Chapter 34: Animal Nutrition & Digestive System
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
tissues
group of cells possessing similar structure, acting together to perform a similar function combine to form organs
Epithelial Tissue
a type of tissue that lines body cavities, covers surfaces, protects (e.g., skin), separates the inside from the outside, and exchange molecules (e.g., blood)
Glandular Epithelium is specialized epithelium that secretes substances, and includes endocrine glands, which secrete ___ the body, and exocrine glands, which secrete ___ the body
inside, outside
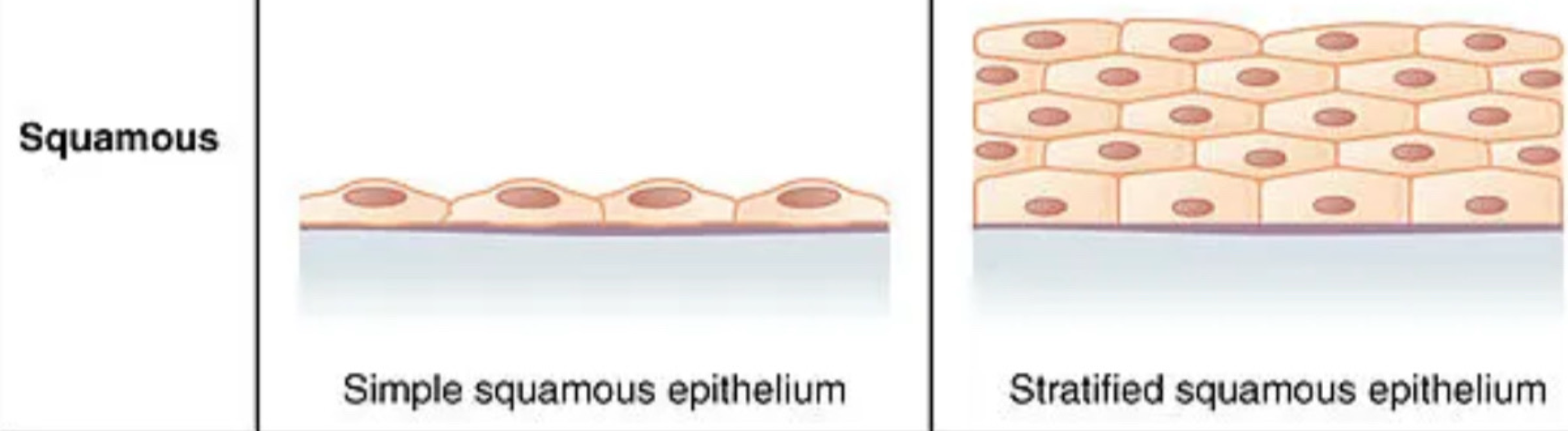
squamous shaped cells are ___, and found in/on ___
flattened, outer skin surface, lining blood vessels, mouth, digestive system
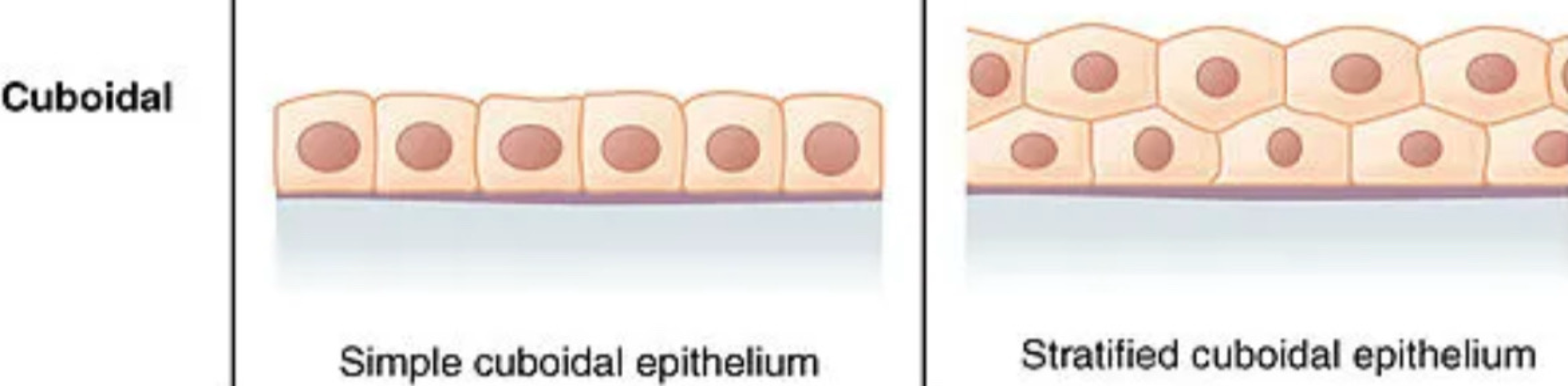
cuboidal shaped cells are ___, and found in/on
cube, all glandular tissue, kidneys, uterus
