A-Level Physics Materials
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Density of a substance
the mass per unit volume of a substance
density formula
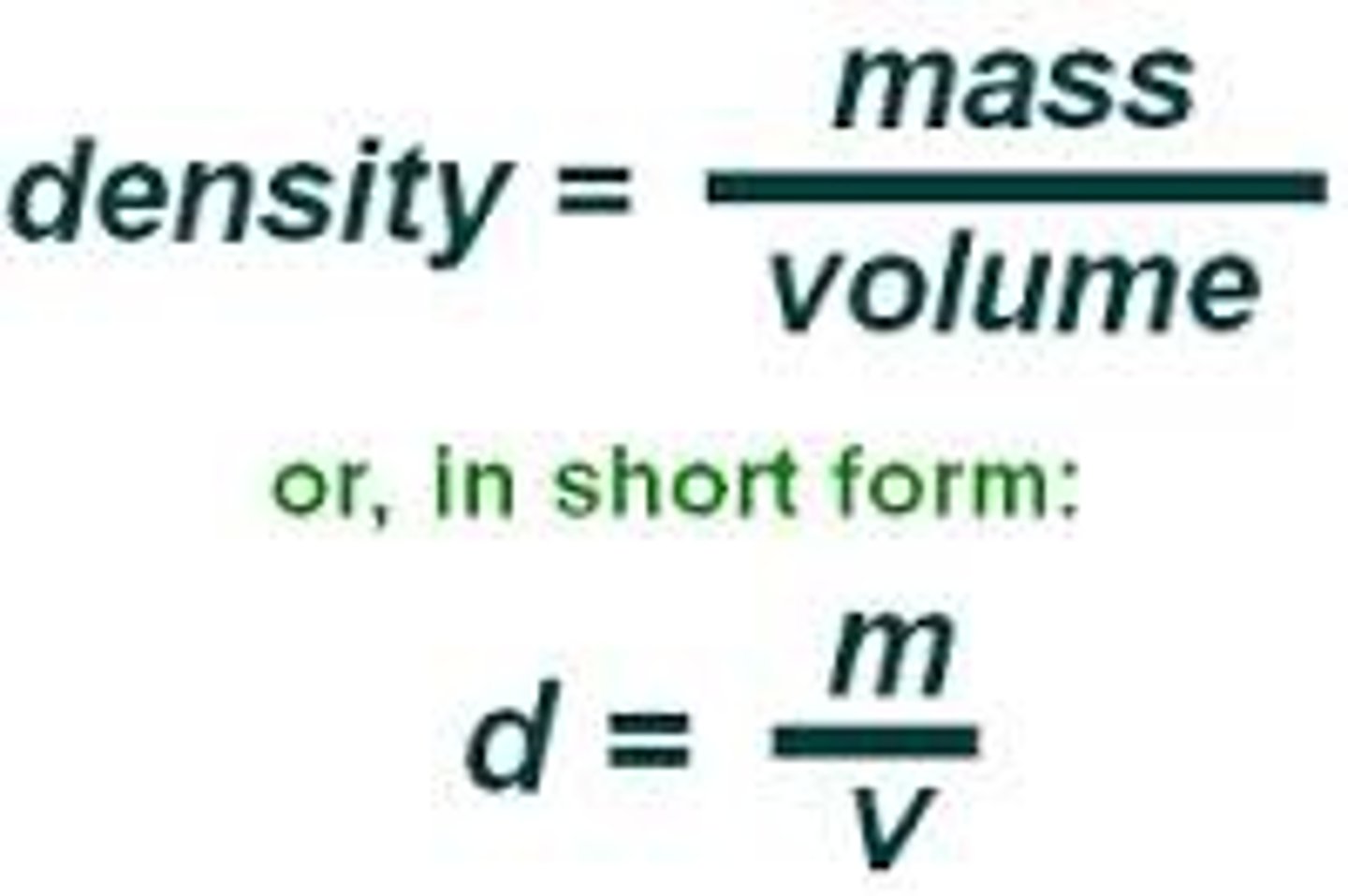
density of alloy formula
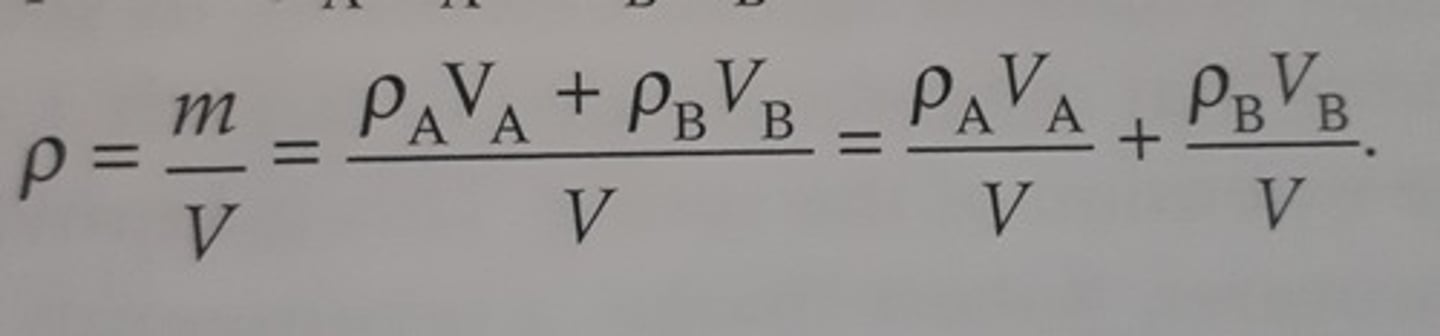
Measuring density of a regular solid
1) Use a scale to measure mass
2)Measure its volume.
6) Use the formula for density
Measuring density of a liquid
1) Place a measuring cylinder on a balance and set it to zero
2) Pour 10ml of the liquid into the measuring cylinder, record the mass
3) Continue until you reach the maximum of the cylinder (10ml)
4) For each measurement, use the density.
5) Finally take an average of all your calculated density.
Measuring density of irregular solid
Measure mass of object using top pan balance.
Place in eureka can.
Volume of water displaced= volume of object.
Use density equation,
What does Hooke's Law state?
The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied, as long as its limit of proportionality is not exceeded.
What happens to the relationship in Hooke's Law once the limit of proportionality is exceeded?
