Ch 14- Pulsed Echo Instrumentation
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What are the two major functions of the ultrasound system?
1. preparation and transmission (sending)
2. reception of signals (receiving)
What are the components of the system?
- transducer
- pulser and beam former
- receiver
- display
- storage
- master synchronizer
What is the function of the transducer?
converts electrical energy to acoustic energy and vice versa
What are the functions of the pulser?
excites the PZT
creates sound beams
Is the pulser adjustable?
yes
The pulser controls the brightness of the ____
entire image
What does the pulser determine?
amplitude
PRP
PRF
The pulser is also known as:
output gain
acoustic power
pulser power
energy output
transmitter output
power
gain
Modern machines use ___ ___ or ___ ___
thermal index; mechanical index
Transducer output power is the ability to adjust the ____ of electricity ____ to the PZT
strength (voltage); transmitted
Low voltage results in ____ ultrasound power, ____ echoes, and a ____ image
weak; weak; dark
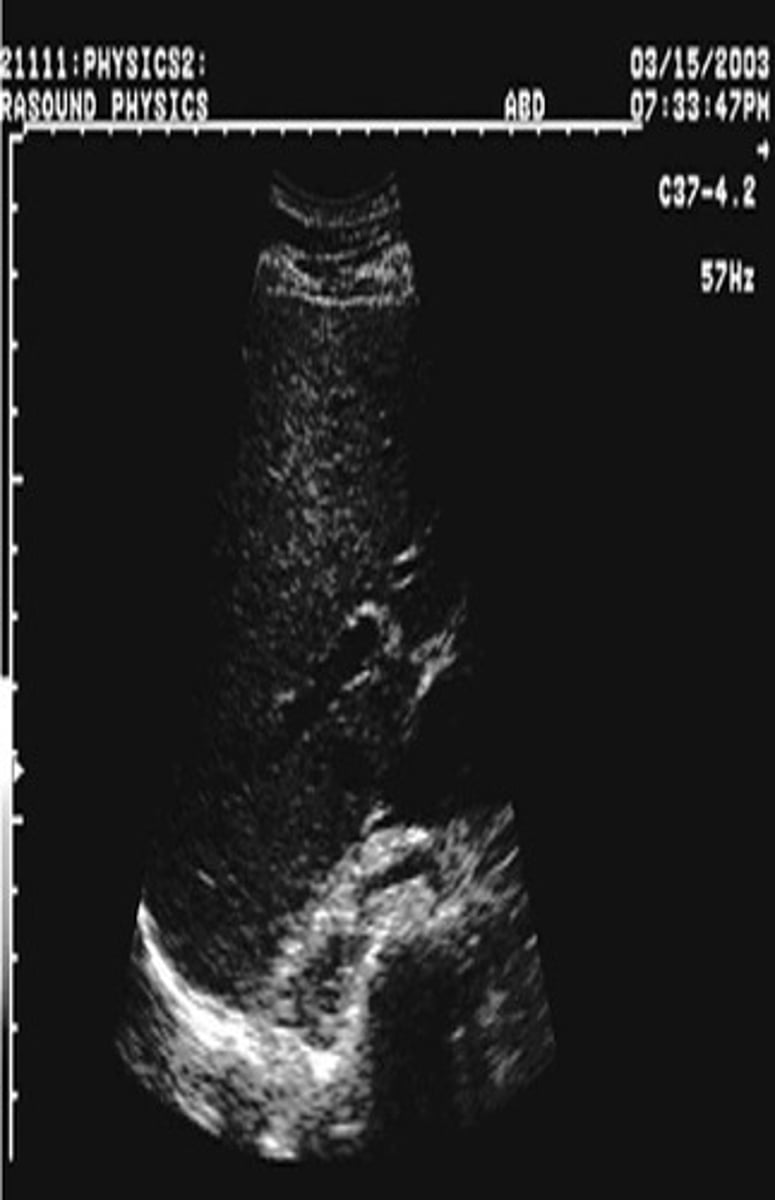
High voltage results in ____ ultrasound power, ____ echoes, and a ____ image
strong; strong; bright
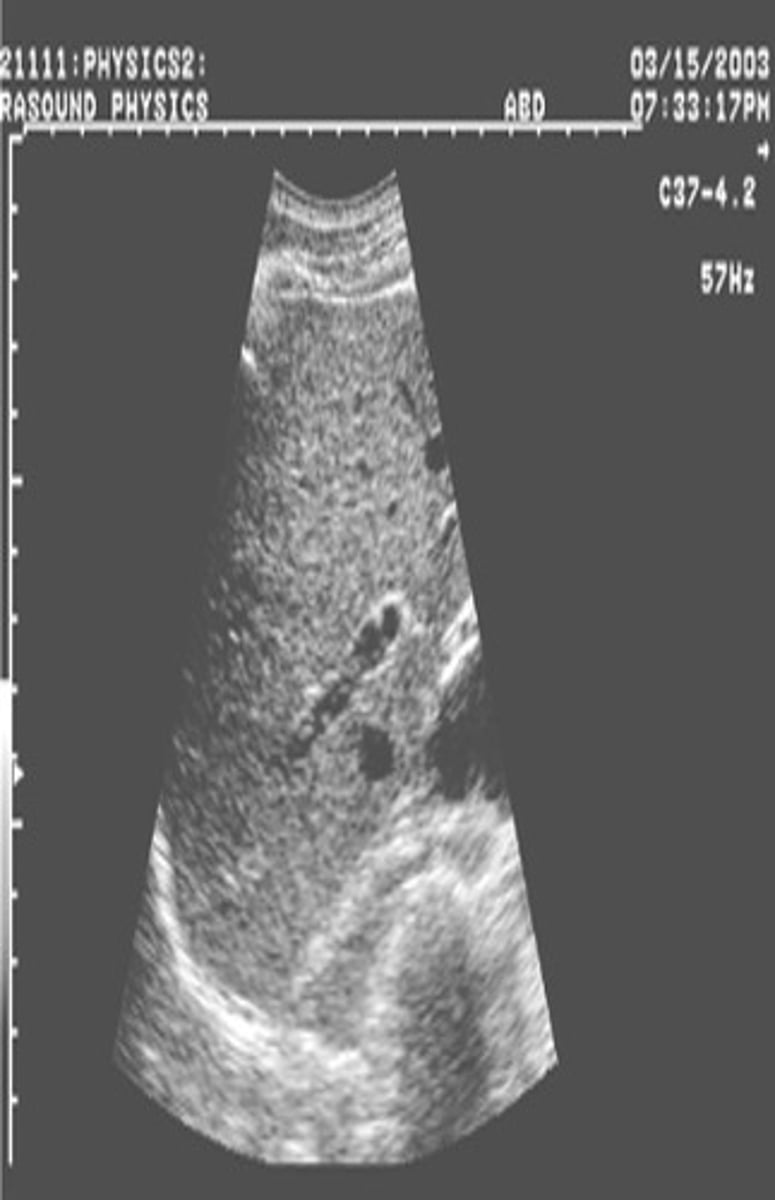
Low voltage is preferred due to ____
bioeffects
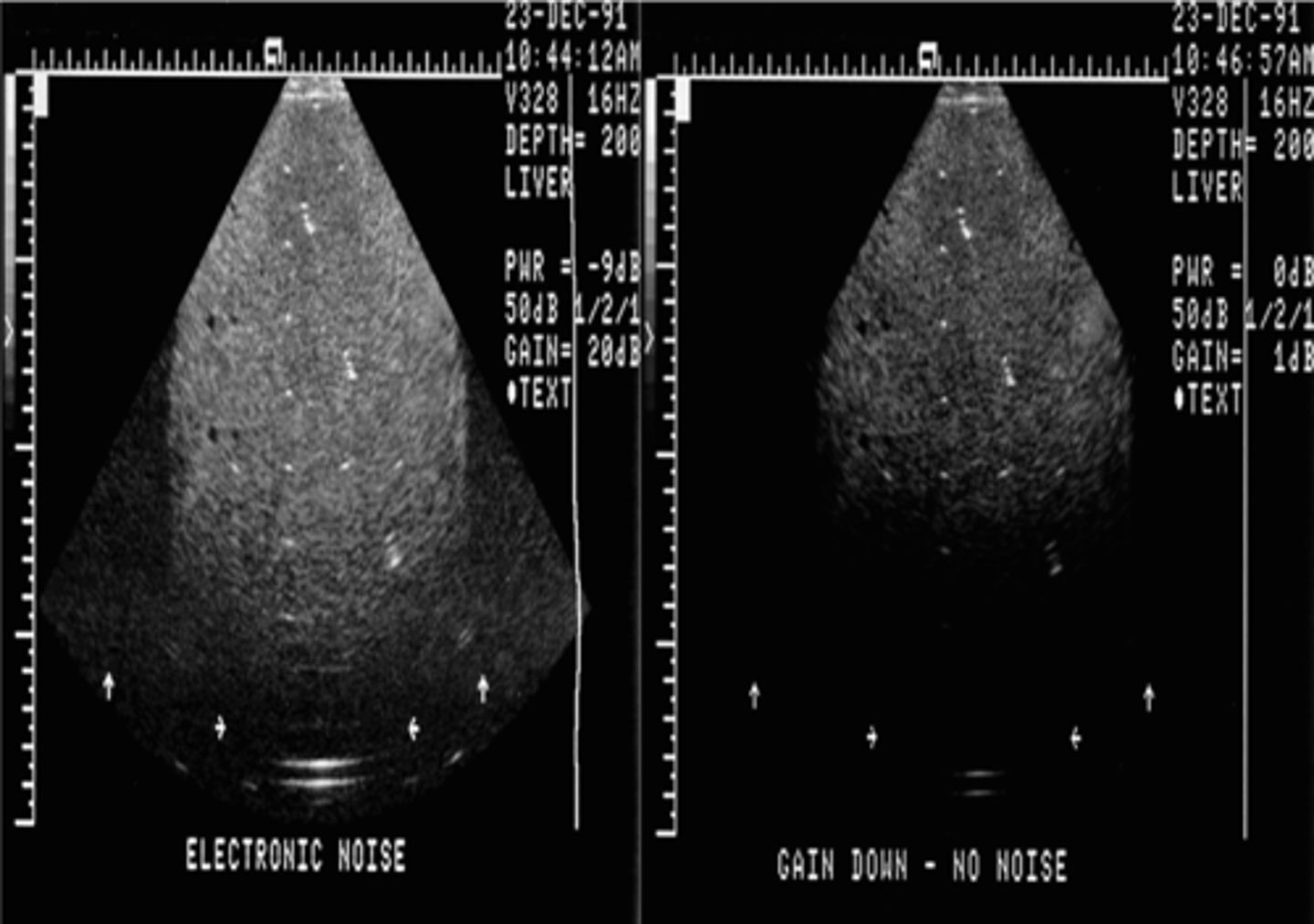
What is noise?
"extra" echoes that degrade the image quality
