pulmonary function, kidneys and urinalysis, liver and pancreas, endocrine, heart, lipid
1/370
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
371 Terms
what are pulmonary function tests (PFTs)
assessments of lung function that are composed of many different components
spirometry is performed to reveal the presence of
obstructive disease
lung volumes determine the presence of
restrictive disease
diffusion capacity tests ascertain the
adequacy of gas exchange
true or false: significant bronchodilator response on spirometry testing can differentiate between COPD and asthma
false (response is common in both)
postbronchodilator spirometry is necessary to determine
the presence of persistent airflow obstruction and the degree of disease severity
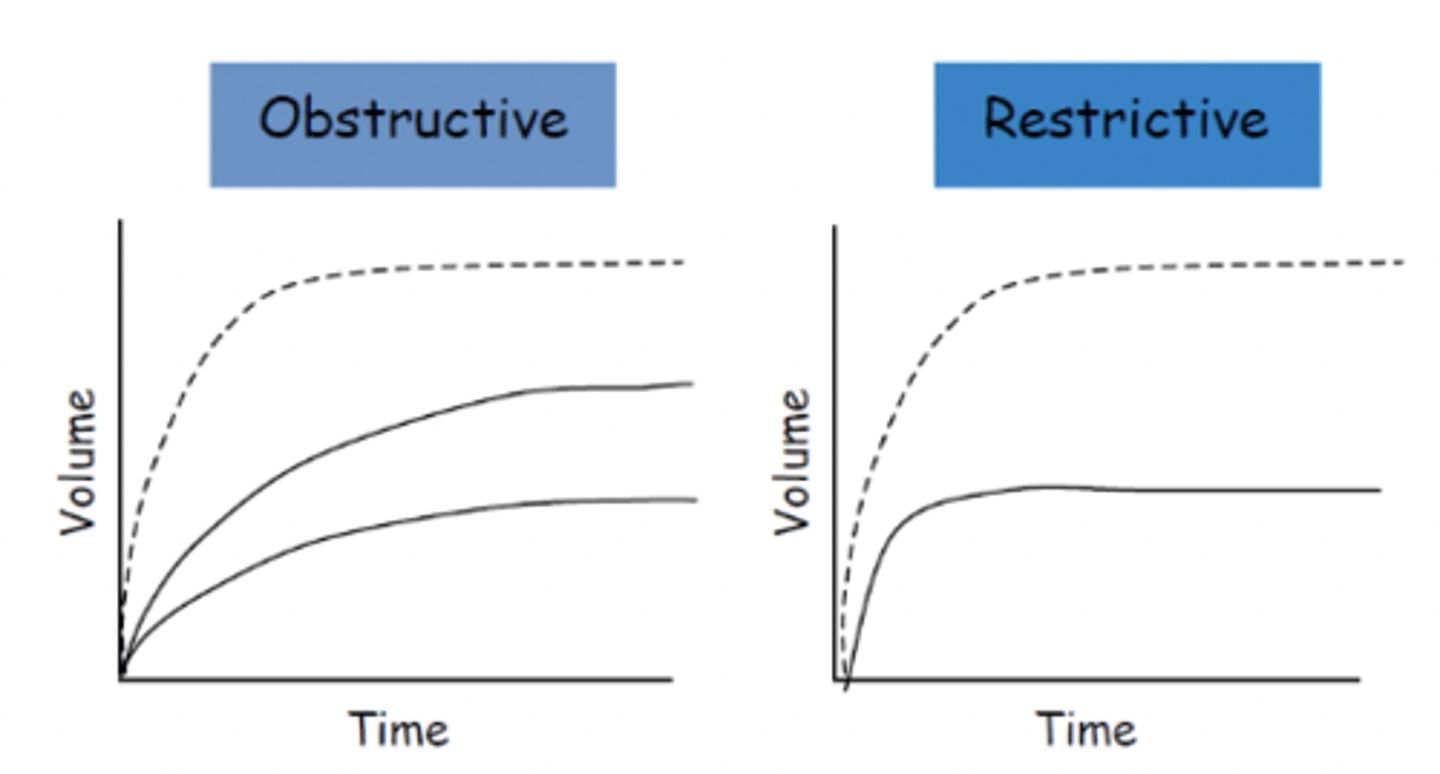
restrictive lung diseases are a decrease in
lung volume; defined by a decrease in TLC
ventilation
movement of air in and out of the lungs
perfusion
movement of blood through the lungs
diffusion
gas exchange that occurs in alveoli across a thin membrane separating capillary blood from exchanged air
bronchi are responsible for
delivering inspired air to the lungs
lungs are in the
pleural cavity in the thorax
the right lung has ___ lobes, the left lung has ____ lobes
3, 2
why are PFTs clinically useful
-diagnosis of respiratory diseases
-classification of diseases
-therapeutic decision making
-monitoring disease progression
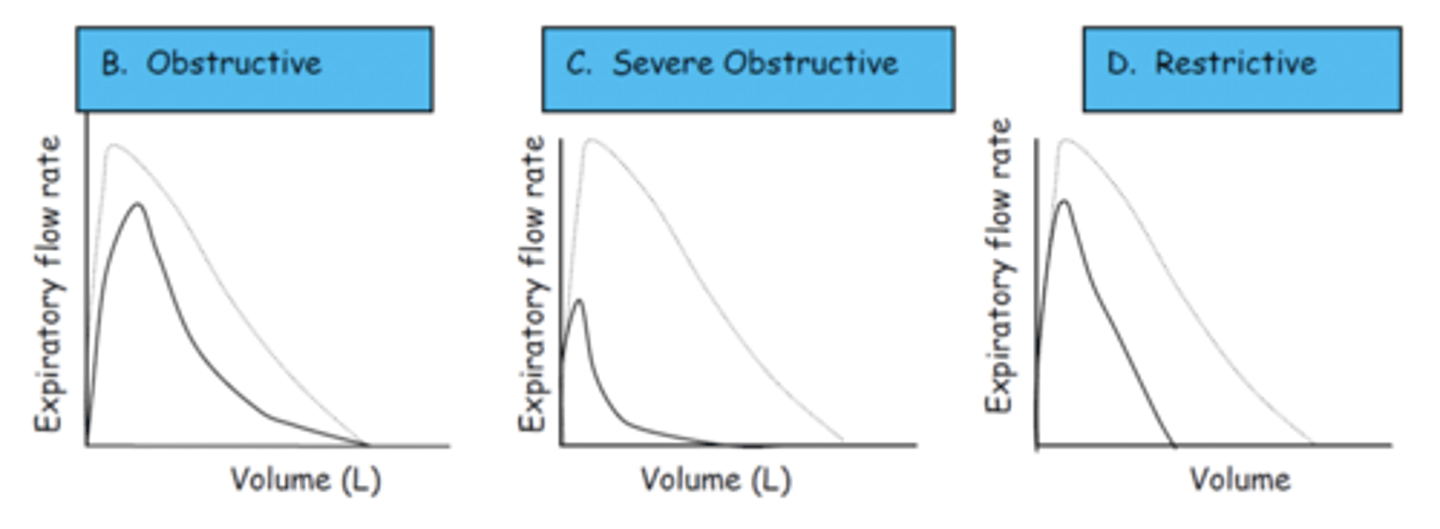
obstructive lung diseases
reversible or persistent blockage in airways; decreased flow rate of air but little impact on total volume per breath
examples of obstructive lung diseases
asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis
restrictive lung diseases
lungs limited in amount of air they contain; decreased total volume of air but little impact on flow rate of air
