BIO 290 JMU EXAM 1
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
Anterior (ventral)
toward the front
Posterior (dorsal)
toward the back
Superior (cranial)
toward the head (top)
Inferior (caudal)
toward the feet (down)
Superficial
above the surface
Deep
below the surface
Lateral
away from the midline
Medial
toward the midline
Midsagittal
divides body into left and right
Parasagittal
divides body into unequal right and left sides
Frontal
divides body into front(anterior) and back(posterior)
Transverse
divides body into upper(superior) and lower(inferior)
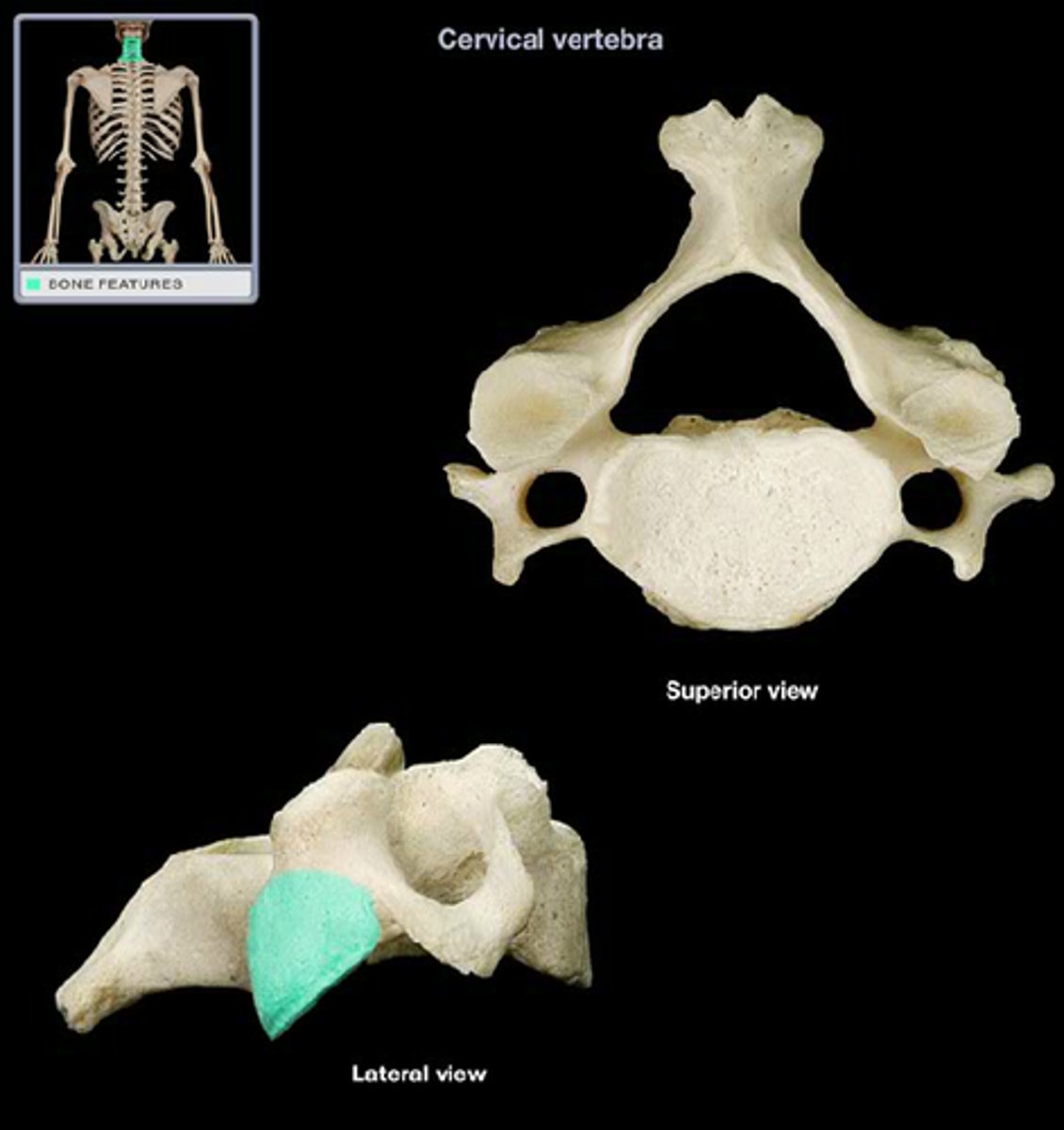
Cervical
7 (C1-C7) vertebrae
has foramen in the transverse processes
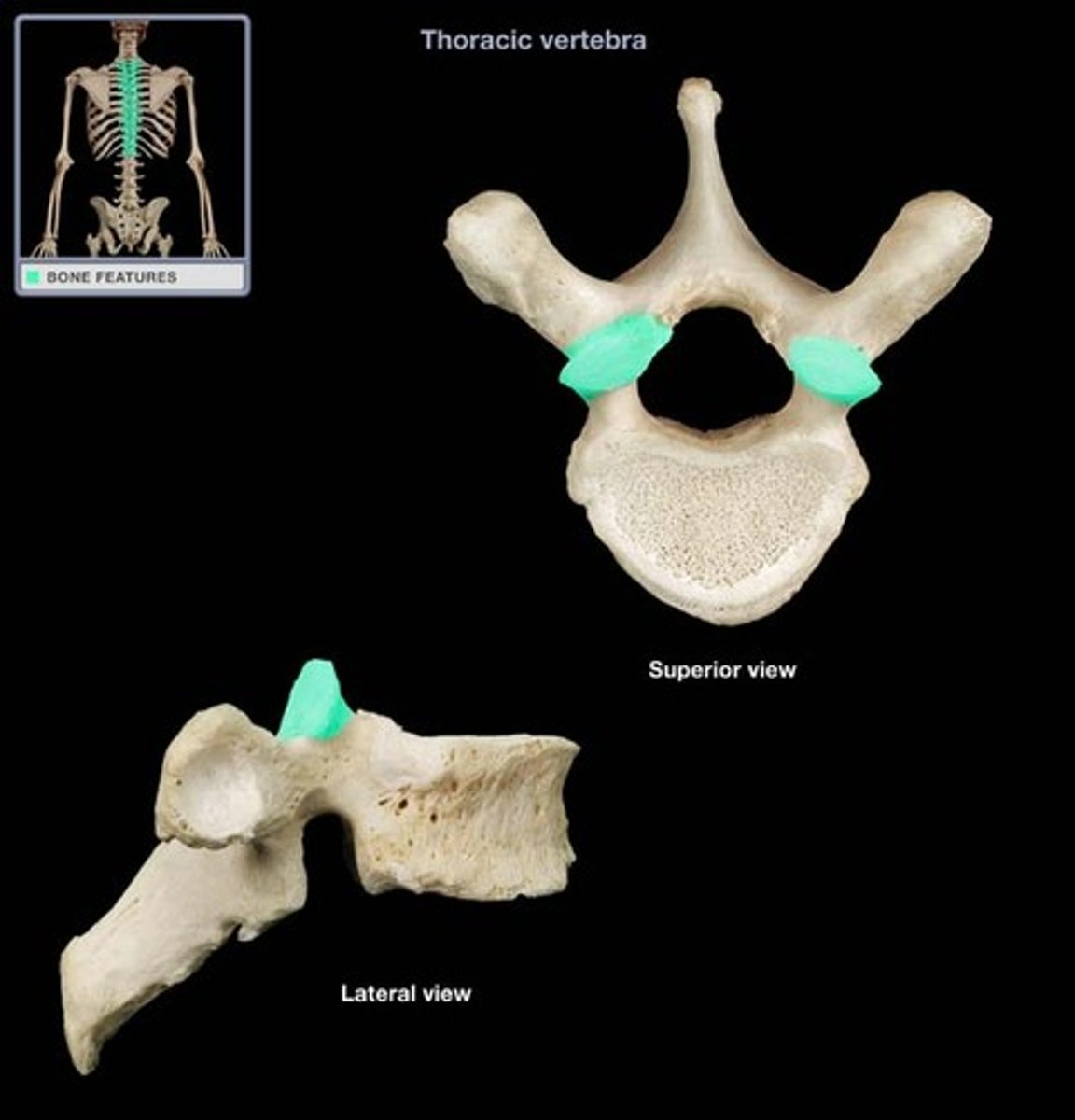
Thoracic
12 (T1-12) vertebrae
has costal facets (where ribs attach)
Lumbar
5 (L1-L5) vertebrae
no costal facets and no foramen in the transverse processes
Sacrum
5 fused vertebrae
Coccyx
3-5 vertebrae
"tail"
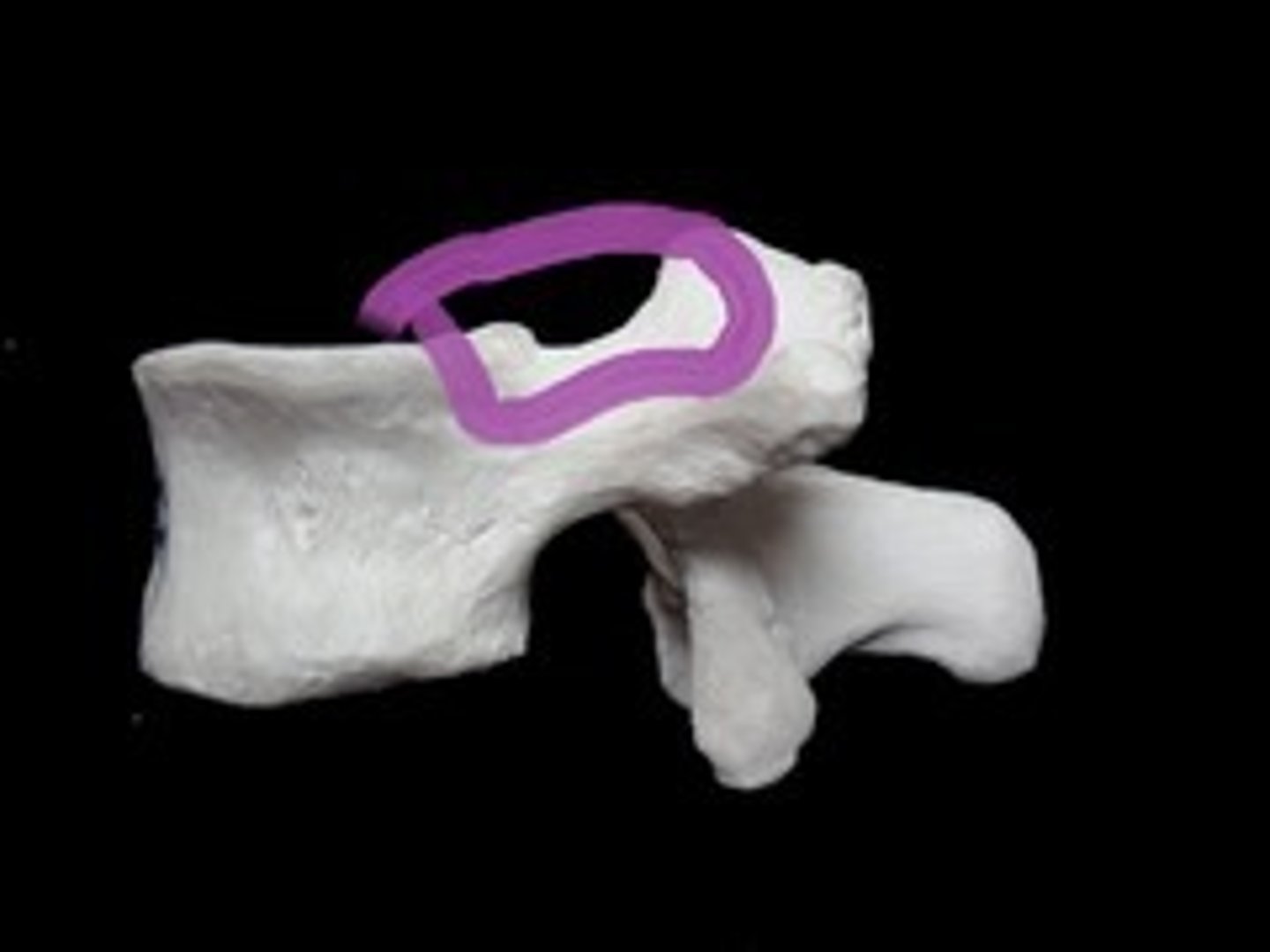
Whats this?
