Introduction to Autoimmune Disease
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the 3 key properties of the immune system?
-Repertoire of antigen receptors
- immune memory
-immunologic tolerance

______ are major tissues and organs of the immune system
lymphoid
What are primary lymphoid tissues?
Bone Marrow & Thymus
What are secondary lymphoid tissues?
-Spleen
-Lymph nodes
-MALT
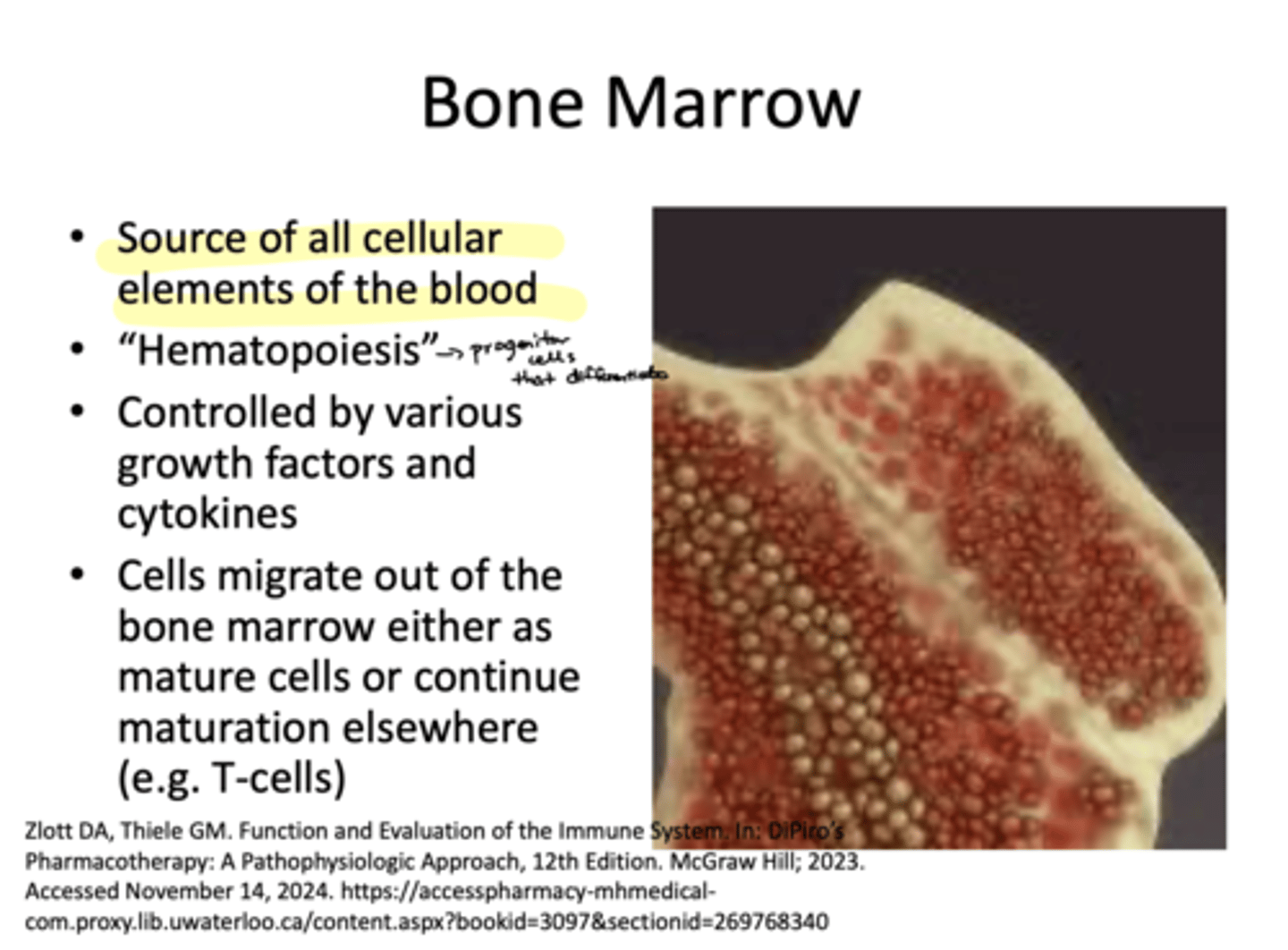
What does the bone marrow do?
