unit 3 properties of substances and mixtures
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
intermolecular forces
columbic forces, weaker than covalent bonds, creating positive and negative
dipole dipole interactions
polar + polar molecules, increased polarity, create a larger dipole moment
dipole induced dipole
polar + non polar molecules, shift electron density to create both positive and negative, induce dipole by pushing electrons and is temporary
London dispersion forces
non polar + non polar molecules, present in all IMF, lower temp enough to slow energy and form bond connection and turn into liquid, need a lot of IMF, temporary, larger the cloud the more polarizable and the stronger the interaction, need large molecule and enough IMF to hold non polar molecule together to form a liquid
hydrogen bonding
hydrogen + FON, very strong interaction
ion dipole
charged ion + polar molecule with dipole moment, dissolves
properties explained by IMF
when IMF are high: melting/boiling point (up), vapor pressure (down), volatility (down), surface tension (up), viscosity (up), heat of vaporization (up)
strength of IMF if size is similar
hydrogen bonding > dipole dipole > London dispersion forces
larger molecules
impact of LDF grows
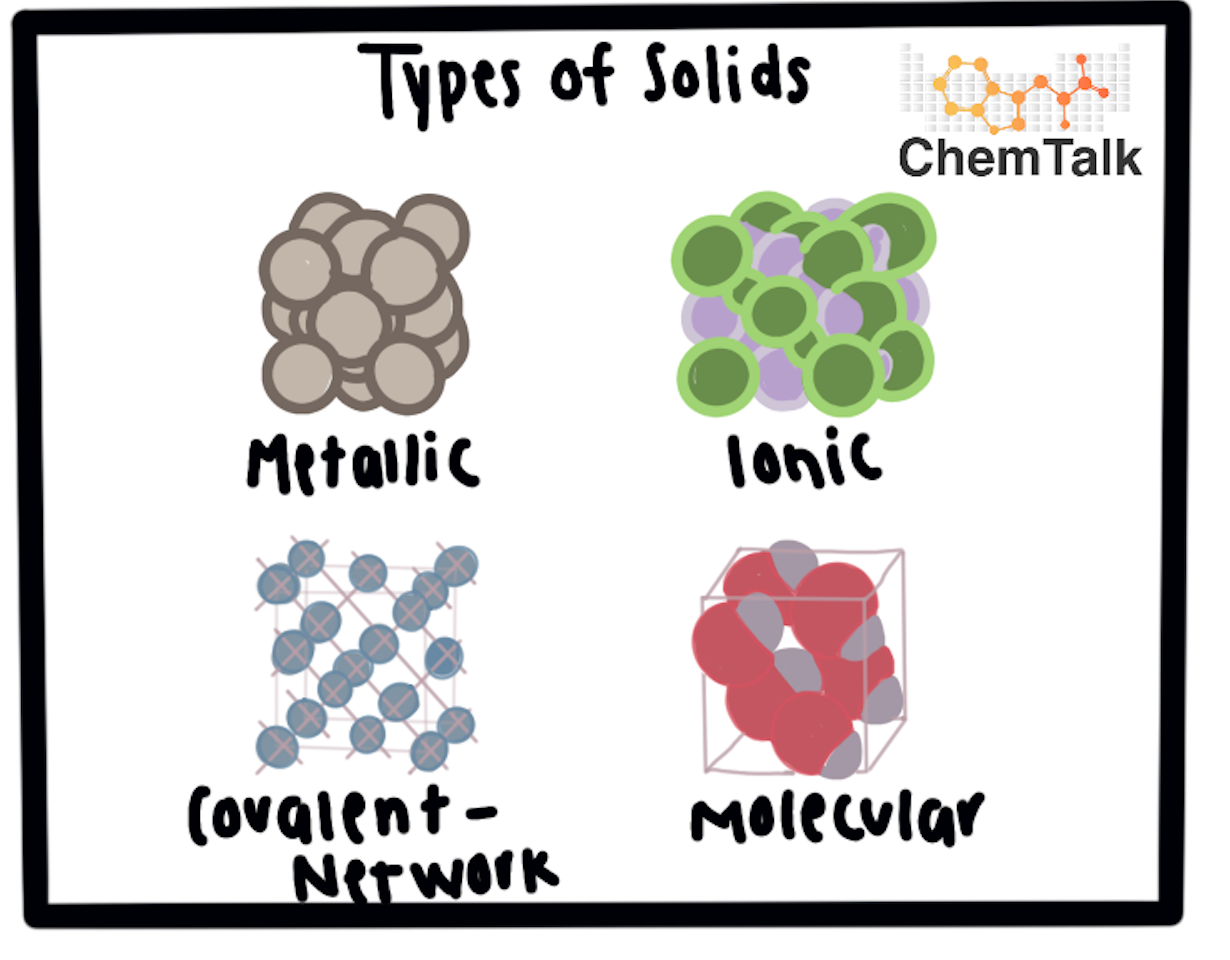
4 types of solids
ionic, molecular, covalent network, metallic
brittle
if when subjected to stress it fractures with little elastic deformation and little plastic deformation
electricity
flow of electrons and charge
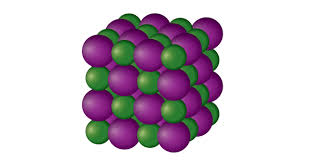
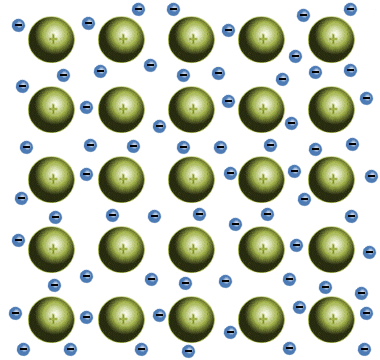
ionic solids
cations and anions arranged in repeating pattern, high boiling and melting, very brittle, cannot conduct electricity unless disolved in H2O, intra and inter strong
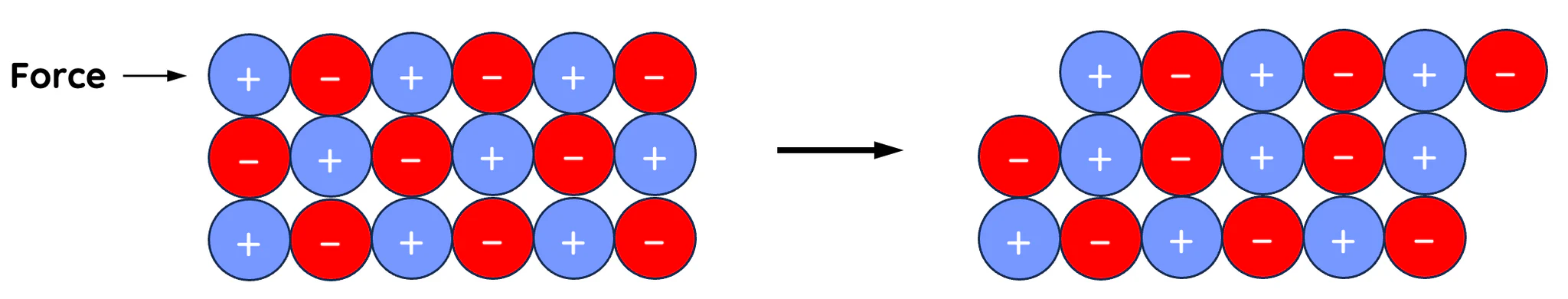
lattice distorted
everything shifts and breaks
molecular solids
neutral molecules form molecular lattice structures, boiling and melting low, cannot conduct electricity (uncharged), intra strong, inter weak
