Exam 4 - Practice Exam A
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1. Which of the following is involved in triggering insulin release from pancreatic b-cells in response to glucose?
A. Potassium channels are closed by increased intracellular calcium.
B. Potassium channels are opened by membrane depolarization.
C. Potassium channels are closed by increased intracellular ATP.
D. Increased intracellular calcium closes potassium channels.
E. Increased intracellular calcium depolarizes plasma membrane.
C. Potassium channels are closed by increased intracellular ATP.
Closing potassium channels lead to membrane depolarization.
Membrane depolarization triggers the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), which increase intracellular calcium.
Increased intracellular calcium triggers insulin release (exocytosis of insulin-containing vesicles).
2. The following about untreated Type I diabetics is FALSE:
A. Patient loses weight as glucose cannot be used and fats must be used for energy.
B. Ketone bodies that build up in the blood cause a decrease in pH.
C. Treated by insulin injections.
D. Patient becomes hypoglycemic (low blood glucose).
E. Breath can smell like alcohol as acetone (ketone body) is exhaled, not used for energy.
D. Patient becomes hypoglycemic (low blood glucose).
3. Enzyme-linked receptors, for example tyrosine kinase receptors like the insulin receptor, require which of the following to become activated:
A. cAMP
B. fatty acid
C. G-proteins
D. auto-phosphorylation
E. None of the above
D. auto-phosphorylation
4. Elevated levels of glucagon normally stimulate which of the following:
A. glycolysis
B. fatty acid synthesis
C. glycogen synthesis
D. gluconeogenesis
E. Pentose Phosphate Pathway
D. gluconeogenesis
5. Which one of the following statements about gluconeogenesis in the liver is FALSE?
A. For starting materials, it can use carbon skeletons derived from glucogenic amino acids.