examples of restrictive lung diseases
kyphosis, sarcoidosis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, myasthenia gravis
what does spirometry measure
air movement in and out of lungs during forced maneuvers (FVC, FEV1)
when is spirometry used
diagnosis of asthma and COPD
what is FVC
forced vital capacity - total volume of air forcefully and rapidly exhaled in one breath
what is FEV1
forced expiratory volume in 1 second - total volume of air a patient is able to exhale in the first second during maximal effort
what does FEV1 indicate
the severity of the obstructive disease
FEV1/FVC is the
percentage of the FVC expired in one second
in COPD, chronic
airway obstruction as an FEV1/FVC ratio is
<70%
what are volume time curves
plot of volume exhaled over time (spirometry)
what does a normal volume time curve look like
rise rapidly and smoothly
plateau within 3-4 seconds
types of PFTs
- Spirometry
- Plethysmography (lung volume assessment)
- Diffusing capacity
- 6 minute walk test (exercise testing)
- Peak flow
- bronchial provocation
what are flow volume curves / loops
diagram with flow on Y axis and volume expired on X axis
what does a normal flow volume curve look like
rapid rise, slow (almost linear) decline
what does bronchodilator reversibility measure
measures air movement in and out of lungs during forced maneuvers (spirometry) after inhalation of SABA (short acting B 2 agonist)
when are bronchodilator reversibility tests used
to measure disease responsiveness to bronchodilator therapy
pulse oximetry measures
oxygen saturation of blood (SpO2)
when is pulse oximetry used
any setting where hypoxemia can occur
what is a normal SpO2
>95%
what does body plethysmography measure
lung volumes
When is body plethysmography used?
