Understanding da concrete industry test 2 review
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Kevins 2nd test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
why do we use reinforcement?
To increase tensile strength and ductility of concrete structures.
whats the difference of yield strength and ultimate strength?
Yield strength refers to the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically, while ultimate strength is the maximum stress a material can withstand before failure.
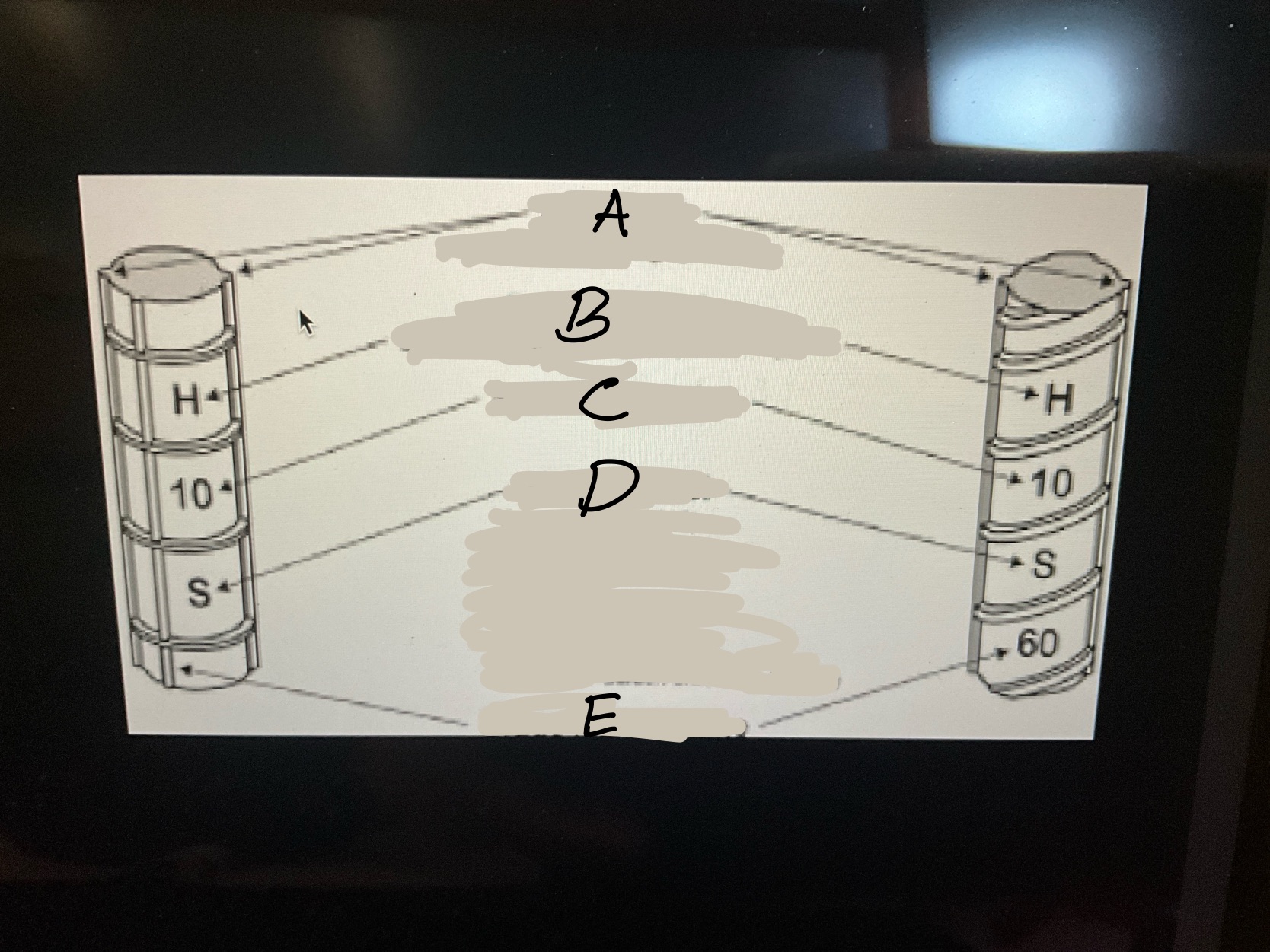
What is A?
The main ribs on rebar.What runs the entire length of a bar

What is B?
the point of origin on rebar. The letter of the producing mill.
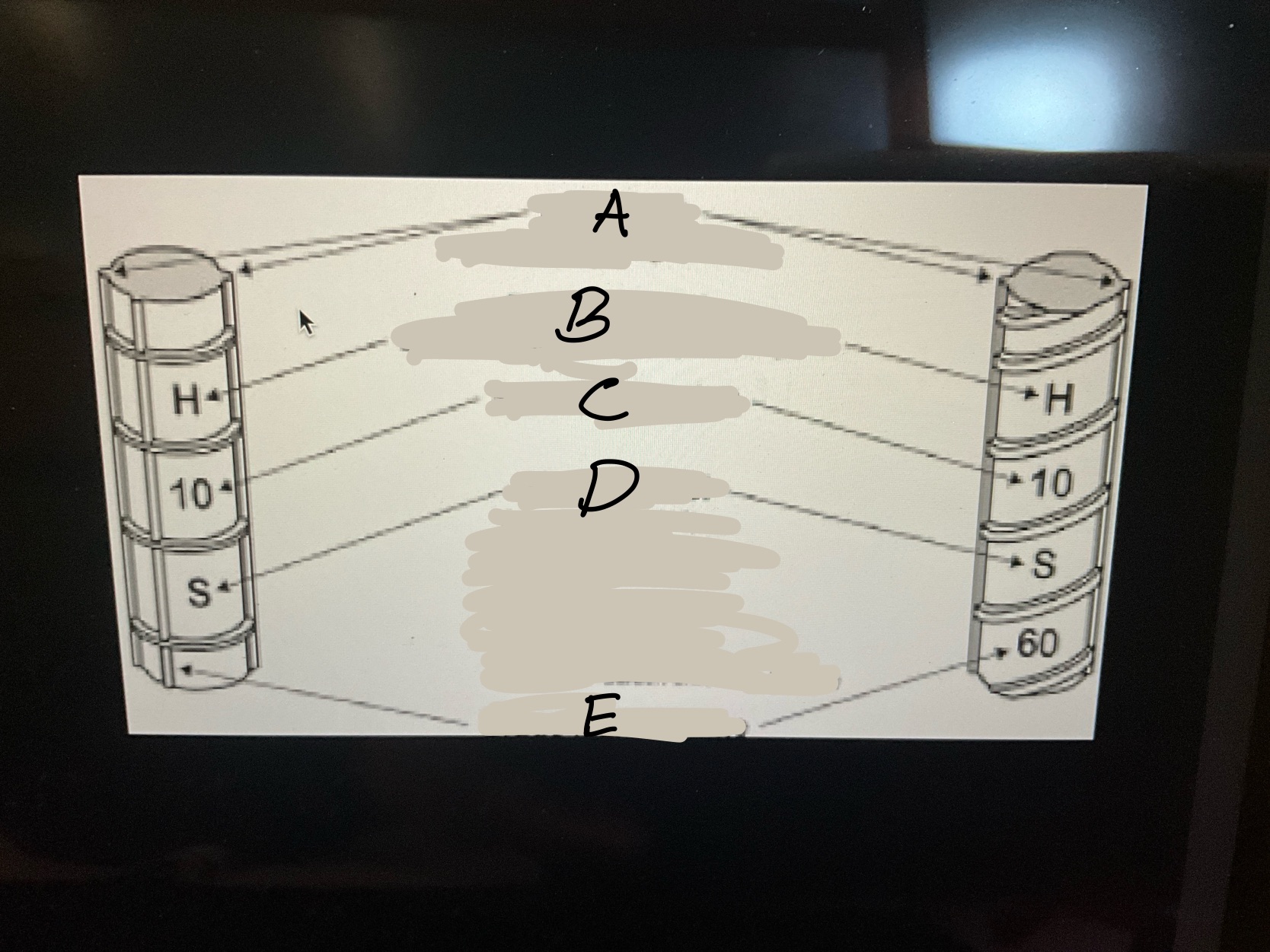
What is C?
the size designation. A number.
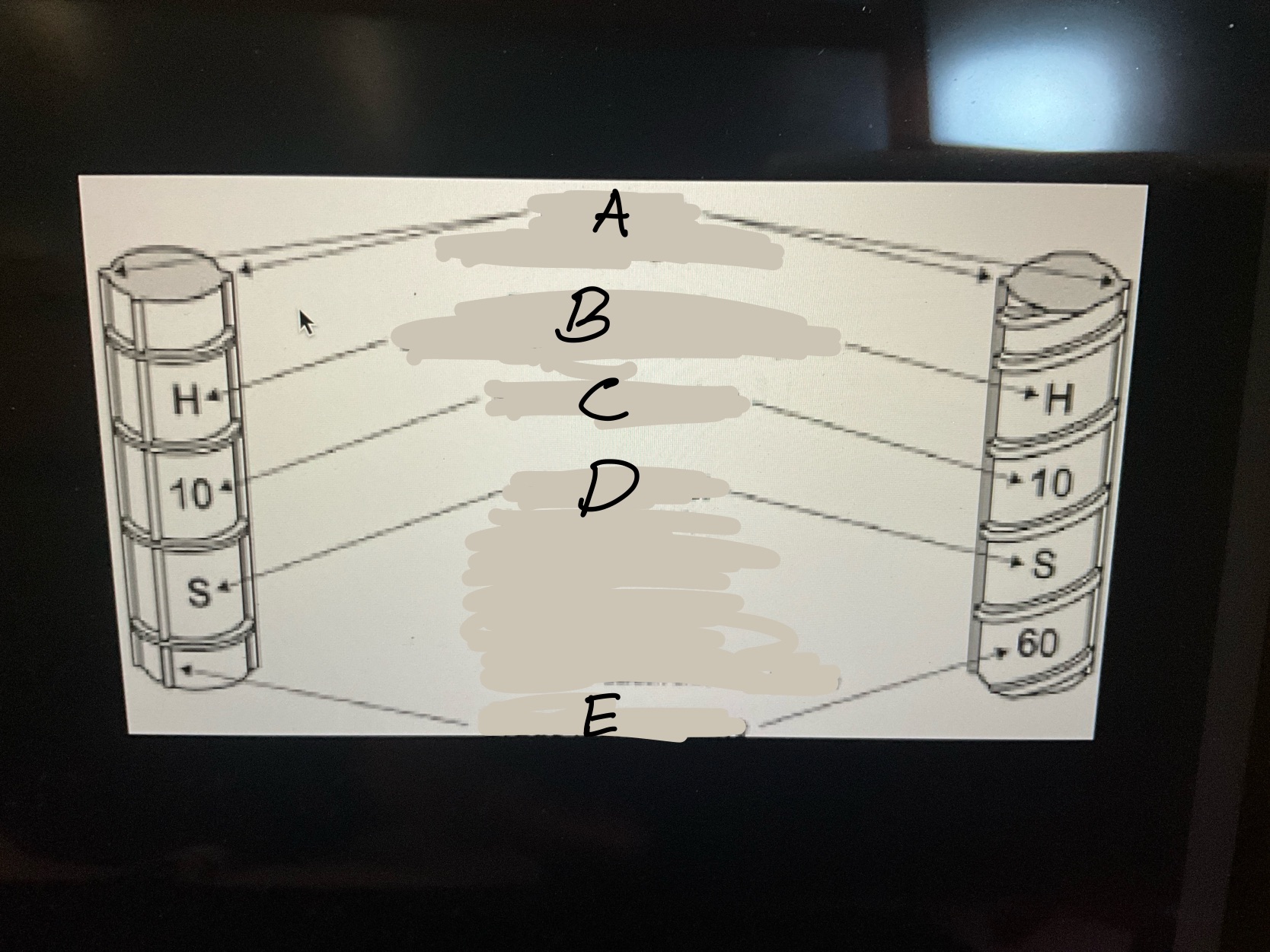
What is D?