Noise occurs when voltage output is too ___
low
What is signal-to-noise ratio?
a comparison of the meaningful information (signal) and the amount of noise
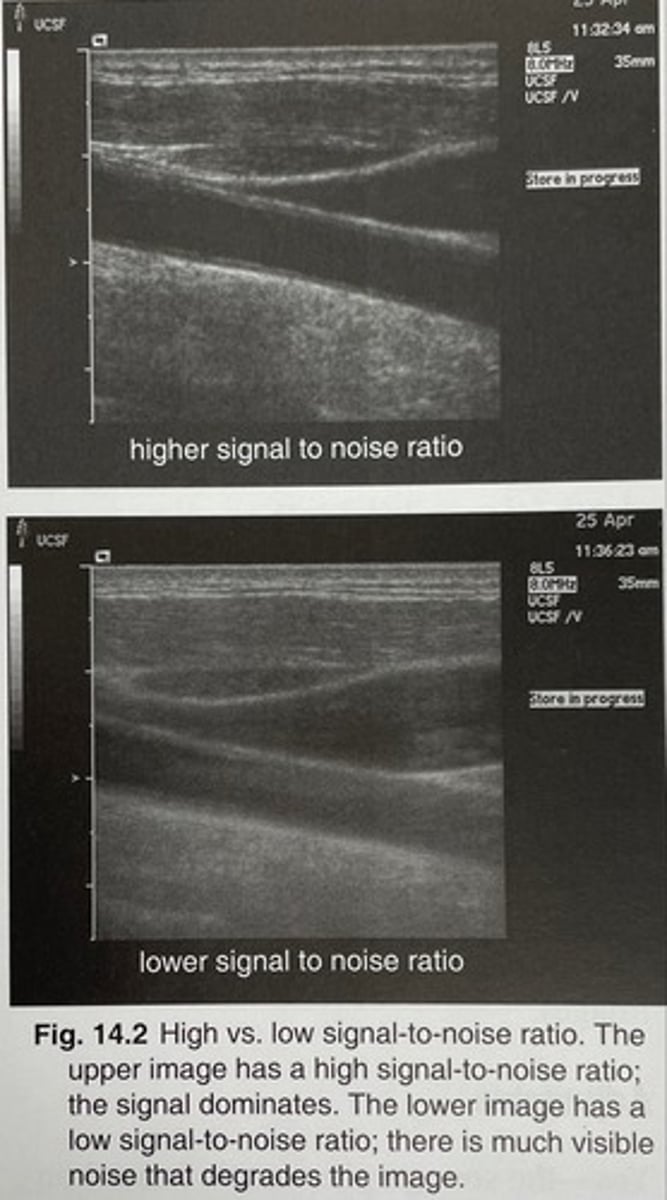
A ____ signal-to-noise ratio = strong signal, low noise
high
A ____ signal-to-noise ratio = weak signal, high noise
low
What is PRP?
one on and off time
What is PRF?
number of pulses per second
PRP and PRF are ____ related and ____
inversely; reciprocals
Shallow imaging results in a ____ PRP and a ____ PRF
short; high
Deep imaging results in a ____ PRP and a ____ PRF
long; low
The beam former is part of the ____, and functions during ____ and ____
transmitter; transmission; reception
The beam former generates the ____ that drive the transducer
voltages
The beam former coordinates electrical signals through ____
apodization
What is apodization?
reduces side and grating lobes- stronger signals in the middle of the beam
The beam former controls ____ during reception
dynamic receive focusing
During transmission, the transmit-receive switch changes ____ voltages from the pulser into ____ voltages to protect the ____
strong; weaker; receiver
During reception, the transmit-receive switch directs electrical signals to the ____
receiver
The transmit-receive switch functions during ____ and ____
transmission; reception
What does the channel consist of?
