Cell Membrane Structures and Transport Mechanisms: Micelles, Aquaporins, and Osmosis
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
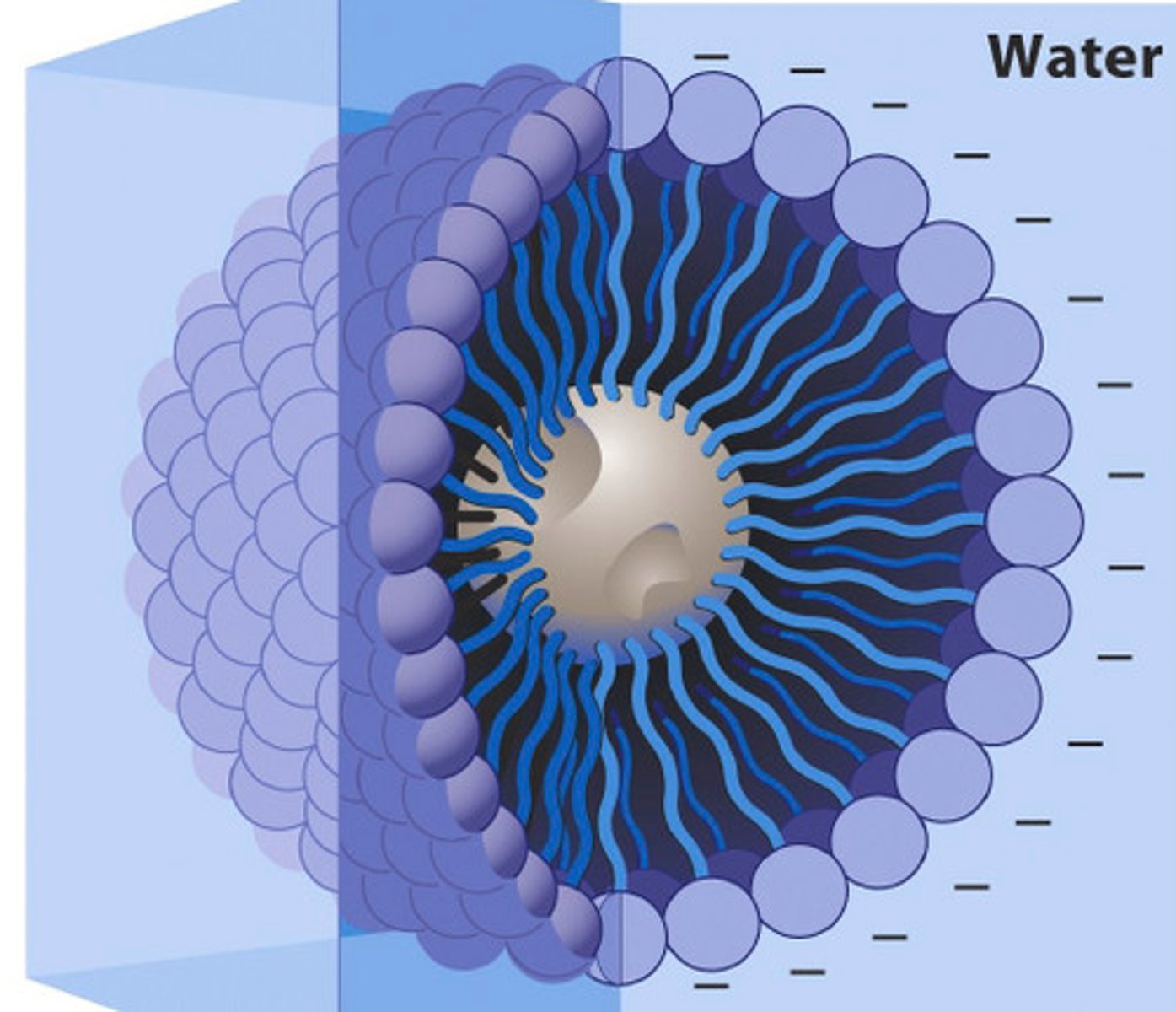
Micelle
Book: A spherical structure in which lipids with bulky heads and a single hydrophobic tail are packed.
My Definition: a ball-like structure that consists of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts.
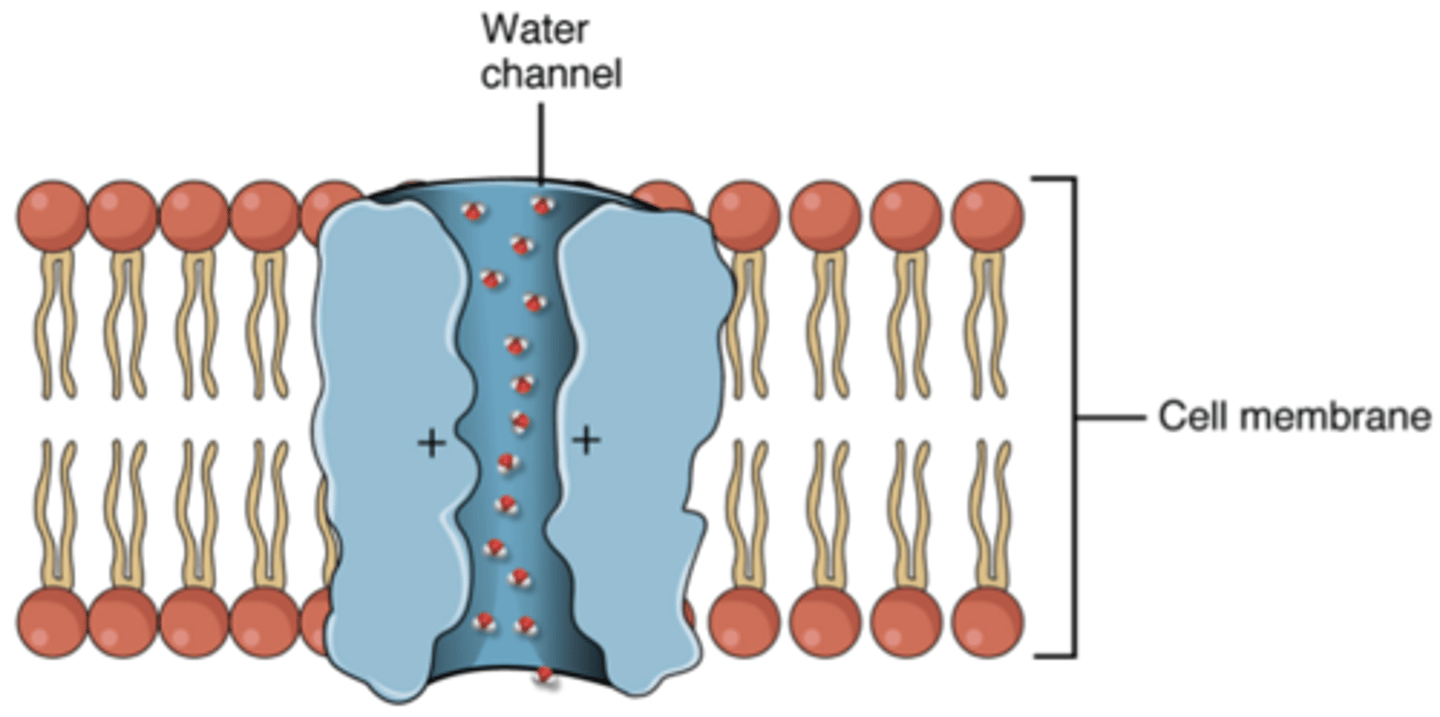
Aquaporin
Book: A protein channel that allows water to cross the cell membrane more readily than by diffusing through the lipid bilayer.