What's this?
Superior vertebrae notch
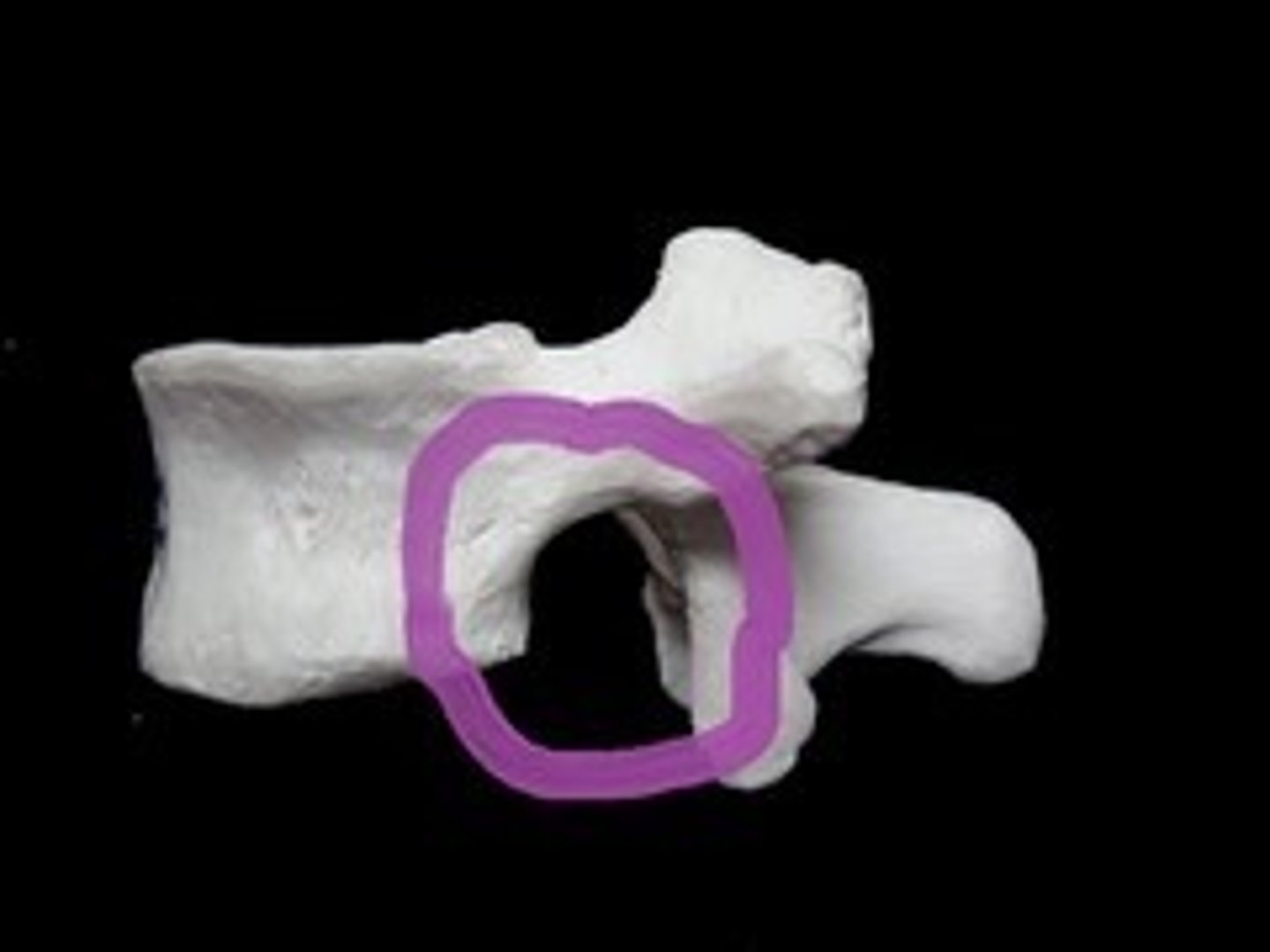
Whats this?
What's this?
Inferior vertebrae notch
embryonic somites give rise to what structures in the trunk?
- vertebrae and ribs
- skin
- back muscles
- body wall muscles
bilateral
two sides
appendicular skeleton
- upper and lower appendages (arms and legs)
- shoulder girdle
- pelvis
lpslateral
same side
vertebrae characteristics
- dorsal hollow nerve cord
- notochord
- pharyngeal arches and pouches
- vertebrae (after birth, this stays the same)
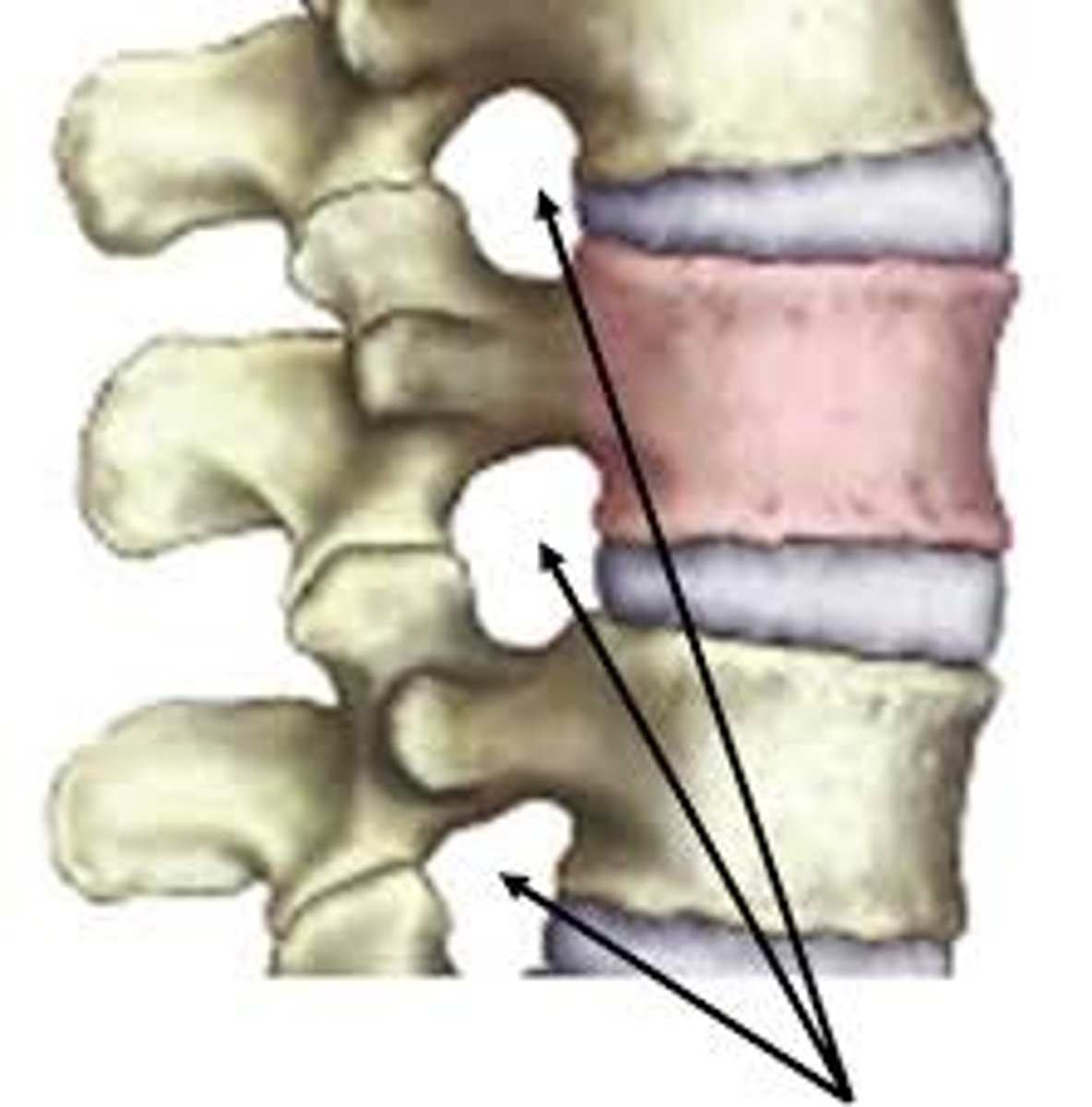
What's this?