The relationship turns non-linear.
Hooke's Law Equation

Hooke's Law graph
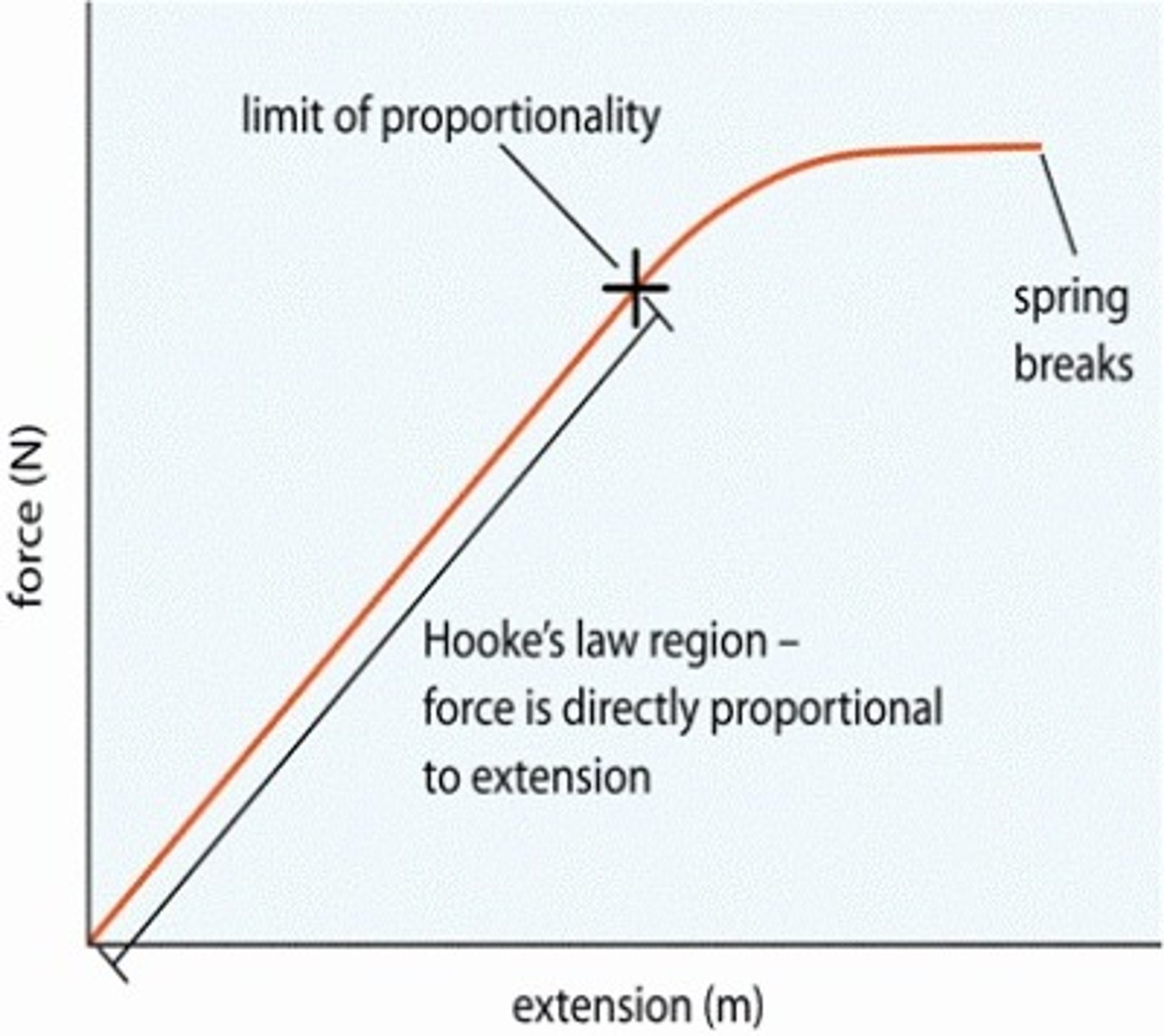
What does a steeper gradient show
That the spring is stiffer because more force is applied for the same extension to occur as for a less stiff spring
Work done on spring formula
force*extension
Energy stored in spring=
or 1/2 fe
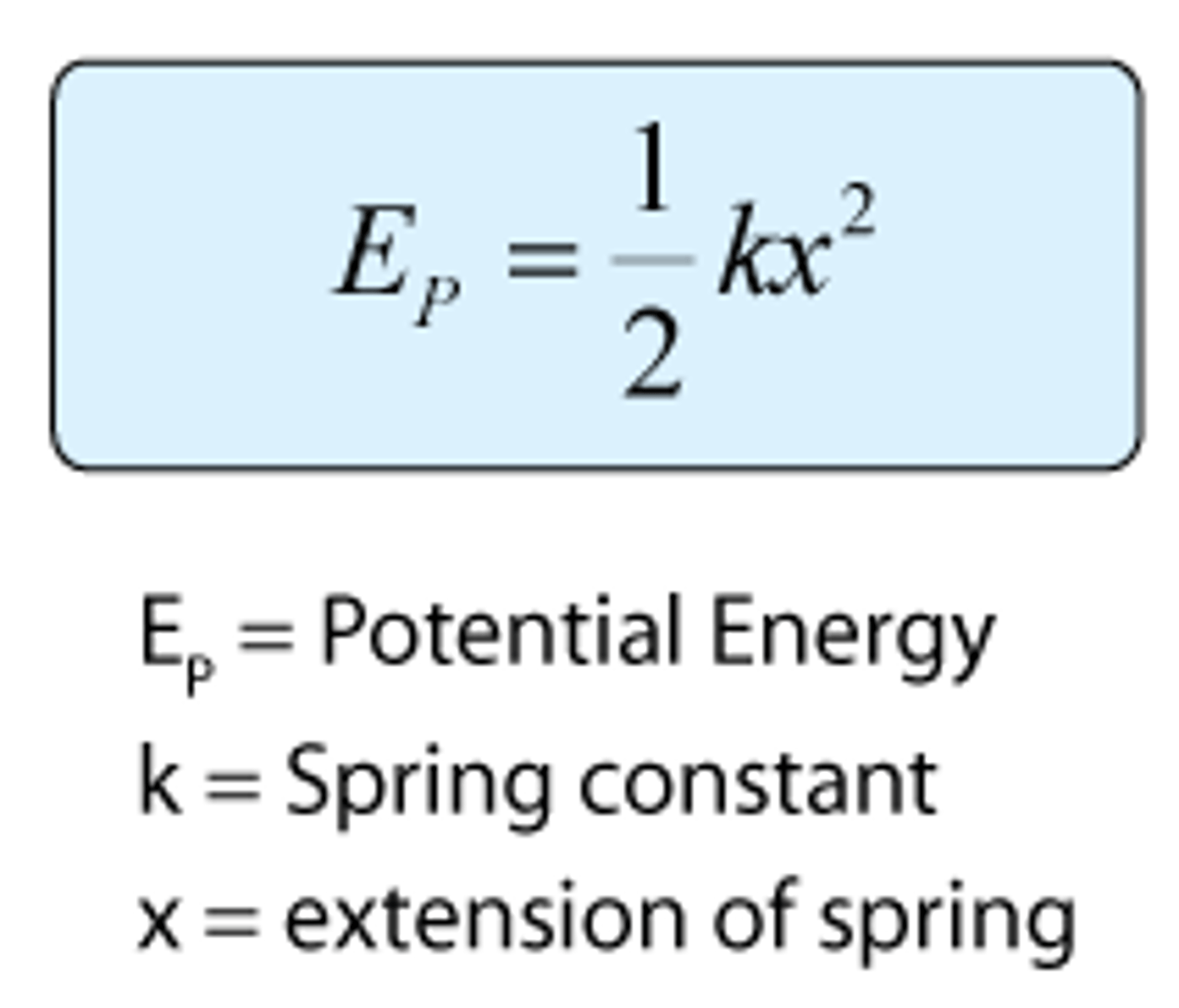
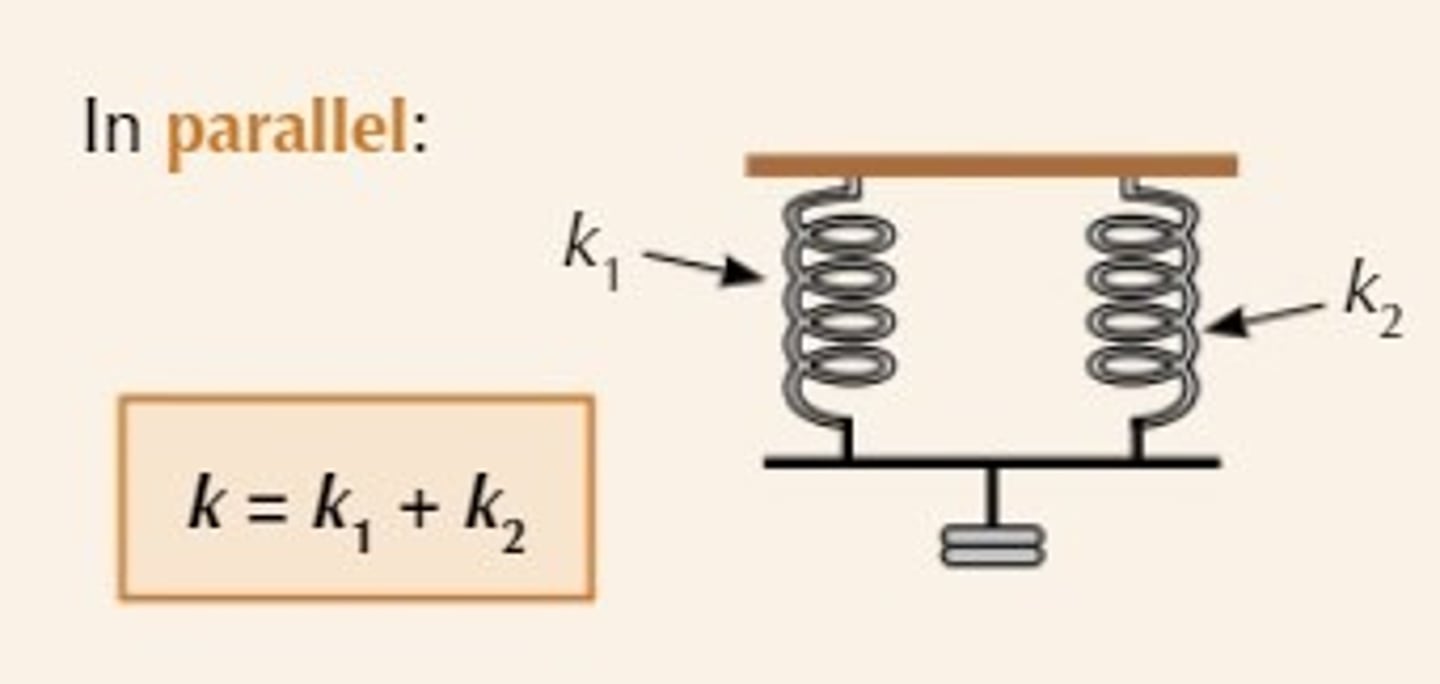
Springs in parallel
keq = k1 + k2
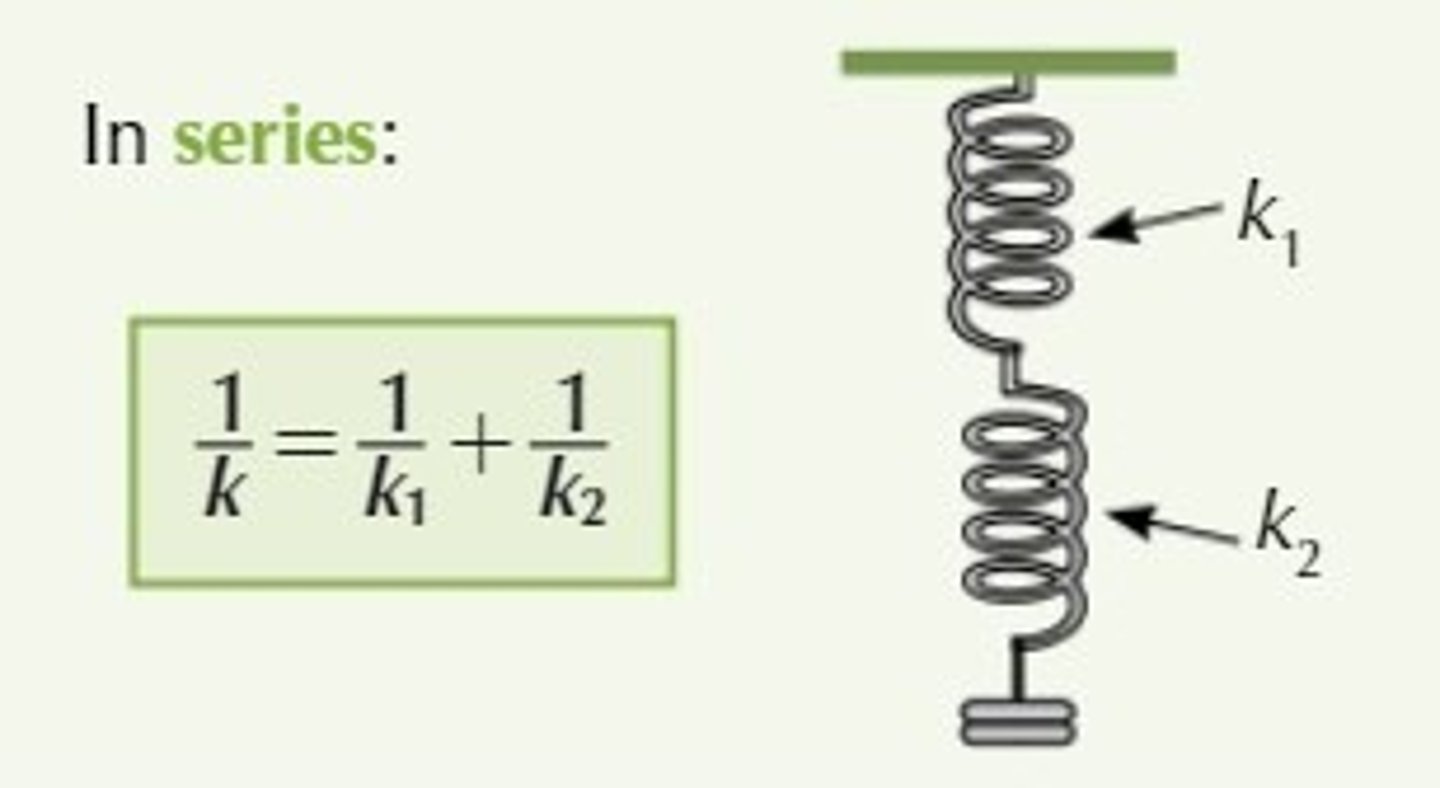
Springs in series
Comparing springs in parallel to springs in series
Springs in Series: The effective spring constant is halved, so for the same displacement, the force is lower compared to a single spring.
Springs in Parallel: The effective spring constant is doubled, resulting in a higher force for the same displacement.
Therefore more force is required for the same extension to occur compared to the springs in series
Elasticity definition
Ability to regain shape after it has been deformed or distorted and forces that deformed it have been released.