It is the source of all cellular elements of the blood- conducts hematopoiesis
What does the thymus do?
Produces T-cells from lymphocyte progenitors
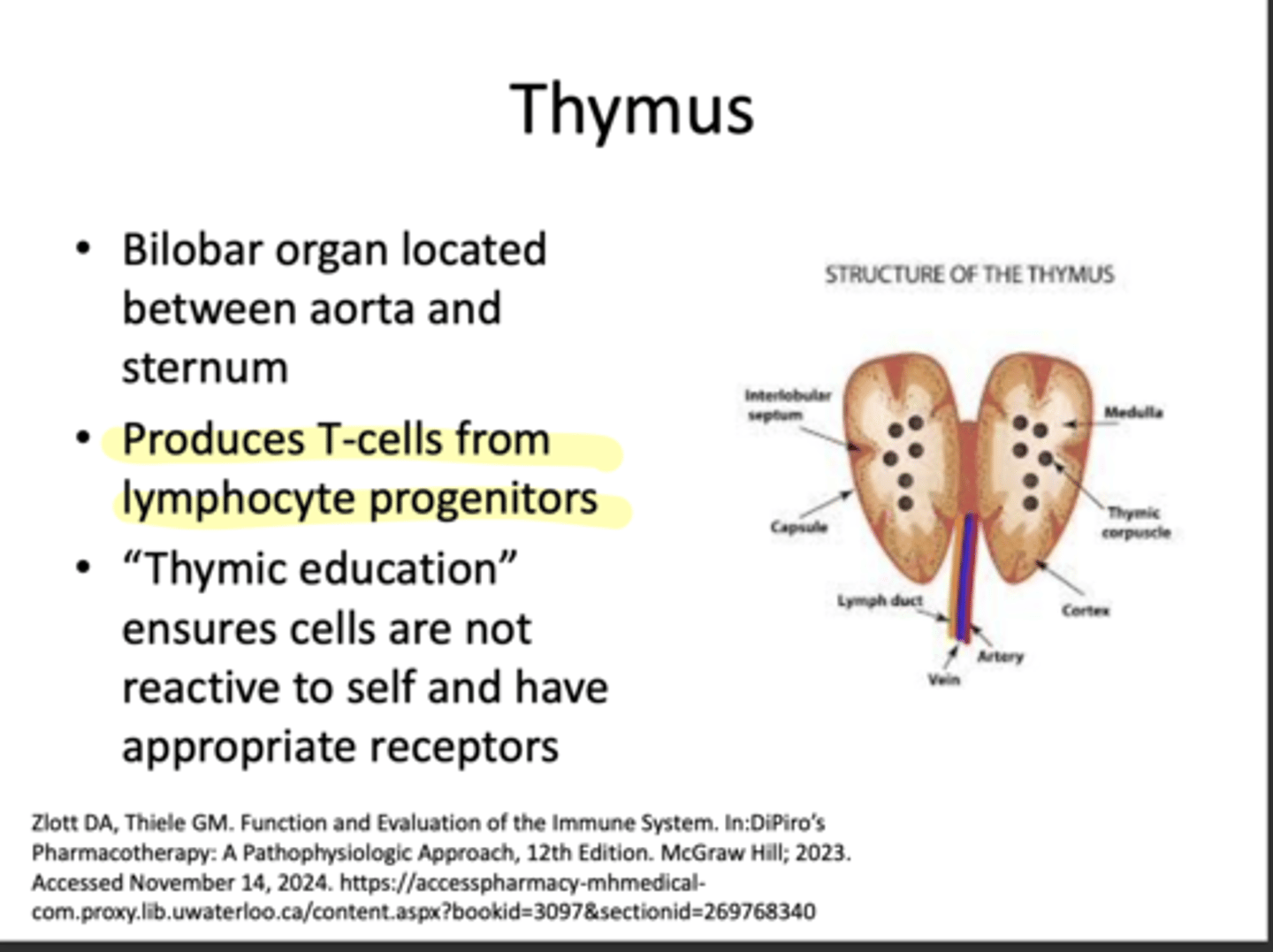
What does the spleen do?
-Removes damaged RBCs from blood
-can also generate immune response for debris in blood
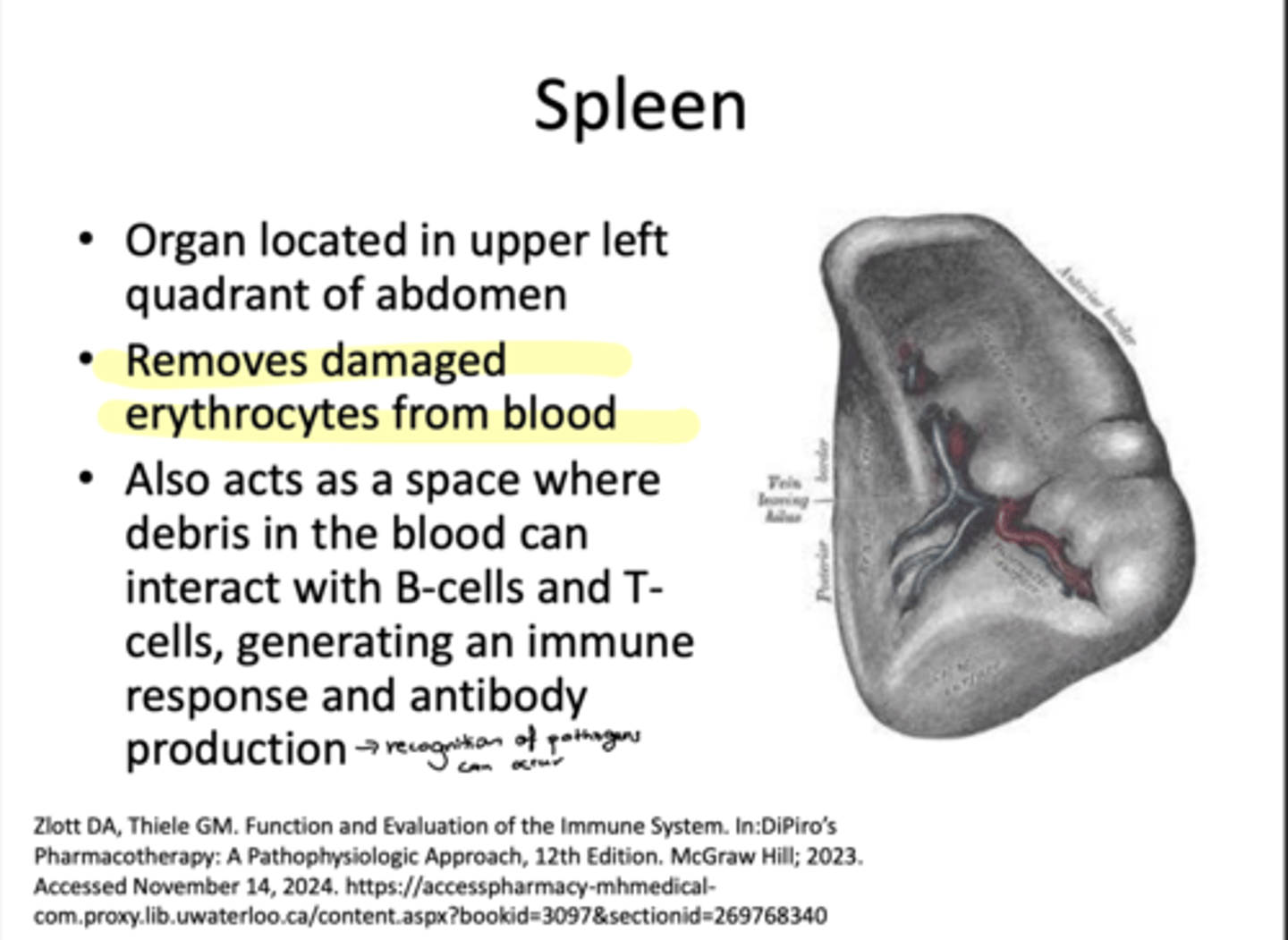
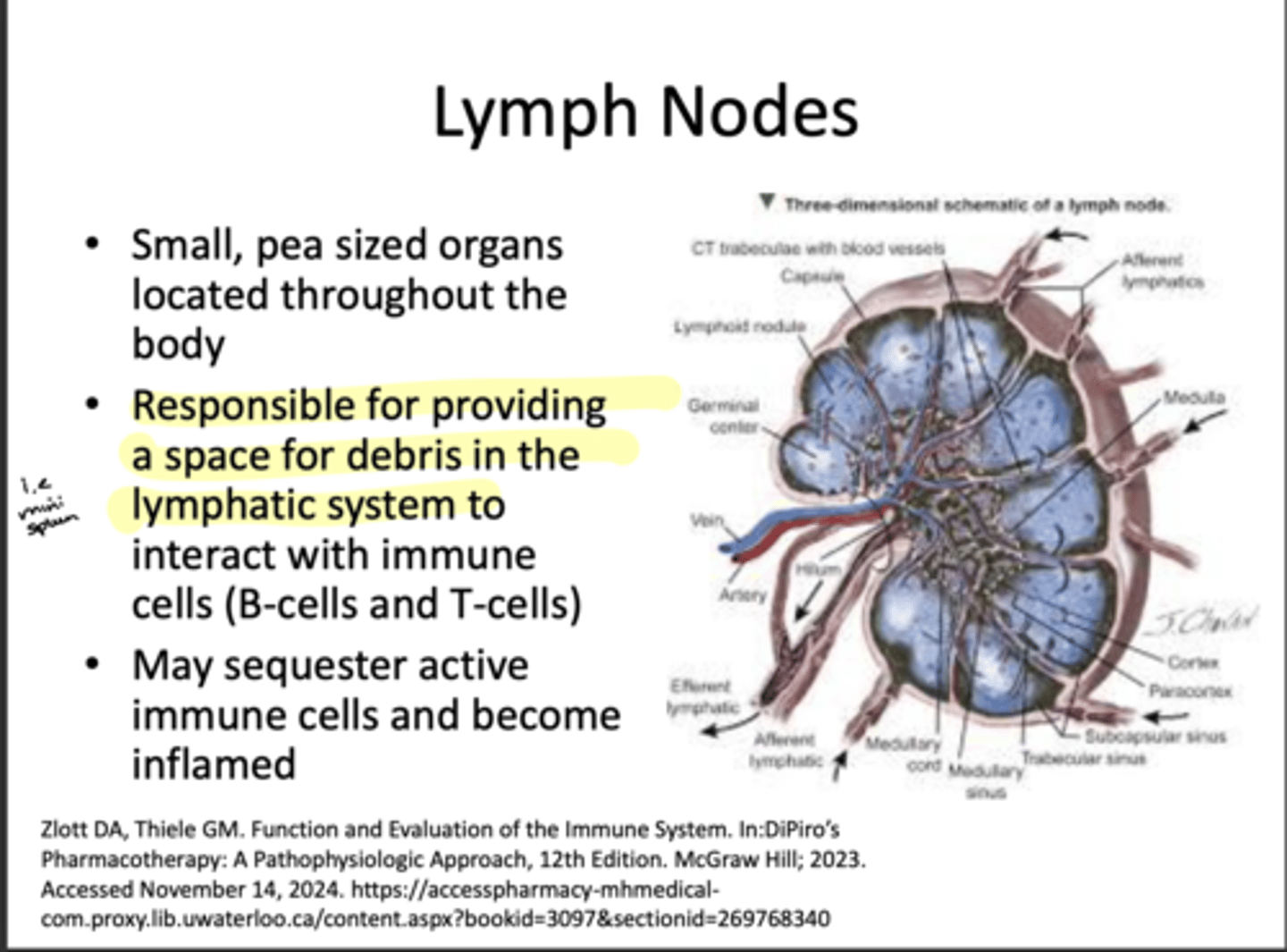
What are the lymph nodes responsible for?
Providing space for debris in the lymphatic system to interact with an immune response