What's this?
intervertebral foramina
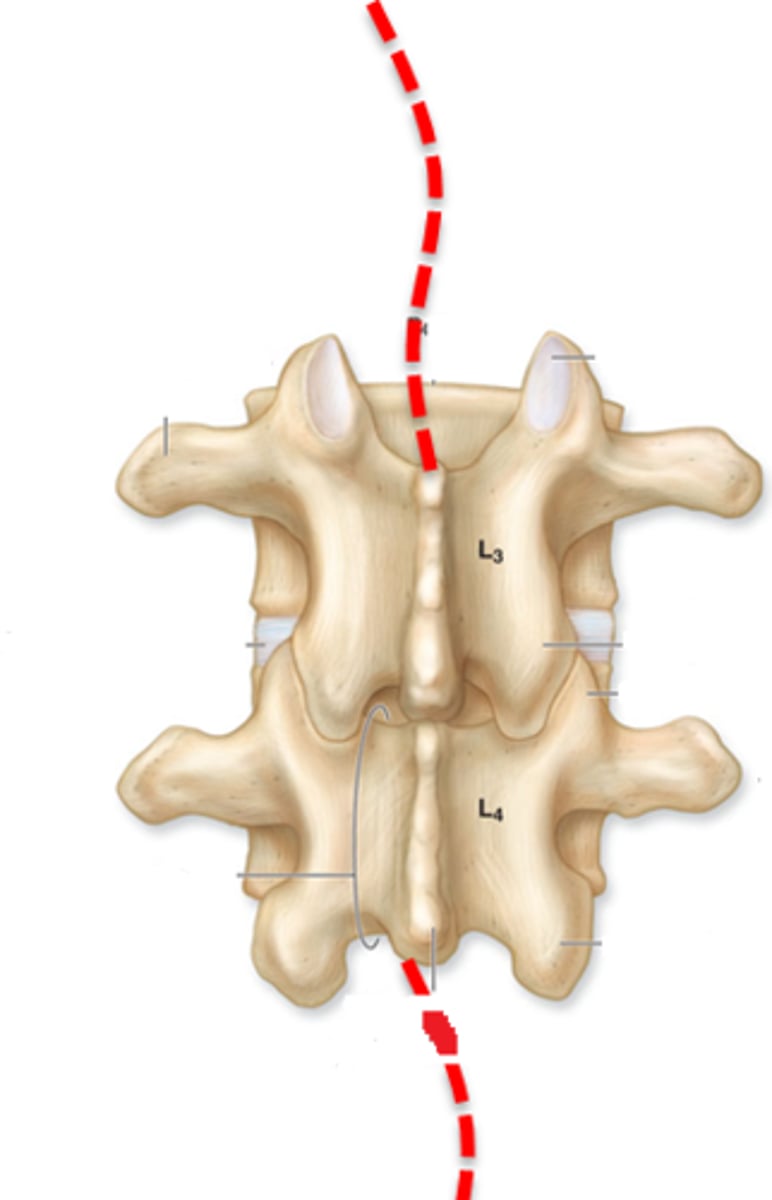
What's this?
What's this?
vertebral canal
What's this?
What's this?
inferior articular process
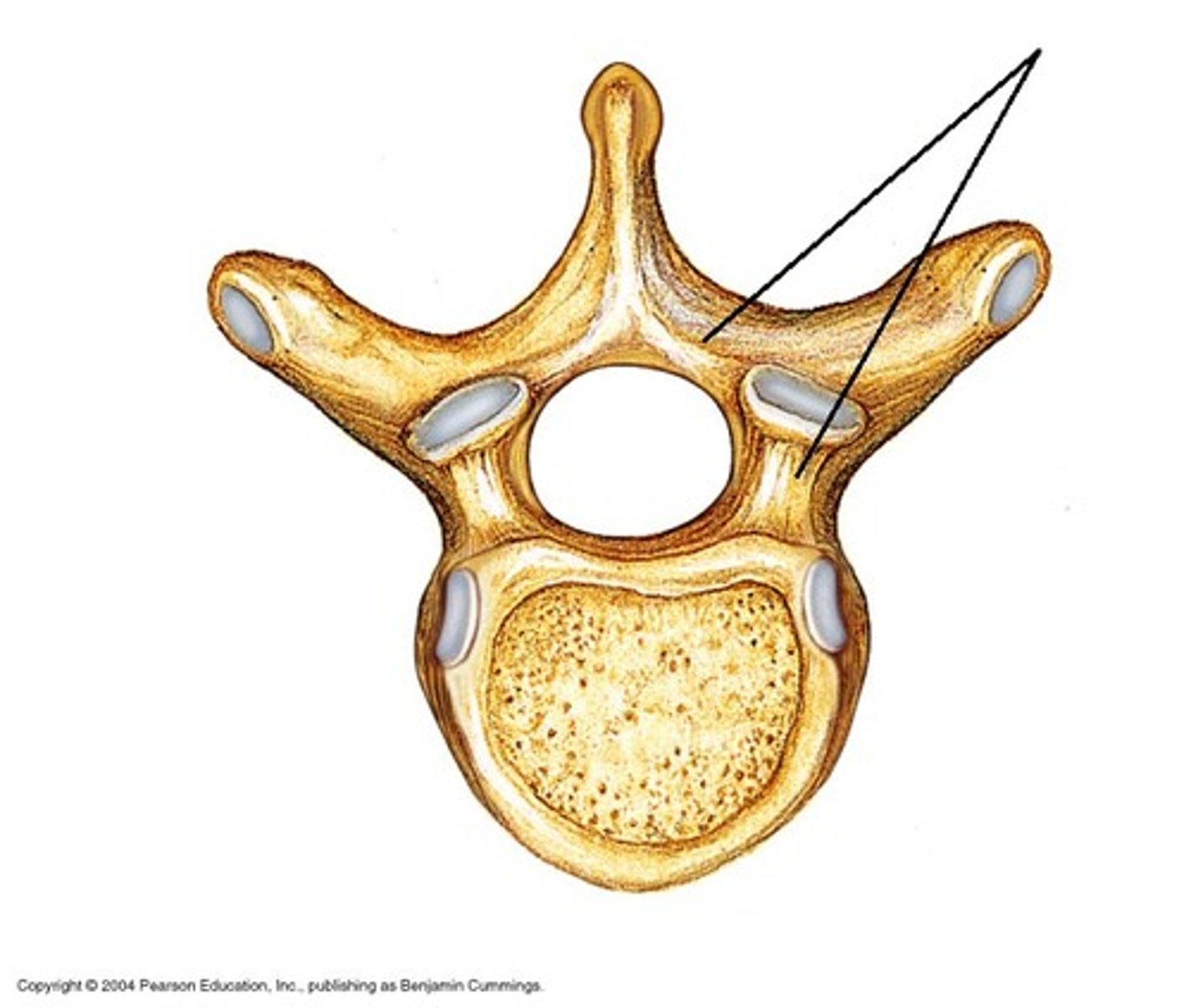
What's this?
What's this?
superior articular process
What are these 2 parts of the vertebral arch?
What's this?
TOP --> lamina (2)
BOTTOM --> pedicle (2)
What is a foreman?
a hole
What is C and B?
What's this?
C --> Spinous process
B --> Transverse processes
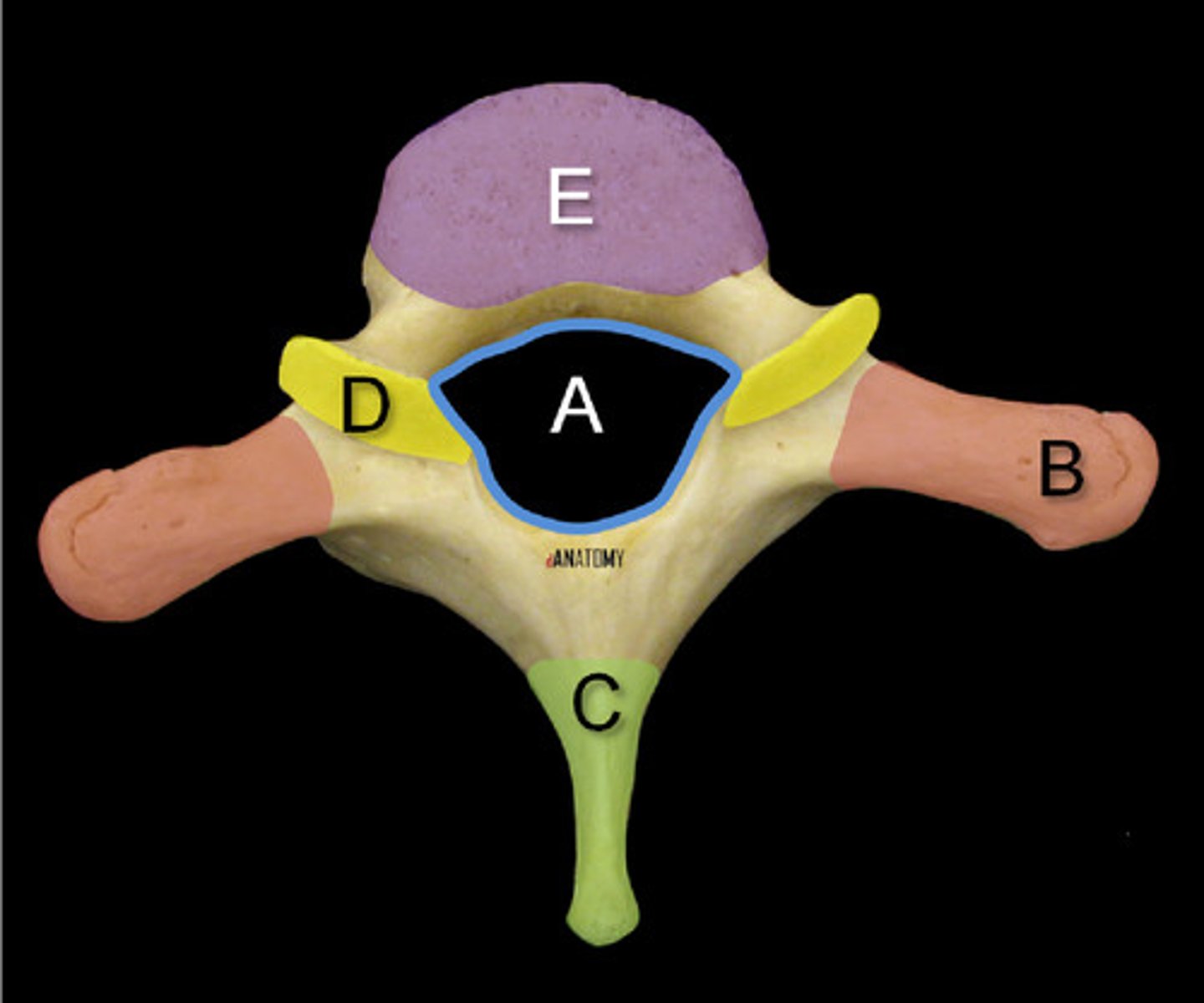
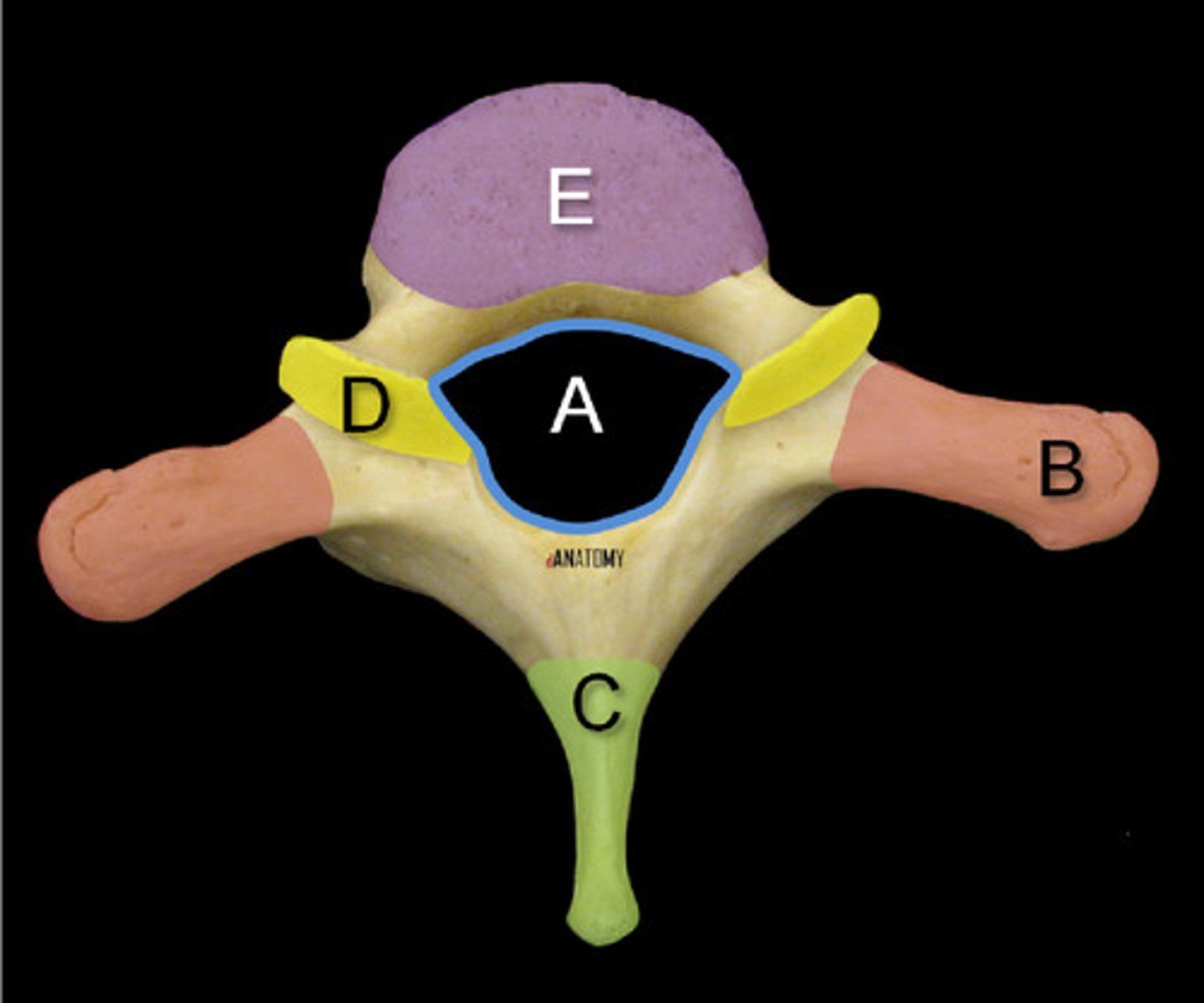
What is A and E?
What's this?
A --> Vertebral foreman
E --> Vertebral body
The spinous process points....?
posterior
The vertebral body points...?
anterior
regions of the trunk
- thorax
- abdomen
- pelvis
- perineum
contralateral
opposite side
vertebrates are...
segmental animals. (they exhibit serial repetition of structures along the longitudinal axis of the body)
Promixal
closer to origin
Distal
Farther away from origin
serial repetition of vertebrae come from what during development?
