MCB 2004 CHAPTER 1 - Microorganisms, Macromolecules, and Taxonomy Overview
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Microorganisms
Living entities too small to be seen without a microscope.
Pathogens
Microbes that cause disease in hosts.

Eukaryotes
Organisms with membrane-bound organelles.

Bacteria
Single-celled prokaryotic microorganisms.
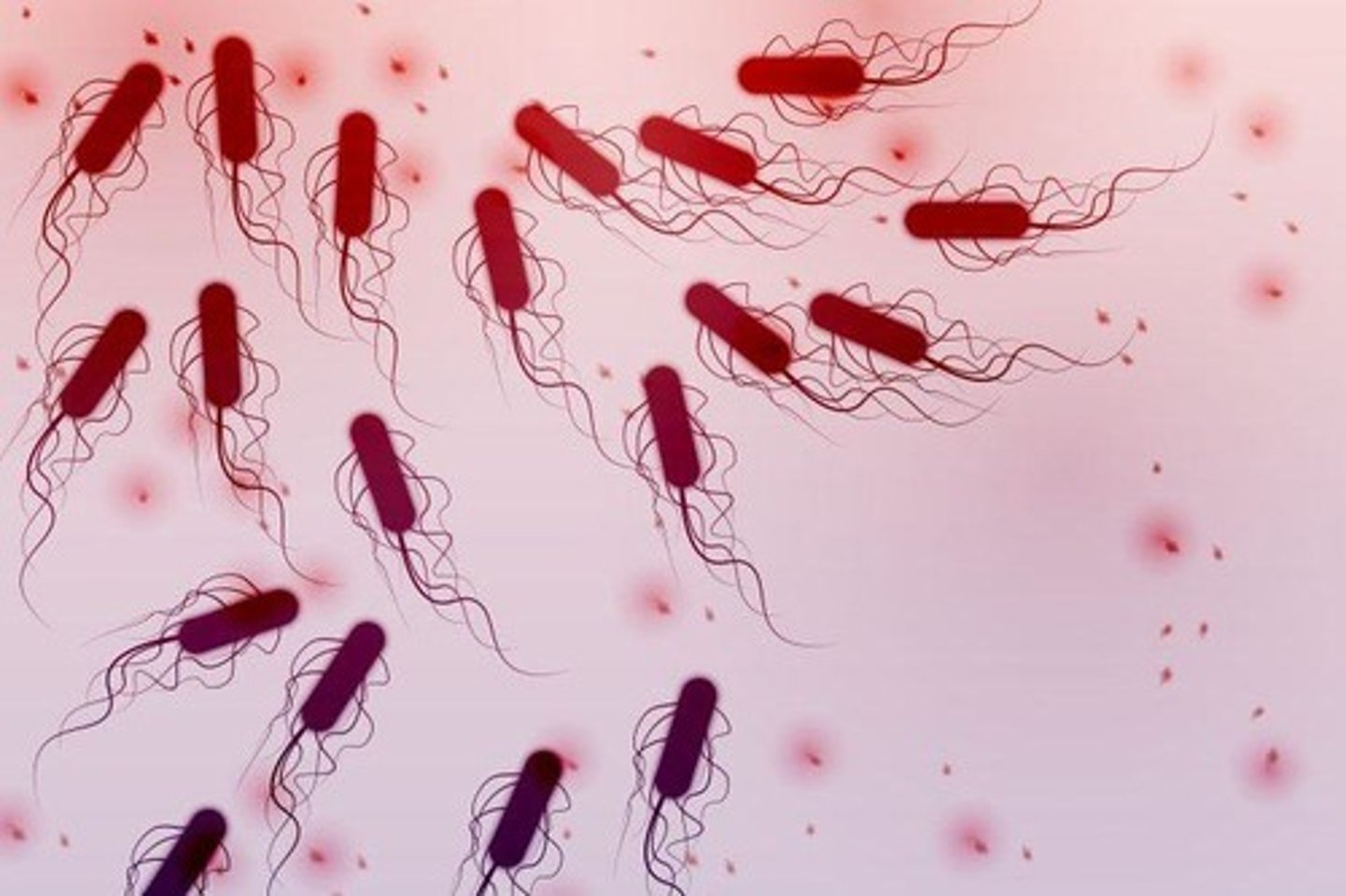
Archaea
Prokaryotic microorganisms often found in extreme environments.
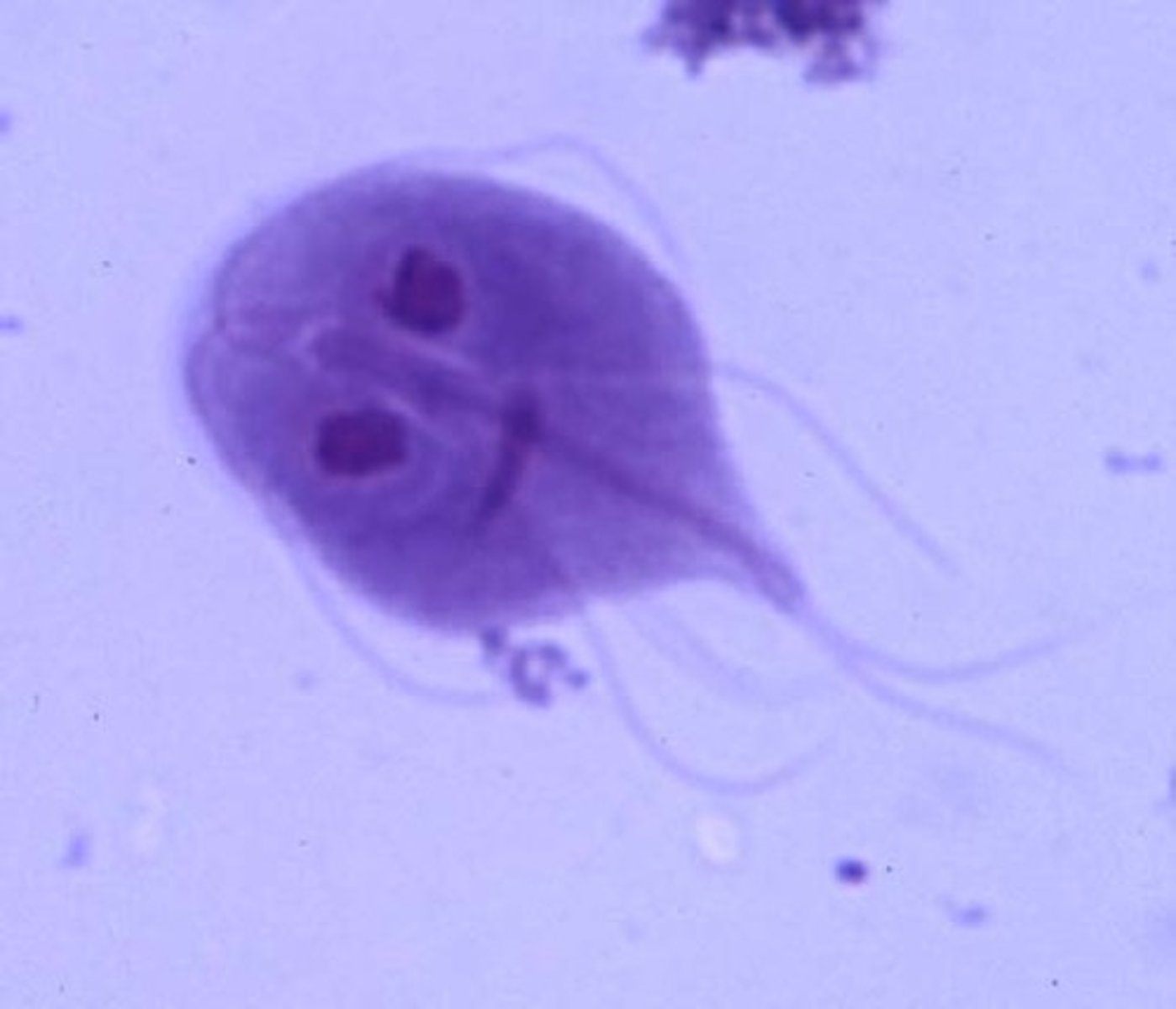
Protozoa
Single-celled eukaryotic organisms, often motile.
