BCM.02 - ELECTRONS
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Amplitude
Height of a wave from rest
Frequency
Number of times a complete wave passes are certain point in 1 second
wavelength
distance from 1 peak to the next peak
velocity + equation
speed of wave propagation
V=yf
Phase
how in synch waves are from eachother
what do progressive waves do
carry energy from one area to another
3 key facts about particles
1) Take a defined space
2) Cannot interfere with one another
3) A group of particles total is equal to their sum
3 key facts about waves
1) Delocalized in space
2) Can interfere with eachother
3) Waves can interfere to make their total sum less or more than just adding their amplitudes
Why cant we see around doors?
Light waves have a wavelength of 500nm so are too small to diffract through holes to allow us to see what is behind the wall. Objects <500nm cannot be seen using visible light clearly.
When diffraction occurs round an object with similar y to the wave:
When diffraction occurs though a gap of similar y to the wave:
Waves leak around the object into its shadow
Waves spread out into the shadow of the two walls
How do we work out the y of a PARTICLE
y is inversely proportional to the momentum of the particle
Constructive vs Destructive interference
• Constructive Interference - waves add together
• Destructive Interference - the waves subtract form each other as they overlap
In the two slit experiment, the maximum amplitude is
In the shadow between the two splits
Describe the results from double split experiment for electrons
When electrons are allowed to pass through the slits they show an interference pattern, even when 1 electron flows at a time and this forms and interference pattern.
When a detector is put in place, this stops and 2 discrete spots appear.
Describe JJ Thompsons Plum Pudding evidence
Placed two metal plates opposite of eachother in a glass container and ran a power source through it, created a cathode ray. +ve and -ve plates placed either side of the ray, the -ve ray repelled the ray suggesting it is -ve charged.
Worked out that what made up the ray was x1000 times smaller than an H atom
Describe G/M/R Planetary model evidence
Gold foil
Describe Bohrs evidence for his model of the atom
