PSL300 Term Test 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/153
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:08 PM on 11/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 5 special senses?
vision, hearing, equillibrium, taste and smell
2
New cards
what are the 4 somatic senses?
touch, temperature, proprioception and nociception
3
New cards
receptors are
cells which convert stimuli into electrical signals (transduction)
4
New cards
what is a neuron?
vision sensory cell
5
New cards
every sensory system begins with
receptors
6
New cards
receptor potential
a receptor cell converts stimulus energy into a graded change in membrane potential
7
New cards
every type of receptor cell has an
adequate stimulus
8
New cards
adequate stimulus
the form of energy to which a receptor is most responsive (ex thermoreceptors are sensitive to temp)
9
New cards
receptors are classified according to their
adequate stimulus
10
New cards
chemoreceptors
respond to specific molecules/ions
11
New cards
mechanoreceptors
respond to mechanical energy such as pressure, vibration, gravity, sound
12
New cards
thermoreceptors
respond to temperature
13
New cards
photoreceptors
responds to light
14
New cards
receptor threshold
the weakest stimulus that will cause a response in a receptor
15
New cards
perceptual threshold
the weakest stimulus that will cause a conscious perception in the organism
16
New cards
sensory systems involve a series of
neurons
17
New cards
primary sensory neurons synapse onto
secondary sensory neurons
18
New cards
convergence allows
secondary and higher neurons to combine data from multiple receptors
19
New cards
sensory neurons carry info about many aspects of the stimulus, one aspect is
modality (what is the mode/source: light, sound, touch)
20
New cards
groups of neurons can represent intensity in __ ways which are
1. population coding of intensity: # of active neurons
2. frequency coding: stronger stimuli may make individual neurons to fire at a faster rate
both mechanisms can work together
2. frequency coding: stronger stimuli may make individual neurons to fire at a faster rate
both mechanisms can work together
21
New cards
receptors are neurons have
dynamics (changes in stimuli, not in steady levels)
22
New cards
different cells have different dynamics, the 3 types of cells are:
1. phasic cells
2. tonic cells
3. phasic-tonic cells
2. tonic cells
3. phasic-tonic cells
23
New cards
phasic cells are
cells which respond to a stimulus for a brief moment/change and then stop (FADE AWAY)
24
New cards
tonic cells
are cells that maintain their activity when the stimulus is not changing (at present level)
25
New cards
phasic-tonic cells
are cells that react to change but don't stop/ go to 0 firing when the stimulus is constant. They also carry info about the steady level
26
New cards
many retinal cells are
phasic
example: waving your arm to get a friend's attention will activate the phasic cells in their retina
example: waving your arm to get a friend's attention will activate the phasic cells in their retina
27
New cards
______ cells make communication more efficient
phasic
28
New cards
since our world is fairly stable, it is more efficient to report changes that occur when there is change between time, this change is called __________
temporal change (change through time)
ex. the weather stations
ex. the weather stations
29
New cards
it is also efficient to report ________ changes, which are:
spatial changes - differences between neighbouring regions in space
ex. darker triangle vs lighter triangle in a square