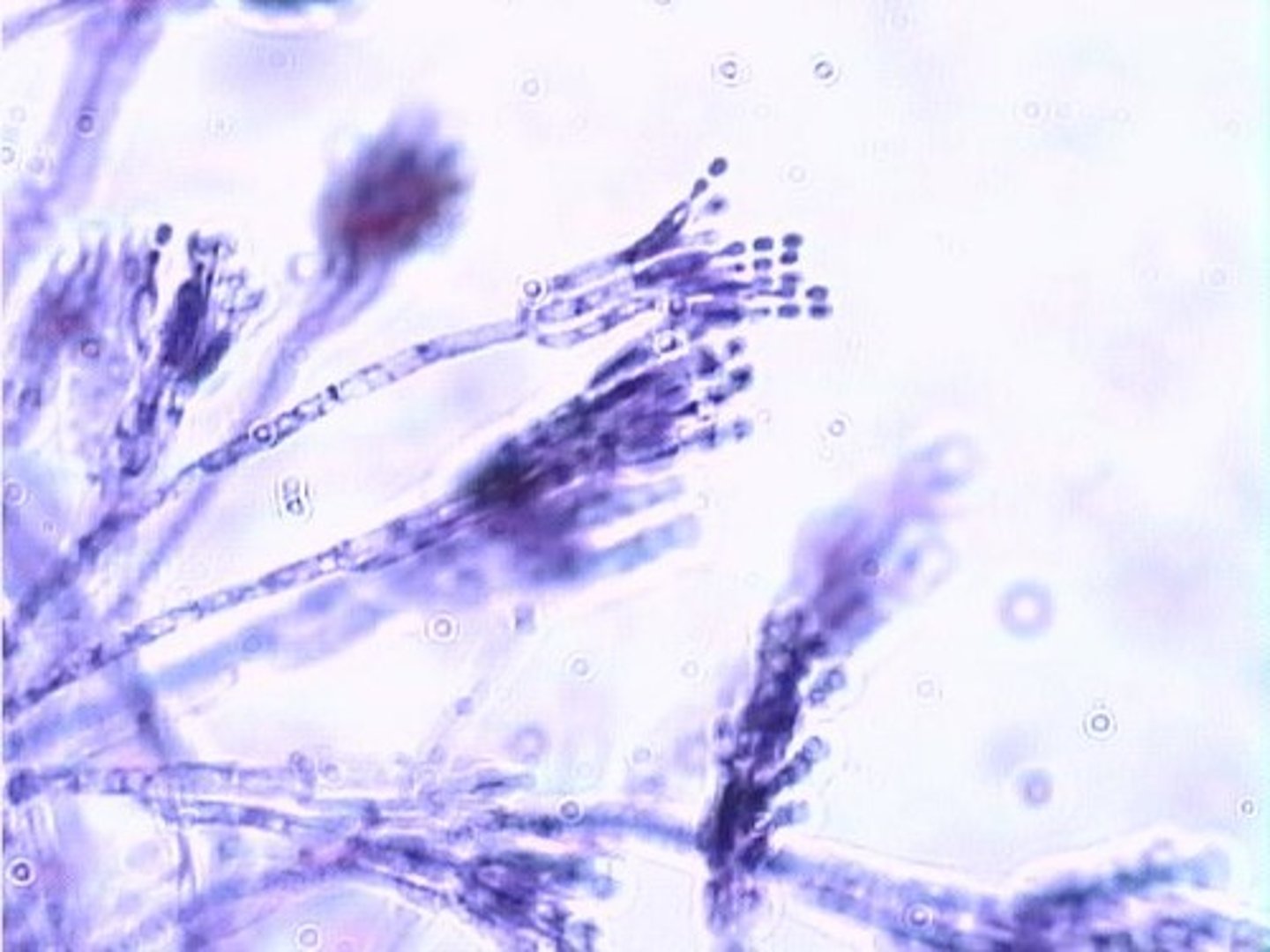
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms that decompose organic matter.
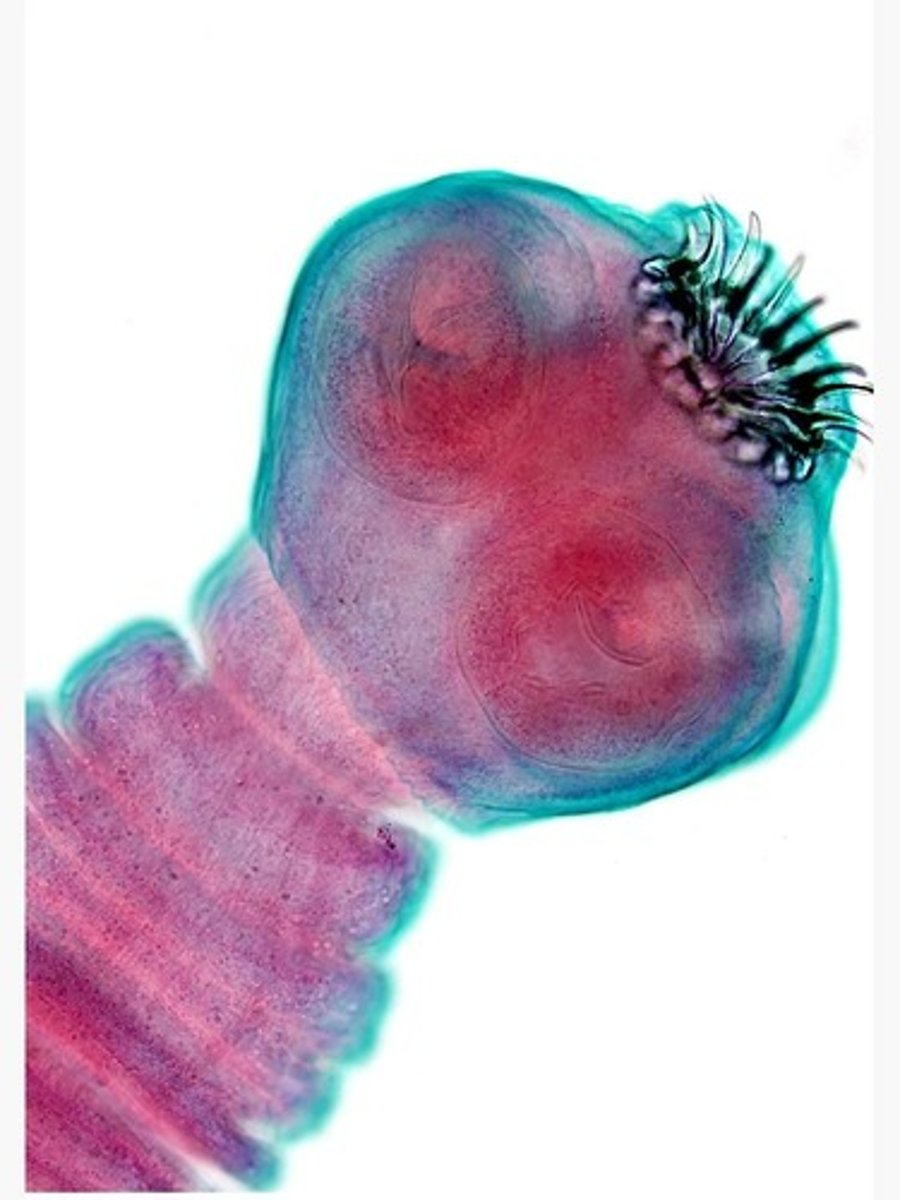
Helminths
Multicellular parasitic worms.
Viruses
Noncellular entities requiring host cells to replicate.
