14. t lymphocytes subsets and effector functions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
how can humoral immunity be transferred?
transfer antibodies from one animal to another
how can cell-mediated immunity be transferred?
transfer T cells from one animal to another
why might transfer of cell-mediated immunity be unsuccessful?
T cell recognition is self-MHC restricted → cannot recognize peptides in new host
transfer of cells between genetically dissimilar animals → rejection by recipient
T-cell mediated defense against intracellular and extracellular microbes
intracellular
infected cell possesses antimicrobial mechanisms (phagocyte) → T cell enhances antimicrobial mechanisms
infected cell lacks intrinsic antimicrobial mechanisms (non-phagocytic cell; e.g. epithelial cell) → T cell kills cells that cannot kill microbes
extracellular
cytokine secretion → inflammation, killing of microbes
what are the general functions of T cell-mediated immunity?
protect against intracellular pathogens and cancer
protect against extracellular pathogens by recruiting inflammatory cells
responsible for graft rejection
what determines the effector functions of CD4+ T cells?
the array of cytokines (effector molecules) they produce
pleiotrophy
a single cytokine can have different effects based on the target cell
redundancy
same functions driven by multiple different cytokines
synergy
the effect of multiple cytokines working together is greater than the sum of their individual effects
antagonism
cytokines produce opposing effects
what determines the functional differentiation/polarization of CD4+ T cells?
cytokines present in the early phases of activation
type 1 immunity is associated with which type of CD4+ cell?
TH1
what cytokine(s) does TH1 produce?
INF-γ
what are the overall effects of type 1 immunity?
classical macrophage activation (enhanced microbial killing)
complement binding and opsonizing IgG antibodies
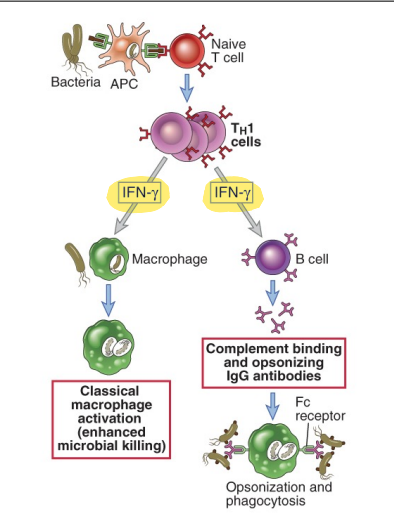
which immune cells are prominent during type 1 immunity?
monocyte/macrophages
(phagocyte-mediated defense)
what type of pathogen is primarily targeted by type 1 immunity?
intracellular (vesicular) pathogens → ex. leishmania, mycobacteria
type 2 immunity is associated with which CD4+ cell?
TH2
what cytokine(s) does TH2 produce?
IL-4
IL-13
IL-5
what are the overall effects of type 2 immunity?
antibody production
mast cell degranulation (IgE)
intestinal mucus secretion and peristalsis
eosinophil activation (IL5 = potent eosinophil activator)
alternative macrophage activation (enhanced fibrosis/tissue repair)
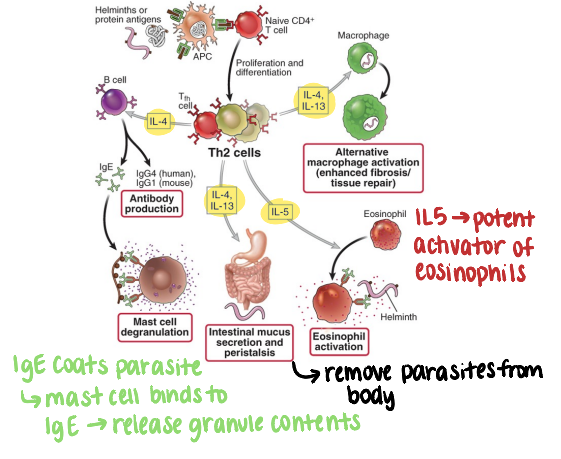
which immune cells are prominent during type 2 immunity?
eosinophils
mast cells
(IgE-eosinophil/mast cell-mediated defense)
what type(s) of pathogens are primarily targeted by type 2 immunity?
parasites (helminths, arthropods); also involved in allergies
type 3 immunity is associated with which CD4+ cell?
TH17
where are TH17 cells often found?
mucosal tissues
what cytokine(s) does TH17 produce?