ex. darker triangle vs lighter triangle in a square
30
New cards
spatial changes are also known as _________
contrast
31
New cards
locations where there is a strong contrast between two spaces are called _______
edges
32
New cards
sensory systems accentuate edges (make them noticeable) by:
lateral inhibition: cells can inhibit their neighbours or they can inhibit the cells their neighbours excite
ex (an object poking the skin would have an edge between contact and no contact)
ex (an object poking the skin would have an edge between contact and no contact)
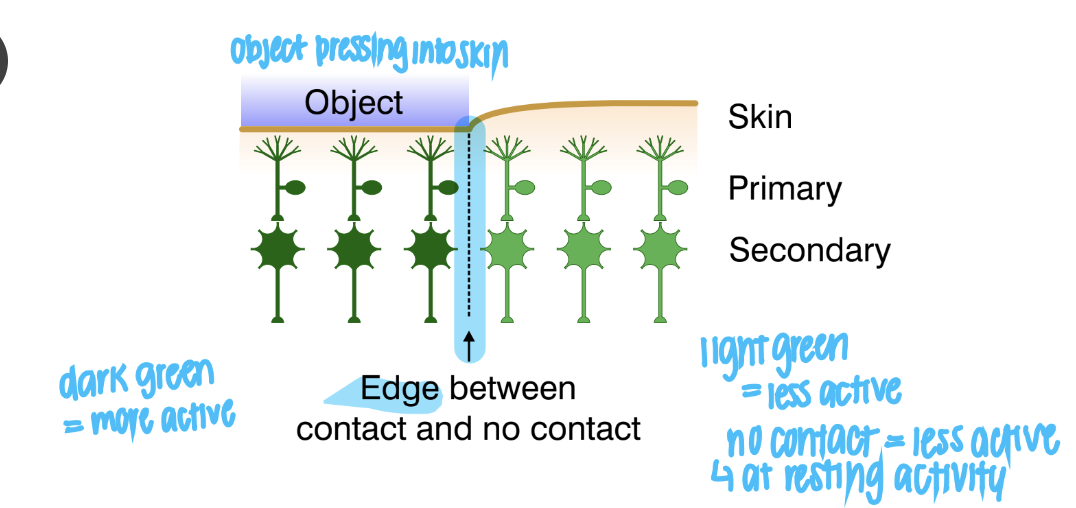
33
New cards
away from the edge, __________ and _________ cancel out
excitation and inhibition
34
New cards
most sensory pathways run via the ________ to the _______
thalamus -> cortex
35
New cards
one pathway that does not send signals from the thalamus to the cortex is the:
olfactory (smell) pathway - goes straight from nose -> cortex
36
New cards
equillbrium (balance) pathways project mainly to the _________
cerebellum
37
New cards
sensory processing is ___________
inference (educational guessing) - unconscious and fast
38
New cards
since the brain has to guess, it can be fooled. the brain also ______ coincidences
mistrusts
39
New cards
the eye is divided into __ chambers by the ___ . These chambers are the:
- 2, lens
- anterior chamber, vitreous chamber
- anterior chamber, vitreous chamber
40
New cards
the anterior chamber:
is filled with aqueous humor (plasma like fluid)
41
New cards
the vitreous chamber is:
filled with clear jelly that maintains they eyeballs shape
42
New cards
the ______ is a transparent buldge, the outer wall of the eye
cornea
43
New cards
the ____ is a transparent disk that focuses light
lens
44
New cards
the _____ and ____ focus light on the _____, the inner lining of the eye which contains photoreceptors
- cornea
- lens
- retina
- lens
- retina
45
New cards
light passes from the ____ to the lens through a hole in the ___ called the ____
- cornea
- iris
- pupil
- iris
- pupil
46
New cards
the pupil can change ___
size
47
New cards
in bright light, the pupil _____ to ____ the amount of light reaching the ____
- constricts/shrinks
- reduce
- lens
- reduce
- lens
48
New cards
in the dark, the pupils ____ to _____ the amount of light that reaches the ___
- dilates/expands
- increase
- lens
- increase
- lens
49
New cards
the pupil is controlled by _____ muscles in the ____
- smooth
- iris
- iris
50
New cards
in bright light, _________ signals from the brain contract the ____ _______ muscle, shrinking the pupil
- parasympathetic (long=light)
- pupillary constrictor
- pupillary constrictor
51
New cards
in the dark, ___________ signals contract the _____ ______ muscle, _____ the pupil
- sympathetic
- radial pupillary
- dilating
- radial pupillary
- dilating
52
New cards
the _____ helps to focus light and control _________________
- pupil
- depth of field (what you can see around you and how much of it)
- depth of field (what you can see around you and how much of it)
53
New cards
when the pupil is dilated, we have a ____ depth of field. this means only objects ___ one specific distance are in ____
- shallow
- near
- focus
- near
- focus
54
New cards
when the pupil is tightly constricted, we have ____ depth of field, which means everything we see is ____ in _____
- full
- equally
- focus
- equally
- focus
55
New cards
the problem with using the pupil alone to focus light is that:
- the retinal image is dull
- enlarging the pupil makes the image brighter and blurrier (B&B)
- enlarging the pupil makes the image brighter and blurrier (B&B)