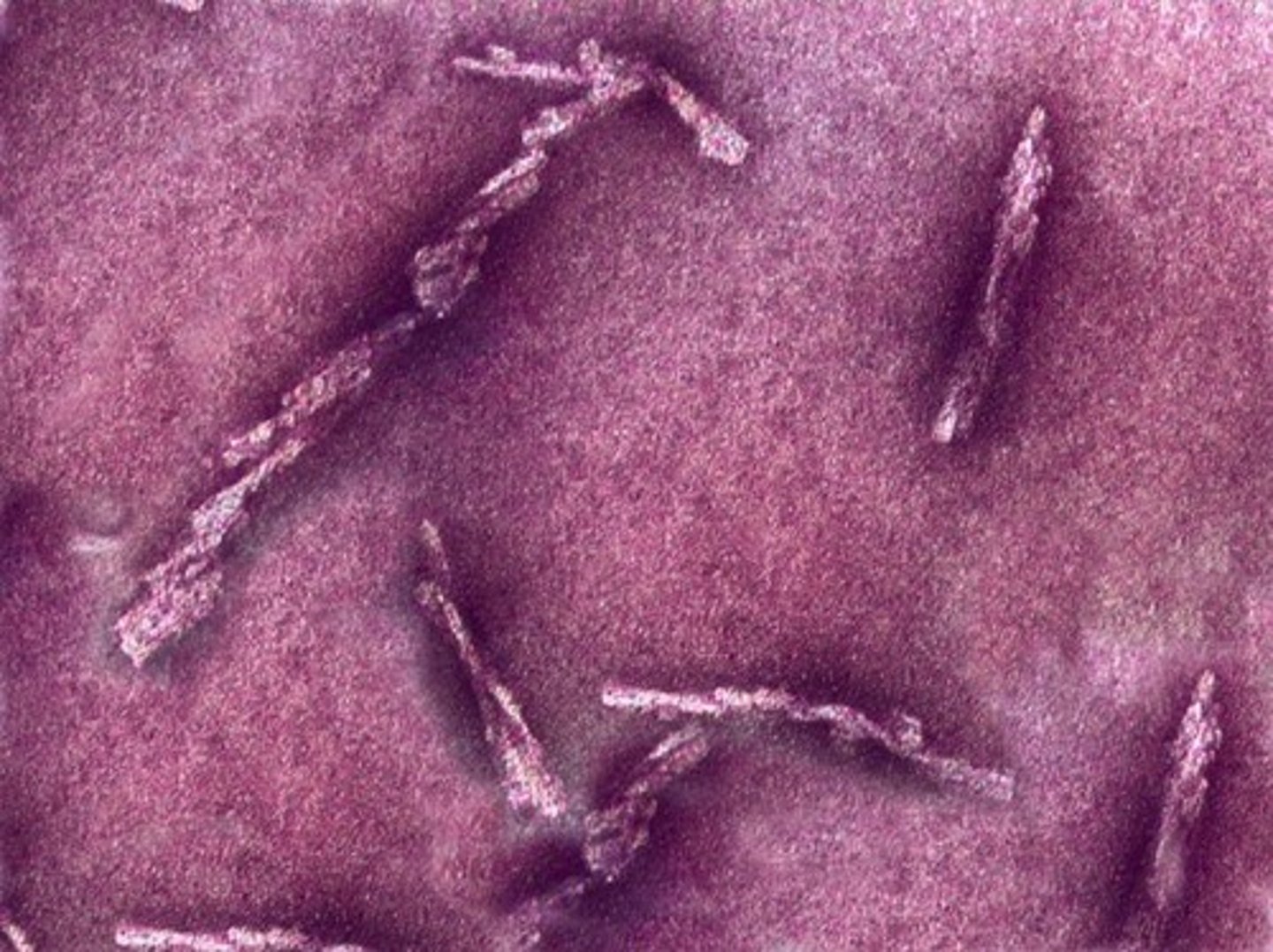
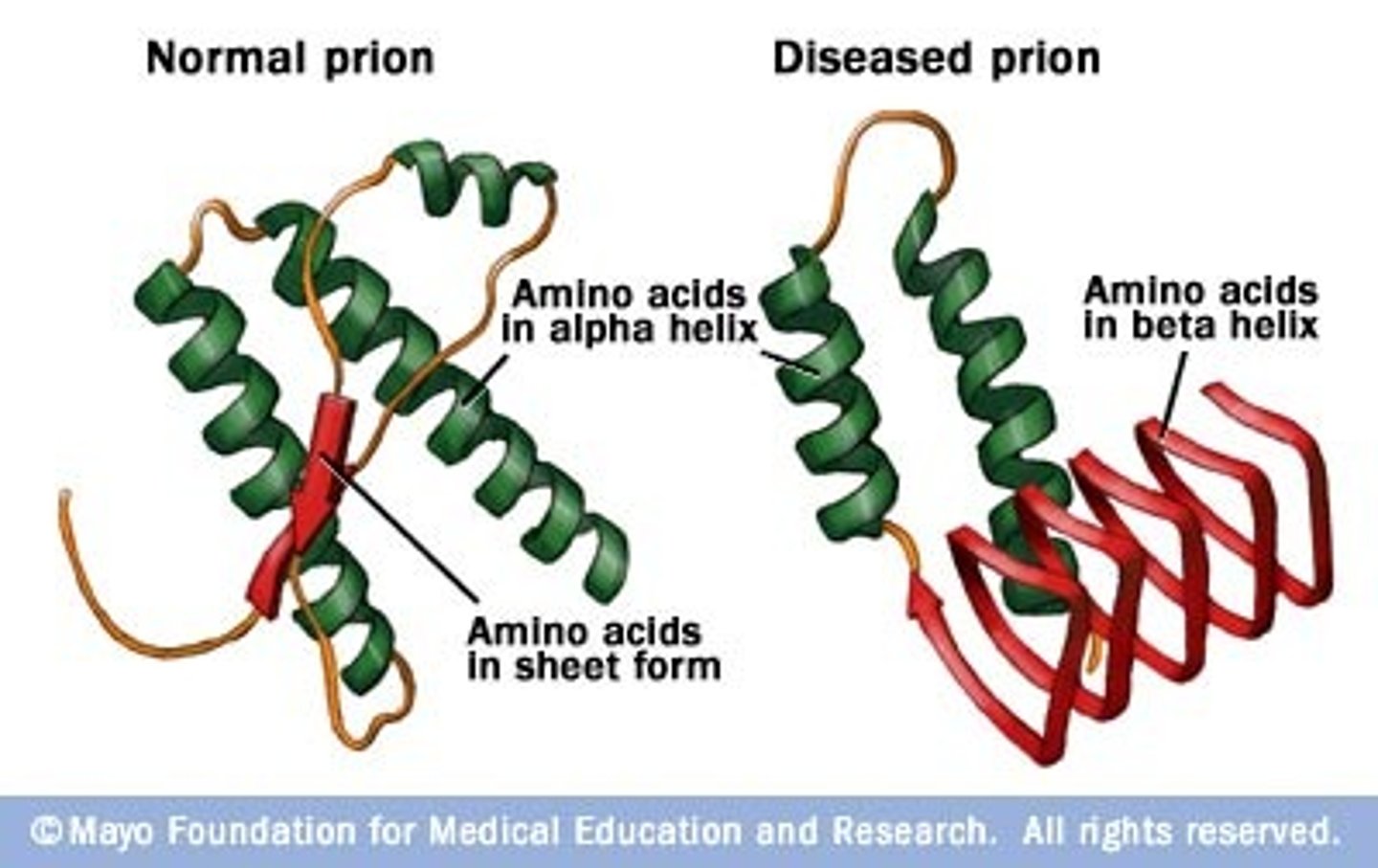
Prions
Infectious proteins lacking nucleic acids.
Genetic Engineering
Modification of organisms' genetic material for desired traits.

Recombinant DNA Technology
Technique for transferring genetic material between organisms.
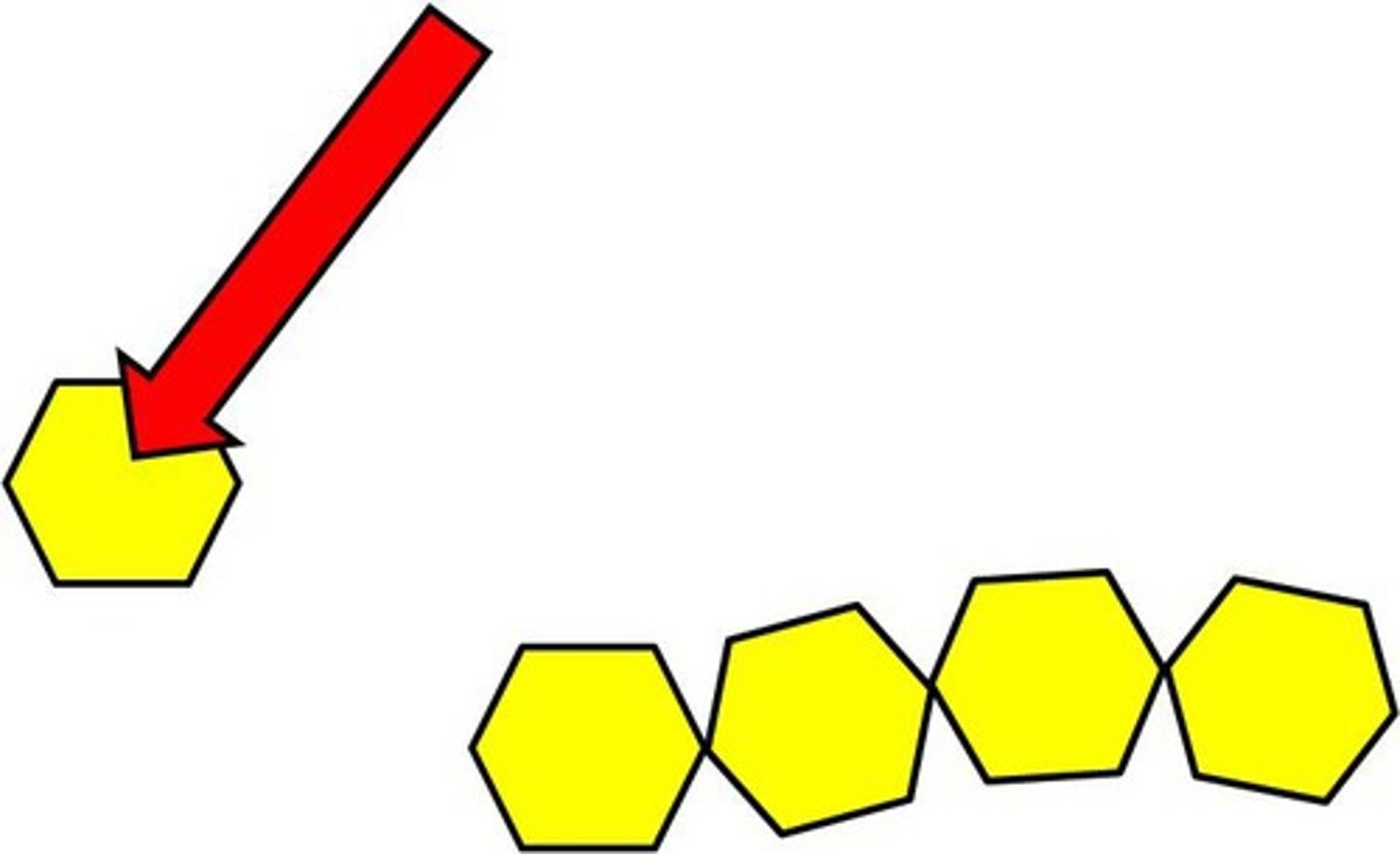
Polymers
Large molecules made from repeating monomer units.