the type of steel and grade
• S-Carbon-steel. •R-Rail steel
• W-Low alloy steel •A-axel steel
•SS-Stainless steel •CS-low carbon Chromium
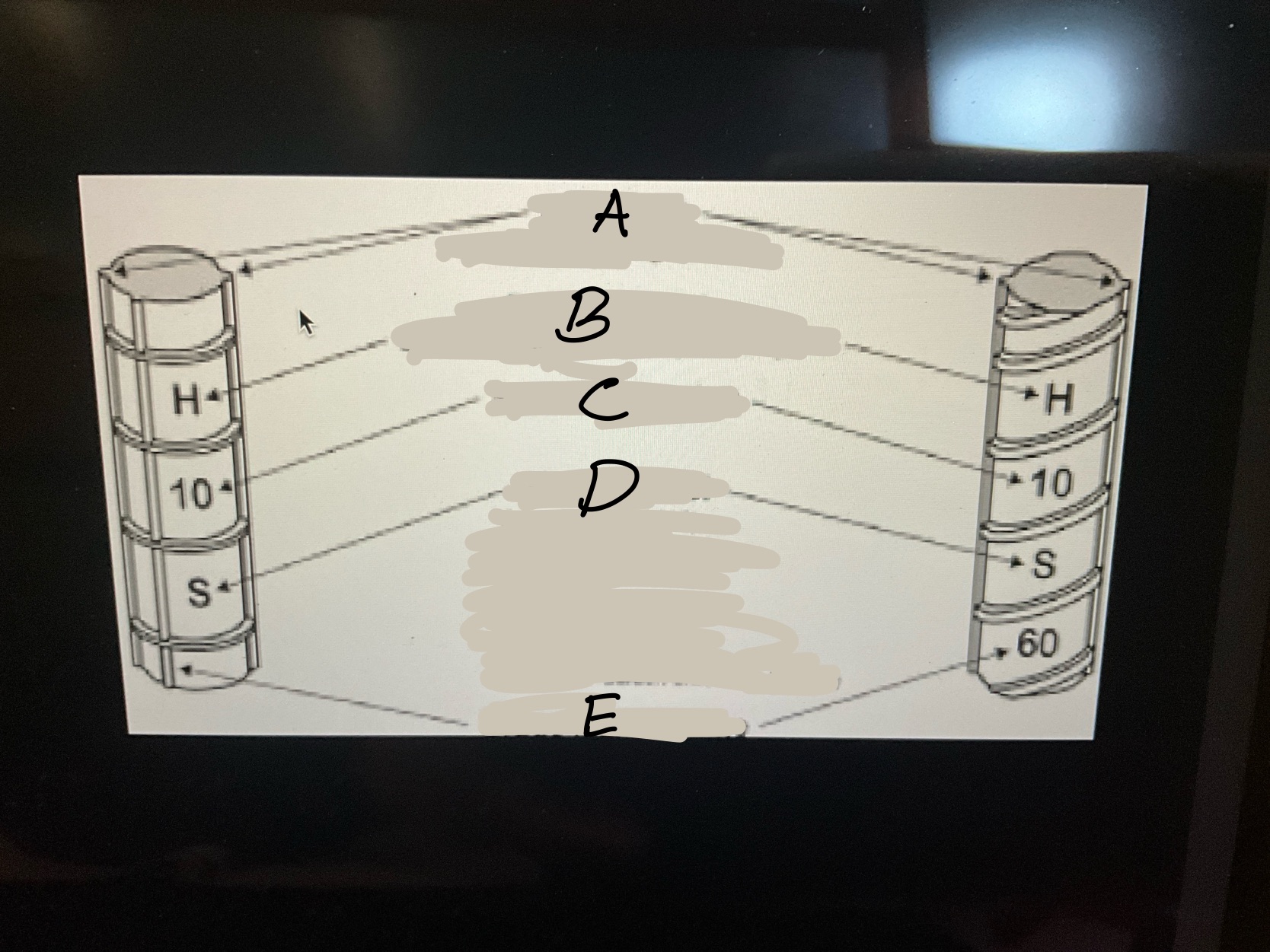
What is E?
Grade mark or line
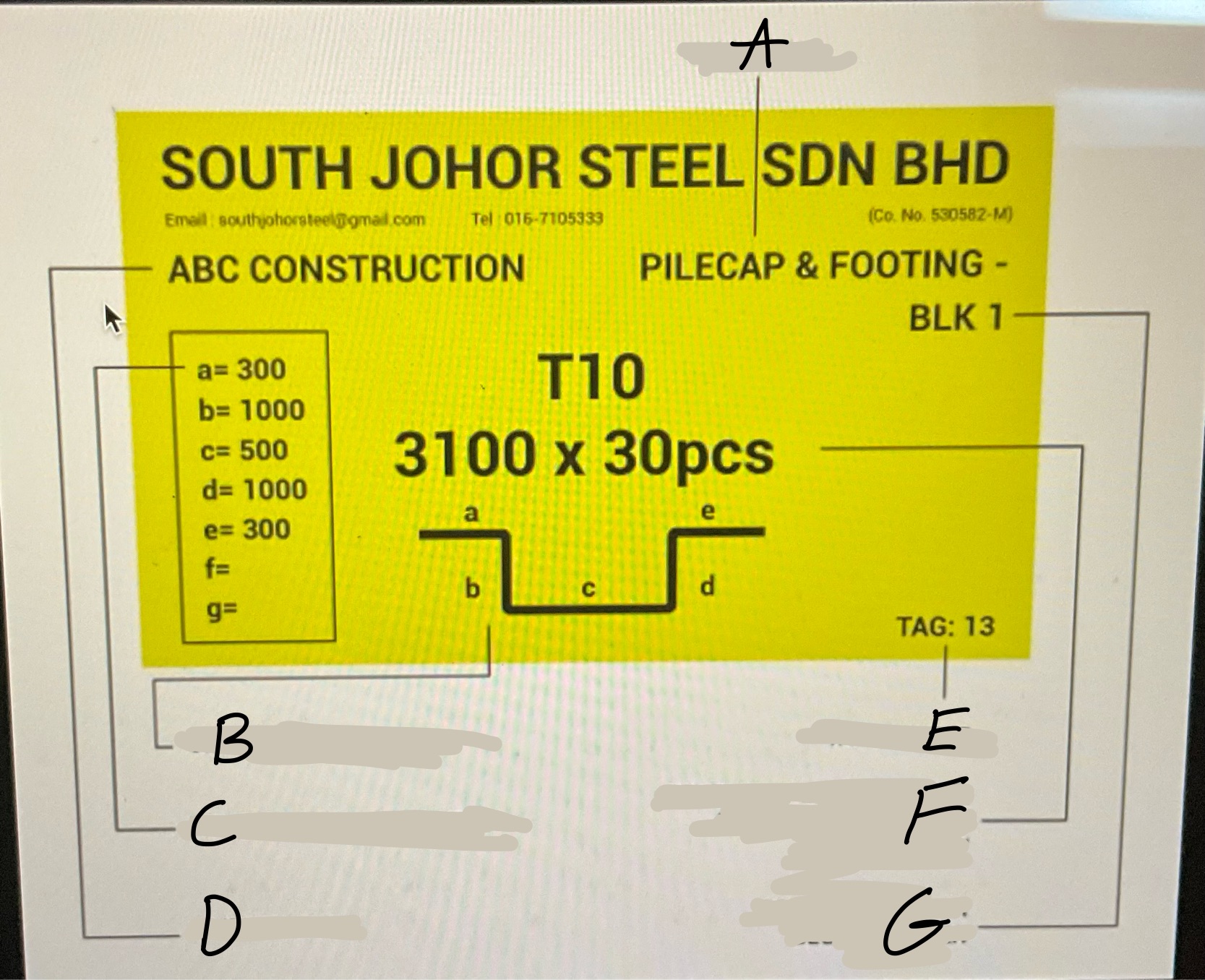
Whats A?
