Histo 40: Oral Cavity
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
space between the lips and teeth:
oral vestibule
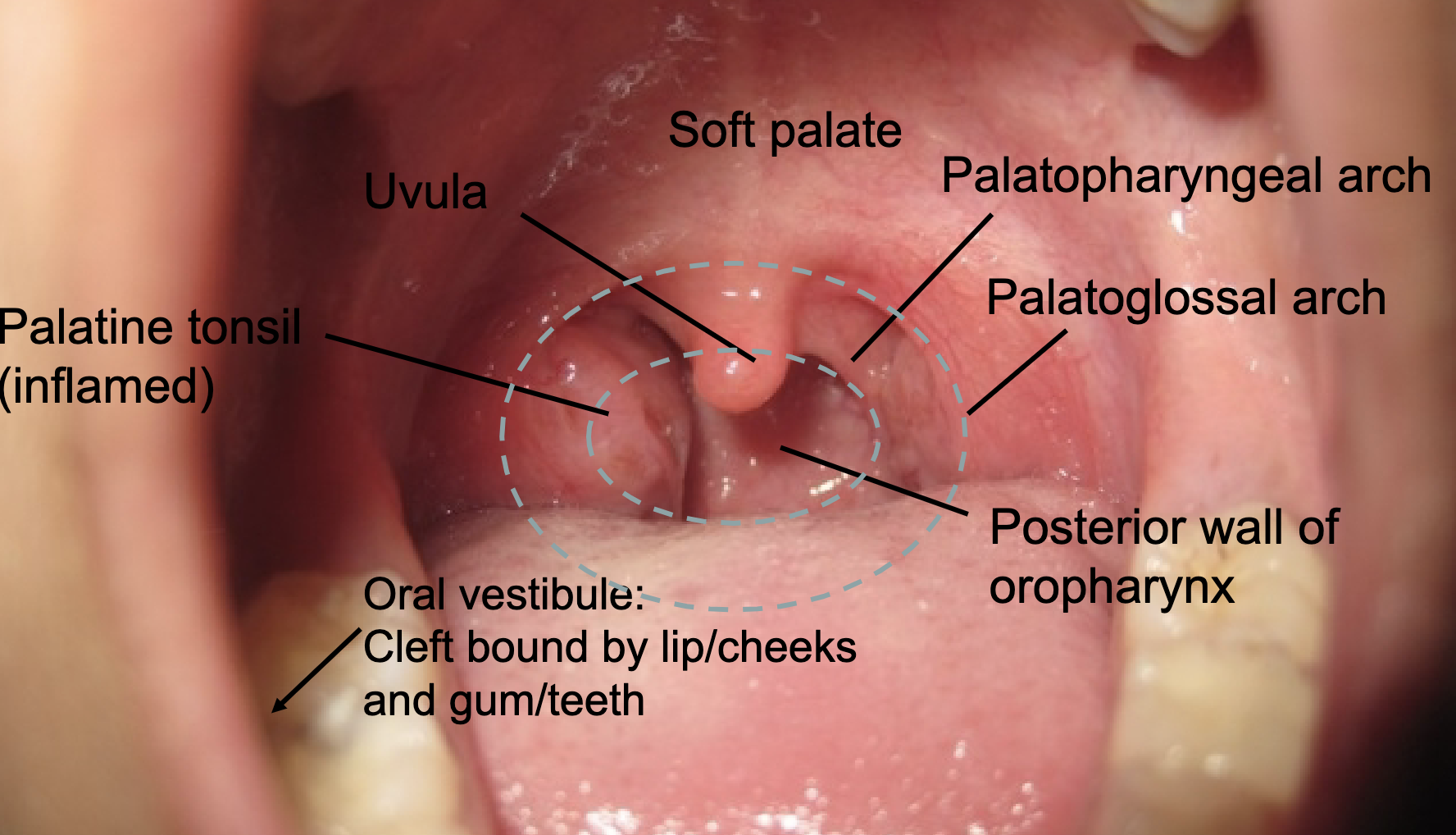
what are the subdivisions of the oral cavity?
oral vestibule
oral cavity proper
fauces
what are the important functions of the oral cavity?
sensory
secretion
mastication
teeth
oral competence
space between teeth and soft palate:
oral cavity proper
what is the gate from the oral cavity proper to the oropharynx?
fauces
what are the boundaries of the fauces:
palatoglossal arch
palatopharyngeal arch
soft palate/uvula
tonsillar fossa w/ palatine tonsils
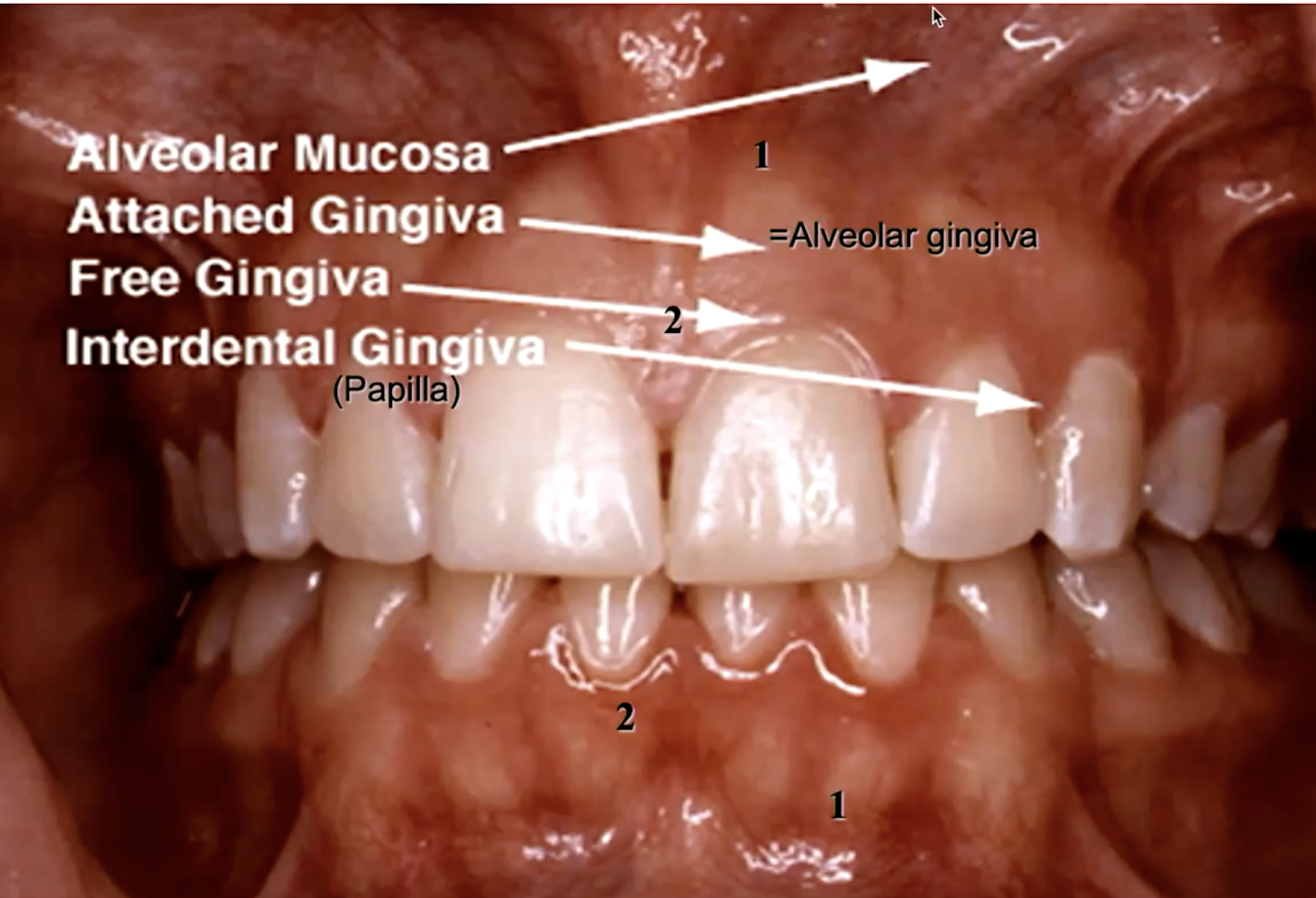
what is #1
mucogingial junction (gingiva and alveolar gingiva separation)
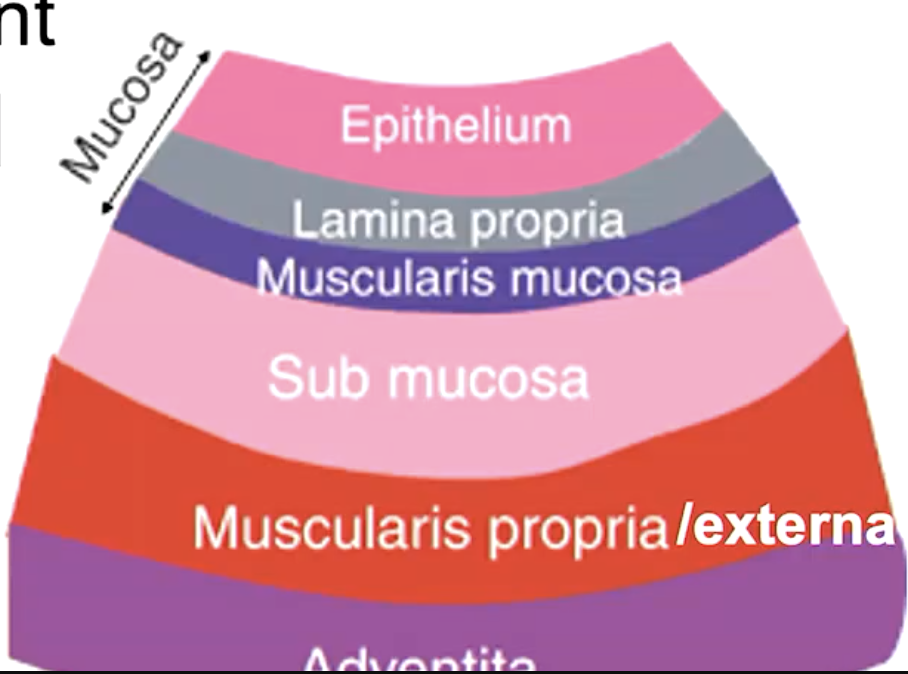
what are the 2 layers of the oral mucosa?
epithelium
lamina propria
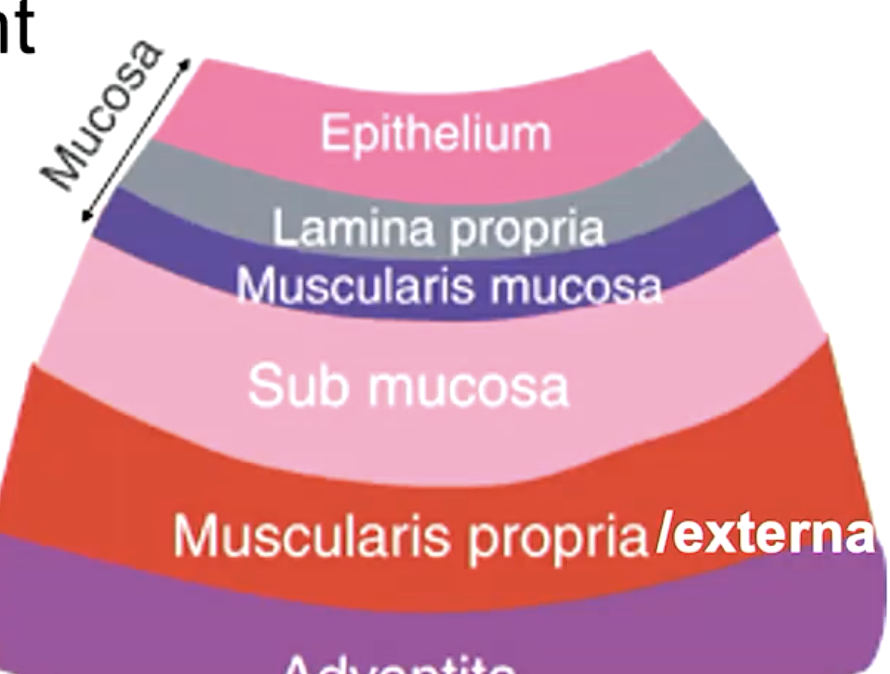
what layer of mucosa is absent in the oral mucosa that is usually present in other mucosa?
muscularis mucosa
what is the CT beneath the mucosa, often w glands?
submucosa (often absent in oral mucosa)
what are the 4 layers of general mucosa?
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
adventitia/serosa
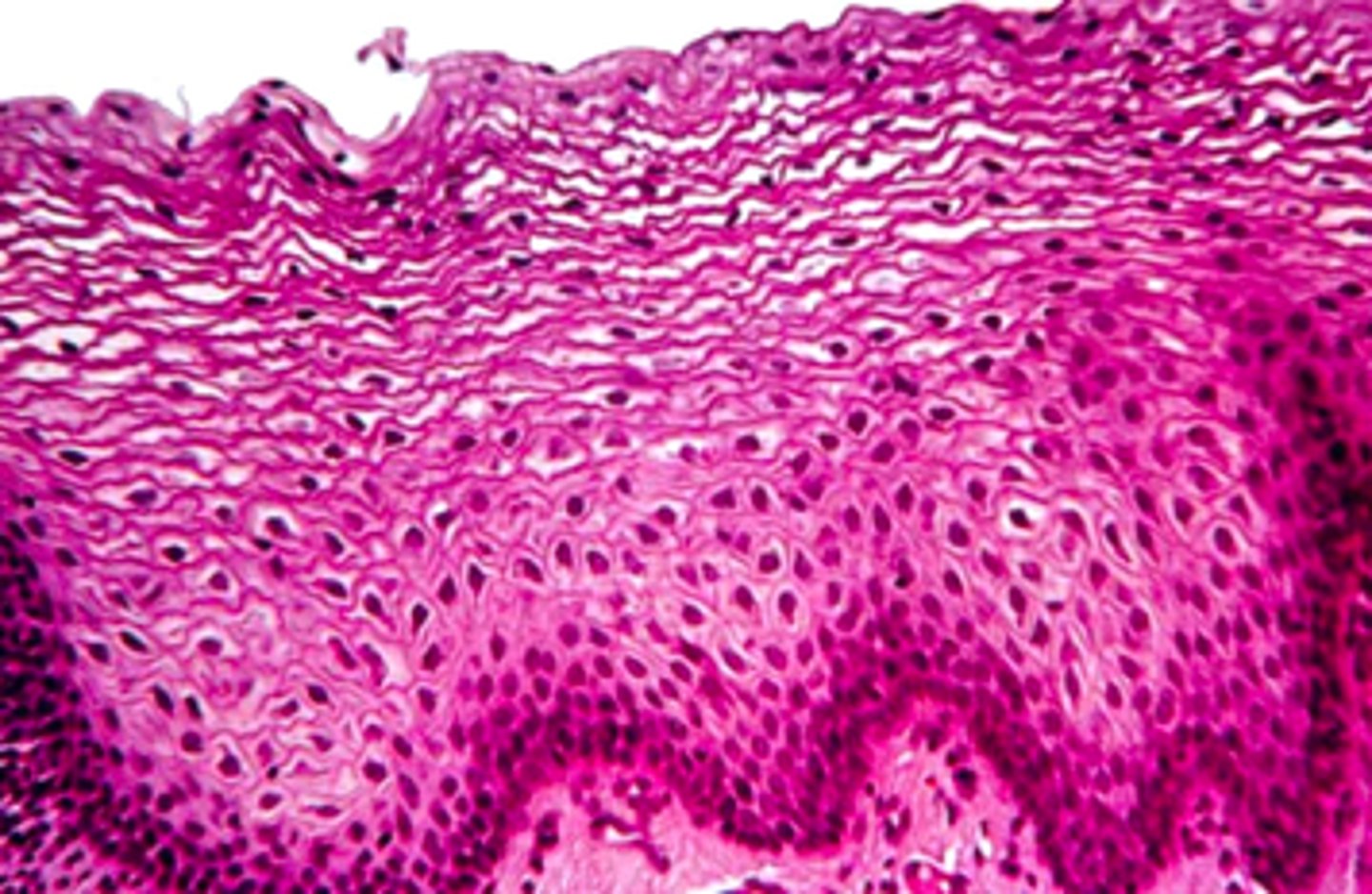
the majority of the oral mucosa is what type of epithelium?
stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
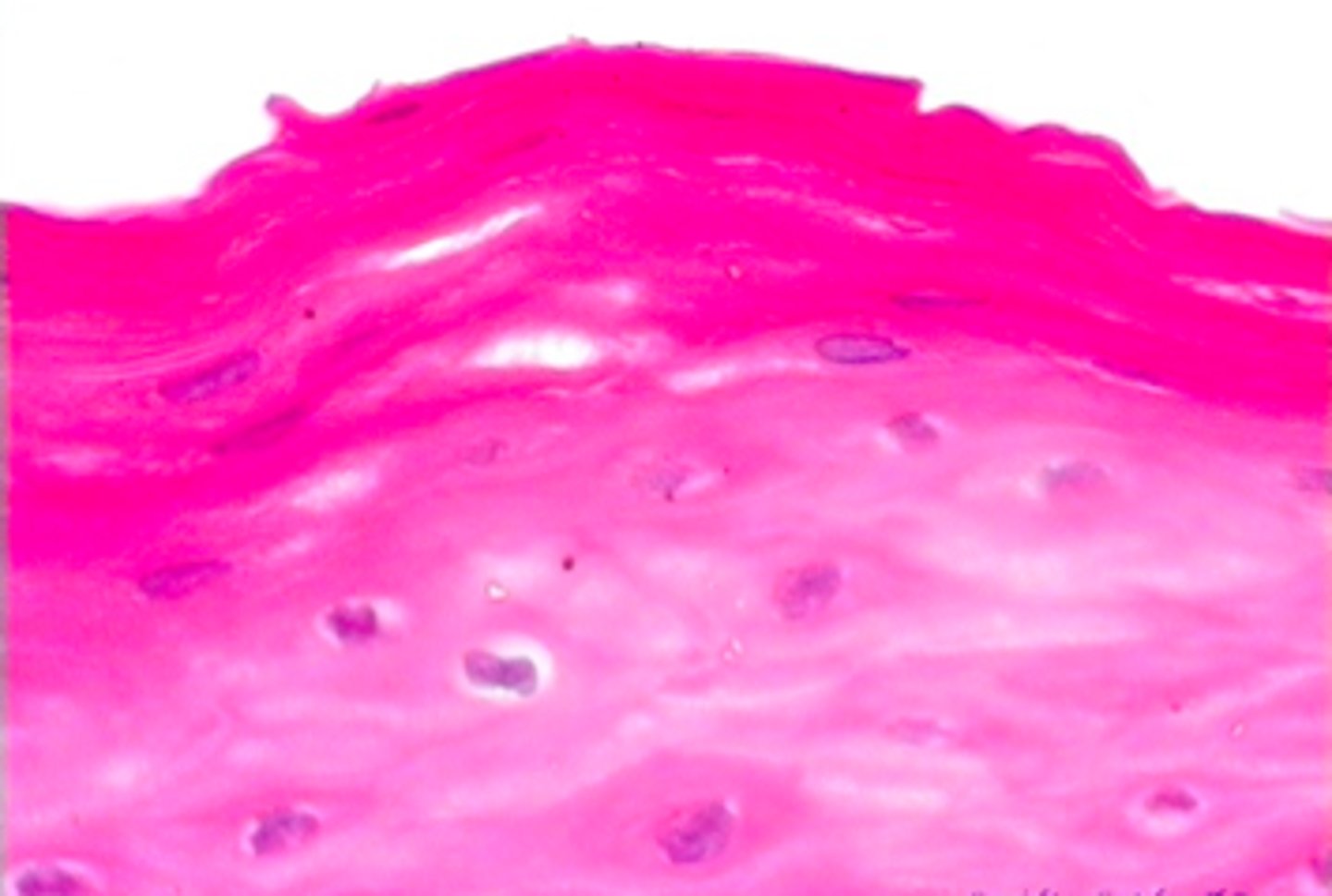
identify the mucosa:
stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
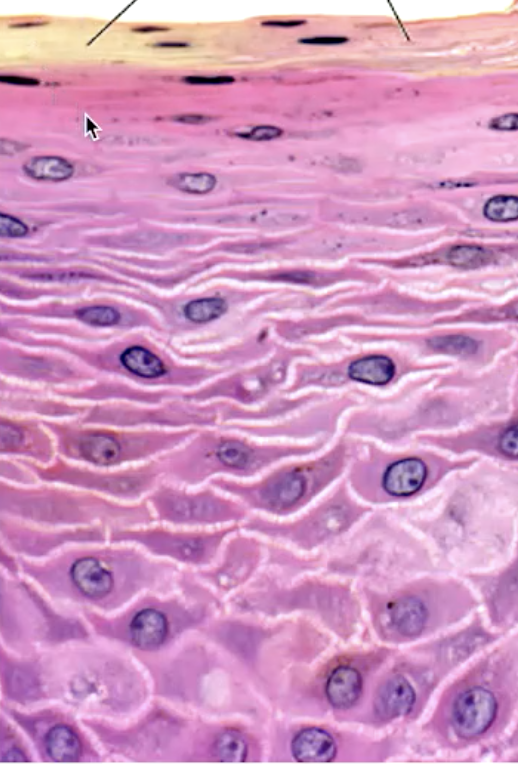
identify the mucosa:
stratified squamous parakeratinized epithelium
identify the mucosa:
stratified squamous parakeratinized epithelium (SSKE)
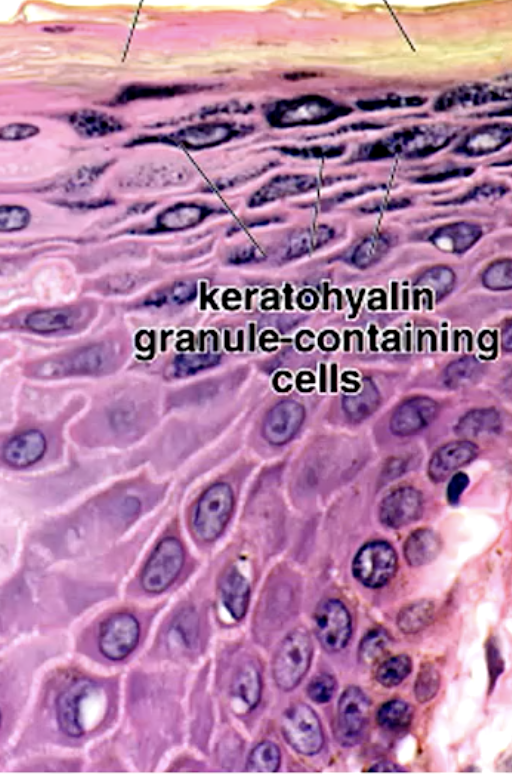
identify the mucosa:
stratified squamous keratinized epithelium (SSKE)
the difference between keratinized and parakeratinized epithelium is the presence of ________ in the stratum corneum
nuclei
functional difference between SSNKE and SSKE
SSNKE = keep surface moist
SSKE = waterproof, dry surface
the vermilion border of lip has what type of epithelium?
stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
lining oral mucosa has what type of epithelium?
stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
masticatory mucosa (gingiva and hard palate) has what type of epithelium?