My Definition: a protein that acts as a water channel and allows water to pass through the cell rapidly.
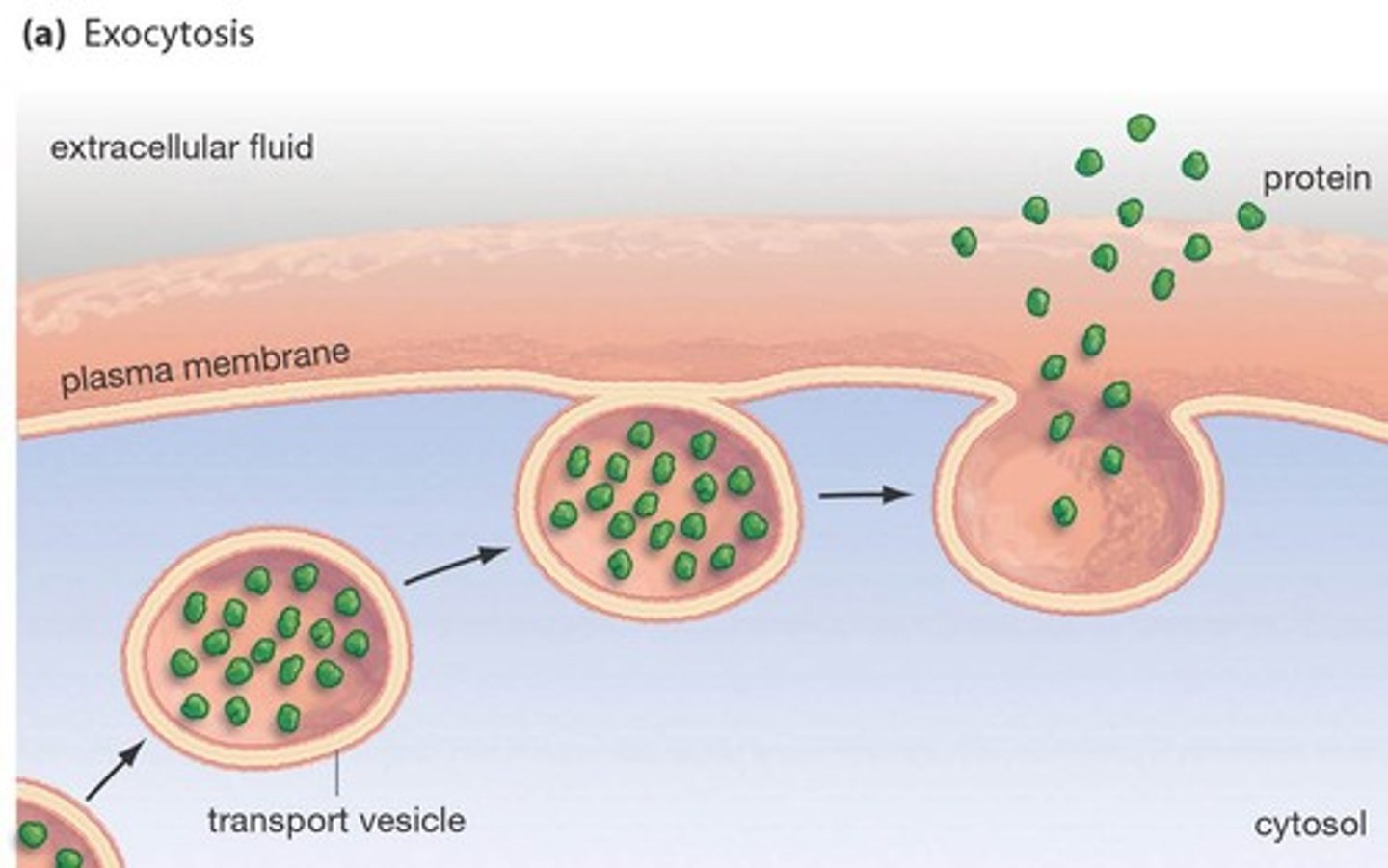
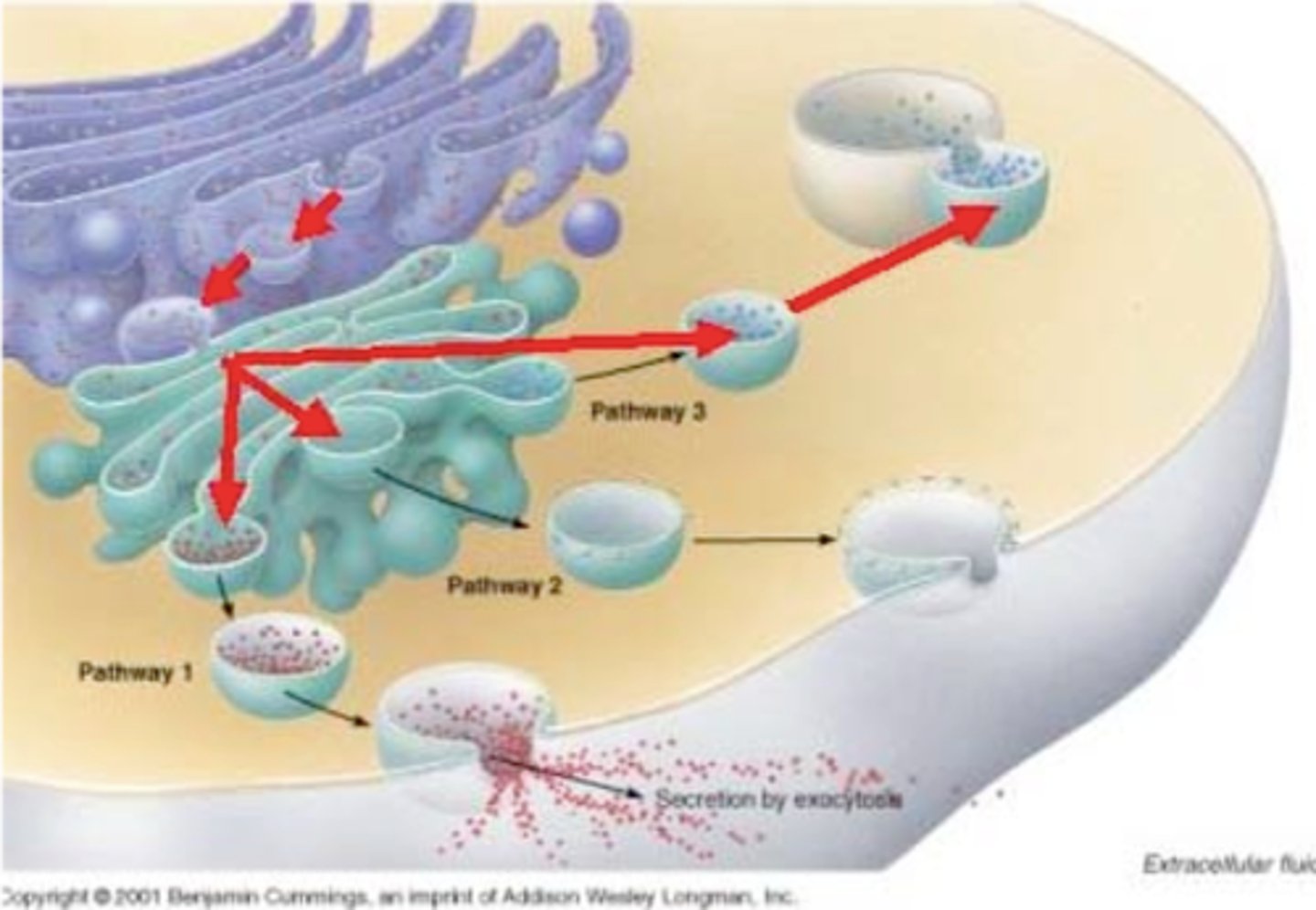
Exocytosis
Book: The process in which a vesicle from the cytoplasm fuses with the cell membrane and empties its contents into the extracellular space or delivers proteins to the cell membrane.
My Definition: the process of moving materials from inside the cell to outside the cell.