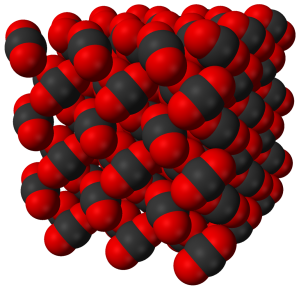
covalent network solids
distinct atoms bonded together covalently in 3D network, presence of metalloid (B, Si, Ge) or Diamond and Graphite, high melting, cannot conduct electricity
metallic solids
sea of electrons, variable melting, malleable and ductile, great conductor
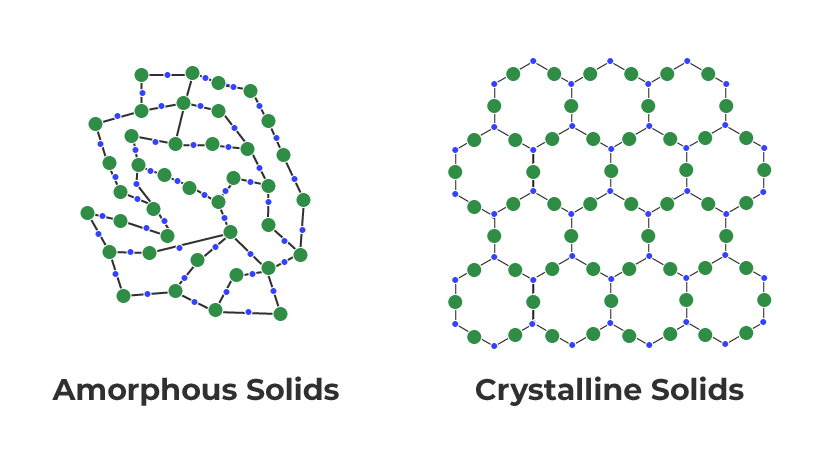
solids
crystalline or amorphous, motion limited, molecules tightly packed
liquids
particles in close contact, molecules spread out
gas
constant motion, frequencies and spacing change
pressure
number and force of collisions with container
temperature
average kinetic energy energy of molecule, increased pressure
volume
amount of space in container
kinetic energy
½ (mass)(velocity)²
effect of volume on pressure
volume up, pressure down (larger space, less collisions)
effect of number of particles on pressure
less particles, less pressure, less collision
effect of temperature on pressure
higher temperature, higher pressure, molecules faster, more collisions
ideal gas law
PV=nRT
principles of ideal gas law
particles in constant, random motion; volume of 1 particle is zero compared to total volume; no attractive forces; collisions conserve kinetic energy; average kinetic energy is directly proportional to absolute temp
what temperature does molecular motion cease at
0 degrees kelvin
same temperature different mass
heavier molecules slower, narrower distributed; lighter molecules faster, wider distribution
same gas different temperature
higher temperature=higher velocity, wider distribution, lower temperature=lower velocity, narrower velocity
kinetic molecular theory
what makes ideal gas law work
how does pressure and size compare between real and ideal
attractive forces cause pressure down, and reduced collisions with wall, larger size has larger pressure
comparisons between ideal and non ideal
temp: higher and lower, pressure: lower and higher, IMF: insignificant, significant, size: smaller and larger