somites (groups of embryonic cells lying in pairs alongside the developing nerve cord.
axial skeleton
- vertebrae
- ribs
- sternum
unilateral
one side
structures in the trunk
segmental (derived from somites)
- skin
- vertebrae
- sternum
- back muscles
- body wall muscles
- kidney and gonads
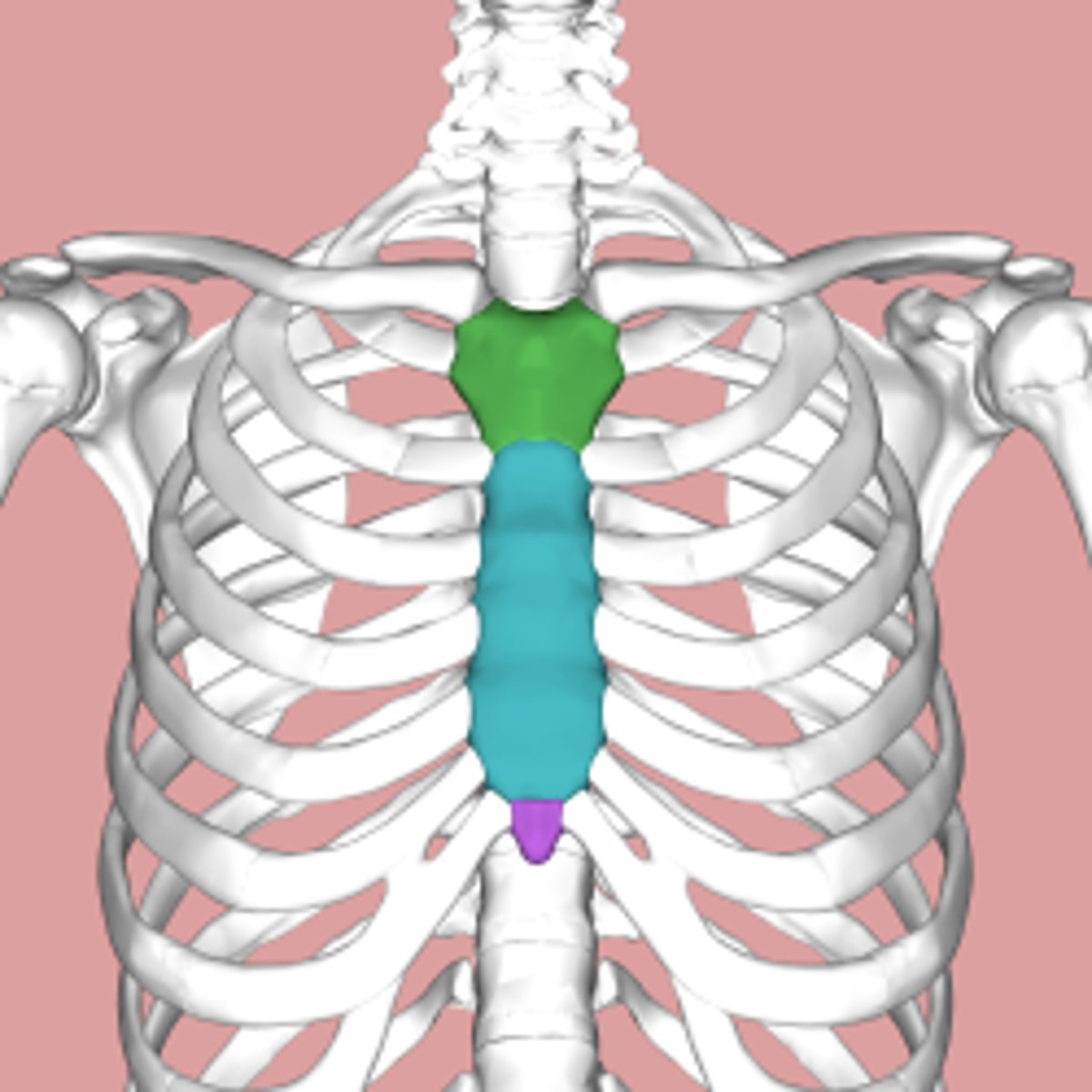
name the sections of the sternum
green --> manubrium
blue --> body
purple --> xiphoid (process)
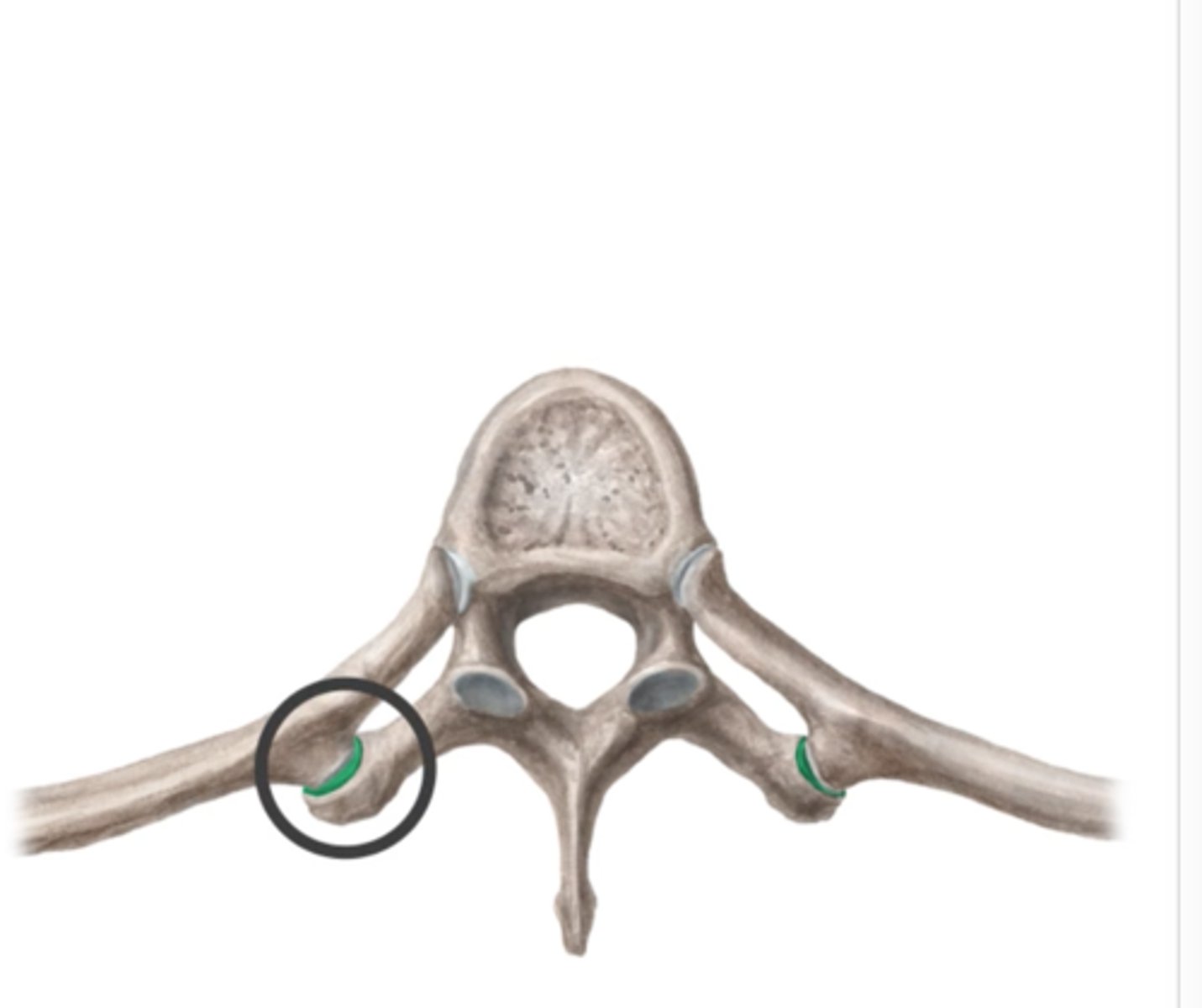
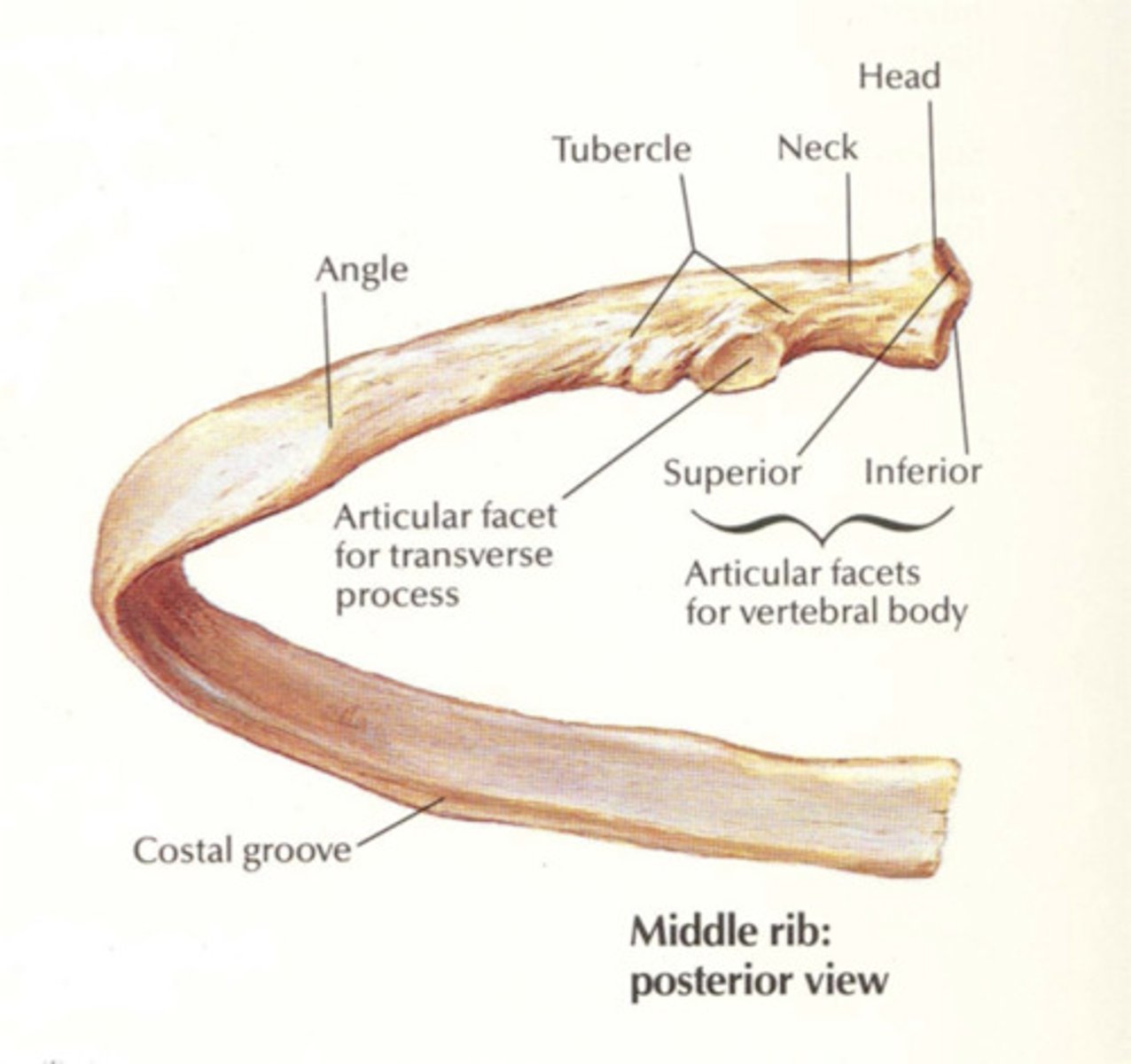
What part of the rib connects to the vertebrae?
Whats this?
black circle --> tubercle
other section with cartilage --> head
true ribs are...
1-7, connect to the sternum
false ribs are...
8-10, connects in the costal facets and have costal cartilages connected to the cartilage above them
floating ribs are...
11 and 12, don't connect to sternum or costal facets
What are the three sections of the OS Coxae?
ilium
ischium
pubis
name the regions of the vertebral column
- cervical
- thoracic
- lumbar
- sacrum