B. It consists entirely of the enzymes and reactions of glycolysis, operating in the reverse direction.
C. It employs a phosphatase enzyme to convert glucose 6-phosphate to glucose.
D. It is one of the ways that mammals try to attain normal blood glucose levels while fasting.
E. It requires chemical energy (ATP or GTP) and reducing power (NADH).
B. It consists entirely of the enzymes and reactions of glycolysis, operating in the reverse direction.
6. Which of the following is a monosaccharide?
A. Sucrose
B. Glucose
C. Glycogen
D. Starch
E. Cellulose
B. Glucose
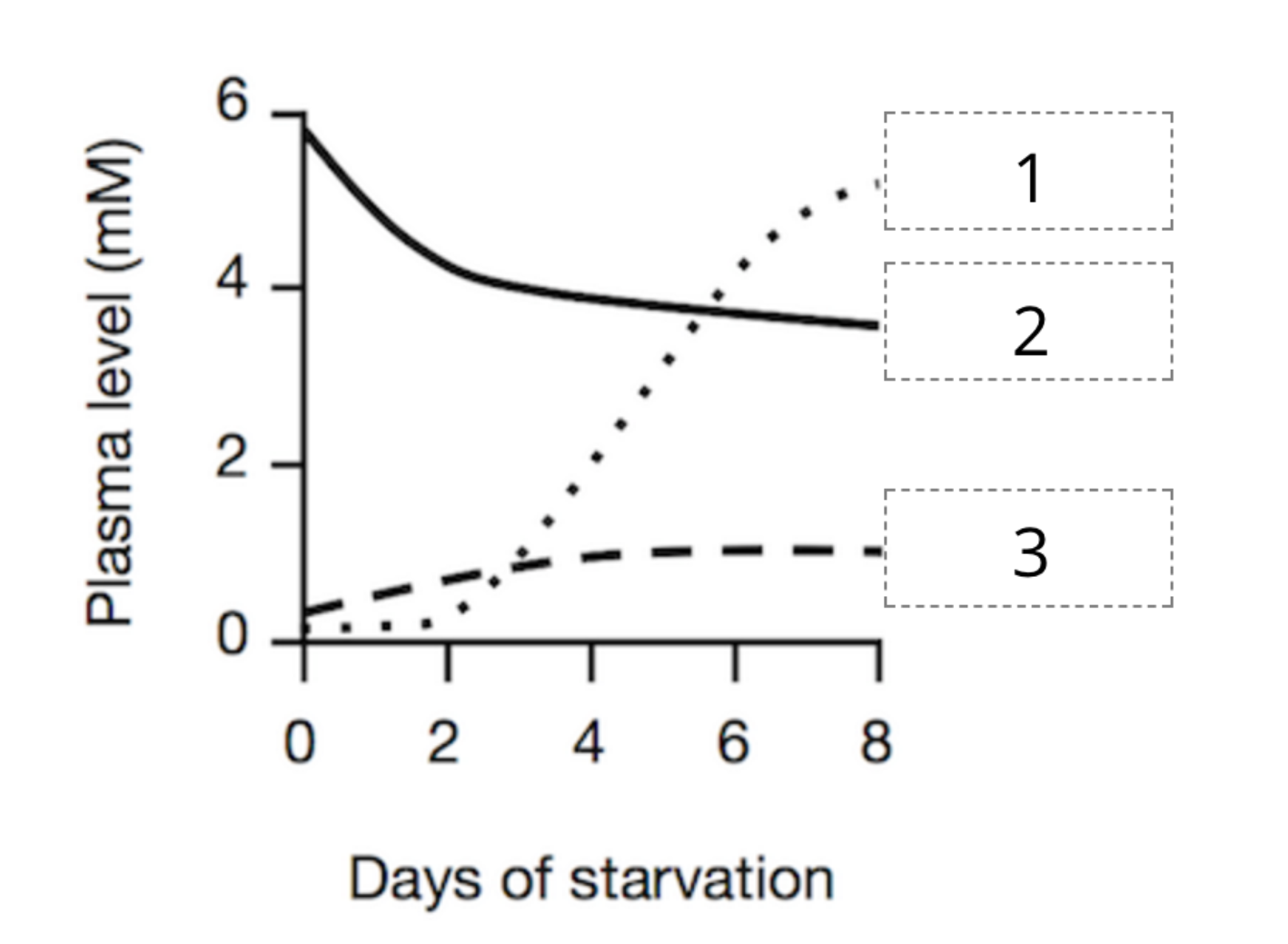
7. The figure below depicts the concentration of different metabolic markers in the blood following the initiation of fasting (or starvation). Based on the numbers in the box, select which marker corresponds to which curve
A. 1 = Fatty acids 2 = Glucose 3 = Ketone bodies
B. 1 = Ketone bodies 2 = Glucose 3 = Fatty acids
C. 1 = Glucose 2 = Fatty acids 3 = Ketone bodies
D. 1 = Ketone bodies 2 = Fatty acids 3 = Glucose
E. 1 = Fatty acids 2 = Ketone bodies 3 = Glucose
B. 1 = Ketone bodies 2 = Glucose 3 = Fatty acids
8. Which of the following statements regarding glycogen metabolism is FALSE?
A. Glycogen synthesis primarily occurs in the liver and muscle.
B. The enzyme responsible for converting glucose 6-phosphate to glucose is not expressed in muscle cells.
C. The breakdown of glycogen in muscle cells is used to generate energy (ATP) via glycolysis.
D. Glucagon stimulates glycogen breakdown in muscle cells while epinephrine stimulates glycogen breakdown in liver cells.
E. Liver glycogen is mostly depleted (gone) 24 hours after fasting.
D. Glucagon stimulates glycogen breakdown in muscle cells while epinephrine stimulate glycogen breakdown in liver cells.
9. Upon insulin signaling, which of the following catalyzes removal of phosphates from serines
in glycogen phosphorylase (the enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen via a
phosphorolysis reaction)?