SSKE, SSPKE
vermilion border of lip what type of epithelium?
keratinized SSKE, SSPKE
the dorsum of the tongue has what type of mucosa?
specialized mucosa
the hard palate has what type of mucosa?
masticatory mucosa
the gingiva has what type of mucosa?
masticatory mucosa
the lips have what type of mucosa?
lining mucosa
the cheeks have what type of mucosa?
lining mucosa
the vestibule have what type of mucosa?
lining mucosa
the alveolar mucosa have what type of mucosa?
lining mucosa
the floor of the mouth has what type of mucosa?
lining mucosa
the soft palate has what type of mucosa?
lining mucosa
the inferior surface of the tongue has what type of mucosa?
lining mucosa
identify the mucosa:
labial mucosa
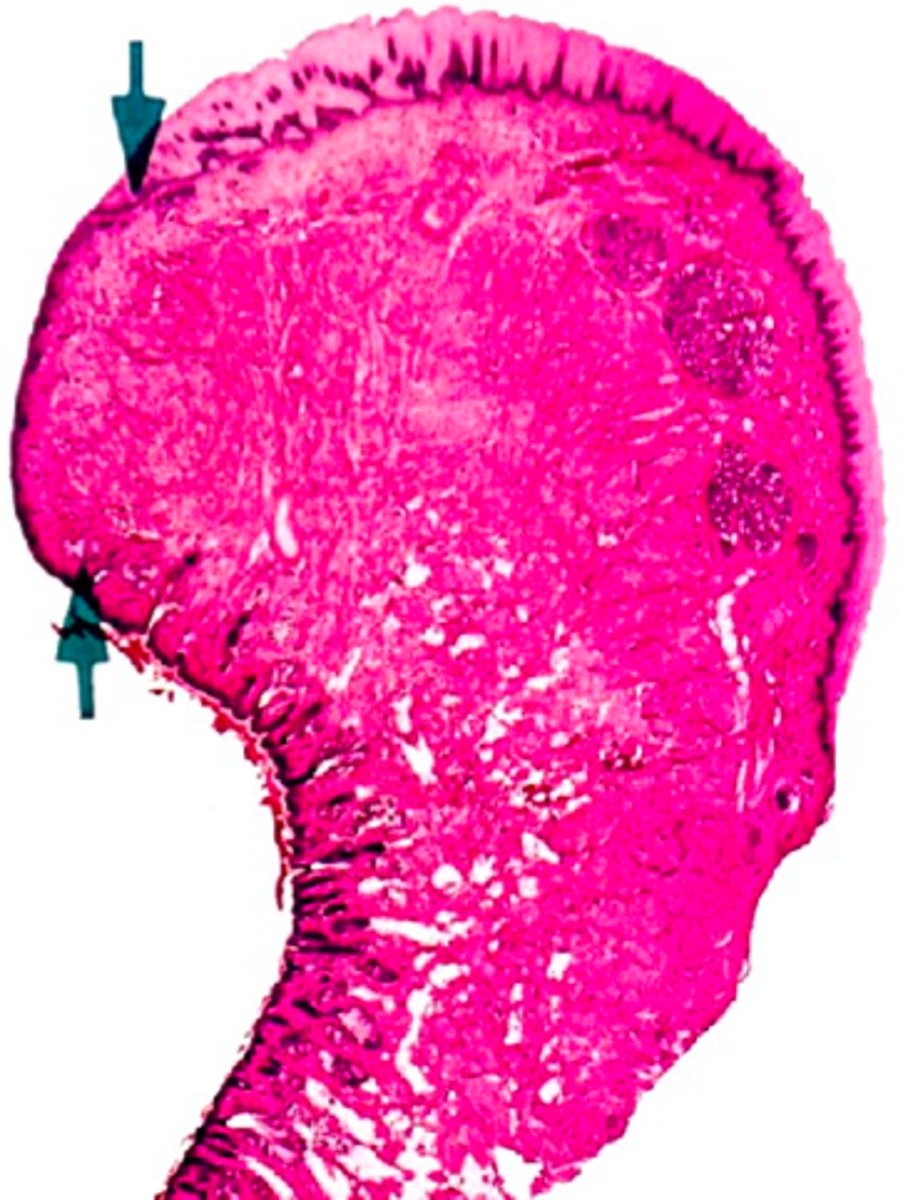
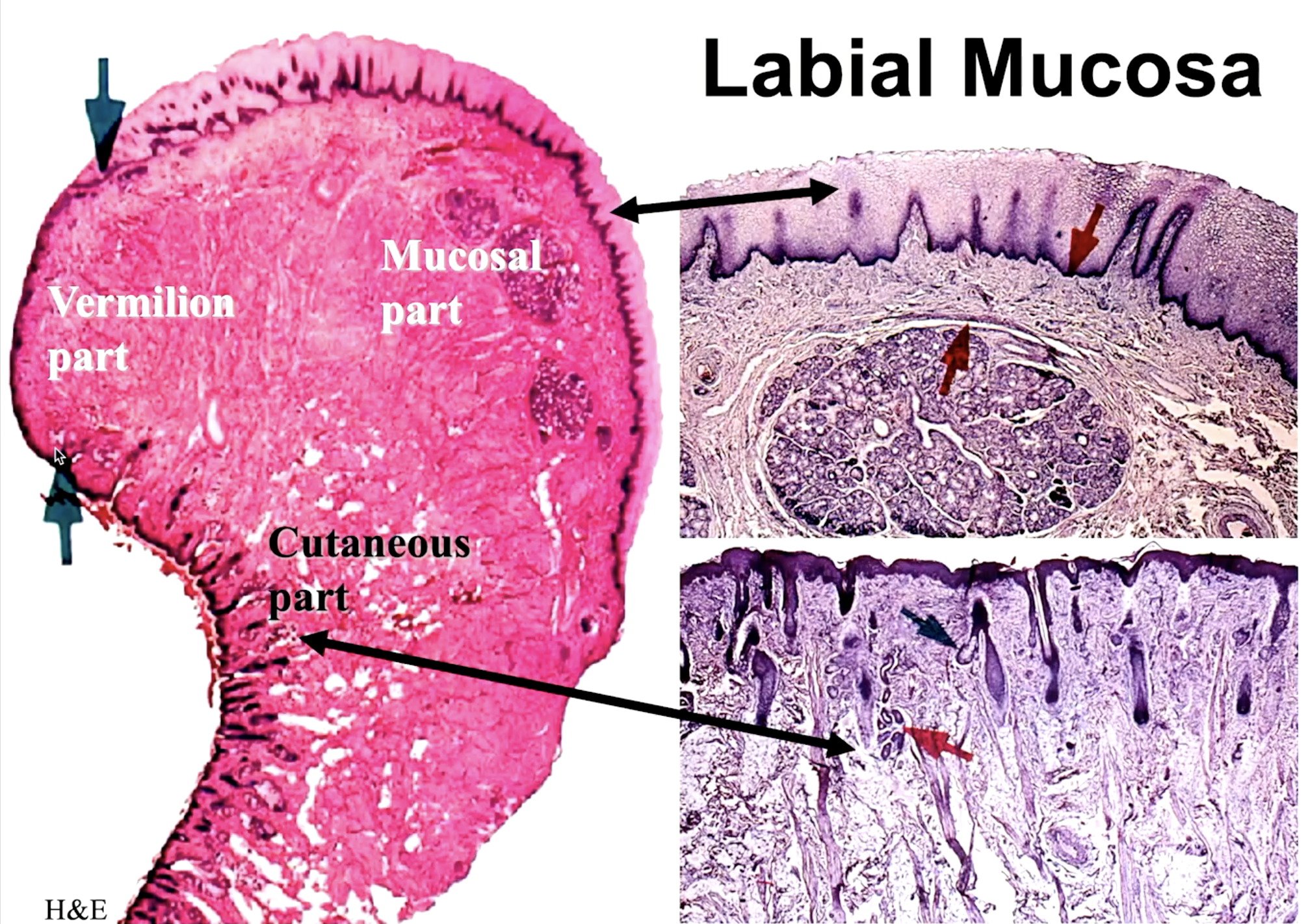
the transitional part between the skin and mucosa part of the lips:
vermillion
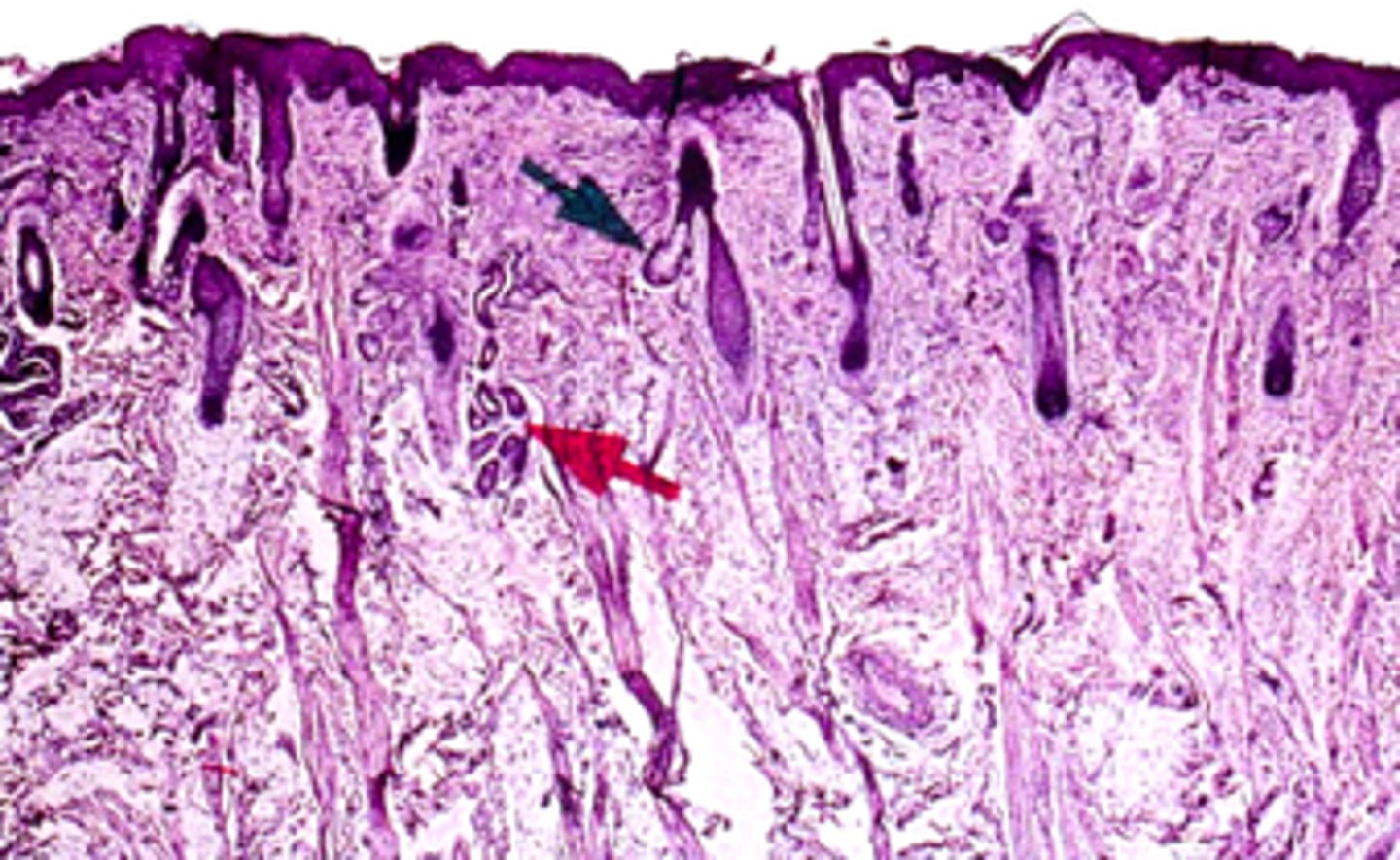
what part of the labial mucosa is this:
cutaneous
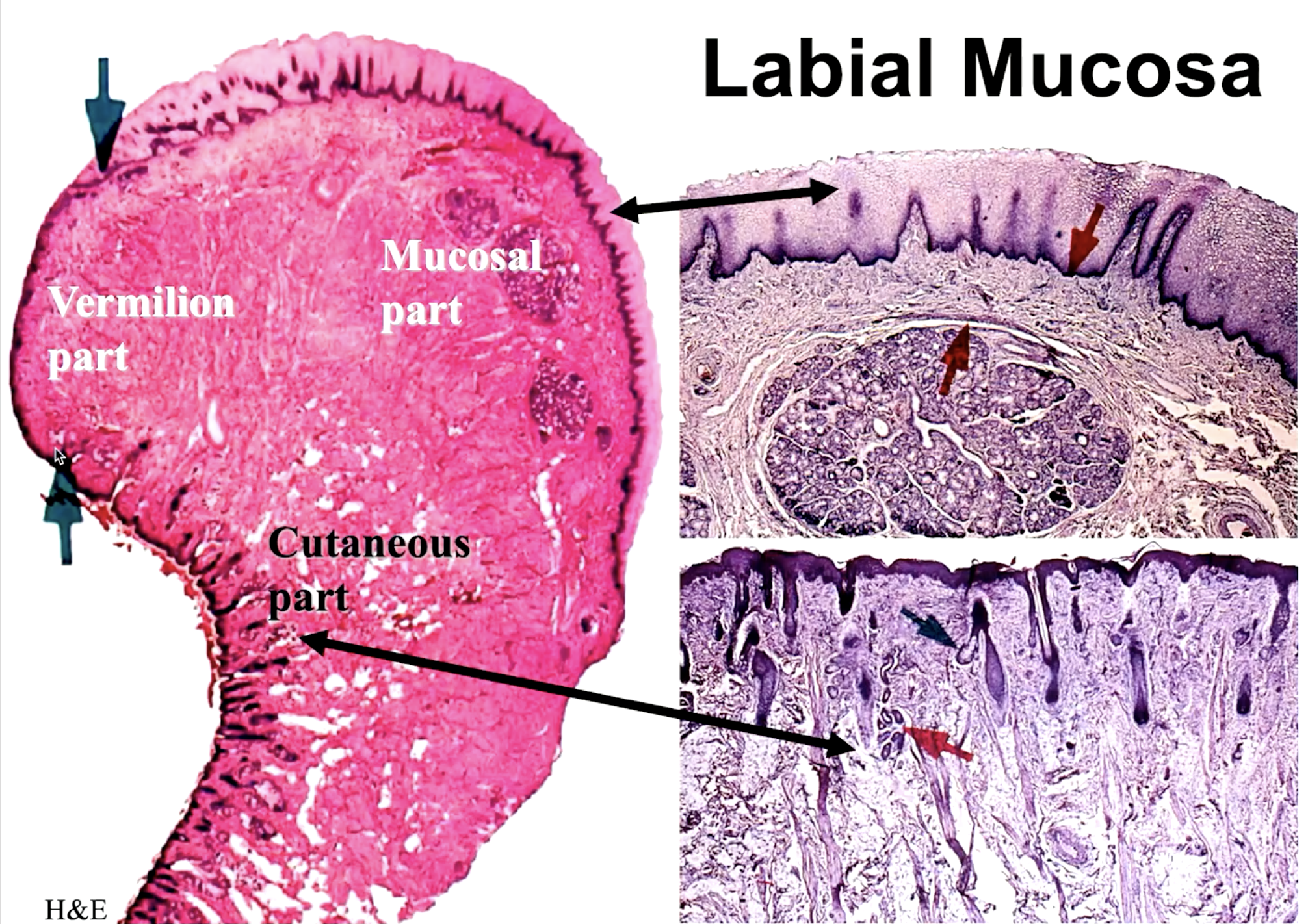
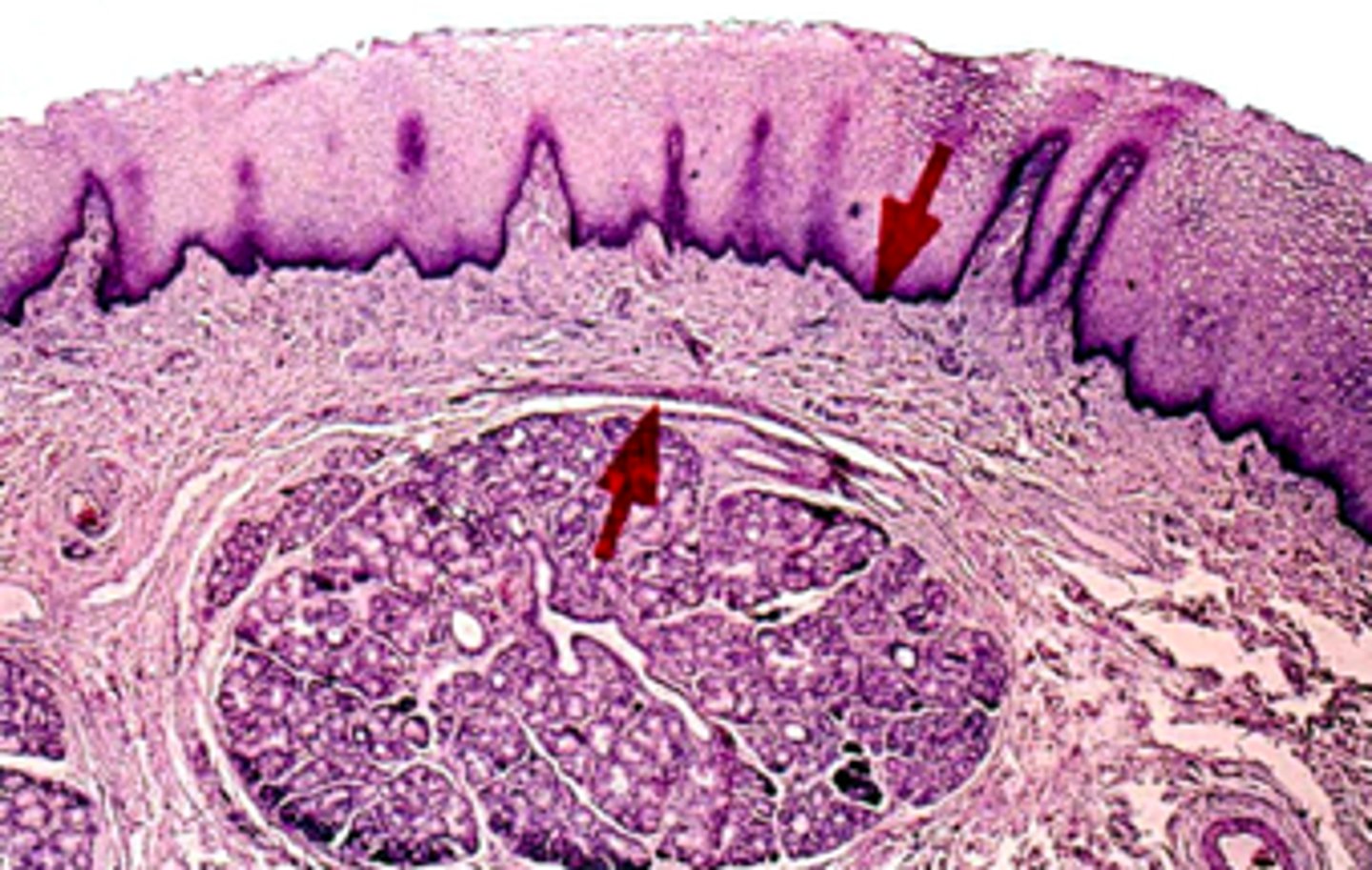
what part of the labial mucosa is this:
mucosal
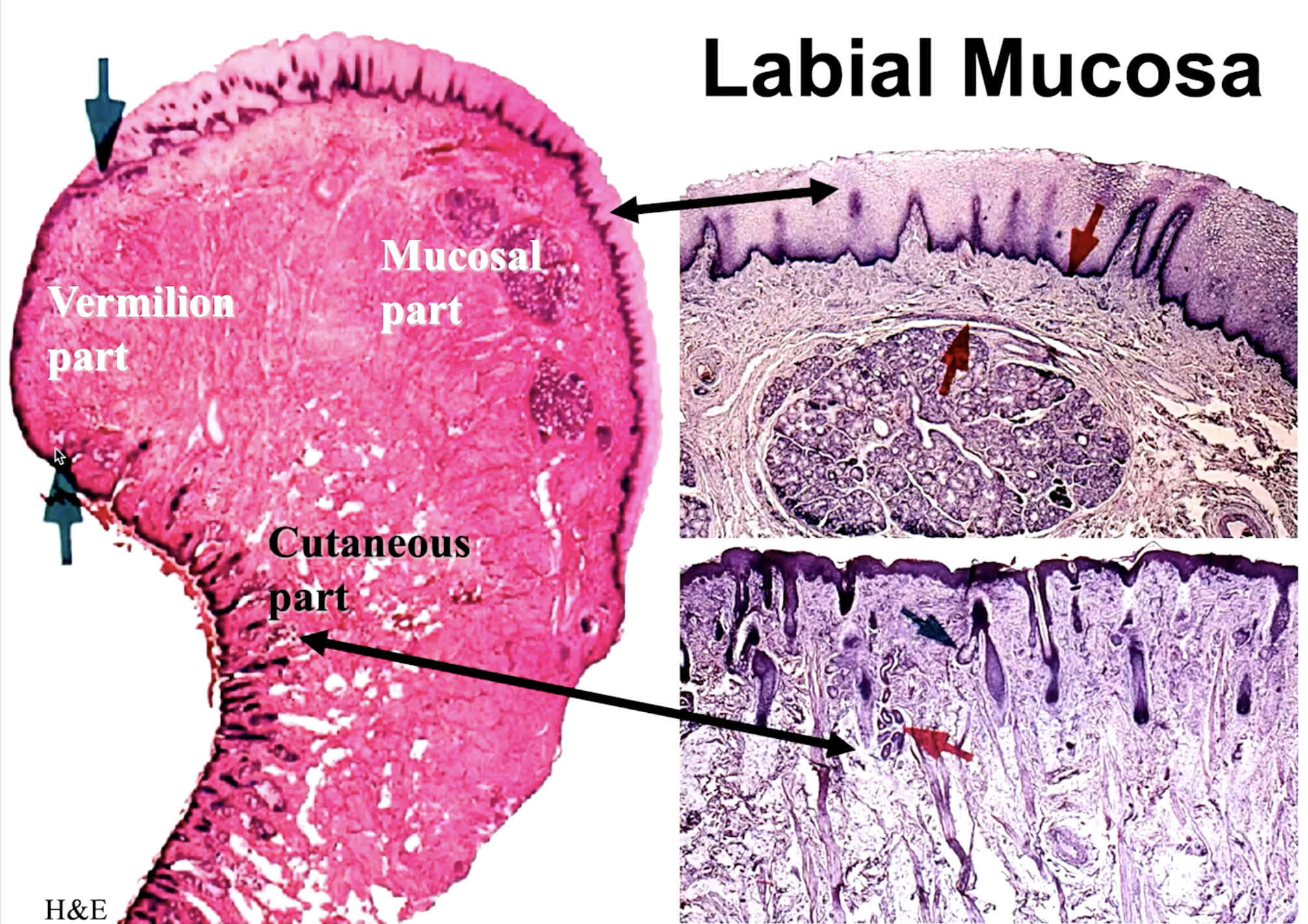