Used calculations to fix the flaws in the planetary model.
Describe Shrodingers evidence for his model of the atom
Shrodinger equation. Used this to map the paths of electrons over a period of time in a H atom.
Issues of the planetary model
- Centripetal force acts on -ve electrons, electrons lose energy as EM radiation
- No energy levels, should show mixed colours of light as there are no discrete steps
- No energy levels to confine electrons to so electrons should spiral towards the nucleus and destroy the atom / spiral away from the nucleus.
When do we see discrete lines of colour? what is the called? What does this help us do?
When atoms are heated ( to become excited ).
Balmer series.
Refuse the planetary model.
2 features of atoms that help us refute the planetary model
Atoms are stable ( no plummeting electrons )
Have a stable VWS radius of 120pm ( something is holding them in place )
How can we model electrons?
As a wavefunction / wavepacket
The probability of finding an electron in a certain area is dependent on
the amplitude of the wave
wave functions are defined as
standing waves of probability
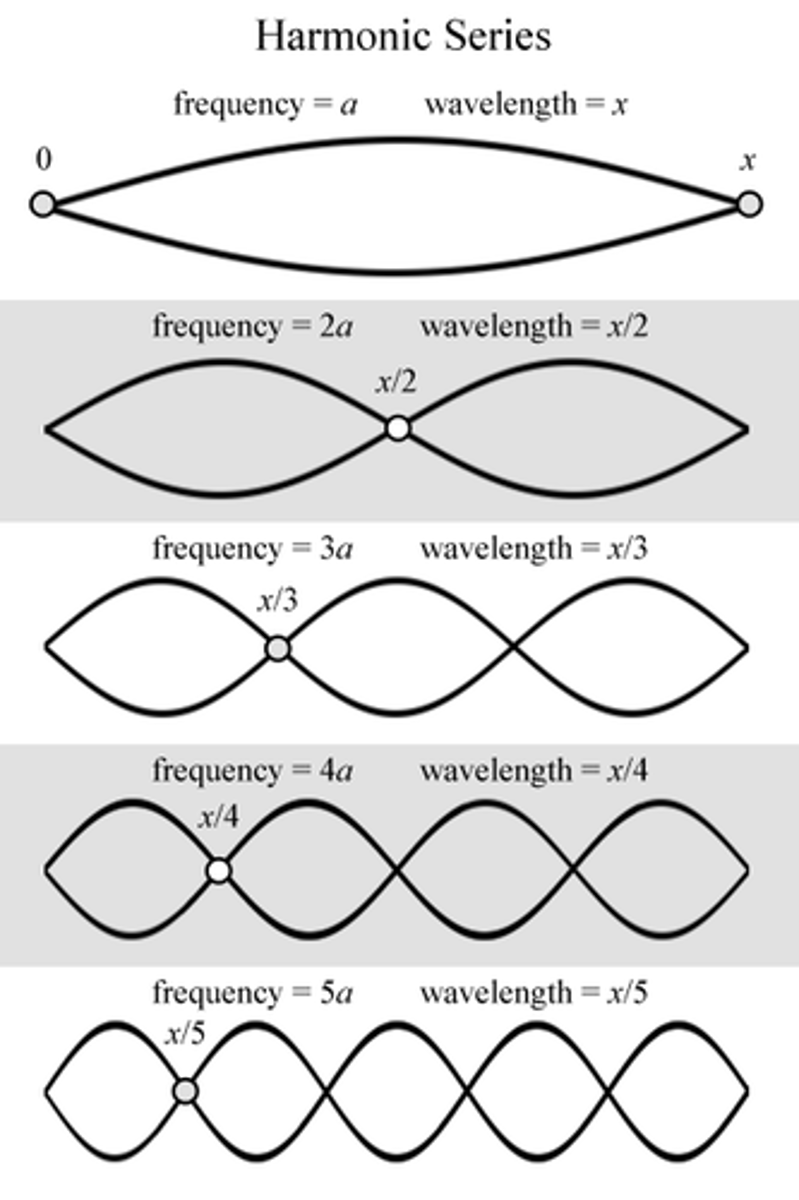