A. Phosphoprotein phosphatase (PP1)
B. Phosphorylase kinase
C. Protein kinase A (PKA)
D. Phospogluocmutase
E. Debranching enzyme
10. Which of the following statements regarding gluconeogenesis in the liver is FALSE?
A. Gluconeogenesis primarily occurs under fasting/starvation conditions.
B. Acetyl-CoA may be used to synthesize glucose in gluconeogenesis.
C. Glucogenic amino acid catabolism results in citric acid cycle intermediates that can be
used to synthesize glucose in gluconeogenesis.
D. The majority of the steps in gluconeogenesis occurs in the cytosol.
E. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are reciprocally regulated, meaning that one pathway is
on while the other pathway is off.
11. How many net molecules of ATP are produced in the muscle during glycolysis from
a monomer of sugar that is derived from the breakdown of glycogen?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
12. A genetic deficiency of which of the following enzymes is highly represented in the human
population in areas where malaria is present?
A. Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) involved in fatty acid synthesis.
B. Protein Kinase A (PKA) involved in glucagon signaling.
C. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) involved in the Pentose Phosphate
Pathway (PPP).
D. Glycogen phosphorylase involved in glycogen breakdown.
E. Fructose 1,6-bisphophatase (FBPase-1) involved in gluconeogenesis.
13. Which of the following pathways will be most active after eating a sugar cookie?
A. Gluconeogenesis
B. Glycogen Breakdown
C. Fatty acid synthesis
D. Lipolysis (Breakdown of fats)
E. Ketogenesis
14. Consider the synthesis of a triacylglycerol (TAG) that would occur after eating a large
sugary cupcake. Which of the following is the CORRECT order of synthesis?
A. Glucose -> acetyl-CoA -> malonyl-CoA -> palmitoyl-CoA -> phosphatidic acid -> TAG
B. Glycogen -> acetyl-CoA -> malonyl-CoA -> palmitoyl-CoA -> phosphatidic acid -> TAG
C. Glucose -> acetyl-CoA -> mevalonate -> palmitoyl-CoA -> squalene -> TAG