columnar shaped cells are ___, and found in/on
column, parts of the digestive system, reproductive organs, larynx, mucus
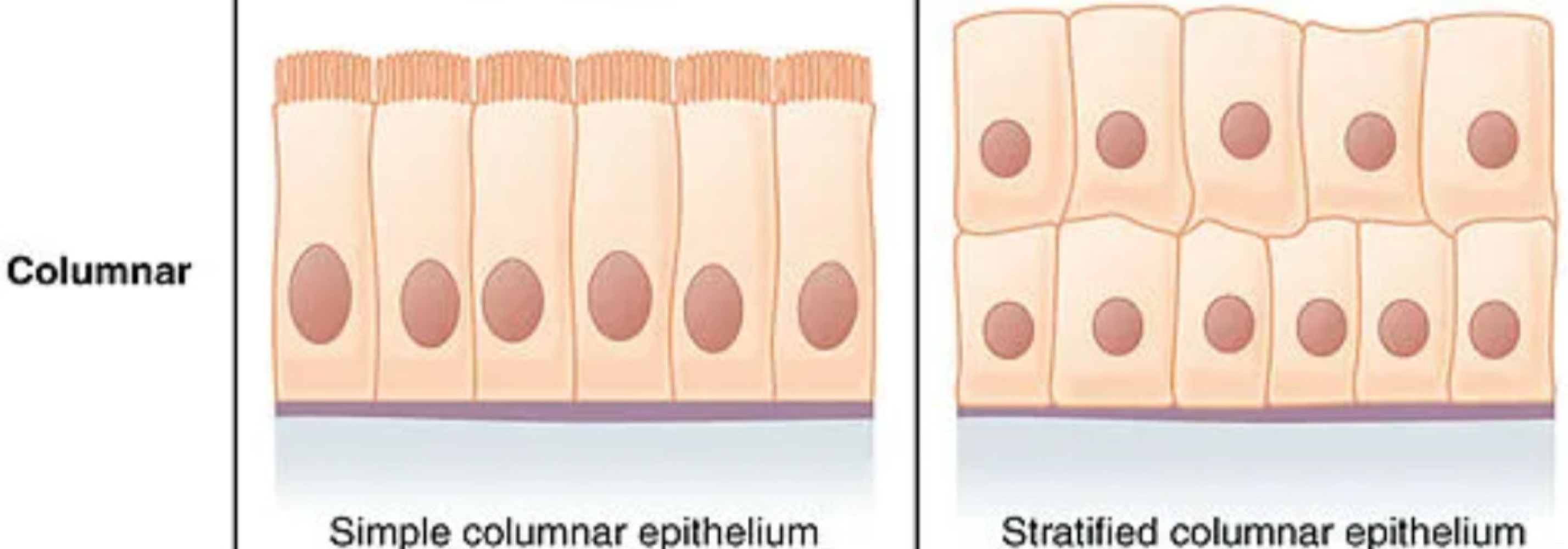
simple organization of epithelial tissue consists of how many cell layers?
a single layer
stratified organization of epithelial tissue consists of how many cell layers?
multiple layers
Connective Tissue
a type of tissue that connects different tissue and parts of the body, stores fat, and produces blood cells
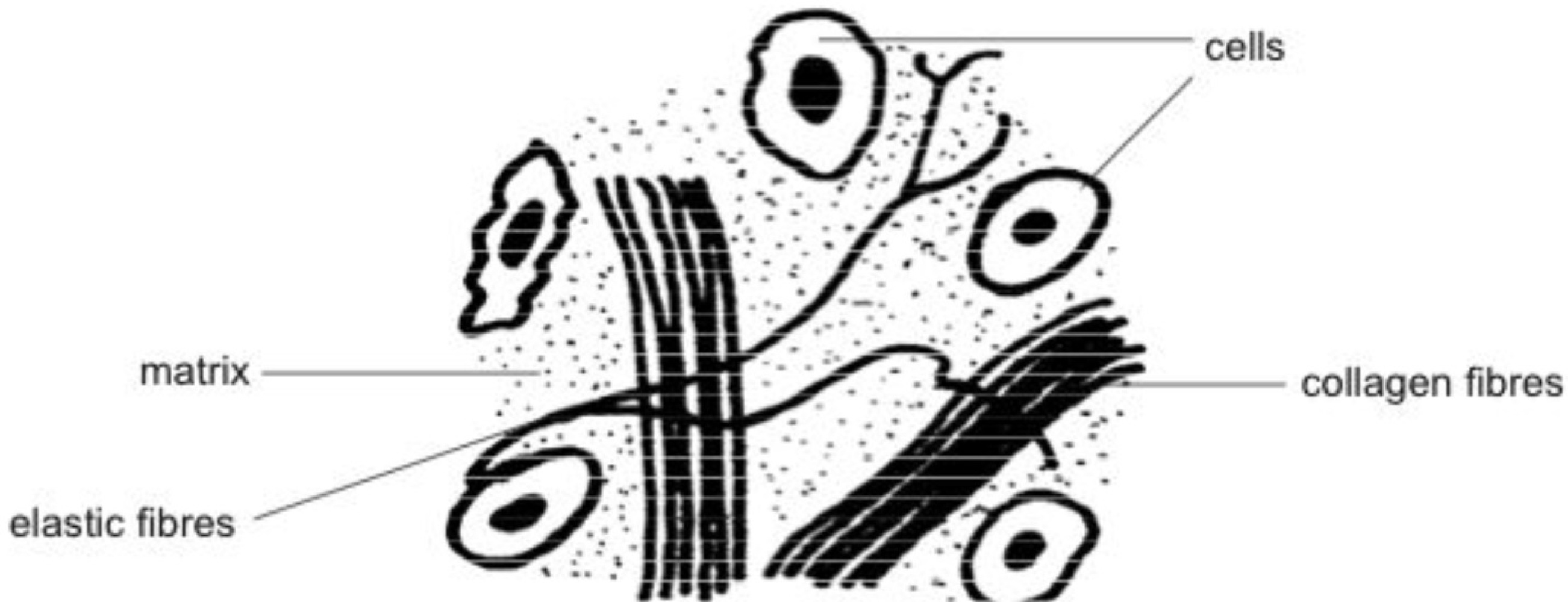

connective tissue cells are embedded in ___, which fills the space between the cells. its content depends on ___
nonliving extracellular matrix, what the cell produces
Cartilage
specialized connective tissue often found in the nose and ears for shape
Bones
specialized connective tissue made of calcium and blood vessels for support
Blood
specialized connective tissue made of red blood cells and white blood cells
