Exam 2 Biochem Structures
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
made by me
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
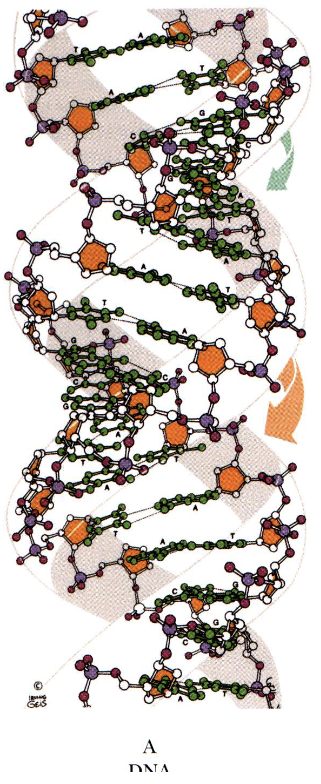
A DNA
DNA:RNA hybrida and RNA:RNA hybrids
11 bp per turn
right-handed helix
short and squat compared to B DNA
B DNA
polynucleotide strands are antiparallel
bases in opposing strands are complementary
10 bp per turn
helix coils clockwise- right handed
major and minor grooves
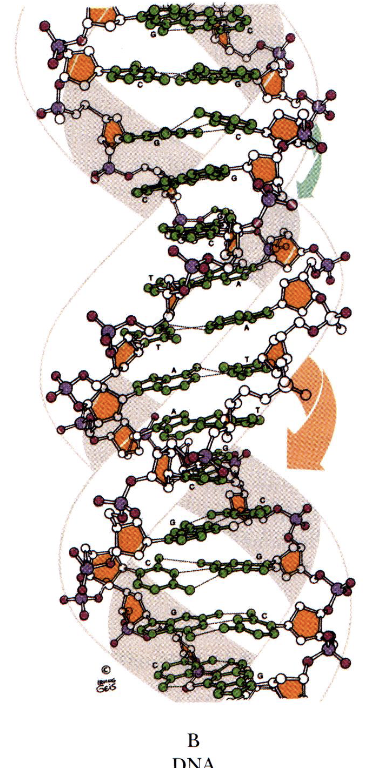
Z DNA
left handed helix
12 bp per turn
thin and elongated compared to B DNA
can occur next to A or B form in DNA
forms with alternating G-C residues
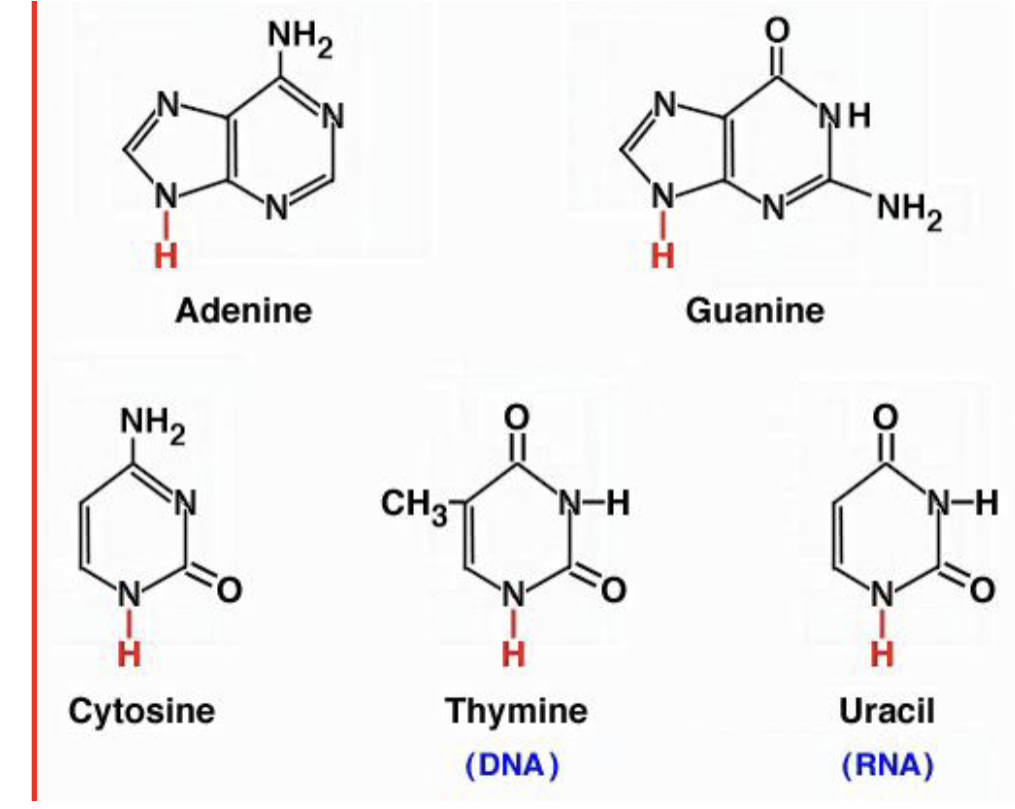
5 nitrogenous bases
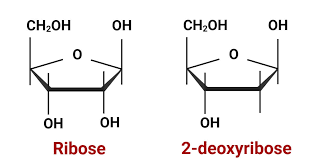
oxynucleic acids
C2 has OH group
deoxynucleic acids
C2 has H group