single PZT
beam former / pulser
wire
Most systems have between ___ and ___ channels
32; 256
The receiver is part of the ____
beam former
The receiver processes the ____ echoes from the patient
returning
Receiver order of operation
1. amplification
2. compensation
3. compression
4. demodulation
5. reject
Amplification is also called ____ ____ or ____ ____
overall gain; receiver gain
Receiver gain changes the brightness of the ____ and does not affect ____
entire image; signal-to-noise ratio
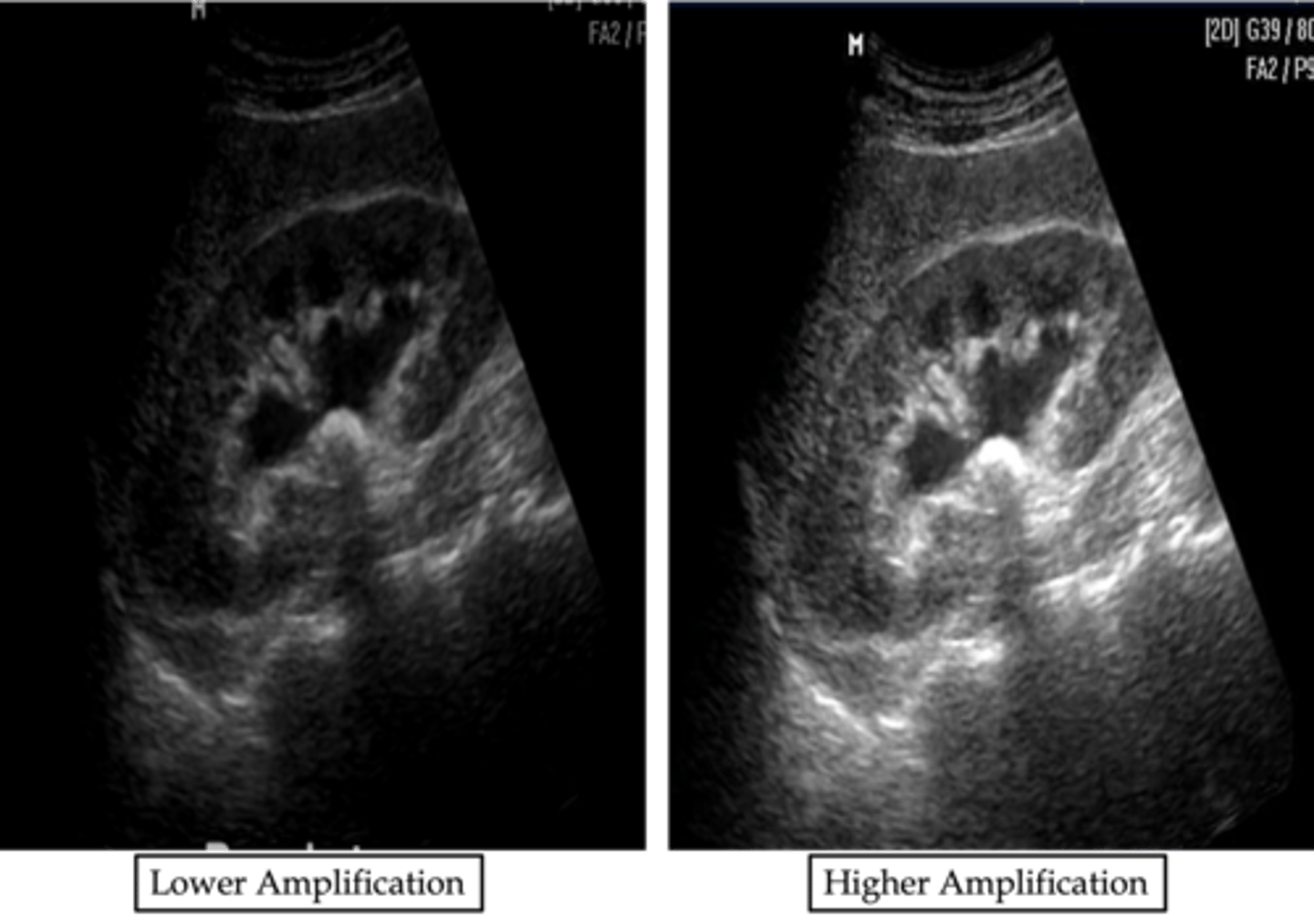
Is receiver gain adjustable?
yes
What are the typical values for receiver gain?
60 to 100 dB
Compensation is also known as ____
time gain compensation (TGC)
Compensation corrects ____ and creates ____ ____ images
attenuation; uniformly bright
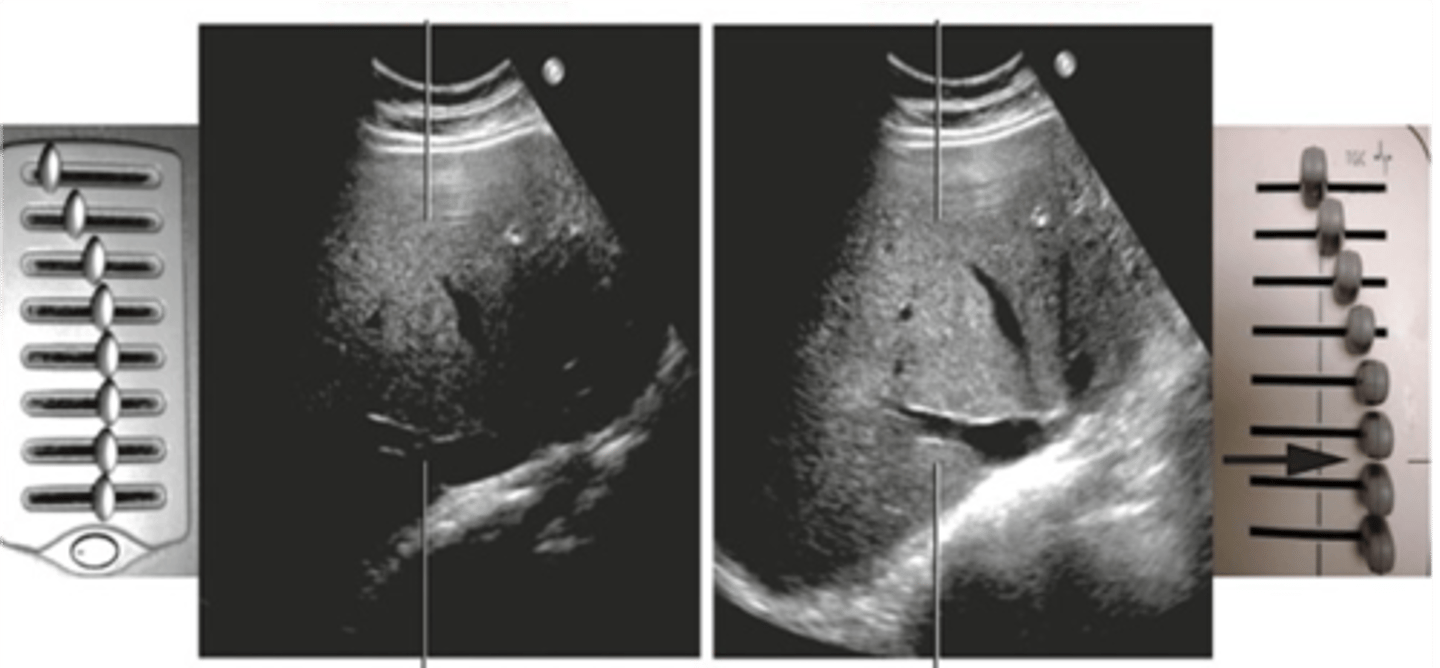
Is receiver compensation adjustable?
yes
What are the units for receiver compensation?
decibels
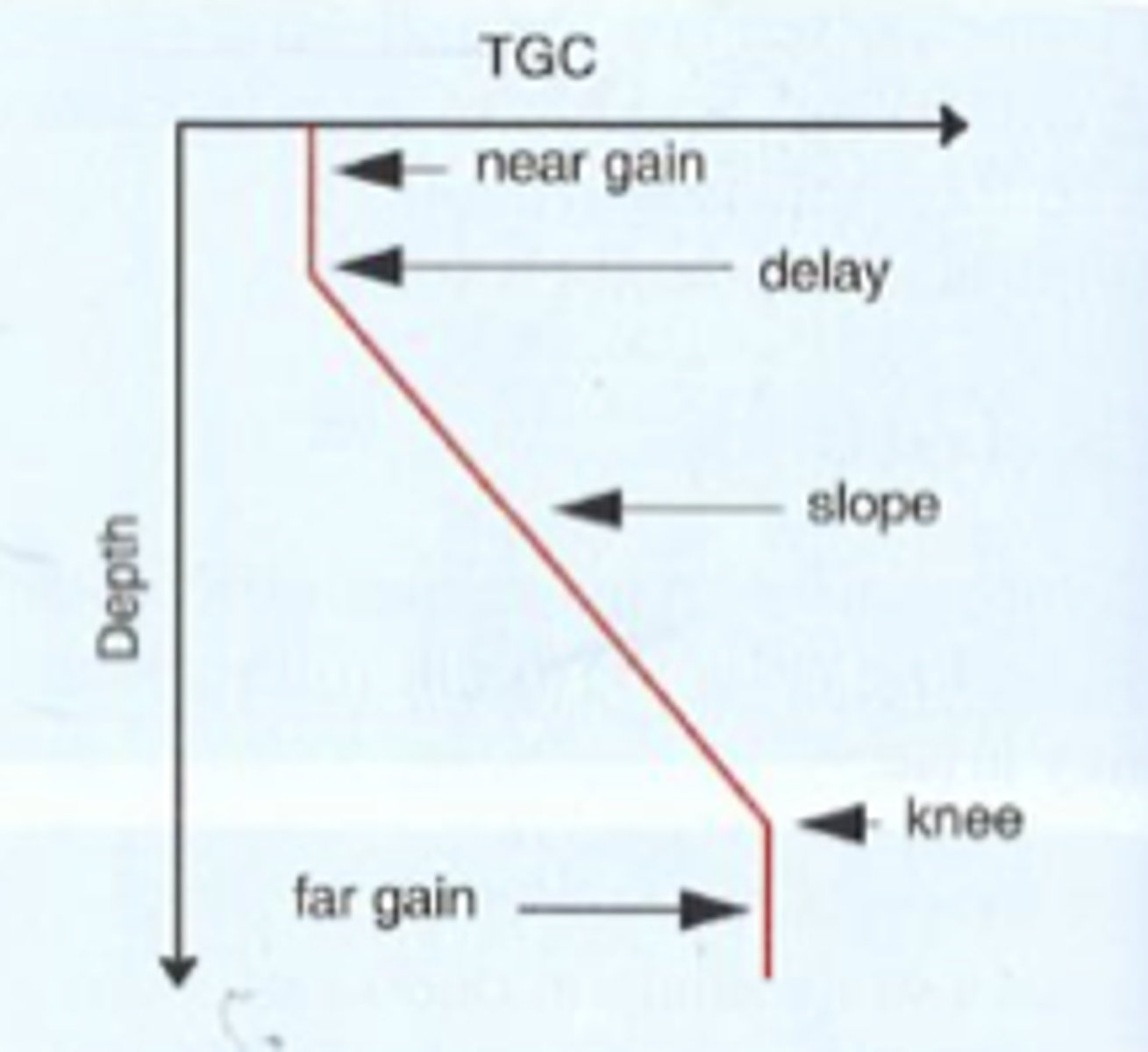
What is the TGC curve in order?
