posc201 final jmu hammond
1/241
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
242 Terms
Spencer
Survival of the fittest, social Darwinism, society as organic
Henry Adams
Dynamo = infinity, electricity in faith
Pope Leo XIII
Church has protected liberty of man from innovators
Pope John XXIII
Church and economy
Jacques Maritain
Individual as part, person as whole
Niebuhr
Social behaviors of individuals and groups
What are the two questions raised throughout the conversation in the Republic?
-What is justice?
-What is more profitable/beneficial, justice or injustice?(why be just?)
What are the two models for the study and practice(application) of politics?
-politics in it's essence is about power-Thrasymachus
-politics is essentially about something other than power-socrates
What is justice, according to Cephalus?
Pay debts, be truthful, meet obligations
what is polymarchus definition of justice?
-justice is to do good for friends and harm enemies
-justice is giving what is owed
What is socrates definition of justice?
-justice is a virtue of the human soul, a quality of being, an objective principle(not based on conditions), eternal and universal
What is Thrasymachus definition of justice?
-justice is the advantage of the stronger
Dikaiosyne
justice, morality
adikia
injustice
pleonexia
outdo, do better, surpass others, have more
Glaucon's definition of justice
If people could do it and get away with it, they would be unjust
Gyges Story
Shepherd finding ring
isomorphic
the city and soul have the same shape
Socrates city in theory
-city of speech, true city, ideal city
-a city "coming to be": nature/necessity/need + function/role
-cities spring from necessity and allow us to fulfill our needs
-we rely on each other
-politics is natural and part of our nature
-aim: "in order to share", people perform their functions because of their nature
socrates second iteration(the febrile city)
-the city in theory is naturally good/just, but the luxurious city helps you understand how injustice emerges
-febrile city: a fevered city
-the fever is injustice
-the true city is burned by a fever(luxury)
-as the city grows, our wants become bigger than our needs
in true city there is no political power, but once injustice is introduced you need it
The guardians
-a guardians needs to always care for the febrile city and serve it
-like a watch dog
-the guardians need nature and nurture
-the nature of the guardian must be good, but they also need to be able to be trained/educated
myth of the metals
-in all of us, we all have a metaphoric metal
gold
-philosopher rules
-aspect of the soul: rational
-primary cardinal virtue: wisdom
silver