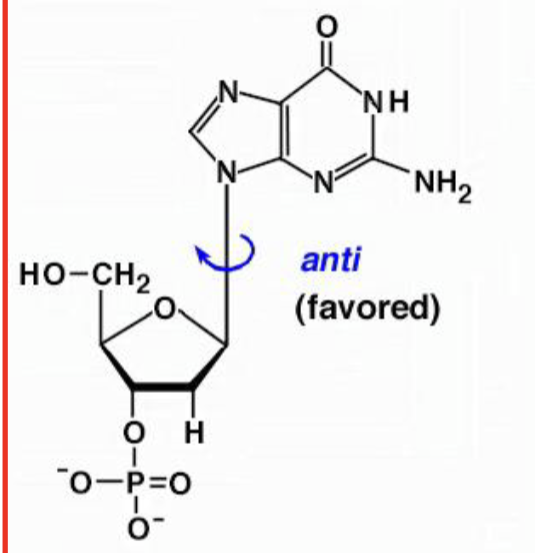
anti base orientation
favored
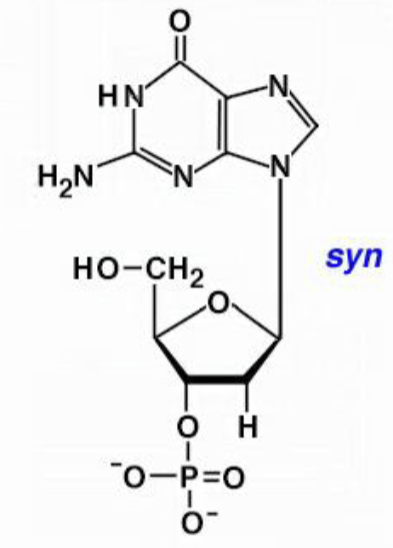
syn base orientation
diastereomers
stereoisomers, or molecules with the same chemical formula and connectivity but different spatial arrangements, that are not mirror images of each other
epimers
diastereomers that differ only at 1 chiral center
alpha anomers
C1 and C6 are opposite direction
beta anomers
C1 and C6 are same direction
sugar alcohols
mild reduction of an aldehye or ketone to an alcohol
add itol to parent sugar name
reducing disaccharides
end of molecule with free anomeric carbon
nonreducing disaccharides
other end of the molecule
glycosidic linkages
a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (monosaccharide) to another group, which can be another carbohydrate, forming a disaccharide or polysaccharide, or another molecule
