A&P Quiz 10 (Ch 28 pt 4)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Puberty in Females
associated with increased rate of estrogen and progesterone secretion by the ovaries
Before Puberty in Females
gnrh secretion from hypothalamus is very low
lh and fsh secretion from anterior pituitary is very low
estrogen and progesterone are secreted in very small amounts
estrogen and progesterone from ovaries have a strong negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
After Puberty in Females
larger amounts of gnrh, lh, and fsh are secreted
estrogen and progesterone have less of a negative feedback effect on hypothalamus and pituitary gland
sustained increase in estrogen concentration has a positive feedback effect
normal cyclic pattern of reproductive hormone secretion is established
Menstrual Cycle
refers to the cycling changes in sexually mature nonpregnant females, normally described as 28 days long
Variation in Menstrual Cycle Length
cab vary between 18-40 days, vary between females and from month to month in the same female depending on different factors (nutrition, stress, level of activity)
Menstrual Cycle is Divided Into
ovarian cycle
uterine cycle
Uterine Cycle (simple)
changes associated specifically with the uterus during menstruation
Ovarian Cycle
regular events that occur in the ovaries of sexually mature nonpregnant females during the menstrual cycle
2 Phases of Ovarian Cycle
follicular
luteal
Ovulation
release of secondary oocytes on day 14 of ovarian cycle
Follicular Phase
phase of ovarian cycle that occurs before ovulation (days 1-14), primordial follicle develops into mature follicle, primary oocyte undergoes first meiotic division
Luteal Phase
phase of ovarian cycle that occurs after ovulation, follicle form corpus luteum that secretes progesterone and small amount of estrogen
Ovarian Cycle Diagram
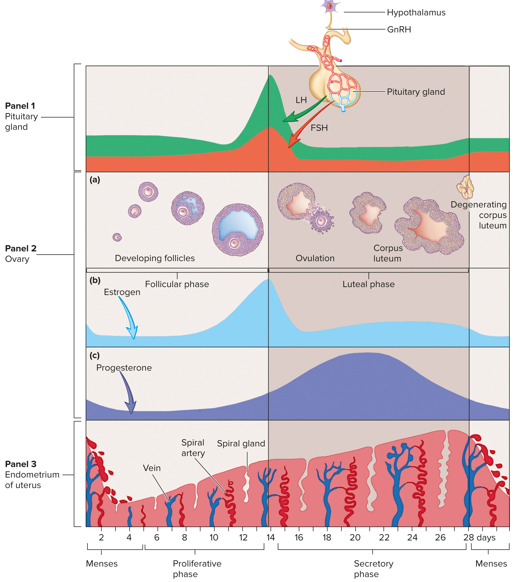
Steps 1-3 of Ovarian Cycle
lh stimulates theca interna cells to produce androgens
androgens diffuse into granulosa cells
fsh stimulates granulosa cells to convert androgens to estrogen and gradually increases lh receptors in granulosa cells
Steps 4-6 of Ovarian Cycle
estrogen increases lh receptors in the theca interna cells
lh stimulates granulosa cells to produce progesterone
progesterone diffused to theca interna cells and is converted to androgens
Steps 7-9 of Ovarian Cycle
androgens are converted into estrogen by granulosa cells
causes a gradual increase in estrogen secretion by granulosa cells throughout the follicular phase
inhibin secreted by the developing follicle inhibits fsh secretion
Early Hormones Secreted During Ovarian Cycle
hypothalamus increases gnrh, which increases secretion of fsh and lh from anterior pituitary
FSH and LH in Ovarian Cycle
stimulate growth and maturation of the ovarian follicles (follicular phase), fsh initiates development of primary follicles (up to 25 per cycle), typically only one is ovulated, can by ovulated during a later cycle, remaining follicles degenerate, both an LH surge and FSH surge occur
Role of Estrogen Secreted by Maturing Follicle
stimulated uterine endometrial proliferation, positive feedback on hypothalamic and anterior pituitary secretion, determination of which follicles degenerate (larger follicles appear to secrete estrogen and other substances that have an inhibitory effect on less mature follicles
LH Surge
occurs several hours earlier and to a greater degree than fsh surge in ovarian cycle, stimulates maturation of follicle and completion of meiosis i, triggers inflammation like events in the mature follicles that result in ovulation
Corpus Luteum in Ovulation
formed shortly after ovulation, secretes progesterone and estrogen
Progesterone and Estrogen in Ovarian Cycle
cause negative feedback on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary to decrease fsh and lh secretion
Ovarian Cycle if Fertilization Occurs
developing embryo secretes hcg
hcg keeps corpus luteum from degenerating
keeps blood levels of estrogen and progesterone from decreasing
menses of the next uterine cycle does not occur
Ovarian Cycle if Fertilization Does Not Occur
hcg is not produced
cells of corpus luteum begin to atrophy after day 25 or 26
blood levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease rapidly
menses occurs
Uterine Cycle
changes that occur primarily in the functional layer of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle, more subtle changes take place in the vagina and other structures
3 Phases of Uterine Cycle
menses
proliferative phase
secretory phase
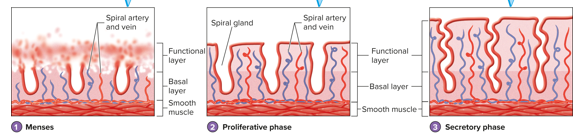
Menses
phase of uterine cycle, period of mild hemorrhage that occurs about once a month, functional layer of the endometrium is sloughed off and expelled from the uterus
Menstruation
discharge of the sloughed endometrial tissue and blood
Proliferative Phase
phase of uterine cycle, time between the ending of menses and ovulation, endometrium begins to regenerate
Endometrium Regeneration During Proliferative Phase
epithelial cells divide to produce low cuboidal epithelial cells that become columnar, spiral glands and spiral arteries reform
Spiral Glands
region of endometrium that regenerates during proliferative phase of uterine cycle, tubular folds of the cells of the functional layer
Spiral Arteries
region of endometrium that regenerates during proliferative phase of uterine cycle, blood vessels project through the delicate connective tissue that separates the individual spiral glands to supply endometrial cells
Secretory Phase
phase of uterine cycle, time after ovulation to the next menses, endometrium becomes thicker, spiral glands develop to greater extent and begin secreting small amounts of fluid rich in glycogen, around day 21 the endometrium is prepared to receive a developing embryonic mass
Uterine Cycle Diagram
What controls female sexual behavior and the female sex act?