Turgor pressure
Book: Pressure within a cell resulting from the movement of water into the cell by osmosis and the tendency of the cell wall to resist deformation.
My Definition: the force created by the water in a plant cell, pushing against the cell wall.
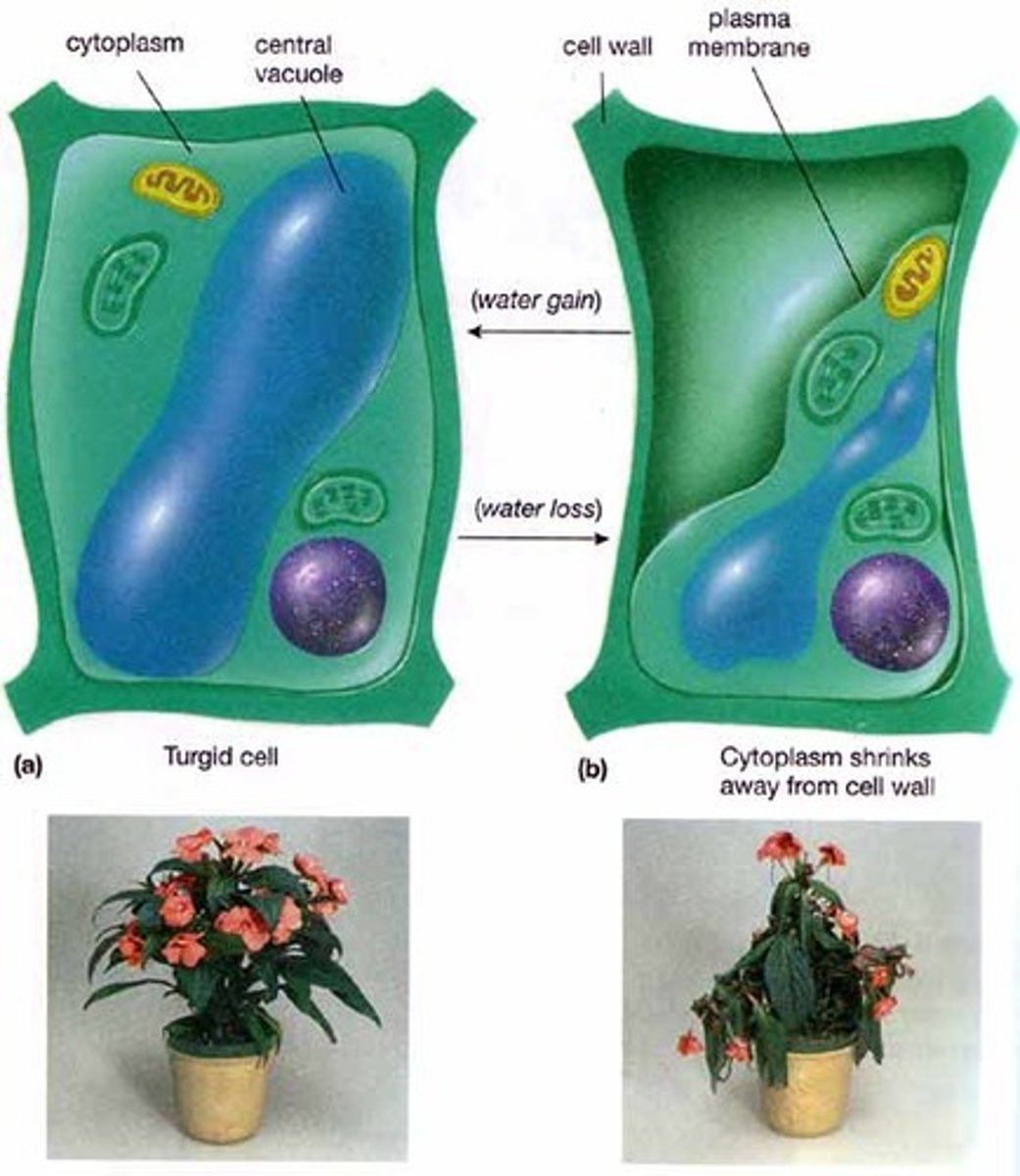
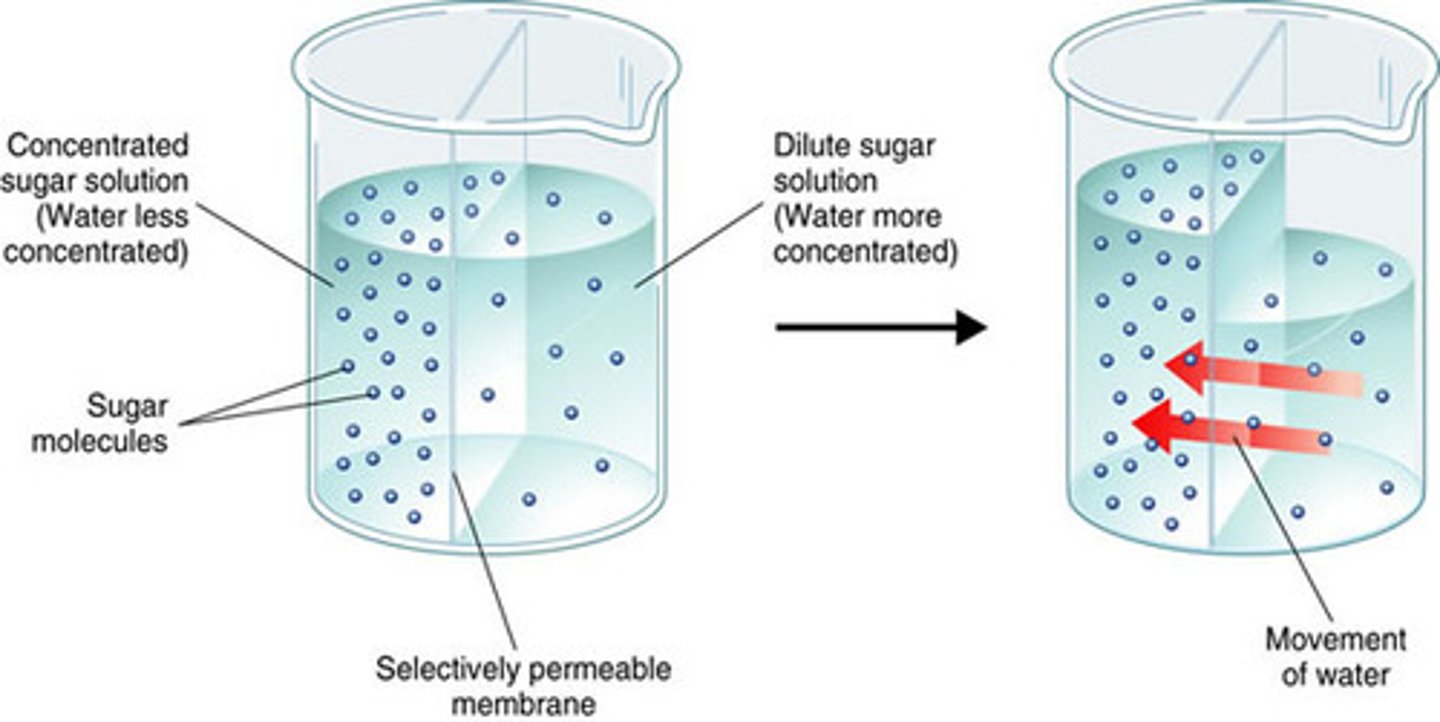
Osmosis