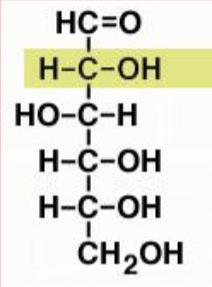
aldose
C double bond O at C1
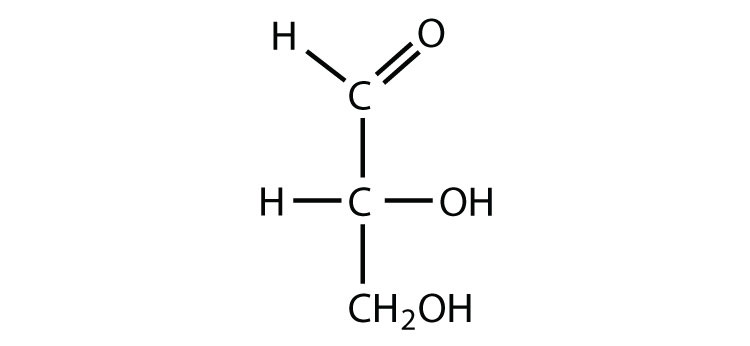
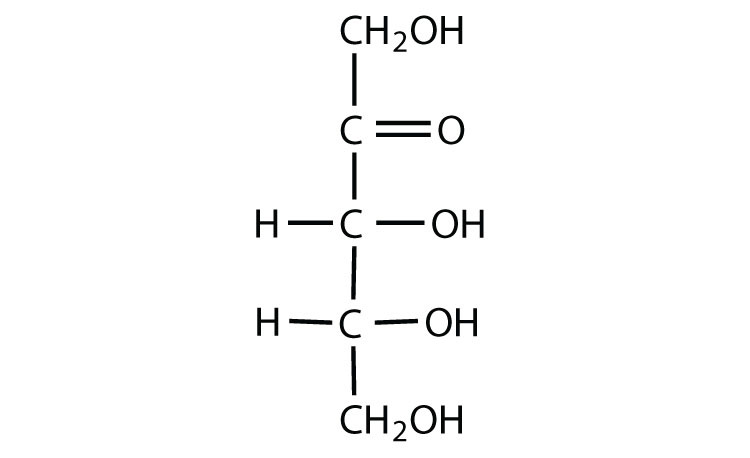
ketose
C double bond O at C2
pentose
ring of 5 Cs
hexose
ring of 6 Cs
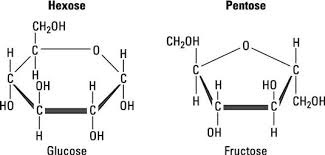
D-glucose
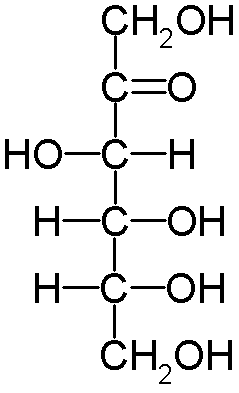
D-ribose
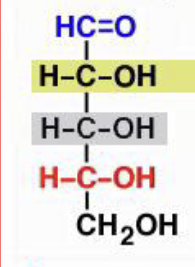
D-galatose
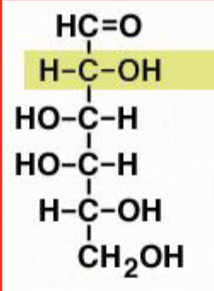
D-fructose
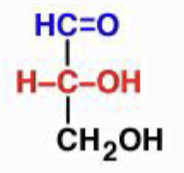
D-glyceraldehyde
saturated fatty acids
single bonds
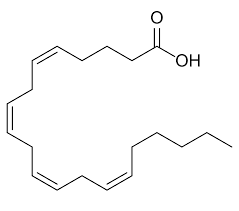
arachidonic acid
20:4 delta 5,8,11,14
cis
unsaturated fatty acid
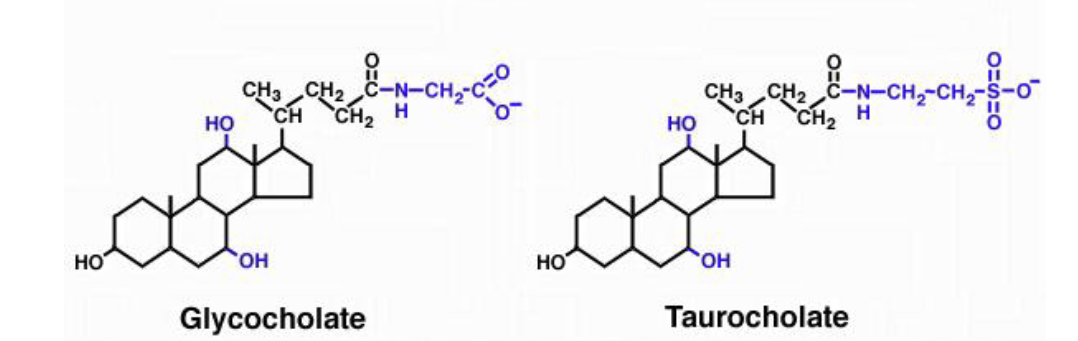
bile salt
net charge -1
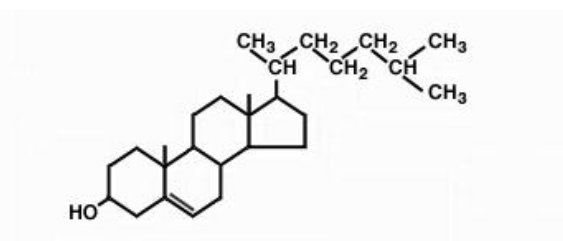
cholesterol
steroid
terpene based
animal cell membranes
lipoprotein complexes in blood