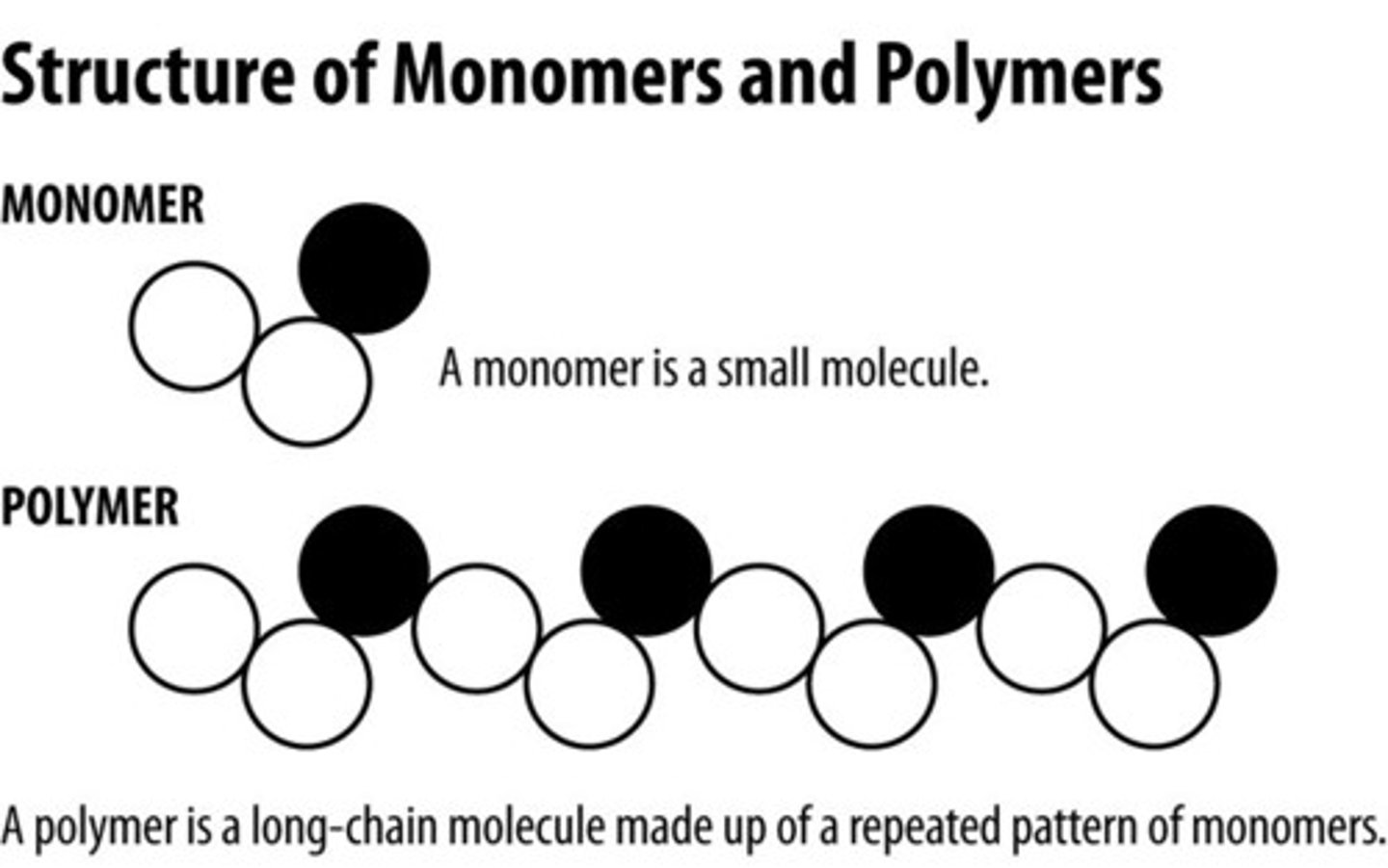
Monomers
Small, basic molecular units that form polymers.
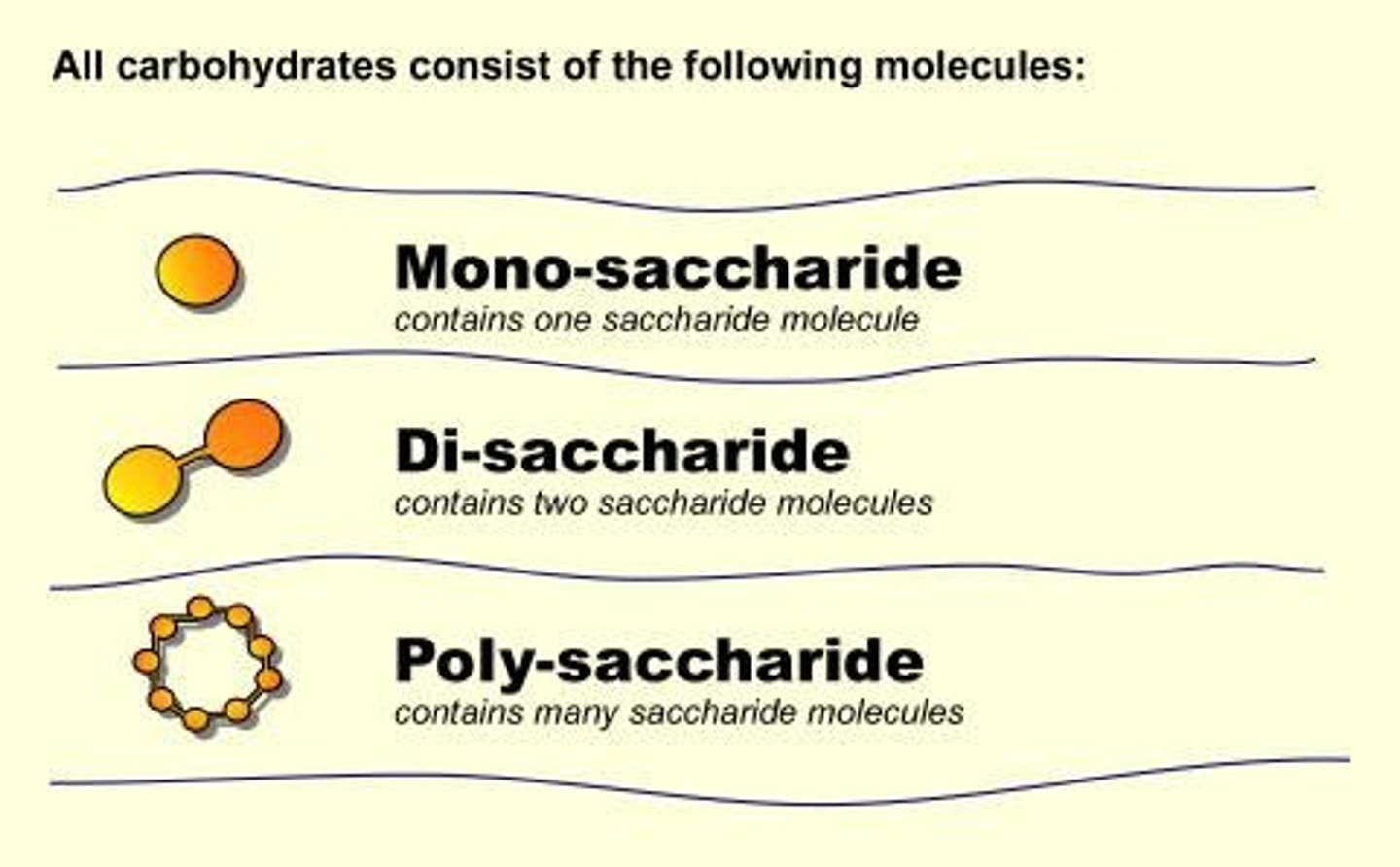
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds made of sugar molecules.
