Genetics: Chromosome Variations, Mutations, and Structural Changes (CH8)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What are the four types of chromosome morphology?
Metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric, and telocentric.
What is karyotyping?
The process of preparing chromosomes from actively dividing cells, halted in metaphase and arranged according to size.
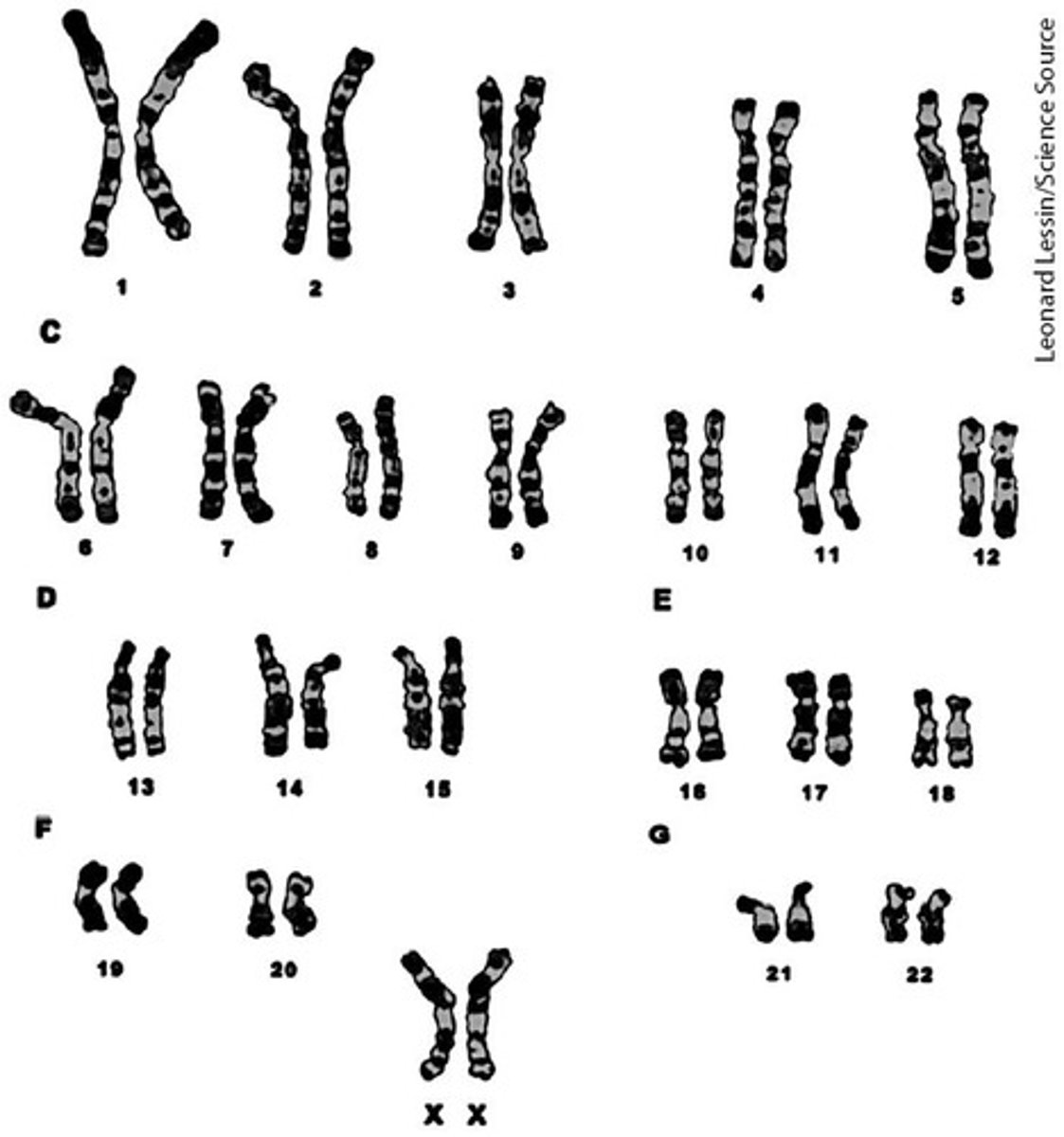
What are G bands in chromosome banding?