net charge 0
covalently attached to proteins to anchor themselves to the membrane
digylceride
diterpene
20 carbons
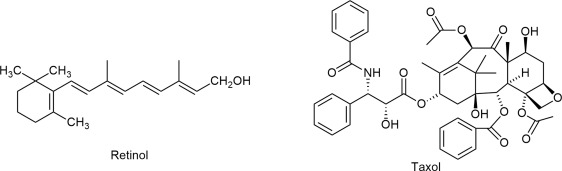
myrisitic acid
14:0
saturated
covalently attached to proteins to anchor themselves to the membrane
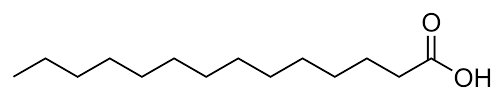
phosphatidic acid
the parent compound
glycerol, two fatty acids and phosphate
fatty acid on C-1 is saturated
fatty acid on C-2 is unsaturated or saturated
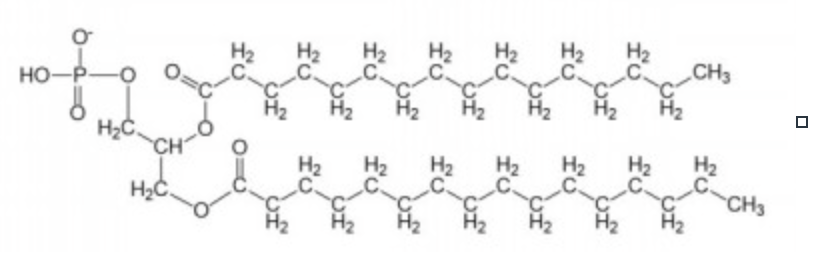
phosphatidyl choline
most common phospholipid
uncharged at pH 7
increases membrane fluidity
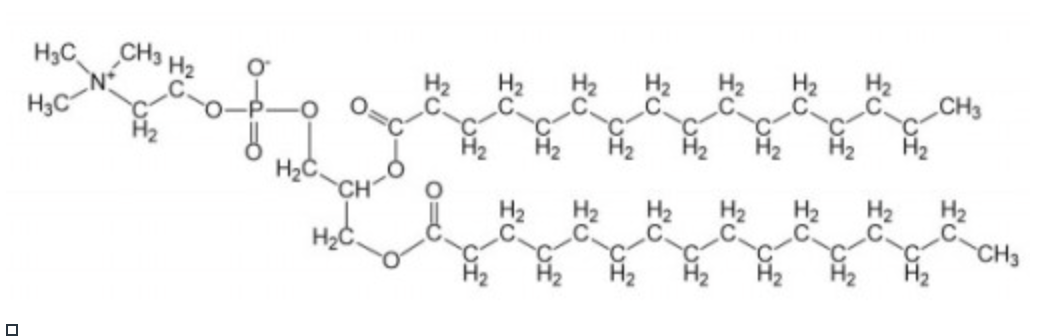
phosphatidyl ethanolamine
uncharged at pH 7
most common lipid in the cell membrane of a red blood cell (erythrocyte)
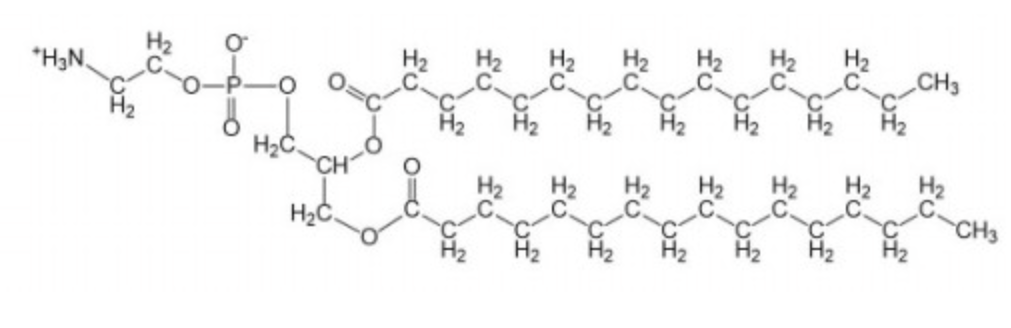
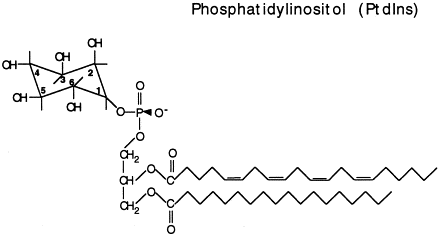
phosphatidyl inositol