- coccyx
how many vertebrae are there?
33 vertebrae
name the atypical cervical vertebrae
C1 --> atlas (has no vertebral body)
C2 --> axis (has a dens)
C7 --> vertebra prominens (has a long spinous process)
how can you tell if a vertebrae is a from the lumbar region?
- no foramina in the transverse processes
- no costal facets
(L1-L5)
how can you tell if a vertebrae is from the cervical region?
has holes in the transverse processes (C1-C7)
somites give rise to what muscles in the trunk?
epaxial:
- dorsal to the transverse processes
- muscles of the back
hypaxial:
- ventral to the transverse processes
- muscles of the lateral/ventral body wall
BOTH ARE SKELETAL VOLUNTARY
what are the actions of the epaxial muscles?
bilateral: contracts on both sides at the same time
extend the vertebral column and head/neck
unilateral: only contracts on one side
laterally flex the vertebral column and head/neck (body moves to 1 side)
What's this?
What's this?
anterior longitudinal ligament
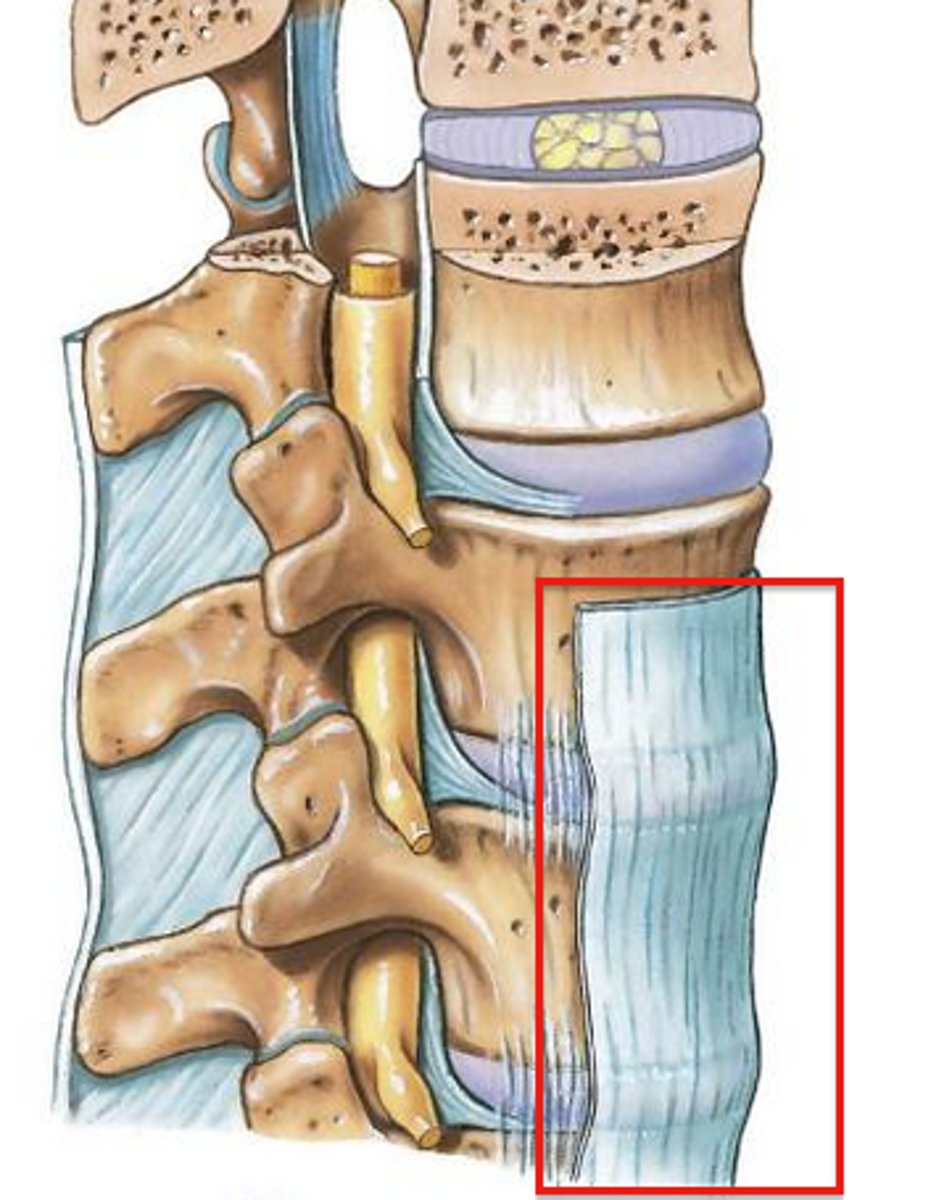
What's this?
