Lab safety & Microscopes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Zacharias Janssen (1590)
He created the design of the compound microscope.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1684)
He is known as the father of microbiology; he viewed the 1st organism and documented different shapes of bacterial cells.
What is the step order of the objective lens of a microscope?
4x (scanning lens)
10x (low power lens)
40x (high power lens)
100x (oil lens)
When should you use the coarse adjustment knobs?
Only use the coarse adjustment knobs on 4x lens.
Base
A platform that supports the microscope.
Arm
Area that connects the body tube to the base of the microscope.
Body tube
Area that transmits light from the head to the eyepiece
Stage
Horizontal platform where the slide with the specimen is placed for observation.
Stage clip
Spring fastener that holds the slide in place.
Top stage control knob
Moves the stage front to back.
Bottom stage control knob
Moves the stage right to left.
Coarse adjustment knob
Moves the stage distance up and down the furthest distance to focus the specimen. You only use with the 4x objective lens.
Fine adjustment knob
Moves the stage distance up and down the shortest distance to focus the specimen.
Revolving nosepiece
Holds the objective lenses and the rotating ring moves each lens into position.
Light source
Projects visible light on to the specimen and is controlled by an ON/OFF switch.
Light intensity control knob
Changes the amount of light illuminating the specimen.
How do you calculate the total magnification?
Objective lens x eyepiece lens magnification = total magnification
*The eyepiece lens is always 10x
Field of view
Refers to the amount of horizontal specimen in focus.
Depth of field
Refers to the vertical distance of the specimen when in focus.
Oil immersion (100x) lens
The closest to the stage and you must use oil when viewing under 100x.
Cocci
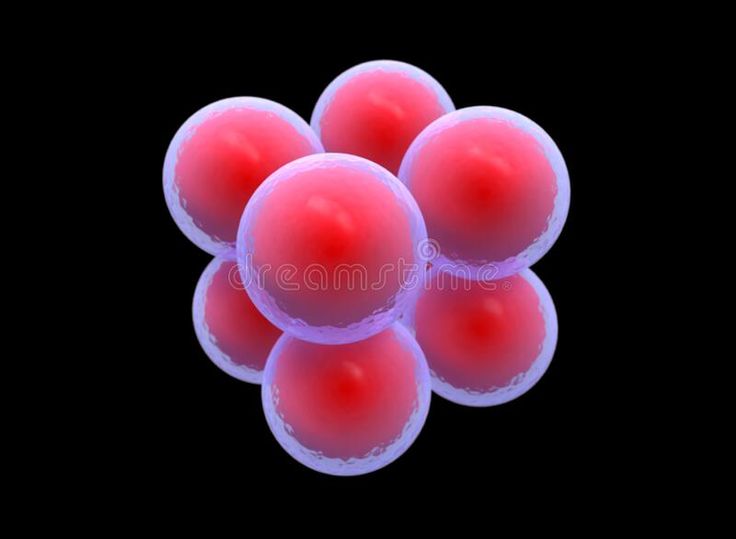
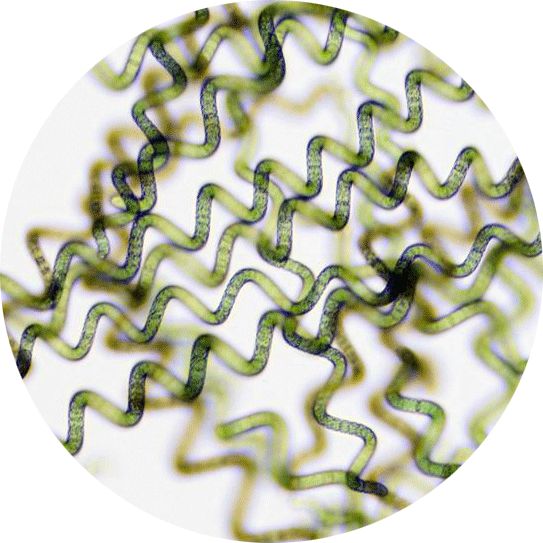
Spirilla

Bacilli