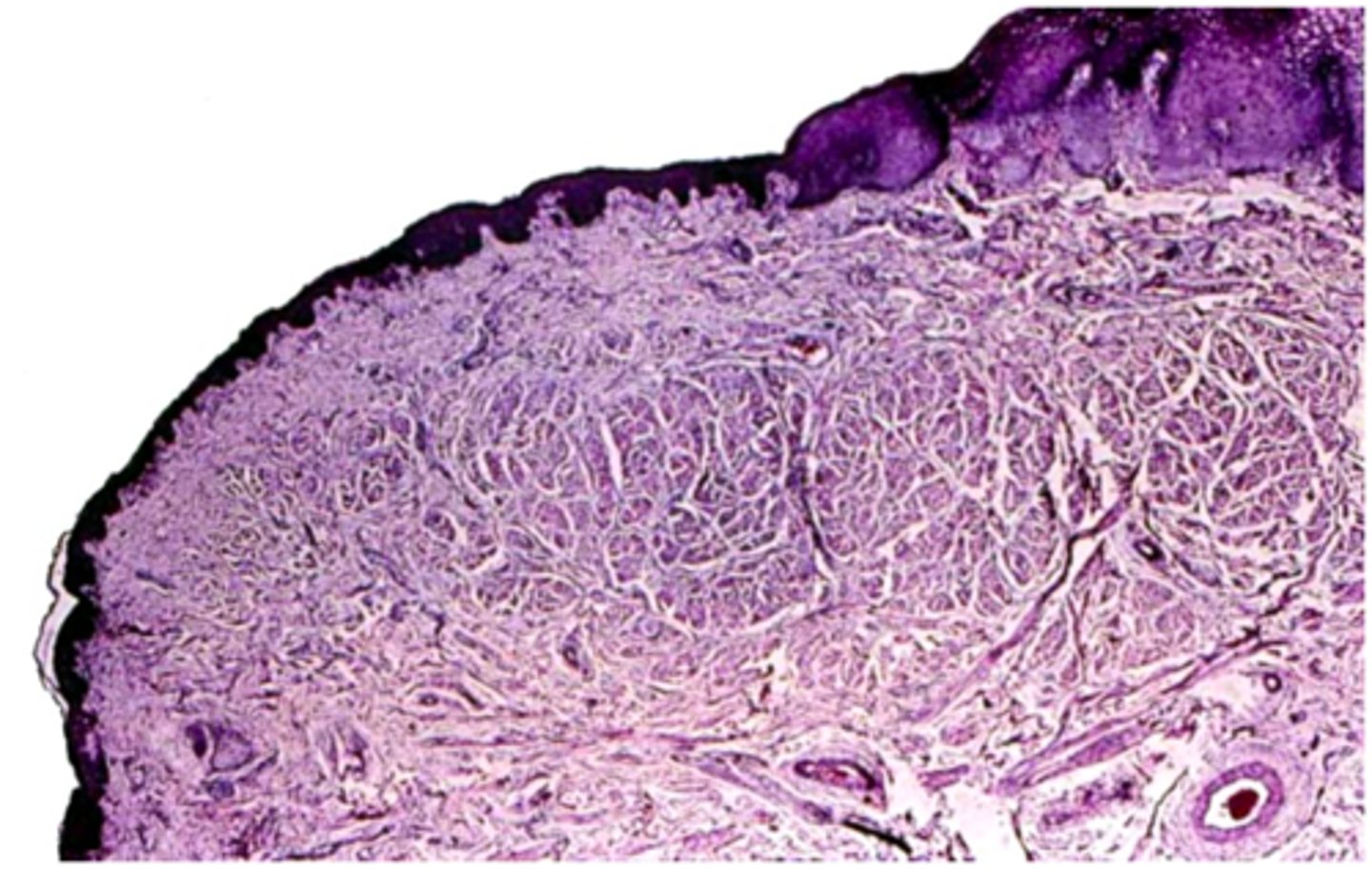
what part of the labial mucosa is this:
vermillion
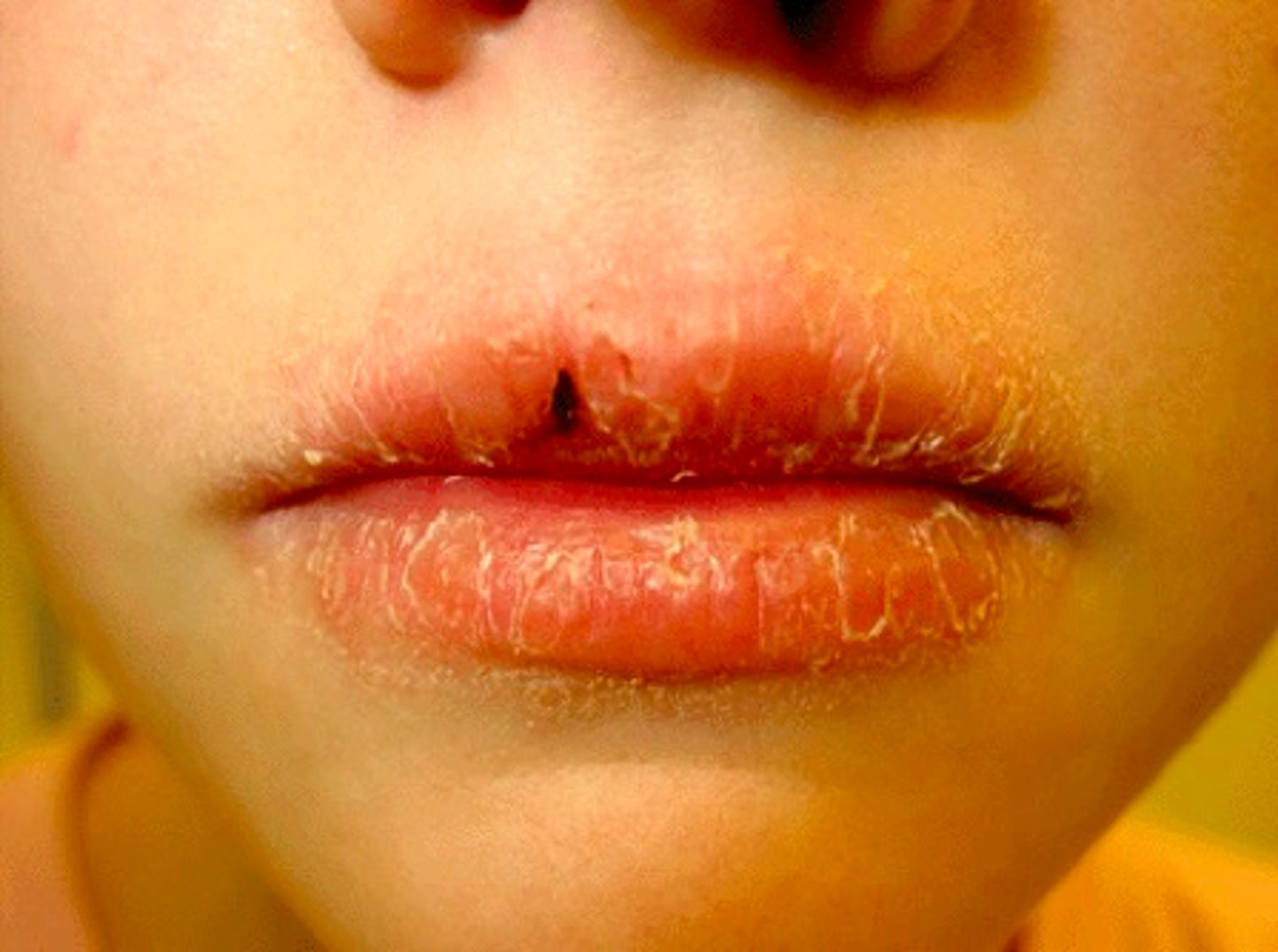
patient presents with the following. They claim that they just tried new lip balm. Only the cutaneous and vermillion part of the are effected. What is the diagnosis?
cheilitis
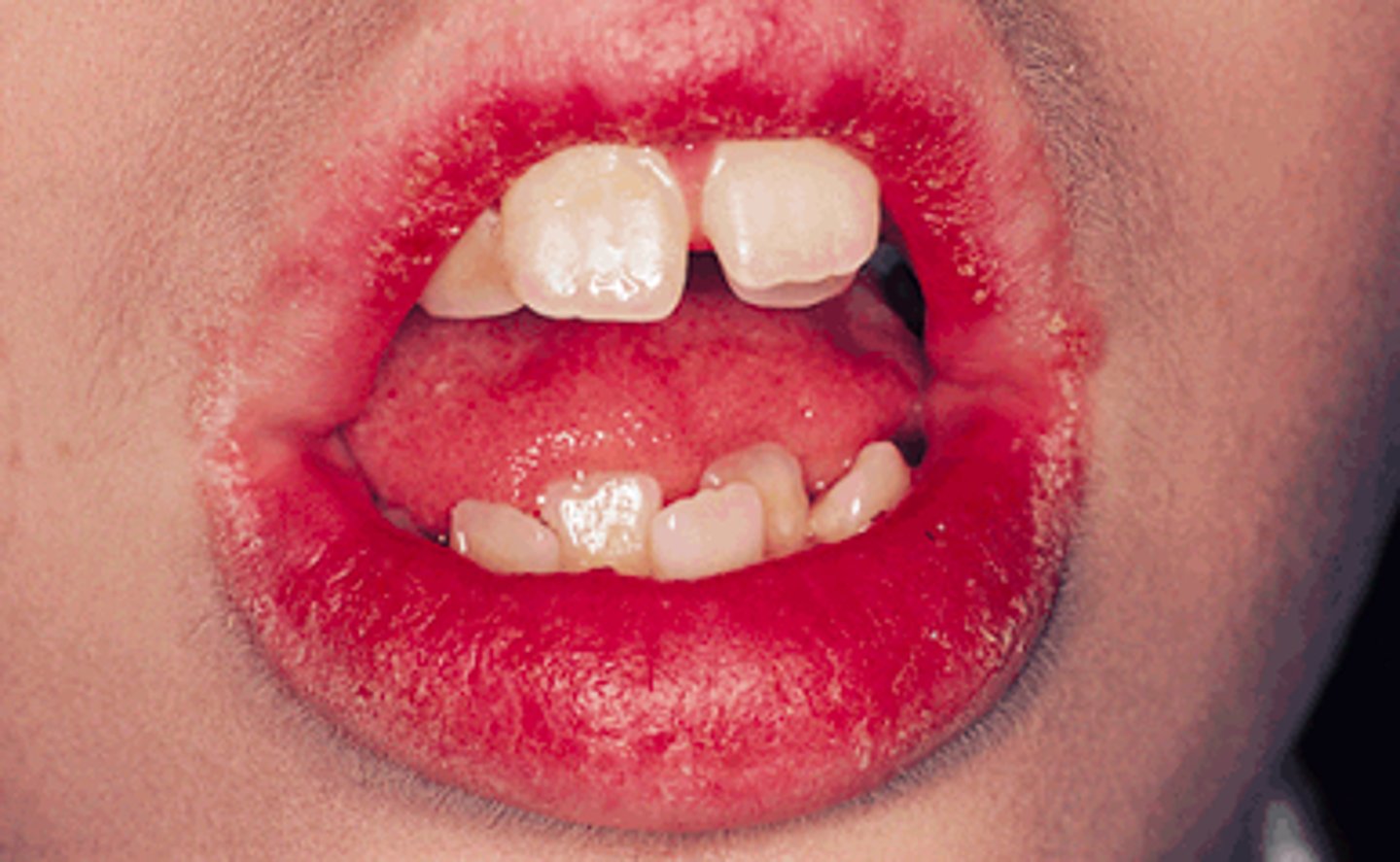
patient presents with the following. They also present with other nutritional deficits. Only the mucosal part of the are effected. What is the diagnosis?
cheilosis
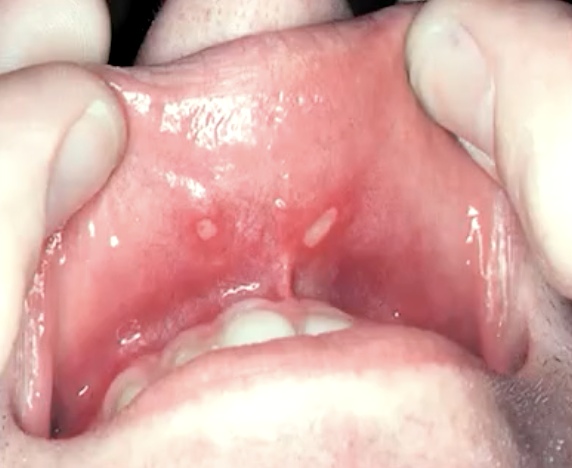
canker sores (most commone ulceration of oral mucosa/cavity)
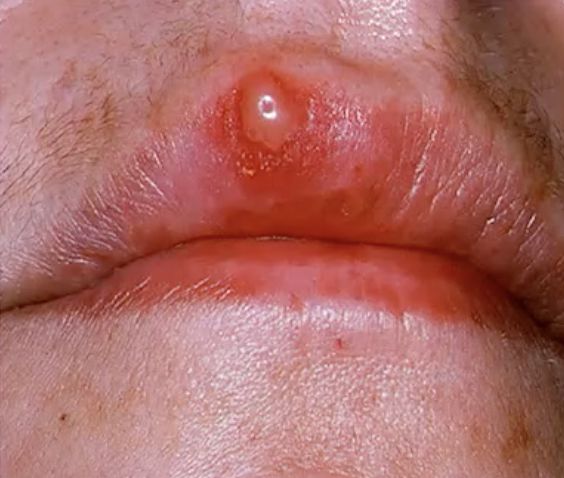
cold sore (caused by herpes simplex virus)
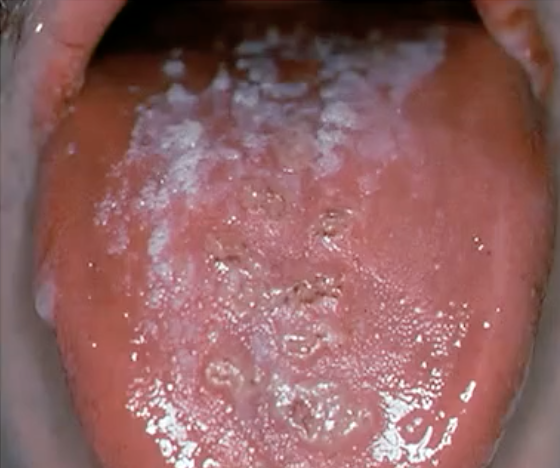
thrush (fungal infection)
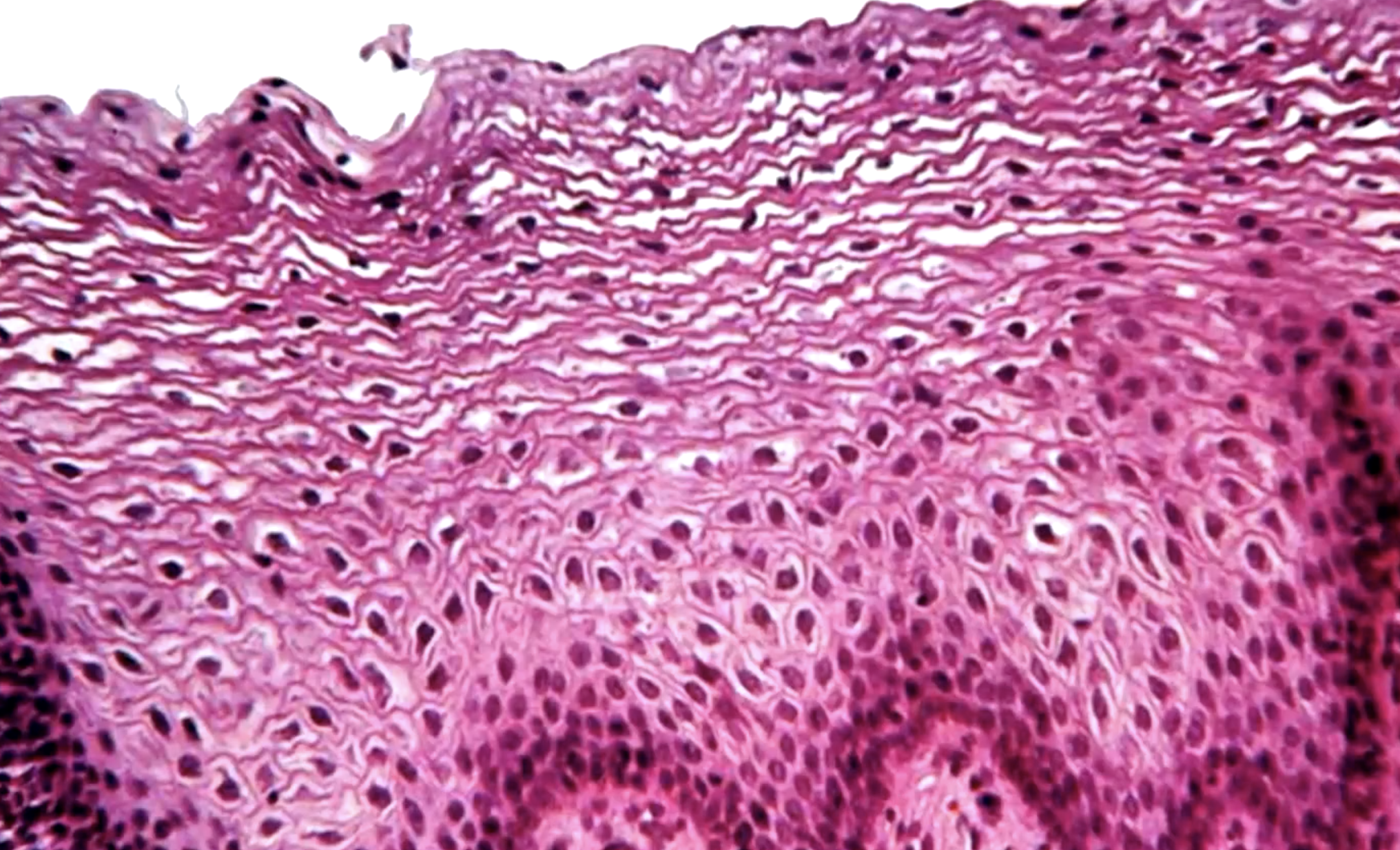
buccal mucosa
identify the mucosa:
buccal mucosa
Sebaceous glands in oral mucosa:
Fordyce spots
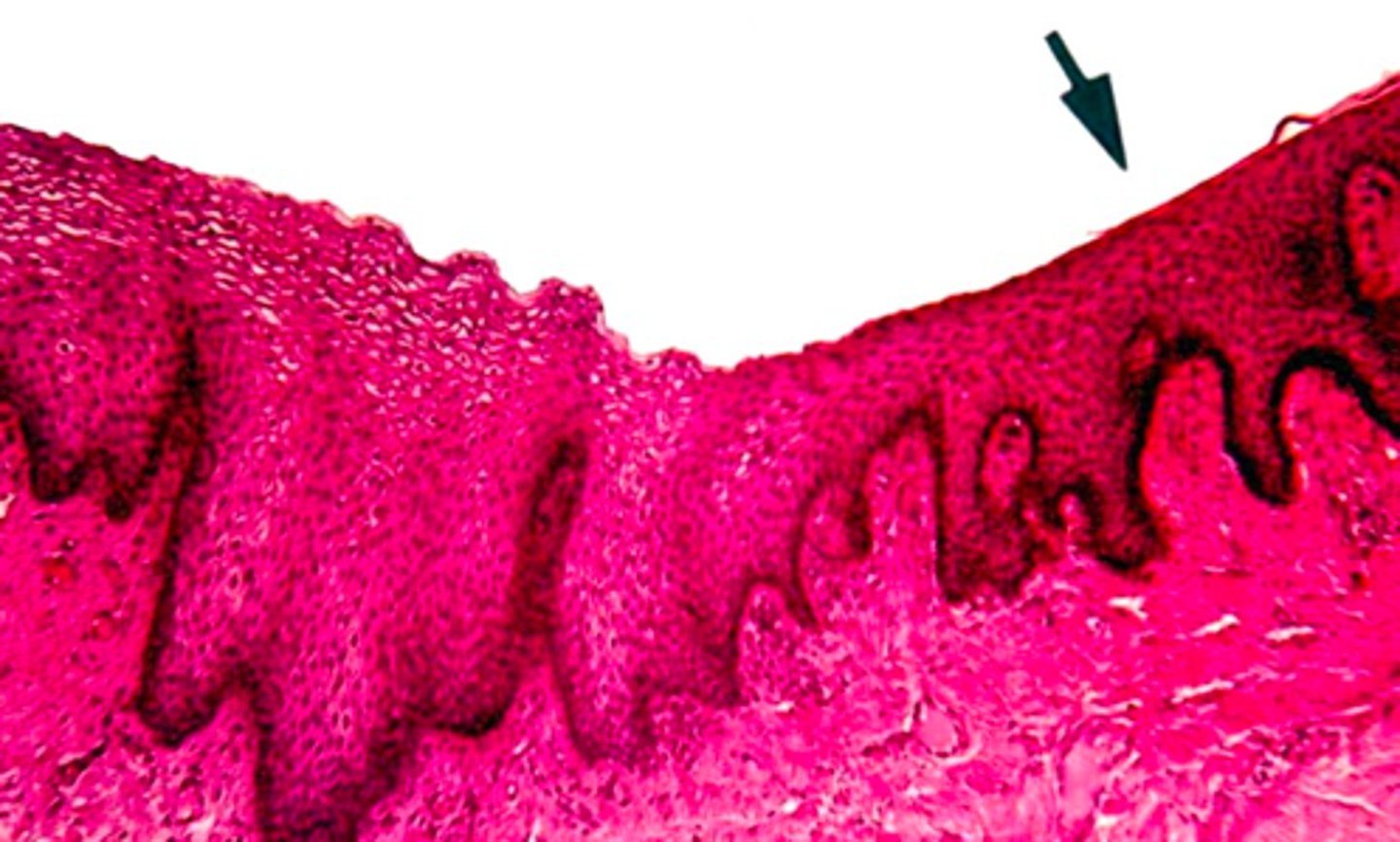
identify the mucosa:
alveolar mucosa
injections for anesthesia painful in gingiva or areas of mucoperiosteum due to the lack of _______
submucosa
what mucosa separates alveolar mucosa and gingiva?