G bands are produced by Giemsa stain and are used to identify specific regions on chromosomes.
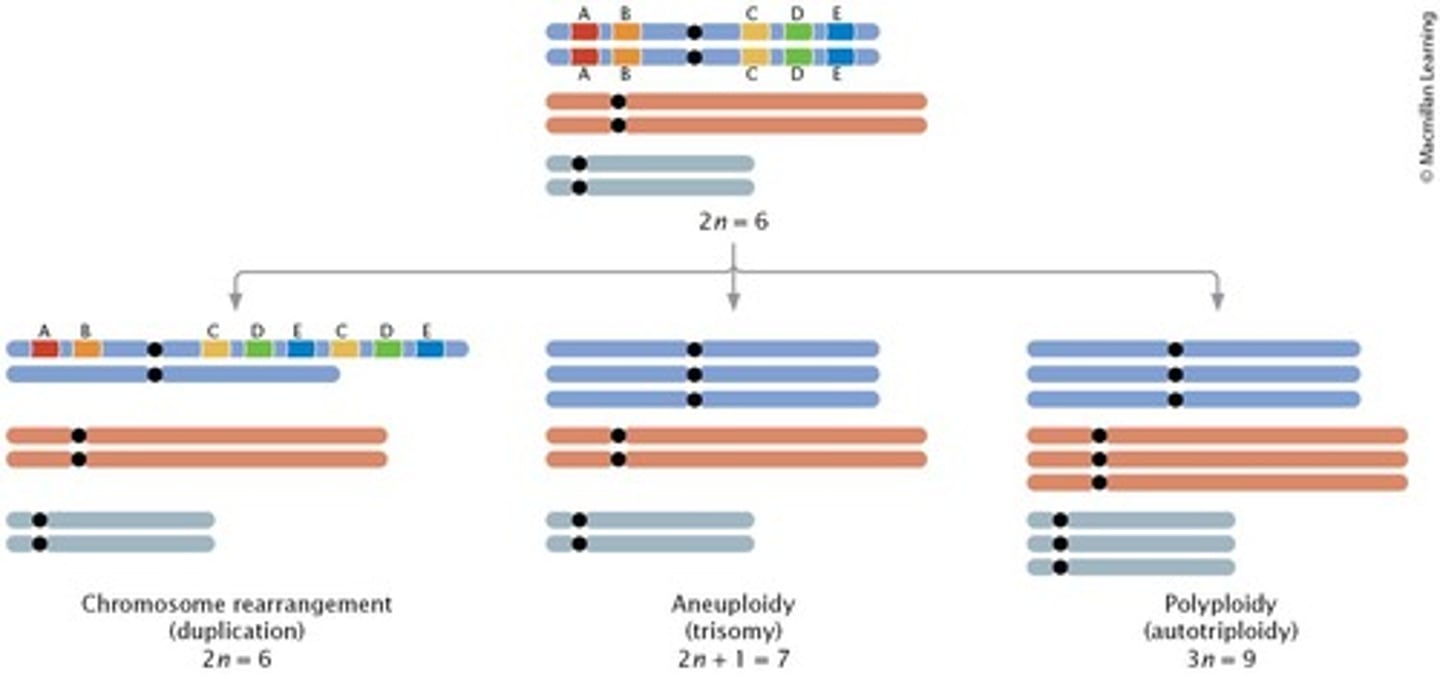
What is aneuploidy?
A type of chromosome mutation that alters the number of chromosomes.
What is polyploidy?
A type of chromosome mutation where one or more complete sets of chromosomes are added.
What is a chromosome rearrangement?
A mutation that alters the structure of chromosomes.
Can chromosome duplications cause negative effects to an organism? Why?
Yes, because they can increase gene dosage, affecting processes like development that require specific amounts of protein.
What is pseudodominance?
A phenomenon where recessive mutations are expressed if the wild-type allele is deleted due to a chromosome deletion.
What are the effects of deletions on chromosomes?
They can cause imbalances in gene products, expression of normally recessive genes, and haploinsufficiency.
What is a monosomic cell?
A cell with one less chromosome than the diploid number.