near gain
delay
slope
knee
far gain
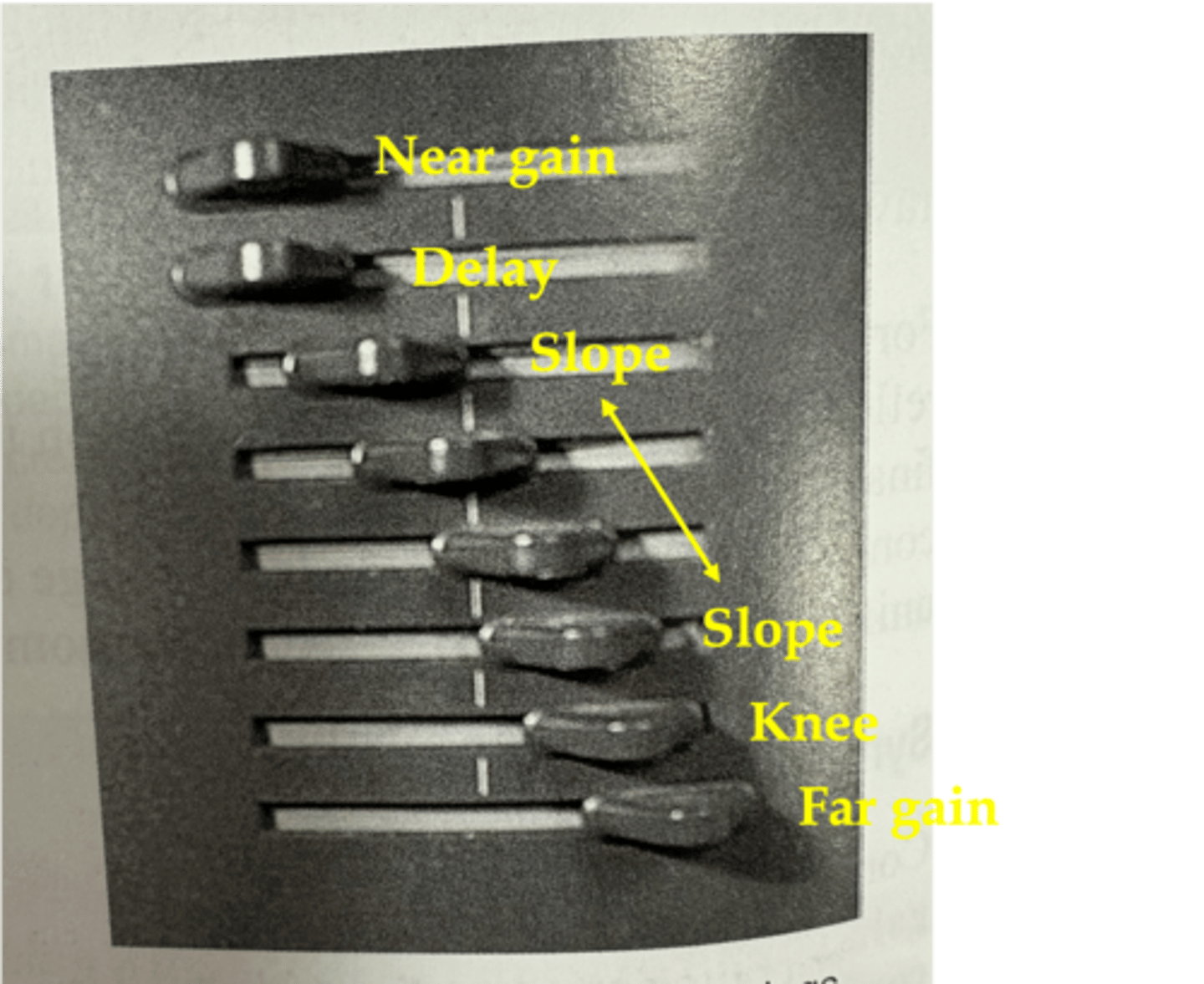
Near gain is at ____ depths with ____ compensation
superficial; constant
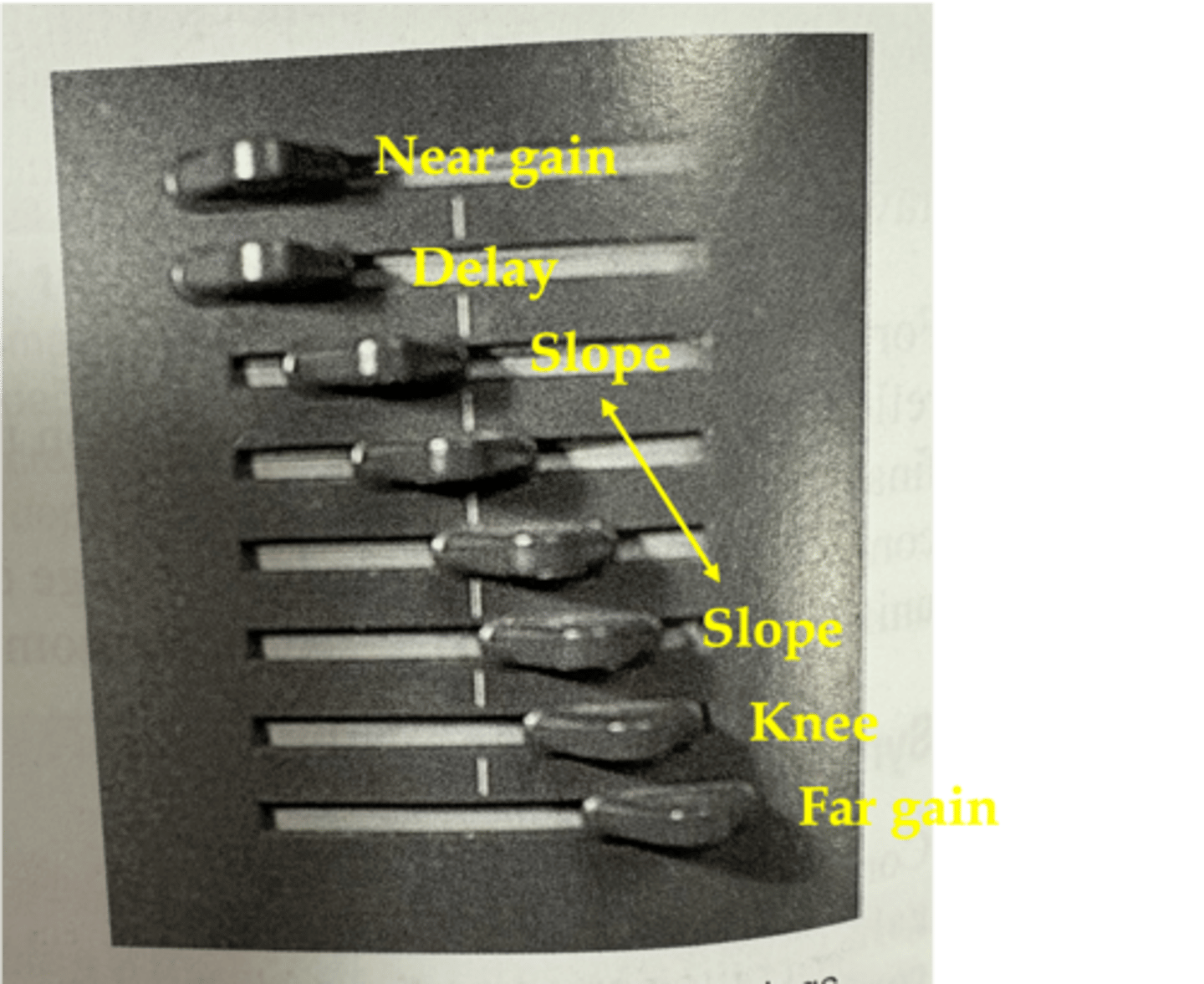
The depth where ____ compensation begins is the delay
variable