the space between blood cells are filled with ___, which is made of ___ water, and other materials such as ___ and ___
plasma, 92%, proteins, hormones
Muscle Tissue
a type of tissue made of muscle fibers that contracts to create movement
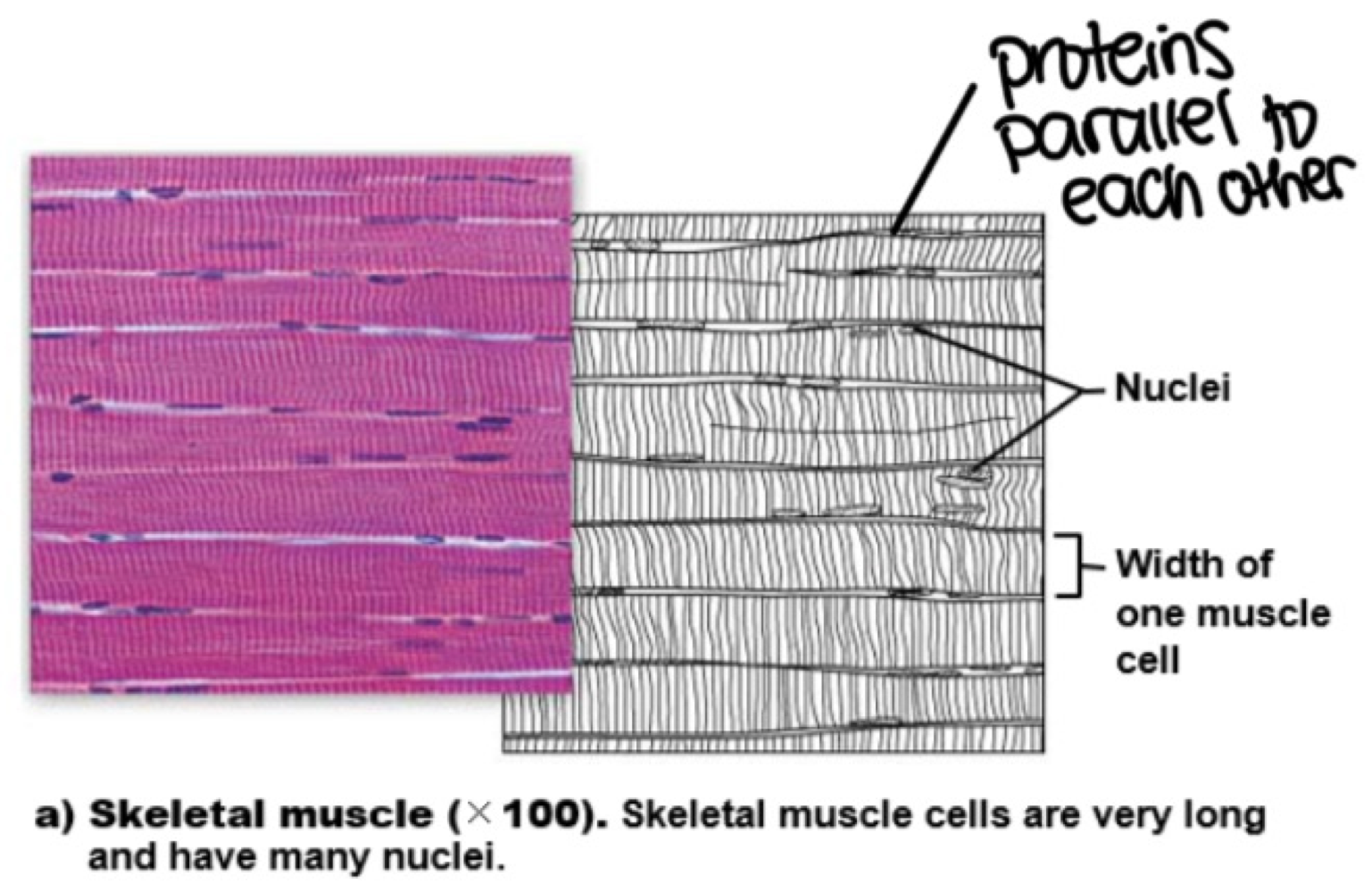
skeletal muscle
specialized multi-nucleate muscle cells used for voluntary movement. these cells are highly organized and striated, and require neurons to function
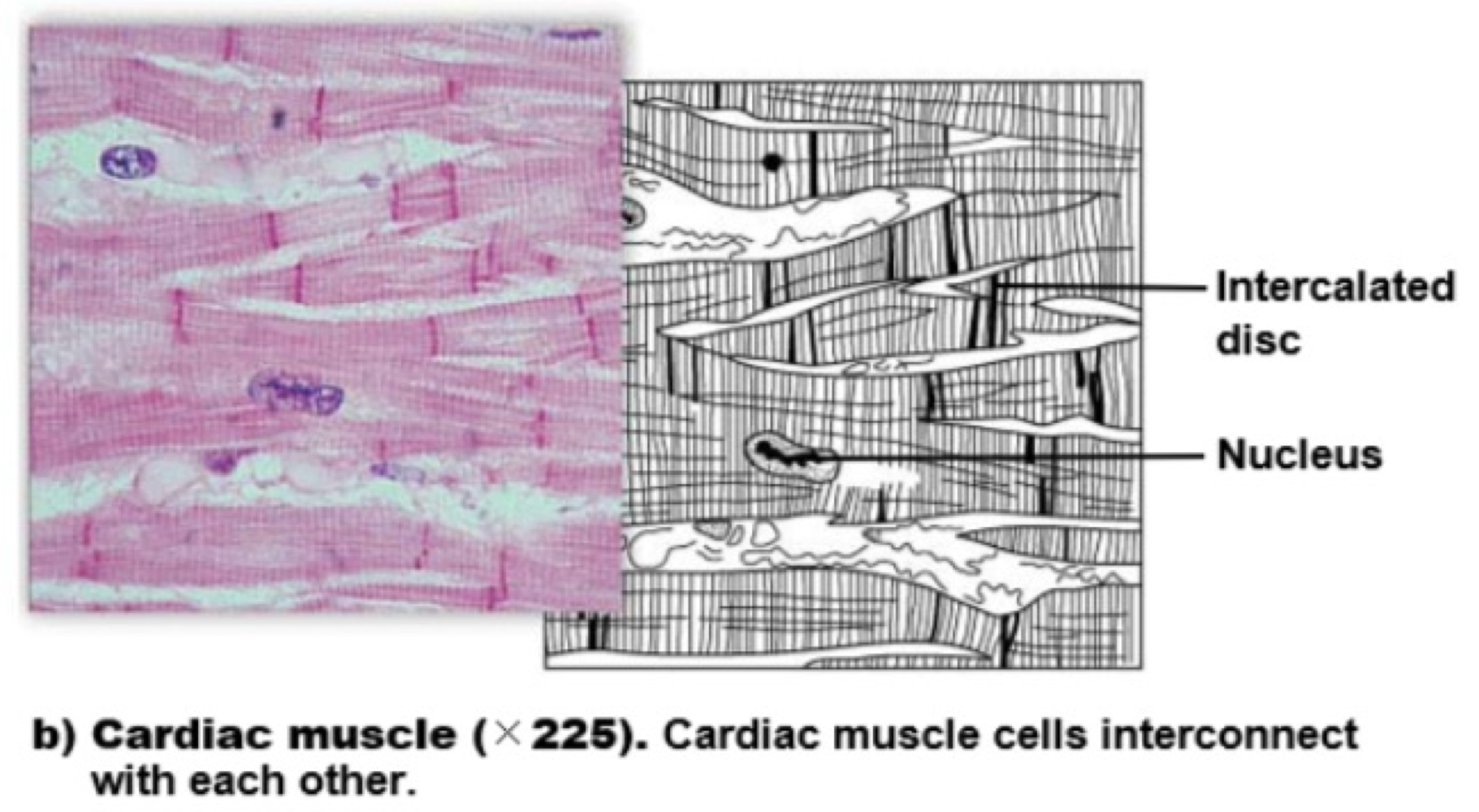
cardiac muscle
specialized mono-nucleated muscle cells used for functions in the heart. these cells are striated and involuntary, and don’t require neurons for contractions
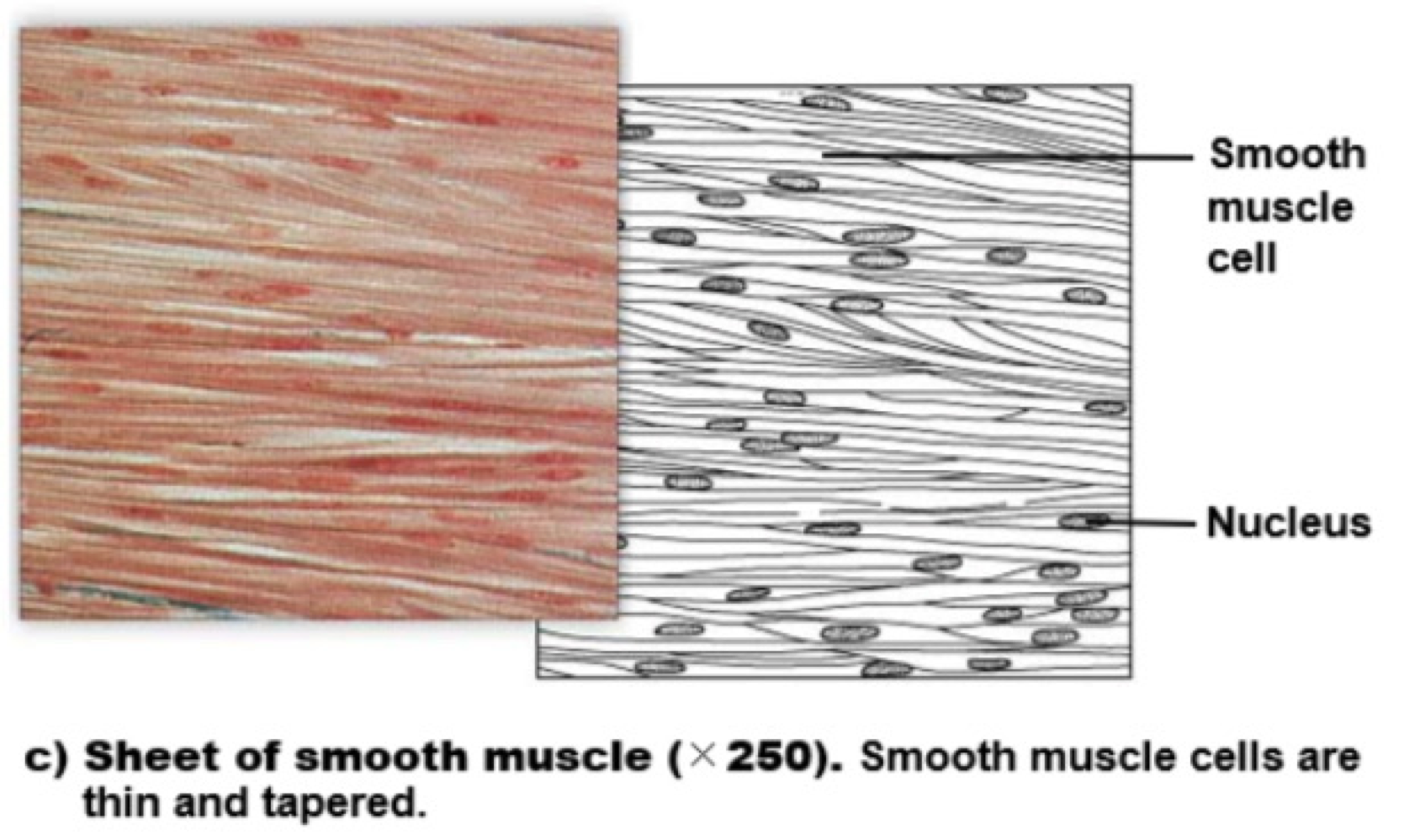
smooth muscle
multinucleate cells used to surround hollow structures (blood vessels, digestive system). these cells are non-striated, and involuntary. their contractions can be moderated by neurons, but they’re not needed to start them