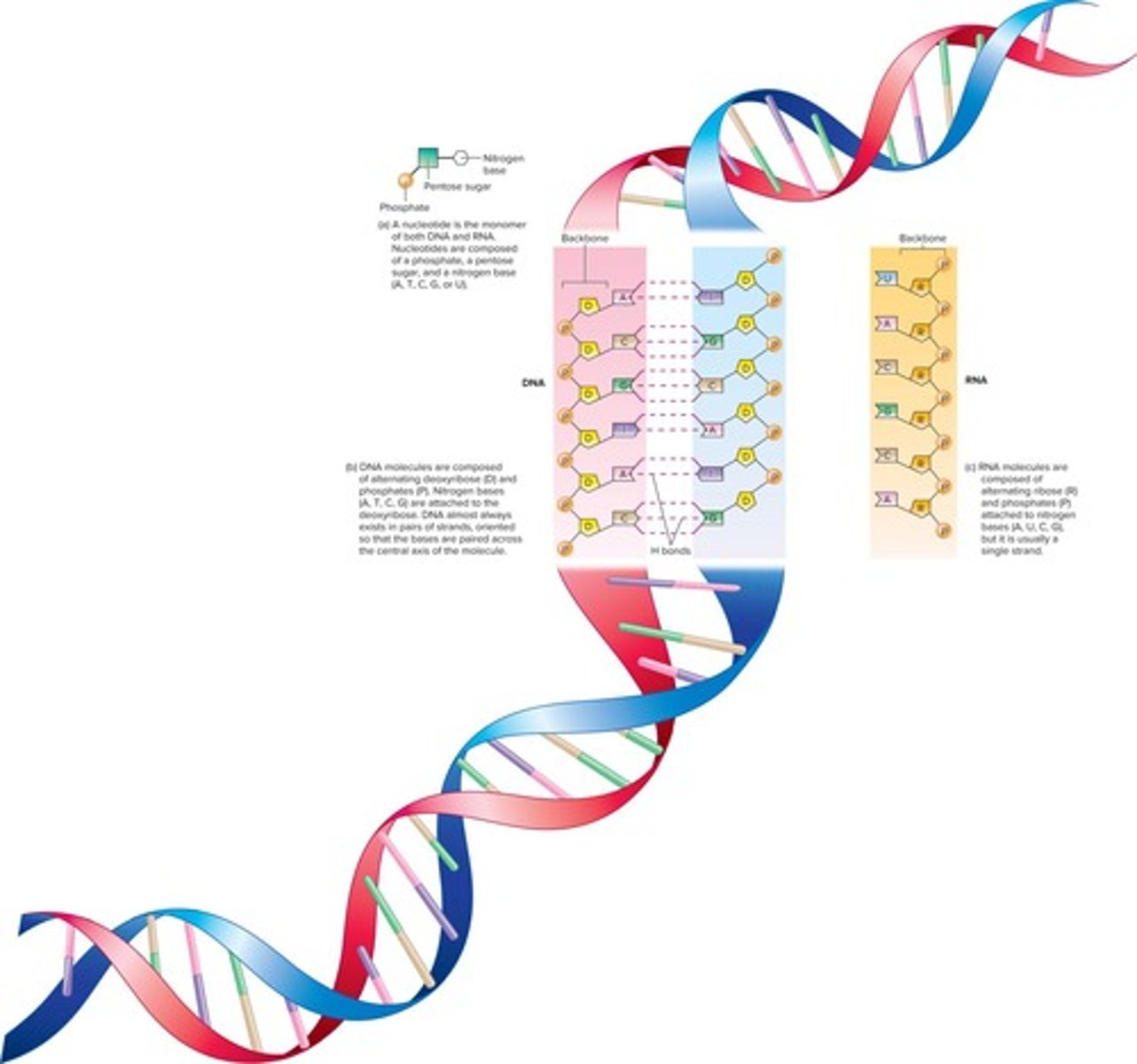
Nucleic Acids
Polymers of nucleotides, including DNA and RNA.
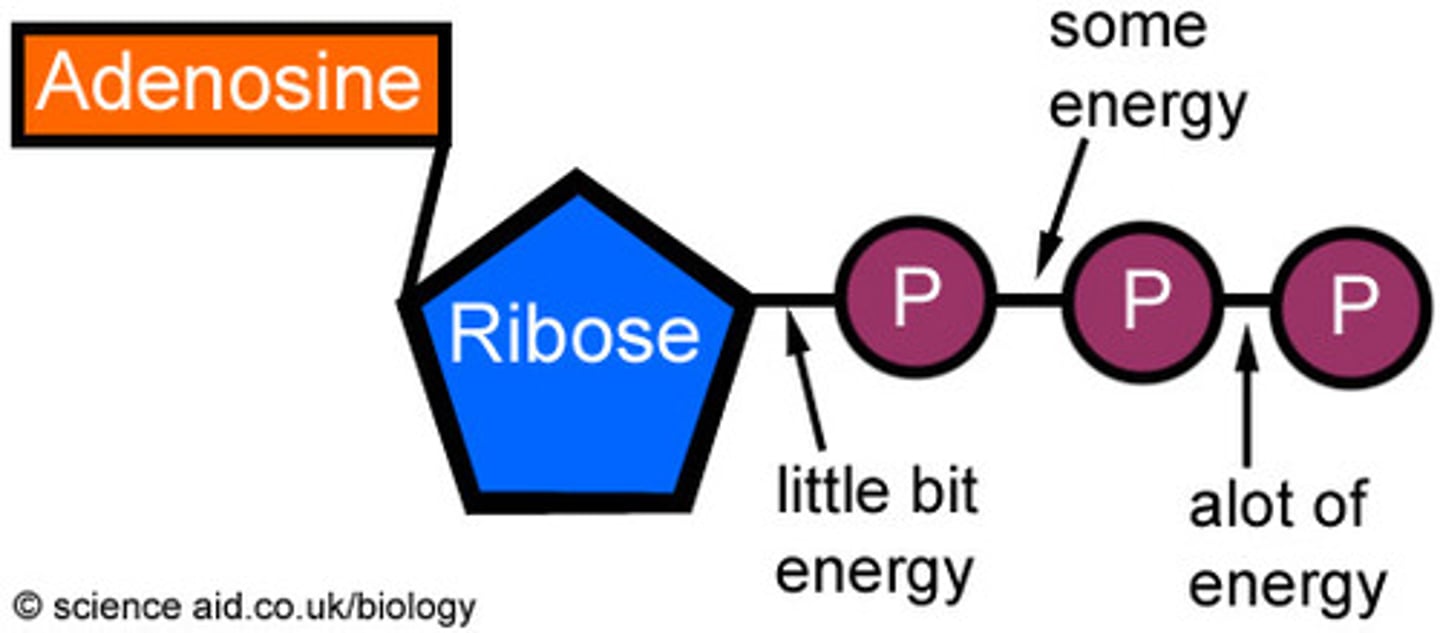
ATP
Energy currency of the cell, adenosine triphosphate.