-auxiliary warriors
-aspect of the soul: spirited
-primary cardinal virtue: courage
bronze
-producers/distributors
-aspect of the soul: appetites and desires
-primary cardinal virtue: temperance, moderation, self-mastery, sophrosyne
socrates thoughts on the sophists
-plato says sophists only give the masses what they want and they call it wisdom
-the "huge strong beast"
-the sophists learn how to control the crowds
-the sophists know nothing in reality
-the sophist controls what they say to what the beast wants
-only the philosopher cares about what is actually true
-the rational, spirited rule the appetitive
-the sophists don't care about wisdom or truth
-sophists teach their student to win arguments
-Wisdom are the things that calm and soothe the strong beast
Socrates’ reforms
guardians do not possess private property
Men and women share power
Guardians share spouses and children
Philosophers should rule
Plato’s lesson about the essence of politics
private wealth and political power must be separate
Superficial differences are irrelevant
Public good and private interests must be separate
Reason should always guide power
true captain
-sailors think they should run the ship(city) but they haven't learned how to navigate yet
-they don't understand that a true captain must know the art of navigating in order to be a captain
-in the eyes of the sailors, the current captain is a 'good for nothing stargazer'(this is the philosophers, they understand there is an art to running a city)
ontology
the theory of being, what is
epistemology
-theory of knowledge, knowing
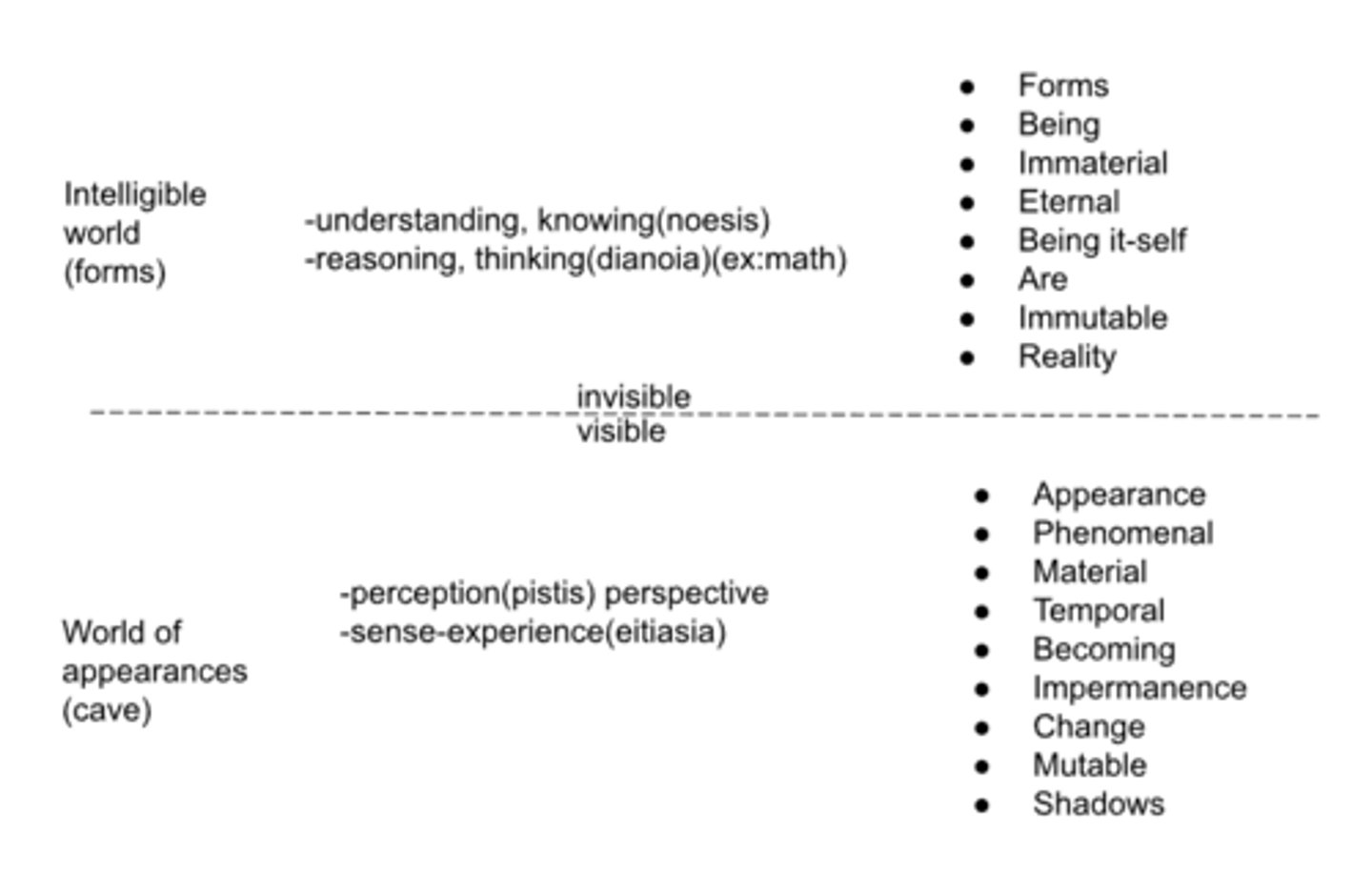
the divided line/forms
-how humans come to know
-the forms are more real
-as we go up the forms we have a deeper understanding of reality
-eidos: forms(ideas)(types)
Allegory of the cave
-what you see is not all of reality
-all the cave men experience is what is right in front of them(the shadows on the wall), but they do not know they are stuck. It is all they know. What they don't know is behind them
-one is able to escape their chains and see's the fire behind them
-what they thought was real was caused by the fire and reality is more then what they originally thought
-plato is not saying our senses are bad , but if we only rely on our sense we only know a fraction of what is real
-the person who escaped see's another source of light and follows it and finds themselves outside the cave
-cave wall to cave(larger pocket of reality) to whole world(whole reality)
the allegory of the sun
-once he gets outside, the fire is painful to his eyes at first
-outside the cave is the realm of being