net charge -1
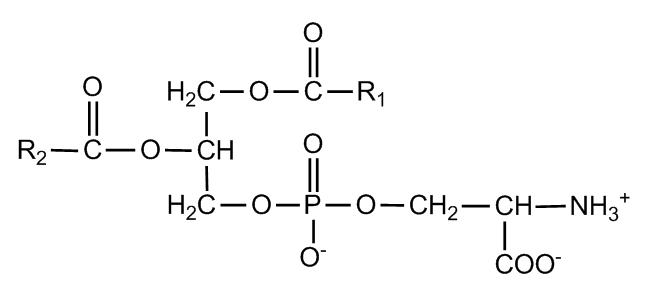
phosphatidyl serine
net charge -1
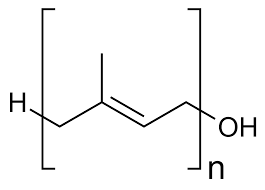
polyprenol
long chain polyisoprenoids plus terminal alcohol
glycoprotein and vitamin synthesis
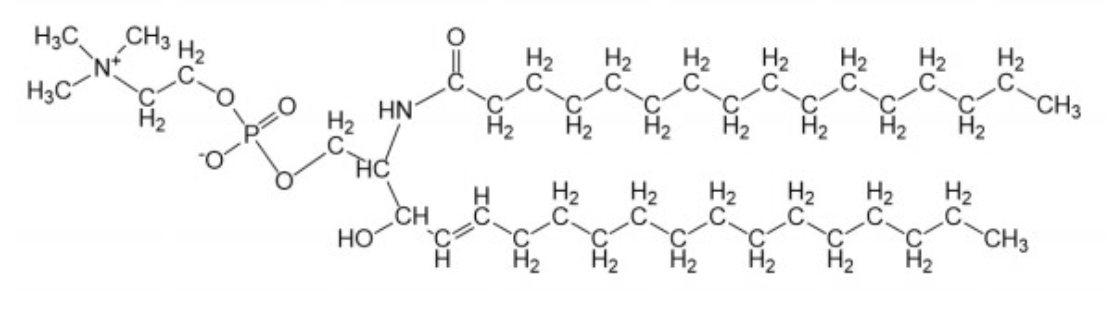
sphingomyelin
~85% of all sphingolipids in man
nervous system and red blood cells
second most common lipid in plasma membrane
has a phosphocholine group
uncharged at pH 7
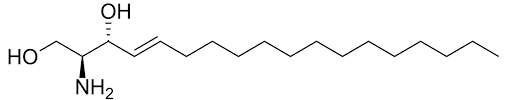
sphinogsine
18C amino alcohol
trans config of C4=C5
count carbons from hydroxyl
net charge +1
tetraterpene
40 carbons
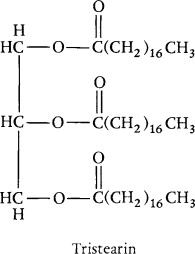
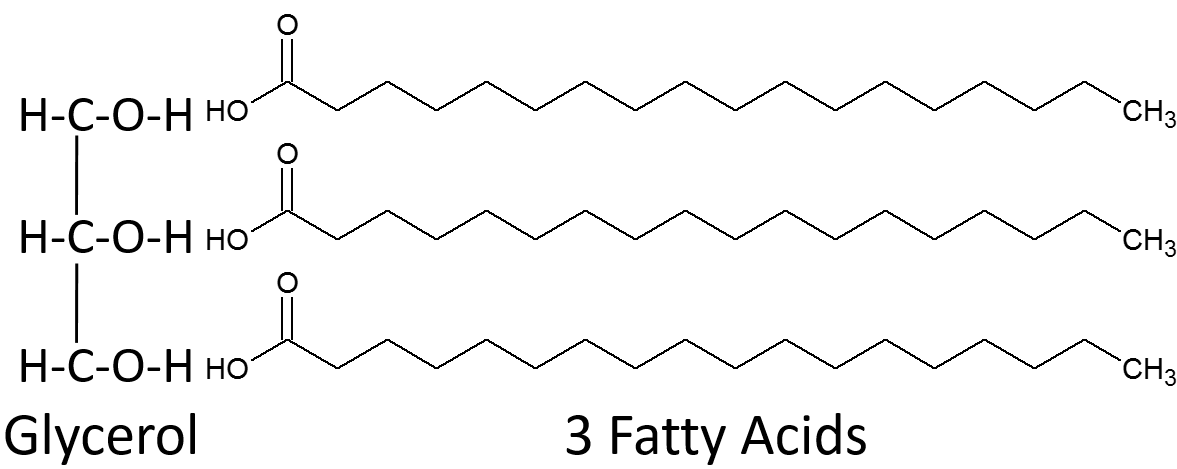
triglyceride
simple: all 3 fatty acids the same
mixed: not all fatty acids
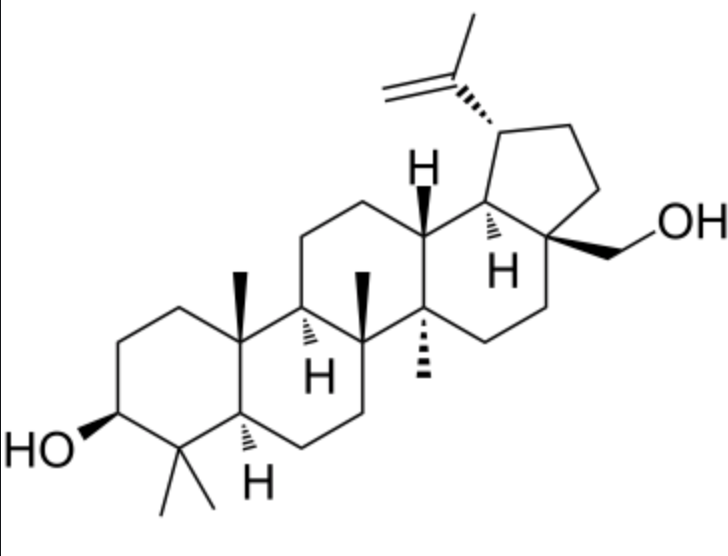
triterpene
30 carbons
sugar acids