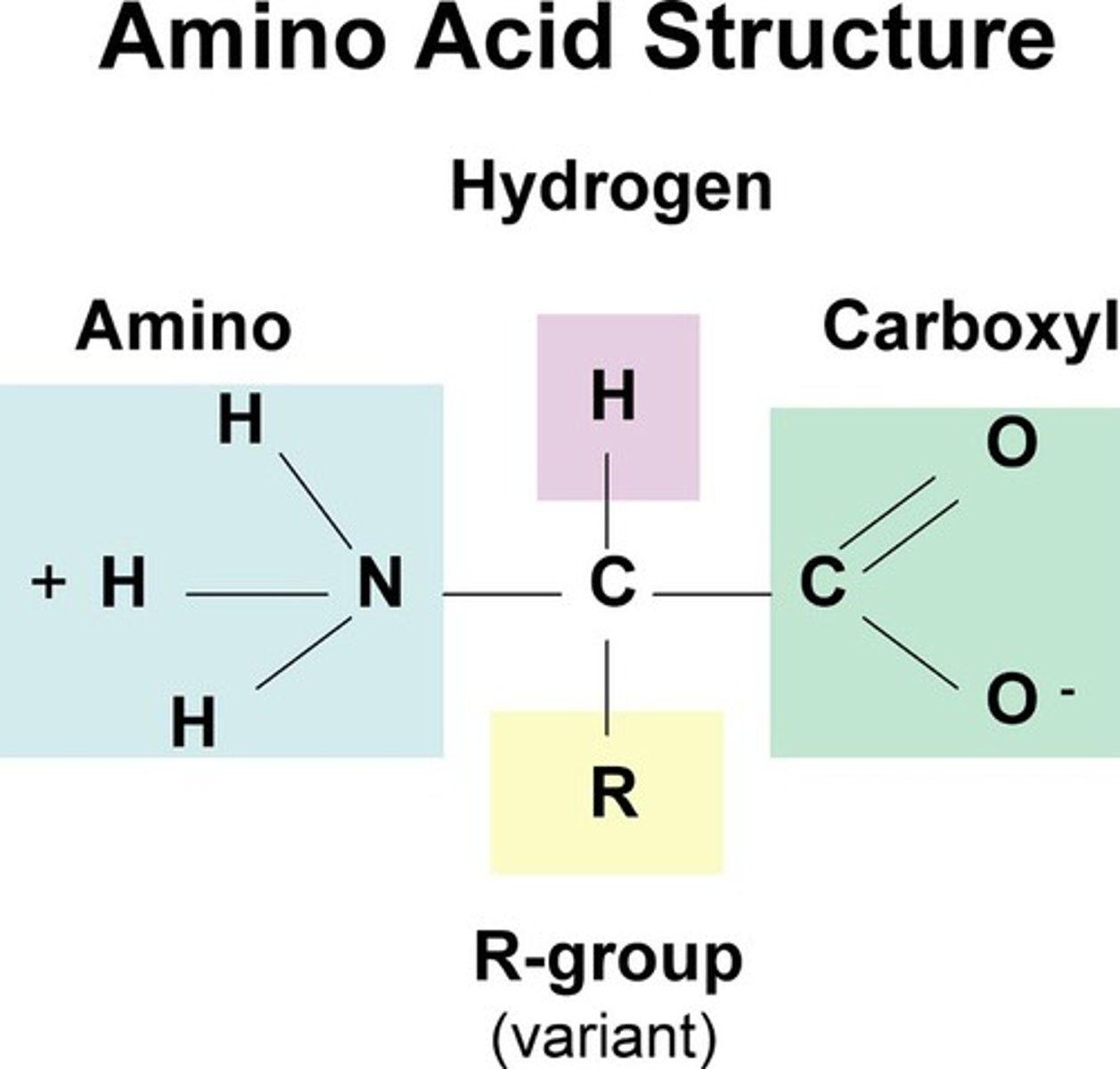
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins, containing R groups.
Primary Protein Structure
Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
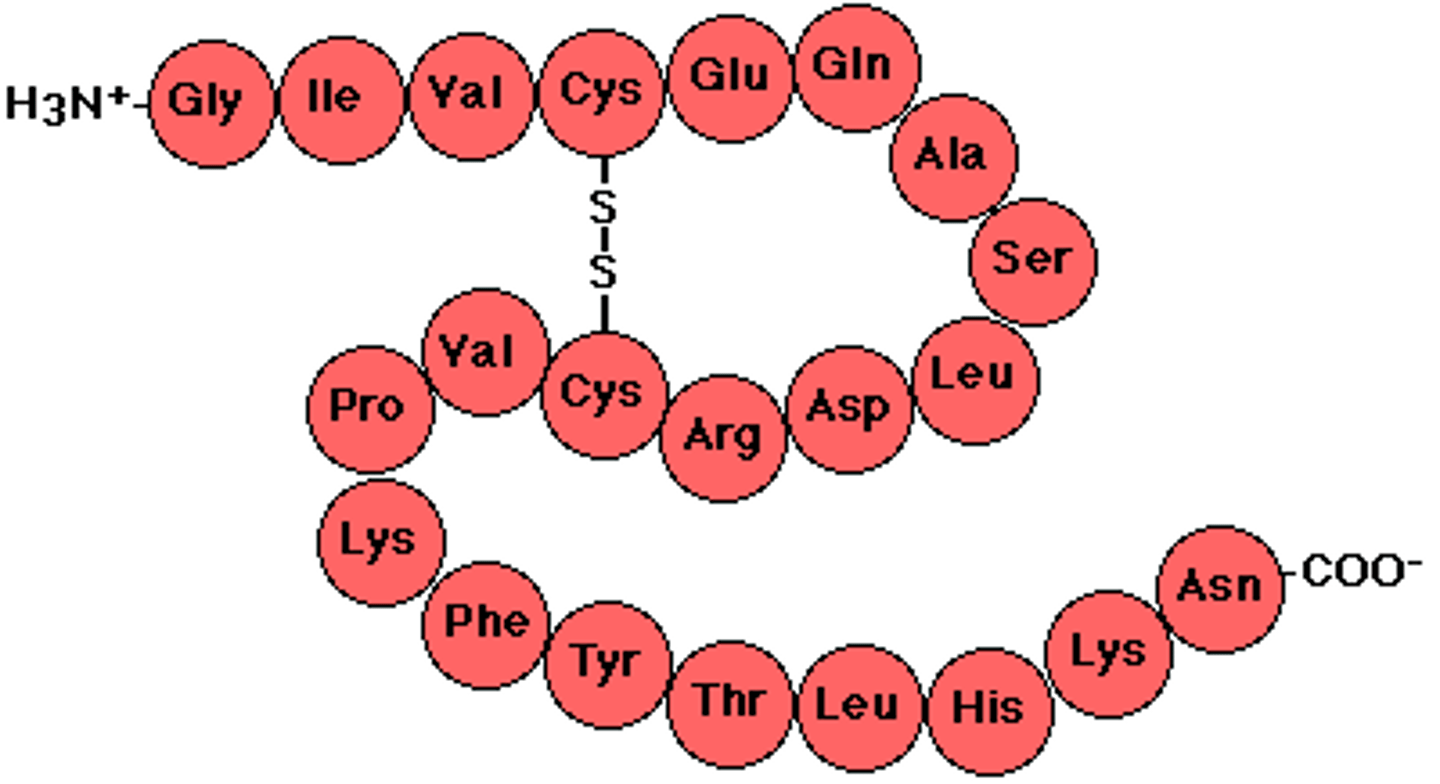
Secondary Protein Structure
Folding patterns formed by hydrogen bonds.

Tertiary Protein Structure
3D shape of a single polypeptide chain.