What's this?
posterior longitudinal ligament
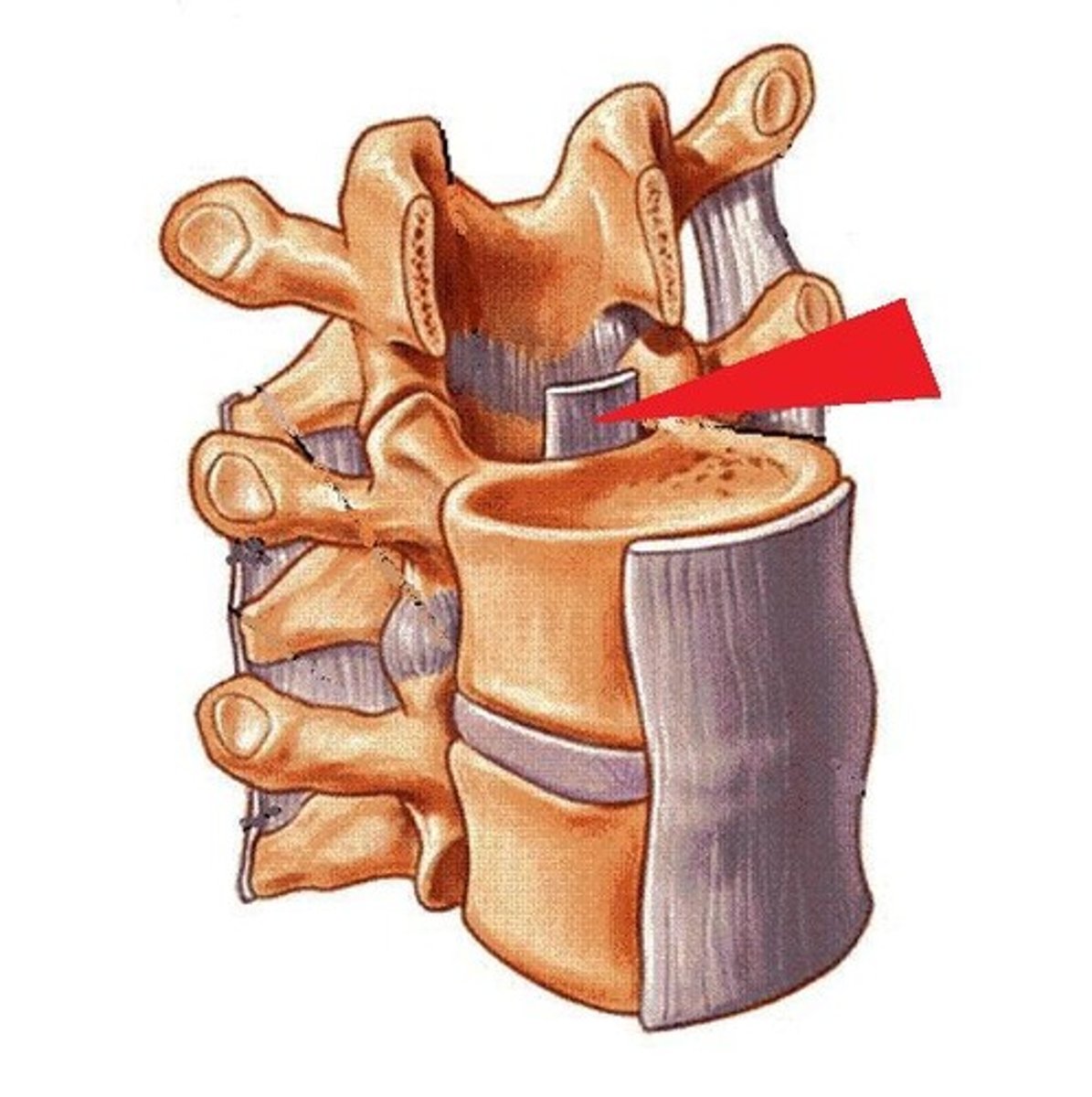
What's this? (green arrow)
What's this? (green arrow)
supraspinous
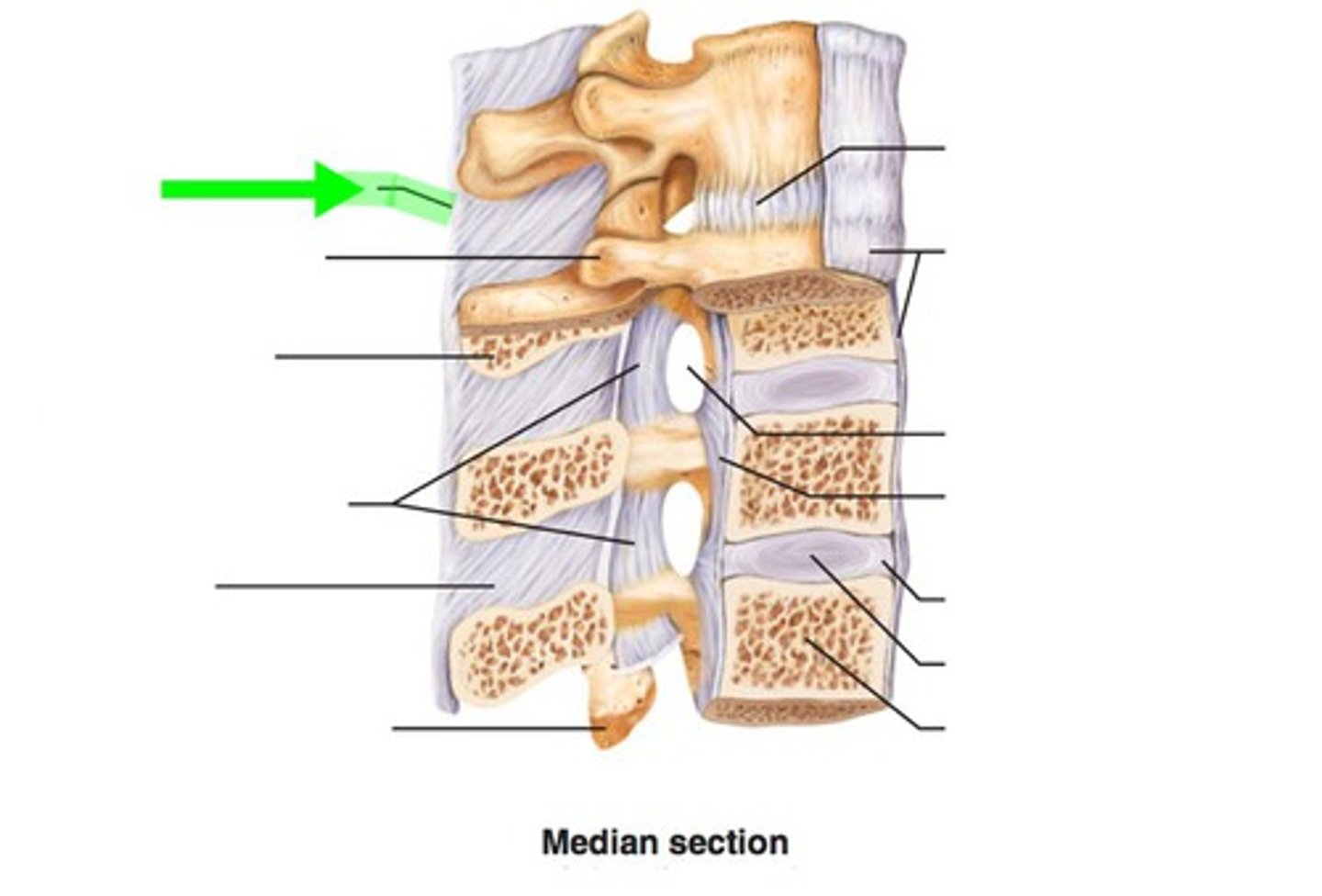
the .... is pulled toward the ....
the insertion is pulled toward the origin
Skeletal muscles are....
voluntary
What's this?
What's this?