mucogingival mucosa
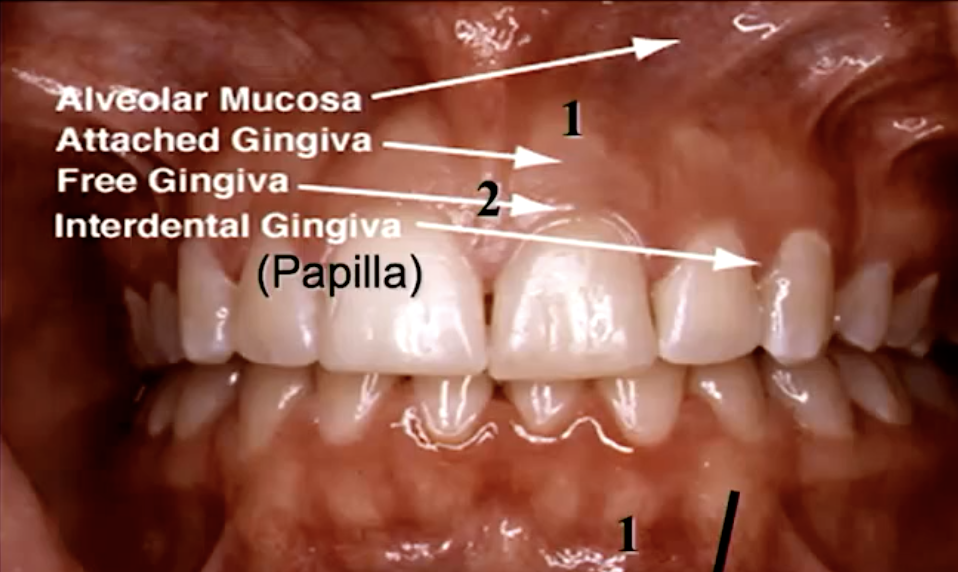
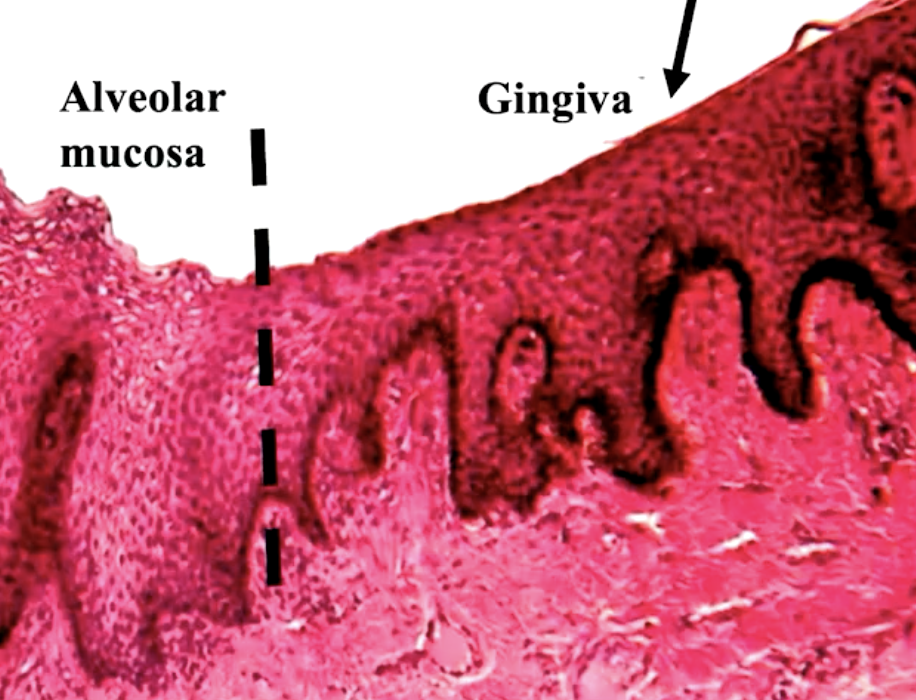
what accounts for the color change betwen alveolar mucosa and attached gingiva?
alveolar mucosa has SSNKE epithelial cells while gingiva has SSKE/SSPKE and a layer of connective tissue (harder to see through the keratonized layer into the blood vessels)
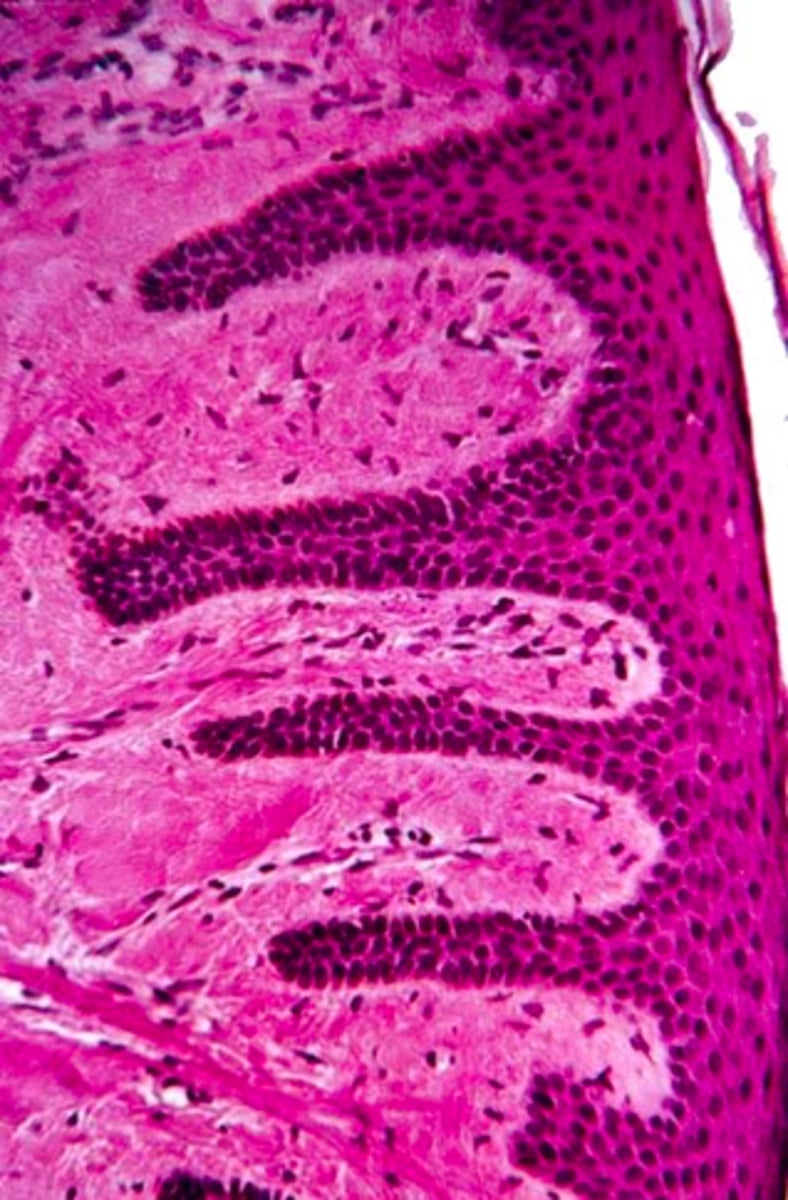
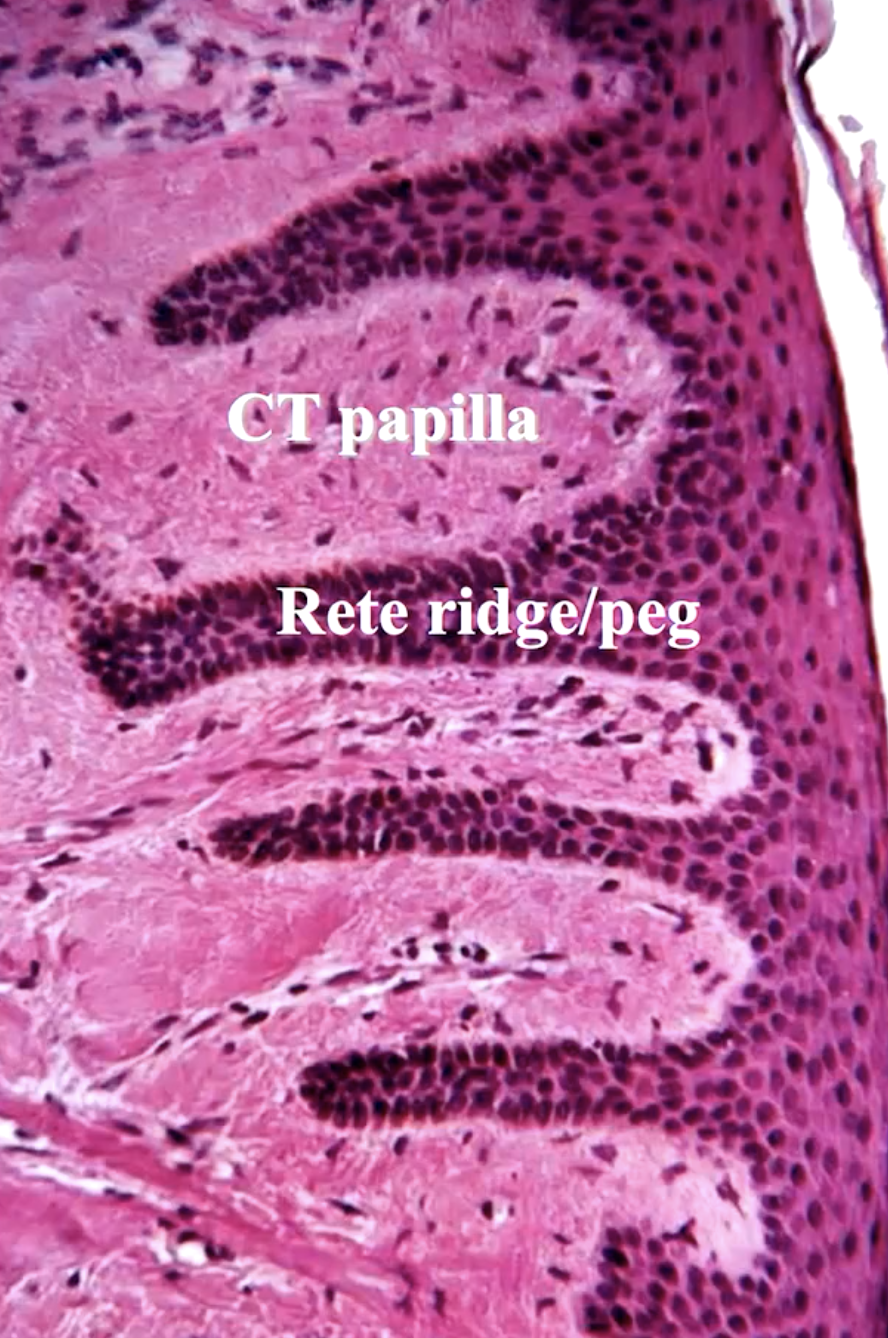
identify the projections:
rete pegs and CT papilla (increases friction to withstand pressures from mastication)
the gingiva covering alveolar bone has _________ over the surface and has a rough, orange peel-like texture
stippling
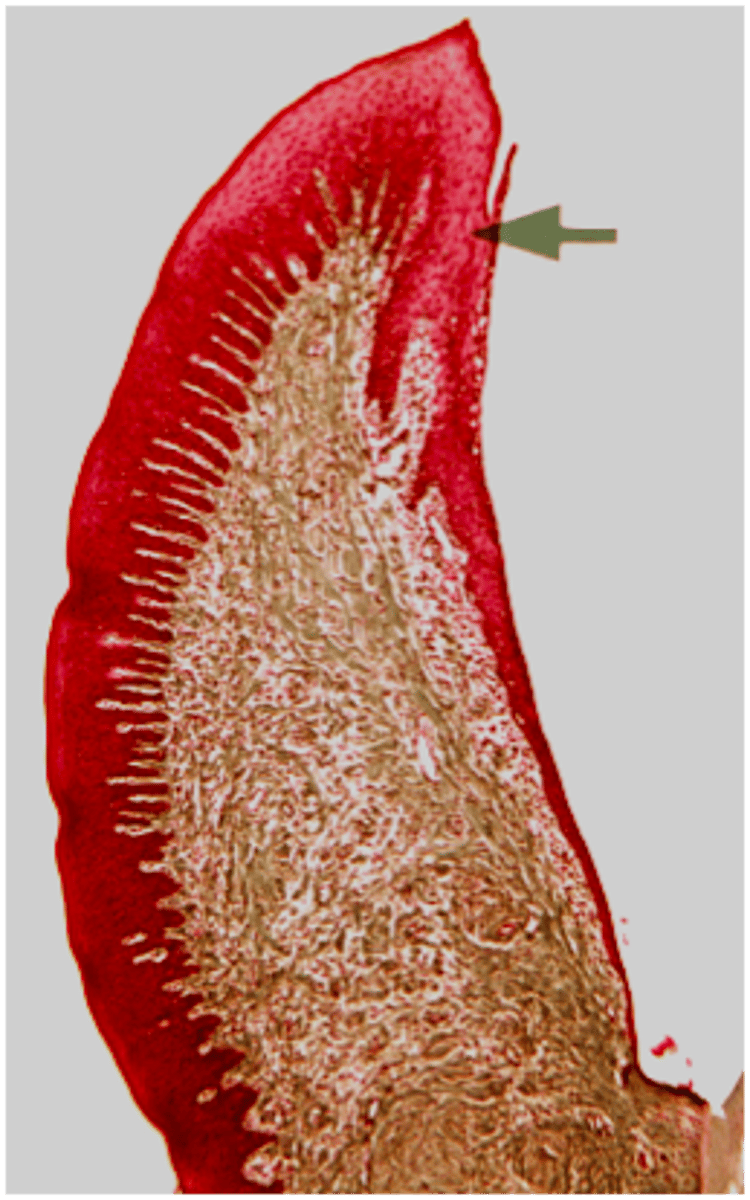
identify the mucosa
sulcular epithelium
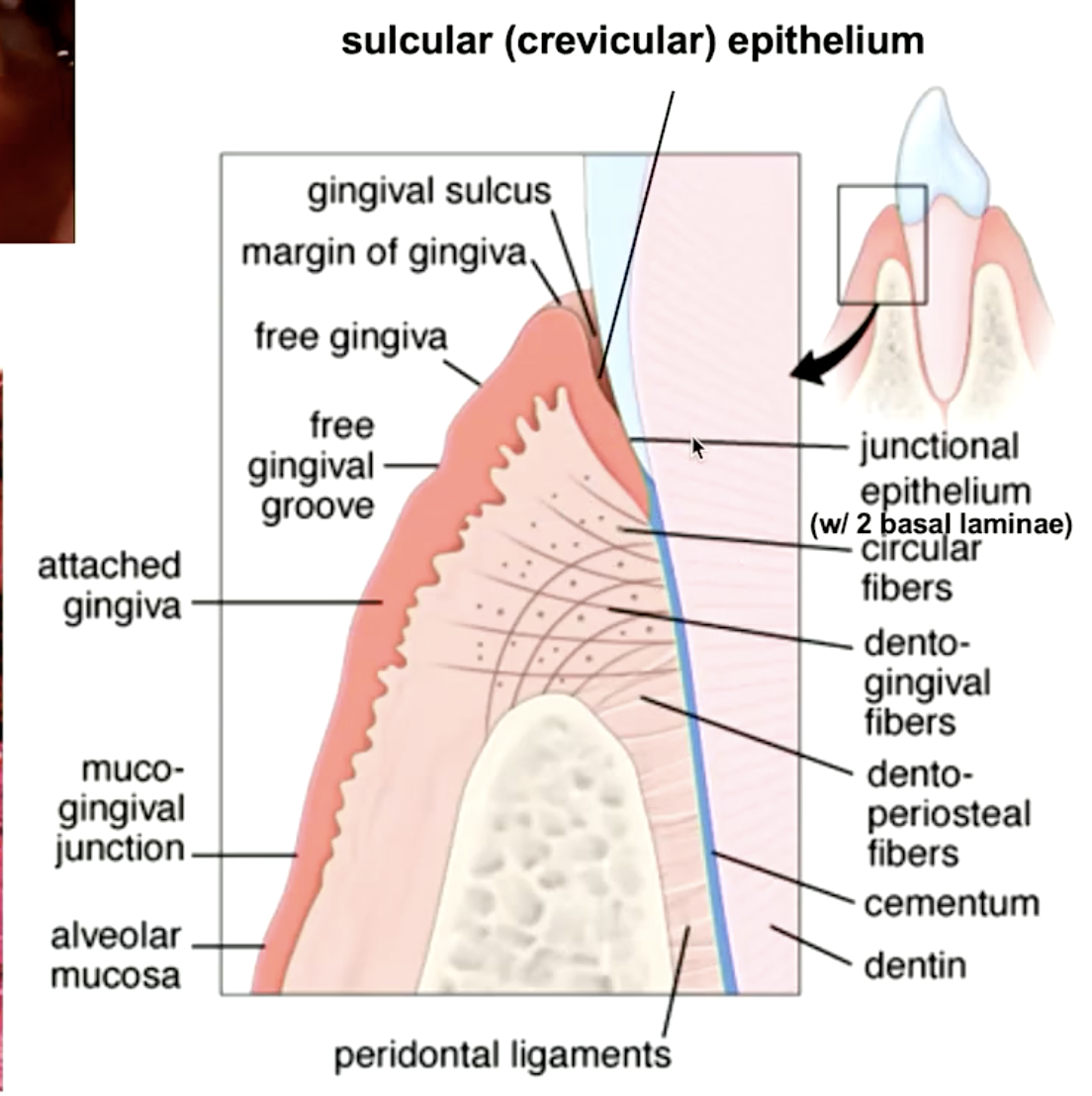