IL-17
IL-22
what are the overall effects of type 3 immunity?
neutrophil recruitment
inflammation
increased barrier integrity
epithelial production of antimicrobial peptides
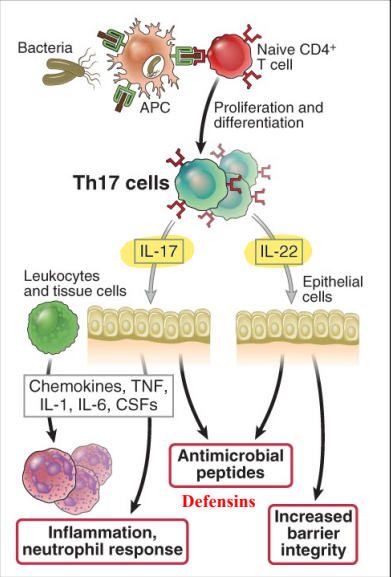
which immune cell is prominent during type 3 immunity?
neutrophils
(inflammation and neutrophil defense)
what type(s) of pathogens are primarily targeted by type 3 immunity?
extracellular pathogens (bacteria)
fungi
what stimuli triggers differentiation into TH1?
IL-12 and IFN-γ
macrophages/dendritic cells produce IL-12
NK cells produce IFNγ
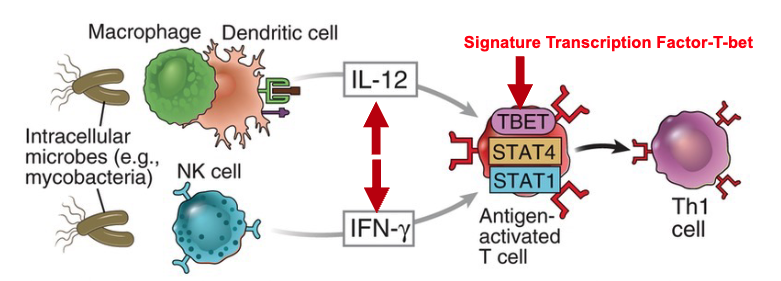
what is the signature transcription factor of TH1?
TBET
what stimuli triggers differentiation into TH2?
IL-4 (IL-25, IL-33, TSLP)
IL-4 produced by mast cells, eosinophils
others produced by epithelium
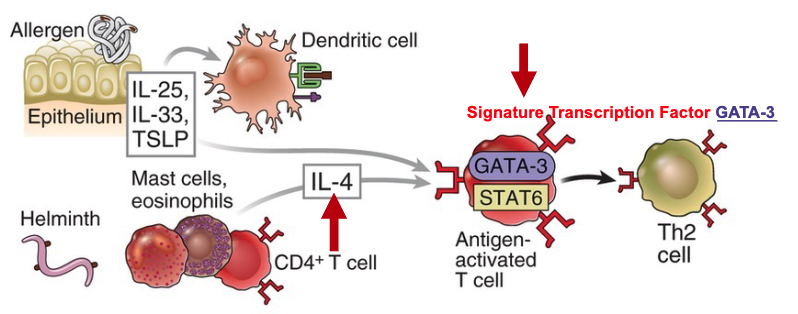
what is the signature transcription factor of TH2?
GATA-3
what stimuli triggers differentiation into TH17?
fungal glycans/peptidoglycans activate macrophages and DCs to produce:
IL-1
IL-6
IL-23
TGF-β
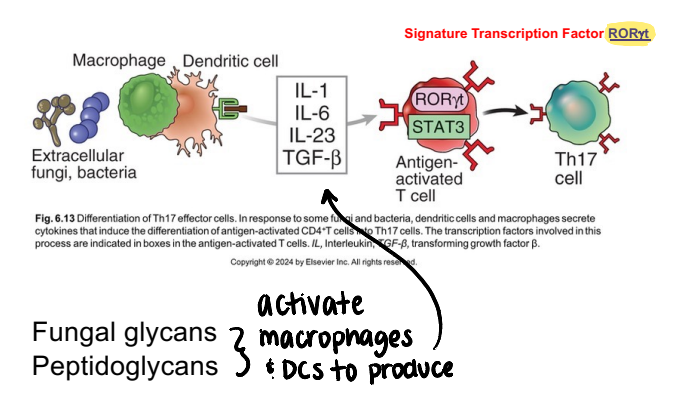
what is the signature transcription factor of TH17?
RORγt
how do TH1 and TH2 activation interact with each other?
antagonistic interaction
TH1 response activates macrophages
TH2 response suppresses macrophages