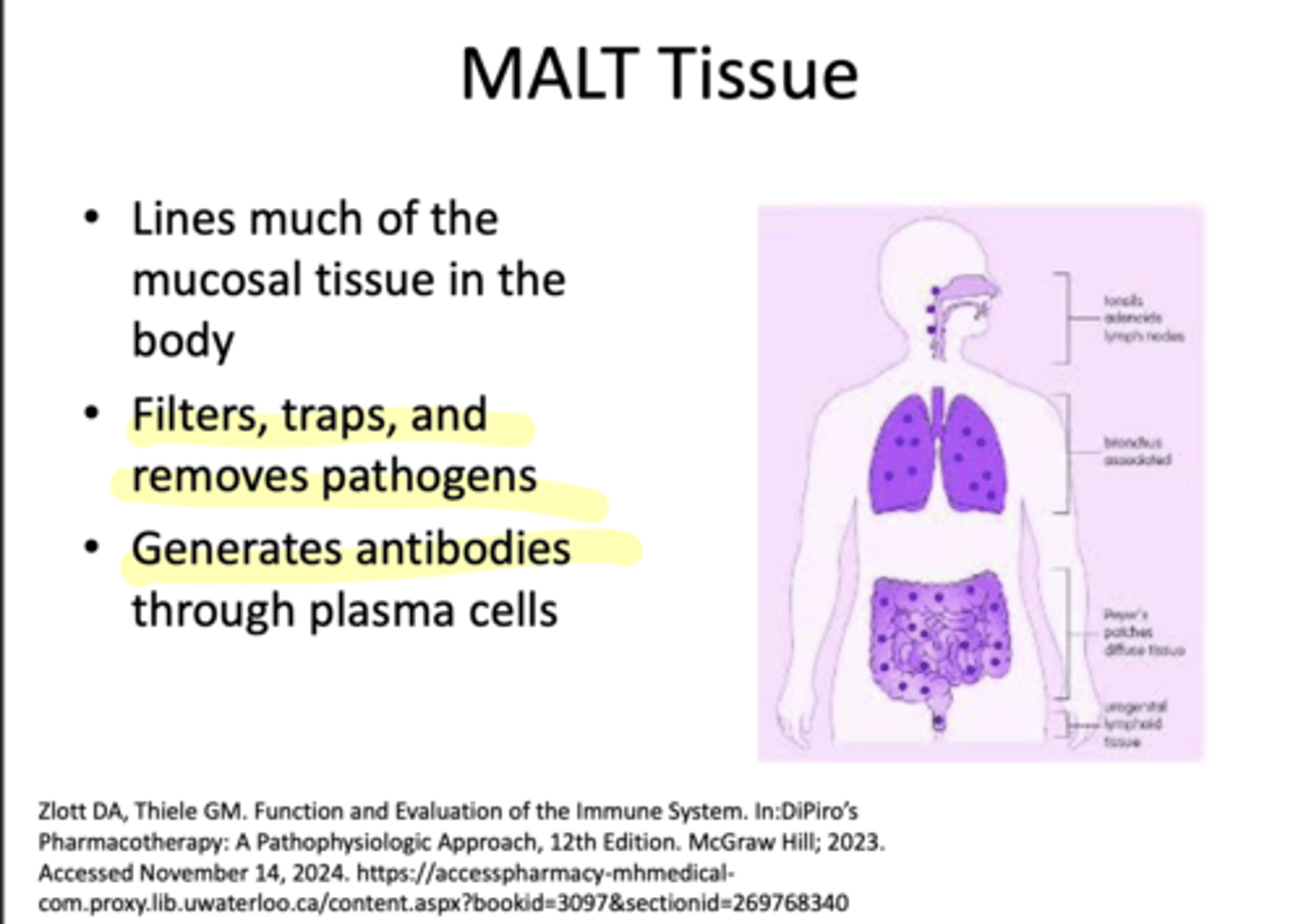
What is MALT Tissue?
-Filters, traps and removes pathogens
-Generates antibodies through plasma cells
The immune system is broadly said to be made up of which 2 types of immunity?
Acquired and Innate
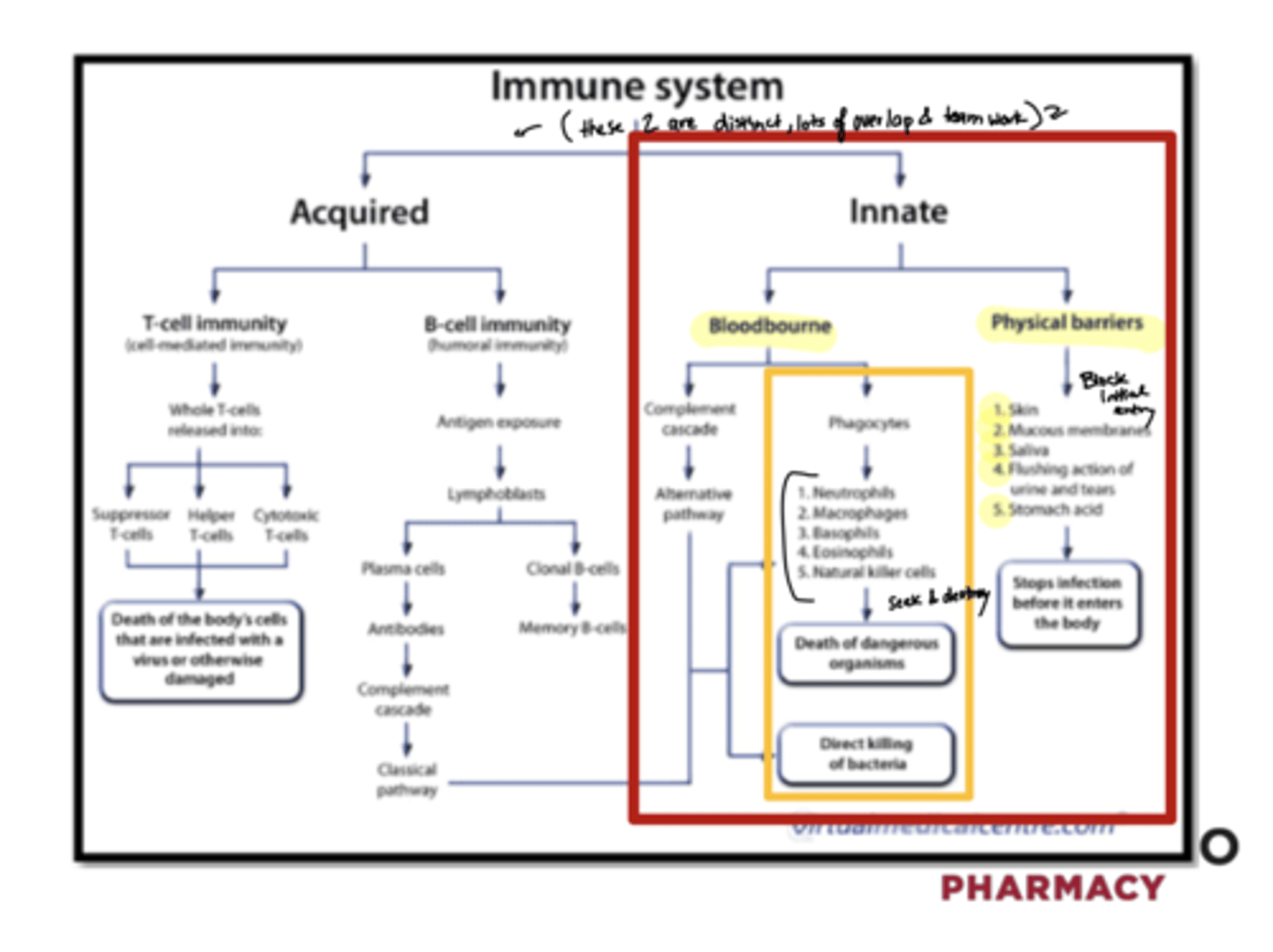
Innate immunity is aka ______
"First line of defense"
What cells allow for recognition in innate immunity through germline-encoded receptors?
Phagocytic cells