epithelial lining of the gingival sulcus:
sulcular epithelium
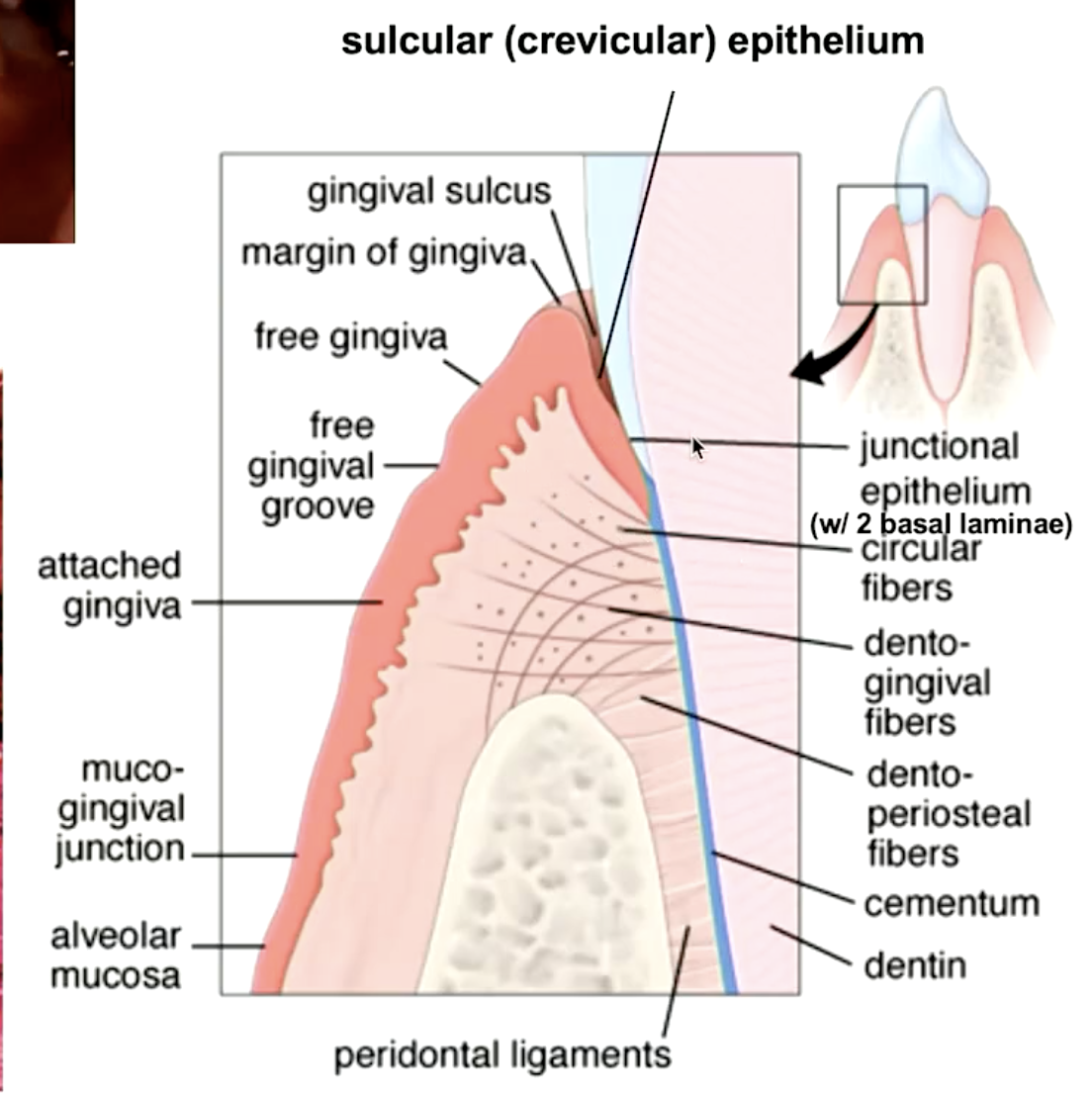
gingiva that attaches to the alveolar bone:
attached gingiva
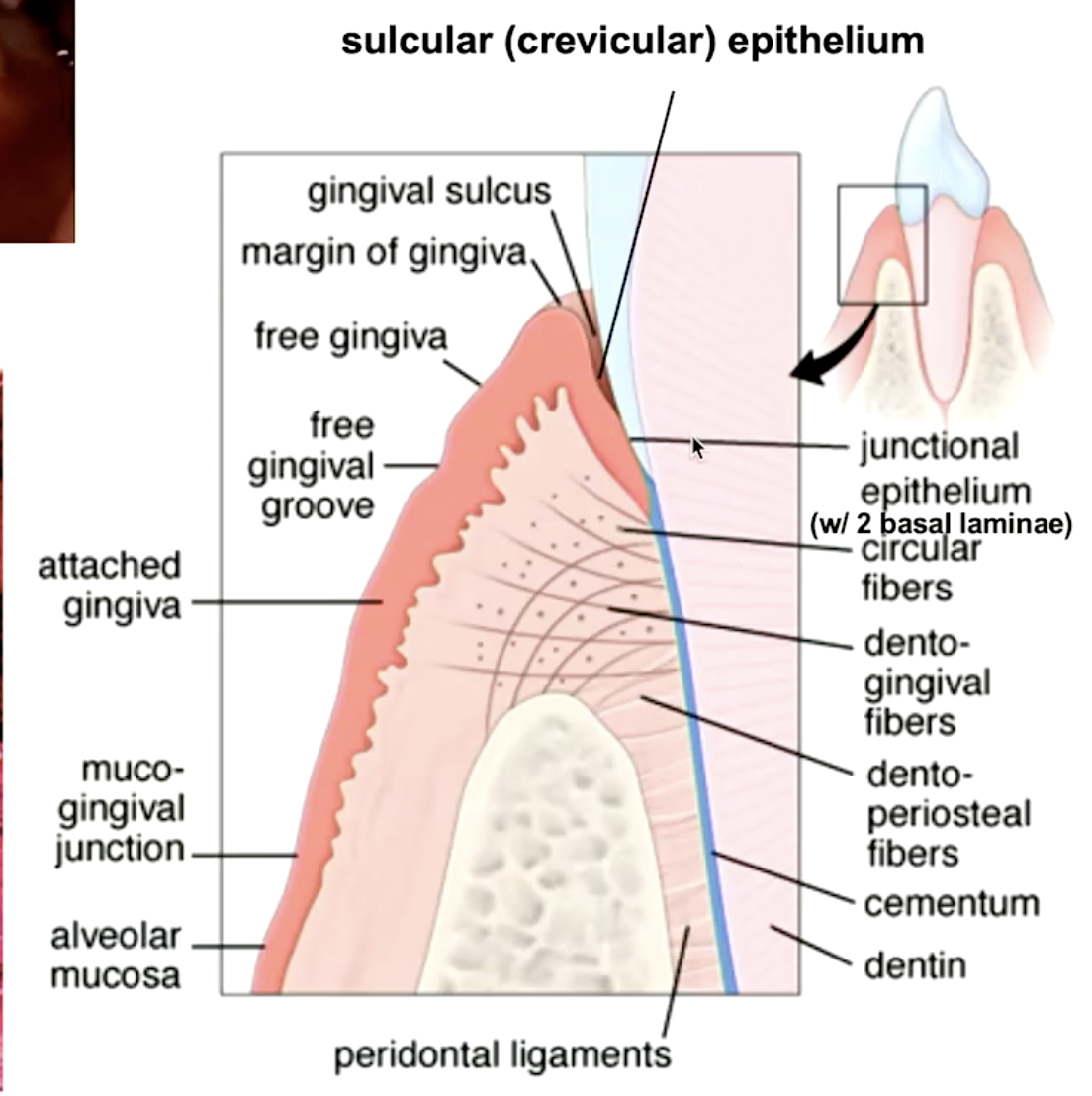
gingival epithelia that attaches to the tooth:
junctional epithelia
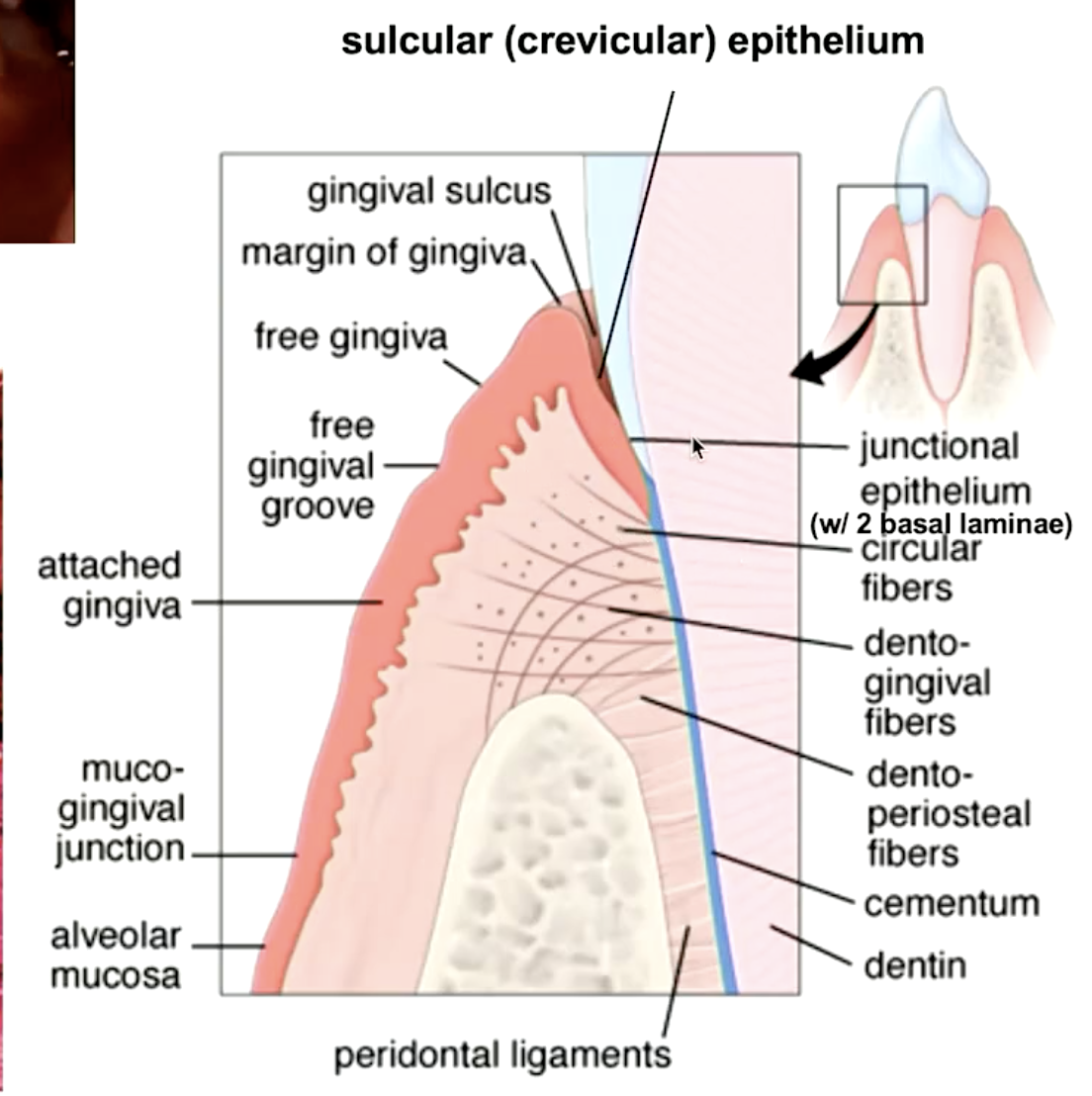
which gingival epithelium has two basal laminae?
junctional epithelia
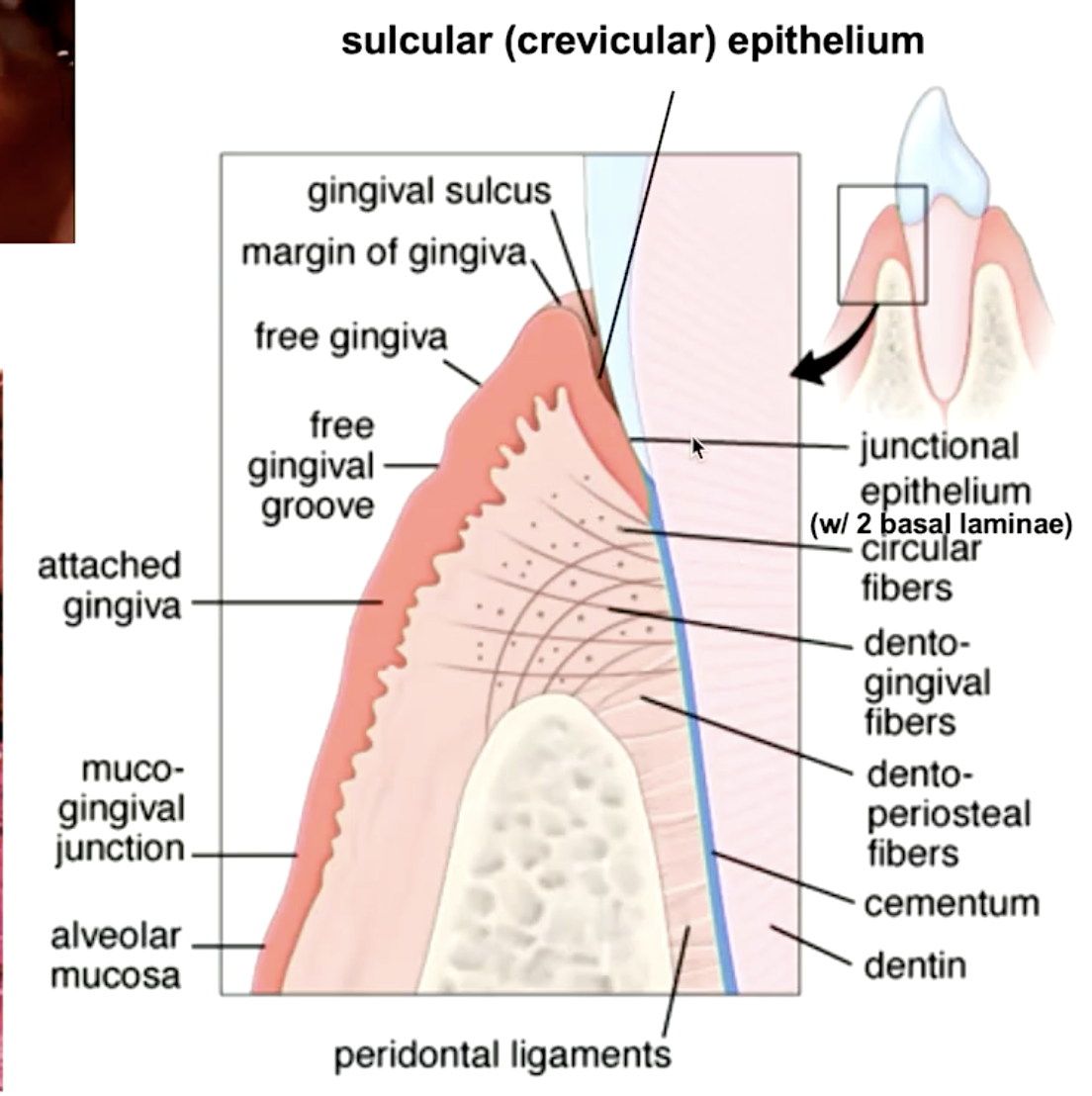
what type of epithelium is junctional epithelia?
stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
what type of epithelium is sulcular epithelia?
stratified squamous parakeratinized epithelium
what is in the anterior region of the hard palate?
fat pad (cushion for food)
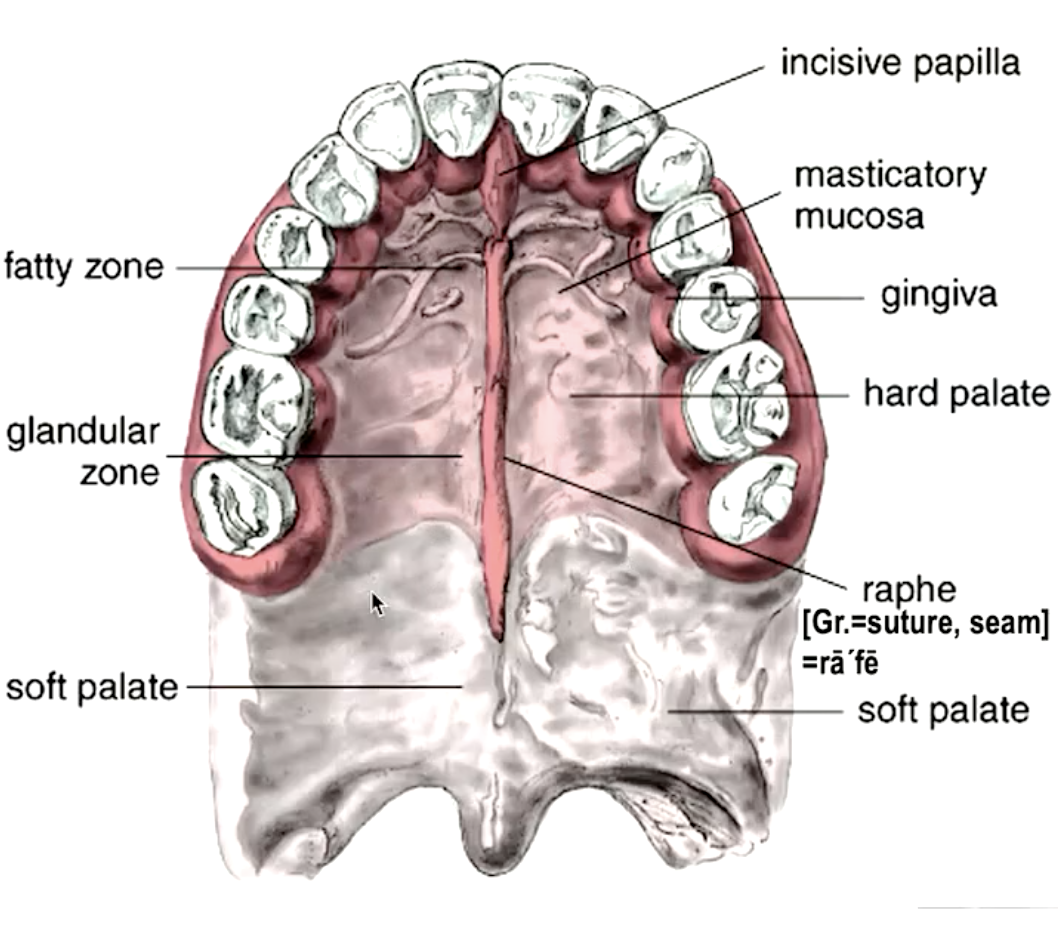
what is in the posterior region of the hard palate?