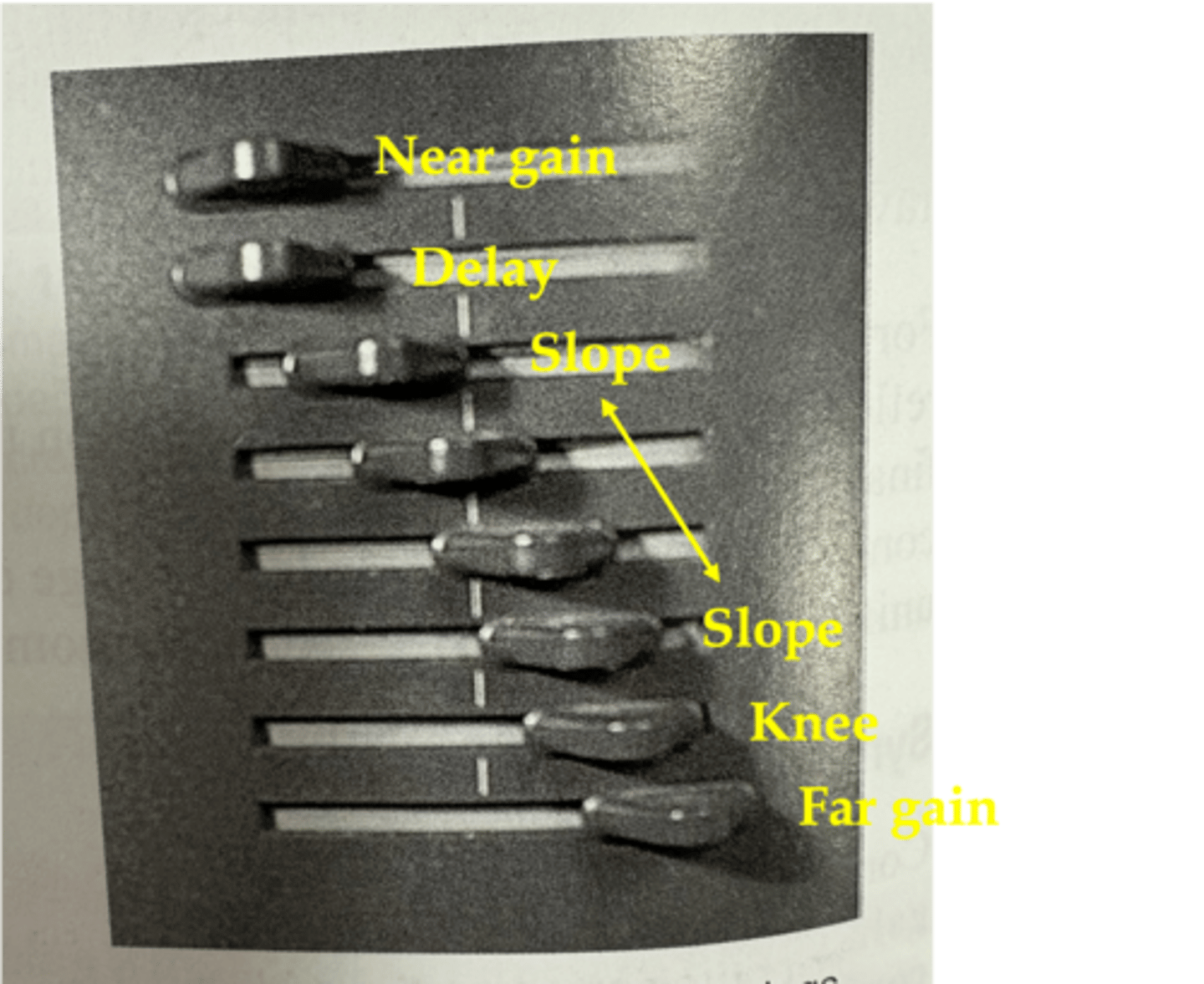
In the region of the slope, compensation corrects for the effects of increasing ____ that result from increasing the ____ ____
attenuation; path length
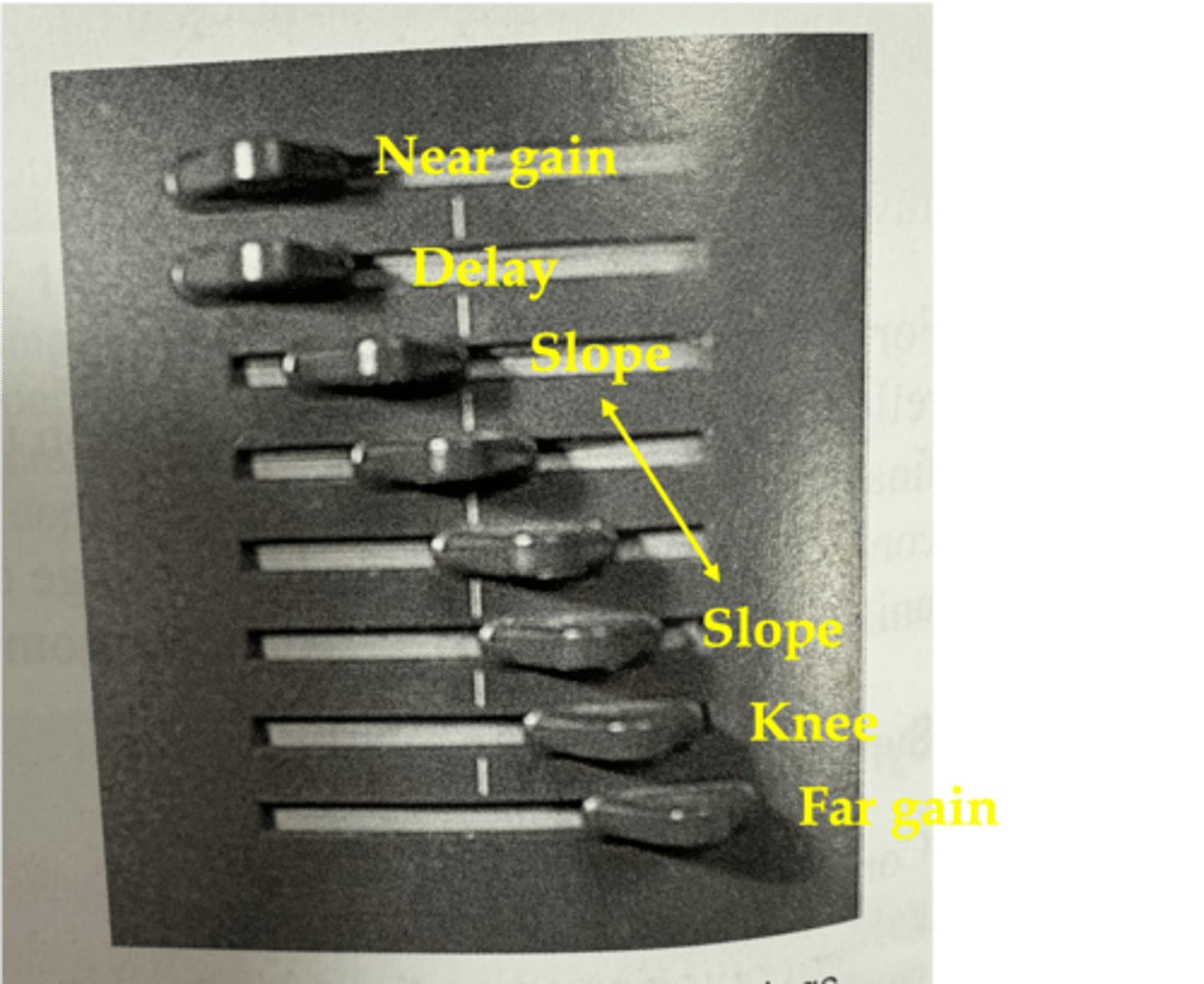