What are some examples of phagocytic cells
-Macrophages
-Neutrophils
-Eosinophils
-Basophils
-NK cells

What is a Macrophage?
First cell to act as sentinel to detect and report what's in it's environment
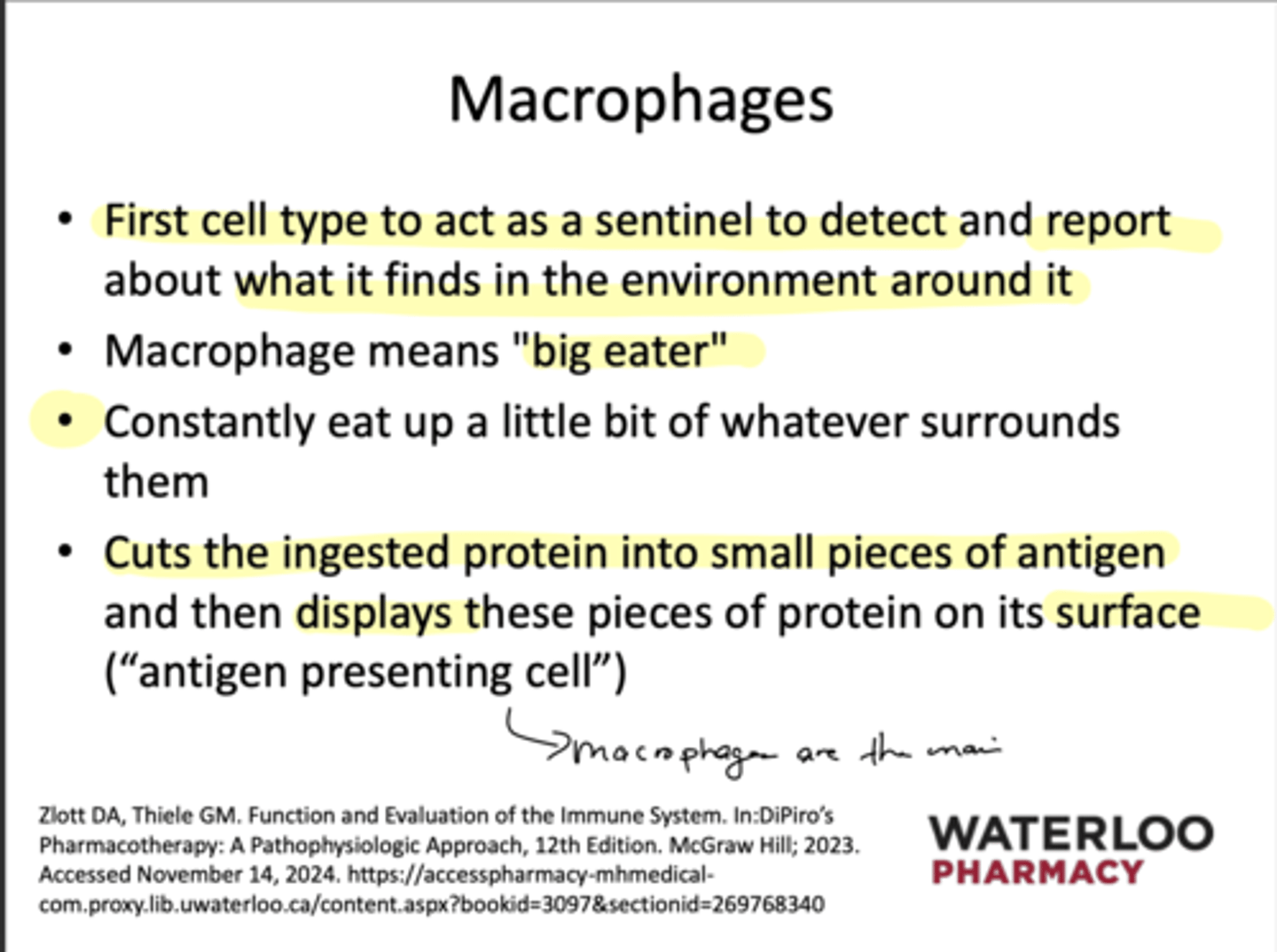
Why does Brynne resonate with a Macrophage?
Because we eat whatever is around
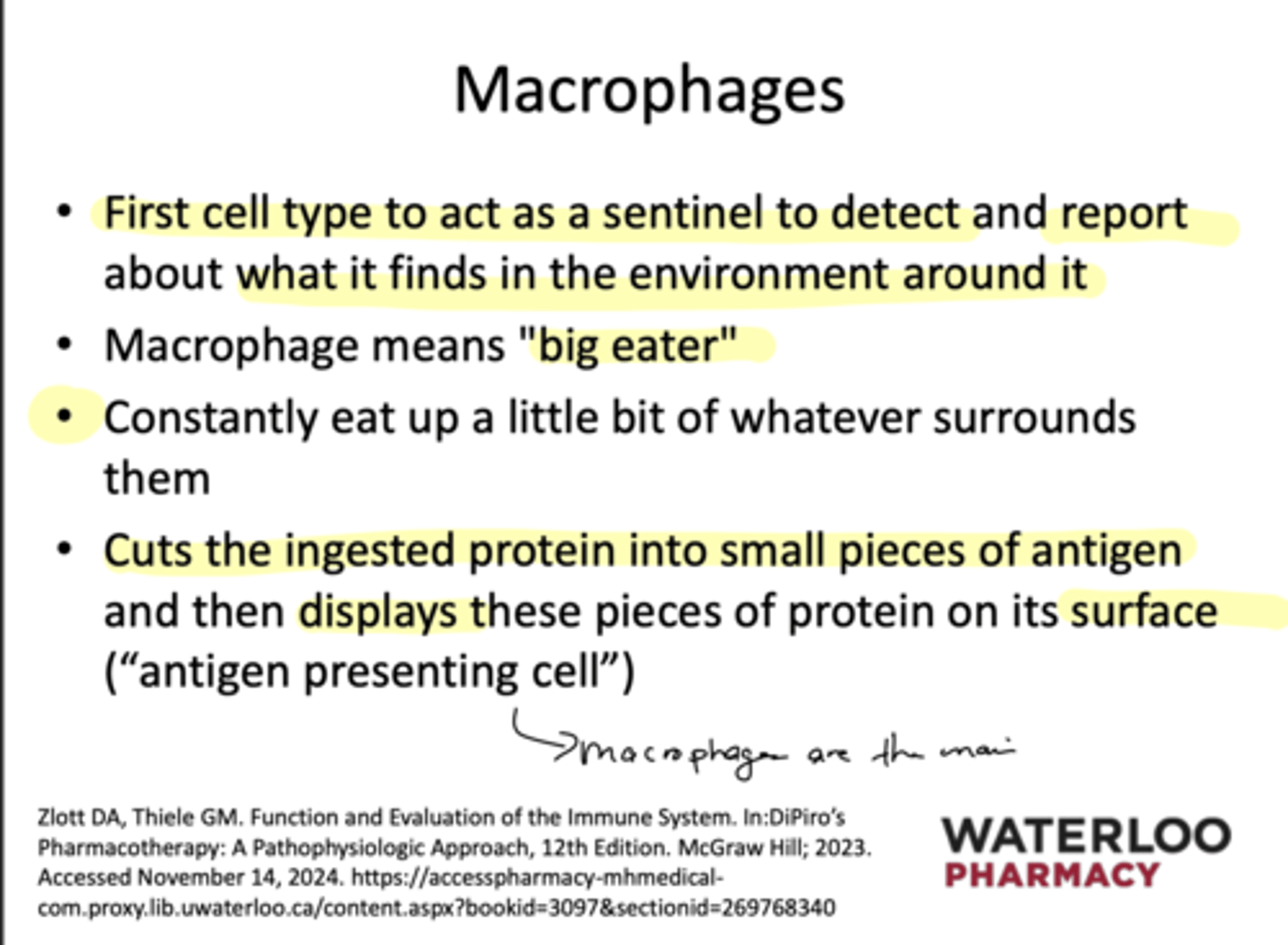
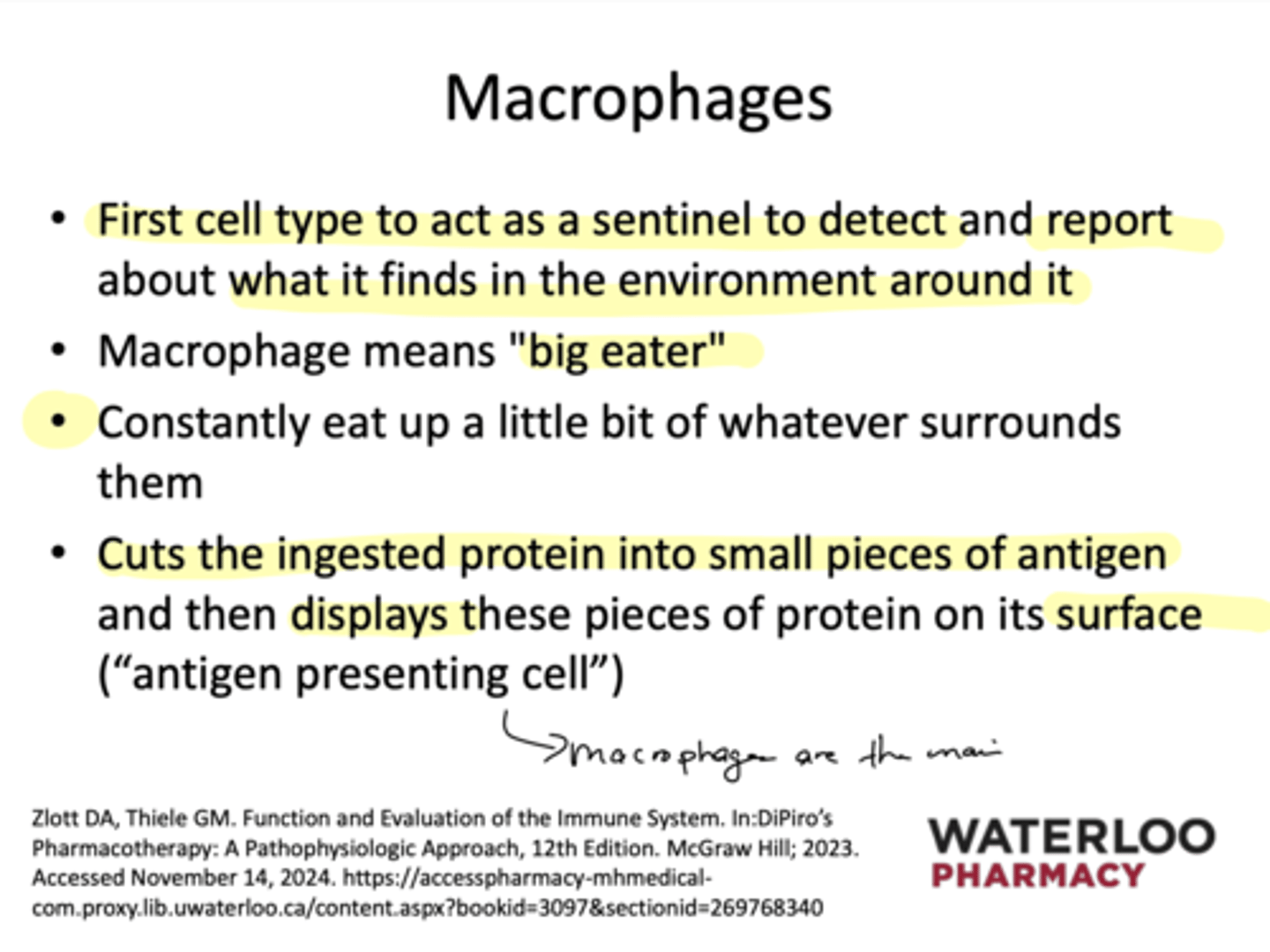
What does the macrophage do when it ingests a protein?
It cuts it up and then serves it up on it's surface
What is released when an immune cell recognizes something as foreign?
Cytokines

