IMOS Moldule 2 -Clay Review
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UF IDS2935: Impact of Material Science Quest Fall 2024 Midterm: Modules 1-6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Properties of Clay
high plasticity (manipulated at room temp.)
good cohesion (maintains shape)
high strength under compression (after drying and baking)
poor tensile strength
opaque
insulator
can be dried
can be chemically transformed (heating above 1000C, shrinks, forms Si-O-Si bond)
Structure of clay
Si has 4 bonds (Si-O-Si)
Al has 6 bonds (Al-O-Al)
Oxygen has 2 covalent bonds (Si-O-Al)
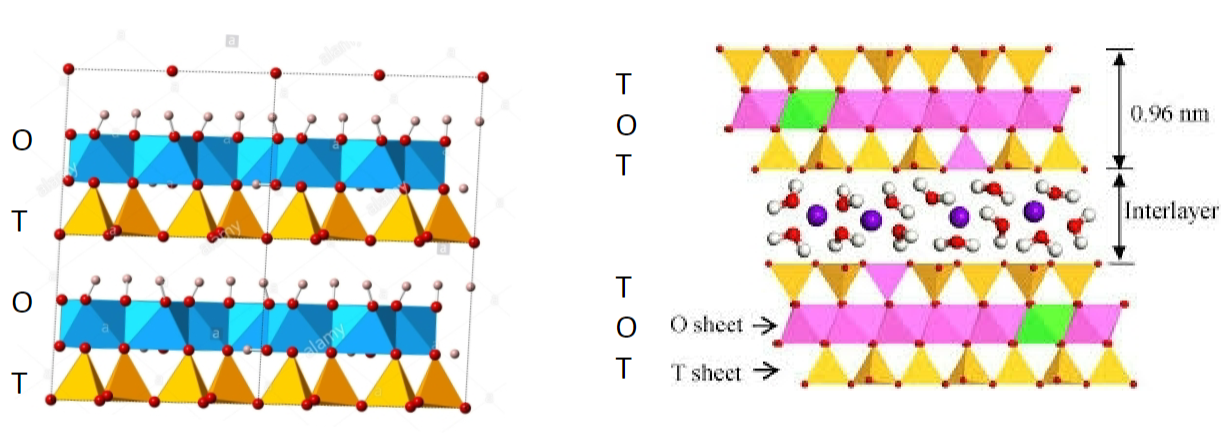
Kaolinite (China clay)
1:1 ratio (O-T-O-T)
lower shrink to swell capacity
heated <500C = drying can be reversed
heated >1000C = stoneware dishes
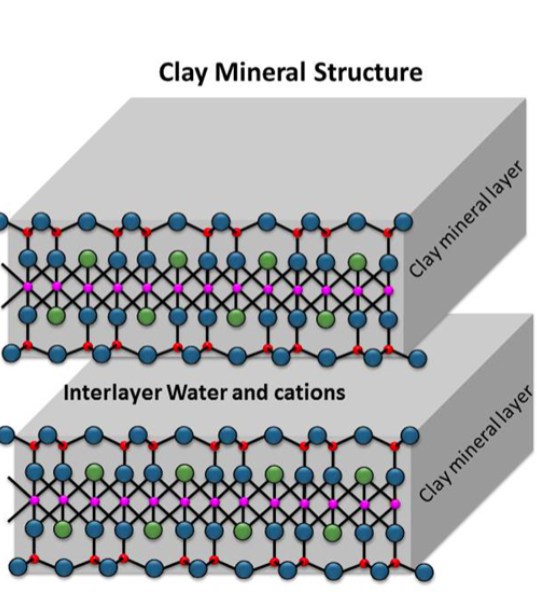
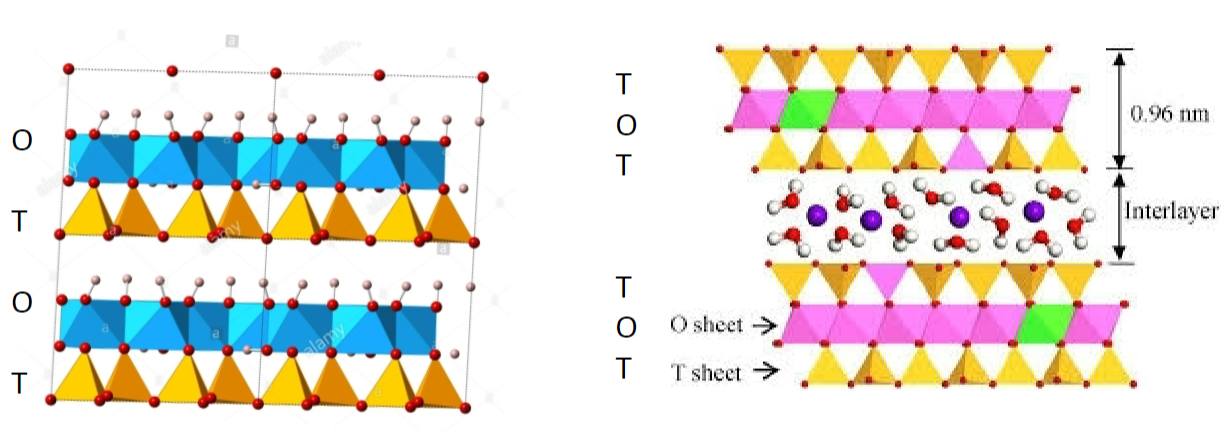
Montmorillonite
2:1 ratio (T-O-T-interlayer-T-O-T)
most common
large shrink to swell capacity
Temper
non-plastic materials used to prevent shrinkage and cracking during drying and firing of vesels (ex. bone, charcoal, wood ash, sand, crushed sandstone, crushed limestone, crushed volcanic rock, crushed shells)
Primary v. Secondary clays
primary: found at the site of formation
secondary: washed downstream
factors for types of clay
minerals
glaciation
ratio
Cuneiform
oldest written story (2700 BC)
account of King Ur’s superhuman strength and journey for immortality
influence Illiad and Odyssey
History of clay
Paleolithic: clay figurines
Mesolithic: Japanese hunter-gatherers used clay pots for cooking
Neolithic: sun-dried clay bricks in Israel, (oldest inhabited cities); crops stored in clay
7000 BC: Chatal Huyuk Clay Society
5000: potters wheel
4000BC: cuneiform tablets
Ancient uses of clay
building materials (Great Ziggurat of Ur)
writing
cooking