oxidation at C1 position of sugar
oxidation at C6 position of sugar
Oxidation at C1 and C6 position of sugar
aldehyde that is a reducing sugar becomes oxidized
deoxysugars
one or more hydroxyl groups on sugar molecules are replaced by H
amino sugars
amino group at C2 position
unsaturated fatty acids
from 1 to 4 double bonds
naturally occurring have cis conformation
synthetic fatty acids have trans conformation
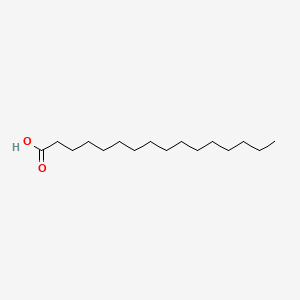
palmitic acid
16:0
saturated
covalently attached to proteins to anchor themselves to the membrane
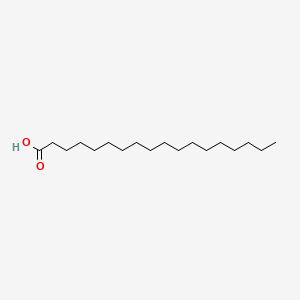
stearic acid
18:0
saturated
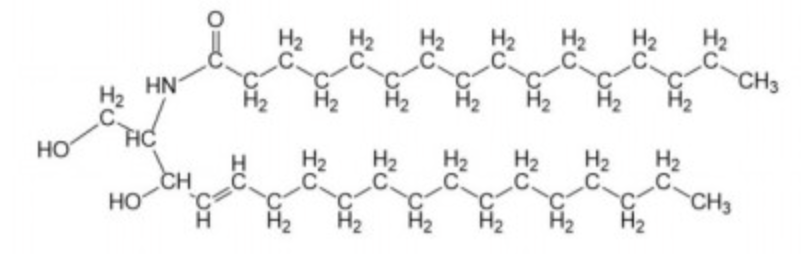
ceramide
sphinogsine and fatty acid via amide linkage
Terpene
simple lipids with no fatty acid components
composed of 2 or more isoprene (C5) units
straight chains or cyclic molecules