How can cytokines modify the behaviour of other cells?
-Recruitment
-Activation
-Growth and Maturation

What are neutrophils attracted to?
Site of injury/invasion by chemokines (cytokine)
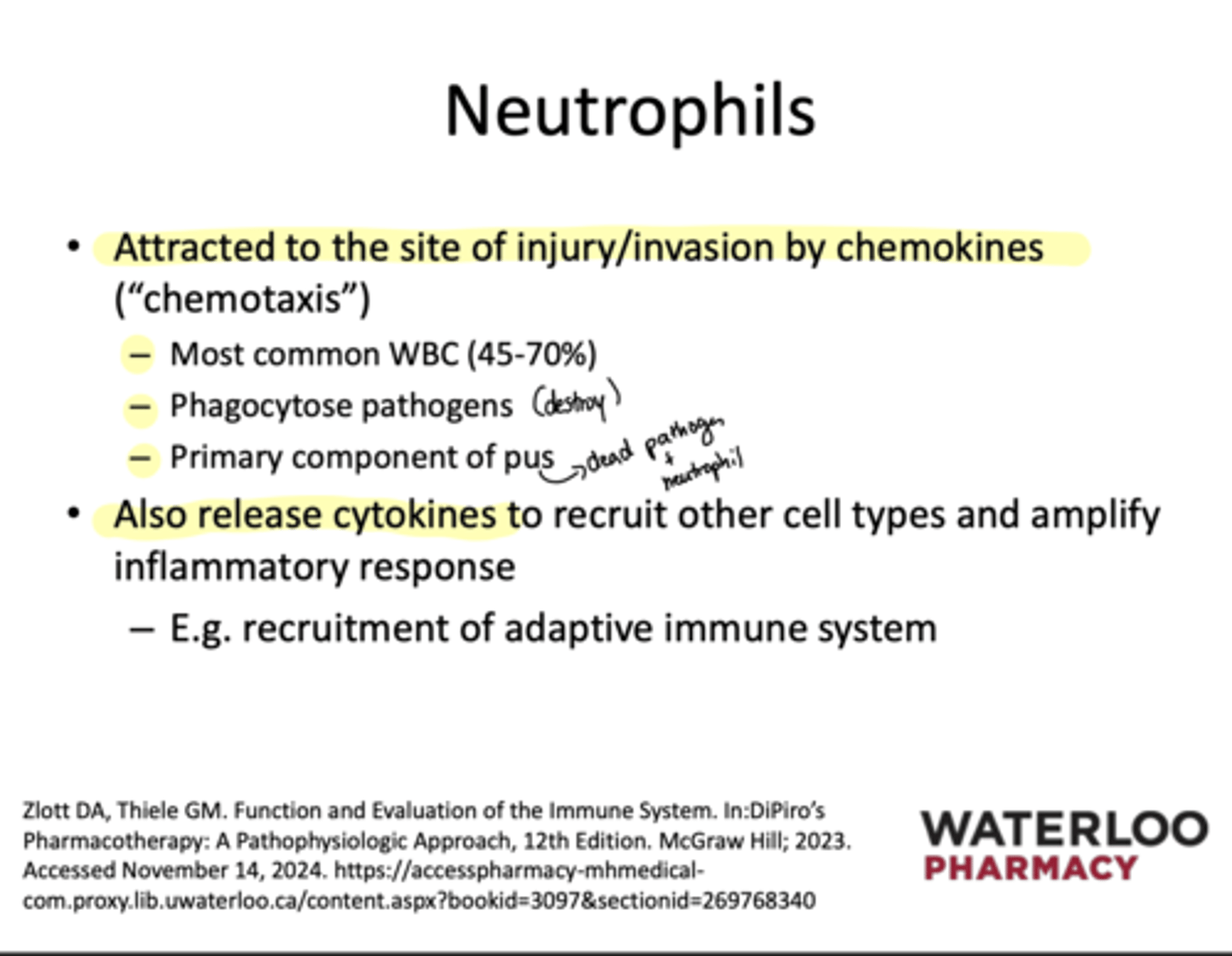
What do neutrophils do?
-Phagocytose pathogen
-release more cytokines to recruit more cells to amplify response
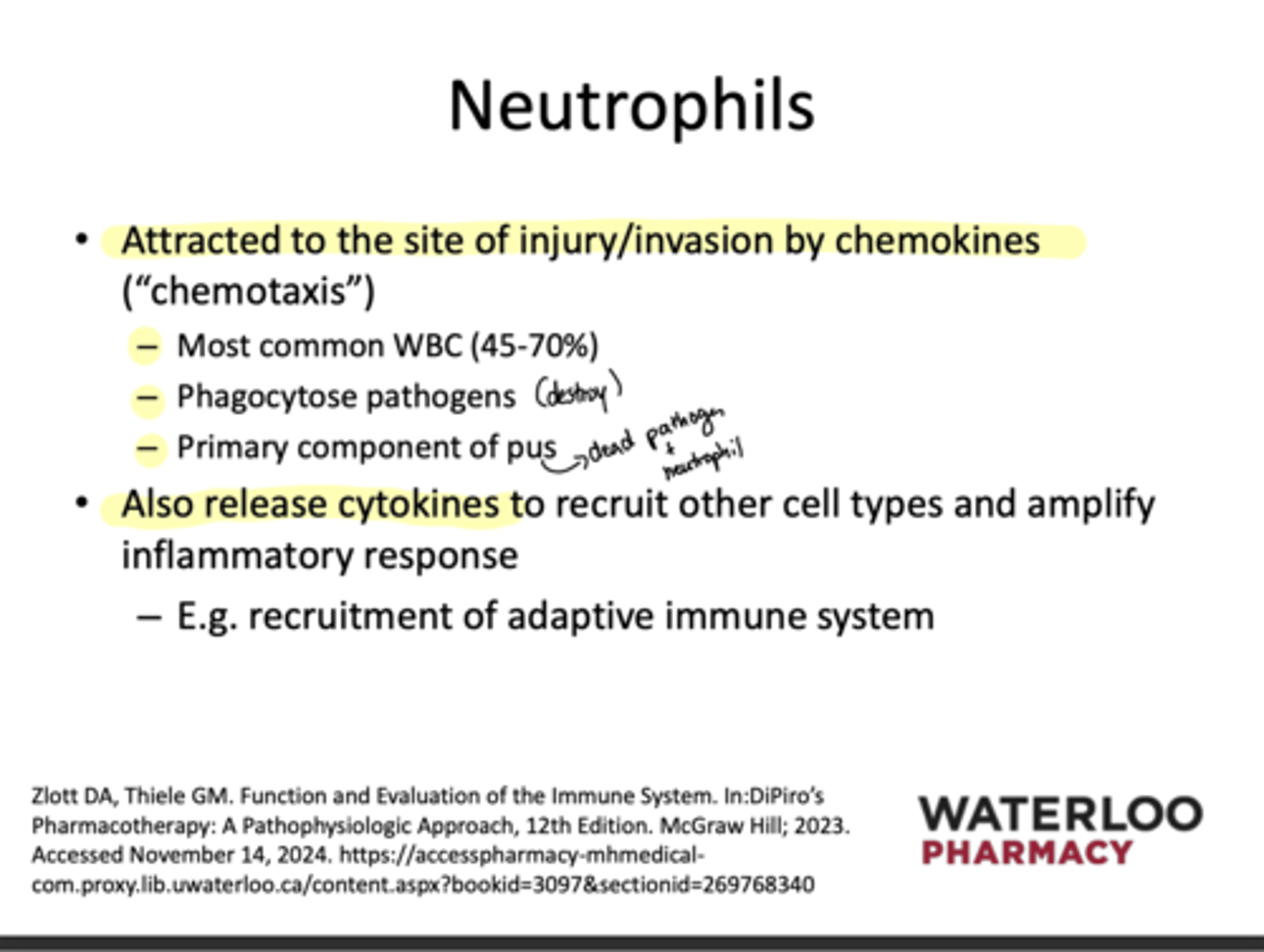
Which phagocyte is a primary component of pus?
neutrophils
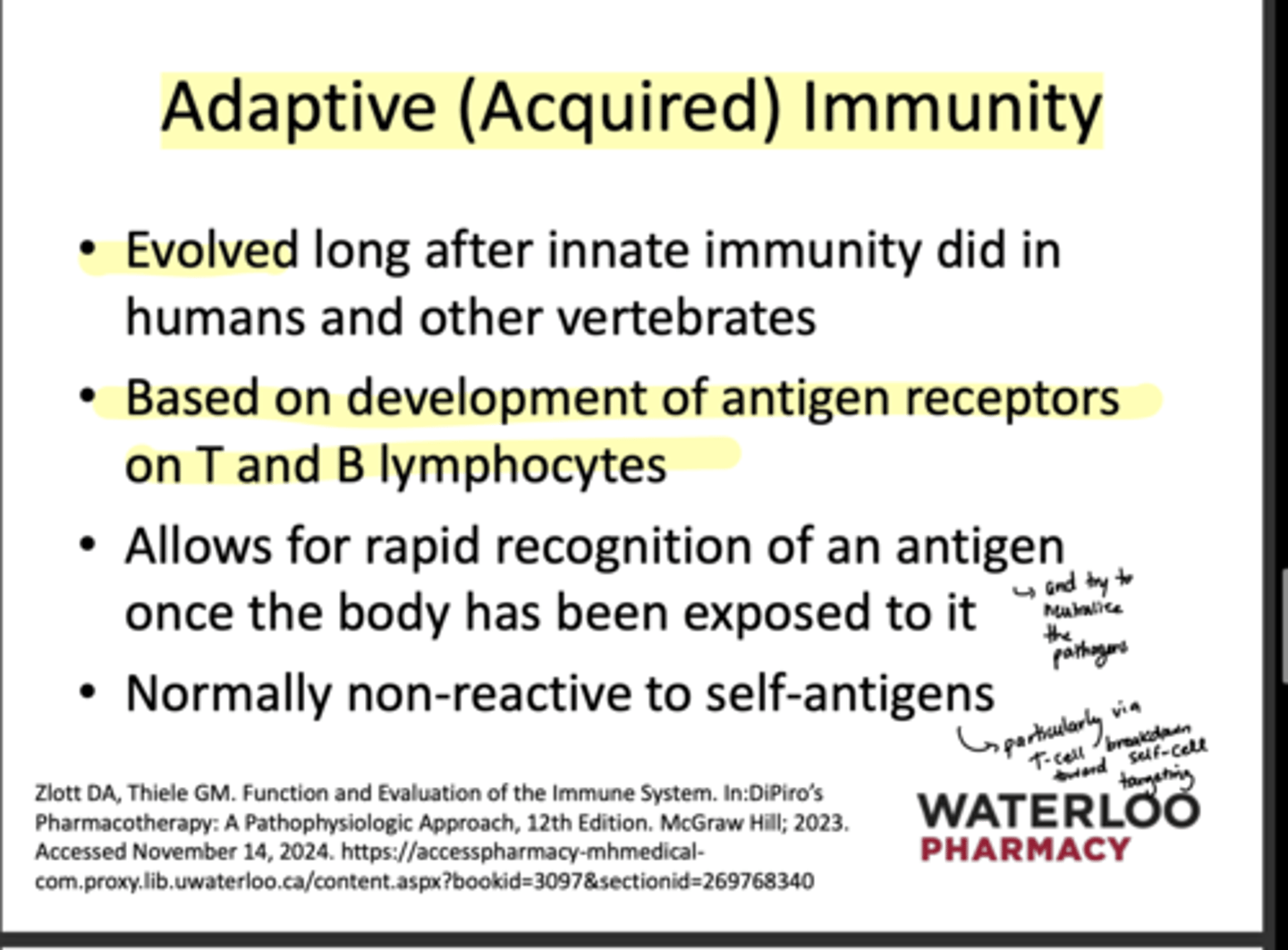
What antigen receptors is Adaptive immunity based on?
Those on T & B lymphocytes