-the shadows are real, but it is only an essence or reflection of the real thing
-the philosopher is the one outside the cave
-the man goes back down to tell the other of what he found but they don't believe him
-the philosopher now understands the cave more than anyone else
-plato thinks ideally reason should guide power, but in the cave power guides reason
-the sun is the highest form in the allegory of the cave(the form of the good)
-no matter how bright the fire in the cave is, it will never compare to the sun
-the good makes cardinal virtues possible
-we love wisdom because that draws us to the good
-as beautiful as truth and knowledge are, good is more beautiful
-the forms are more real than material
Where do Aristotle and Plato converge
-Plato: every craft, light of inquiry, and action seems to seek some good
-Aristotle: understand the good but not to adopt the forms, disagree with friends to preserve truth, different ways to think about the good
qualified good (Aristotle)
-secondary goods
-serve another good
unqualified good (Aristotle)
-good in itself
-directive/primary
-good without further explanation
Aristotle’s four explanatory causes
-material: that "out of which" it is made
-efficient: the source of the objects principle of change or stability
-formal: the essence of the object, what somethings meant to do(ex: formal cause of chalk is to write)
-final(telos): end or aim(ex: the final aim of chalk is to convey knowledge)
arete
excellence, character, moral virtue
the doctrine of mean
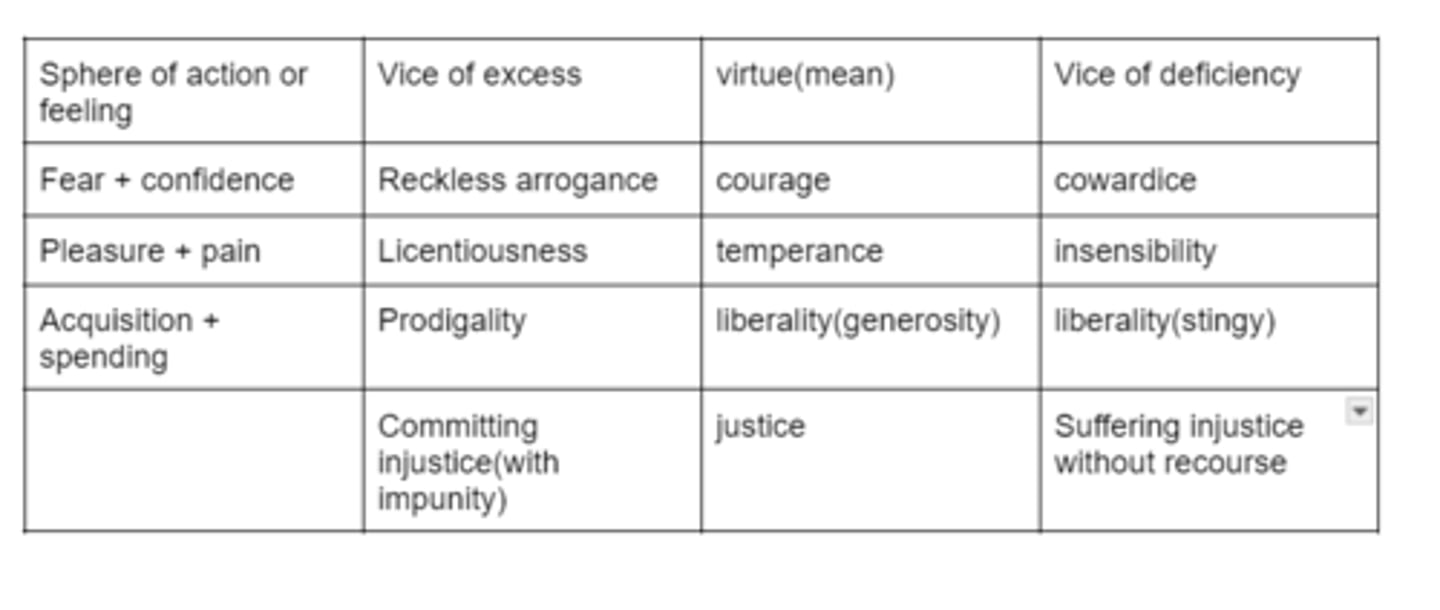
Aristotle's general qualities of justice
-lawful and fair
-decency
-produces eudaimonia
-complete virtue, aims at another's good
Aristotle's general qualities of injustice (adikia)
-lawlessness
-overreaching(pleonexia)
specific kinds of justice (Aristotle)
-proportional(distributed, desert, merit)
-reificatory(corrective, restorative)
-political(legal and natural)
proportional justice
-admits some inequality
-whatever it is your distributing
-social goods that we value as a community like Honor. can be discriminatory based on merit.
reificatory justice
-corrects an inequality
-aims at equality
legal political justice
based upon laws that will vary from place to place
natural political justice
-what is just by nature
-eternal and constant
-physein dikaion
-will not vary from place to place
Aristotles critique of platos city in theory
-excessive unity destroys a city
-Aristotle thinks justice and friendship are essential to political life
-Plato undermines friendship(when everyone is friends, then friendship is watered down)
-Guardians are deprived of happiness and if they aren't happy, how could they govern a city?