deformation that stretches an object is
tensile
deformation that compresses an object is
compressive
Tensile stress equation
F/A
(Pa)
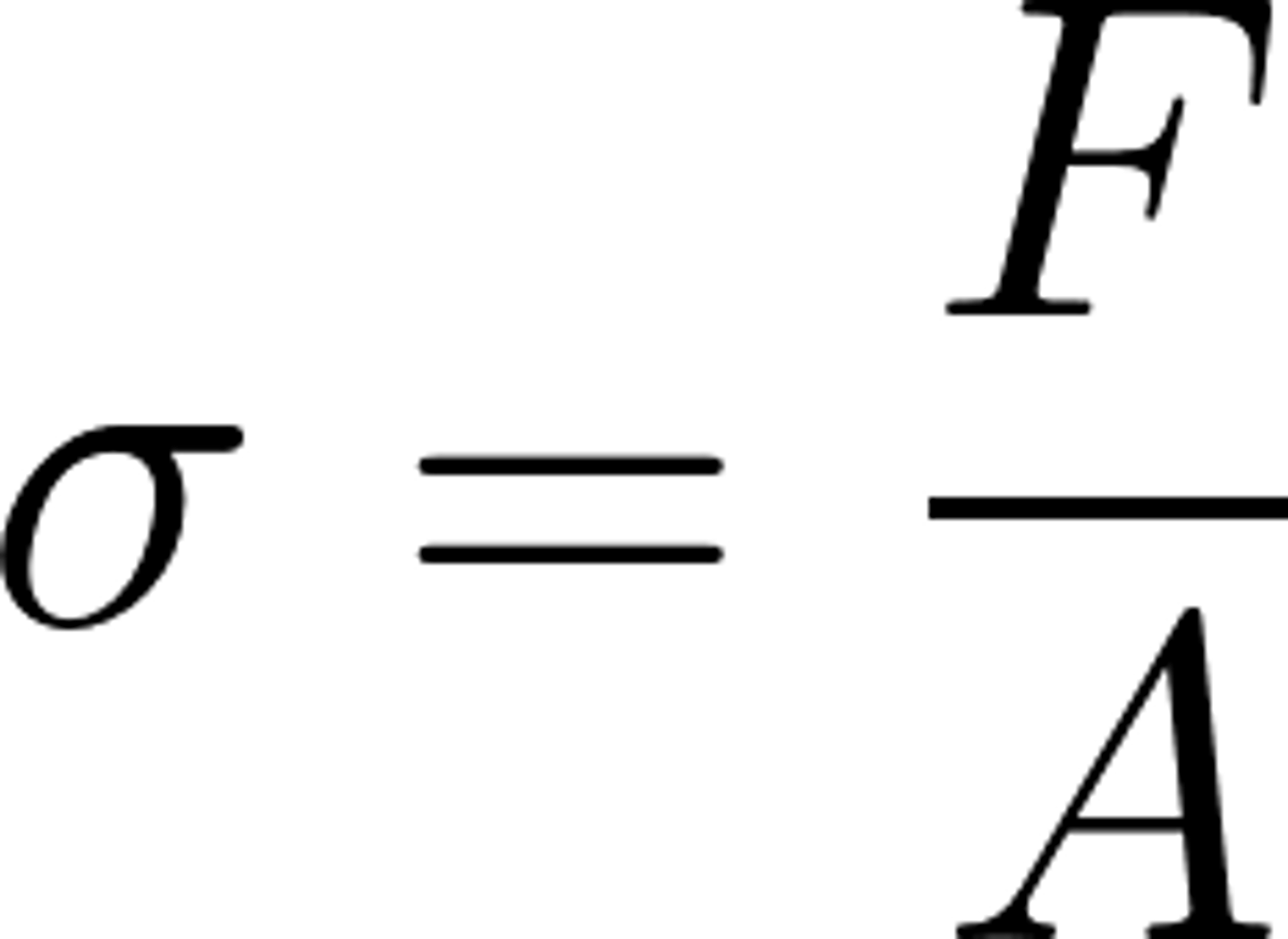
Tensile strain calculation
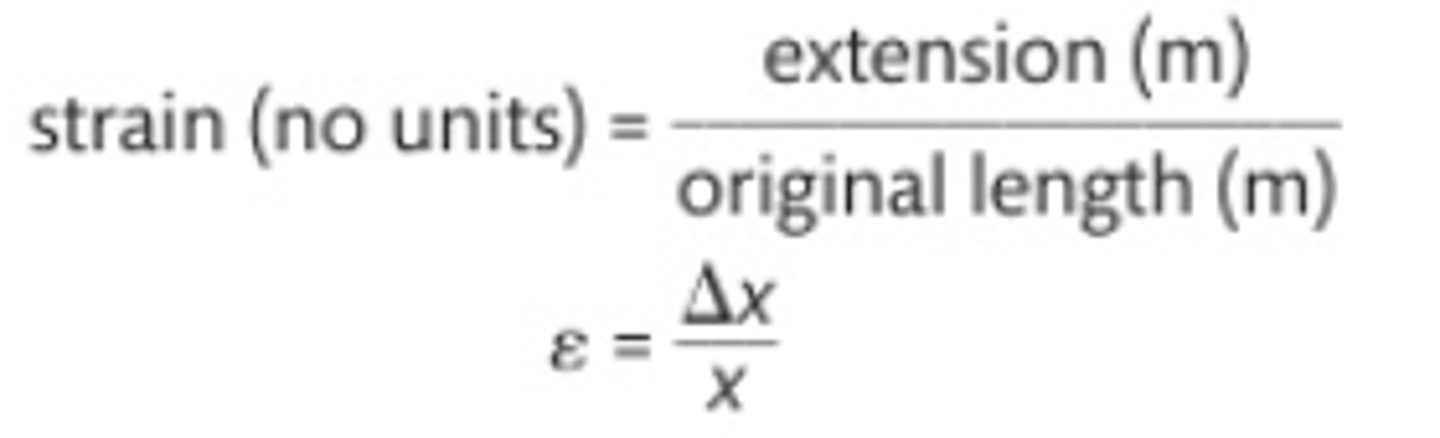
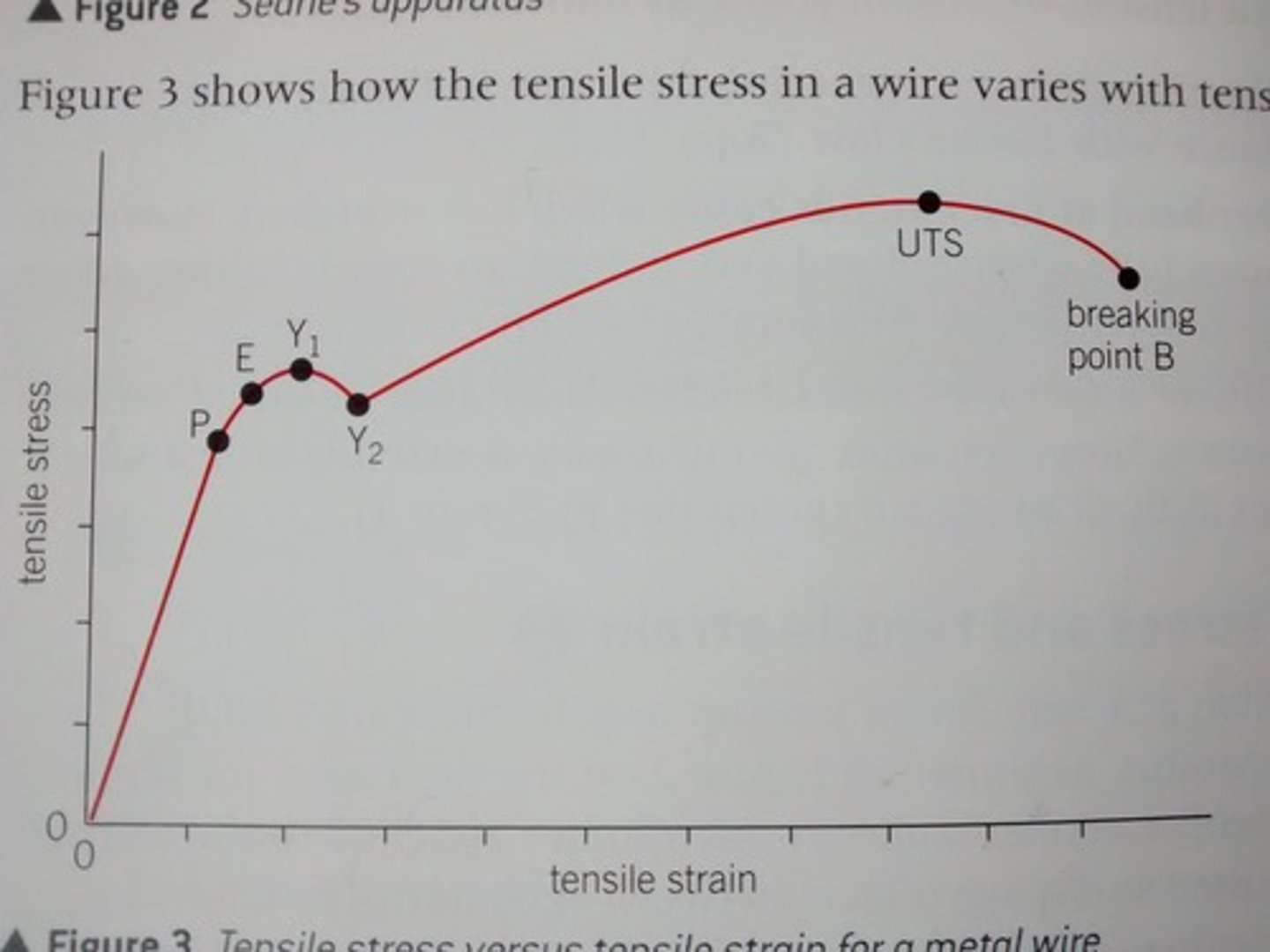
What does the tensile stress-tensile strain graph show up to the limit of proportionality?
Tensile stress is proportional to tensie strain in a linear relationship, and Young's modulus can be determined in this range.
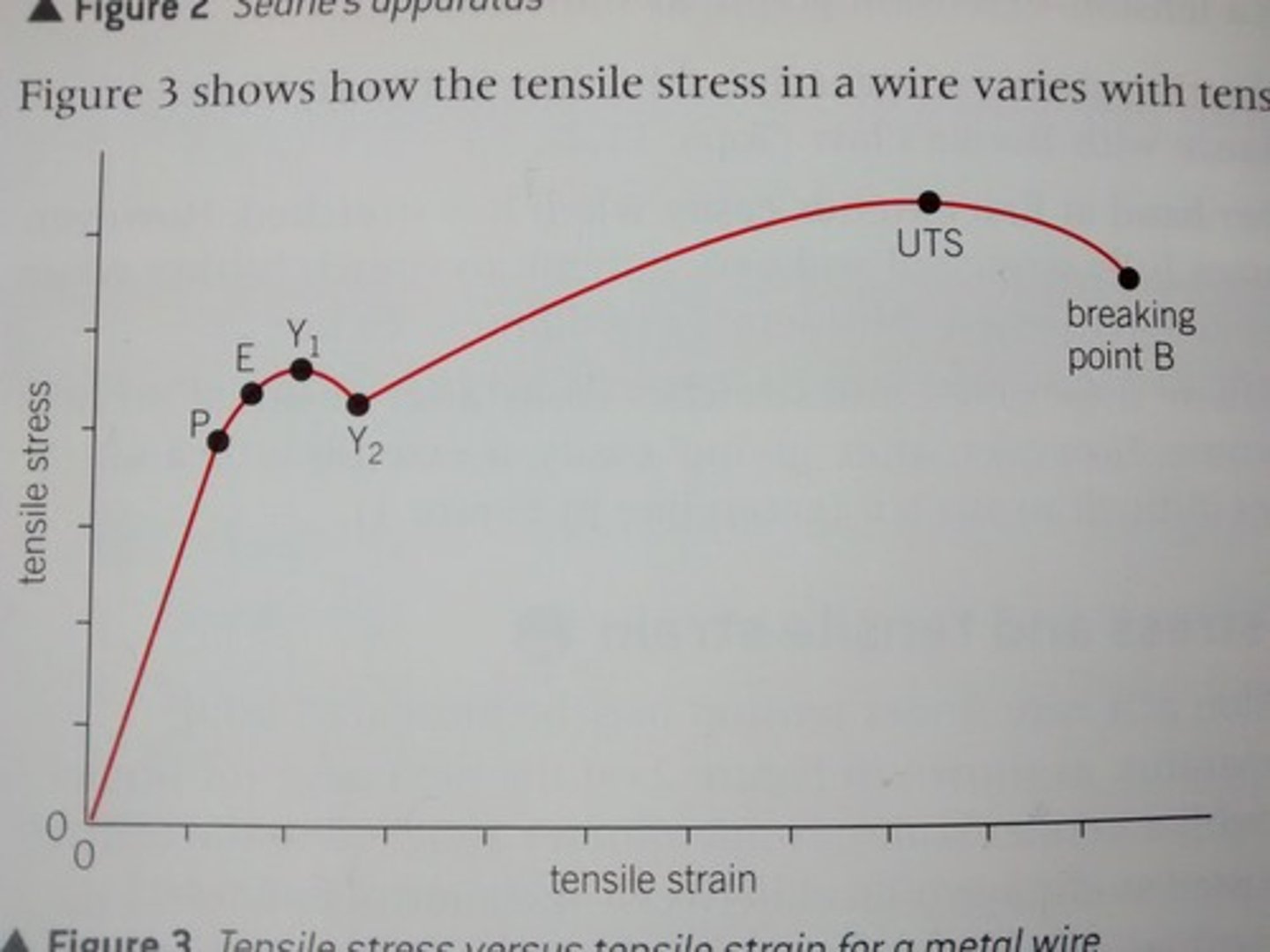
What happens beyond point P (Limit of proportionality)
Beyond P: the line curves and continues beyond the elastic limit (E) to the yield point (Y1). Which is where the wire weakens temporarily. The elastic limit is the point beyond which the wire is permanently stretched and suffers plastic deformation.