What is a trisomic cell?
A cell with one extra chromosome than the diploid number.
What is an autotriploid cell?
A cell with three complete sets of chromosomes.
What types of chromosome mutations can result from nondisjunction?
Trisomy and monosomy can result from nondisjunction during meiosis I, meiosis II, or mitosis.
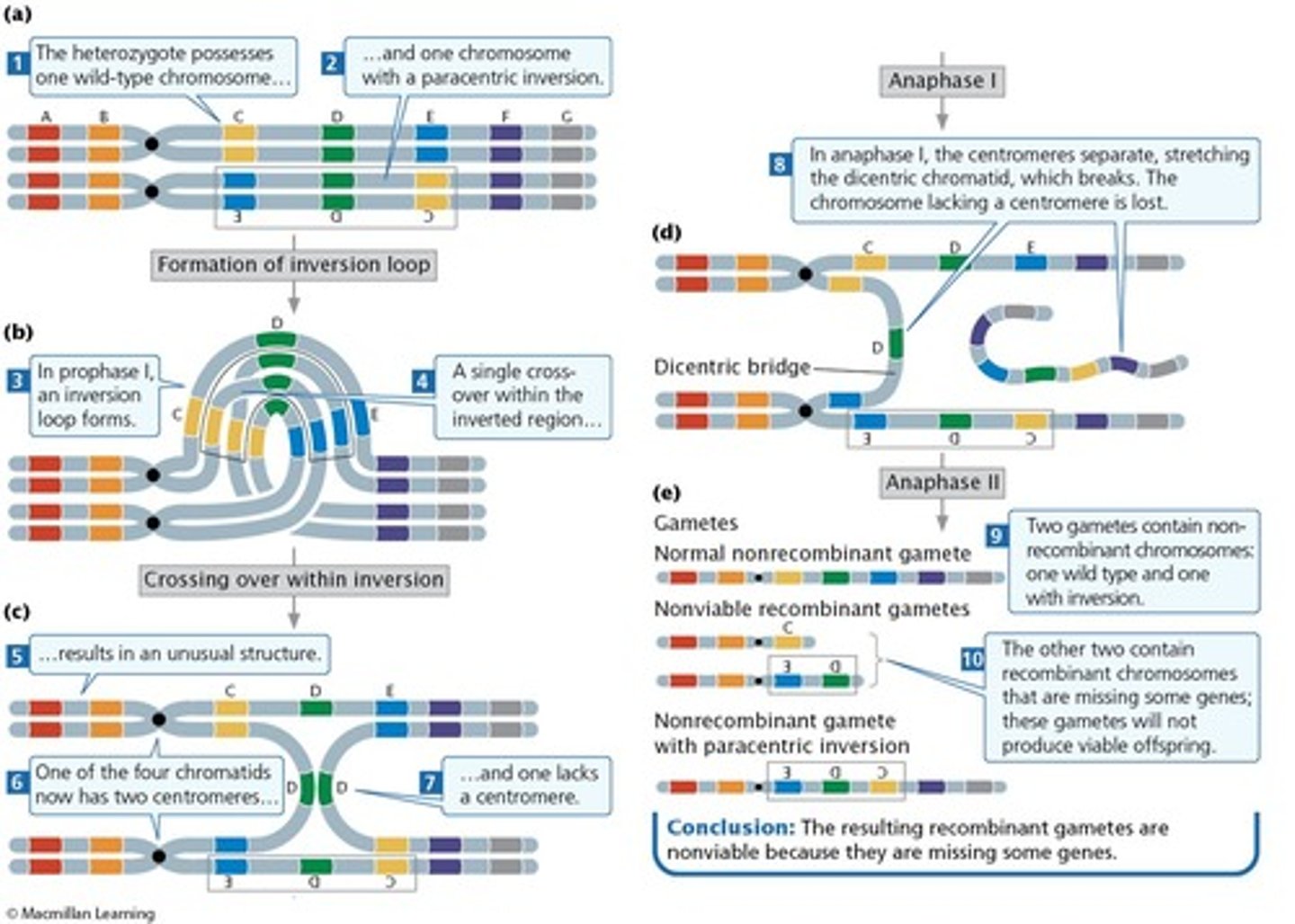
Which chromosomes are less likely to result in a live birth when aneuploid?