D. Glycogen -> acetyl-CoA -> mevalonate -> isoprene -> squalene -> TAG
E. Glycogen -> acetyl-CoA ->malonyl-CoA -> squalene -> phosphatidic acid -> TAG
15. Which of the following statements regarding cholesterol is CORRECT?
A. Cholesterol is primarily synthesized in adipocytes (i.e. fat cells).
B. Humans require cholesterol in their diet.
C. High levels of cholesterol can lead to Type I diabetes.
D. Glucogenic amino acids are used to synthesize cholesterol.
E. Transport of cholesterol through the blood is facilitated by lipoprotein particles.
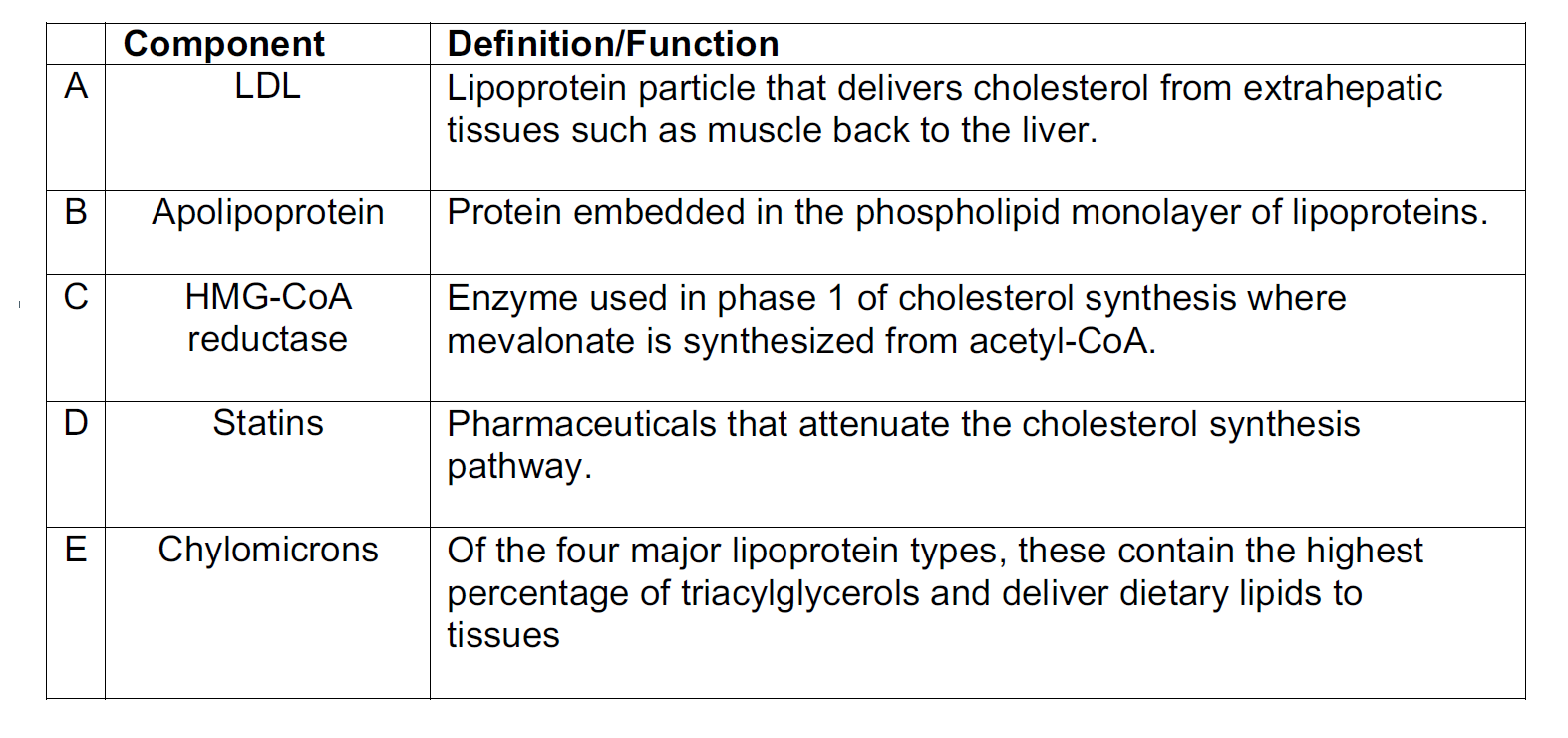
16. Consider cholesterol synthesis and transport. Identify the INCORRECT choice.
17. There is reciprocal regulation of glycolytic and gluconeogenic reactions interconverting
fructose-6-phosphate and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Which one of the following statements
about this regulation is FALSE?
A) Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F 2,6-BP) activates phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1).
B) Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F 2,6-BP) inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1)
C) Phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK-2) catalyzes the phosphorylation of Fructose 6-Phosphate
(F 6-P) forming Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate.
D) Insulin activates Phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1), which activates Fructose 2,6
Bisphosphatase (FBPase-2), which catalyzes the phosphorylation of Fructose 6-
Phosphate (F 6-P) forming Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F 2,6-BP).
E) This regulation allows control of the direction of net metabolite flow through the pathway.
18. When ketogenesis (formation of ketone bodies) is readily occurring in the liver, what
other process is also occurring in this tissue type?
A. Glycogen synthesis
B. Gluconeogenesis
C. Fatty acid synthesis
D. Cholesterol synthesis
E. Glycolysis
19. Which of the following molecules interacts with the LDL receptor to stimulate endocytosis
of the LDL particle?