Names the first few wave types
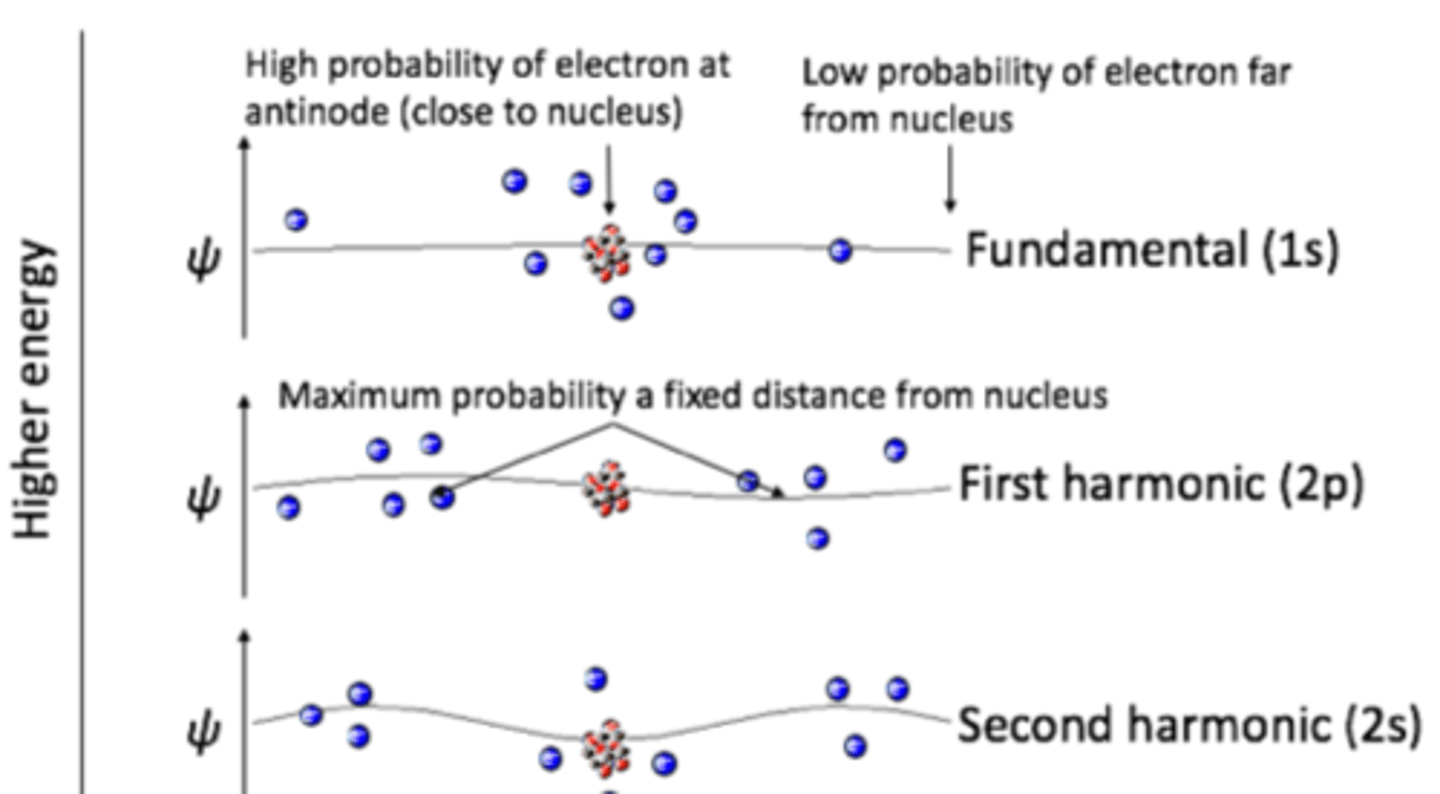
waves used as models are
standing waves
ie their location and energy are constrained to a single place
wavelength must be
a whole number fraction of the cavity length for constructive interference to occur
any other number will cause destructive interference
Describe Bohrs model of the atom
- Maintains features of planetary model
- Electrons are considered 1 dimensional circular standing waves. Only waves with the right sized wavelengths can fit round the atom.
- There is a lowest level which they cannot drop below. Each wave corresponds to an energy level, hence when electrons move energy levels, we see discrete lines of colour.
Example of 2 colours emmitted from Balmer series
Red - 700nm, low energy difference
Violet -400nm, high energy difference
radius of the atom is proportional to
the number of shells ^ 2
the change in energy from shell jumping can be calculated using
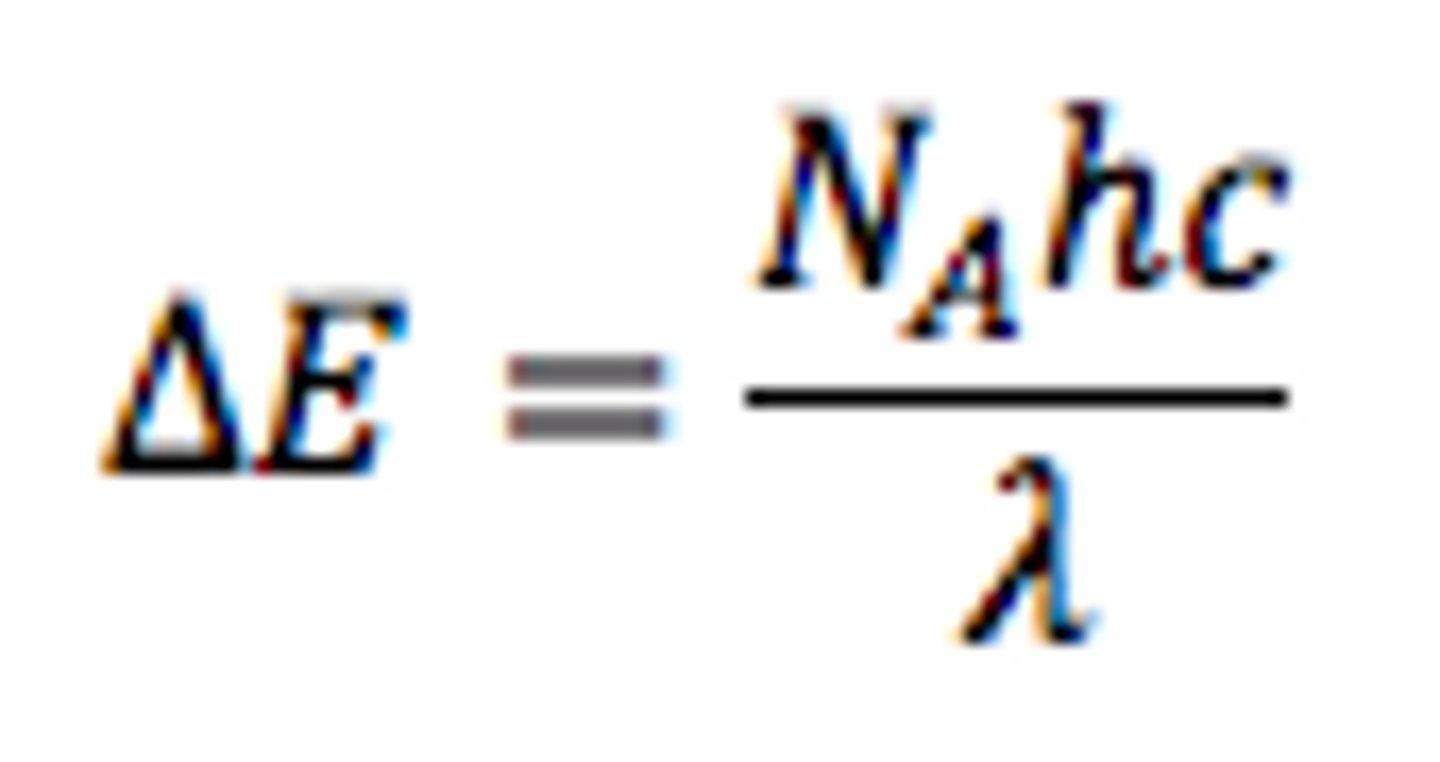
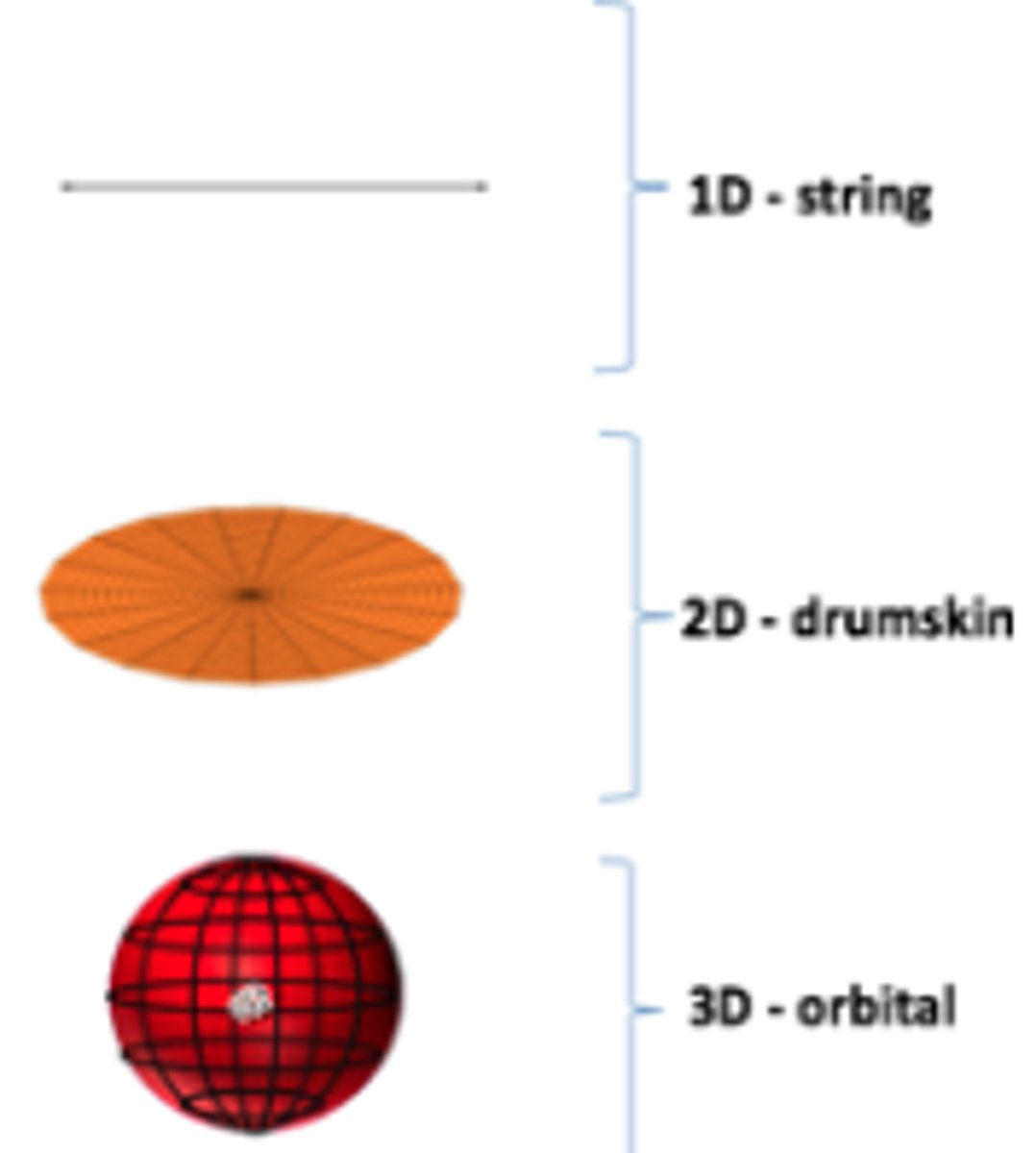
Describe the 1s shell shape
1D - no nodes, vibrates between +ve and -ve wave function, vibrates on 2 axis only.