salivary glands
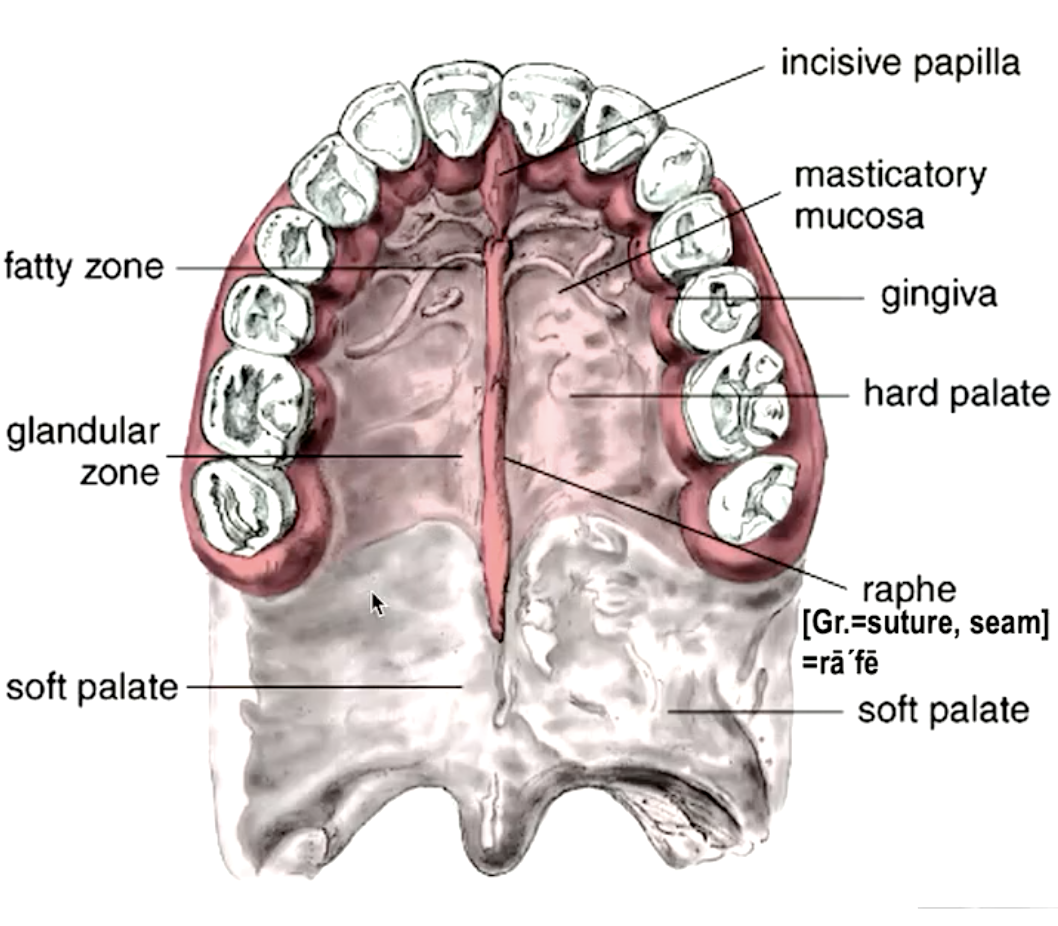
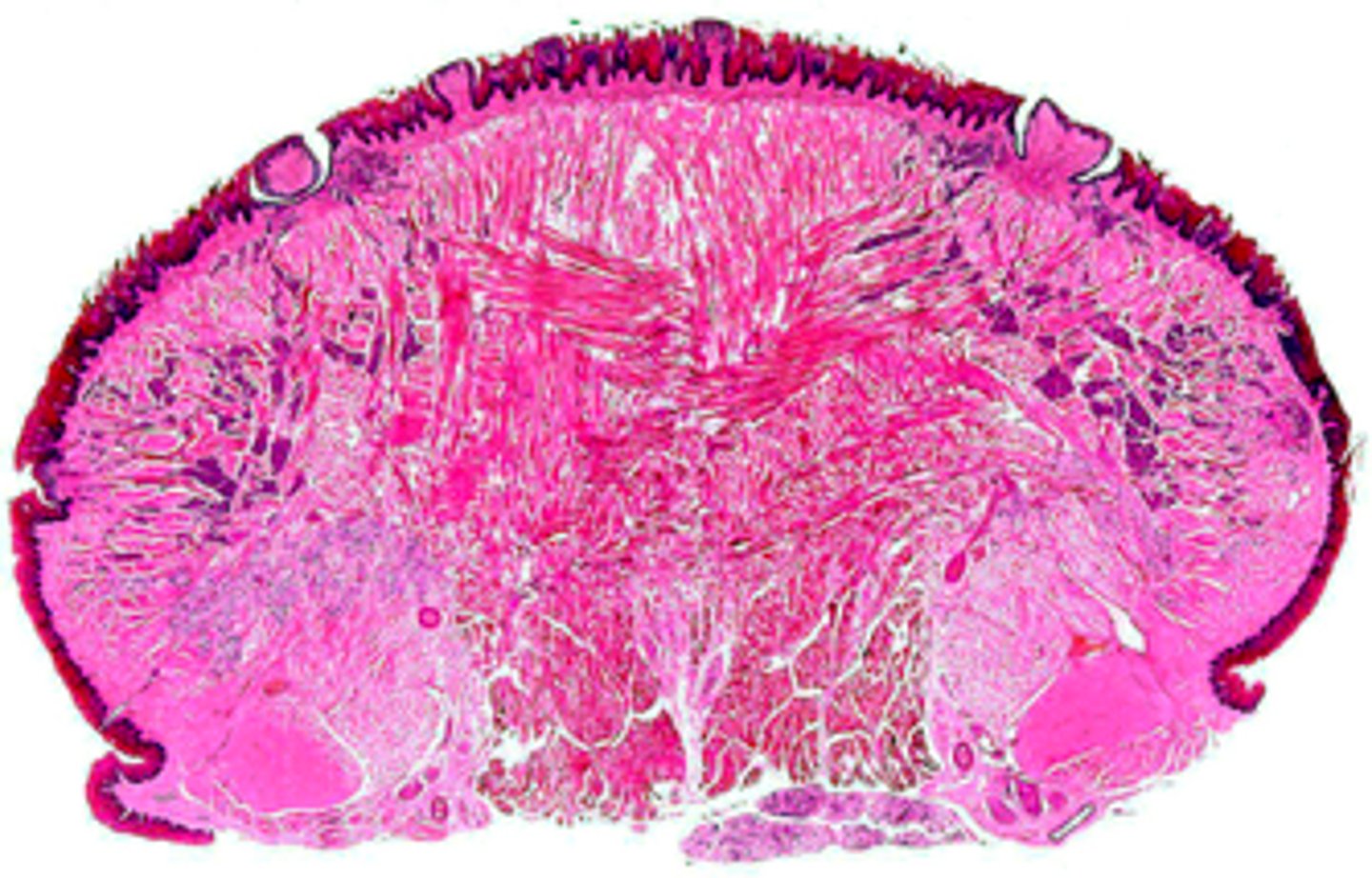
identify the mucosa:
specialized mucosa
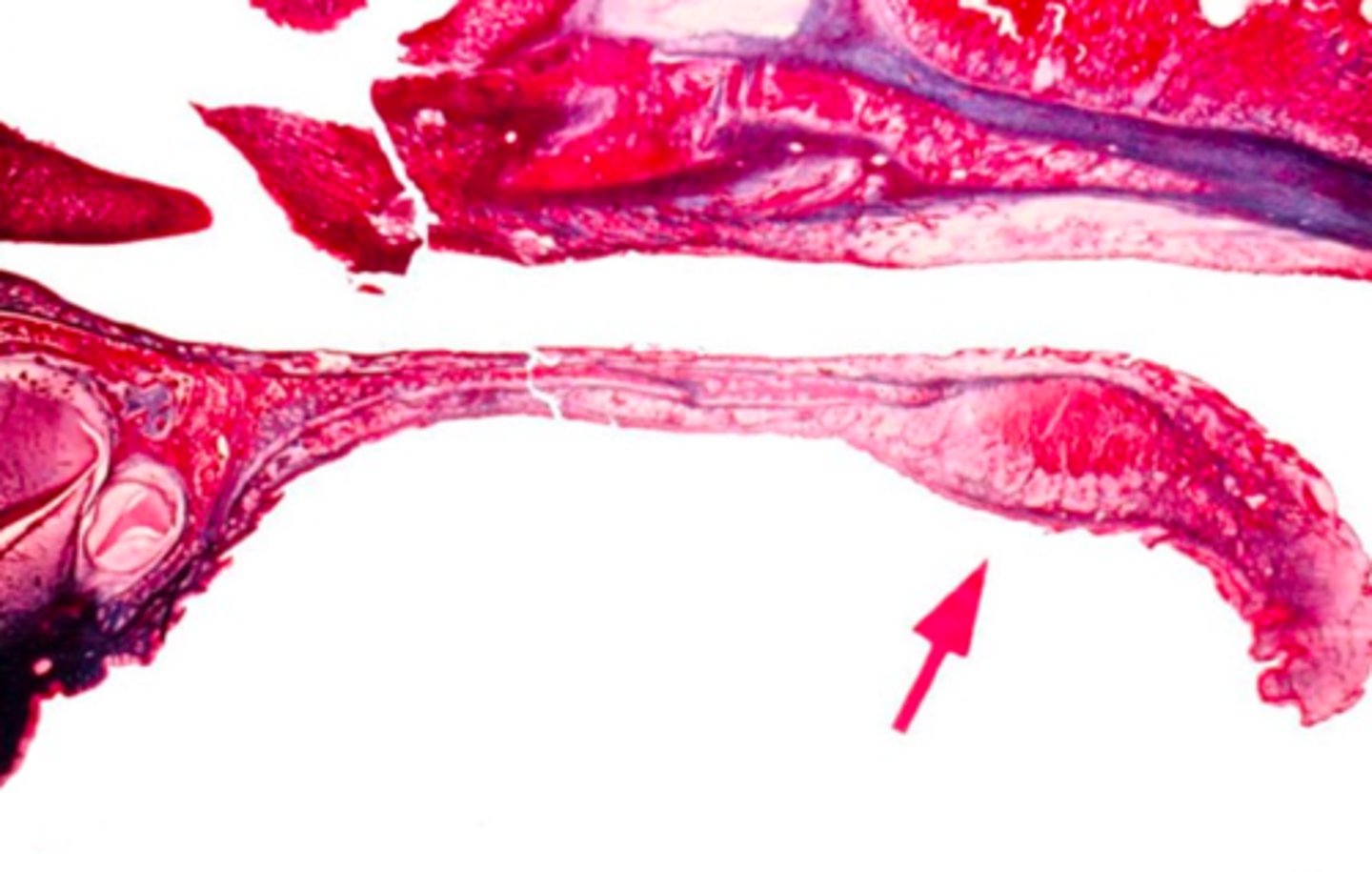
identify the mucosa:
palatine mucosa
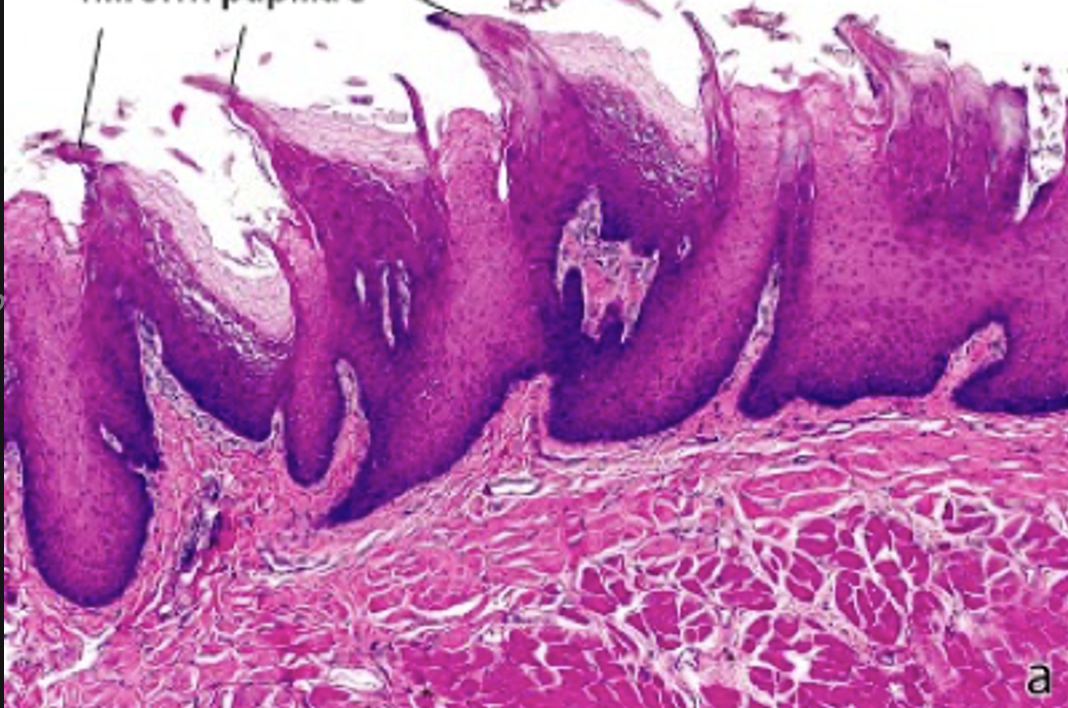
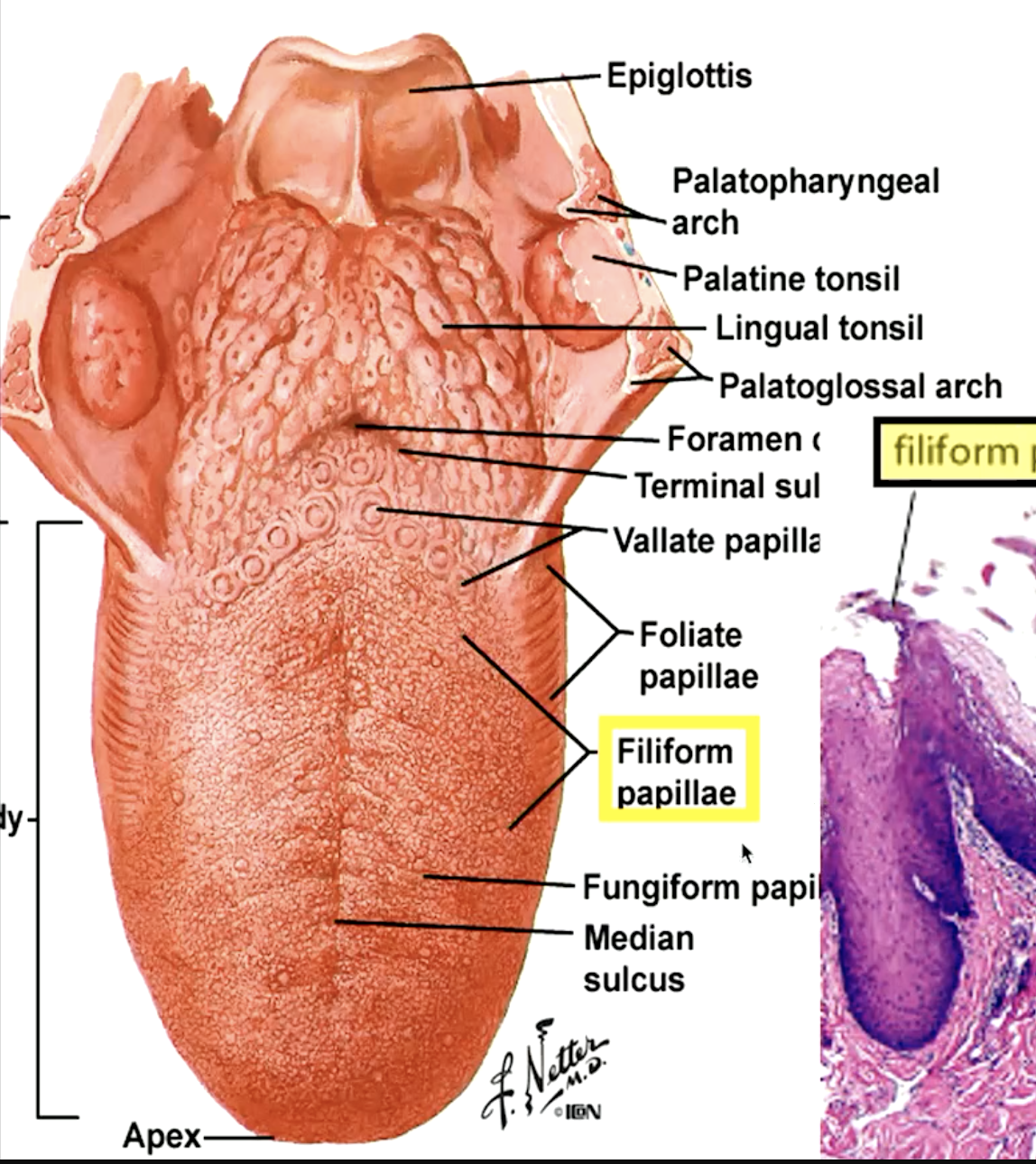
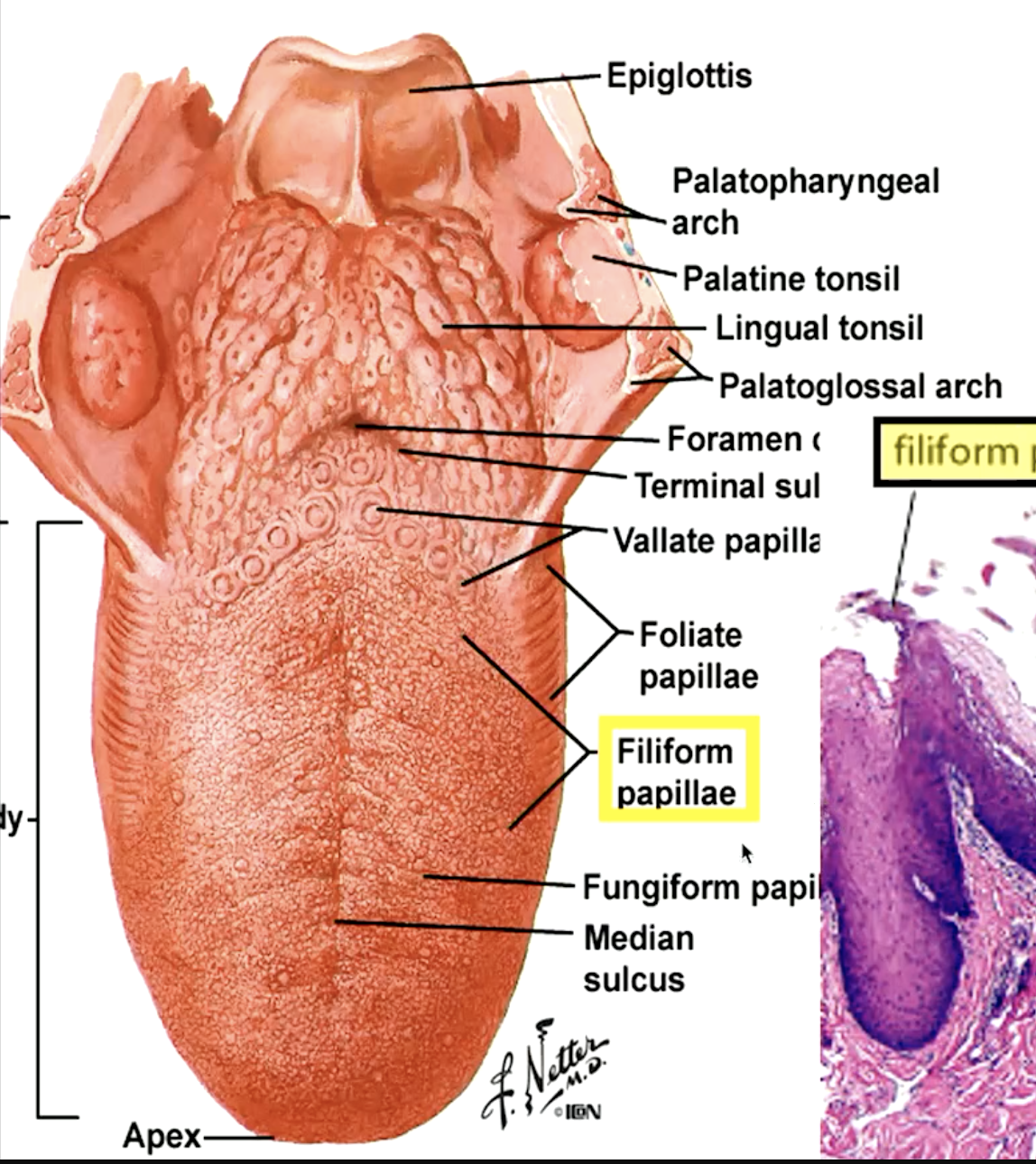
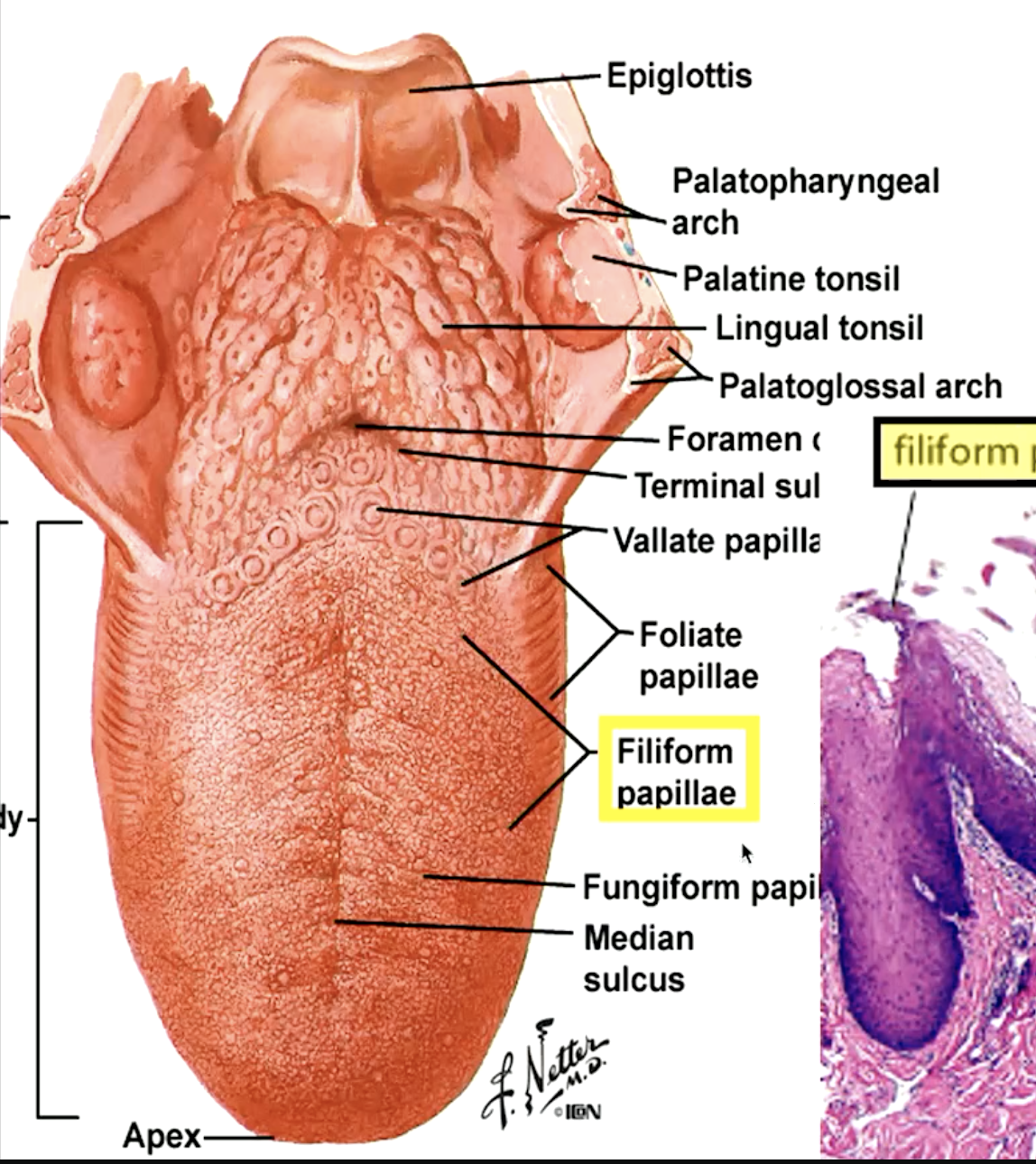
identify the papillae:
filiform papillae (“hooks” that move food toward pharynx)