At the depth of the knee, reflections are ____ compensated by the ultrasound system
maximally
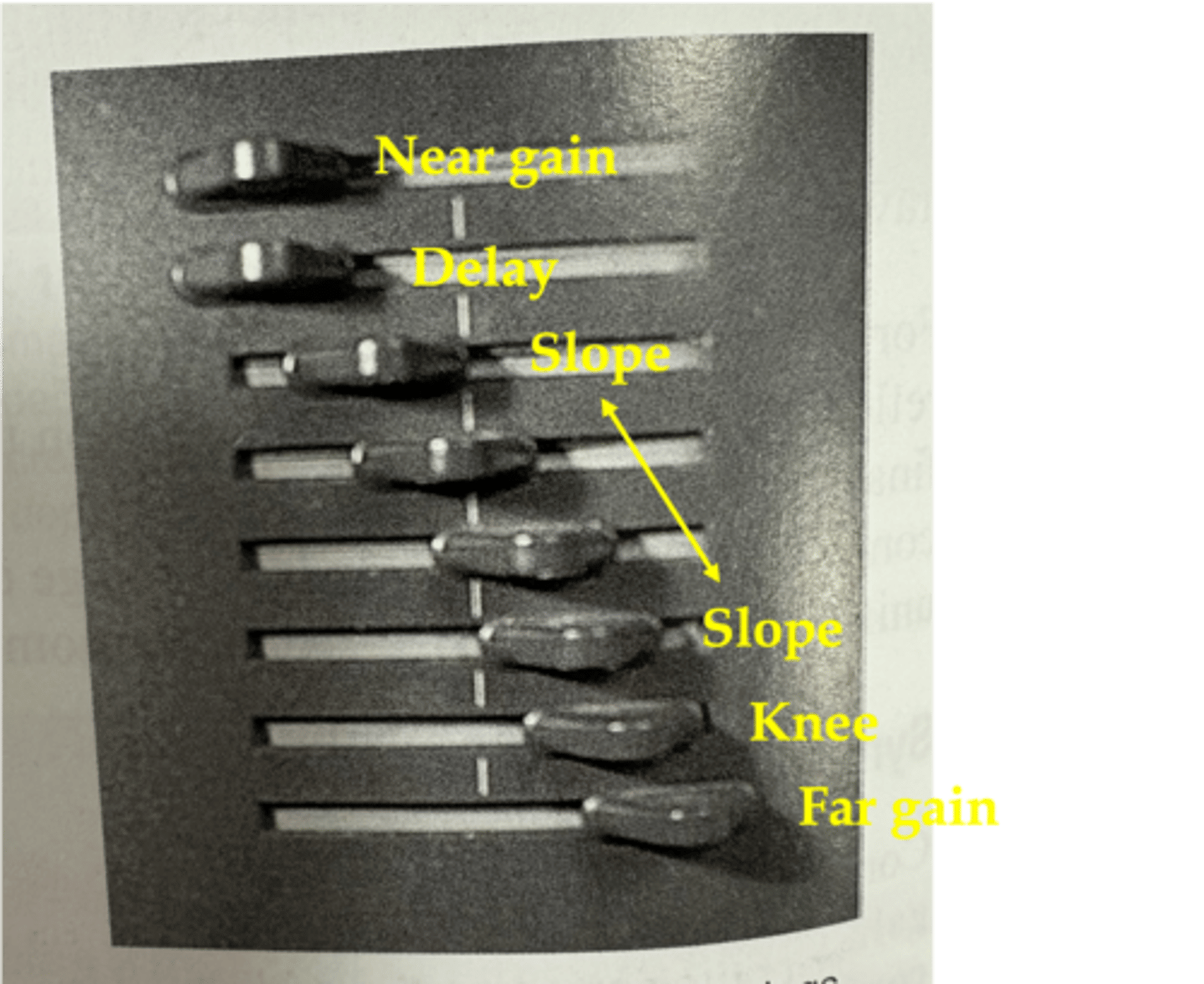
The far gain is the ____ amount of compensation that the receiver can provide
maximum
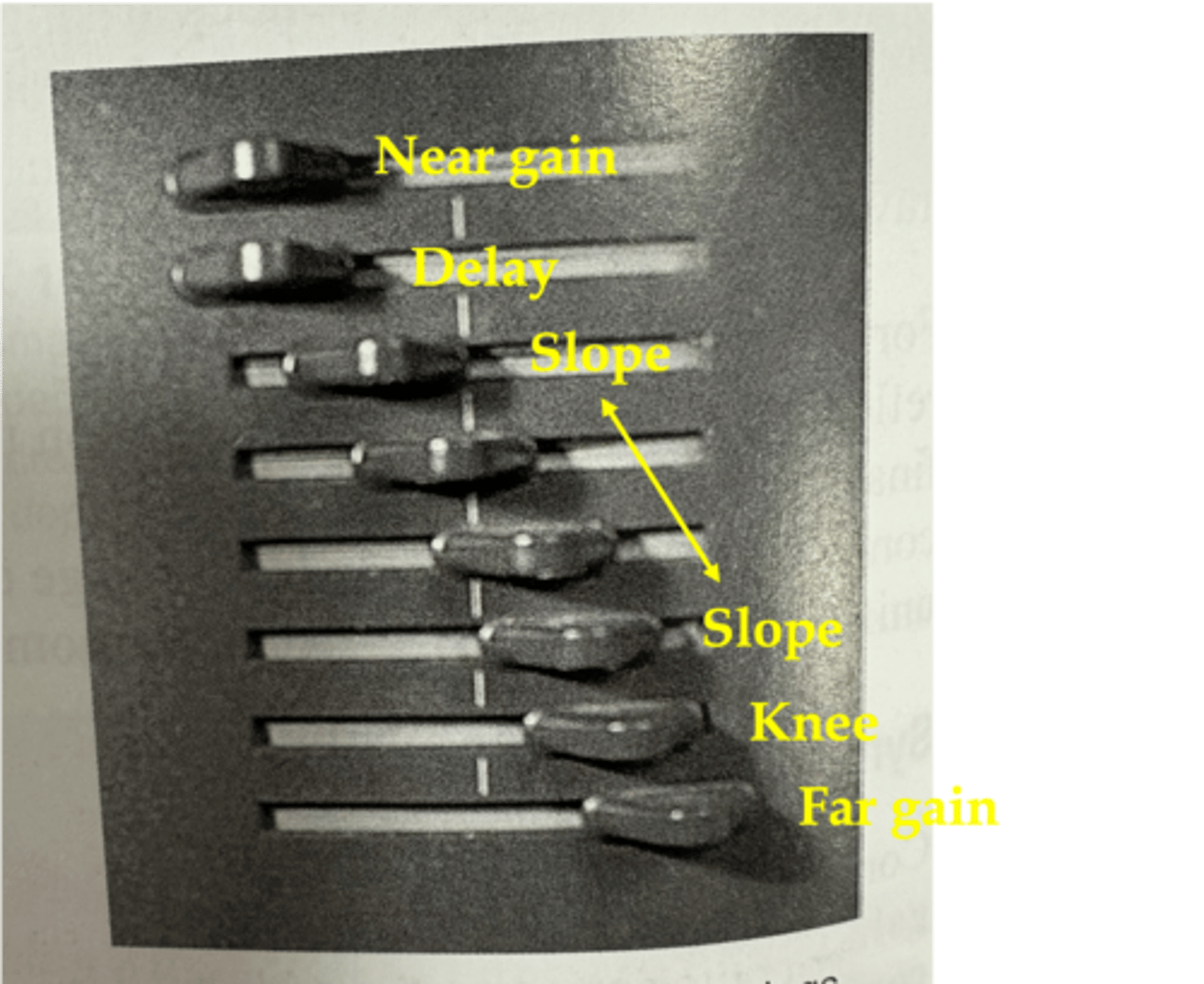
What does a TGC curve look like?