Nervous Tissue
a type of tissue that receives and sends information
neuron cells
specialized nervous tissue cells that generate and transmit information in the form of electrical impulses
glial cells
specialized nervous tissue cells that surround, protect, and provide nutrients to neurons
organs
two or more tissue types joined together to perform specific functions
organ system
a group of organs that perform a common function
body cavities
spaces in the body from the coelom that allow organs to grow
anterior cavity
separate into the pelvic cavity (reproductive organs), abdominal cavity (most of the digestive system) and thoracic (pericardial [heart] and pleural [lungs]) cavity
cranial cavity
contains the cranial (brain) and vertebral (spine) cavity
homeostasis
optimal state for an organism’s survival that must be relatively constant internally even when the external environment changes
Negative Feedback Loop
regulatory mechanisms in which the results of one process inhibits that same process (e.g., dopamine release stops hunger)
within the negative feedback loop, a controlled variable is ___
a physical/chemical property that must be controlled to maintain homeostasis
within the negative feedback loop, a sensor (receptor) ___
monitors current value for controlled variable; sends information to control center
within the negative feedback loop, the control center ___
receives input from the sensor, compares value to set point, and signals the effector (if necessary)
within the negative feedback loop, the effector ___
takes action to correct the balance, based on information from the control center
Positive Feedback Loop
regulatory mechanisms in which the results of one process intensify that same process (e.g., child birth)
glucose obtained from food is stored as ___ in the liver and muscle with many ___, so its heavy