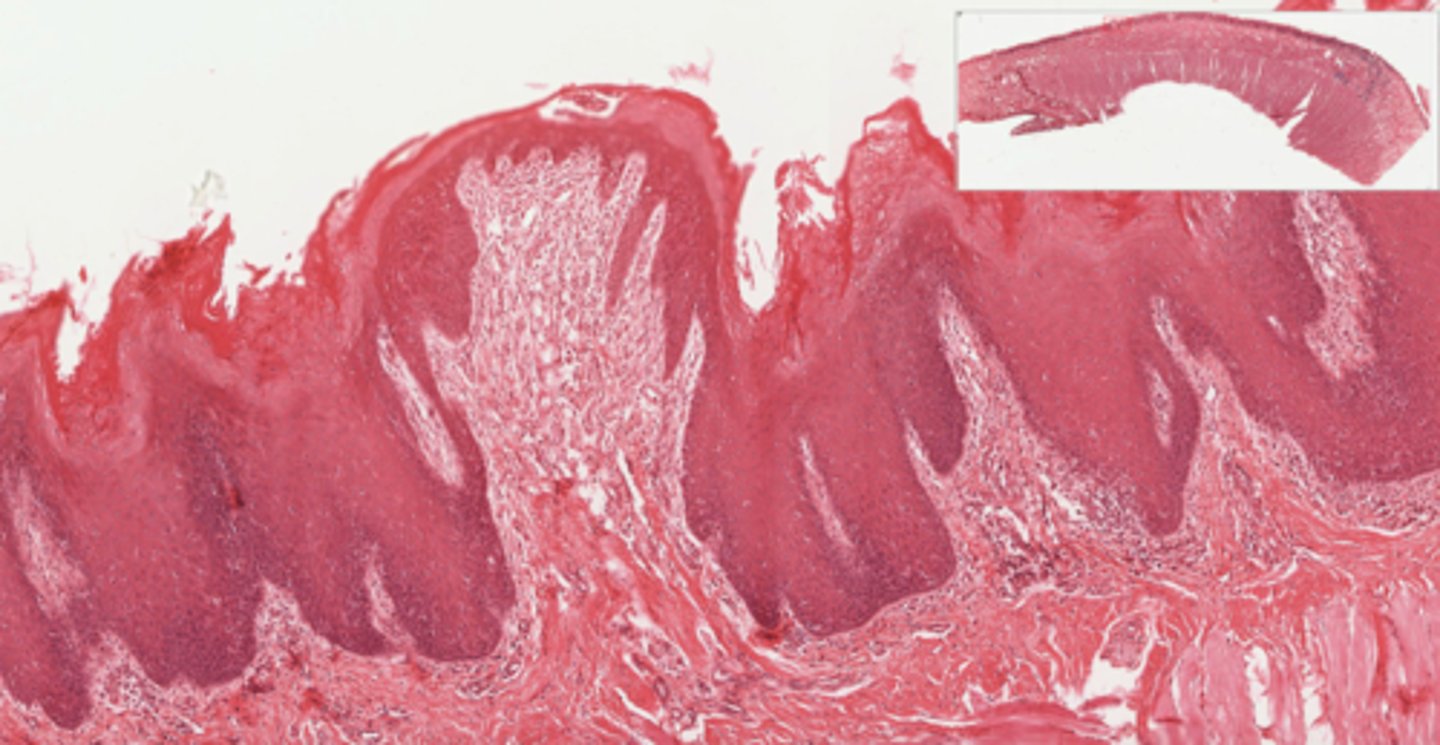
identify the papillae:
fungiform papillae (“mushroom”)
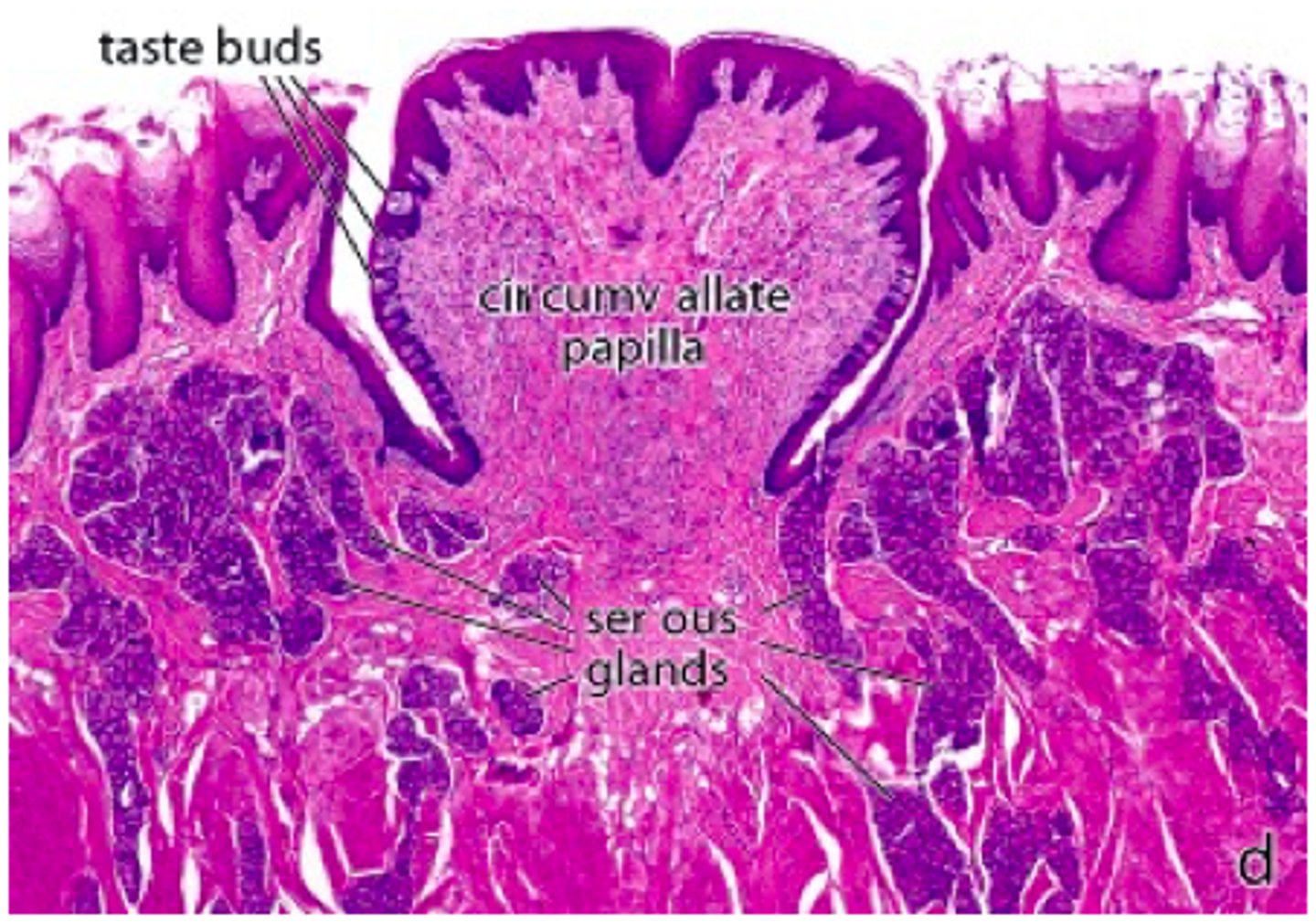
identify the papillae:
circumvallate papillae (“moat”)
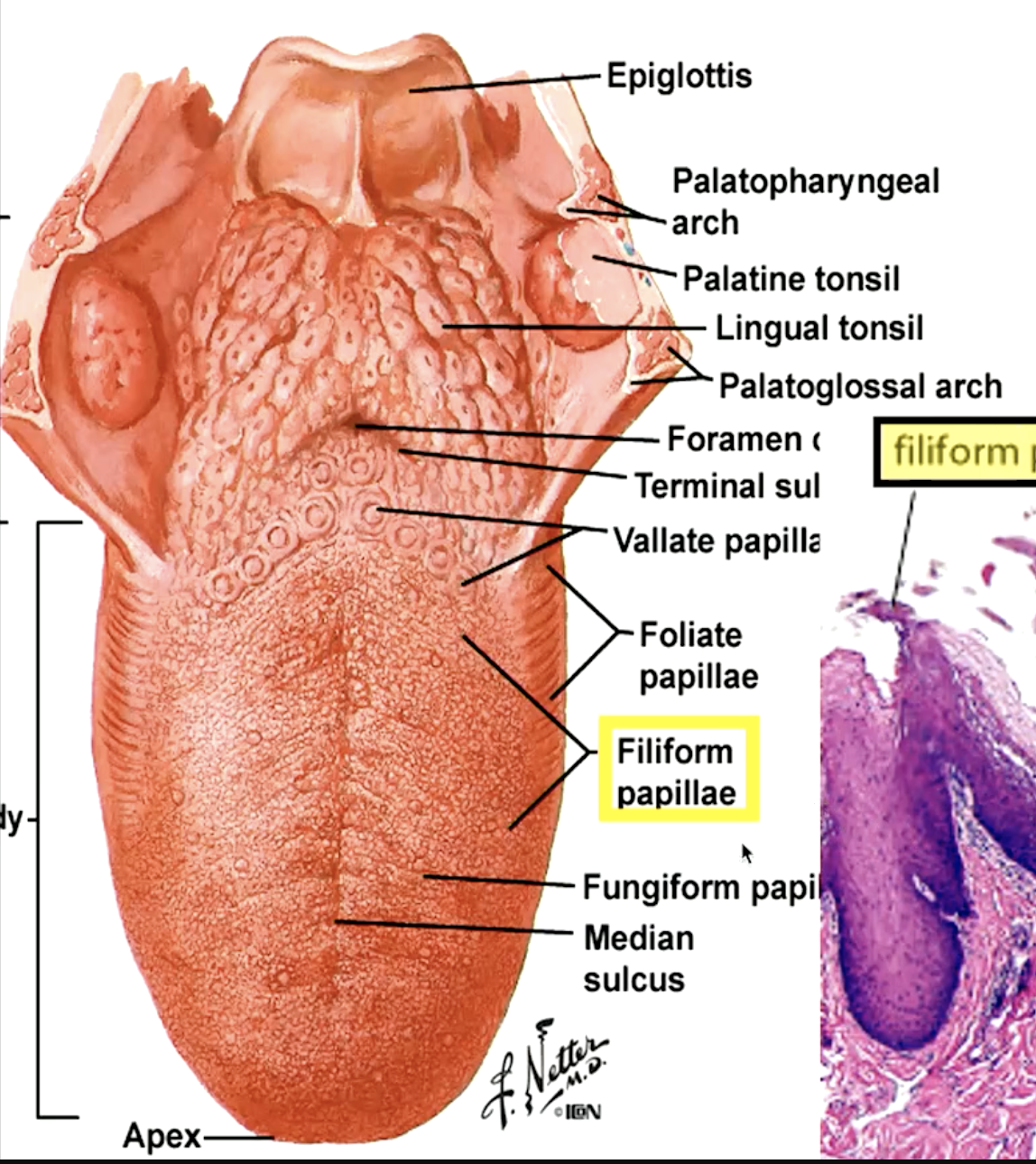
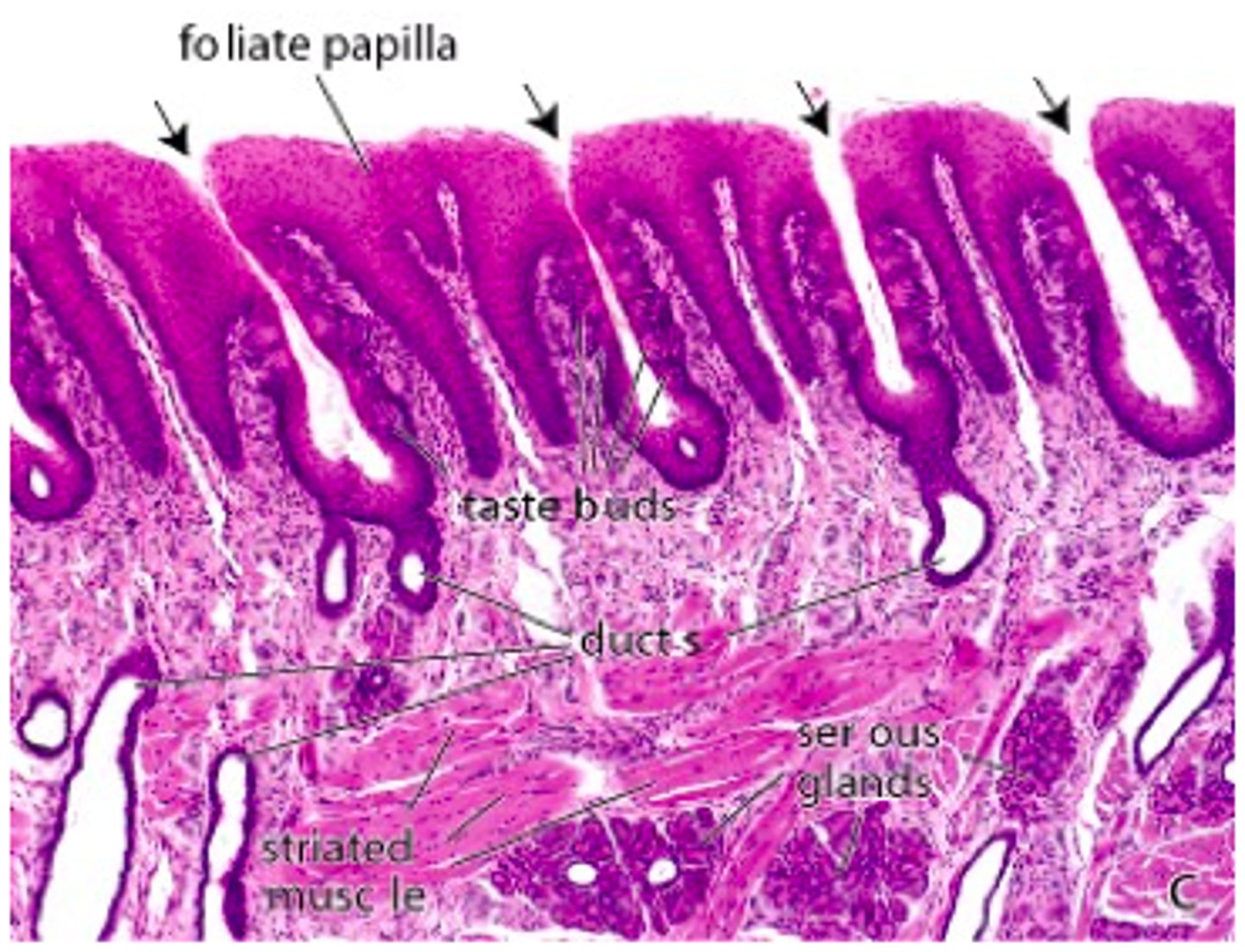
identify the papillae:
foliate papillae
which papillae are located on the lateral side of the tongue:
foliate papillae
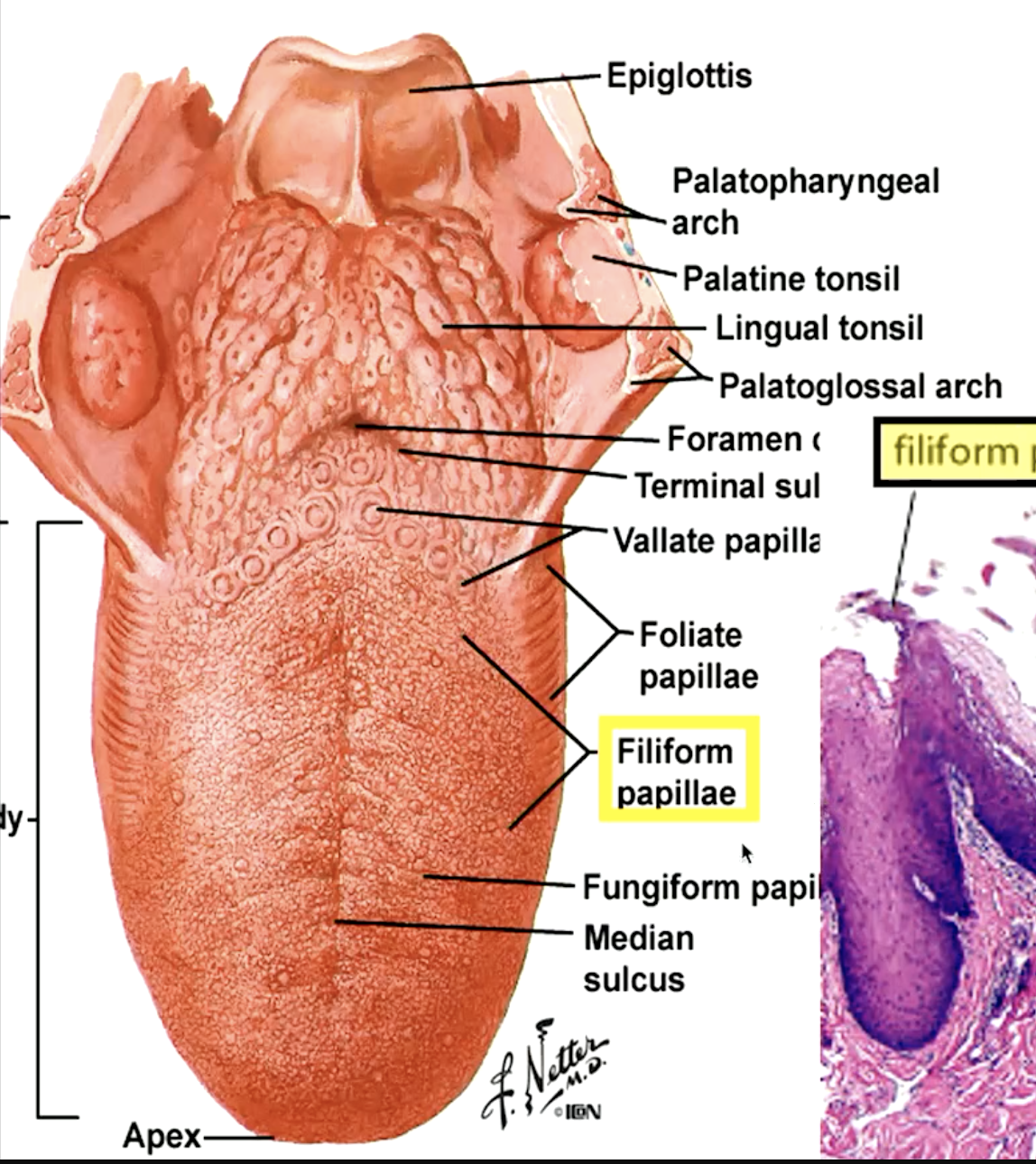
which papillae are most numerous on the dorsum of the tongue?