Compression ____ the range of signal amplitudes
decreases
Compression keeps an image's gray scale content within the ____ ____ ____ by the human eye
range of detection
Humans see ___ shades of gray
20
Is compression adjustable? What does it modify?
yes, modifies gray scale mapping
Compression is also called what?
log compression or dynamic range
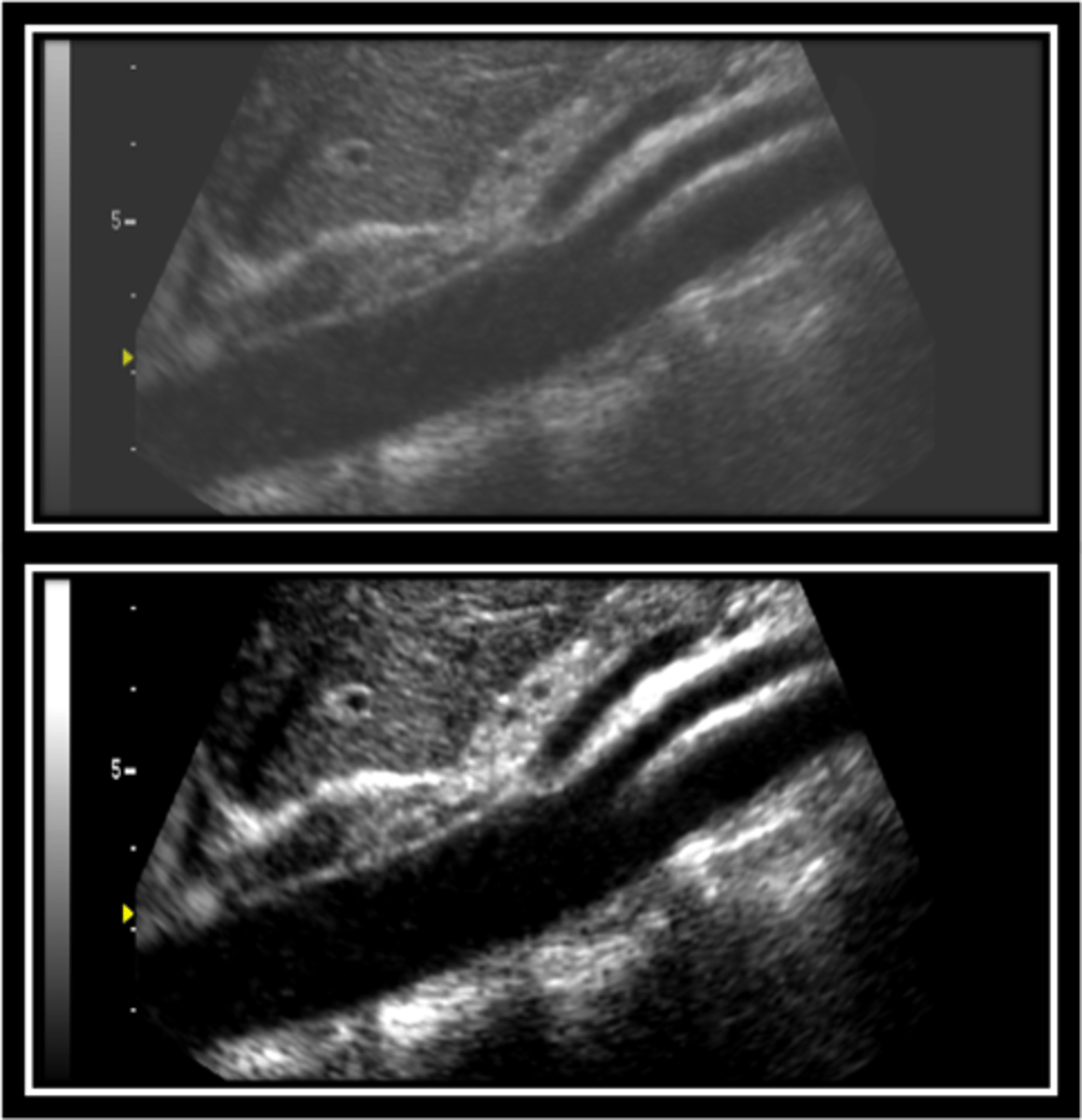
What effect does compression have on an ultrasound image?
less shades of grey, makes image more black and white
Demodulation processes the ____ signals to make it easier for the machine to display
return
What are the two components of demodulation?
1. rectification
2. smoothing
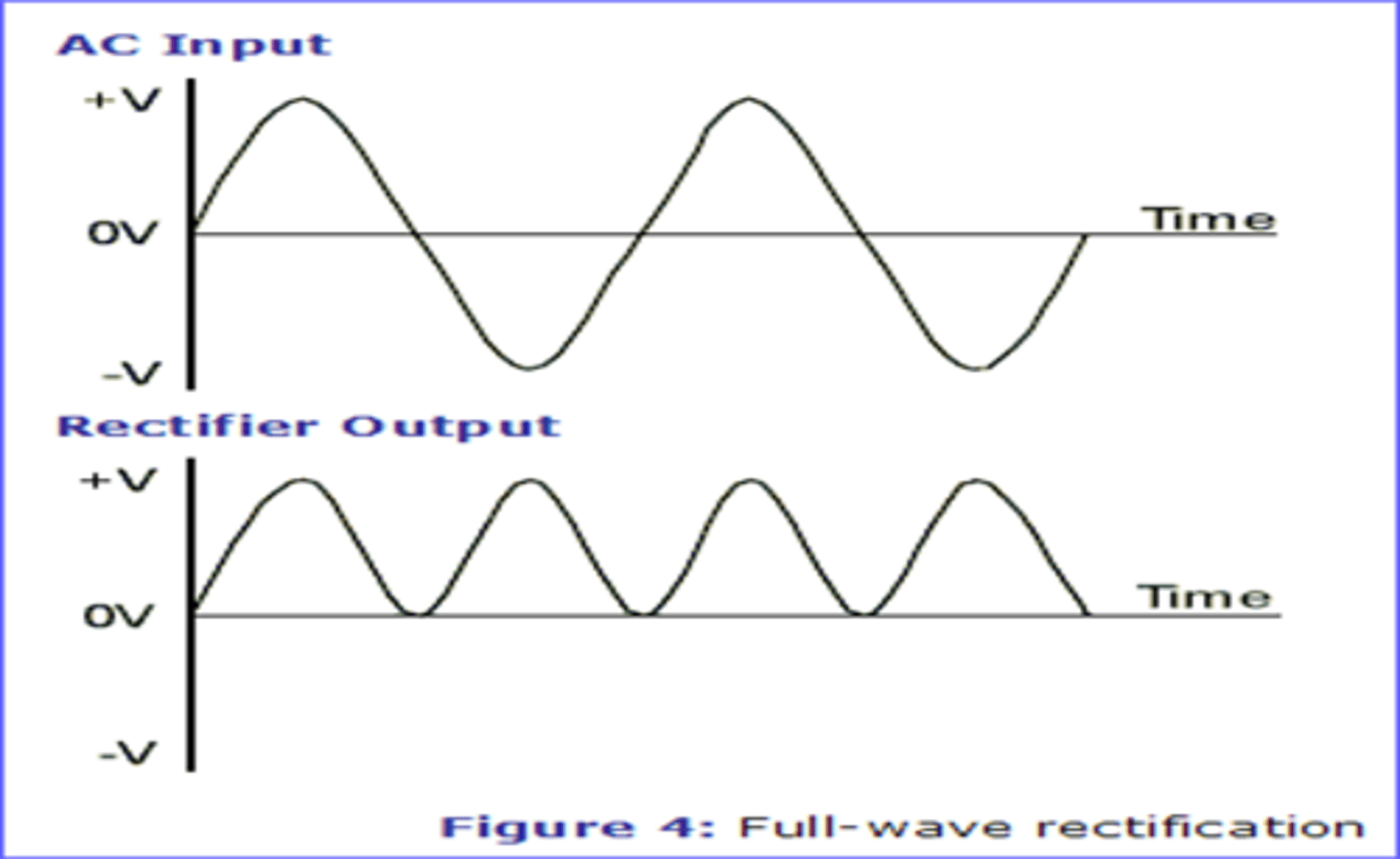
What is rectification?
