Penumbra
What is motion penumbra
Movement of source of light, object, or IR spreads penumbra
What is magnification
Difference between the size of the real object and the size of its projected image
What is Shape Distortion
Difference between the shape of the real object and the shape of its projected image
In a given axis of direction, (lengthwise or crosswise), shape distortion will consist of either __________________________ of the image or ________________________ of the image.
Elongation; Foreshortening
Is unsharpness a subjective or objective quantity
objective
How is unsharpness an objective quantity (List 3)
directly measured
geometrically predicted
mathematically calculated
Mathematical expressions of sharpness are always _________
derived and expressed as ________ numbers.
indirectly; relative
What are the 3 controlling factors of unsharpness in projection geometry of an x ray beam
FSS
OID
SOD
What is the formula for Geometrical Unsharpness
U = FS x OID/SOD
What is the formula used to calculate SID using OID and SOD
OID + SOD = SID
What is the spread of penumbra (precisely) with a
FSS = 0.6 mm
OID = 40 cm
SOD = 80 cm
0.6 mm x 40
80
40/80 is simplified to ½
Since we are already multiplying to a decimal (0.6), ½ can be converted to 0.5
0.6 × 0.5 = 0.3
U = The penumbra spreads across an area of 0.3 mm
1 inch = ______ cm
2.54cm
What is the inverting formula used for sharpness
SOD/OID
Why is the inverting formula used for sharpness
For a given particular focal spot size the SOD/OID ratio becomes an indicator of the relative sharpness that will be produced in an image
How will image sharpness be affected in the second exposure?
First exposure: the SOD is 45 cm and the OID of 2.5 cm.
Second exposure the SOD is changed to 90 cm and the OID is reduced to 1.25 cm
First Exposure: 45/2.5 = 18
Second Exposure: 90/1.25 = 72
Second Exposure/First Exposure: 72/18 = 4
Second Exposure is 4 times sharper than the First Exposure
Is high contrast the same as high sharpness
NO
How is sharpness measured
Sharpness is measured by how quickly the transition from light to dark changes as image is visually scanned
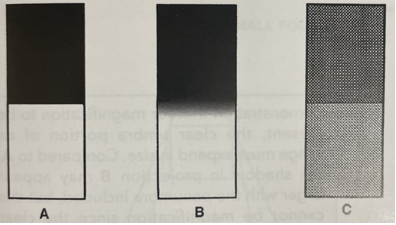
Select 2 images that have high sharpness
A and C
Scatter radiation cannot affect sharpness
T/F
TRUE
Does scatter radiation increase penumbra?
YES
Can scatter radiation decrease the visibility of the edges of a radiograph
YES
What factors primarily control sharpness
SID
SOD
OID
FSS- biggest factor that affects sharpness
Motion
In a magnified image the objects length and width will measure ______ than the real object by _______ __________
larger; equal porportions
Magnification is based solidly on the
geometry of similar triangles
What is the formula for magnification
Image Size = SID
Object Size SOD
Magnification is the _________ between the size of the real image and the size of the real object
RATIO
An object measuring 20 cm in width is radiographed using an
SID of 40 inches and an SOD of 35 inches.
How wide is the projected image of the object?
Use the magnification formula
Image Size/Object Size = SID/SOD
Input the information provided into the formula
X/20 = 40/35
Cross multiply
40 × 20 = 800; 35x
Divide 35 from 800
800/ 35 = 22.86
The projected image of the object is 22.86 cm wide
A radiograph is taken of an object 2 cm in width and the resulting image measures 8 cm in width. If a 125 cm SID was used, what was the SOD?
Use the magnification formula
Image Size/Object Size = SID/SOD
Input the information provided into the formula
8/2 = 125/x
Cross Multiply
8x = 250
Divide 8 from 250
250/ 8 = 31.25
SOD = 31.25cm
What is the magnification factor
Represents the multiplication factor by which the length and width of the object in the image is increased
Factor of linear magnification
What is the formula for Magnification Factor
(SID/SOD - 1) x 100
An object is radiographed at 183 cm SID and 150 cm SOD.
What is the percentage magnification?
Use the magnification factor formula
(SID/SOD - 1) x 100
Input the information provided into the formula
((183/150) - 1) x 100
Solve using PEMDAS
183/150 = 1.22
1.22 - 1 = 0.22
0.22 × 100 = 22
Magnification Factor: 22%
What is resolution
The ability to distinguish any two adjacent details in the image as being separate and distinct from each other
What are the 2 most important aspects contributing to resolution
Sharpness (Recognizability factor)
Contrast (Visibility factor)
Both poor ________ and poor _________ can degrade overall image resolution
sharpness; contrast
List some factors that could cause shape distortion
Angle and alignment of the x-ray beam
Angle and alignment of the part of interest
Angle and alignment of the IR
What should you look for in sharpness
Abruptness; How abrupt in goes from one part to the next part
Why is a large FSS used for larger parts
The xray beam penetrates in a shorter amount of time than using a small FSS on a large body part
Prevent motion blur
What part of the Xray tube do you choose the FSS
Cathode
What is it called when the electrons in the anode hit the same part of the tube every time
PITTING
The line focus principle
By angling the face of the anode target, a large actual focal spot size can be maintained, and a small focal spot can be created
relationship between actual and effective focal spot
Does FSS affect shape distortion
Not a whole lot but yes
Does SID or OID affect shape distortion
NO; affects size distortion
If there is an angle on the tube and the part of interest becomes 2 times bigger, what type of distortion takes place?
Size AND shape distortion
As penumbra increases, umbra _________
decreases
Forshortening is caused by magnification
T/F
FALSE; shape distortion
Will you see more sharpness on a long or short SID?
LONG; A longer SID reduces penumbra
What focal spot is recommended for high sharpness
short fss