Book: The net movement of a solvent, such as water, across a selectively permeable membrane toward the side of higher solute concentration.
My Definition: the net movement of water across a permeable membrane, from an area of higher water concentration to a lower water concentration.
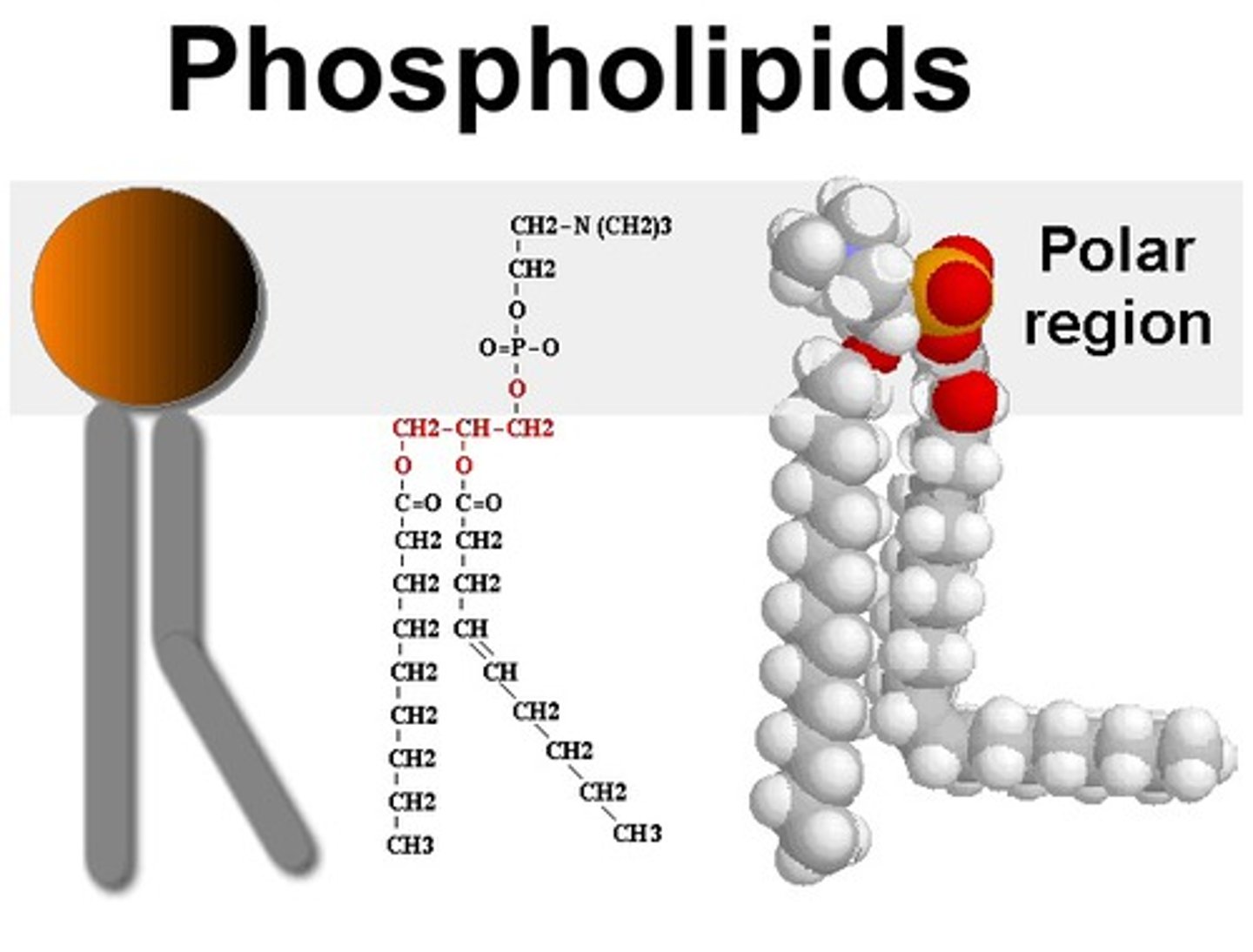
Amphipathic
Book: Having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
My Definition: a molecule that has parts that are both hydrophobic and hydrophilic.