Location
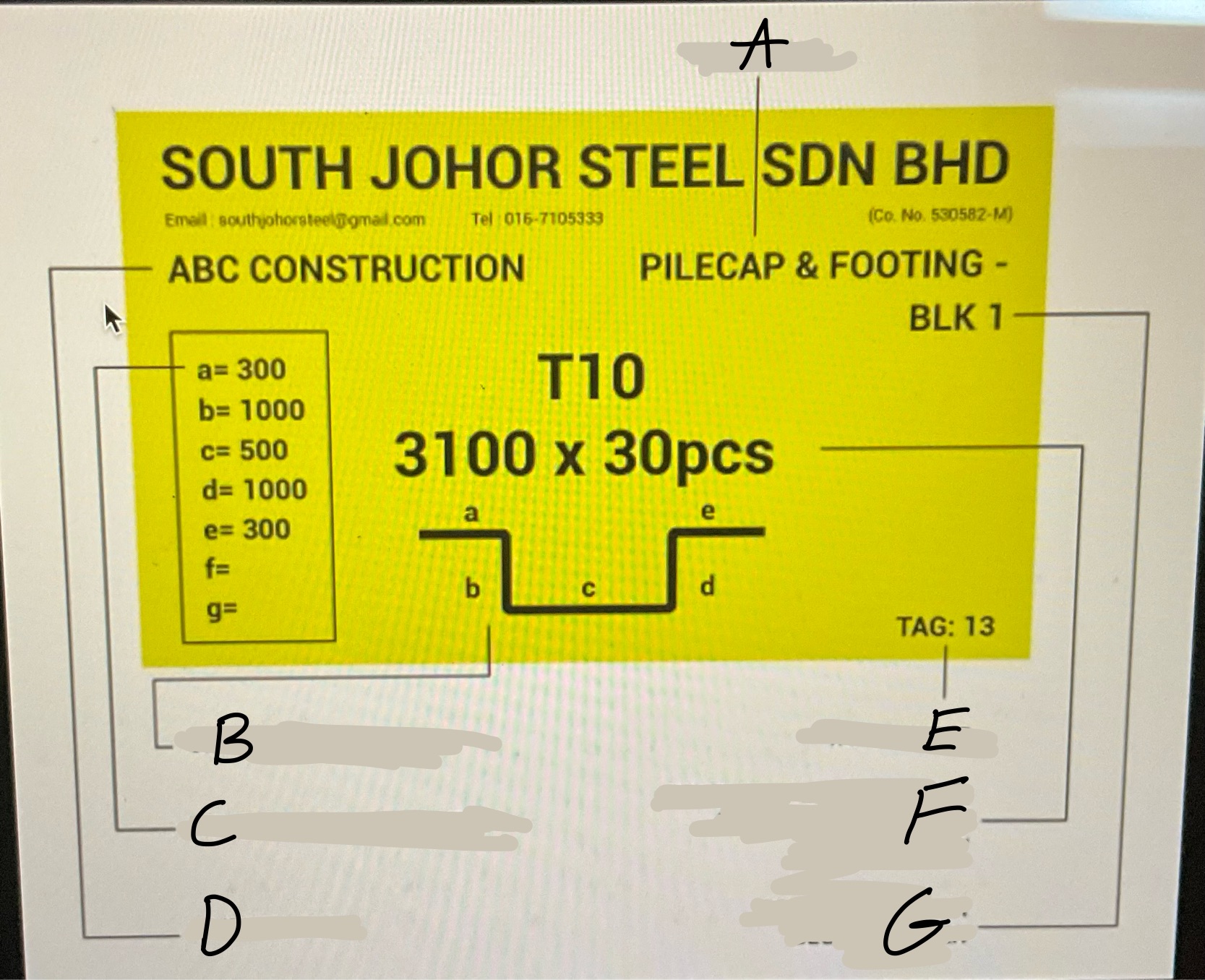
Whats B
Graphical Bar Shape
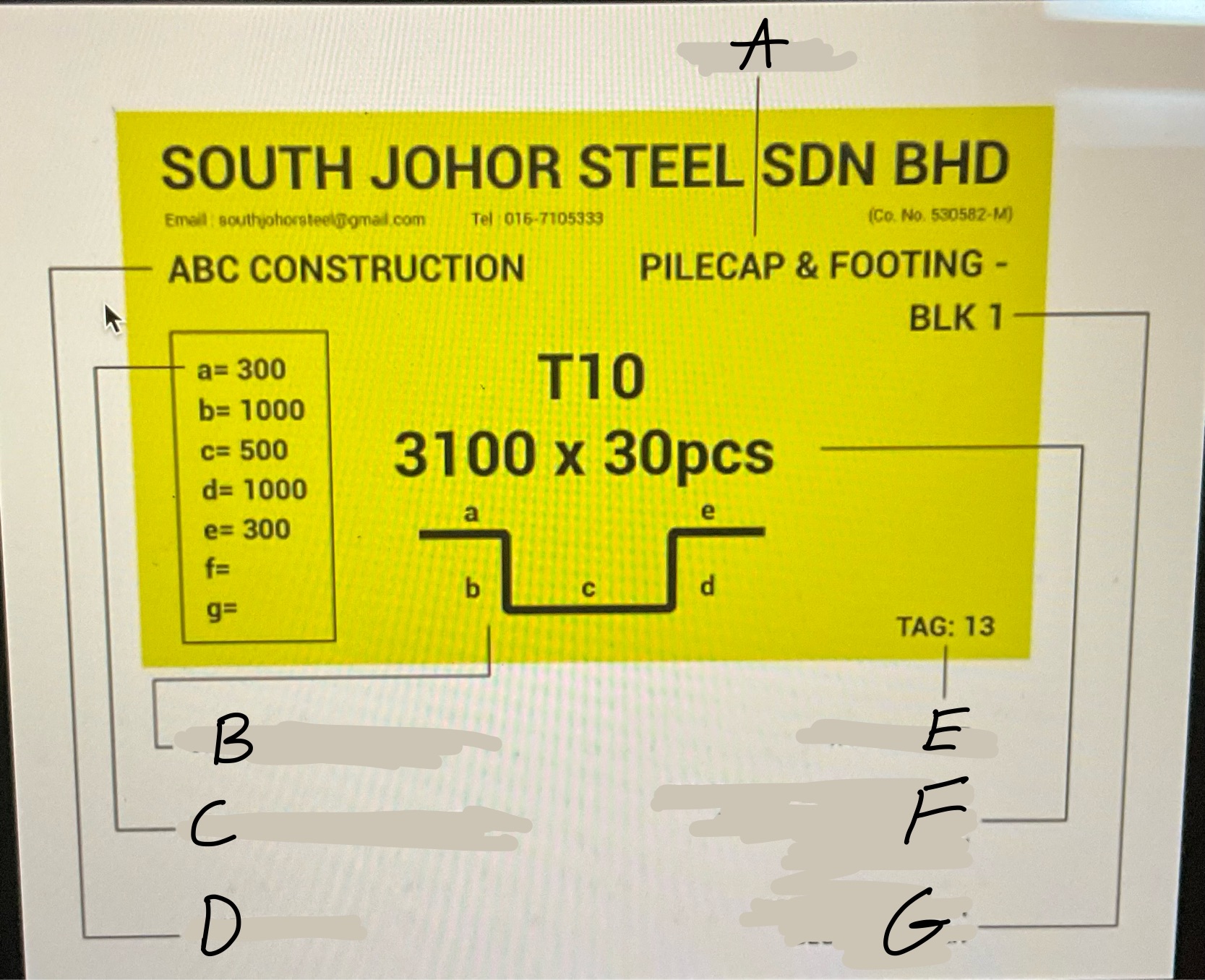
Whats C?
Length of each Diameter
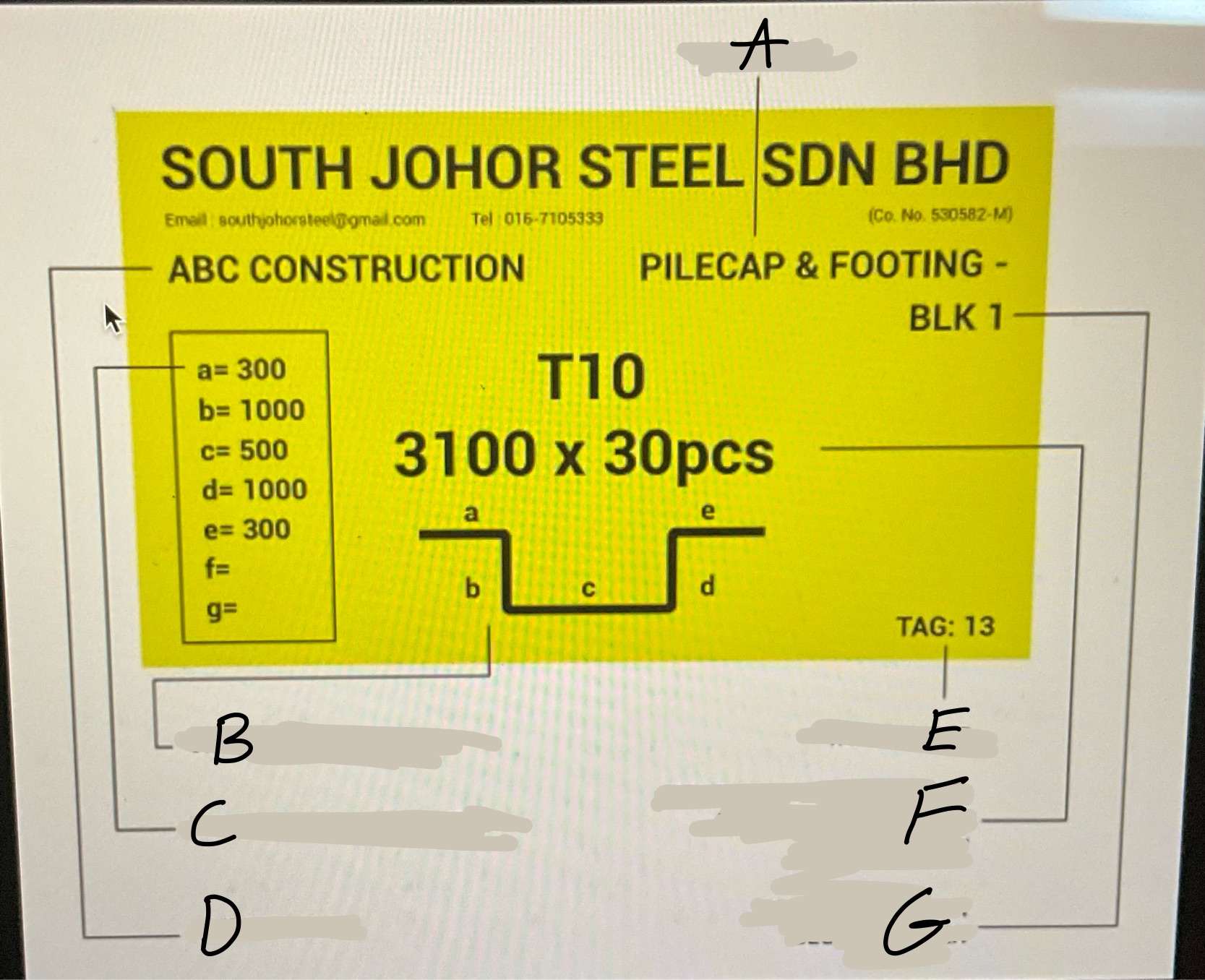
Whats D?