nuchal ligament
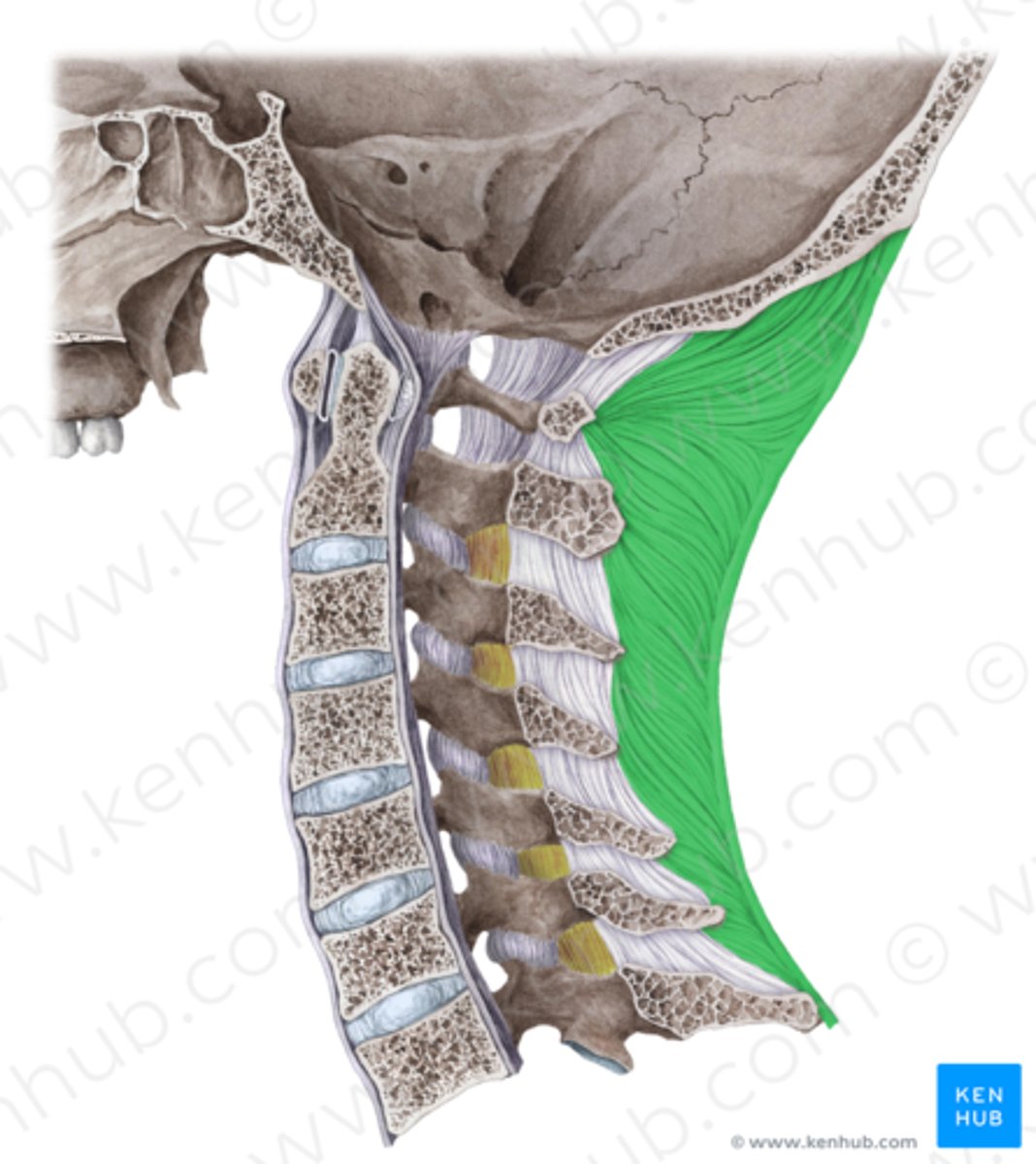
What's this?
What's this?
ligamentum flavum
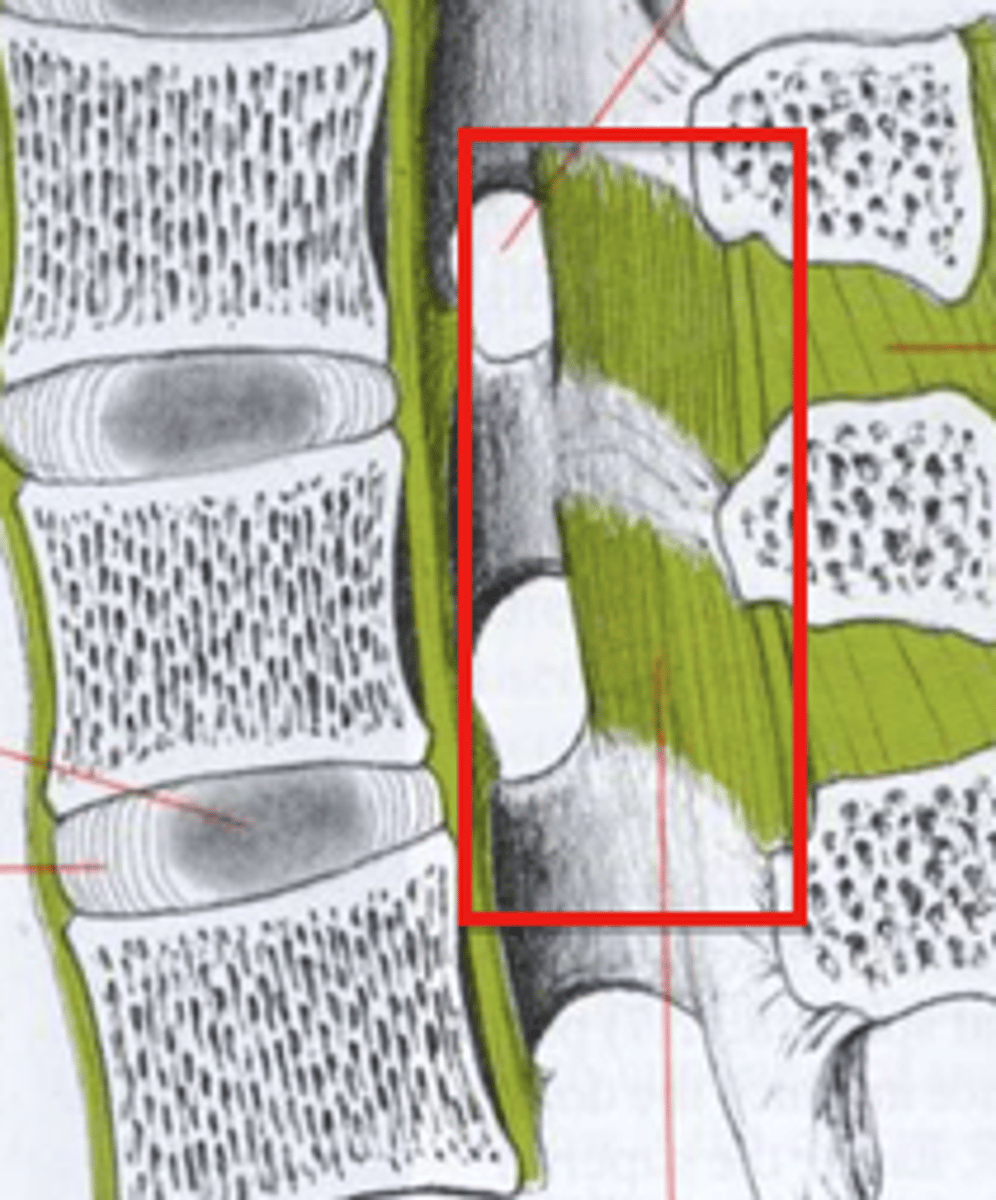
whats pressing on the spinal nerve cause?
herniated "slipped" disc
curvatures 2° is...
secondary curvature
- cervical spine
- lumbar spine
curvatures 1° is...
primary curvature
- thoracic spine
- sacrum
what is a tendon?
connects muscle to bone
what are ligaments?
connective tissue that connects bone to bone
whats the distinctive features of the coccyx?
the tail "vestigial tail"
whats the distinctive features of the sacrum?
5 fused vertebrae (S1-S5)
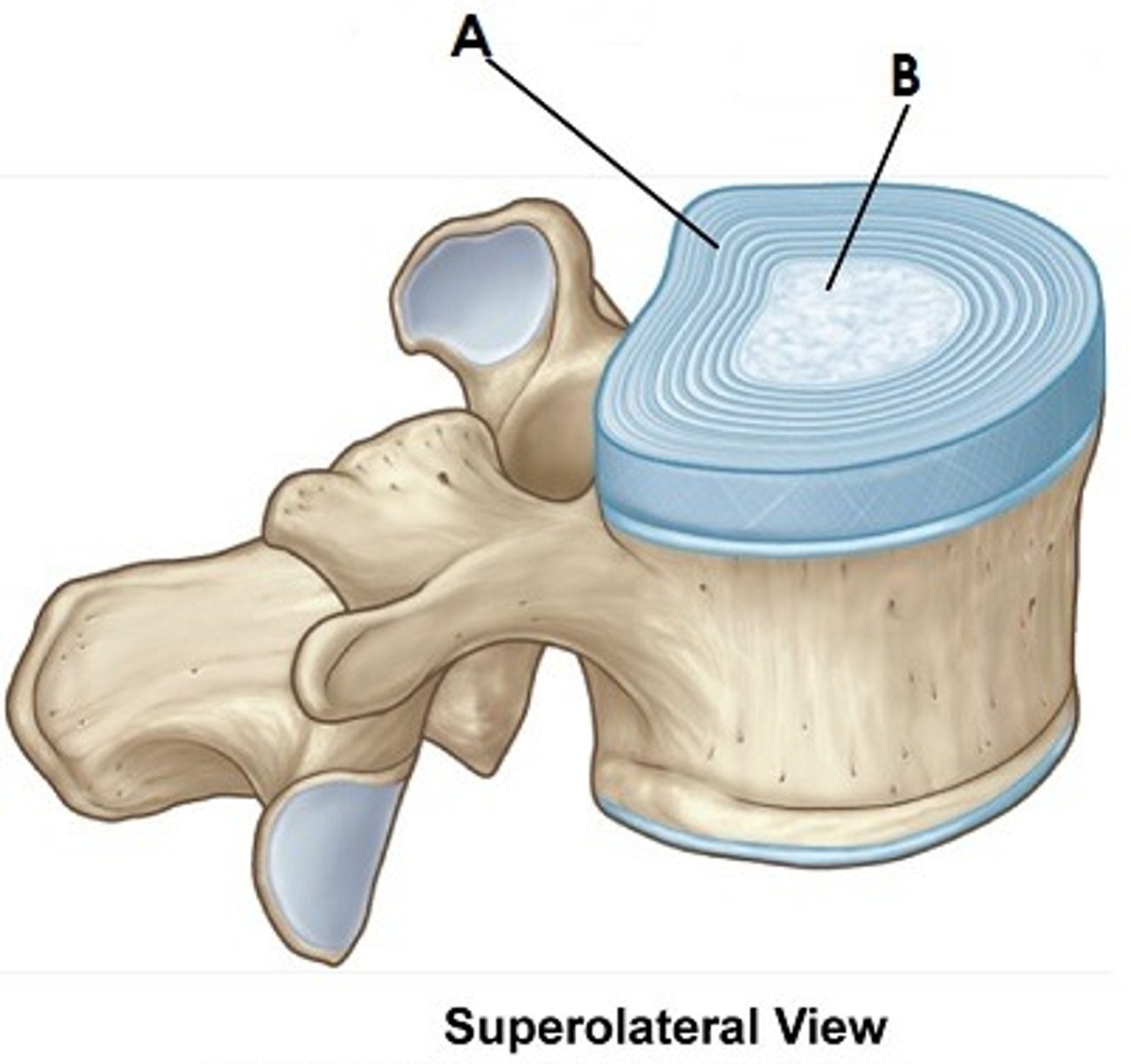
What are the sections of the intervertebral disc?
Whats this?