Larger autosomes are less likely to result in a live birth.
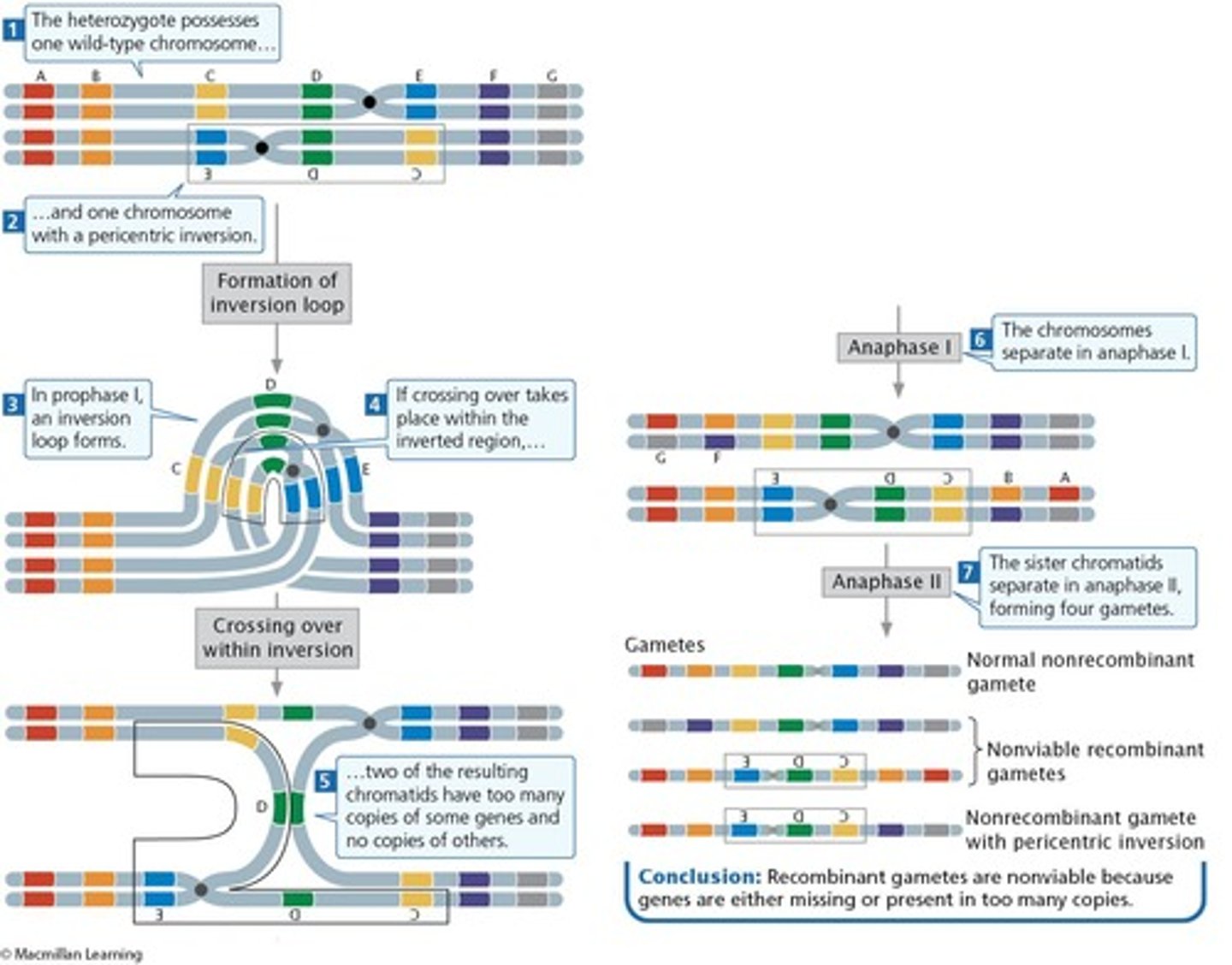
What are the two types of inversions in chromosome rearrangements?
Paracentric inversion and pericentric inversion.