Client Name
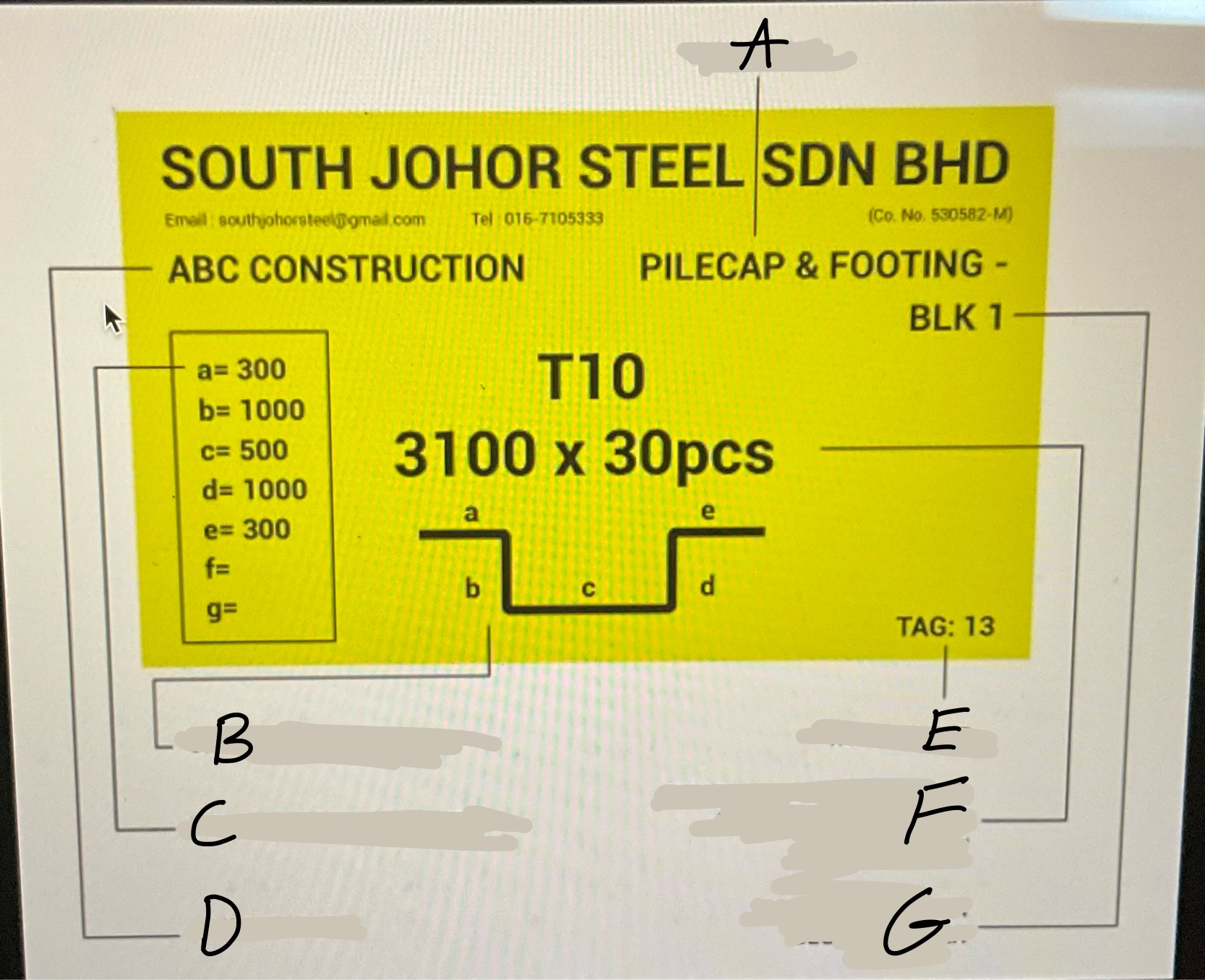
Whats E?
Tag number
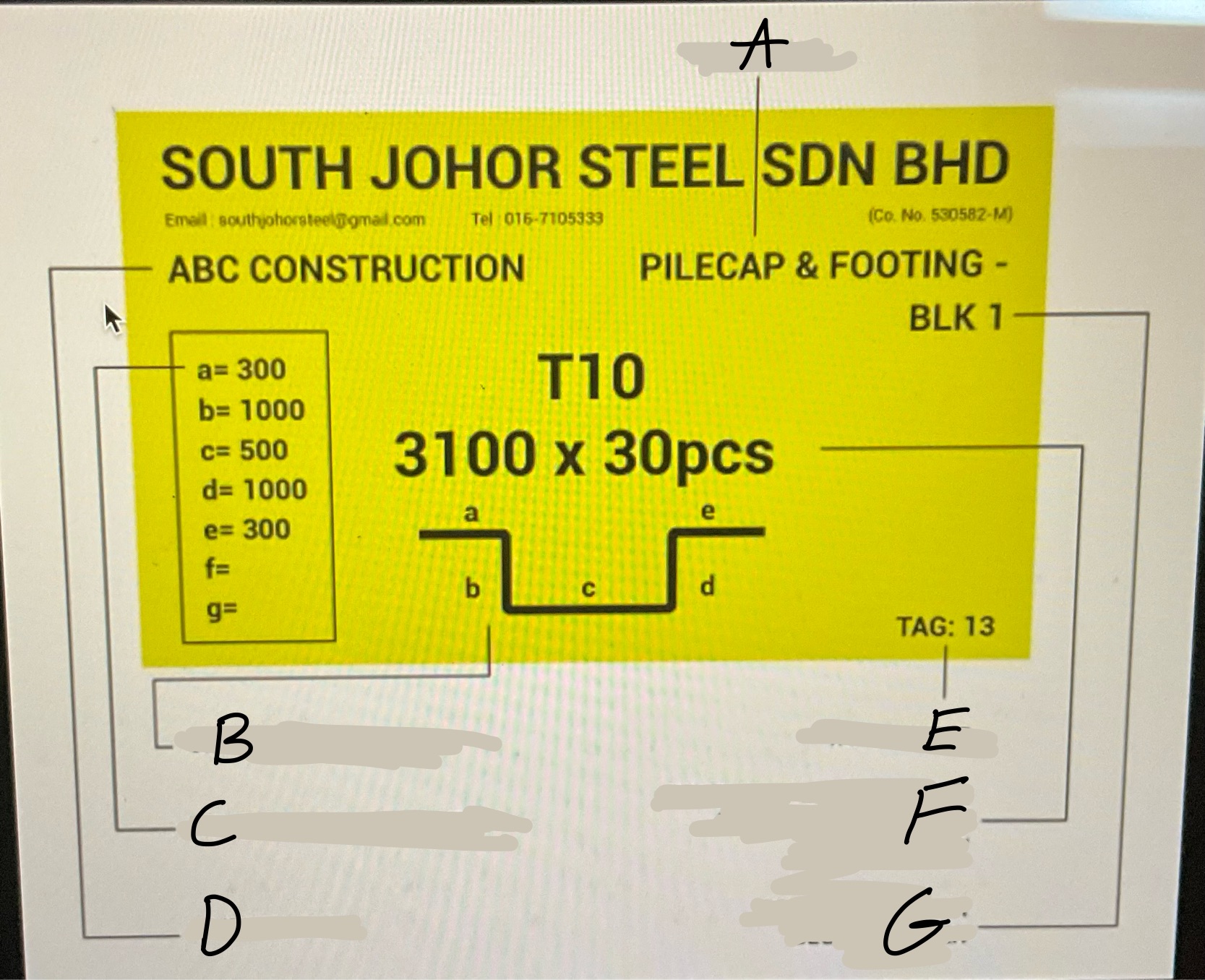
Whats F?
Developed Bar diameter, length in meter and bar quantity
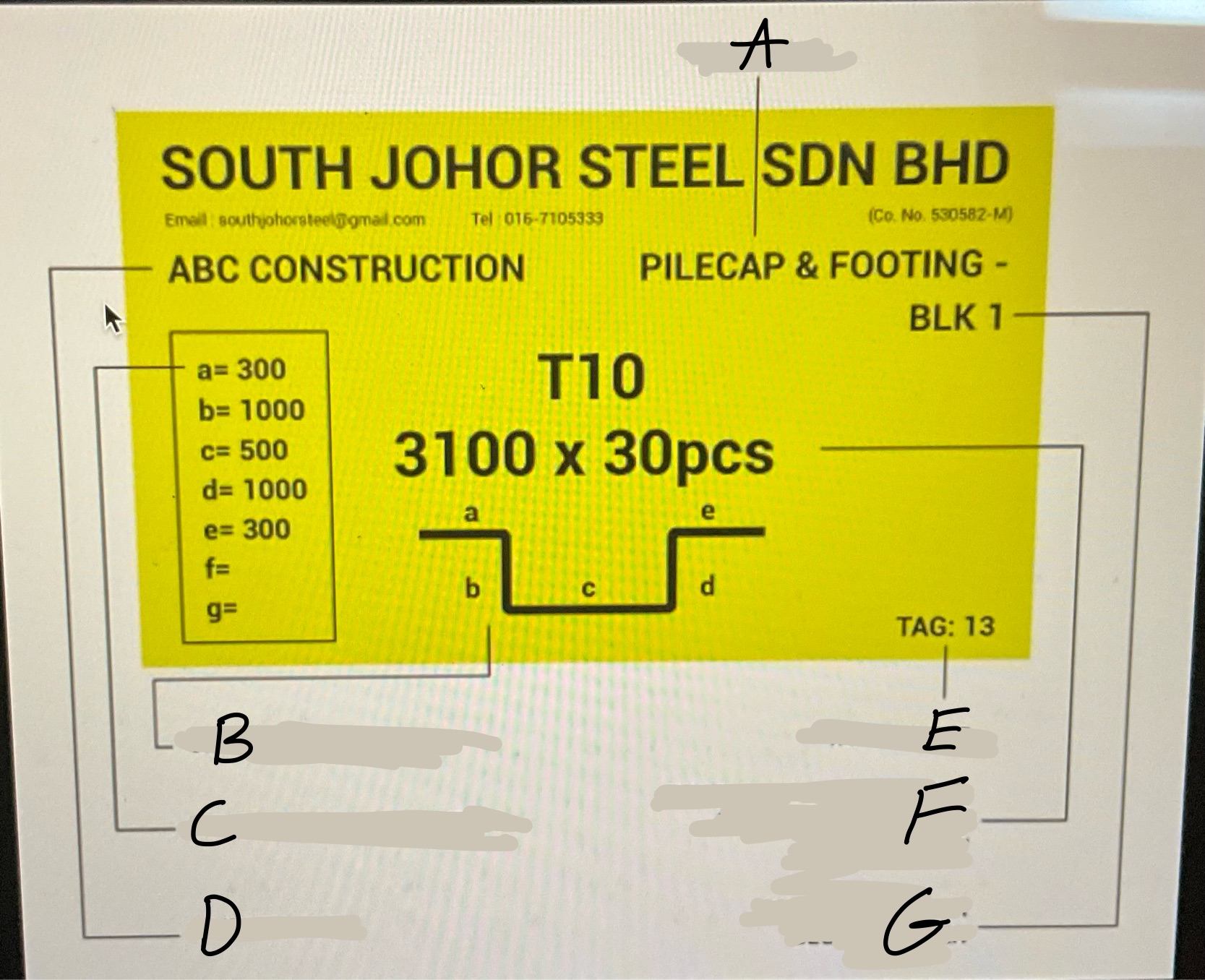
What’s G?