56
New cards
in order to get a retinal image that is both ____ and _____, we rely on ________
- bright
- focus
- refraction
- focus
- refraction
57
New cards
the bending of light is known as:
refraction
58
New cards
light ____ when it enters a medium with a ______ refractive index
- bends
- different
- different
59
New cards
our corneas are made of _______. they bend strongly because there is a big difference between the ____ _____ of air and collagen
- collagen
- refractive index
- refractive index
60
New cards
the cornea is responsible for _____ of the eye's refraction. while the lens accounts for ____
- cornea = 2/3
- lens = 1/3
- lens = 1/3
61
New cards
the lens of the eye is ____. These lenses are flatter in the middle and thinner at the edges. (ex: magnifying glass)
- convex
62
New cards
refraction depends on the:
angle of incidence
63
New cards
a ____ lens bends light more, and so it has a closer _____ _____
- rounder
- focal point
- focal point
64
New cards
for clear vision, the ____ ____ must fall on the ___
- focal point
- retina
- retina
65
New cards
if the objects draws closer, but the lens stays flat, focus falls ___ the ____
- behind
- retina
- retina
66
New cards
to bring a closer object into focus, we make the lens ______. This process is called ______ and is an _____ reflex
- rounder
- accomodation, unconscious
- accomodation, unconscious
67
New cards
what is hyperopia? where does the focal point fall and how can it be solved?
- far-sightedness
- behind the retina
- solved by convex lens (reading glasses)
- behind the retina
- solved by convex lens (reading glasses)
68
New cards
what is myopia? where does the focal point fall and how can it be solved?
- near-sightedness (MY EYESIGHT)
- in front of the retina (NEAR AND FRONT)
- can be solved with concave lens
- in front of the retina (NEAR AND FRONT)
- can be solved with concave lens
69
New cards
a ______ lens causes light rays to ____ ____ more, which is the opposite of a ____ lens
- concave
- spread out
- convex
- spread out
- convex
70
New cards
photoreceptors are found in the
retina
71
New cards
our retina has ___ types of photoreceptors which are:
- rods
- cones
- cones
72
New cards
rods and cones are ______, however they do not fire ________ potentials. instead, the respond to ______ with _____ membrane potentials
- neurons, action potentials, stimuli, graded
73
New cards
cones and rods have the ______ basic structure. in the ___ segment, the membrane folds into ___________ layers which contain __________ that respond to light
- same
- outer
- disk-like
- visual pigments
- outer
- disk-like
- visual pigments
74
New cards
how do photoreceptors detect light?
- they detect light using membrane bound visual pigments
75
New cards
photoreceptors are _______ and more ______ in darkness. this means they release lots of ________
- depolarized
- active
- glutamate
- active
- glutamate
76
New cards
each photoreceptor contains ____ of molecules of its _______. However, each type of photoreceptor has just ____ type of _____.
- millions
- pigments
- one
- pigment
- pigments
- one
- pigment
77
New cards
the visual pigment for rods is:
rhodopsin
78
New cards
photoreceptors are not distributed ________. They are most densely packed in the _____, and especially in its central pit called the ______.
- uniformly/equally
- macula
- fovea
- macula
- fovea
79
New cards
we use the ______ for detailed vision
fovea
80
New cards
there are _____ photoreceptors in the ____ spot. The ____ spot is the hole where axons carrying ____ info exit the eyeball to form the ____ nerve.