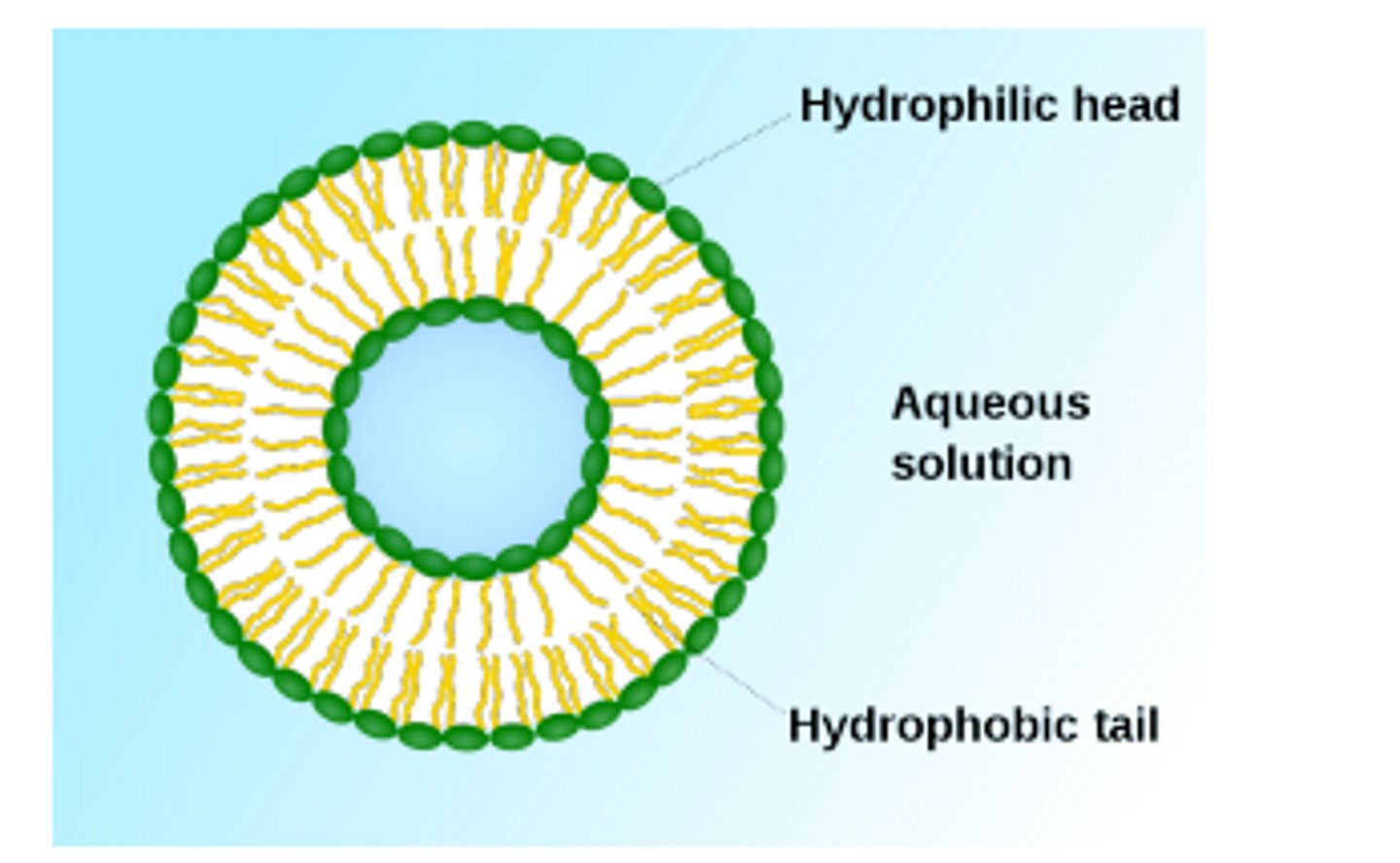
Liposome
Book: An enclosed bilayer structure spontaneously formed by phospholipids in environments with neutral pH, like water.