A --> annulus fibrosus
B --> nucleus pulpous
list the curvature abnormalities
- Kyphosis: involves the upper back curving forward. The condition can create the form of a hump. (thoracic spine)
- Lordosis: is also known as swayback. (lumbar spine)
- Scoliosis: is a frontal deformity in which the spine, when viewed straight on, curves to the left or the right.
how can you tell if a vertebrae is from the thoracic region?
costal facets (connection between a rib and vertebrae)
a fetus spine has a ... shape spine
c shaped spine
STUDY THE RIB
What's this? (medial view)
What's this?
iliac fossa
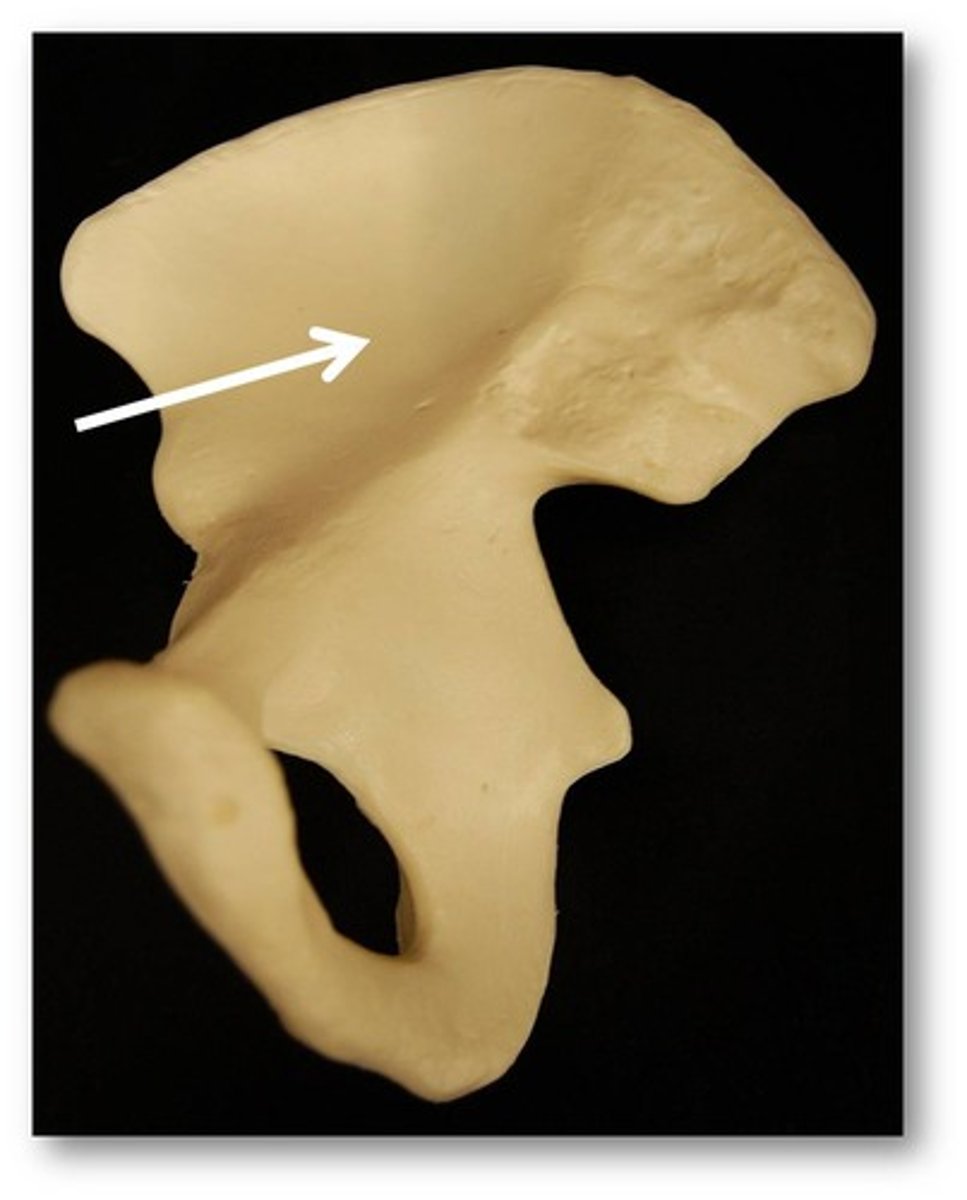
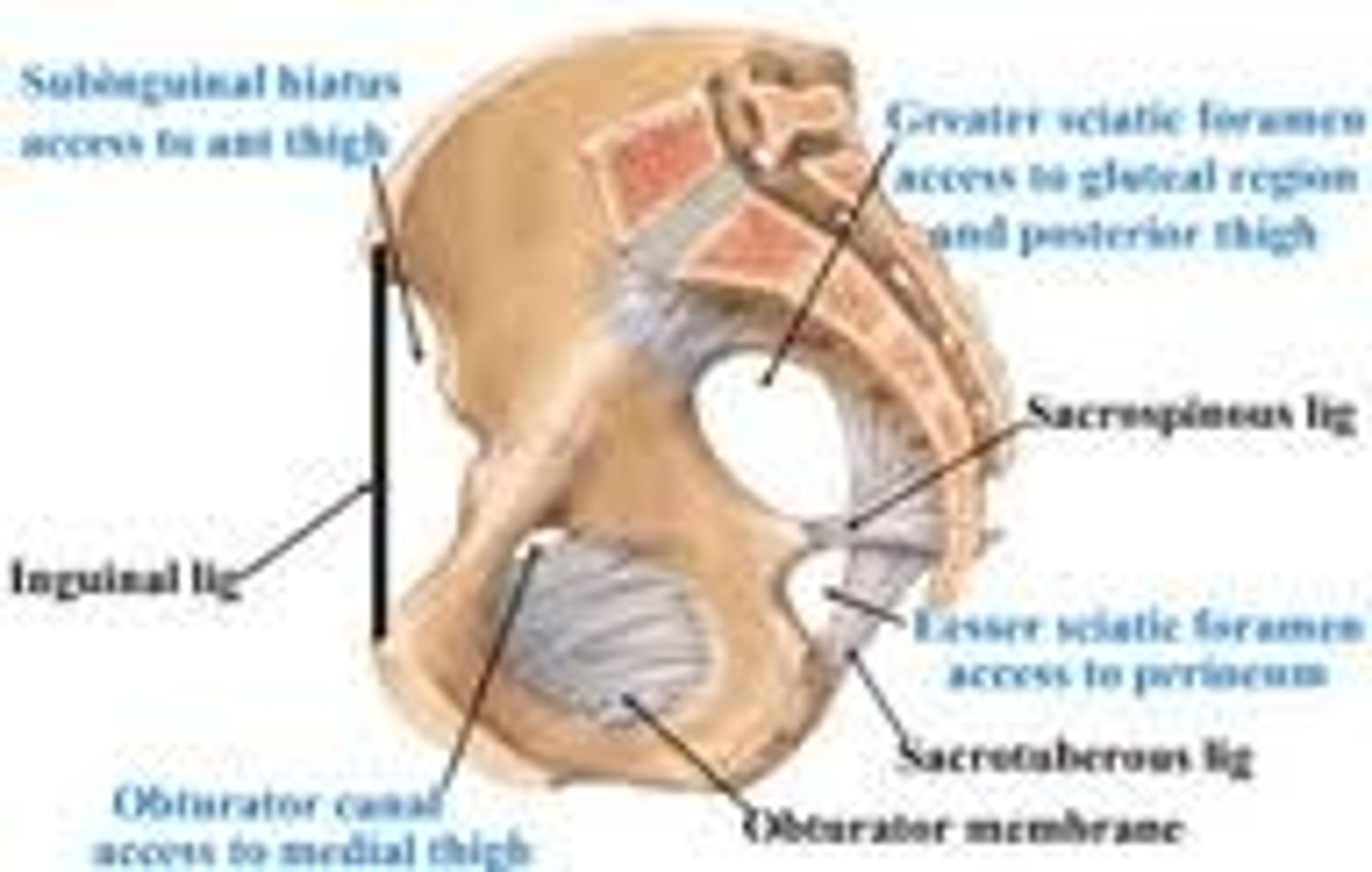
STUDY THE LIGAMENTS OF THE PELVIS
purpose of the vertebral column
- protection
- support
- posture
- balance
- movement (locomotion)
we remove what muscles to view the epaxial muscles
- trapezius
- latissimus dorsi
STUDY THE LABELED AREAS OF THE PELVIS
name all epaxial muscles (superficial --> deep) how do they run?
SUPERFICIAL LAYER:
- splenius m.
INTERMEDIATE LAYER: (erector sprinae)
- iliocostalis m.
- longissimus m.
- spinalis m.
DEEP LAYER:
- semispinalis m.
* run lateral to medial
female pelvis has a .... opening while male has a .... opening
female pelvis has a LARGER opening while males have a SMALLER opening
what makes up the central nervous system?
- spinal cord
- brain
what makes up the peripheral nervous system?
- spinal and cranial nerves
- ganglia
Peripheral nervous system: Sensory VS Motor
SENSORY:
- transmit sensory info to CNS from receptors
- nerve impulse travel towards CNS
MOTOR:
- transmit motor commands away from CNS to effectors
- nerve impulse travel away CNS
what does afferent mean?
going into a structure (sensory input)
what does efferent mean?
leaving a structure (motor output)
somatic nervous system: somatosensory
sensory from skin
what are the segmental structures from the somatic nervous system?
- skin
- skeletal muscle
somatic nervous system: somatomotor
- output to skeletal muscle (epaxial and hypaxial)
- voluntary
autonomic nervous system: viscerosensory
sensory from viscera
what are the non-segmental structures from the autonomic nervous system?
- smooth muscle
- cardiac muscle
- glands, viscera
STUDY THE PARTS OF THE NEURON
nerve is a...
bundle of axons
a neuron is a...
nerve cell
STUDY THE TYPICAL SPINAL NERVE
spinal nerves exit the vertebral canal via the ....
intervertebral foramina
STRUCTURES ----> COMPONENTS?
dorsal roots
ventral roots
spinal nerves
dorsal rami
ventral rami
dorsal roots- SENSORY
ventral roots - MOTOR
spinal nerves - SENSORY AND MOTOR
dorsal rami - SENSORY AND MOTOR
ventral rami - SENSORY AND MOTOR
what are dermatomes?
ares of skin innervated by the cutaneous branches from a single spinal nerve
what do cutaneous nerves do?
they provide sensory innervation to segmentally-derived skin