glycogen, water molecules
lipids obtained from food are stored as ___ (glycerol + FA) in ___ tissue with less ___, so its lighter
triglycerides, adipose, water
Food Energy is expressed in calories (cal)/kilocaleries (kCal), which is the ___
amount of heat required to raise the temperate of 1g of water by 1°C
Essential Nutrient
a nutrient that the animals can’t synthesize by itself
Essential Amino Acids
Tryptophan, Methionine, Valine, Threonine, Phenylalanine, Leucine, Isoleucine, and Lysine. humans have 20 amino acids; 9 are essential in adults; 8 are essential in children
Essential Vitamins
a group of carbon compounds your body needs in small amounts. many are coenzymes (e.g. thiamine [B1])
Essential Minerals
chemical elements animals require, in addition to carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen (e.g., calcium [Ca] for bones, Iron [Fe] for RBCs)
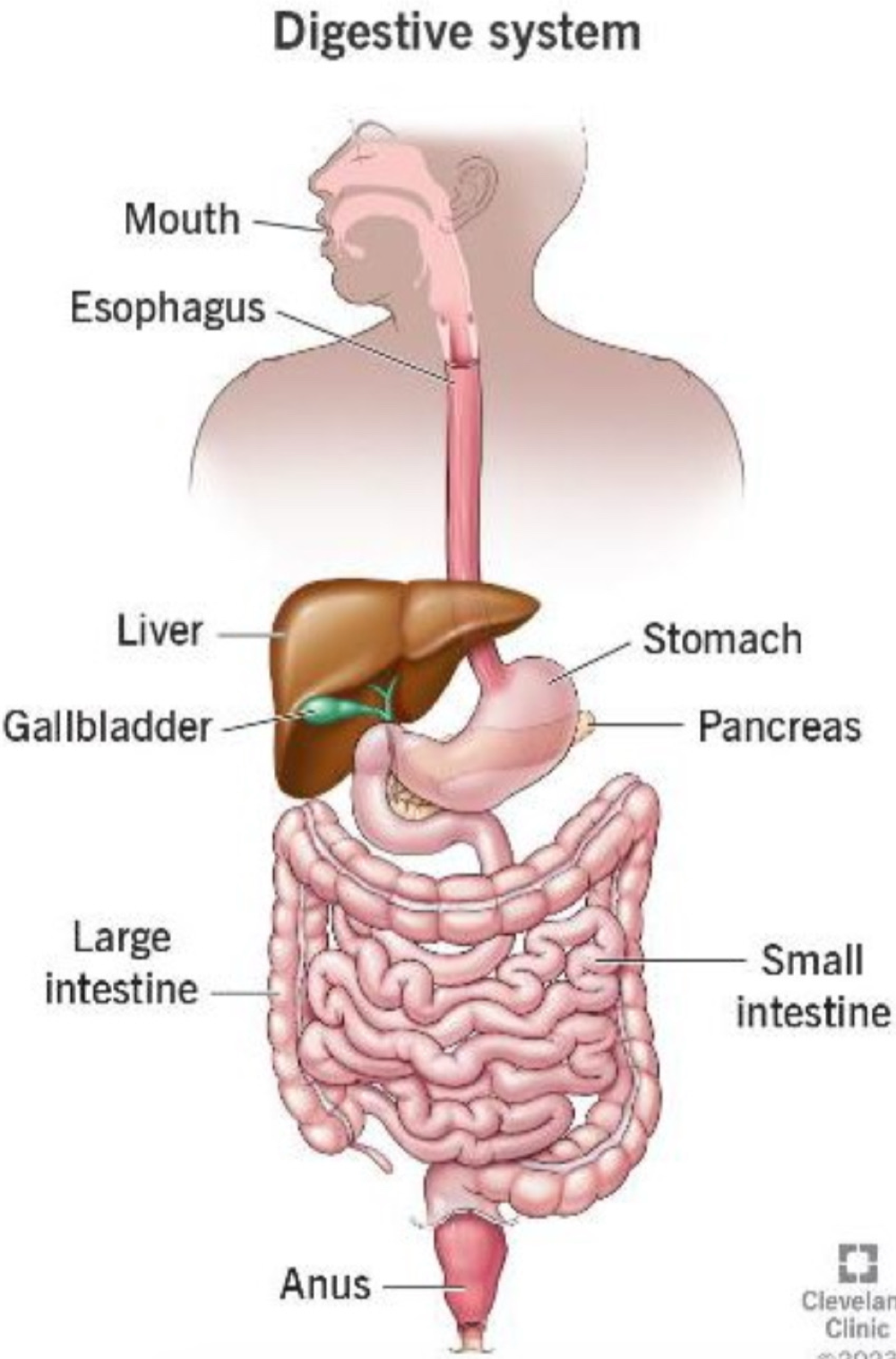
the digestive system is made of ___
the oral cavity (mouth and pharynx), esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine
accessory organs in the digestive system are ___
the salivary glands, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder
the functions of the digestive system are digestion, or ___, and absorption, or ___
breaking down, carrying molecules to other parts of the body
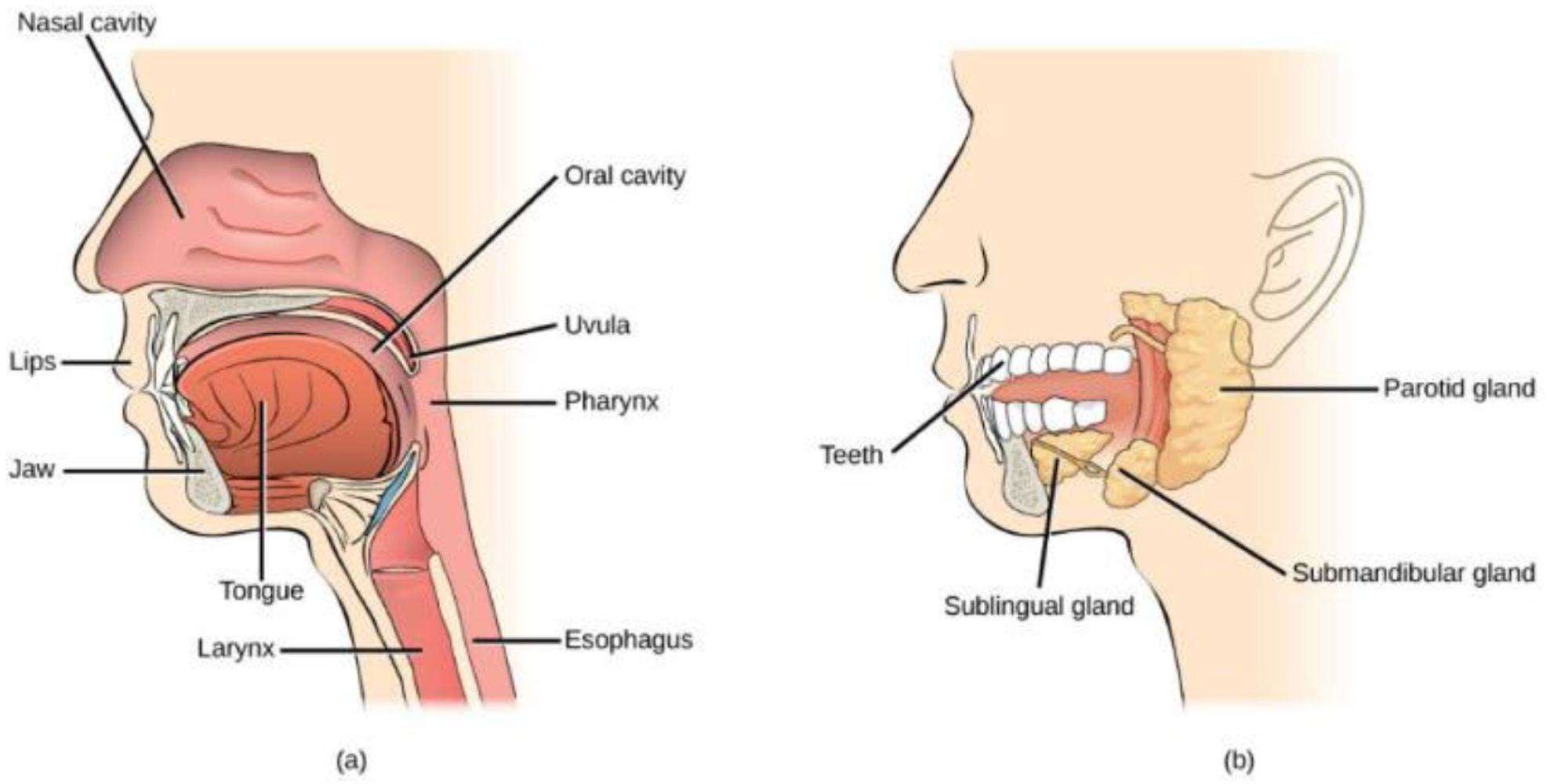
in the oral cavity, the ___ break apart food, and the ___ secrete amylase and lipase to digest ___ and ___, respectively
teeth, salivary glands, starch, fats
in the pharynx, the ___ (food and saliva) move towards the esophagus, where swallowing via ___, voluntary smooth muscle movement, occurs
food bolus, peristalsis
in the esophagus, the ___ (controls when food moves to the next organ) opens in response to swallowing and the pressure from the food bolus