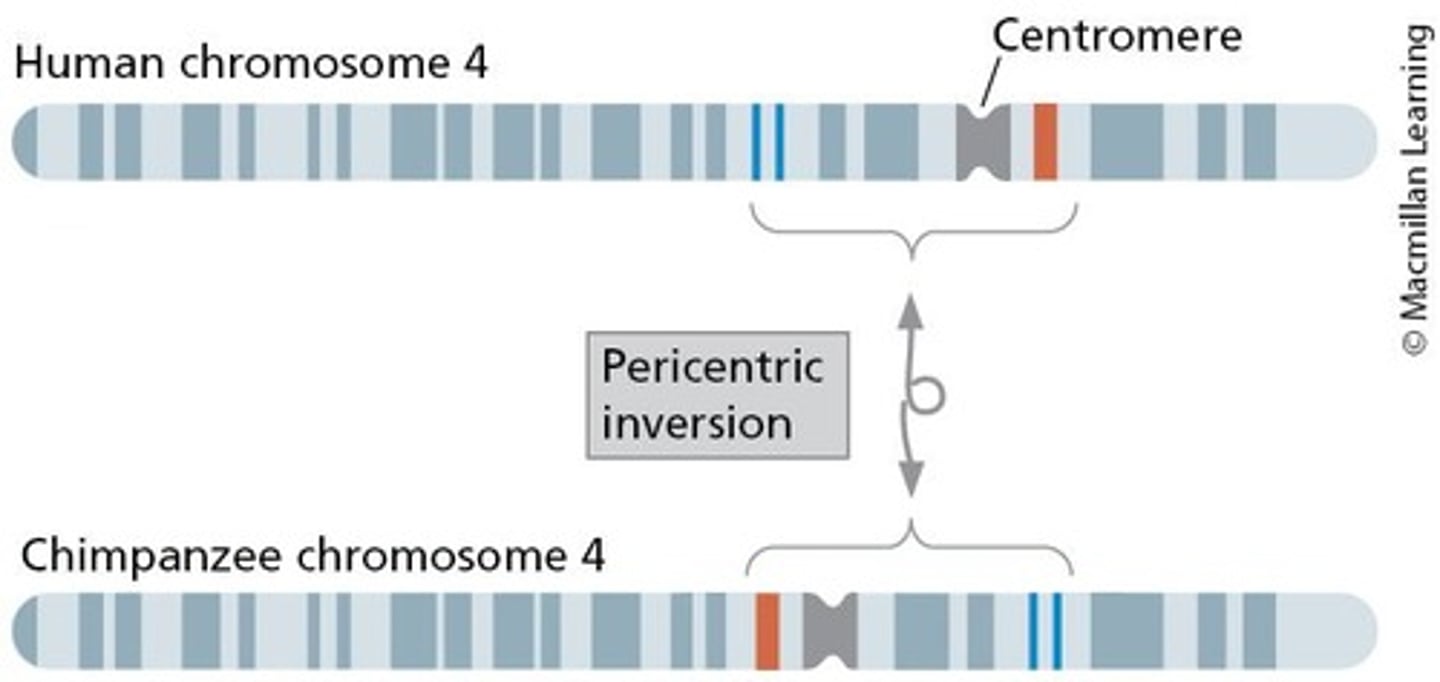
What happens during meiosis in individuals with inversions?
Homozygous individuals have no problems, while heterozygous individuals may form inversion loops leading to reduced recombination.
Which chromosome rearrangement is most likely to cause a position effect phenotype?
Inversion is most likely to cause a position effect phenotype.
What is a dicentric chromosome?
A chromosome with two centromeres, produced when crossing over occurs in an individual heterozygous for a paracentric inversion.
Which chromosomal mutation results in a dicentric bridge?
Inversion
What percentage of meiotic products result in nonviable gametes during crossing over in a paracentric inversion loop?
50%
What is NOT an effect of chromosomal translocations?
Translocations can cause regions of the chromosome to be duplicated.
Which chromosomal rearrangement suppresses crossovers?
Inversions
What is the outcome of a Robertsonian translocation?
One metacentric chromosome and one chromosome with two very short arms.