Project Name or block number
What is welded wire?
square rectangular mesh used for reinforcement in concrete structures, providing additional tensile strength and stability.
whats the difference of transversal and longitudinal wire.
Transversal wire runs the width while longitudinal runs the length.
What’s another name for welded wire
Wire mesh
What are the two type of wire mesh?
•W- smooth wire
•D- deformed wire
What is macrofiber?
Increases
• mechanical properties. •x>.1
•fatigue endurance
•flexural toughness
What is microfiber?
• +resistance to plastic shrinkage
• + resistance to settlement
•diameter < .01
• helps control bleeding
What are good practices for handling rebar?
•Eliminate jobsite storage
•Store bars by size length and keep tags on same end
•Dont stockpile on formwork
•Bars should be free from coating(mud, grease, oil, or loose mortar)
•surface rust is ok
What’s a concrete cover?
The distance from the outside of the bar to the surface of the concrete. It protects the rebar from corrosion and damage.
with concrete cast against and permanently in contact with ground requires what?
All members and reinforcment to have a cover of at least 3 inches
Concrete exposed to weather or in contact with the ground requires what?
All members with #6 - #18 must have a 2 inches while #5 bars and W31 or D31 wire and smaller needs 1-½ inches of cover
Concrete thats not exposed to neither the ground or the weather require what?
•Slabs, joists, and walls with #14 and #18 bars must have 1-½ inches. If they have #11 or smaller, they must have ¾ inches.
•Beams, columns, pedestals, and tension ties thats primary use stirrups, ties, spirals, and hoops as reinforcement must have 1-½ inches of cover.
Why is the placement of steel reinforcement important?
The strength and loading capacity of the concrete can be reduced by up to 20%
where can you find the tolerances and specifications of where to place the reinforcement?
ACI 117
What’s good practice when placing reinforcement for a footing?
•Bottom bars need 3” clearance
•No clay bricks
•use chairs, bolsters, or concrete bricks
What’s good practice when placing reinforcement for vertical dowels?
•Tied to cages/mats
•Use templets to keep proper positioning
•Do not wet stick dowels
What are the construction procedure for walls?
one side is formed first
Reinforcement is tied
Formwork is set and bulkheads are installed
approval from engineer in writing is required if changes are made
What is tie wire?
•usually #6 gauge black, soft wire
• serves no structural purpose besides holding bar tgthr
•should not be in contact with face of form
In terms of bar support, what is class 1 maximum protection?
concrete exposed to sever conditions. The wire is coated in plastic. concrete may be sandblasted.
In terms of bar support, what is class 1A maximum protection?
Epoxy coated, vinyl, or plastic coated. Concrete is exposed to sever conditions, no sandblasteing or ground concrete.
In terms of bar support, what is class 2 moderate protection?
supports are made from stainless steel, or feet are stainless steel. Moderate exposer concrete with exposure to sandblasting or grinding.
In terms of bar support, what is Class 3 no protection?
plain carbon steel wire with no protection from rusting
What are bar supports often referred as/
Chairs
What do slab bolsters do?
They’re used to support the bottom mat of steel
What are spacers and what are they used for?
They’re plastic non corrosive devices used to keep rebar in place and maintain proper concrete cover in walls.
What are lap splices in reinforcement?
continuous bar that overlap
Where should lap splices occur?
They should be staggered in horizontal and vertical applications to maintain structural integrity and avoid weakening the concrete.
What are the two types of mechanical lap splices?whats the difference
•Couplers- resist tensile and compressive forces
•End-bearing- 4 splice cables that transfer compressive forces only
What are some benefits of coordinating the arrival of rebar?
Increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved scheduling on construction sites.
What is formwork?
a temporary structure that contains concrete until its curing and hardening. It can also take up to 60% of all costs for a project.
What does formwork include?
•forms facing the concrete
•equipment
•all supporting members
What other things do forms have to support?
•itself
•workers
•building materials
•other live loads
What are 7 things that help work sites be safer?
competent supervision
knowledgeable workers
following construction designs precisely
adhering to proper erection and stripping procedures
planning procedures in advance
routine safety inspections
everyone on site is a “safety inspector”
What are the most common practices when erecting job-buit forms?
•Fastening a base plate to a slap or footing
•studs are nailed to base plates
•sheathing is nailed to base plates
• walers are placed outside studs
•spreaders are used to keep interior dimensions correct
•wall ties are placed through predrilled holes on the sheathing
•turnbacks and braces used for alignment
What are prefabricated forms?
forms used for many projects that can be assembled quickly on-site, designed for efficiency and often used to create consistent shape and quality in concrete construction.
What are the different types of prefabricated forms?
•Ready made
•Gang forms
•Flying table forms
• Pan forms
•Void/carton forms
•Panelized formsClamp-style gang forms
What are column forms?
Forms made for columns that can be square or rectangular. Can be made out of Laminated fiber, metal, glass fiber reinforced plastic, or steel.
What are laminated fiber tubes?
One time use forms that are lightweight, strong, and often used for pouring concrete columns, providing an efficient way to achieve the desired shape and strength.
What are some examples of stay in place forms?
•Insulating Concrete Forms(ICFs)
•Tunnel Forms
•bridge decks
•concrete roofs and roofs
What are ICFs
Hollow foam interlocking blocks that stay in place and are reinforced from webbing
What are the four types of nails?
Duplex Nails
Common Nails
Finishing nails
Box nails
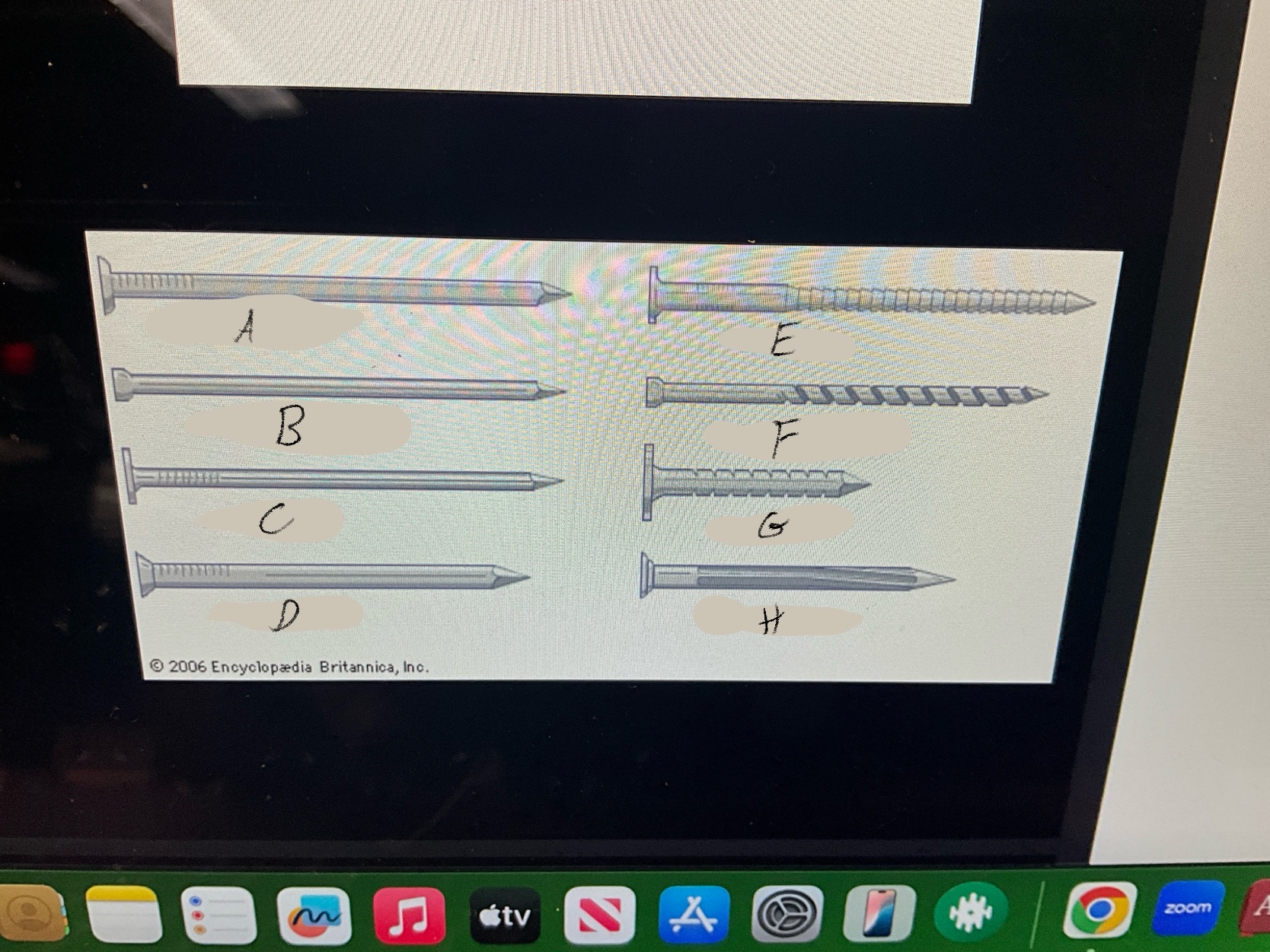
What type of nail is A?