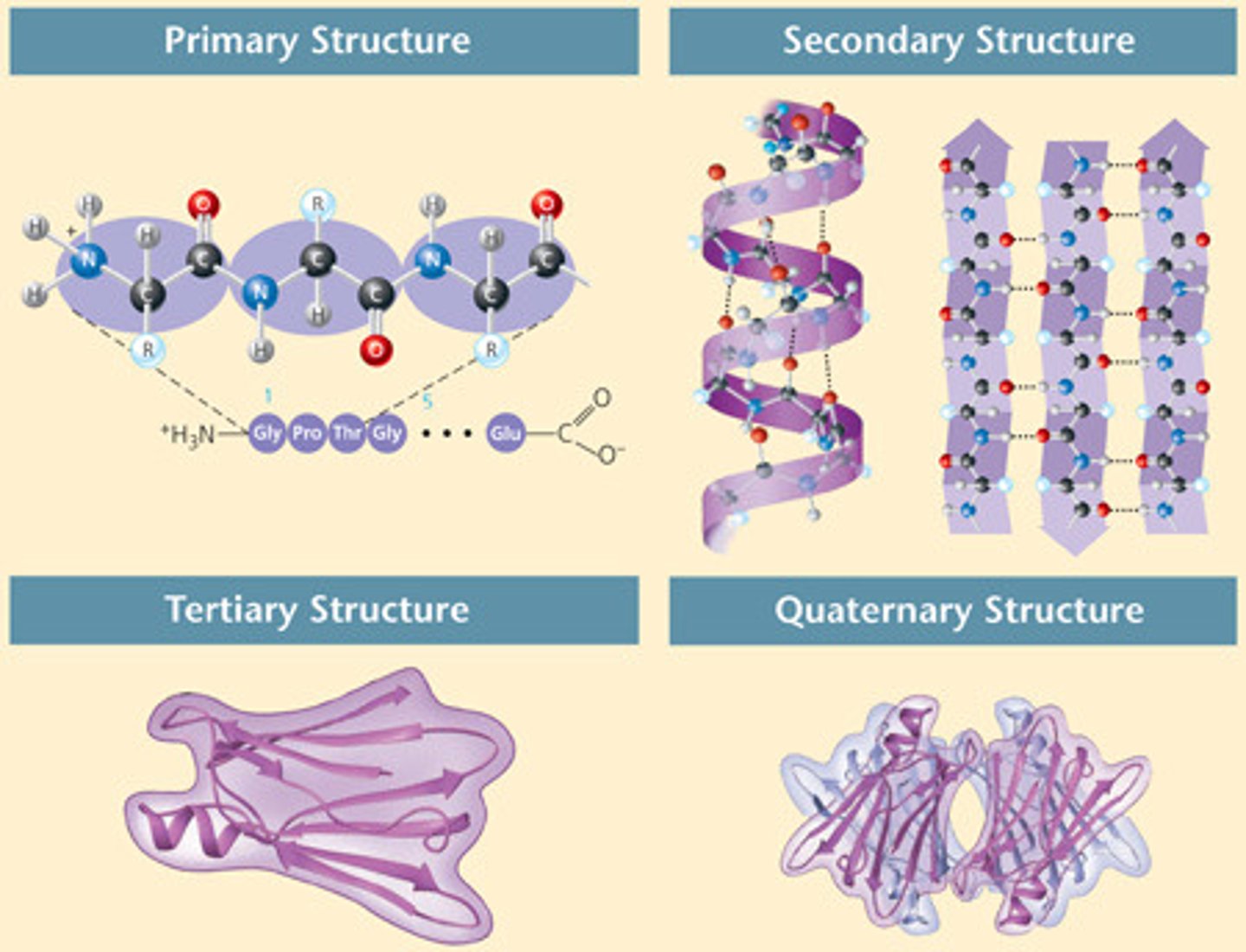
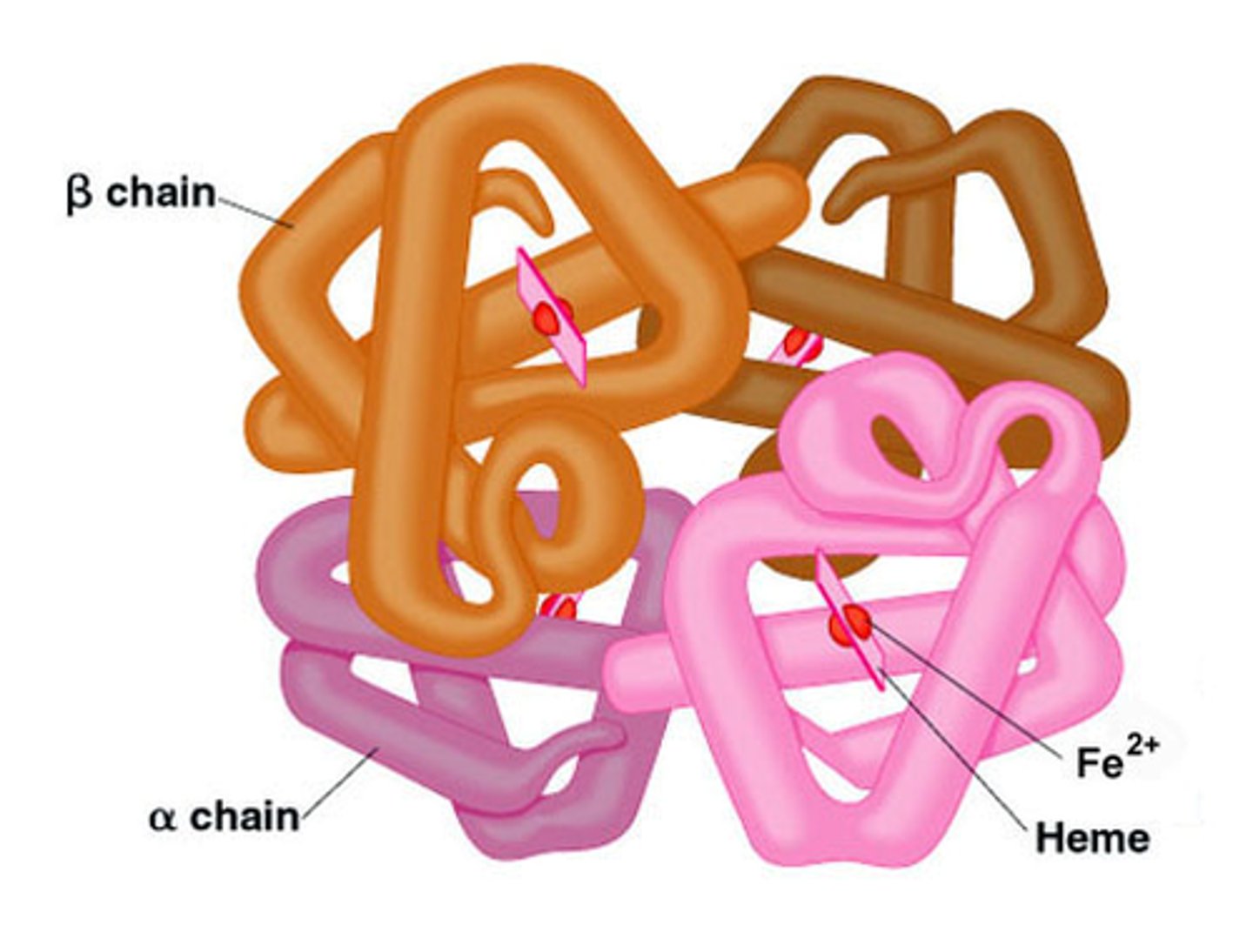
Quaternary Protein Structure
Complex of multiple polypeptide chains.
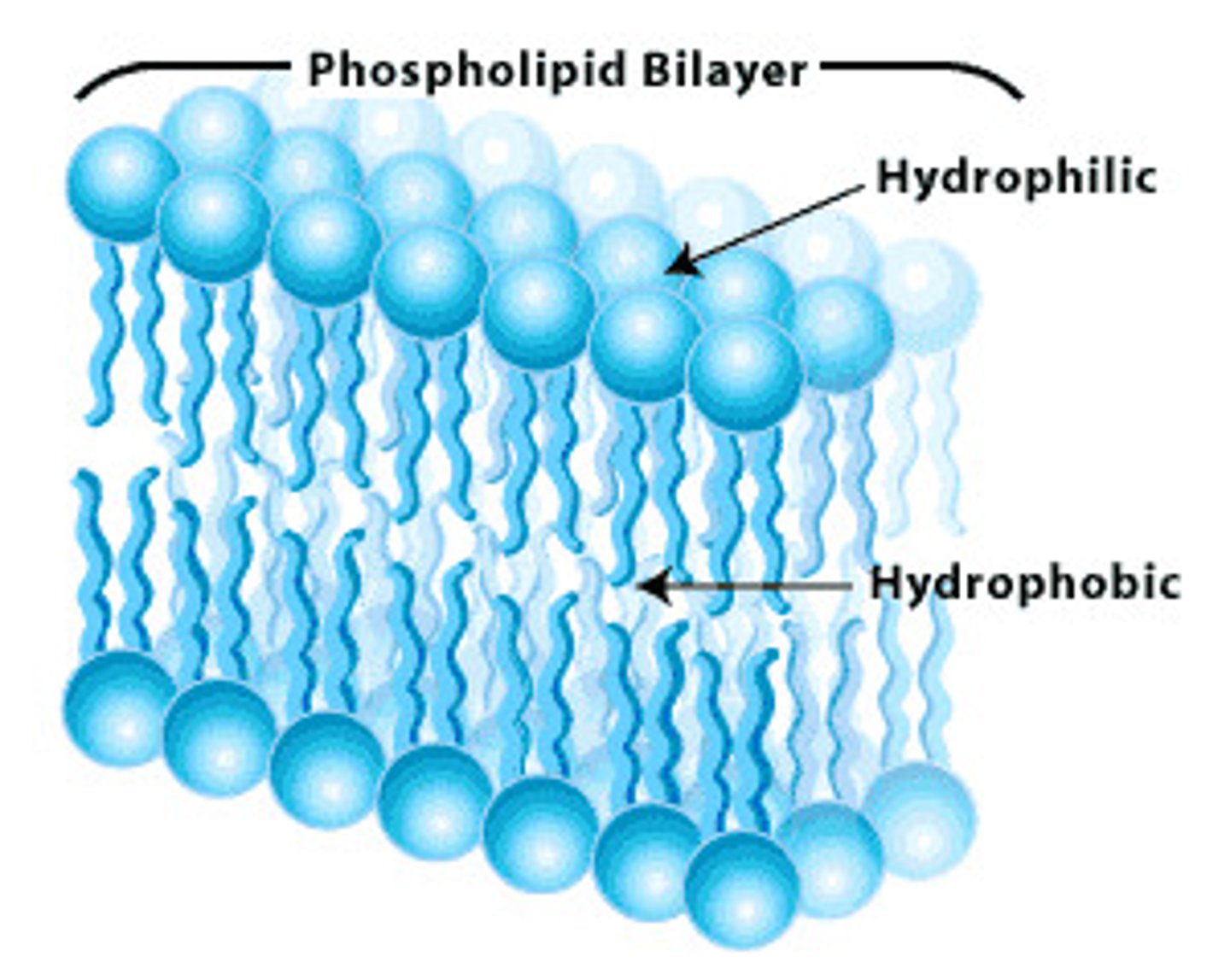
Phospholipids
Molecules forming cell membranes with hydrophobic tails.