My Definition: a sphere made of a double layer of lipids that surrounds a watery core
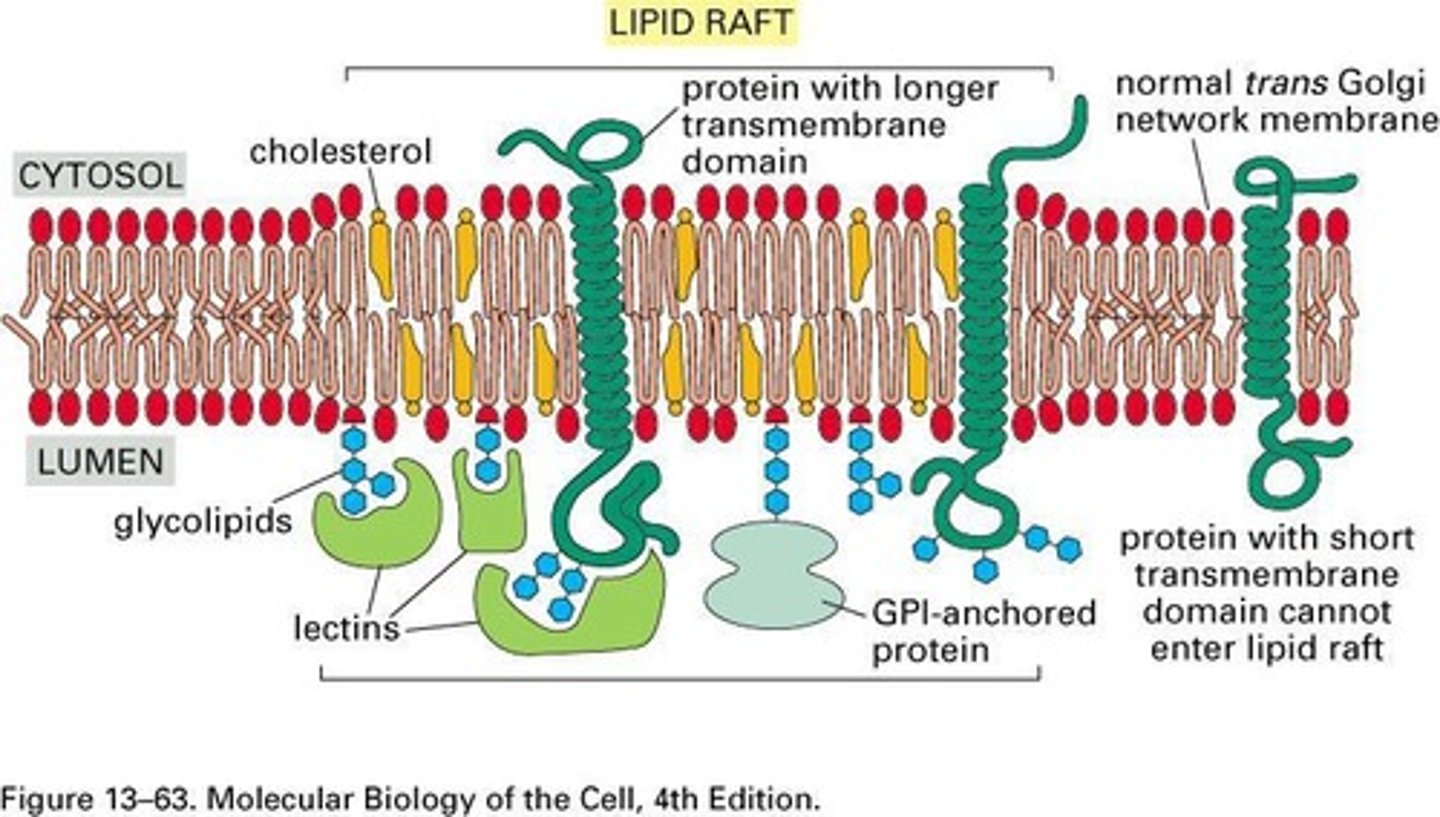
Lipid raft
Book: Lipids assembled in a defined patch in the cell membrane.
My Definition: a part in a cell's membrane that is made of specific lipids, that act as a place for proteins to perform cellular functions.
Anchor
Book: A membrane protein that attaches to other proteins and helps to maintain cell structure and shape.
My Definition: provides stability or holds objects in place in a cell
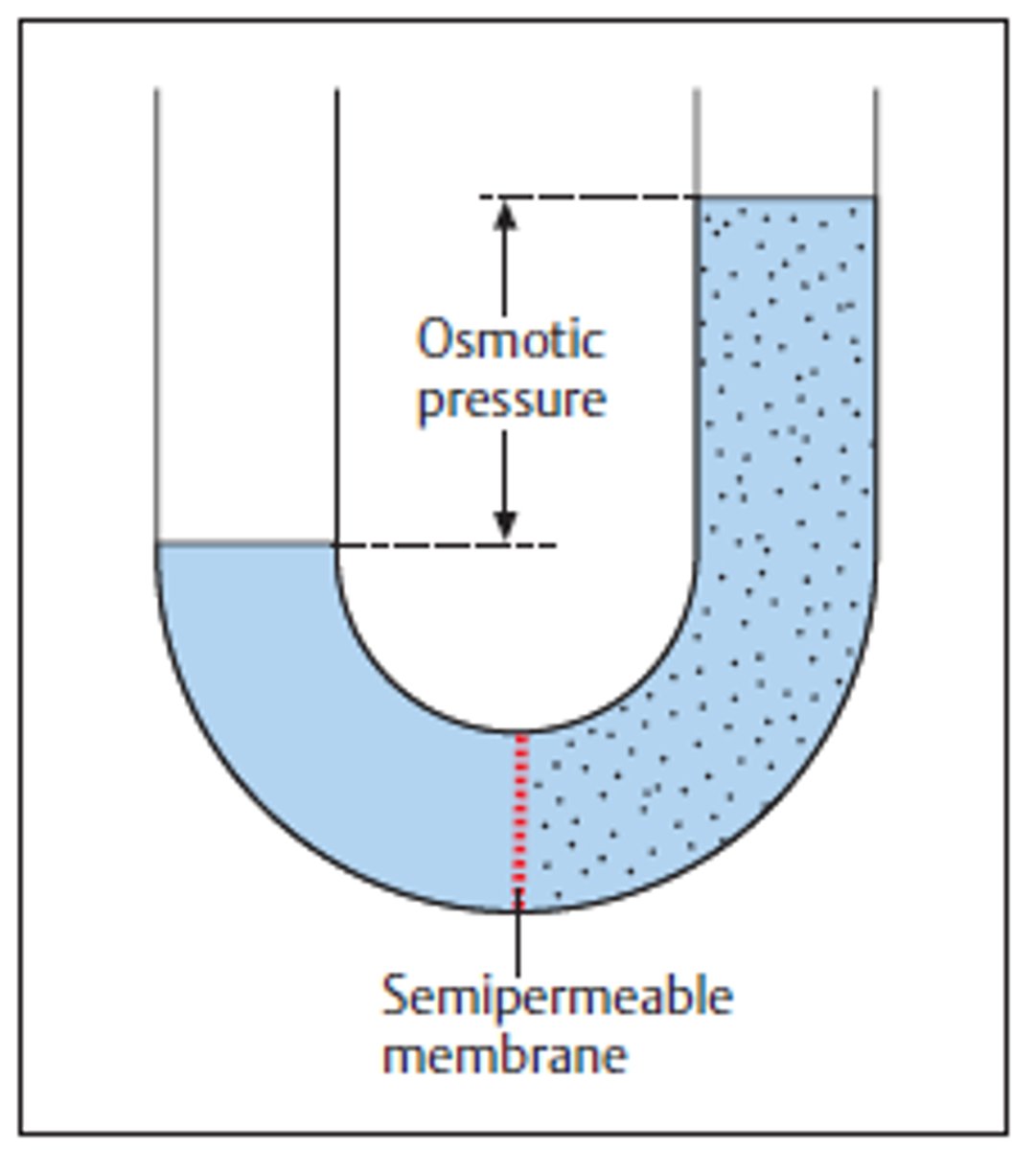
Osmotic pressure
Book: The pressure needed to prevent water from moving from one solution into another by osmosis.