A. Glycerophospholipid
B. ApoB-100
C. HDL
D. Chylomicrons
E. VLDL
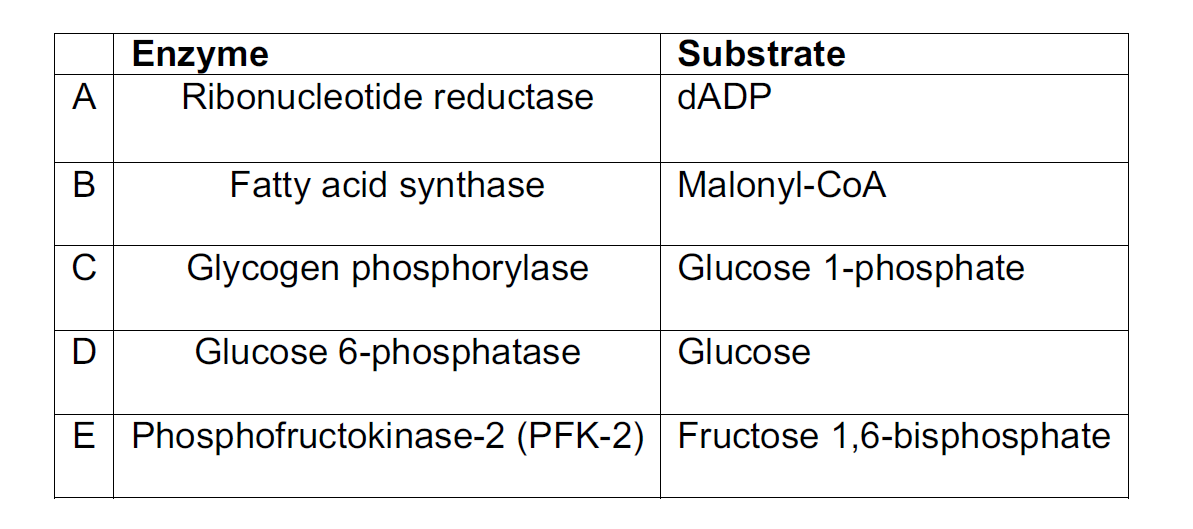
20. Identify the CORRECT choice.
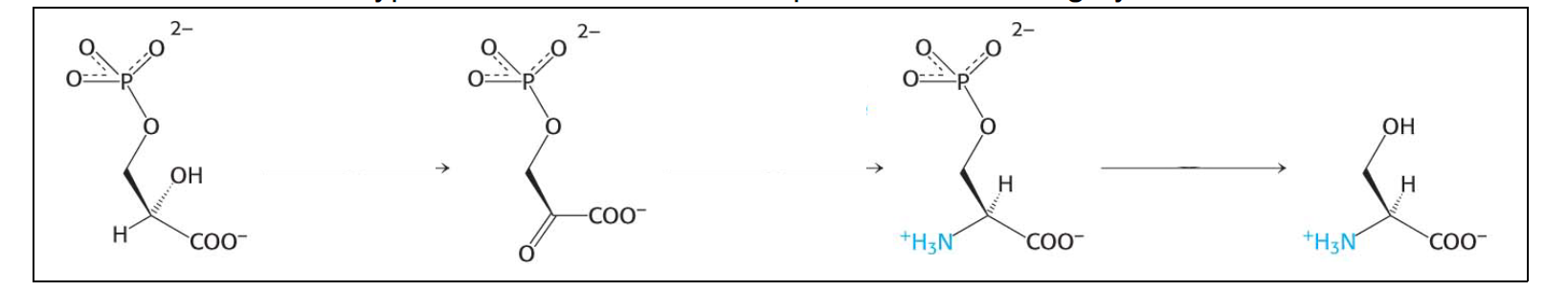
21. List the order of the types of reactions that take place below during synthesis of serine:
A) Oxidation, Transamination, Dephosphorylation
B) Transamination, Oxidation, Dephosphorylation