What does adaptive immunity allow for?
Rapid recognition of an antigen after initial exposure
Which cell is the primary decision maker of the immune process?
T cells
What cells are highly specialized?
T-cells
What happens when a APC and T-cell encounter each other?
They will see if an antigen on the APC fits the T-cell receptor
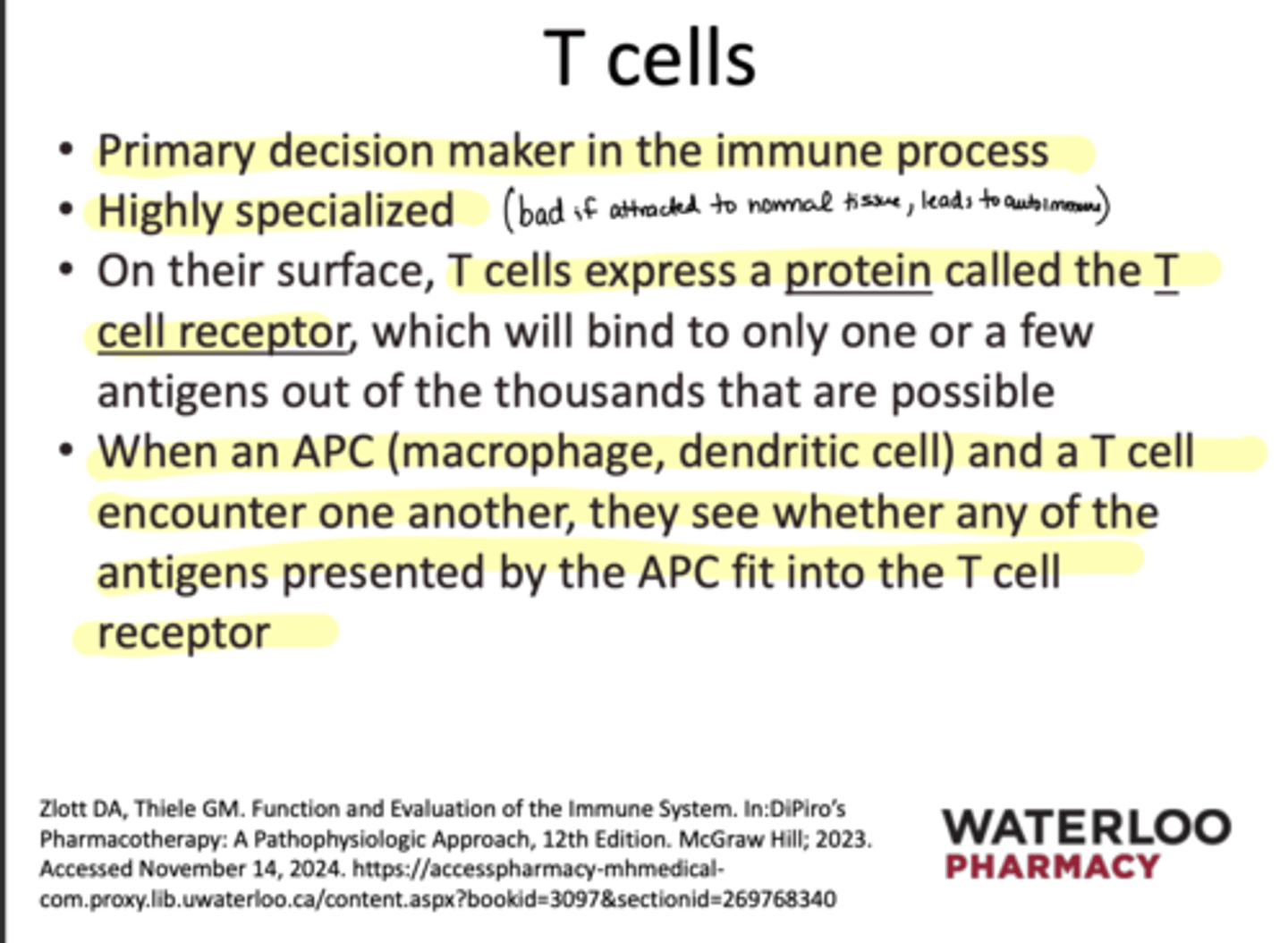
T or F: Antigens usually fit the T-cells
F