Aristotles search for an ideal city
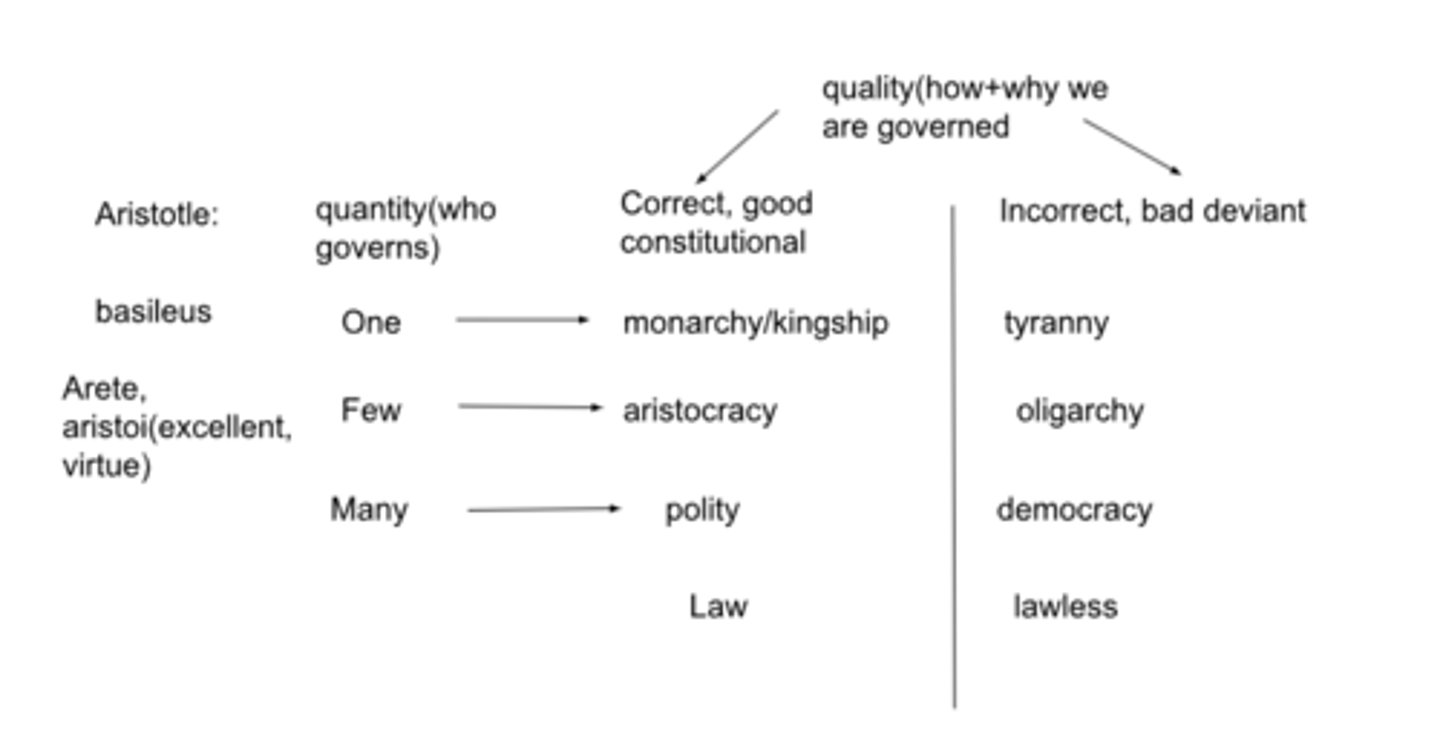
Why is oligarchy, democracy, and tyranny bad
-oligarchy benefits wealthy
-democracy benefits poor
-tyrants rule like masters over slaves. masters are those who rule but cannot be ruled. slaves are those who are ruled but cannot rule
why is monarchy, aristocracy, and polity good
-rule for the common good or benefit (GOVERN citizens)
plato and aristotle express phronesis
-practical wisdom
-to engage in political activity requires common sense and good judgement
monarchs vs tyrants
-monarchs and king have authority but understand that its limited
-tyrants recognize no limits to their authority
-even the best person, without limits, will become a tyrant
-reason must guide power. you aren't going to have philosophers rule, you must have law rule. Law is reason without passion
What is the best regime according to Aristotle?