2D - vibrates along the xyz planes from +ve to -ve wave function
3D - vibrates along 4 axis, changes from -ve to +ve wave function ( imagine the ball changing colour )
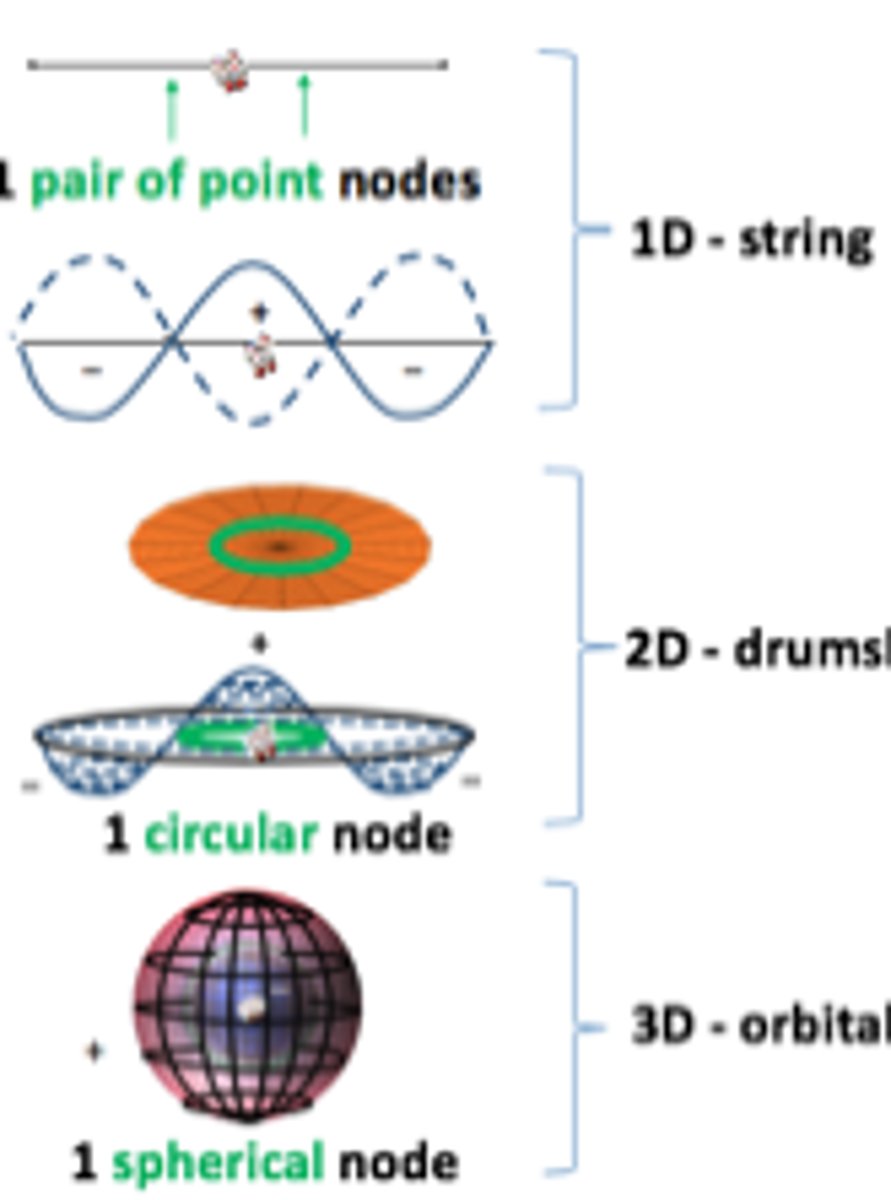
Describe the 2s shell
Same concepts as 1s
There is a node between the inner and outer spheres, which have +ve and -ve wave functions respectfully
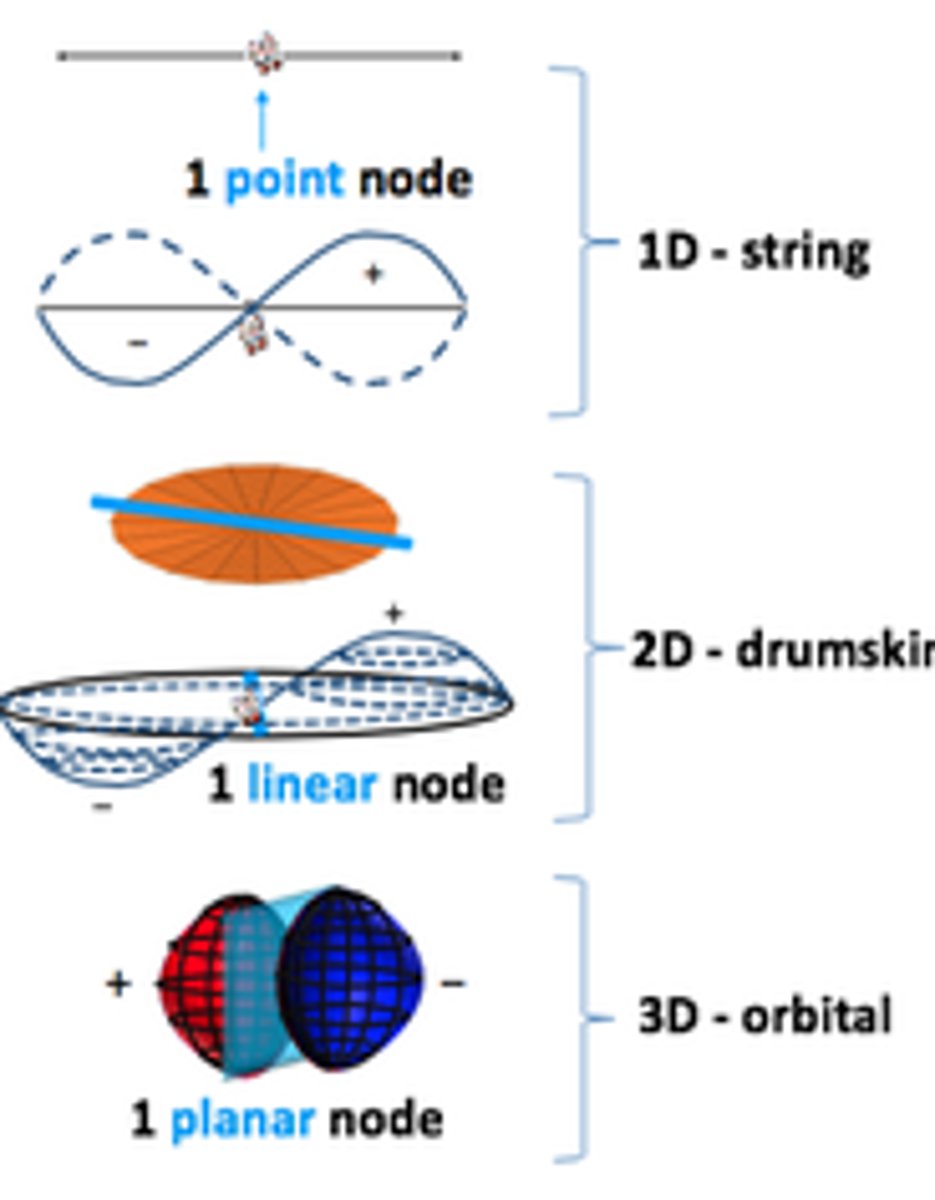
Describe the 2p shell
Planar node, vibrates in x,y,z dimension, dumbbell shaped.
Half the wave function is +ve and the other is -ve.
The principal quantum number, n ( shell ), of a waveform relates to the number of nodes:
[number of symmetric pairs of nodes] + [number of central nodes] + 1
When does n increase?
PQN 'n' increases every 2 nodes due to the changing of pair to central node.
It takes a value from 1 to infinity.
'n' is a measure of the overall orbit size.
In hydrogen all orbitals are :
degenerate ( same energy )
after this they are not due to shielding / energy levels splitting
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin direction
The Aufbau Principle
Electrons fill orbitals from the lowest energy up
Hunds rule
Degenerate orbitals are filled in in such a way as to maximise spin
periodicity
the repeating pattern of chemical and physical properties of the elements. this results due to having the same / similar numbers of outer shell electrons.