Common nail
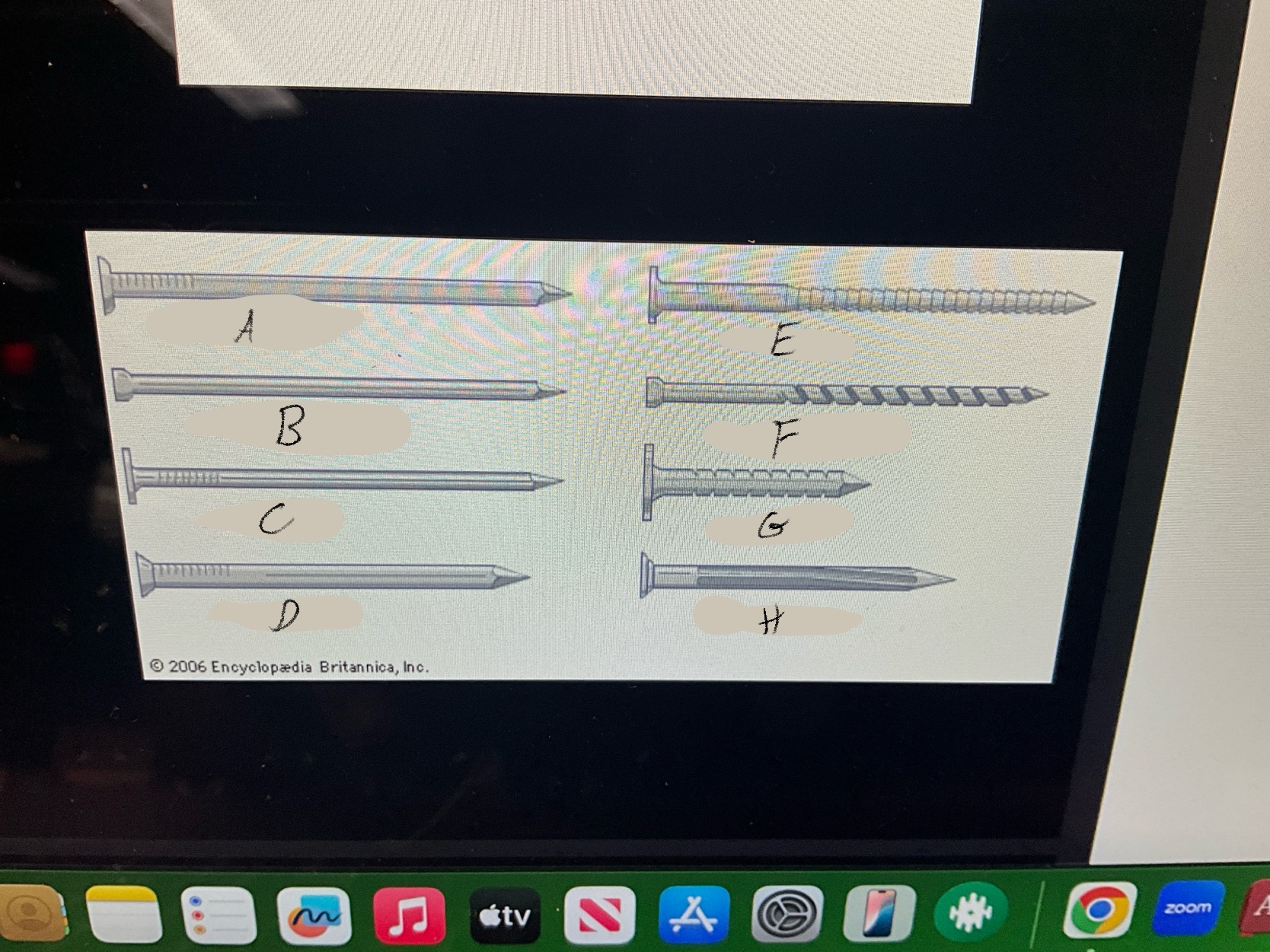
What type of nail is B?
Finishing nail
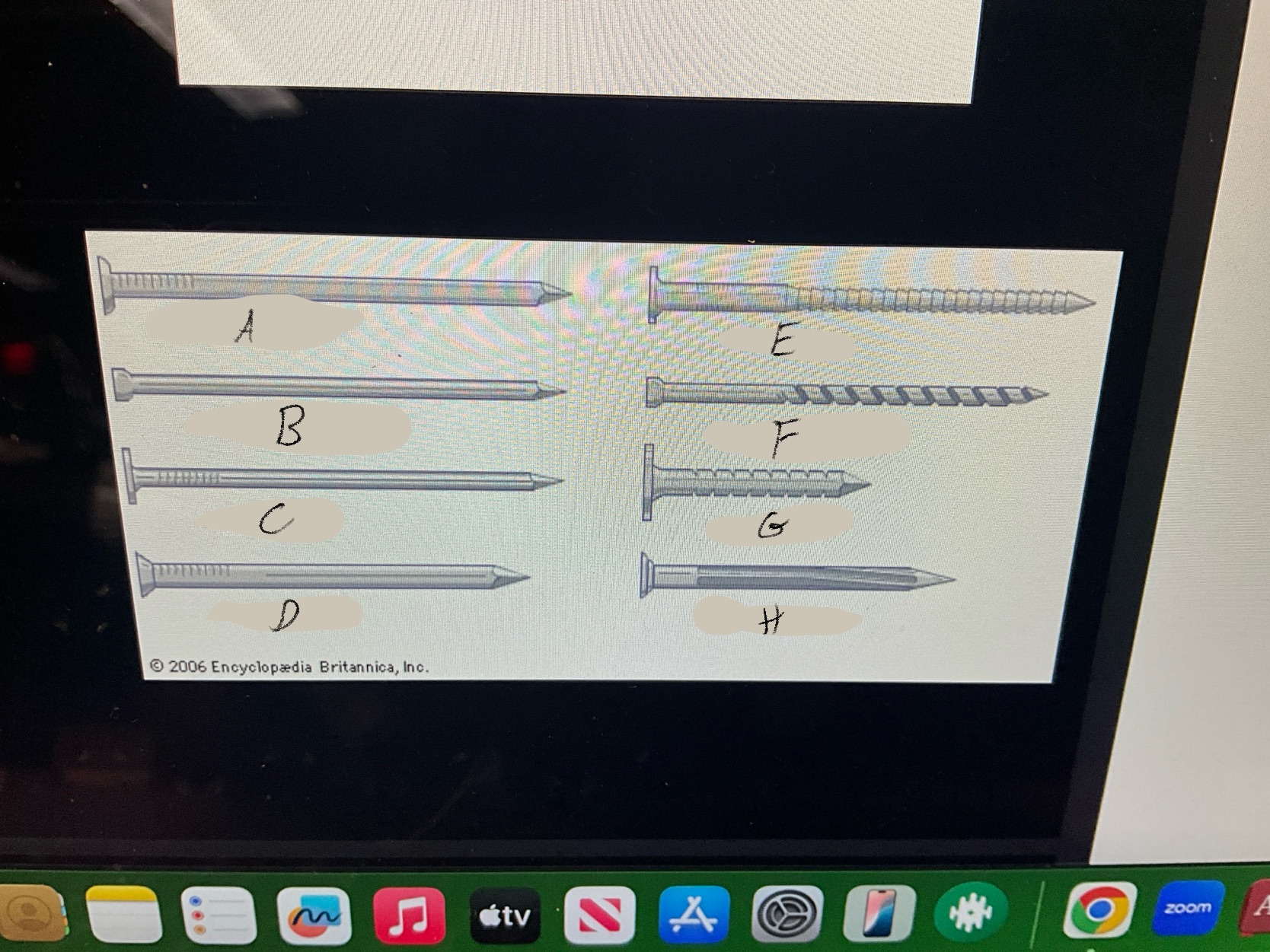
What type of nail is C?
box nail
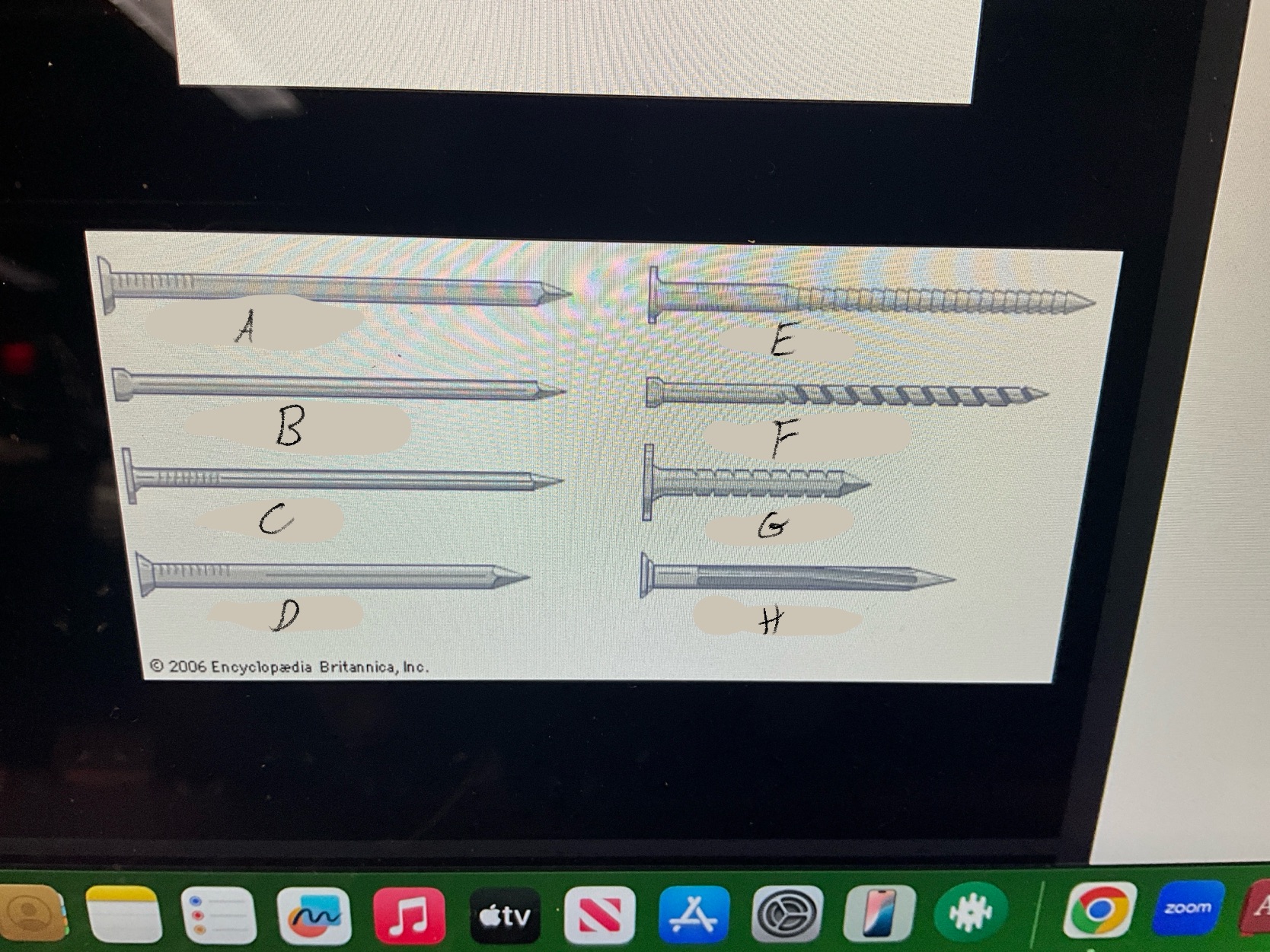
What type of nail is D?