- no
- blind
- blind
- optic
- blind
- blind
- optic
81
New cards
cones are for _______ and rods are for ________.
- bright light
- dim light
- dim light
82
New cards
Therefore, _____ are considered to be more sensitive than _____ because they can detect single photons but they only operate in _____ light.
- rods
- cones
- dim
- cones
- dim
83
New cards
During daylight, ____ are bleached out, which means their _____ is broken down so they can't sense light
- rods
- rhodopsin
- rhodopsin
84
New cards
cones and rods are distributed differently in the _______. The _____ contains exclusively ______ and the more peripheral ______ contains mainly _____. Therefore, there is a ____ density of _____ in the fovea.
- retina
- fovea
- retina
- rods
- high
- cones
- fovea
- retina
- rods
- high
- cones
85
New cards
photoreceptors synapse onto ______ cells, which synapse onto _______ cells. up to ______ photoreceptors may converge on a single _______ cell, the BP cells in turn converge on ___.
- bipolar
- ganglion
- 45
- GC
- ganglion
- 45
- GC
86
New cards
convergence is greatest in the peripheral _____ and least in the ______
- retina
- fovea
- fovea
87
New cards
everyone neuron in the visual system has a _______________ also called the _____ field. the ______ is the region of the ____ where light affects the cell's activity.
- receptive field/visual field
- visual field
- retina
- visual field
- retina
88
New cards
bipolar cells receptive fields can be on centre or off centre. ___________ are excited by light in the centre of their field and ____________ by light in the surround. These cells respond most when a light spot fills their _____ and the surround is _____.
- on centre cells
- inhibited
- centre
- dark
- inhibited
- centre
- dark
89
New cards
off centre cells are ___________ by light in the centre, and excited by ______ in the surround. they respond best when a _____ spot fills their centre and the surround is _________.
- inhibited
- light
- dark
- light
- light
- dark
- light
90
New cards
both types of bipolar cells react to ___________. when lighting is _________, neither type of _____________ responds. this is because the effects of the centre and surround ___________, which leaves the cell at its ___________ level.
- contrast
- uniform
- bipolar cells
- cancel
- resting
- uniform
- bipolar cells
- cancel
- resting
91
New cards
bipolar cells project to ___________ ___________ ______.
- retinal ganglion cells
92
New cards
retinal ganglion cells unlike photoreceptors and bipolar cells, do:
- fire action potentials
93
New cards
ganglion cells in ___________ parts of the retina have different sized ___________. Therefore, a ganglion cell near the ______ gets input from only a few ___________, which are mostly ____.
- different
- receptive fields
- fovea
- photoreceptors, cones
- receptive fields
- fovea
- photoreceptors, cones
94
New cards
farther out, each ganglion cell gets input from many ________, which are mostly ______.
- receptors
- rods
- rods
95
New cards
in the periphery, each ganglion cell is very ___________ to light, but ____ at reporting spatial detail. this is because it blends information from a wide range of ________.
- sensitive
- poor
- receptors
- poor
- receptors
96
New cards
___________ are also classified based on how their signals are used in the brain.
ganglion cells
97
New cards
large ganglion cells are ___________. these cells provide info about ___________ and are ________. they account for about _____ of RGC.
- magnocellular ganglion cells/ M cells
- M = MOVEMENT
- phasic
- ~10%
- M = MOVEMENT
- phasic
- ~10%
98
New cards
small ganglion cells are ___________. these cells provide info that is used to infer form and fine detail, like texture. they are less ______ and more ___________. they account for about ___ of RGC.
- parvocellular / P cells
- phasic-tonic
- ~70%
- phasic-tonic
- ~70%
99
New cards
~1 % of ganglion cells are ___________ ganglion cells. there are photoreceptors with their own ________ ___________.
- melanopsin
- visual pigment (melanopsin)
- visual pigment (melanopsin)
100
New cards
half the optic-nerve fibres cross at the _______ ___________.
optic chiasm.