My Definition: pressure that needs to be applied to stop water from moving across the membrane.
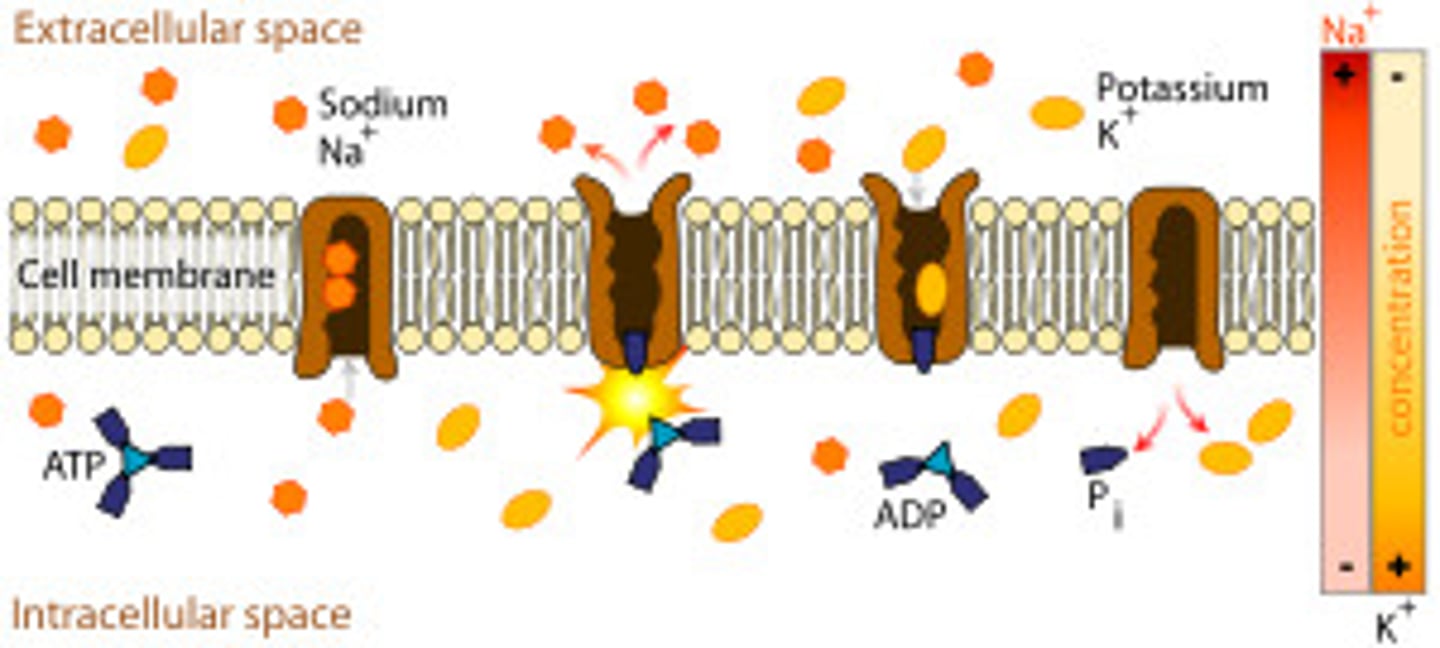
Electrochemical gradient
Book: A gradient that combines the charge gradient (difference in charge across a membrane) and chemical gradient (difference in concentration across a membrane).
My Definition: the combined force of a concentration gradient and an electrical gradient, which drives movement of ions.
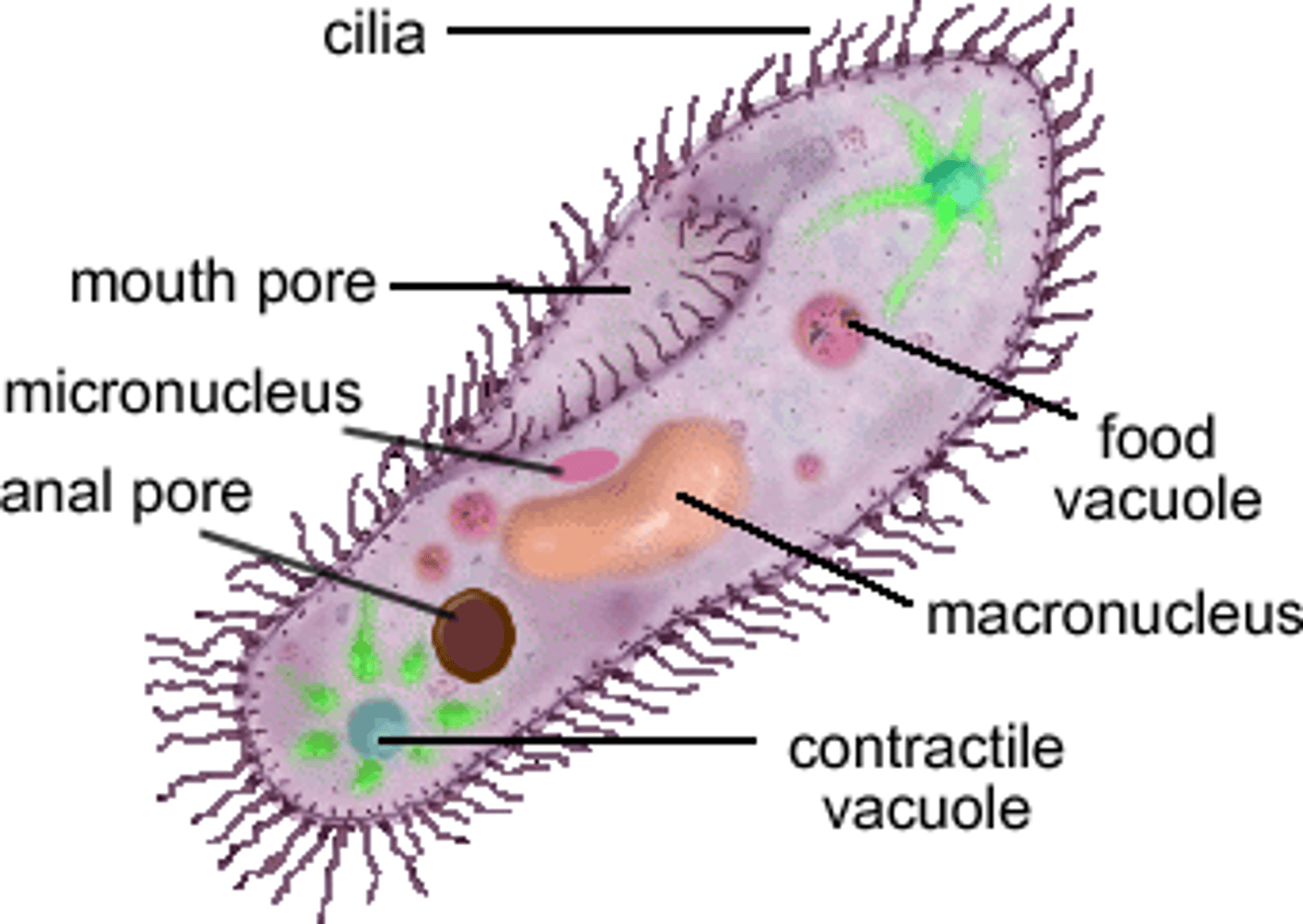
Contractile vacuole
Book: A type of cellular compartment that takes up excess water and waste products from inside the cell and expels them into the external environment.