lower esophageal spincter
in the stomach, gastric digestive juices composed of ___ begin digesting food, but ___ does not occur yet
Hcl, lipase, and pepsin, absorption
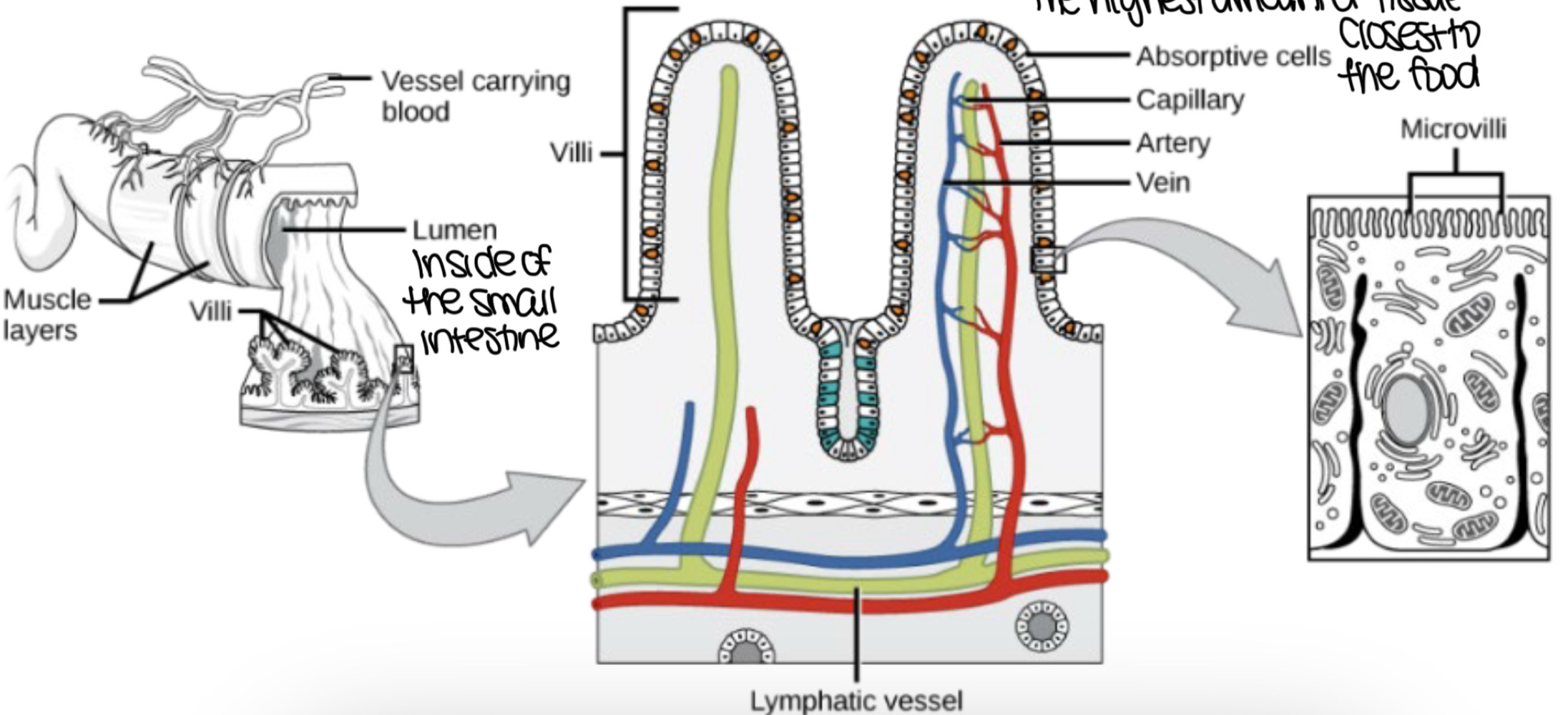
in the small intestine, (long hollow tube-like structure closest to the food), ___ occurs and ___ is no longer happening
absorption, digestion
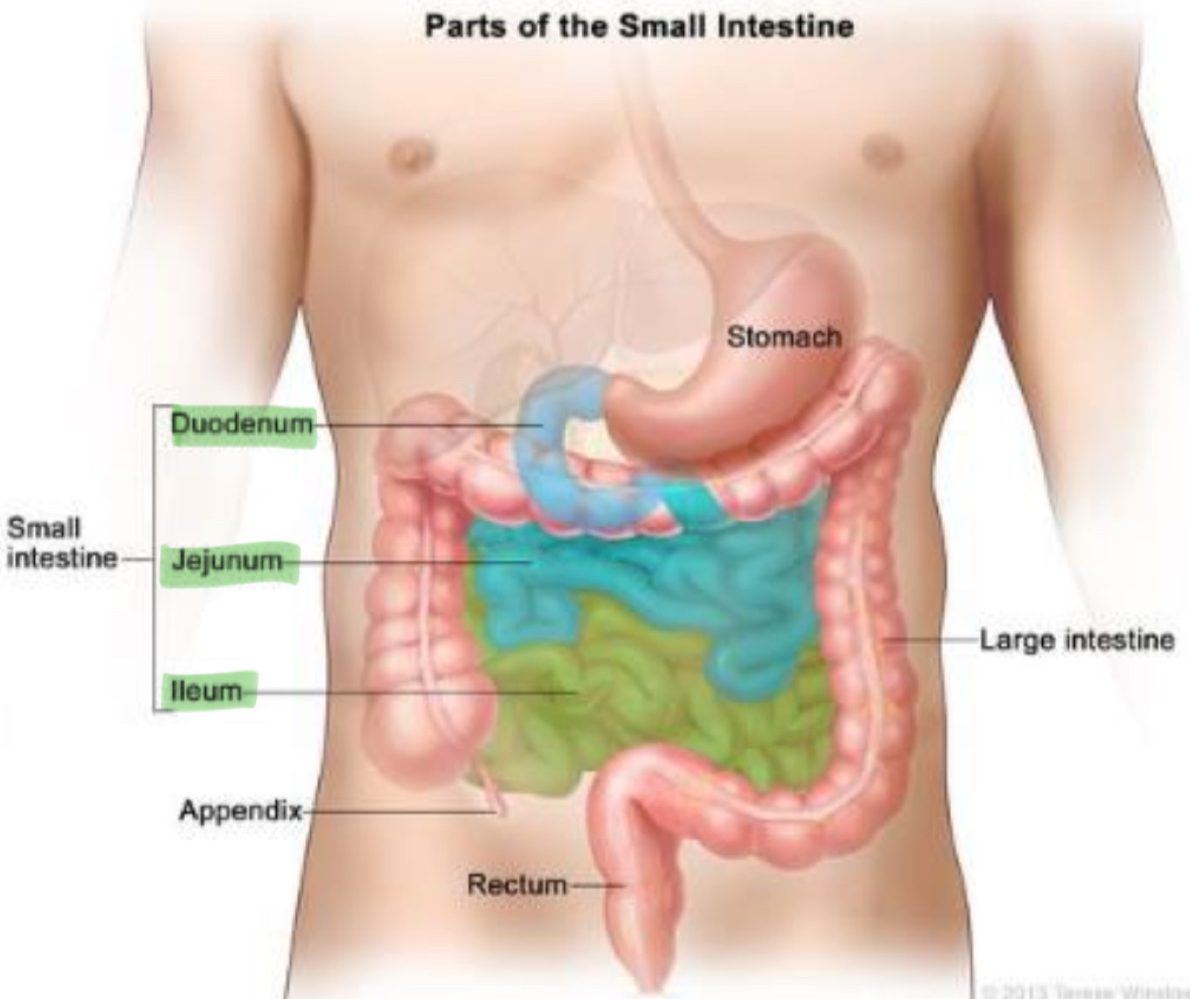
the duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine connected to the ___, which releases pancreatic juices high in ___ to counteract with the acidic gastric acid
pancreas, bicarbonate (HCO3-)
___ is produced in the liver and stored in the ___ to break down lipids
bile, gallbladder
other sections of the small intestine are the ___ and ___
jejunum, ileum
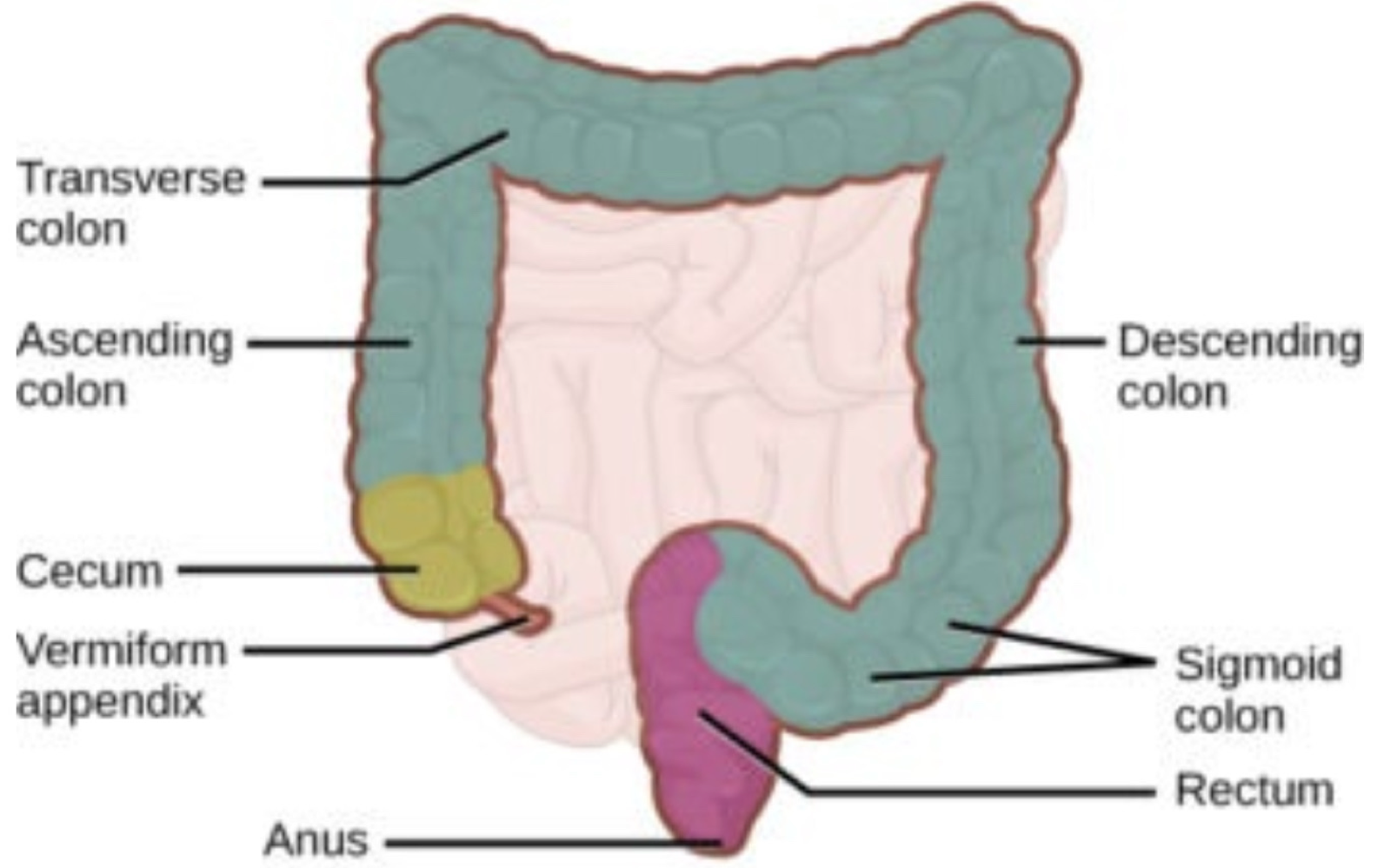
in the large intestine, water is ___ from undigested food and ___ is stored until elimination
absorbed, waste