C) Dephosphorylation, Oxidation, Transamination
D) Oxidation, Dephosphorylation, Transamination
E) Transamination, Dephosphorylation, Oxidation
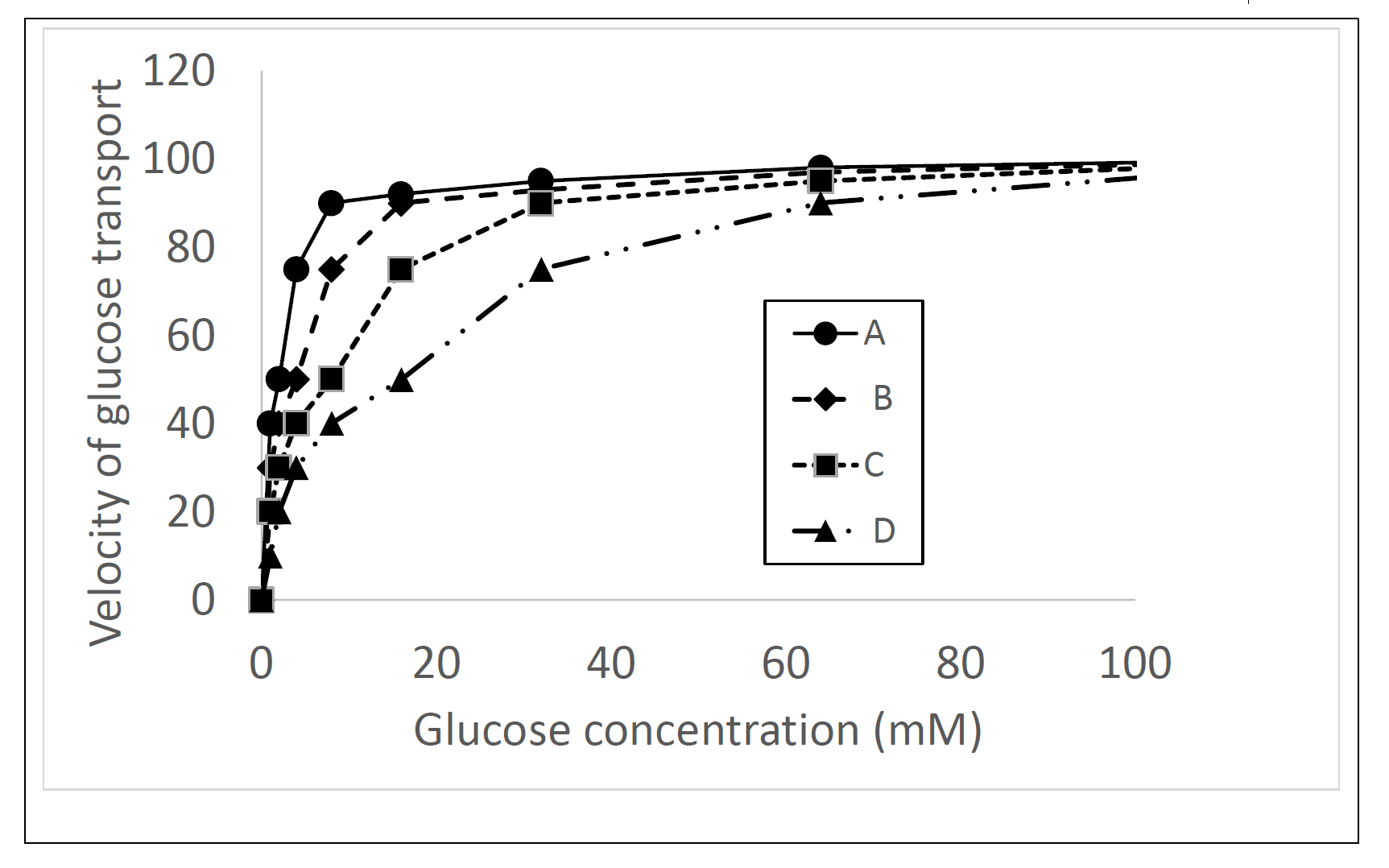
22. You characterize four novel glucose transporters and label them as A, B, C, and D. Which
of the following transporters has the slowest velocity of glucose transport at 20 mM glucose?