Polity and aristocracy
Regimes according to Plato-laws
-plato says we must rule over ourselves as kings
-anyone can rule if they are clever enough but not every can navigate the ship(problem with democracy)
-there are necessary appetities that are in the city of theory and as the regimes become imperfect, unnecessary appetites arrive
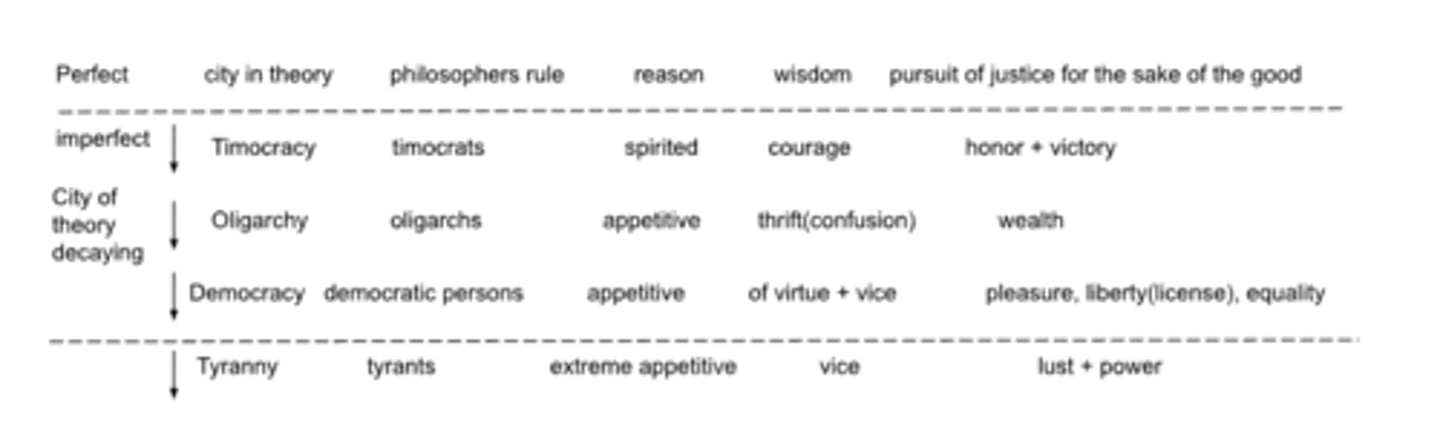
Whats wrong with democracy according to Plato
-assumes all pleasure are equal
-doesnt compel good to rule
-democracys are permissive
-extreme freedom will eventually lead to extreme slavery, which will eventually lead to the worst regime, tyranny
-liberty without license
-appears to be the most beautiful but is not
Platos Athenian stranger
-all other regimes emerge from monarchy and democracy
-monarchy represents authority; can lead to despotism(extreme)
-democracy represents liberty; can lead to anarchy(extreme)(mob rule)
-its essential for a political system to combine monarchy and democracy to avoid the extremes
-good judgement is the benefit of monarchy(phronesis) but if you go towards the extreme you lose good judgement
-freedom and friendship are the benefits of democracy
Athenian stranger - second best city
-the stranger says the city of theory is fit for gods but unobtainable for humans. The mixed regime is the "second best city". The city of theory should still be the ideal and we should still resemble our cities after it
-since philosophers can't rule, the laws provide reason. Those who govern us are servants to the law. The guardians are servants
Socrates arguments about injustice
Says it’s better to suffer injustice than to commit it
socrates jar metaphor
-say you have a large jar that you fill and seal with a lid. say there is another jar with holes/cracks and the spoon being used to fill the second jar also has holes in it. whatever you try and put into the second jar will leak out and never fill
-the filled jar represents the moderate soul, the appetites are satiate. represents temperance
-the jar with hole represents insatiable appetites. this person is a slave to their appetites
Overall Epicurus and epicureanism
-you shouldn't worry about things beyond your control, politics cause pain/disturbance
-first innate good: pleasure
-self-sufficiency, prudence
what is stoicism?