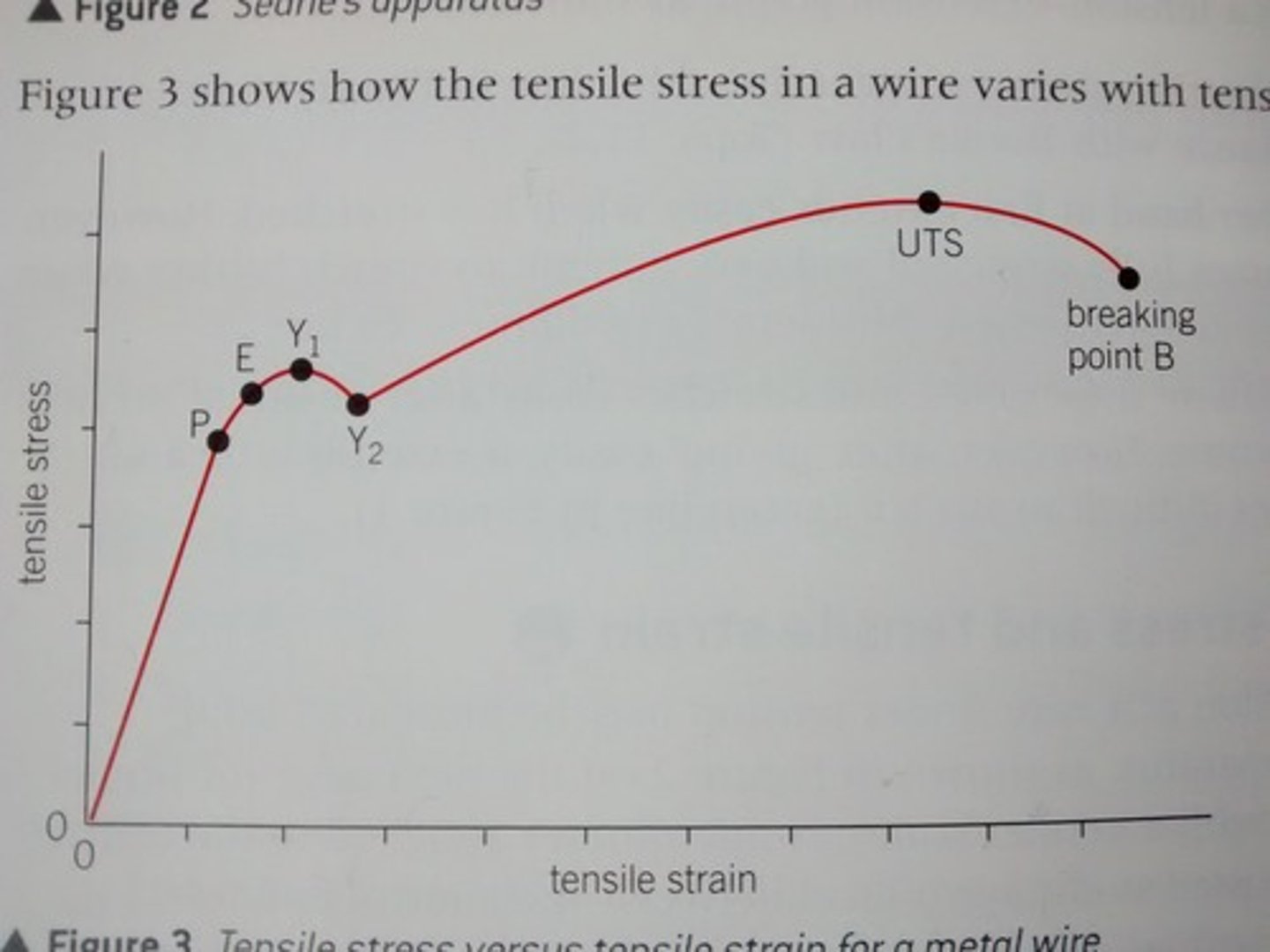
What happens beyond Y2
Beyond Y2, a small increase in the tensile stress causes a large increase in tensile strain as the material of the wire undergoes plastic flow untile the UTS
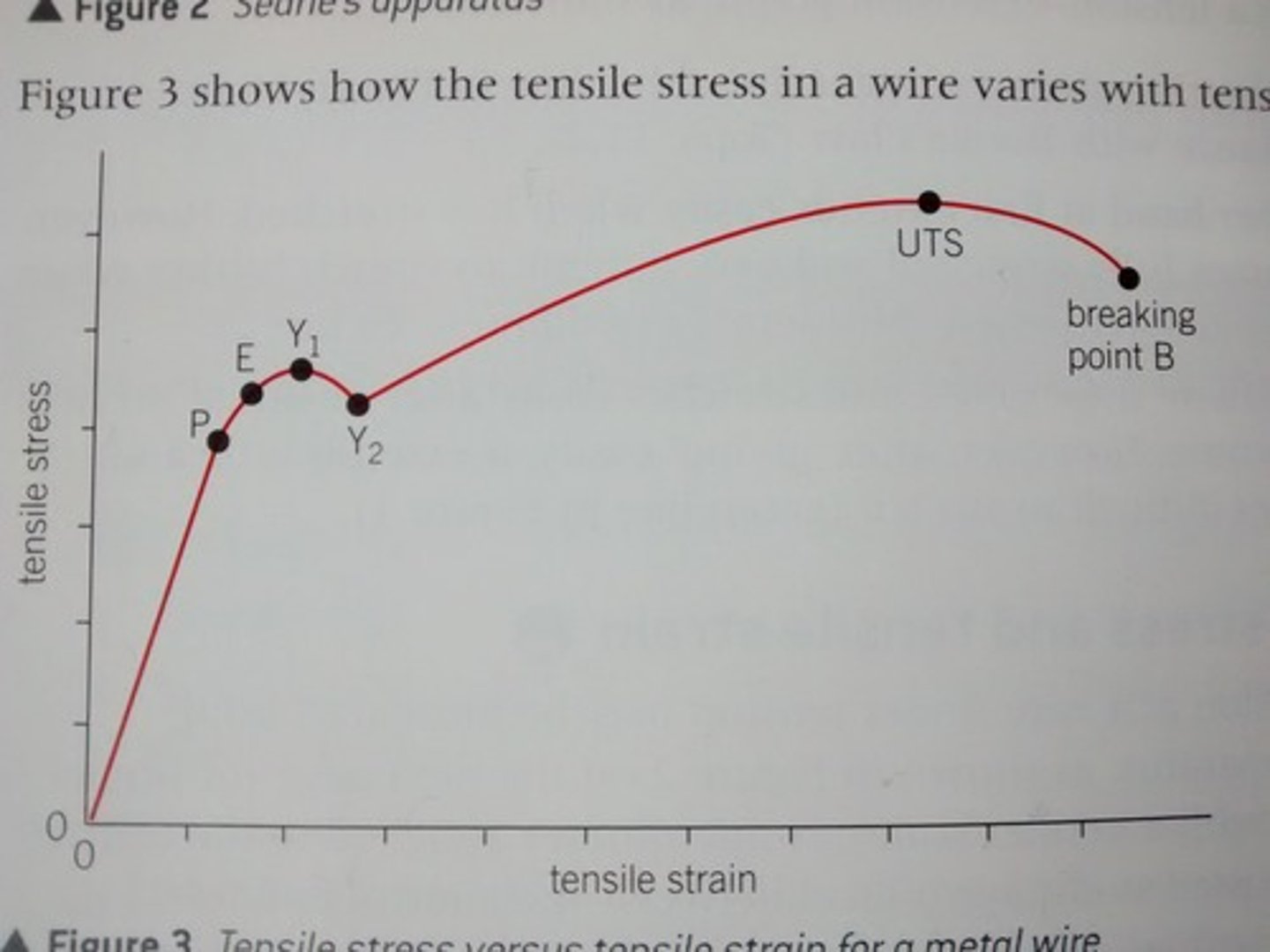
What happens at UTS point
Beyond the ultimate tensile stress, where there is maximum stress, the wire loses its strength, extends and becomes narrower at its weakest point. Increase of tensile stress occurs due to the reduced area of cross section at this point until the wire breaks at B. UTS is also called breaking stress.
The cross-sectional area of the material decreases significantly at a localized point.
Although the material continues to deform under the load, the decrease in the cross-sectional area dominates, causing the true stress (force per unit area) to increase in that localized region.

Young's modulus equation
E=stress/strain
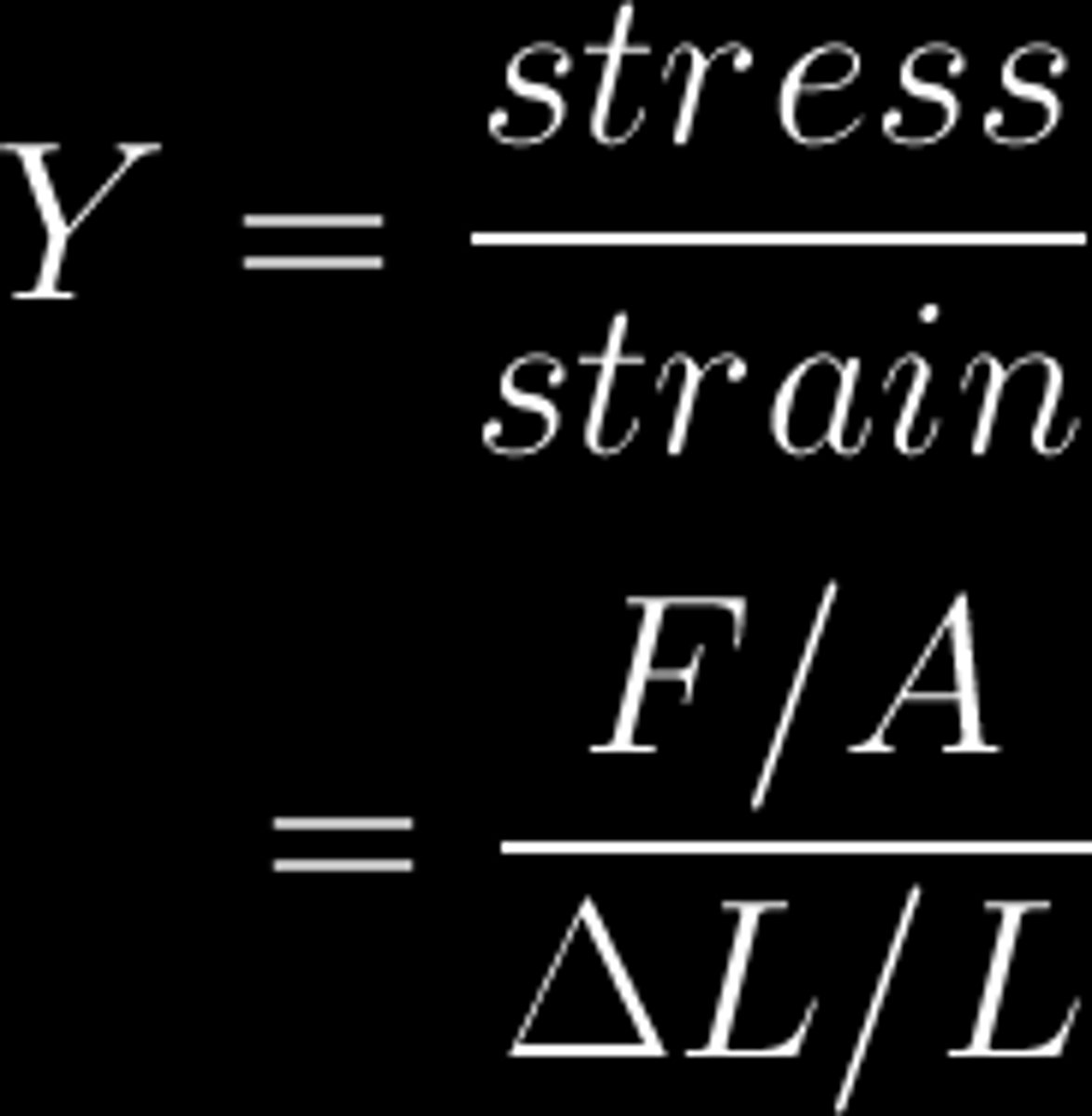
What does the gradient represent in a stress-strain graph?
The gradient represents the stiffness of the material. Stiffer materials have steeper gradients.
How does the gradient relate to the strength of a material?