filiform papillae
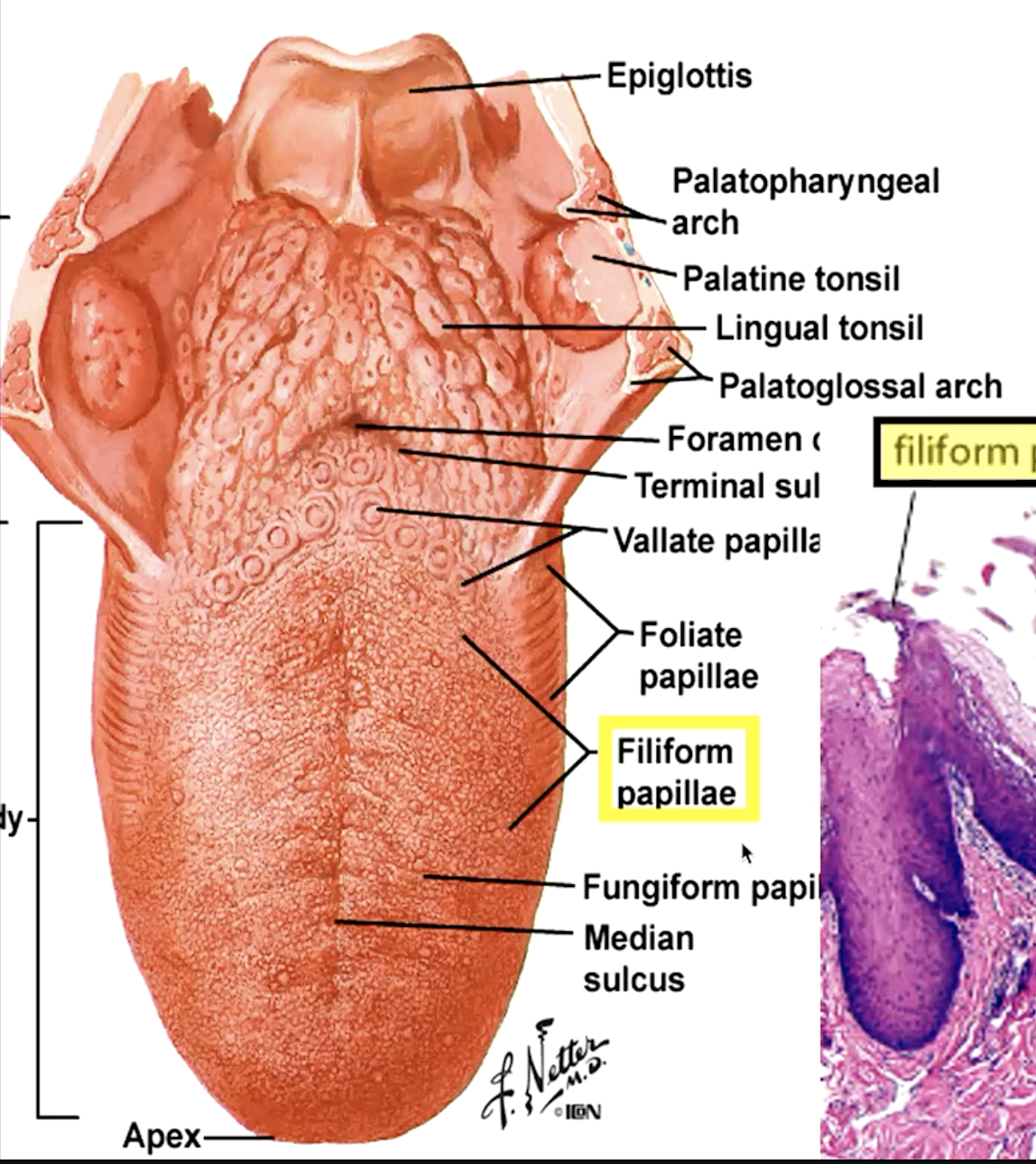
which papillae do not contain tastebuds?
filiform papillae
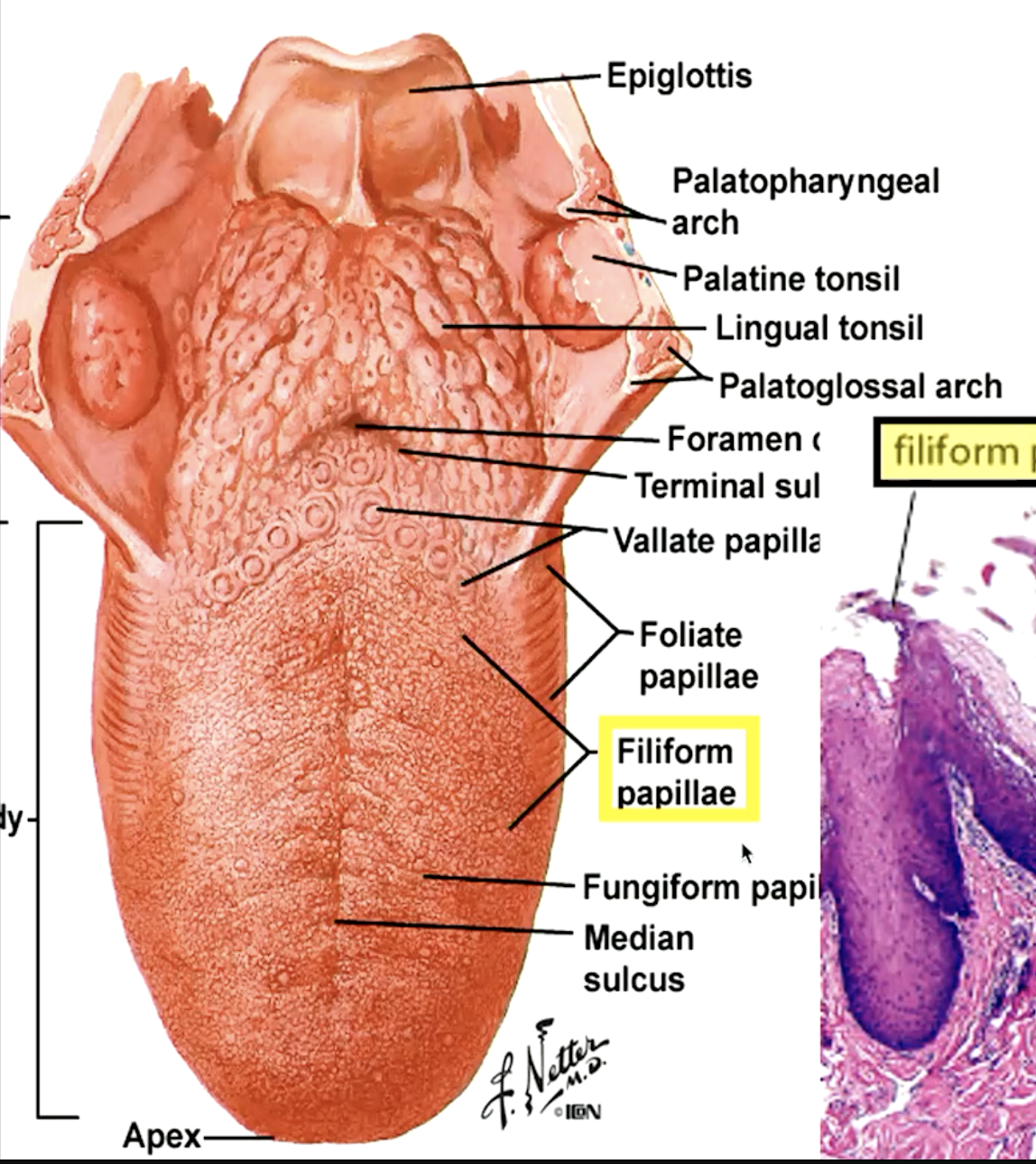
which papillae contain 1-3 tastebuds and are located on the dorsum of the tongue?
fungiform papillae
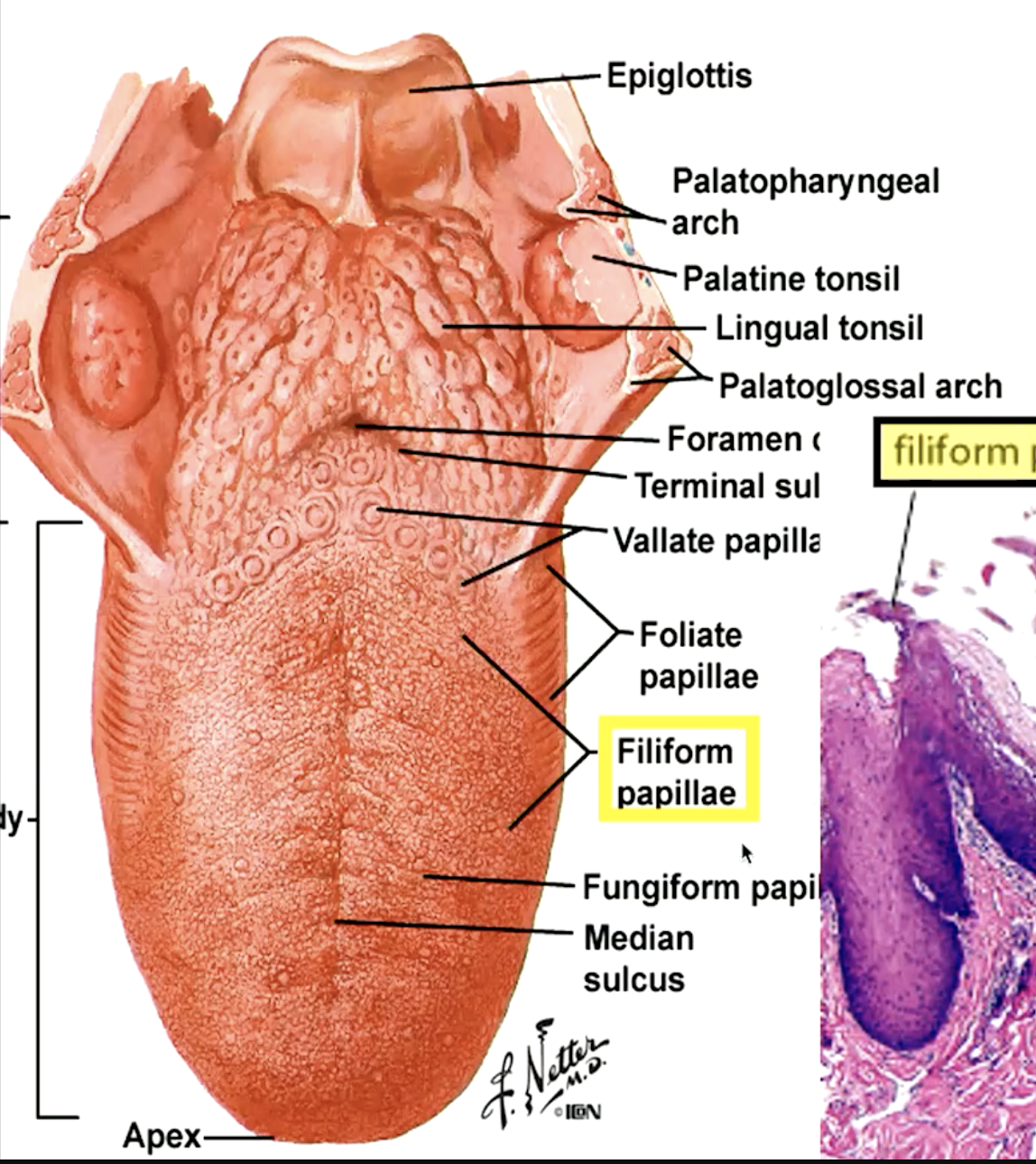
which type of papillae is on lateral of tongue and is poorly developed in humans containing variable number of taste buds?
foliate papillae
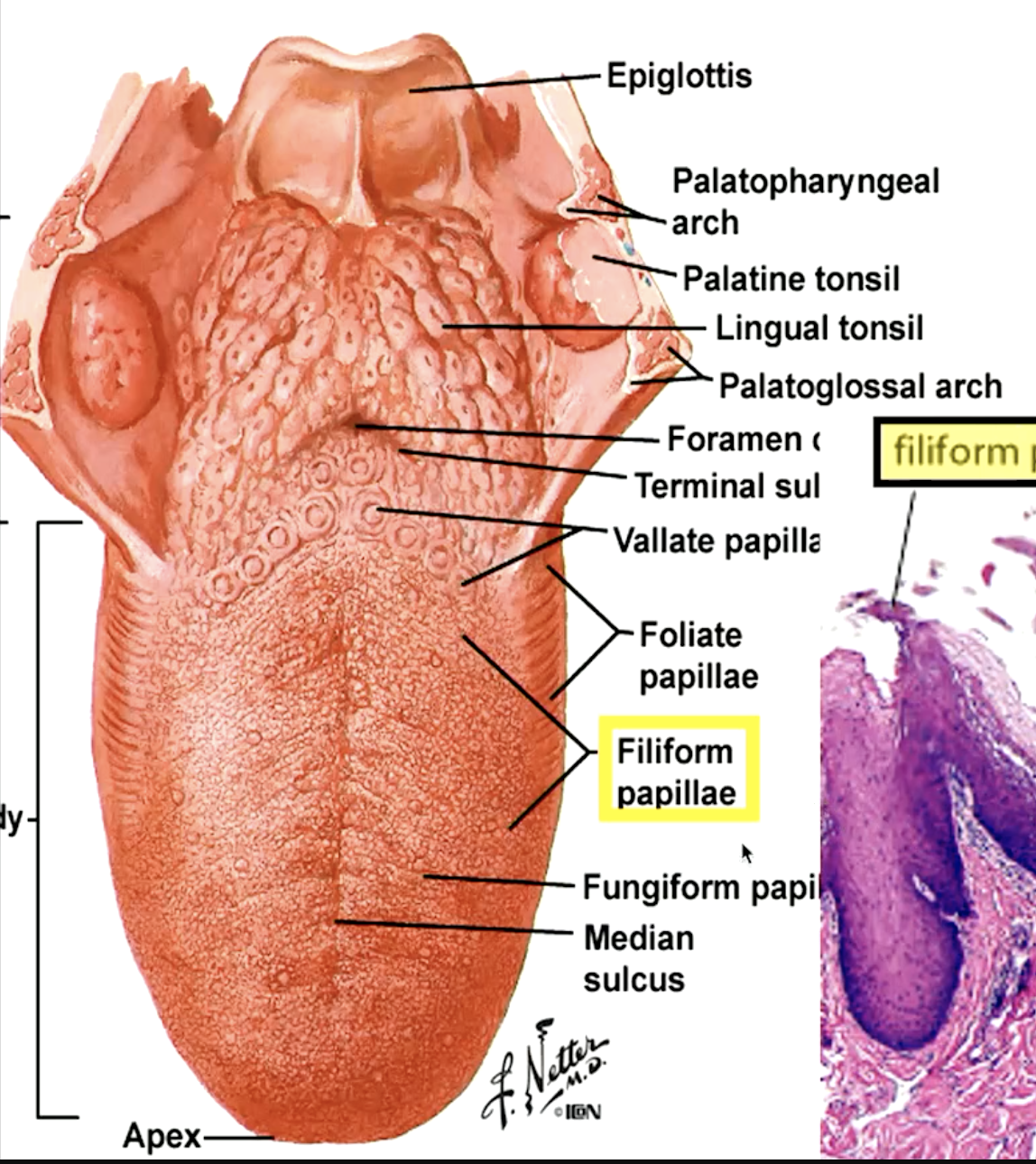
which papillae contain 8-10 papillae surrounded by wall (vallum) nad have numerous taste buds on lateral surfaces of papillae and walls?
circumvallate papillae
which papillae have Ebger glands? what are they?
circumvallate papillae
wash out taste buds so we can taste new things
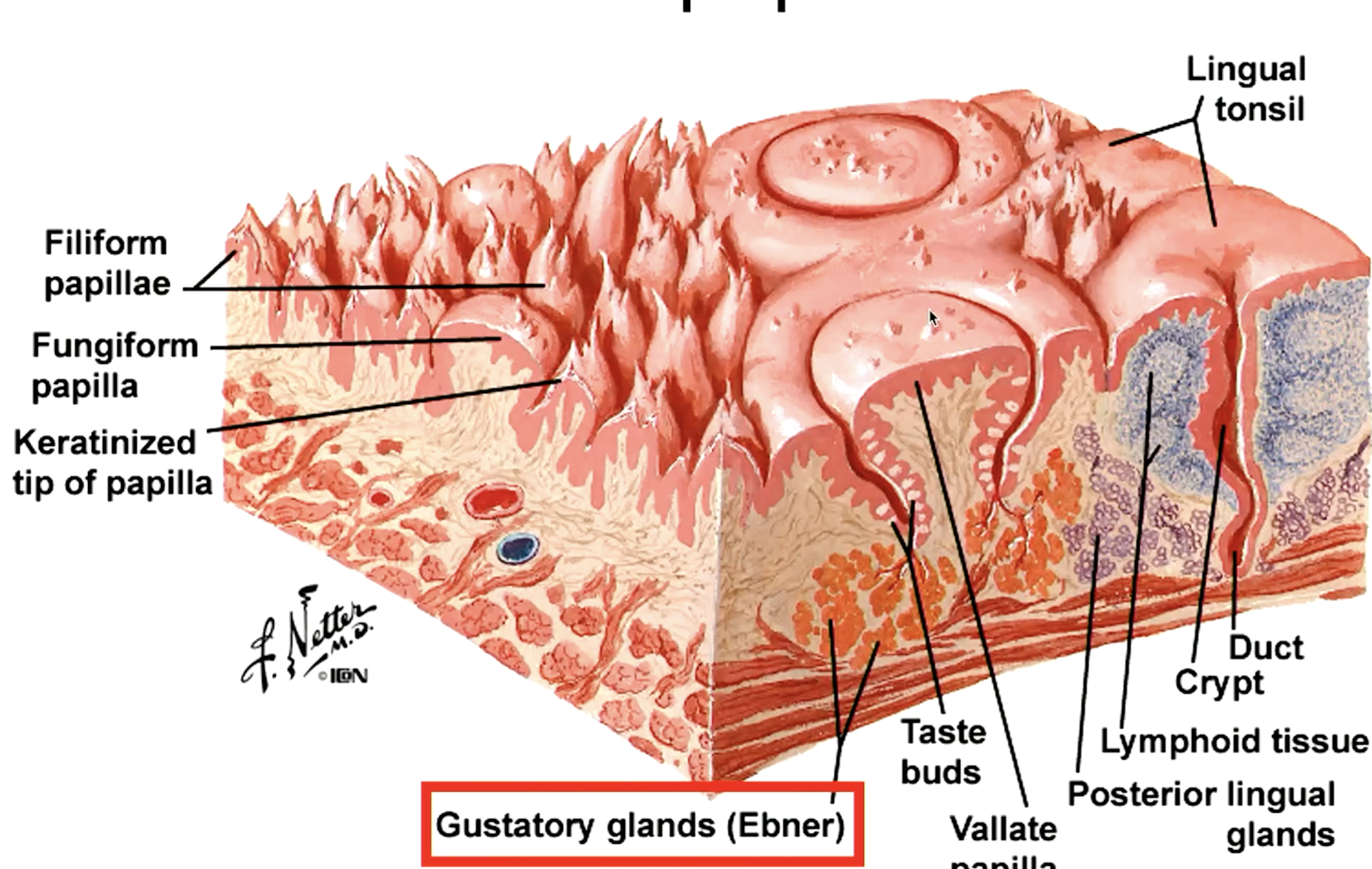
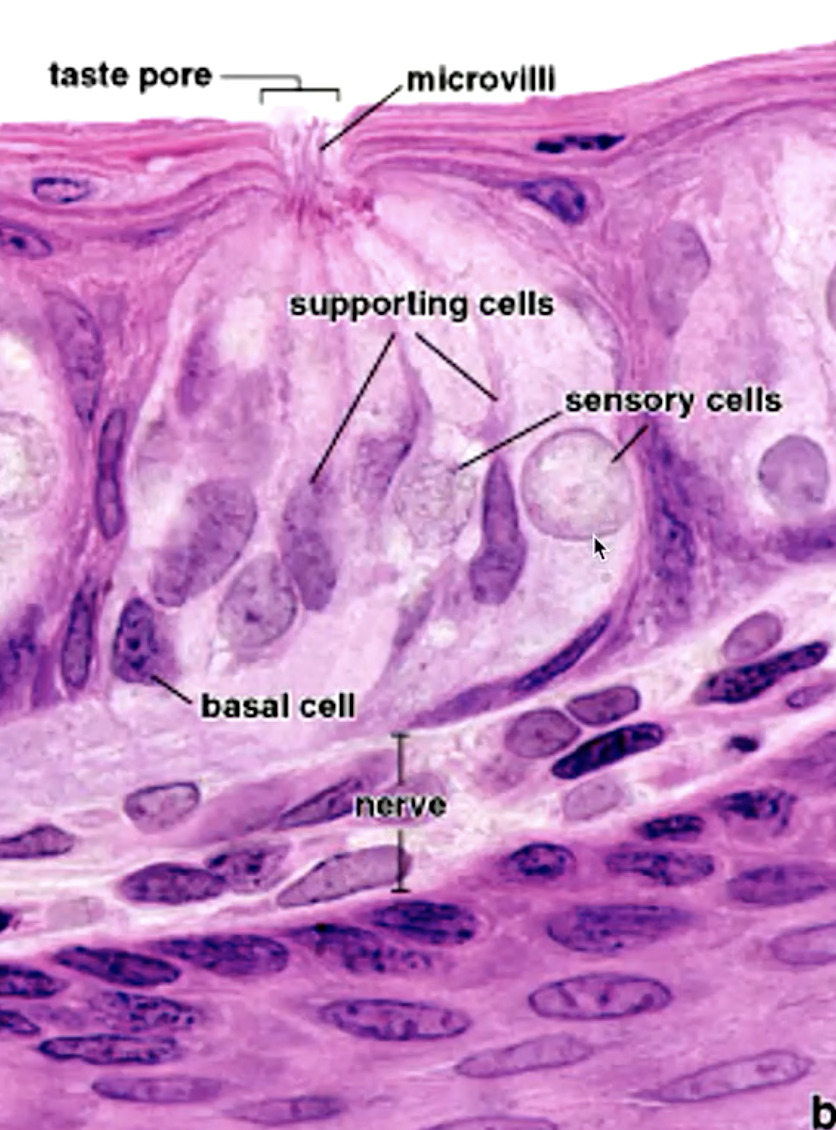
taste (gustatory) buds have 50-150 receptor cells on
microvilli