23. Which of the following metabolites is derived from amino acids and is a major donor of
methyl groups?
A. The neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin
B. Glutathione
C. S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM)
D. Porphyrin rings (e.g. heme)
E. Melanin
24. Which of the following is FALSE about fatty acid synthesis in animal cells?
A. NADPH is produced in the cytosol by the pentose phosphate pathway.
B. Malonyl-CoA is formed in the cytosol.
C. Acetyl-CoA is transported out of the mitochondrion in the form of citrate via the citrate
shuttle.
D. Pyruvate is transported across the mitochondrial membrane.
E. NADPH is produced in the mitochondria by an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of
malate to pyruvate.
25. If a person cannot use the oxidative phase of PPP, how can they generate ribose-5-
phosphate for nucleotide synthesis?
A. They can only get it from their diet.
B. These people usually die young. There is no way to generate it, except via the oxidative
phase of the PPP.
C. The reactions of the non-oxidative phase are reversible, intermediates from glycolysis
can be used to generate ribose-5-phosphate.
D. Synthesis of nucleotides only requires purine and pyrimidine rings, which are derived
from amino acids, thus ribose-5-phosphate is not needed.
E. None of the above
26. Which of the following is FALSE concerning the reaction catalyzed by ribonucleotide
reductase?
A. dATP is a negative allosteric effector that inhibits its activity
B. It acts on nucleoside diphosphates (i.e. ADP, CDP, GDP, UDP).
C. ATP is a positive allosteric effector that stimulates its activity
D. There is a separate enzyme for each nucleoside diphosphate (ADP, CDP, GDP, UDP).
E. Hydroxyurea is a treatment for certain cancers because it inhibits the activity of the
ribonucleotide reductase.
27. The cofactor Biotin is a component of which of the following enzymes?
A. Dehydrogenases (e.g. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, G6PD))
B. Carboxylases (e.g. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase)
C. Kinases (e.g. Protein Kinase A, PKA)
D. Phosphatases (e.g. Phosphoprotein Phospatase-1, PP1)
E. Reductases (e.g. HMG-CoA reductase)
28. Which of the following statements regarding eicosanoids is TRUE?
A. Phospholipase A2 catalyzes the release of arachidonate from phoshpholipids
B. They include prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes.
C. Aspirin inhibits the activity of COX enzymes by acetylation of a serine in the active sites
of a COX enzyme
D. NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, inhibit the activity of COX enzymes by acting as competitive
inhibitors.
E. All of the above are true
29. Which of the following molecules may be used to synthesize glucose?
A. Glucogenic amino acids
B. Glycerol
C. Pyruvate
D. Lactate
E. All of the above
30. Salvage pathways synthesize nucleotides by
A. using preformed bases, recovered from the breakdown of nucleic acids.
B. using bicarbonate and amine groups from glutamine to make bases.
C. using ribose 5-phosphate directly from the Pentose Phosphate Pathway
D. using amino acids, such as aspartate, glycine, and glutamine to form the base that is
attached to the sugar.
E. None of the above.
31. Which of these statements about triacylglycerol synthesis is CORRECT?
A) Humans can store more energy in glycogen than in triacylglycerols.
B) Insulin stimulates conversion of dietary carbohydrate into triacylglycerols.
C) It is not a hormone-sensitive process.
D) Mammals are unable to convert carbohydrates into triacylglycerols.
E) Acetyl-CoA is not on the pathway of triacylglycerol synthesis.