female sex drive depends on hormones, psychological factors can affect sexual behavior, neural pathways controlling sexual responses are the same as in males
Hormones of Female Sex Act and Sexual Behavior
adrenal glands and other tissues convert steroids to androgens, androgens and possibly estrogen affect brain cells (hypothalamus) to influence sexual behavior but no not control sex drive alone
Neural Control of Female Sexual Behavior and Female Sex Act
sensory action potentials conducted from genitals to the sacral region, integrate reflexes regulating sexual responses, ascending pathways (spinothalamic tracts) carry sensory information to the brain, descending pathways carry information back to the sacral region to influence sacral reflexes
Motor AP of Female Sexual Behavior and Sex Act Carried By
parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve fibers from the spinal cord to the reproductive organs
somatic motor nerve fibers to the skeletal muscles
Parasympathetic Stimulation in Female Sexual Behavior Causes
erectile tissue in the clitoris and around vaginal opening to become engorged with blood, nipples often become erect, mucous glands in the vestibule secrete mucus, large amounts of mucus like fluid are extruded into the vagina through the vaginal wall
Function of Parasympathetic Vaginal Secretions
lubrication allows for easy entry and movement of the penis during intercourse
Orgasm
triggered by tactile stimulation of female’s genitals and psychological stimuli, vaginal/uterine/perineal muscles contract rhythmically, muscle tension increases throughout the body, not required for fertilization to occur
Resolution
characterized by sense of satisfaction and relaxation, successive orgasms are possible
Travel of Sperm for Fertilization
sperm are transported through the cervix, body of the uterus, and uterine tubes after ejaculation
What allows sperm to move?
sperm’s ability to swim
muscular contraction of the uterus and uterine tubes
Capacitation
removal of proteins and modification of glycoproteins of the sperm cell plasma membrane after which sperm cells can move
What causes muscular contractions of the uterus and uterine tubes?
oxytocin (posterior pituitary) and prostaglandins (semen) stimulate smooth muscle contractions
Fertilization in Uterine Tubes
one sperm cell enters the secondary oocyte, oocyte can be fertilized up to 24 hours after ovulation, some sperm cells remain viable in the female reproductive tract for up to six days (most degenerate after 24 hours), sexual intercourse must occur between five days before and one day after ovulation
Fertilization to Pregnancy
series of cell division occur for several days following fertilization, developing embryo passes through the uterine tube to the uterus, 7-8 days after ovulation (day 21-22 of the menstrual cycle) endometrium is prepared for implantation, implantation of trophoblast (developing embryo) begins
Implantation of Trophoblast
outer layer of trophoblast secretes proteolytic enzymes that digest cells of endometrium to form part of the placenta, placenta and ovary secrete several hormones throughout pregnancy (hcg, estrogen, progesterone)
Pregnancy Hormones
embryo and developing placenta secrete hcg
progesterone secretion increases during most of the pregnancy until end of third trimester
estrogen levels increase slowing throughout pregnancy (increase more rapidly near the time of birth)
hCG Functions in Pregnancy
causes the corpus luteum to remain functional
corpus luteum increases estrogen and progesterone levels
secretion increases rapidly and peaks around 8-9 weeks after fertilization
levels decline until around week 16 and then remain relatively constant through pregnancy
Pregnancy Hormones
corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogen that are essential for maintenance of pregnancy, placenta form and secretes progesterone and estrogen
3 Months Into Pregnancy
corpus luteum is no longer needed to maintain pregnancy
Perimenopause
menstrual cycles become less regular and ovulation often does not occur consistently around age 40-50 years, lasts 3-5 years
Menopause
cessation of the menstrual cycles, associated with changes in the ovaries, treated with hormone replacement therapy (hrt)
Changes in Ovaries During Menopause
few follicles remain, remaining follicles are less sensitive to stimulation by lh and fsh
Symptoms of Menopause
uncomfortable sweating (hot flashes), fatigue, anxiety, temporary decrease in sex drive, occasionally severe emotional disturbances