What happens if an antigen fits a T-cell receptor?
The cells stick and activation of chemical messengers leads to the T-cell becoming active; Helper CD4+ cells release cytokines and Cytotoxic CD8+ cells recognize and destroy antigens

T or F: B cells make surface proteins
F: They differentiate into plasma cells

What do B-cells make?
Antibodies

What to antibodies do?
Tag antigens for destruction

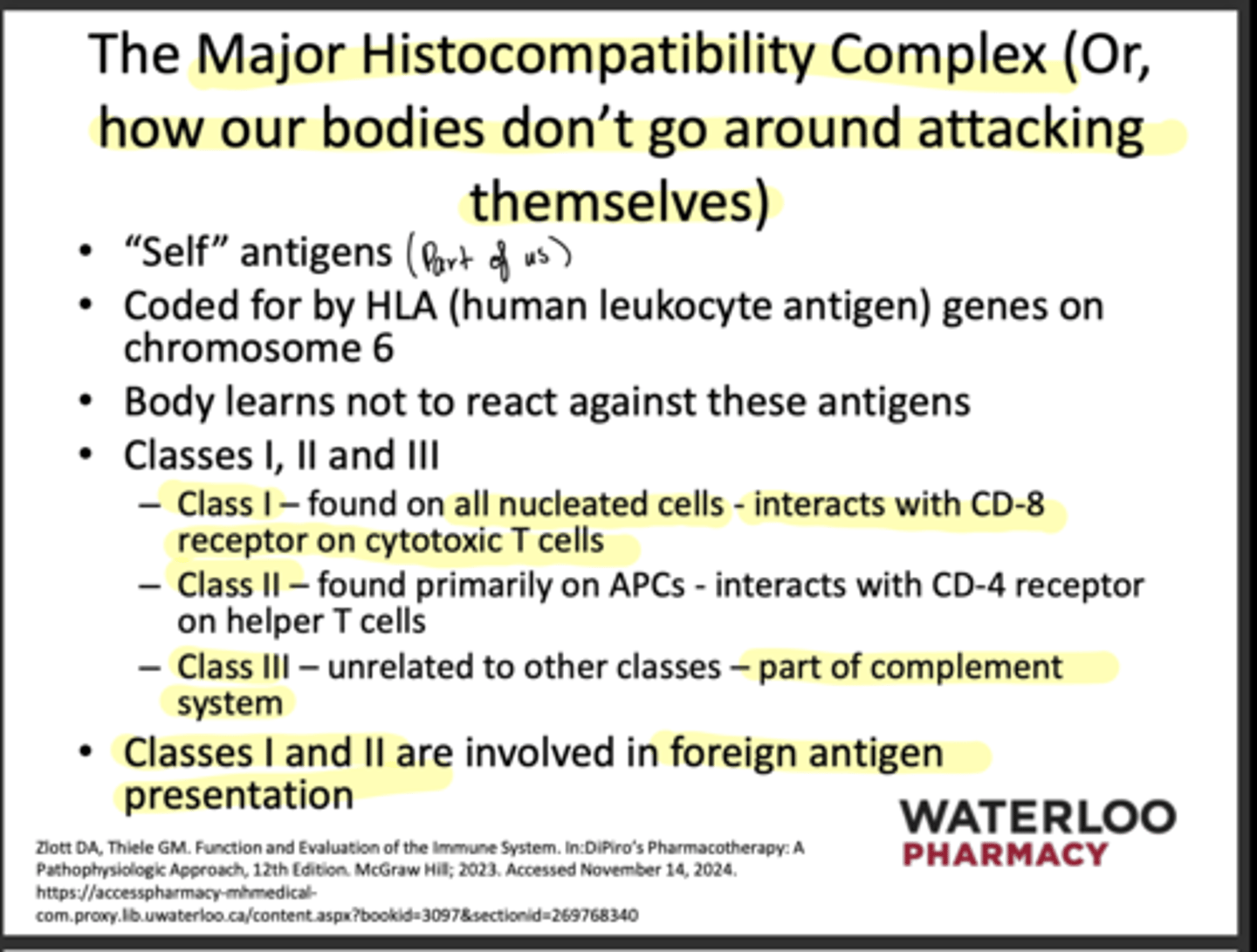
What chromosome are human leukocyte antigen genes on?
chromosome 6

T or F: the body learns to not react to HLA
T

What are the 3 classes of the Major Histocompatibility Complex?
-Class 1: found on all nucleated cells- interaction CD8
-Class 2: found on all APC's, interaction CD4
-Class 3: unrelated to other classes- part of complement system
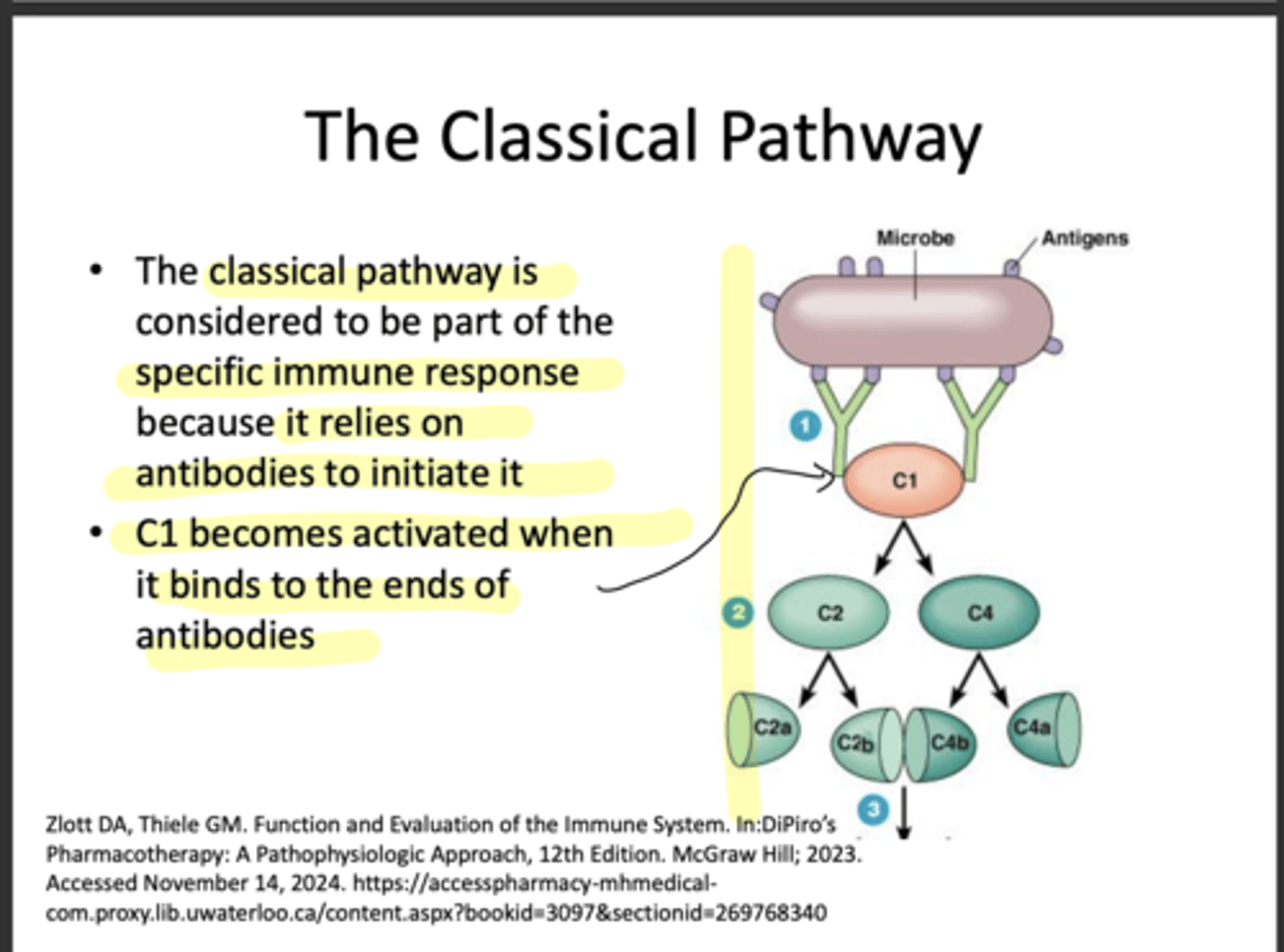
What are the 2 pathways of the complement system?
Alternative (part of innate) & classical (part of adaptive)