My Definition: an organelle that regulates cell water balance by collecting and expelling excess water and waste
Vesicle
Book: A small membrane-enclosed sac that transports substances within the cell.
My Definition: structure that transports, stores, and digests substances in the cell.
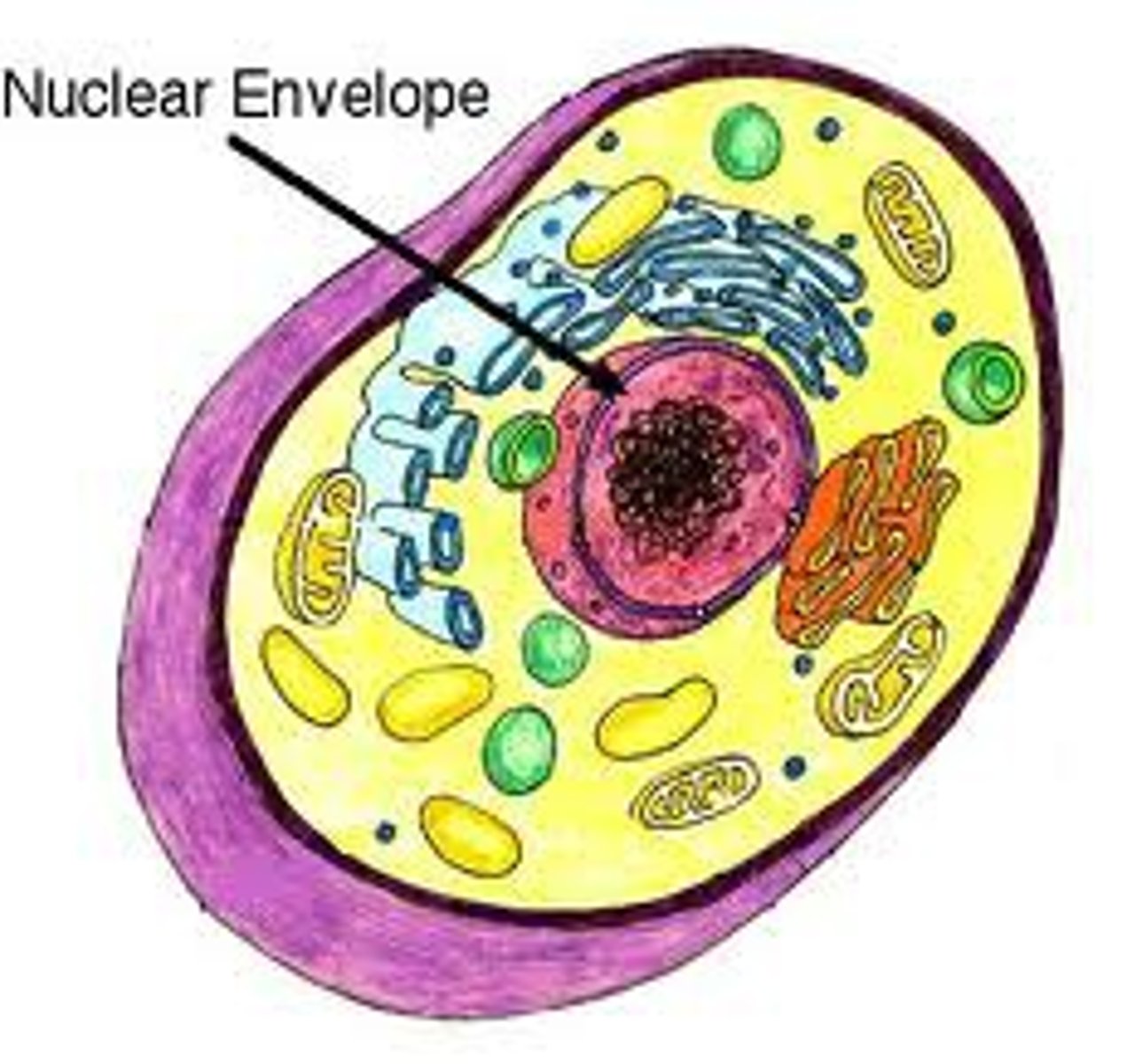
Nuclear envelope
Book: The cell structure, composed of two membranes, inner and outer, that defines the boundary of the nucleus.
My Definition: a membrane that acts as a barrier, that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell
Lumen
Book In eukaryotes, the continuous interior of the endoplasmic reticulum; in plants, a fluid-filled compartment enclosed by the thylakoid membrane; generally, the interior of any tubelike structure.
My Definition: interior of membrane-bound organelles and the central space of tubelike structures.