Materials with steeper gradients (higher Young's modulus) are stiffer, with higher Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS).
Does a brittle material snap with any noticeable yield
No.
Breaks without any give
Ductile material
A material which can be drawn out into a wire. This implies that plastic strain occurs under enough stress.
elastic vs plastic deformation
Elastic deformation- when an object returns to its original shape after stress is removed
Plastic/permanent deformation- when enough stress has been applied to make it permanently stretched out.
Tensile strain definition
measure of how material stretches, extension divided by original length
elastic limit
Maximum stress that a material will withstand without permanent deformation.
How can the strength of a material be determined from stress-strain graph
Strength of a material is its ultimate tensile stress (UTS).Which is its maximum tensile stress.Steel is stronger than copper because its maximum tensile stress is greater.
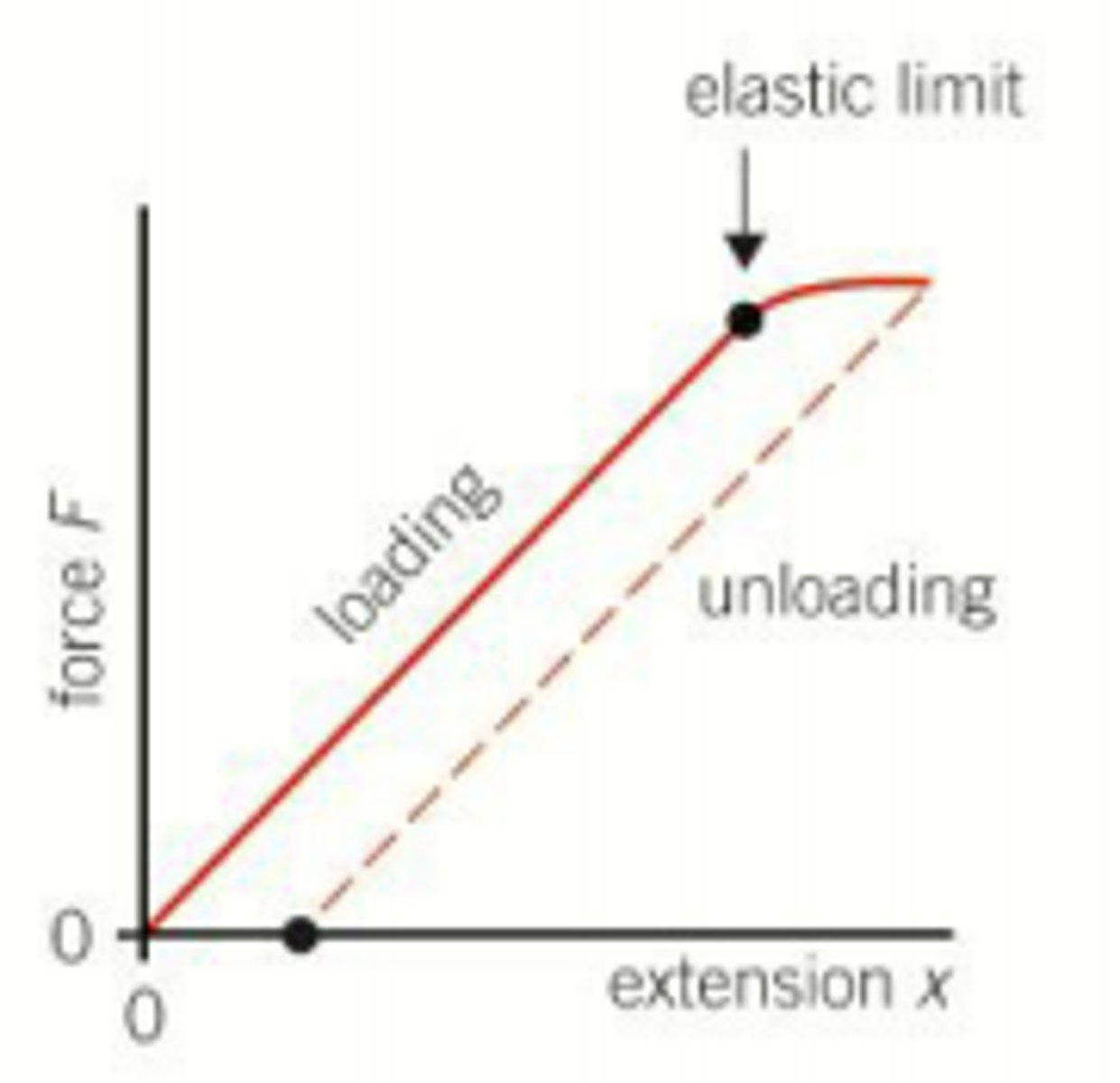
What happens to a metal wire's loading and unloading curves if its elastic limit is not exceeded?
The loading and unloading curves are the same, and the wire returns to its original length when unloaded.
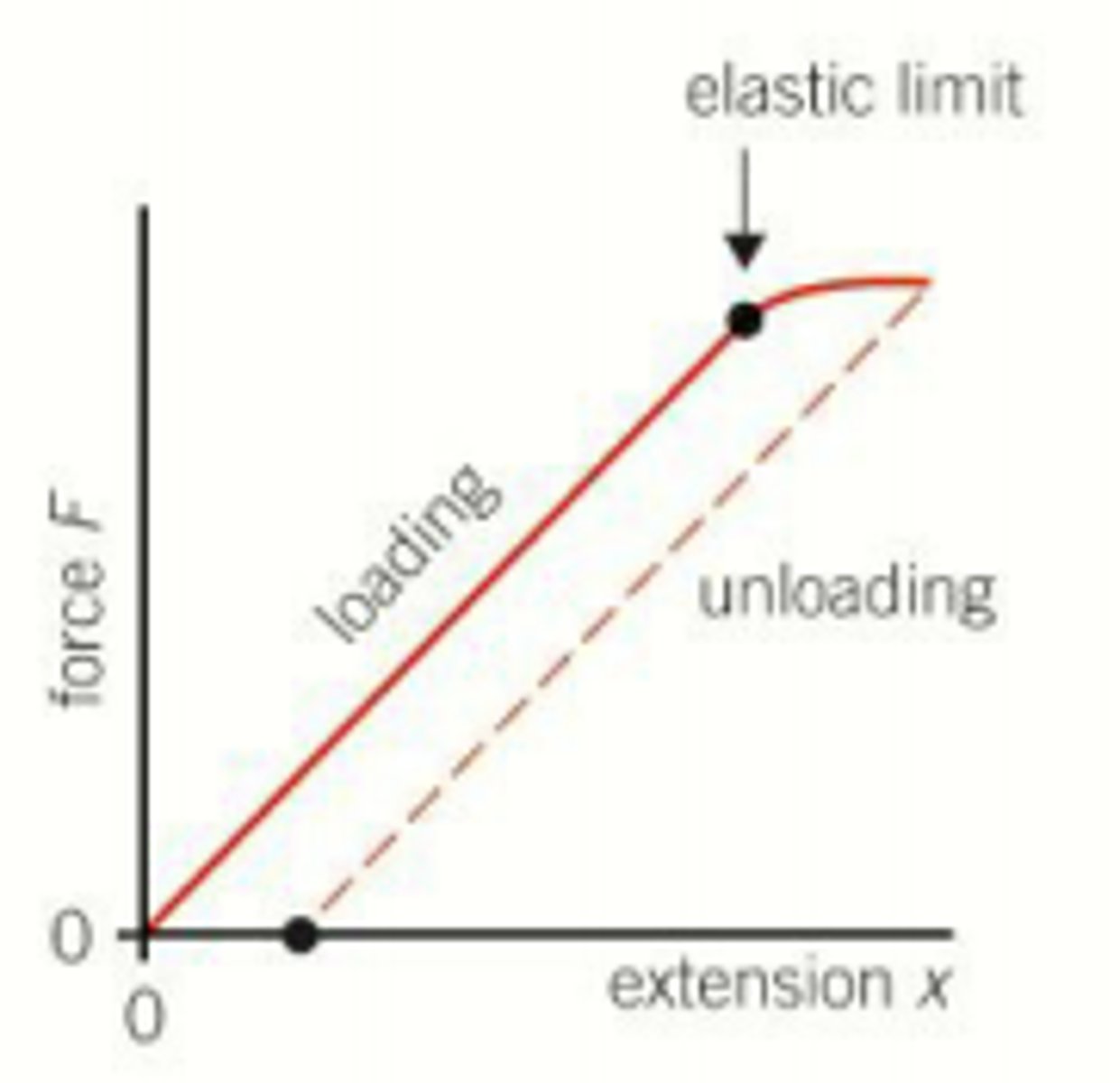
What occurs when a metal wire exceeds its elastic limit during loading?
The unloading line becomes parallel to the loading line.
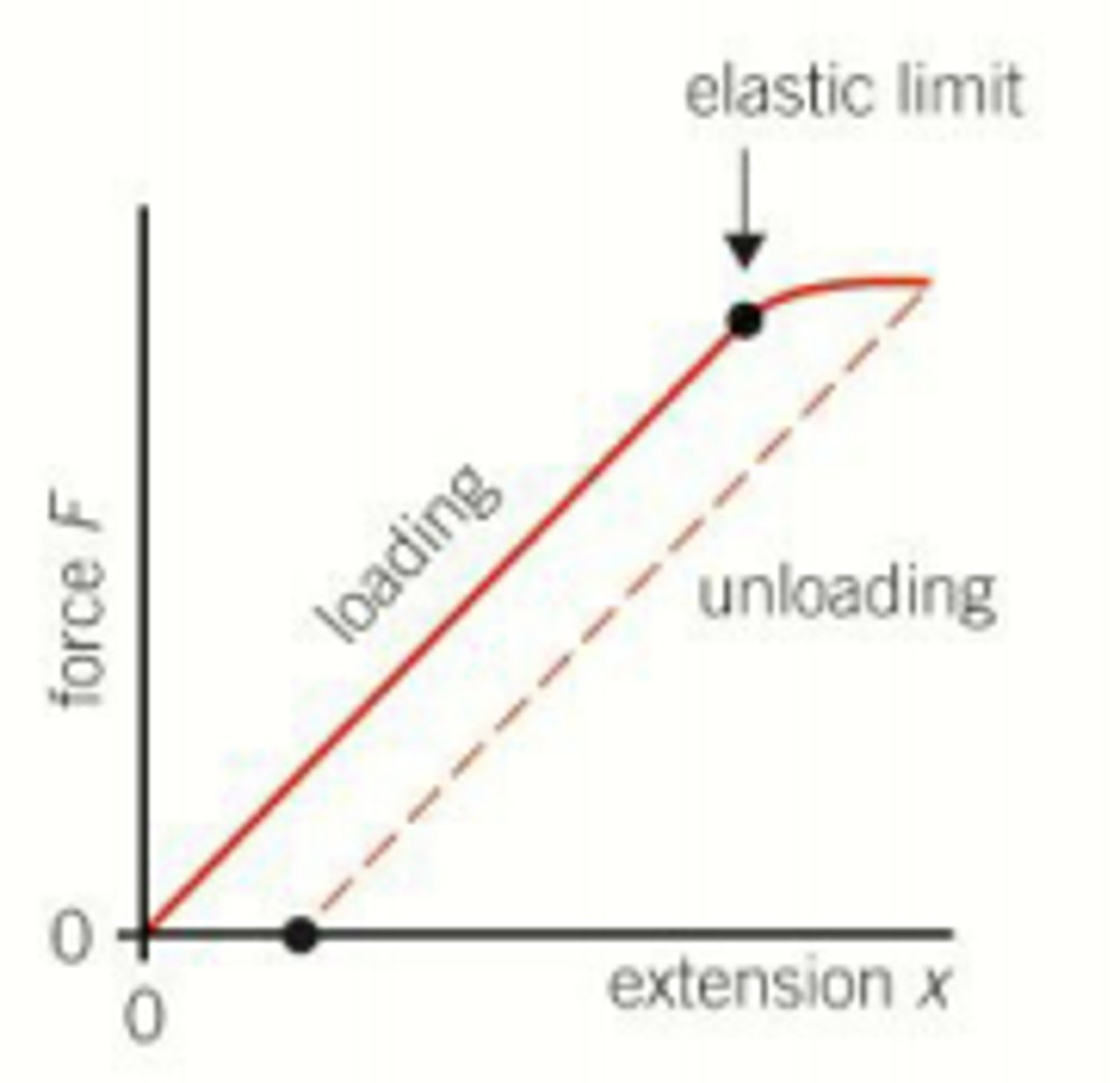
What is the result of unloading a metal wire that has exceeded its elastic limit?