Casting nail
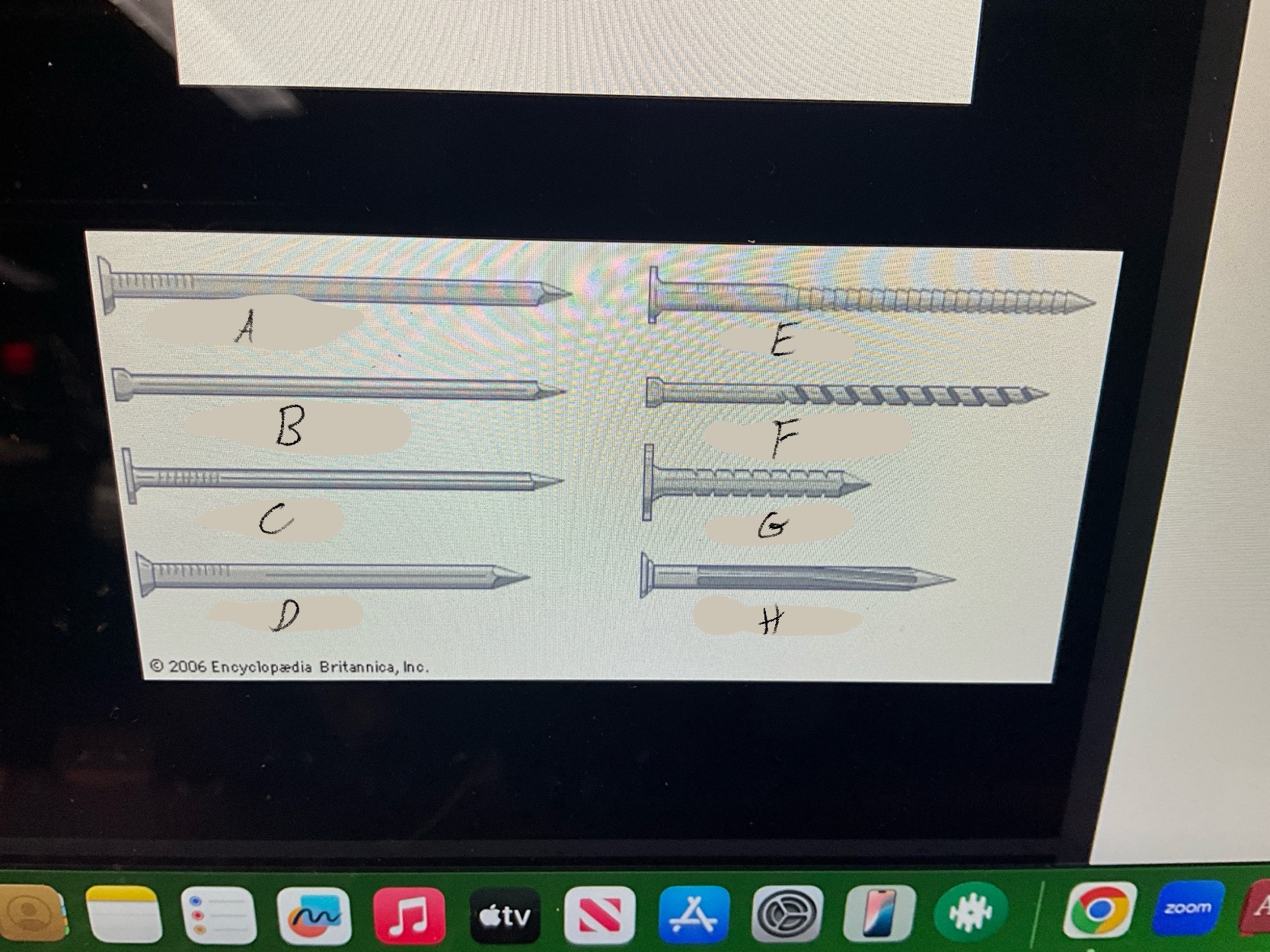
What type of nail is E?
Ring nail
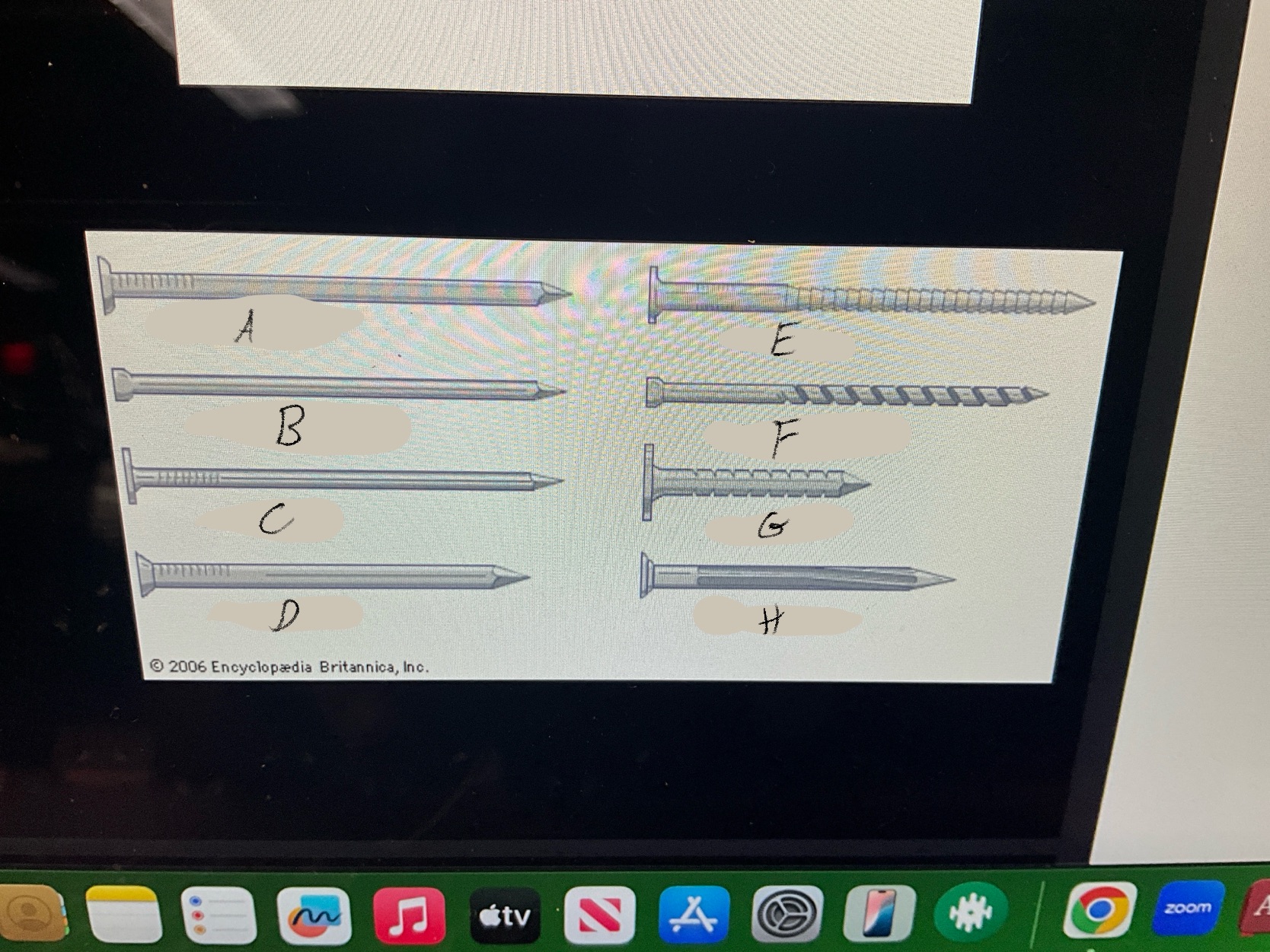
What type of nail is F?
Spiral shank nail
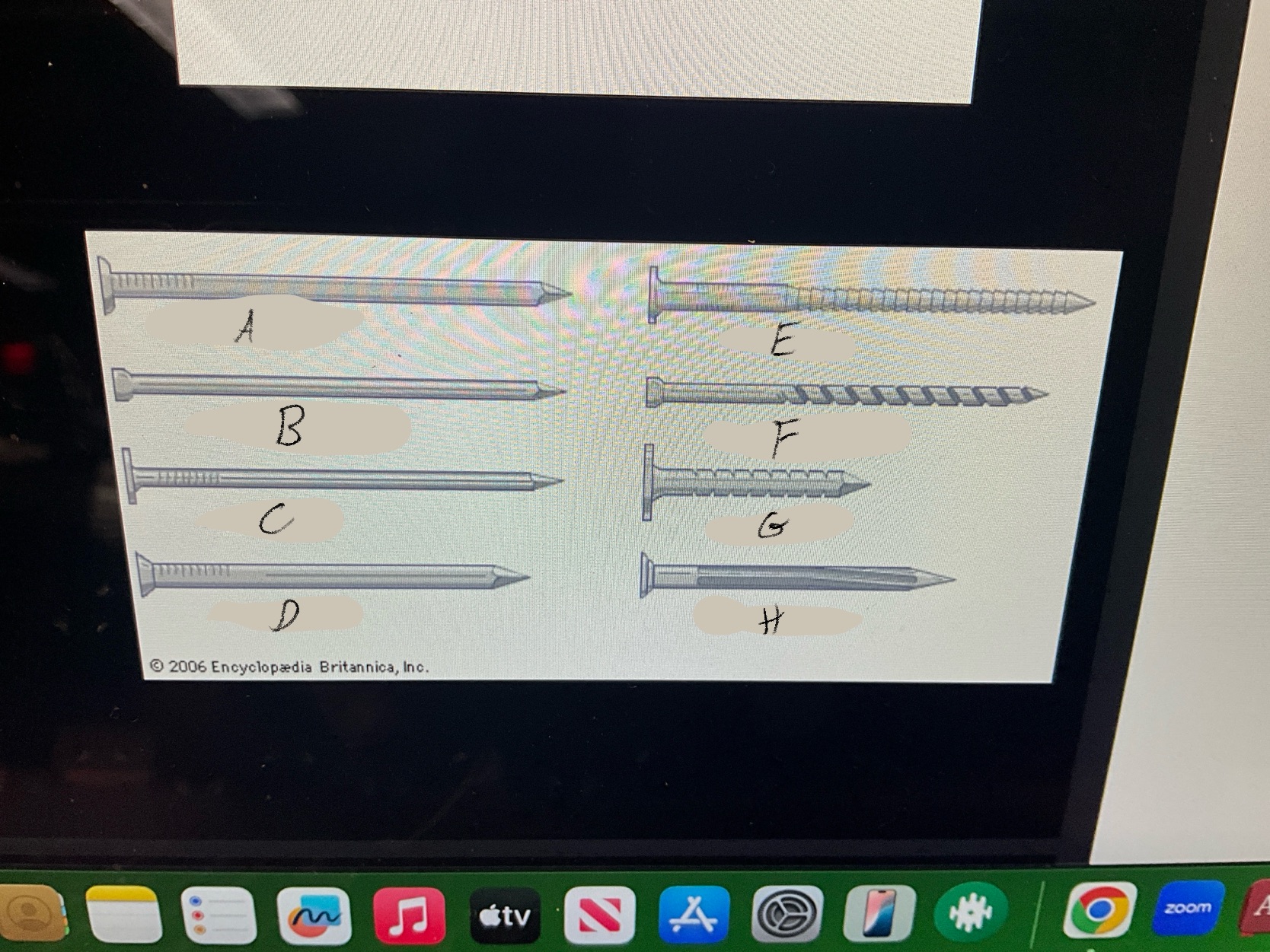
What type of nail is G?