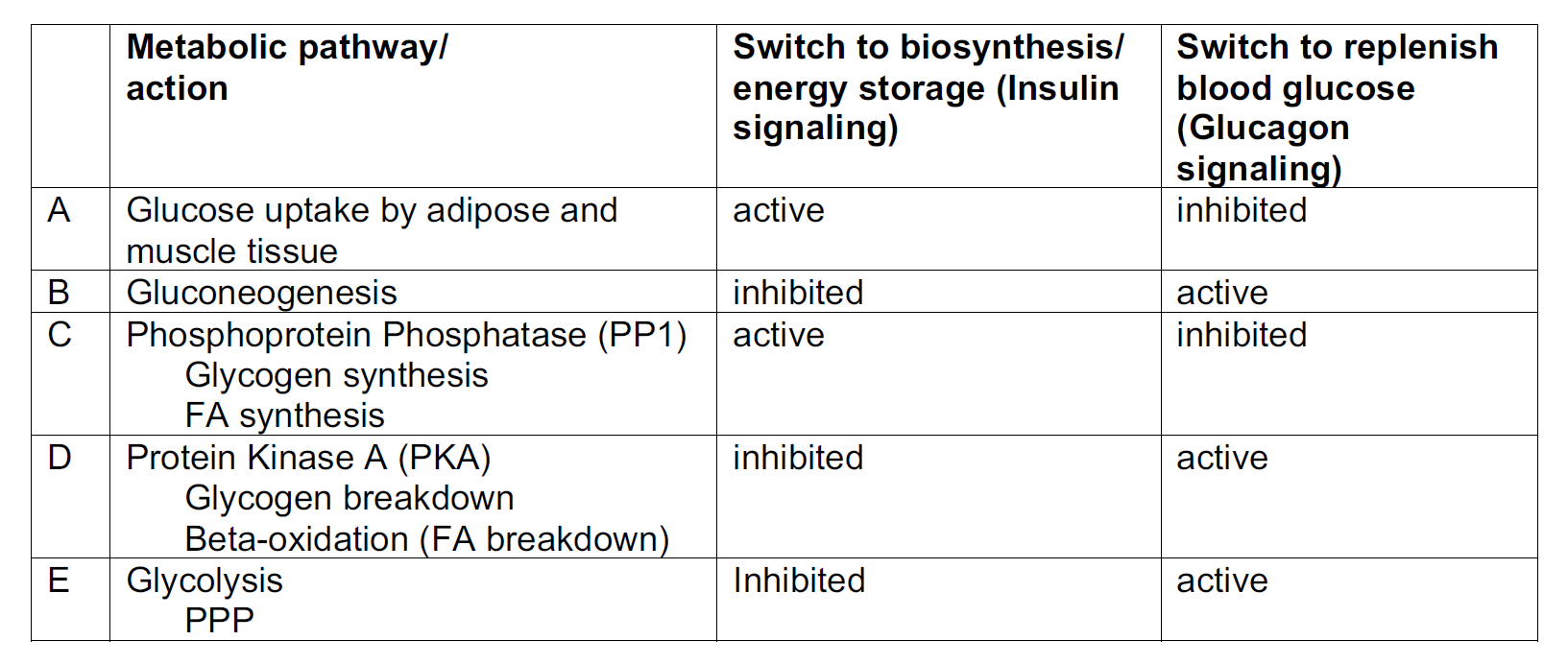
32. Identify the INCORRECT choice
33. Which of the following most likely occurs after 48 hours of fasting?
A) Glucagon mediated inactivation of Acetyl CoA carboxylase (enzyme involved in fatty
acid synthesis) by phosphorylation.
B) Glucagon mediated activation of Acetyl CoA carboxylase (enzyme involved in fatty acid
synthesis) via phosphorylation.
C) Increased export of Acetyl CoA to the cytosol from the mitochondria.
D) Glucagon mediated inactivation of glycogen phosphorylase (enzyme involved in
glycogen breakdown) via phosphorylation.
E) Glucagon mediated inactivation of glycogen phosphorylase (enzyme involved in
glycogen breakdown) via dephosphorylation.