The wire becomes slightly longer, resulting in a permanent extension.
elastic energy stored in a stretched wire formula
(1/2)TΔL
T: The tension or force applied to the material.
ΔL: The extension of the material (how much it stretches from its original length).
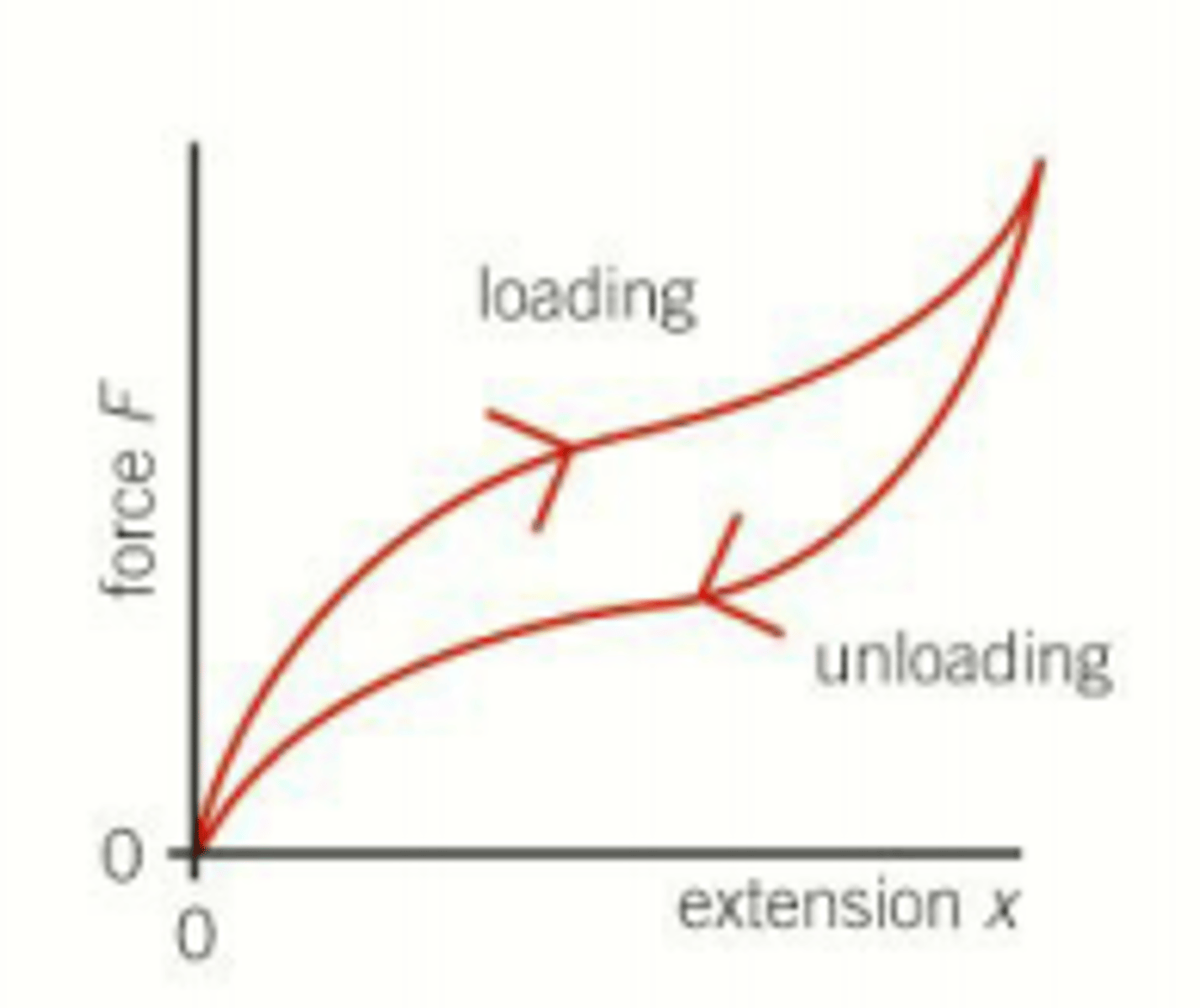
What happens to the length of a rubber band during unloading compared to loading?
The change of length during unloading is greater than during loading for a given change in tension.
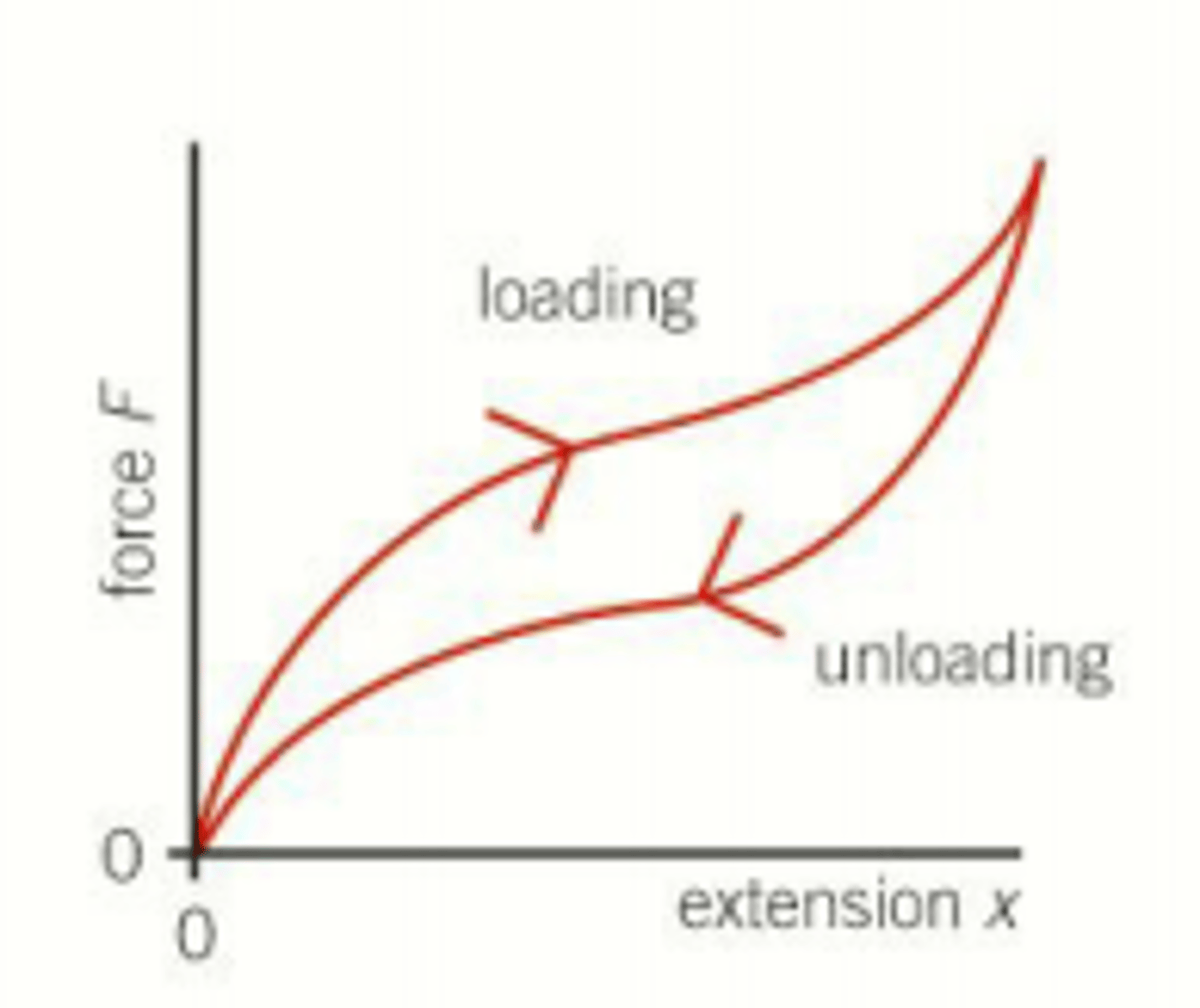
What is the shape of the unloading curve of a rubber band compared to the loading curve?
The unloading curve is below the loading curve except at zero and maximum extension.
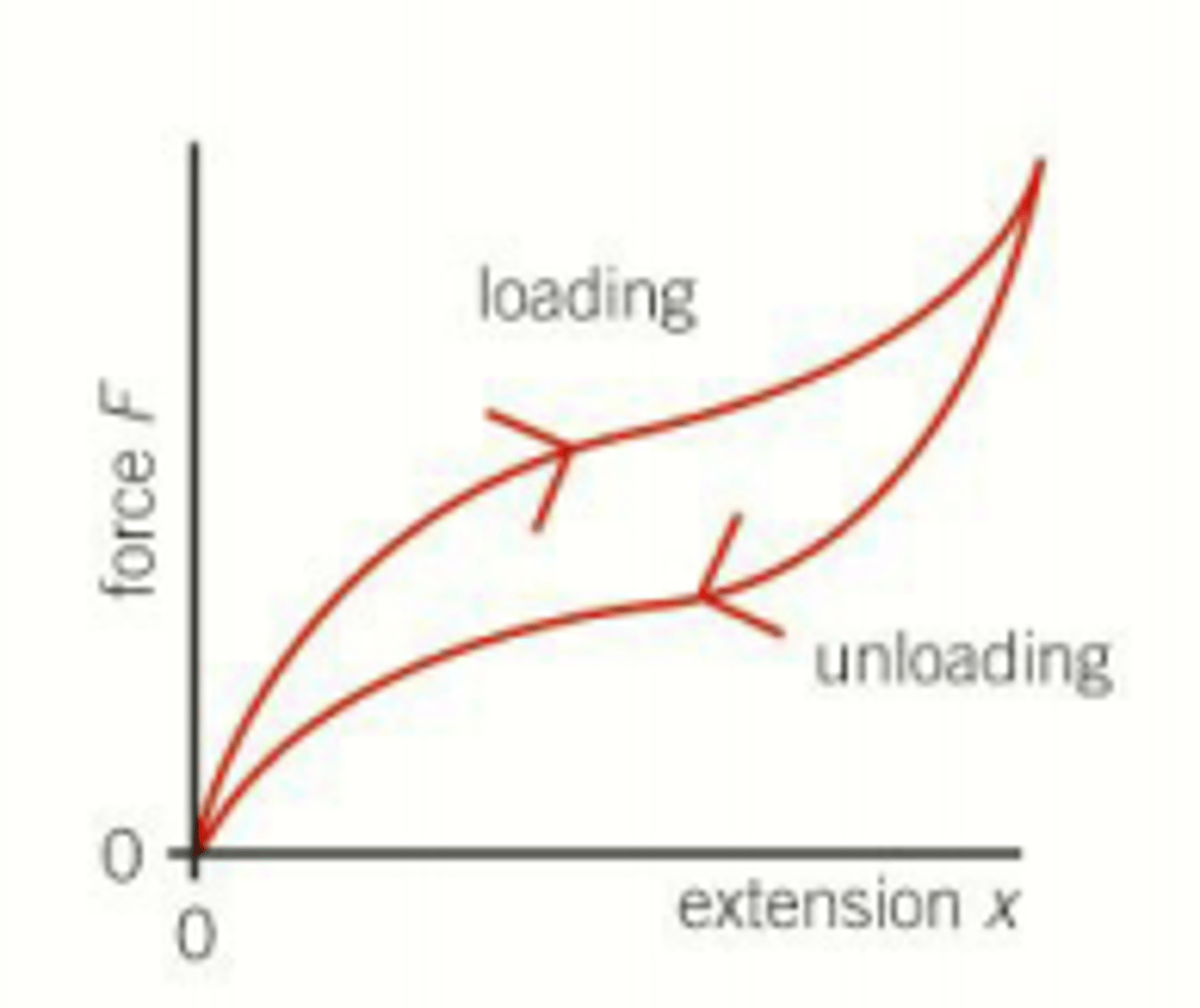
Does a rubber band remain elastic when it regains its original length?
