3.3.4 Normal profits, supernormal profits and losses
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
PROFIT- DEFINITION
diff between revenue and costs
CONDITION FOR PROFIT MAXIMISATION
profit is maximised when TR and TC are furthest apart, w/ TR above TC
also occurs when MC=MR:
sometimes, MR and MC may cross at 2 points and thus profit maximising point is where MC rises as it crosses the MR line
NORMAL PROFIT
return that is sufficient to keep FOPs committed to the business
costs include level of profit needed to keep the producer in the market and to cover the opportunity cost
so if firm covers its costs it earns normal profit
where AC=AR or TC=TR
SUPERNORMAL PROFIT
if profit is greater than normal profit , it is earning supernormal
occurs where AR>AC or TR>TC
LOSS
where firm fails to cover its costs
AR<AC or TR<TC
SHORT RUN AND LONG RUN SHUT DOWN POINTS
when a business is making a loss, it may not necessarily be best decision to shut down straight away- depends on AVC
LR- firm needs to make at least normal profit for them at stay in industry
SR- should produce as long as their revenue covers their variable costs
so short run shut-down point is where AVC=AR
LOSS- POS CONTRIBUTION
AVC<AR then firms should continue production
each good they make will generate more revenue than it cost for them to make it, and so this will help them to reduce the size of the loss by covering some of the fixed cost (pos contribution)
so should only shut down when their fixed costs increase
LOSS- NEG CONTRIBUTION
if AVC>AR then producing more goods will increase the loss- should leave industry immediately
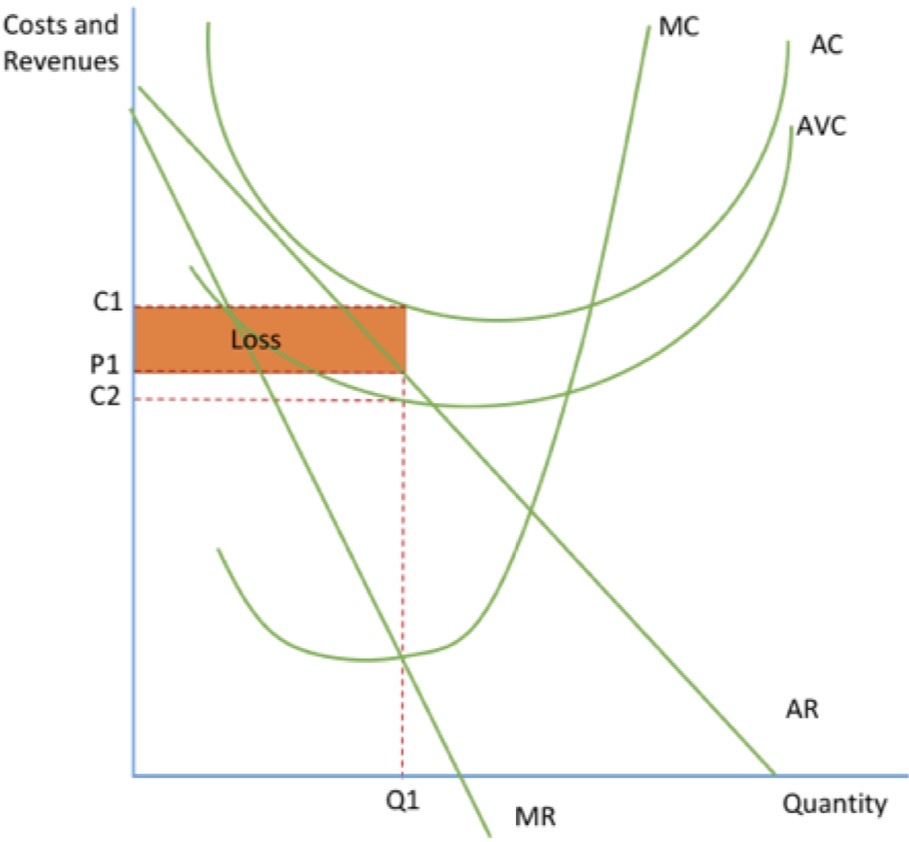
LOSS- DIAGRAM
if they’re profit maximising, they will produce where MR=MC at the output Q1
will mean their price is P1 and costs are C1
making a loss of the shaded area
but their AVC cost is only C2 and AR>AVC so they will produce in the short run