What are fragile sites in chromosomes?
Chromosomal regions that are susceptible to breakage.
What is nullisomy?
Loss of both members of a homologous pair of chromosomes; 2n − 2.
What is monosomy?
Loss of a single chromosome; 2n − 1.
What is trisomy?
Gain of a single chromosome; 2n + 1.
What is tetrasomy?
Gain of two homologous chromosomes; 2n + 2.
What causes red-green color blindness in humans?
Unequal crossing over of X chromosomes.
How many chromosomes will be found in a trisomic member of a species with 2n = 36?
37 chromosomes.
What is the total chromosome number of an autotetraploid if the diploid number is 30?
60 chromosomes.
What is the significance of polyploidy?
Increase in cell size and larger plant attributes; may lead to new species.
What is uniparental disomy?
Both chromosomes inherited from the same parent.
Why are sex-chromosome aneuploids more common than autosomal aneuploids?
Most autosomal aneuploids are spontaneously aborted.
What is the effect of maternal age on aneuploidy?
Increased maternal age is associated with higher rates of aneuploidy.
What is genetic mosaicism?
A condition where an individual has two or more genetically different cell lines.
What is the role of nondisjunction in aneuploidy?
Nondisjunction during meiosis or mitosis can lead to aneuploidy.
What is the outcome of crossing over in a paracentric inversion?
It can lead to nonviable gametes.
What is a balanced reciprocal translocation?
A chromosomal rearrangement where segments from two different chromosomes are exchanged without loss of genetic material.
What is the primary cause of primary Down syndrome?
Random nondisjunction in egg formation.
What is familial Down syndrome?
Caused by a Robertsonian translocation between chromosomes 14 and 21.
What is the typical stage of mitosis for performing a karyotype?
Metaphase.
What type of translocation can lead to changes in gene regulation?
Translocations can cause translocated genes to come under the control of different regulatory sequences.
Is there only one naturally occurring, viable polyploid in mammals?
False
What is the ploidy level of wheat compared to humans?
Wheat is hexaploid; humans are diploid.
What is the approximate size of the wheat genome compared to the human genome?
The wheat genome is about 17 million base pairs; the human genome is about 3.2 billion base pairs.
What can uniparental disomy cause?
Phenotypic problems due to the presence of two copies of a gene from one parent and none from the other.
What are human fragile sites associated with?
Chromosome breakage, replication late in S phase, stalling of DNA replication enzymes, and genetic disorders.
How many chromosomes would be found in an allotriploid of species A (2n = 16) and species B (2n = 14)?
21 or 24 chromosomes.
What are structural variants in chromosomes?
They include chromosome rearrangements, copy-number variations, inversions, and translocations, but not point mutations.
In an allotriploid of two species with 32 and 24 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would there be?
40 or 44 chromosomes.
What is the ploidy level of many varieties of bananas?
Polyploid.
What is a likely explanation for a mother with Turner syndrome (45,X) having a son?
The mother is a genetic mosaic.
Why do species usually have a characteristic number of chromosomes?
Chromosome number stability is crucial for proper reproduction and genetic integrity.
What happens during prophase I of meiosis in an individual with a reciprocal translocation?
Chromosomes pair in a specific way that can lead to reduced fertility.
How can monozygotic twins differ in chromosome number?
One twin may have a chromosomal abnormality like trisomy 21 while the other does not.
Why is trisomy of the X chromosome more common than trisomy of chromosomes 4 and 5?
Differences in the viability and developmental impact of the trisomies.
What is the relationship between chromosome nondisjunction and aneuploidy in humans?
Most nondisjunction occurs during oogenesis, leading to a high rate of aneuploidy.
What might have been an adaptive reason for high levels of chromosome nondisjunction in human evolution?
It could have provided a selective advantage in certain environmental contexts despite the risks of aneuploidy.
Can homologous chromosomes be identical?
Yes, if they are identical alleles inherited from both parents.
Why do trisomics often have more developmental problems than triploids?
Trisomy results in an imbalance of gene dosage, leading to more severe developmental issues.
What does the CRISPR-Cas technology finding suggest about chromosome number?
Chromosome number may not be as critical for species function as previously thought.