Yes, a rubber band remains elastic as it regains its original length.
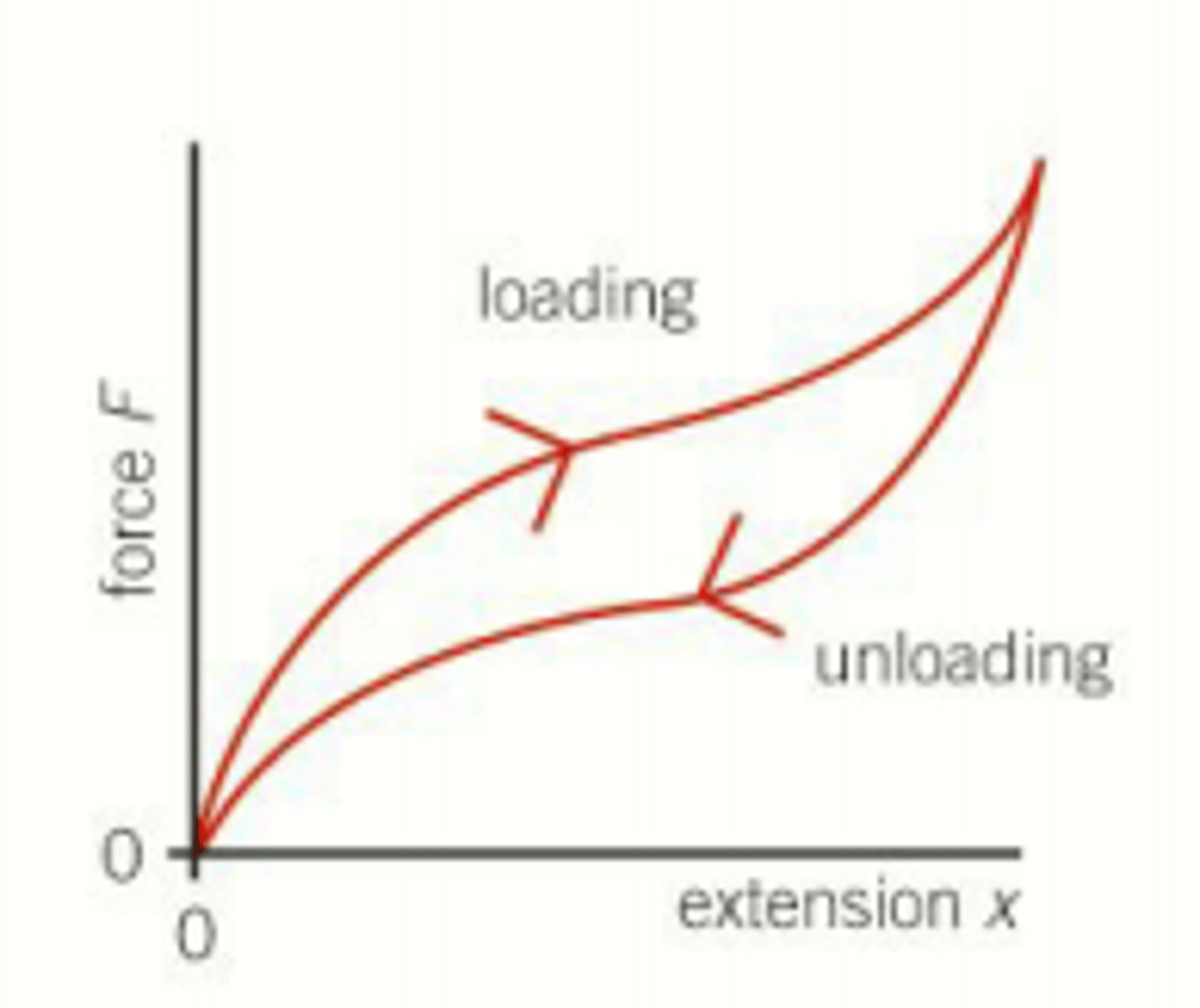
What is a characteristic of a rubber band regarding its limit of proportionality?
A rubber band has a low limit of proportionality.
Work done to stretch a rubber band
area under loading curve
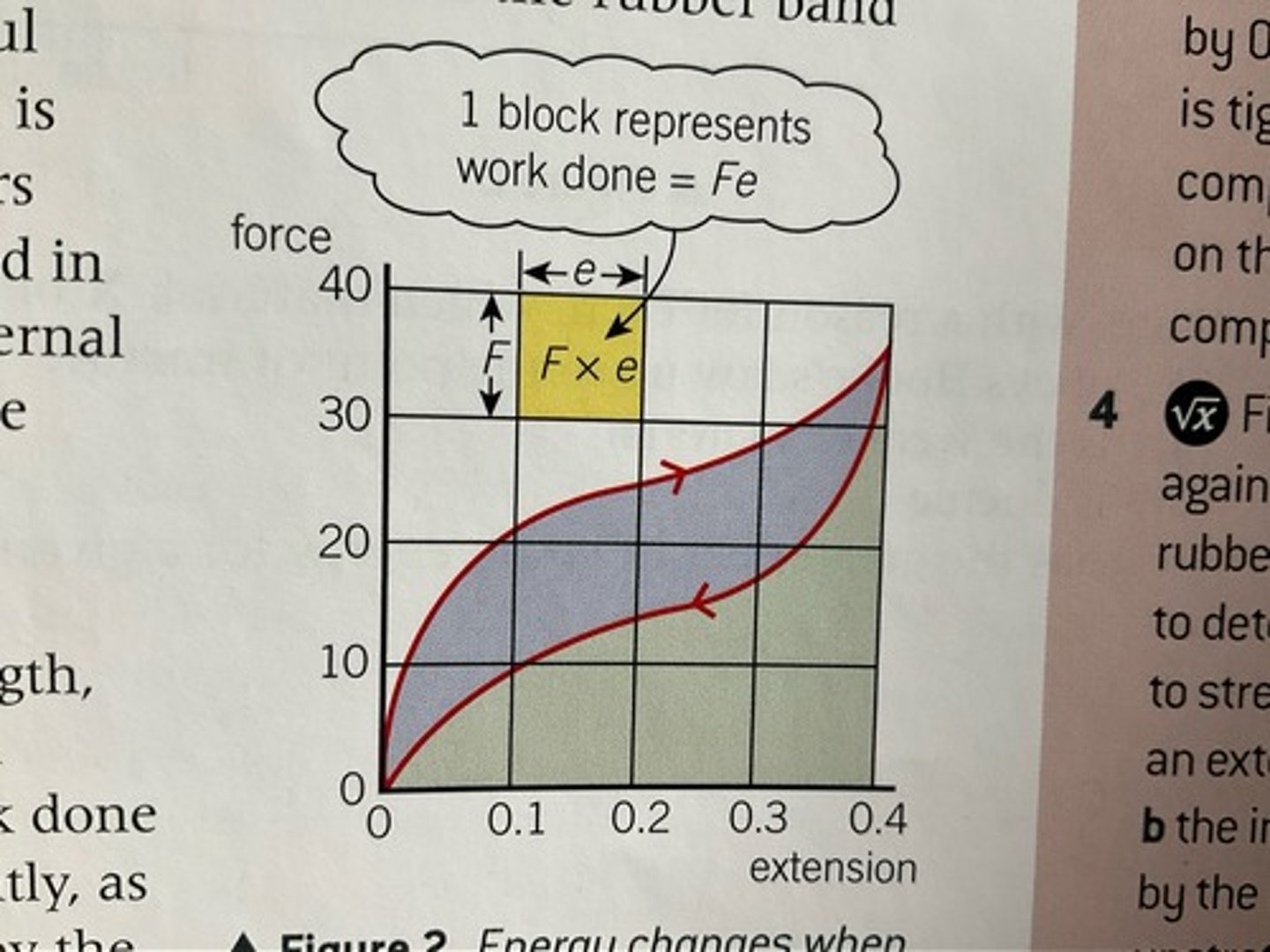
work done by rubber band when unloaded
area under unloading curve
Area between loading and unloading curve
Difference between energy stored in rubber band when stretched when stretched and useful energy recovered when unstretched
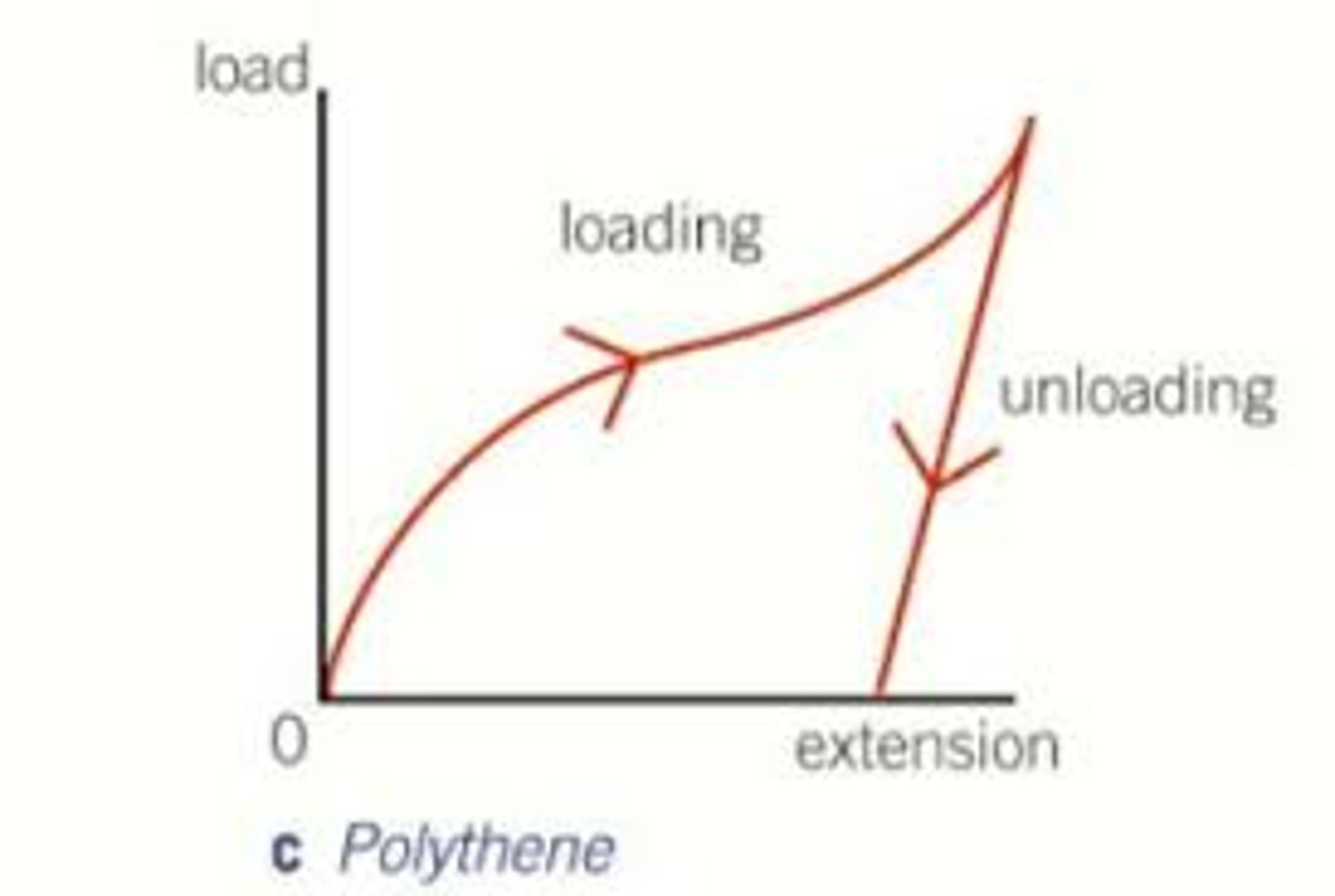
What happens to the extension of a polythene strip during unloading compared to loading?