The ______ pathway is considered a part of the specific immune response because it relies on antibodies to initiate it
Classical
T or F: Innate can activate adaptive
T
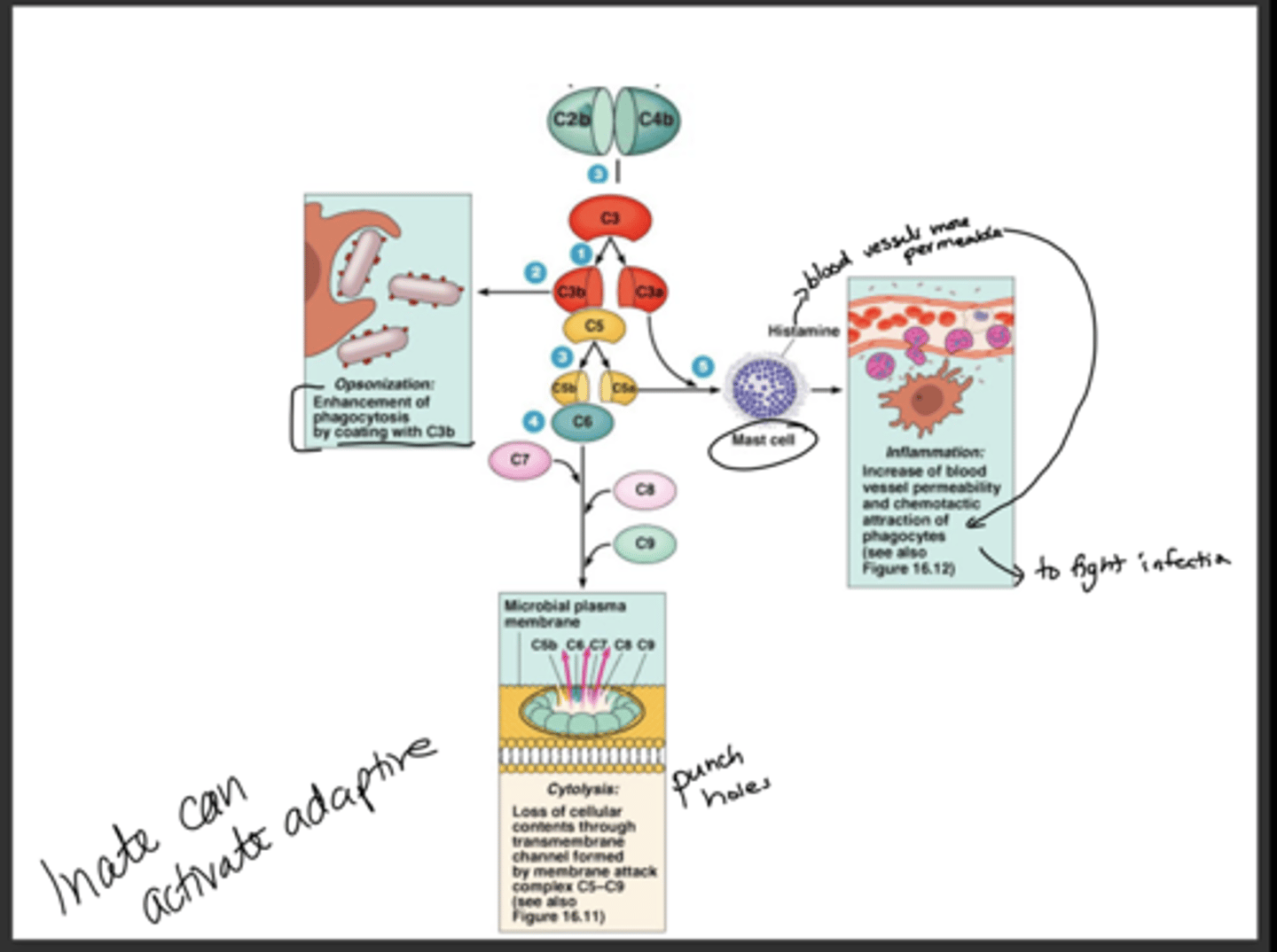
Why is the alternative pathway apart of the non-specific defense?
Because it doesn't need antibodies to activate it

Which is slower, classical or alternative?
Alternative

When does autoimmunity occur?
When T cells create immunologic response against health tissue

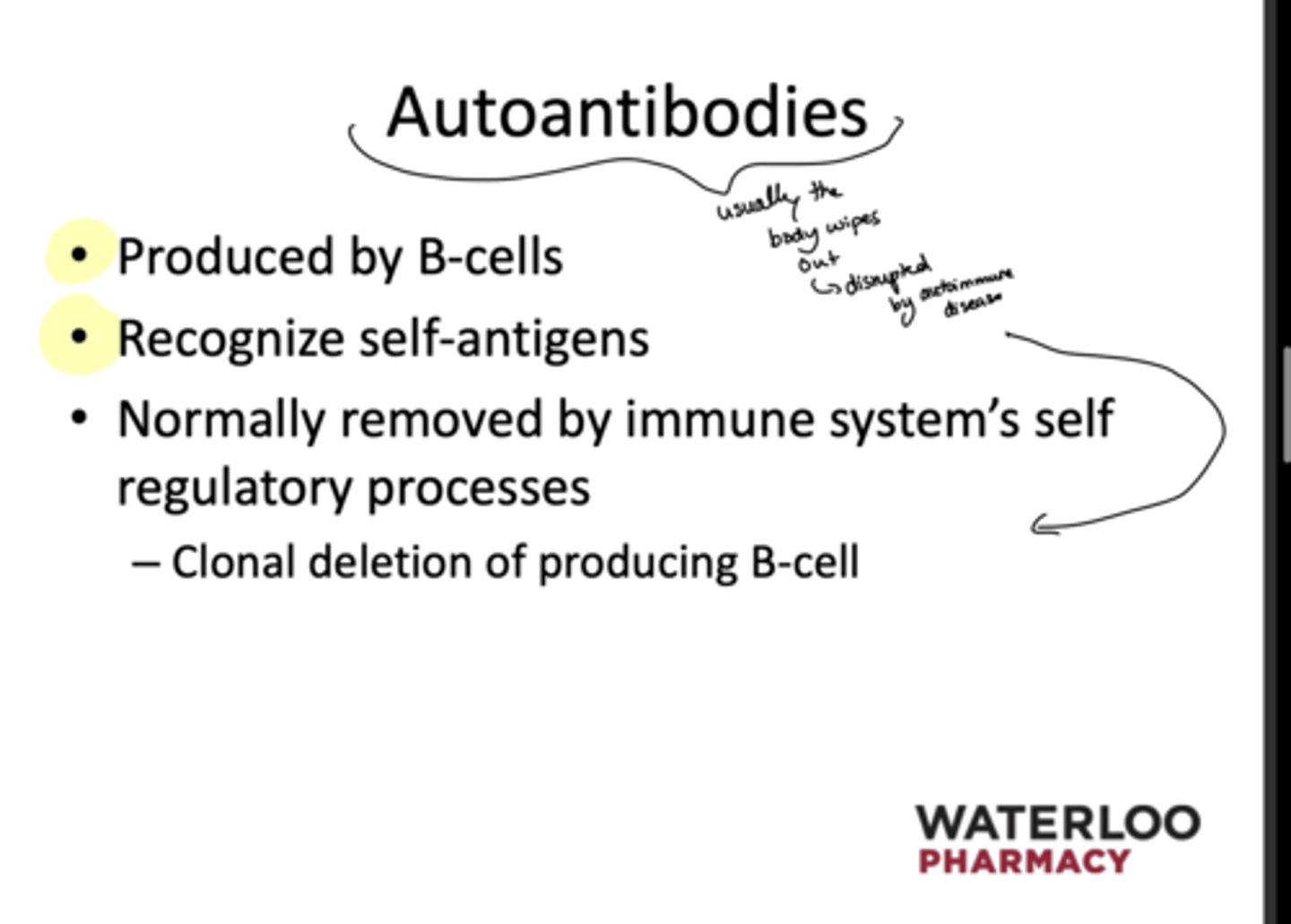
What are autoantobodies?
-Produced by B-cells
-Recognize self-antigens
-usually wiped out
What are some factors for those who get autoimmune diseases?
- Family history
-Certain environment exposures
-Certain races/ethnicities
-Women of childbearing age
-