storage
sling ammunition
medical (Armenian bole medicine drink)
musical instruments (ocarina flute)
Modern uses of clay
sealing of oil drilling, landfills, and dams
building materials
odor absorbents
pottery
toothpaste
cosmetics
paint
gasoline production
papermaking
cement production
byproduct of phosphate mining
chemical filtering
organic farming
quick-clot combat gauze
hazardous waste clean-up
Carbon capture
contains olivine (MgSiO4)
traps Co2 into solid form
captures up to 1/3 of weight in CO2
could remove up to 1.7 trillions lbs of CO2 (5% of excess CO2 per year)
Affordances v. Constraints
affordances: durable, hard, watertight, thermal conductivity
constraints: brittle
Catalhoyuk clay society
mound settlement; entangled with clay
Theory of Entanglement
humans depend on things
things depend of things
things depend on humans (chains of interdependence)
humans depend of things that depend on humans/other things
Things
an assembling or bringing together of properties (potential and actualized)
Material entanglement
influences social and cultural traits over time
creates “thingworlds”
new materials are selected if they fit within existing entanglements
social change is not dependent on human intervention
Rare Earths
not easily smelted
hard to isolate
often found in clay
polluting to extract
chemically similar (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb)
Uses of rare earths
low-energy LEDs
strong magnets
wind turvines
electrical vehicles
polishing lgass
alloying agent for stell
phone LEDs
Extraction of rare earths
China extracts 63%
byproduct of steel production
restricted exports and caused a the price spike
removed export restrictions and dropped worldwide prices
source may not be sustanible (critical material)
Rare earth sustanibility
massive recycling effort
use less waste during extraction