converts negative voltages to positive voltages
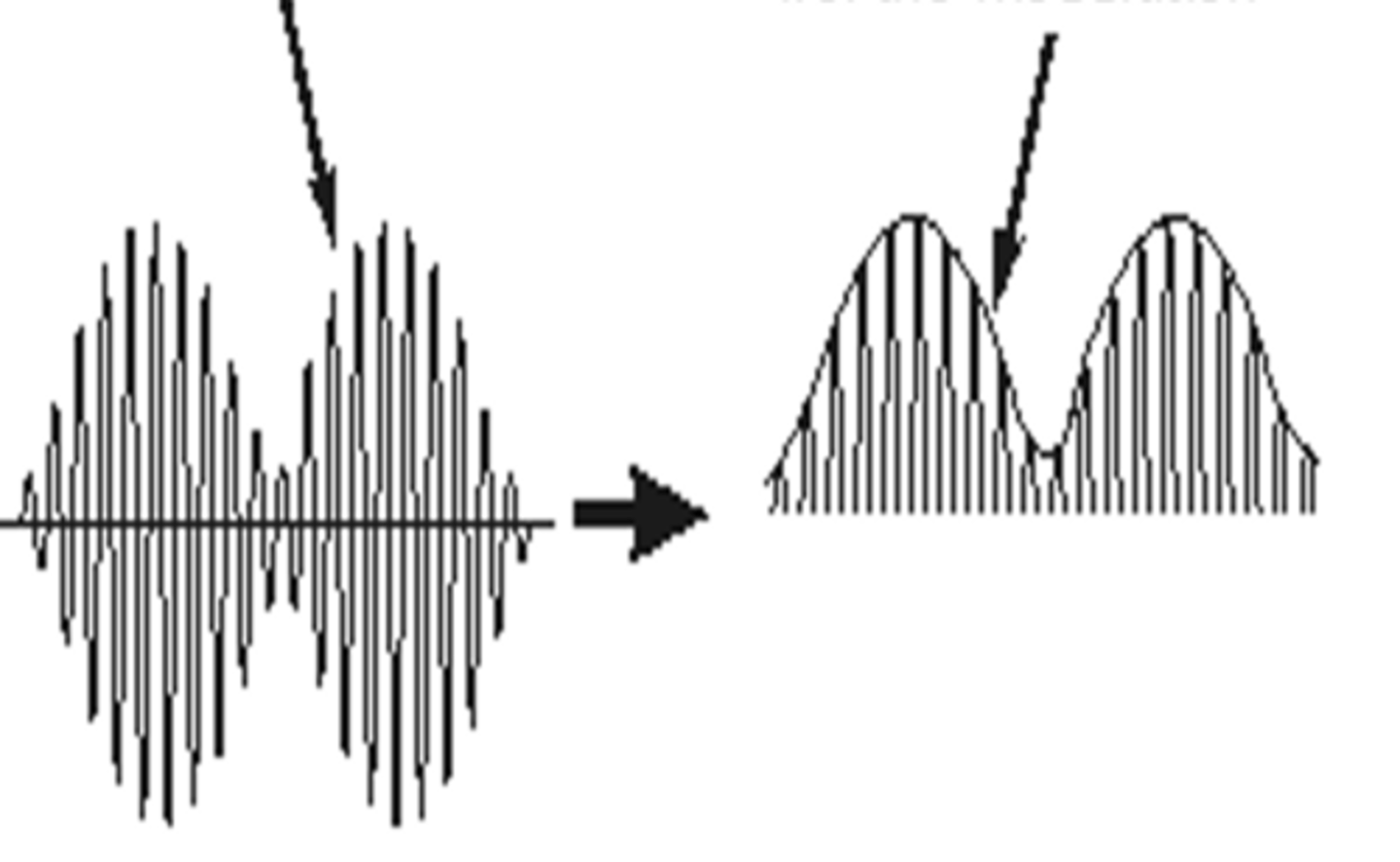
What is smoothing?
places a smooth line around the "bumps" in a signal and evens them out
Does demodulation have an effect on the image?
no, changes electrical signal only
Is demodulation adjustable?
no
What is the function of reject?
eliminates low-level (weak) echoes ONLY
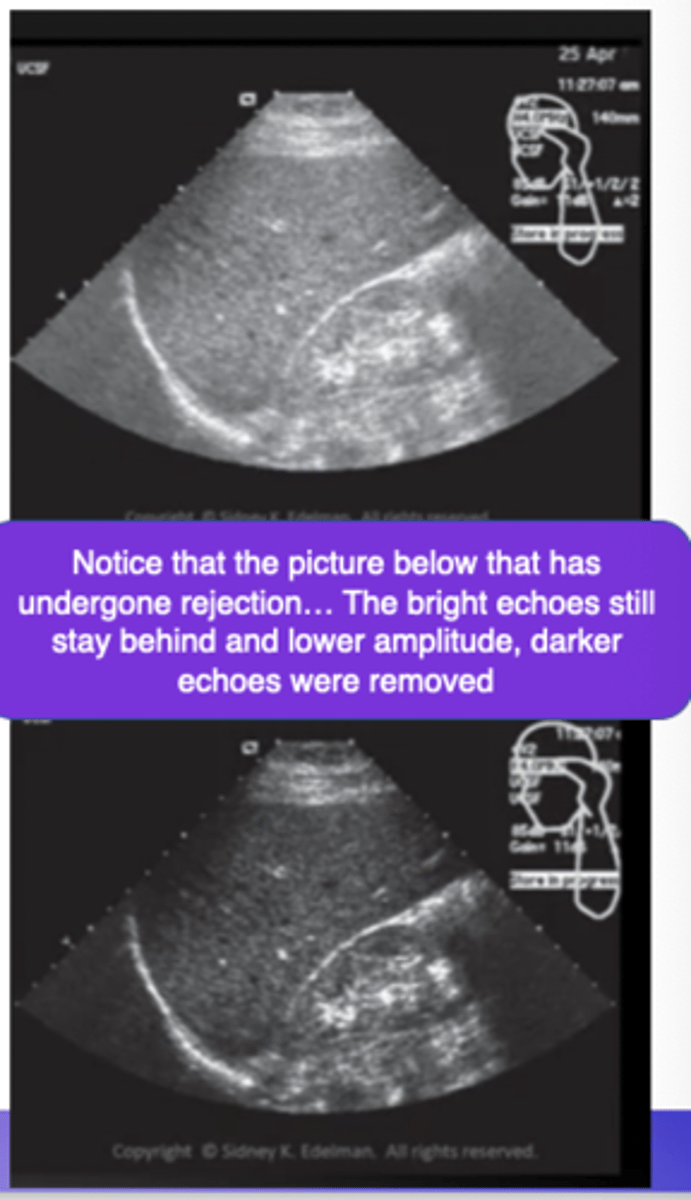
What is reject also called?
threshold
suppression
Is reject adjustable?
yes on SOME systems
Amplification:
- adjustable?
- signals processed
- effect on image
- yes
- all signals treated identically
- entire image gets brighter/darker
Compensation:
- adjustable?
- signals processed
- effect on image
- yes
- signals treated differently based on reflector depth
- image will be uniformly bright from top to bottom
Compression:
- adjustable?
- signals processed
- effect on image
- yes
- signals treated differently depending on strength
- changes grayscale mapping
Demodulation:
- adjustable?
- signals processed
- effect on image
- no
- prepares electrical signals to be suitable for display
- none
Reject:
- adjustable?
- signals processed
- effect on image
- yes
- only weak signals affected
- weak echoes appear or are eliminated from image
Systems with dynamic frequency tuning use only the ____ frequency part of the reflected pulse's bandwidth to create the ____ portion of the image
high; superficial
Systems with dynamic frequency tuning use only the high frequency part of the reflected pulse's bandwidth to create the superficial portion of the image because higher frequency sound has superior ____ ____
axial resolution
The ____ frequency portion of the bandwidth is used to create ____ portions of the image
lower; deeper
Do all systems have dynamic frequency tuning?
no
Output power vs. receiver gain:
- what changes the brightness of the entire image?
- what alters signal-to-noise ratio?
- what alters patient exposure?
- both
- output power
- output power