AP Bio Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
1/186
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
element
substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions
matter
takes up space and has mass
compound
substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio
atom
smallest unit of matter that has the properties of an element
neutrons
subatomic particle, no electrical charge
protons
subatomic particle, positive charge
neutrons
subatomic particle, negative charge
atomic nucleus
neutrons and protons
daltons
unit of measurement for neutron and proton mass
atomic number
number of protons in the nucleus
mass number
number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
isotopes
two atoms of the same element with different amount of neutrons
half-life
time it takes for a parent isotope to decay into its daughter isotope
energy
capacity to cause change
potential energy
energy matter has because of its location and structure
electron shell/energy level
electron’s state of potential energy
2n²
shell capacity
valence electrons
electrons in the outermost shell
covalent bond
sharing of a pair of valence electrons, non metal x non metal
molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
single bond
a single covalent bond sharing one pair
double bond
a double covalent bond sharing two pairs
valence
bonding capacity of an atom
electronegativity
atom’s attraction to electrons in a covalent bond
non polar covalent
atoms share electrons equally
polar covalent
atoms share electrons unequally, one atom is more electronegative
ionic bond
attraction between an anion and cation, one atom strips the electron from the other, non metal x metal
ion
charged atom/molecule
cation
positively charged ion
anion
negatively charged ion
hydrogen bond
hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to one electronegative atom that is also attracted to another electronegative bond
water can make up to
four hydrogen bonds
water is
polar covalent
cohesion
hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together for transportation
adhesion
attraction between different substances
surface tension
measure of how difficult it is to break the surface of a liquid
kinetic energy
energy of motion
thermal energy
random motion of atoms or molecules
temperature
average kinetic energy in a body of matter
heat
thermal energy in transfer
specific heat
amount of heat that must be absorbed/lost for 1g to change to change its temperature
heat of vaporization
heat a liquid must absorb for 1g to be converted to gas
evaporative cooling
liquid evaporates —> remaining surface cools
solution
liquid that is completely alike mixture of substances
solvent
dissolving agent of a solution
solute
substance that is dissolved
aqueous solution
one in which water is the solvent
hydration shell
ions of a ionic compound surrounded by a sphere of water molecules
hydrophilic
polar, substance that has an affinity for water
hydrophobic
non-polar, substance is one that does not have an affinity for water
hydrogen ion (H+)
hydrogen atom in a hydrogen bond leaves it’s electron and becomes a proton
hydroxide (OH-)
molecule that lost the proton
hydronium ion
molecule with the extra proton
ions conduct
electricity
acid
increases the H+ concentration of a solution
base
reduces the H+ concentration of a solution
acidic solutions have pH values
less than 7
basic solutions have pH values
greater than 7
buffers
substances that minimize changes in concentrations of H+ and OH-
ocean acidification
CO2 dissolved in seawater forms carbonic acid
ocean acidification negatives
H+ use carbonate ions that are needed for marine organisms to produce bicarbonate
carbon can make
4 bonds
organic chemistry
study of compounds that contain carbon
hydrocarbons
consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
isomer
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
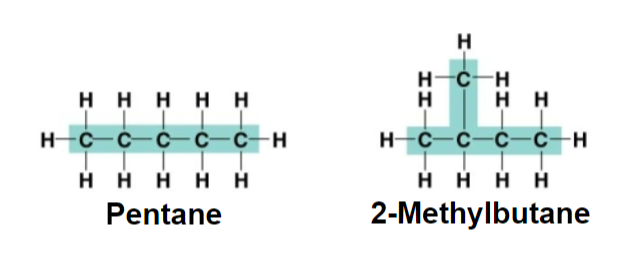
structural isomers
drawn differently
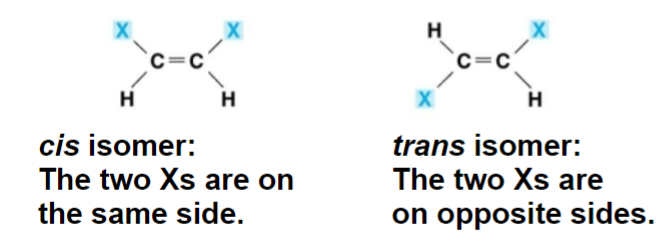
cis-trans/geometric isomers
the element is rotated around a double bond
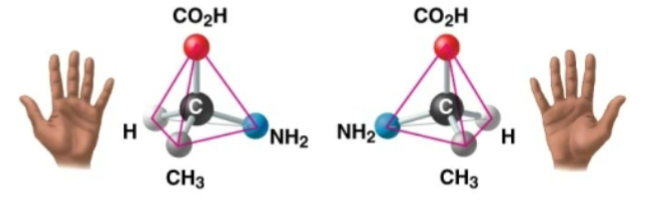
enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of one another
steriods
form of four fused rings
functional groups
common components of organic molecules
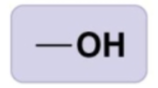
hydroxyl group
-OH or HO-
carbonyl group
C--O
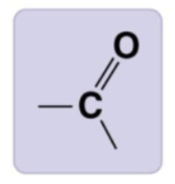
ketone group
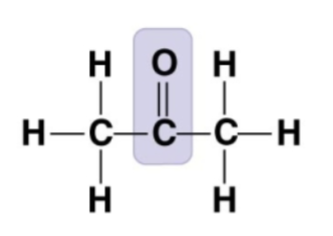
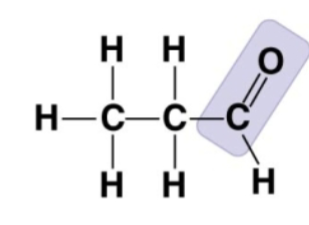
aldehyde
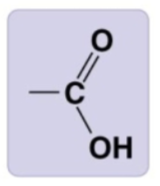
carboxyl group
-COOH, carboxylic acid
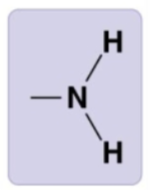
Amino group
-NH2
sulfhydryl group
-SH or HS-

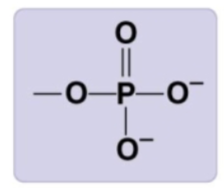
phosphate group
-PO4 2-
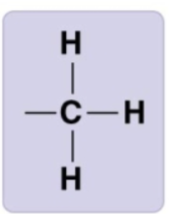
methyl group
-CH3
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
three phosphate groups
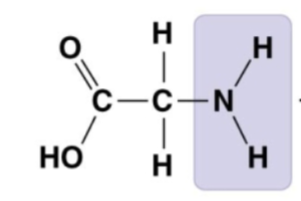
contains both an amino group and carboxyl group
monomer
repeating units of a polymer
polymer
long molecule of many like building blocks
enzymes
specialized protein macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions
dehydration reaction
water removed —> two monomers bond
hydrolysis
water added —> polymers split into monomers
carbohydrates
sugars and polymers of sugars
monosaccharides
multiples of CH2O, most basic sugars
Glucose
most common monosaccharide, represented by a green hexagon
disaccharide
two glucose connected
starch
storage polysaccharide of plants, amylose is simplest form
glycogen
storage polysaccharide in animals
cellulose
polysaccharide, polymer of glucose, two ring forms (alpha and beta)
chitin
structural polysaccharide found in exoskeletons of arthropods
glycosidic linkage
covalent bond between two monosaccharides due to a dehydration reaction
-ose
sugar
-ine
triple bond
-ane
single bonds
-ene
double bond
lipids
large biological class that does not have polymers