roofing nail
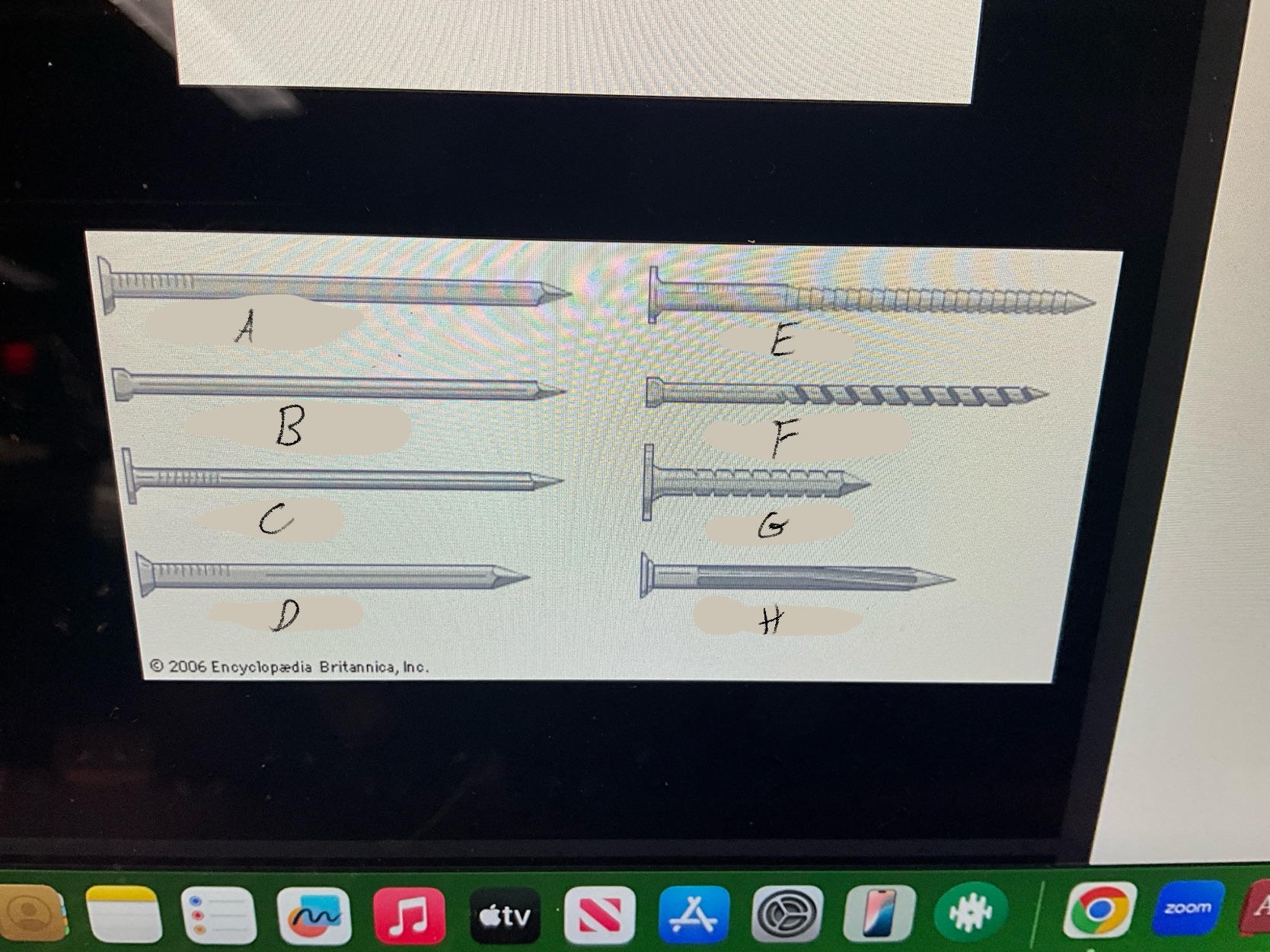
What type of nail is H?
Masonry Nail
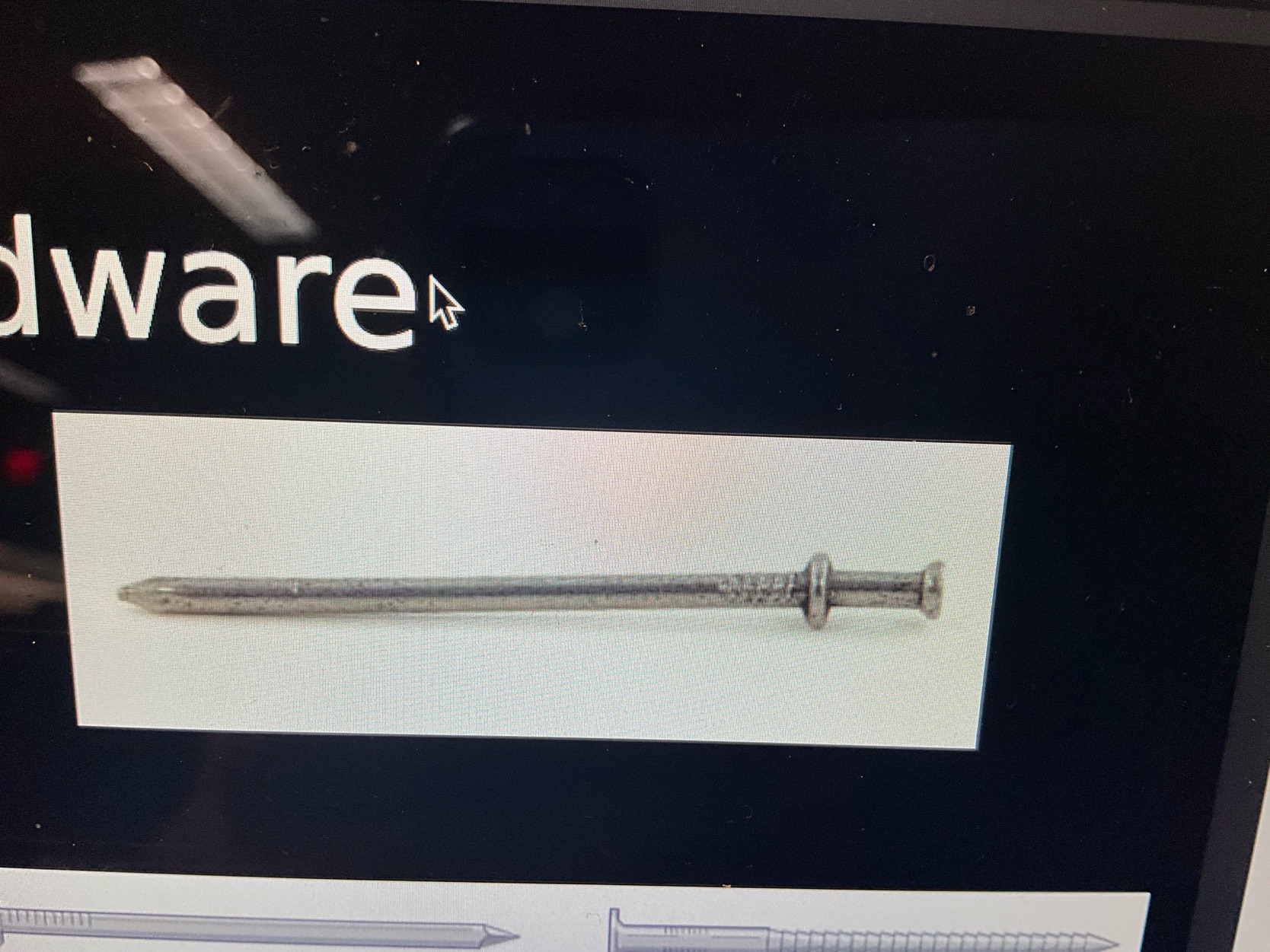
What type of nail is this?
Duplex nail
What are form ties?
Special metal or plastic units that hold forms against lateral pressure of fresh concrete. The layout should be planned and the spacing should be uniform.
What are form anchors?
devices used to secure form work. can be embedded in concrete during placement but it must be able to have enough tensile strength.
What are form liners?
Stamps. They provide texture. They are usually expensive and can provide brick, stone, or wood patterns.
What are some drawbacks to using liners?
They require skilled labor and are expensive
What things should a formwork inspection include?
What is external vibration?
vibrators attached to the outside of forms that may be specialized.
What is internal vibration?
The ones you know that are inserted directly in fresh concrete.
Why does the outside temperature matter when pouring?
Cause higher temperature makes the concrete set faster while the cold slows the set time.
What should you be looking for in the formwork as its being poured?
strings, lasers, and levels for any deflection. Strengthening may be necessary
Why should edge sealer be applied to formwork and when should it be applied?
•to increase its longevity
•in the field
When storing forms how should they be stored?
Face to face or frame to frame
What are some tolerances that need to be considered when erecting forms?
•Form dimensions
•Variation from grade
•Variation from level
•Dimensions between members
What are shores?
The posts used to hold up concrete and construction loads
What is shoring?
Erecting shores in their places
What is reshoring/reshores
re using the shores that have been removed.
What is required for footing construction?
•stakes
•nail pins
•turn buckles
•screeds
•same things as a slab