When spirometry shows decreased FVC, but FEV1/FVC is within normal limits (suggests restrictive lung disease)
to identify air trapping or hyperinflation (obstructive)
tidal volume (TV)
amount of air that moves in and out of lung during inspiration
residual volume (RV)
air left in the lungs after a maximal expiratory effort
inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
air inspired after maximal effort
expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
air expired after active expiratory effort
total lung capacity (TLC)
tidal volume (TV) + residual volume (RV) + inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) + expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
vital capacity (VC)
amount of air exhaled after a maximal inspiration
what does diffusion capacity (of the lung for carbon dioxide) measure
measure of gas exchange (DLco)
what is a normal DLco
>70% predicted
what causes decreased DLco
diseases with decreased blood flow or damaged alveoli
high DLco is representative of
asthma or pulmonary hemorrhage
normal DLco can be associated with what diseases
with restriction: morbid obesity, pleural effusion, neuromuscular weakness
with obstruction: asthma, chronic bronchitis
when is exercise testing used to assess pulmonary function
to confirm or rule out exercise induced bronchospasm and to evaluate effectiveness of medications
types of exercise tests used to assess pulmonary function
spirometry during exercise
six minute walk test
what does the bronchial provocation test measure
reactivity of airways to agents that induce airway narrowing
when are bronchial provocation tests used
-aid in asthma diagnosis (spirometry and symptoms not enough)
-evaluate drug therapy on airway hyperactivity
-evaluation of drug effectiveness
-when PFTs are normal but disease is suspected
what does peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) measure
maximum airflow rate
when is PEFR used
to determine severity of asthma exacerbations
what do carbon monoxide breath tests measure
how much CO is in the lungs and how much is attached to Hgb in blood
what is a negative value for CO breath tests
< 10 ppm
what test is thought to motivate smokers in quitting
CO breath tests
also calculating lung age using FEV1
PFT results associated with chronic obstructive lung diseases
decreased: FEV1, FEV1/FVC
decreased/normal: FVC
normal/increased: RV, TLC
PFT results associated with reversible obstructive lung disease (asthma)
all results are normal
PFT results associated with restrictive lung diseases
decreased: FEV1, FVC, RV, TLC
normal/increased: FEV1/FVC
PFT results of mixed obstructive and restrictive lung diseases
decreased: FEV1, FVC, TLC
decreased/normal: FEV1/FVC
RV can be increased, normal, or decreased
urea is a byproduct of
hepatic protein metabolism
BUN represents
the concentration of nitrogen in the serum
prerenal causes of elevated BUN and SCr
Dehydration, blood loss, shock, CHF, hypotension
intrarenal causes of elevated BUN and SCr
Acute or chronic renal failure due to any cause, glomerulonephritis, acute tubular necrosis, severe hypertension
postrenal causes of elevated BUN and SCr
Obstruction of ureter, bladder neck, or urethra due to stones, enlarged prostate, or stricture
drugs that increase BUN
Corticosteroids, tetracyclines
ACE inhibitors, APAP, acyclovir, diuretics, antibiotics , NSAIDs
causes of low BUN
malnourishment, excess intravascular volume, liver damage
causes of low serum creatinine
aging, malnourishment
creatinine is a waste product of
creatine and creatine phosphate; produced in muscle
kidneys are responsible for maintaining
homeostasis within the body
-excretion of water/solutes
-maintain BP
-mineral metabolism
-RBC production
functional unit of kidneys
nephron
tubules of the kidney
Renal corpuscle → proximal convoluted tubule → nephron loop → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct
normal GFR
about 125 mL/min
GFR is a measure
of kidney excretory function
exogenous markers of GFR
inulin clearance, Iothalamate and Cr-EDTA clearance
endogenous markers of GFR
cystatin C, serum creatinine, urea
what is the gold standard for measuring GFR in adults
inulin clearance
what is inulin
Fructose polysaccharide freely filtered through glomerulus without being metabolized, secreted, or absorbed
what does Iothalamate and Cr-EDTA clearance involve
Injection of radioactive marker, repeated blood sampling, and timed urine collection
inulin clearance normal ranges
Men: 125 + 15 (SD) mL/min/m2
Women: 110 + 15 (SD) mL/min/m2
normal range for Iothalamate and Cr-EDTA clearance
87-141 mL/min/SA
why is cystatin C considered more sensitive than serum creatinine in tracking changes to renal function
unaffected by diet and muscle mass
what is cystatin C
Indirect reflection of GFR
Protease inhibitor filtered by glomerulus but not reabsorbed or secreted
normal range for serum creatinine
0.6-1.2 mg/dL
normal range for blood urea nitrogen
8-23 mg/dL
BUN levels associated with uremic syndrome
>100 mg/dL
severe renal failure
azotemia
elevated BUN
there is an _______ relationship between SCr and renal function
inverse
direct measurement of creatinine clearance requires
24 hour urine collection
ways to estimate CrCl
Cockcroft - gault equation
MDRD equation
stage 1 of CKD
GFR (mL/min/1.73m2) = >90
Normal or kidney damage and normal GFR
stage 2 of CKD
GFR (mL/min/1.73m2) = 60-89
Slightly diminished GFR with kidney damage
stage 3 of CKD
GFR (mL/min/1.73m2) = 30-59
Moderately decreased GFR with kidney damage
stage 4 of CKD
GFR (mL/min/1.73m2) = 15-29
Significantly decreased GFR with kidney damage
stage 5 of CKD
GFR (mL/min/1.73m2) = <15
Kidney failure or on dialysis
three types of urinalysis testing
macroscopic, microscopic, chemical
macroscopic urinalysis considers
general appearance, color
microscopic urinalysis considers
cells, casts, crystals
chemical urinalysis considers
bile, protein, pH, specific gravity, bilirubin, urobilinogen, blood/hemoglobin, leukocyte esterase, nitrite, glucose, ketones