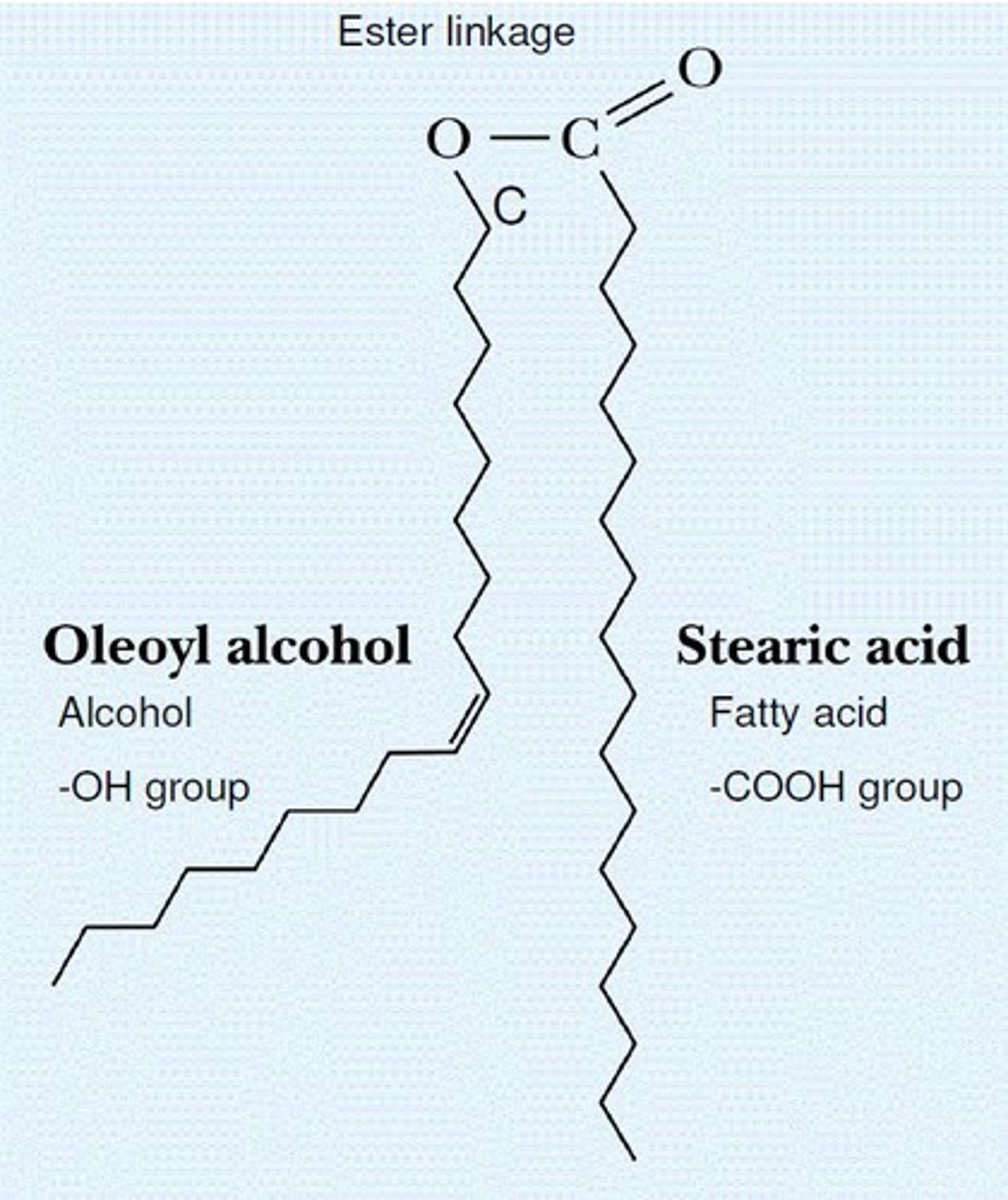
Waxes
Hydrophobic substances providing water resistance.
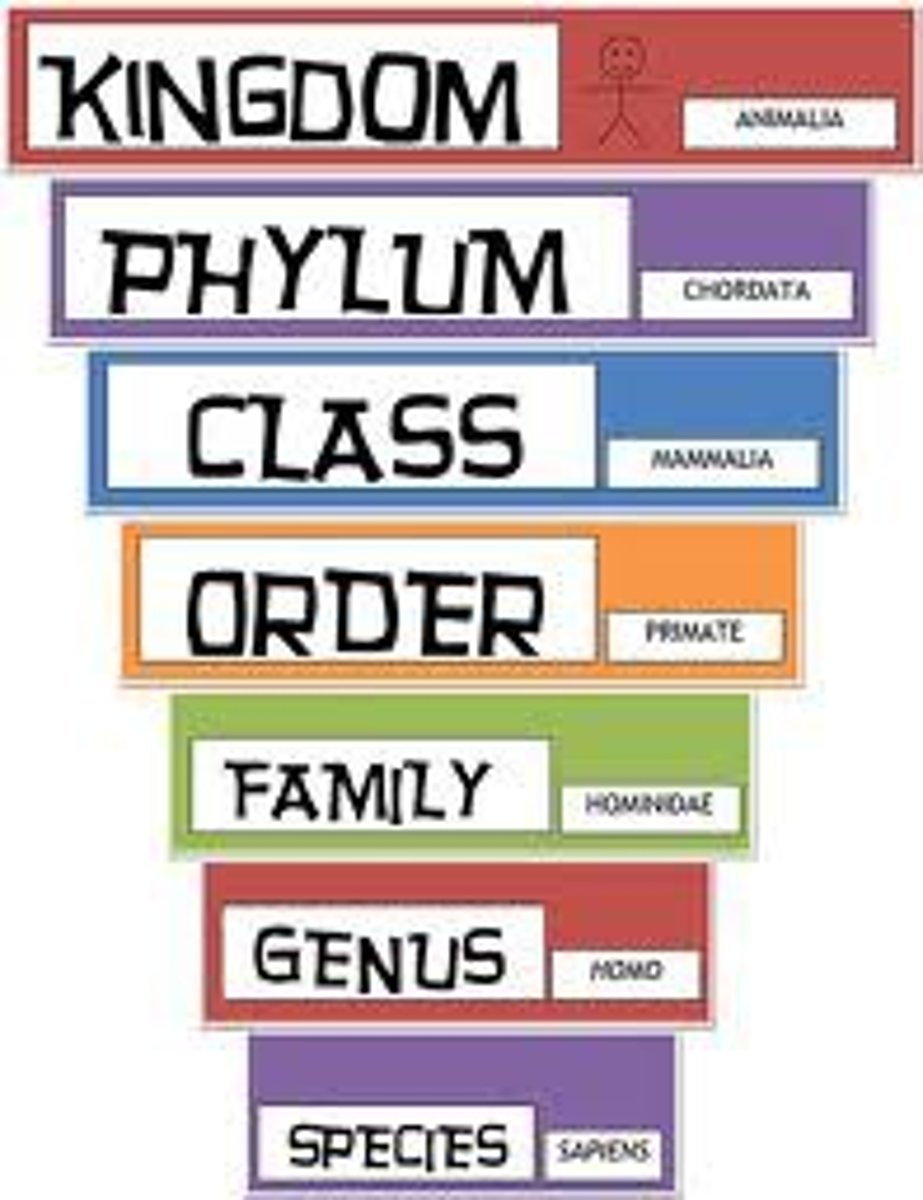
Taxonomy
Science of naming and classifying organisms.
Binomial Nomenclature
Two-part naming system for species identification.