The extension during unloading is greater than during loading.
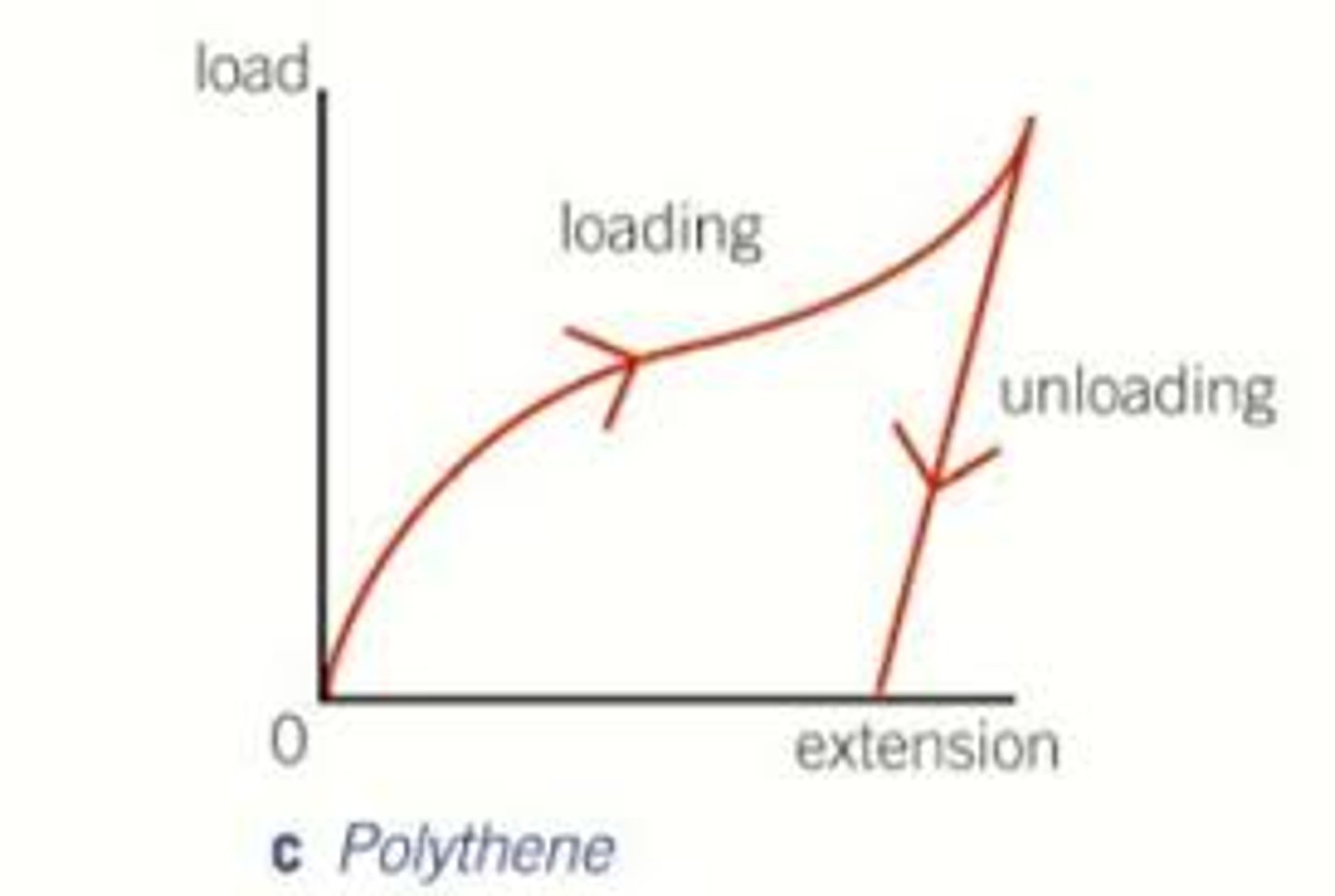
Does a polythene strip return to its initial length after being completely unloaded?
No, it does not return to the same initial length.
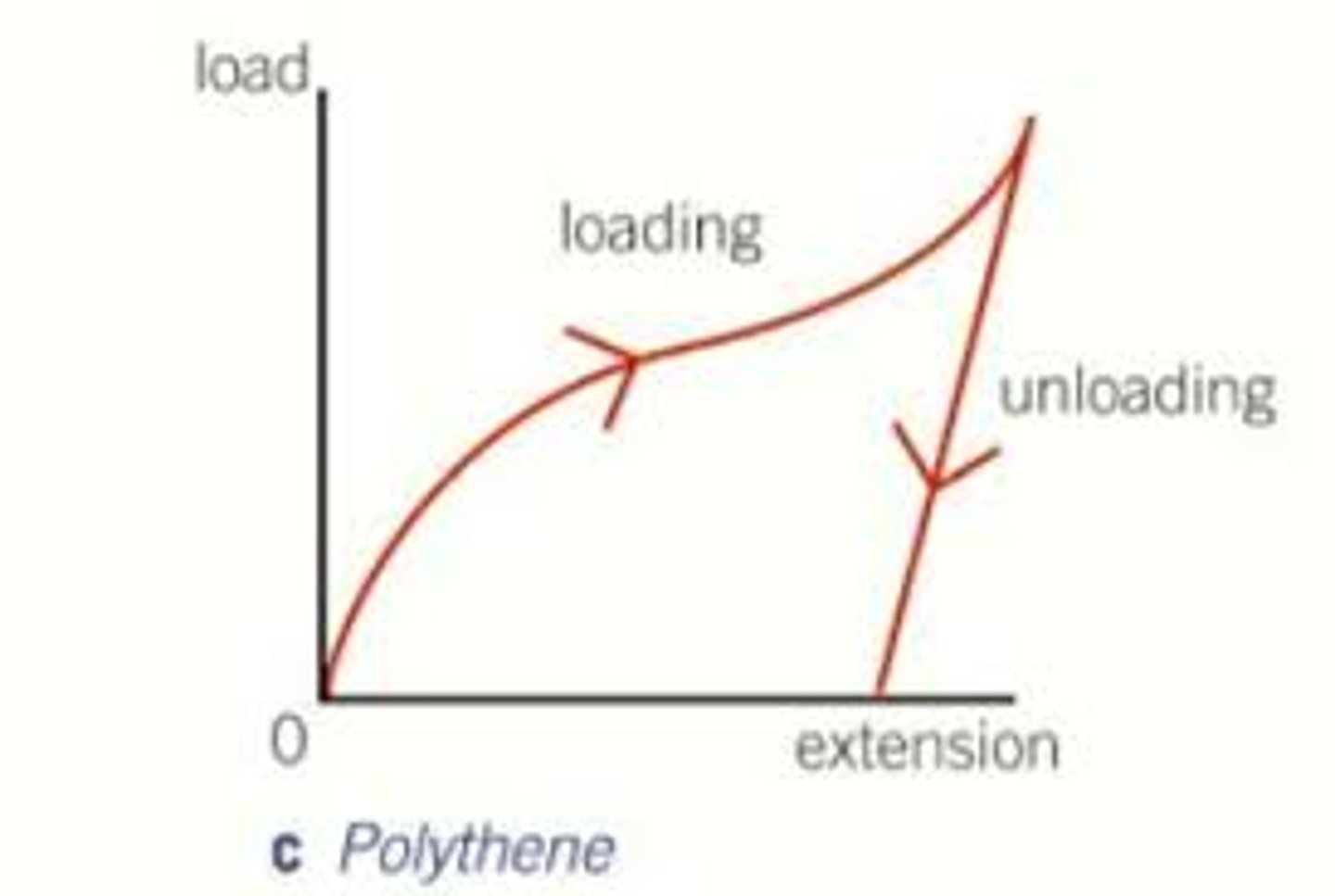
What is a characteristic of the polythene strip regarding its limit of proportionality?
The polythene strip has a low limit of proportionality.
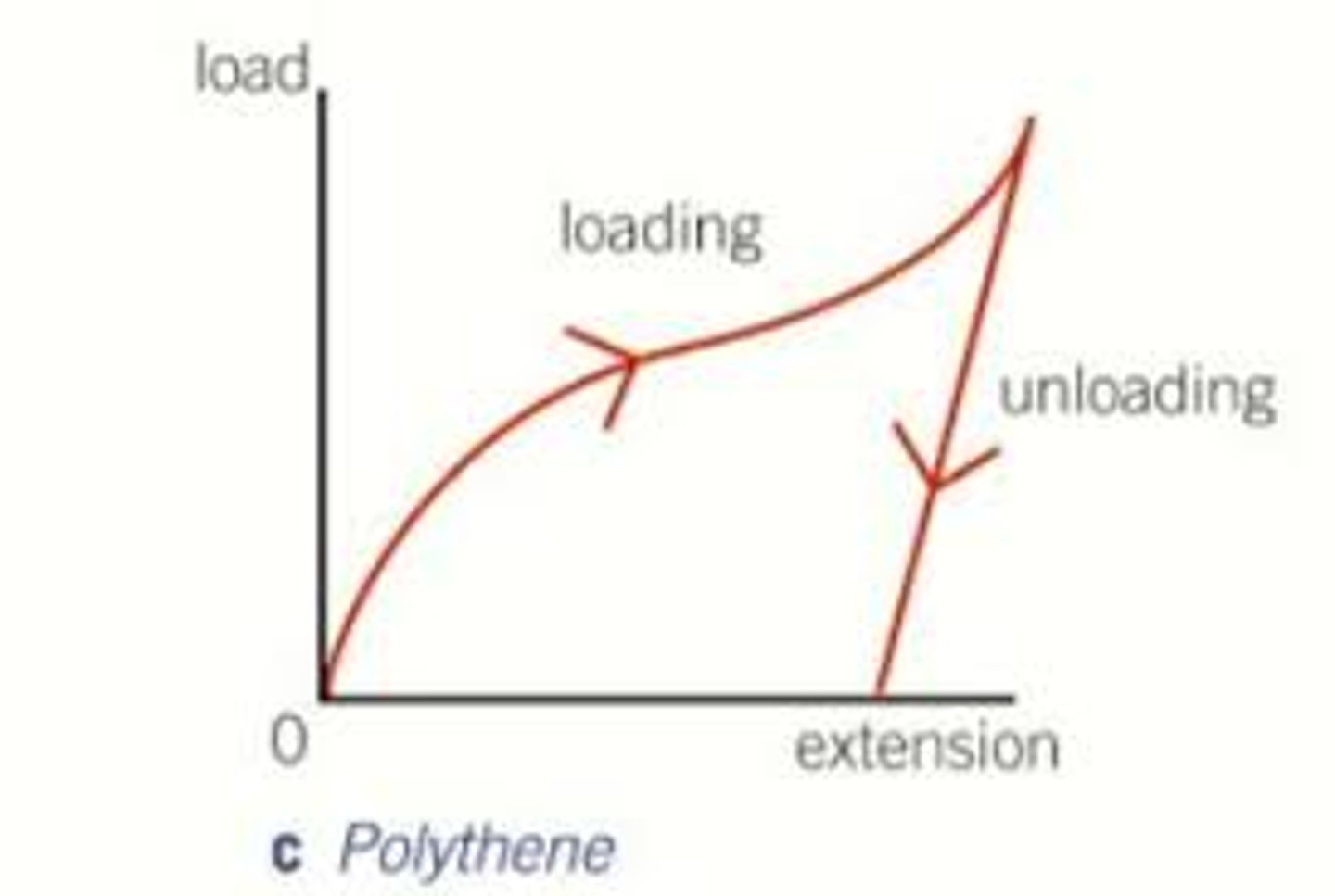
What type of deformation does a polythene strip suffer?
Plastic deformation.