The boundary between fate and freedom
Cynics
-they think politics should be avoided completely, we need to turn back to nature
-we should become citizens to the world(cosmopolis)
What does Seneca think?
-Seneca says we are all chained to fortune, fate, and necessity. Much of what happens to us is beyond our control
-no situation is so harsh that a dispassionate mind cannot find tranquility
-apatheia: dispassionate
-maintain an even temper, no matter what happens to you
-avoid luxury
-all excesses are luxurious, but modern prosperity is most dangerous of all
Cicero's thoughts on law
-Law is the highest reason in nature
-natural Law is not a product of human thought, but civil law is
-natural Law is the primal and ultimate mind of God
-We are not God, but we share reason with the divine
-those who share Law, must also share natural justice
-Law as right reason -> reason shared by all
-he see's his duty to Rome
-says there's a natural inclination to love our fellow humans
-Cicero adds a quote from Carneades
Carneades
-Carneades is opposed to the ideas of Cicero
-laws are obeyed because of the penalty's they would inflict, not because laws of our own justice
-men are not just by virtue
-there is no natural law, humans are led by their own self-interest
Polybius's typology of regimes
-only solution to not have regimes deviate is to mix regimes
-if you combine elements of the good regimes, that will reduce the chances of the regime becoming corrupt
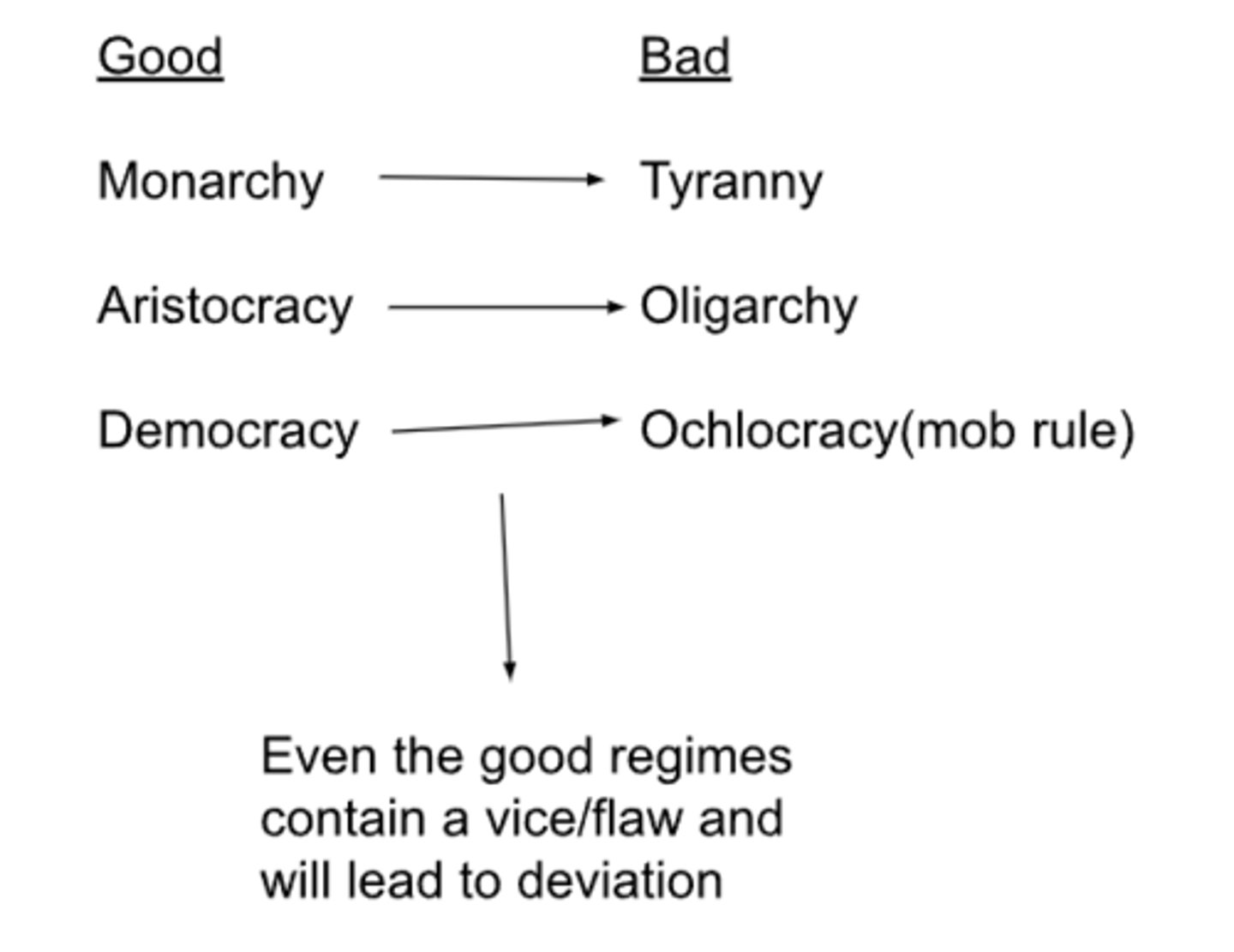
Cicero's thoughts on regimes
-a composite/mixed regime
-monarchy is the best of the 3 good regimes, but a mixed regime is the best
-Rome is an example of the best city
St. Augustine influences and ideas
-influenced by the Christian faith
-influenced by Cicero and Plato
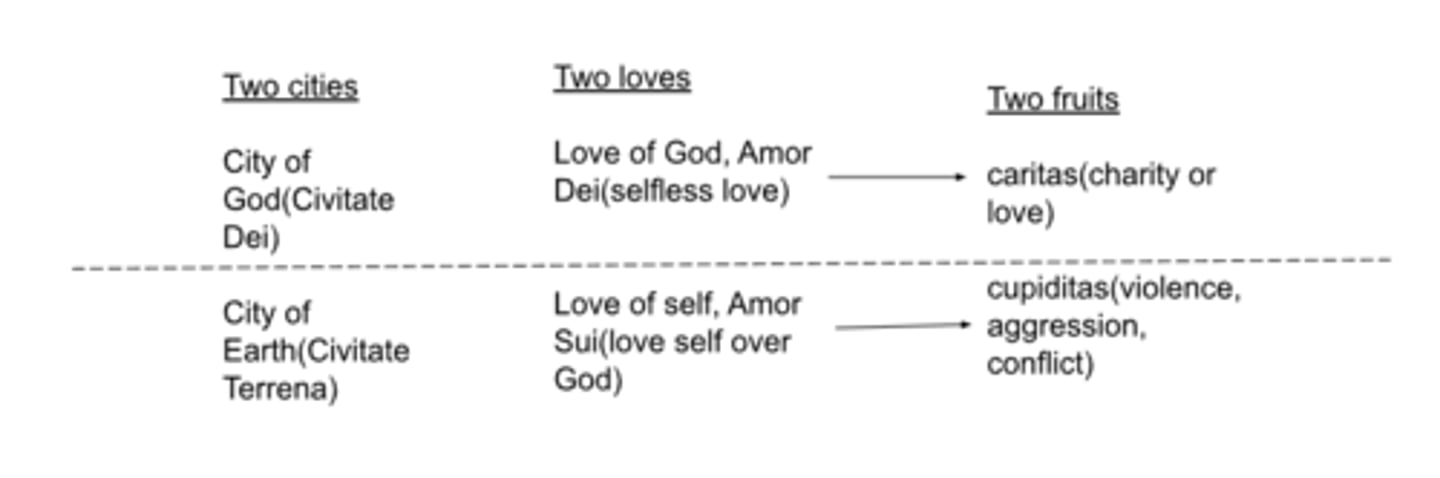
-two cities: there are 2 kinds of human societies, 2 cities
St. Augustine two cities
-any city that is not the city of god is not perfect and will have a hard time being just
-sin has not obliterated our original goodness, our inner goodness is a gift from god and will always remain
-the only truly just city is the city of god
-the rulers of the earthly city are covetous but also have impunity
-emperors and pirates are both covetous, unjust, etc.
-even benevolent cities contain injustice
Alfarabi's aim
-heavily influenced by plato
-the virtuous city
-aims at encouraging virtue of citizens
-understand principles of being itself
-even if we never achieve the virtuous city, we must aim for it
Plato vs St. Augustine vs Alfarabi in terms of cities
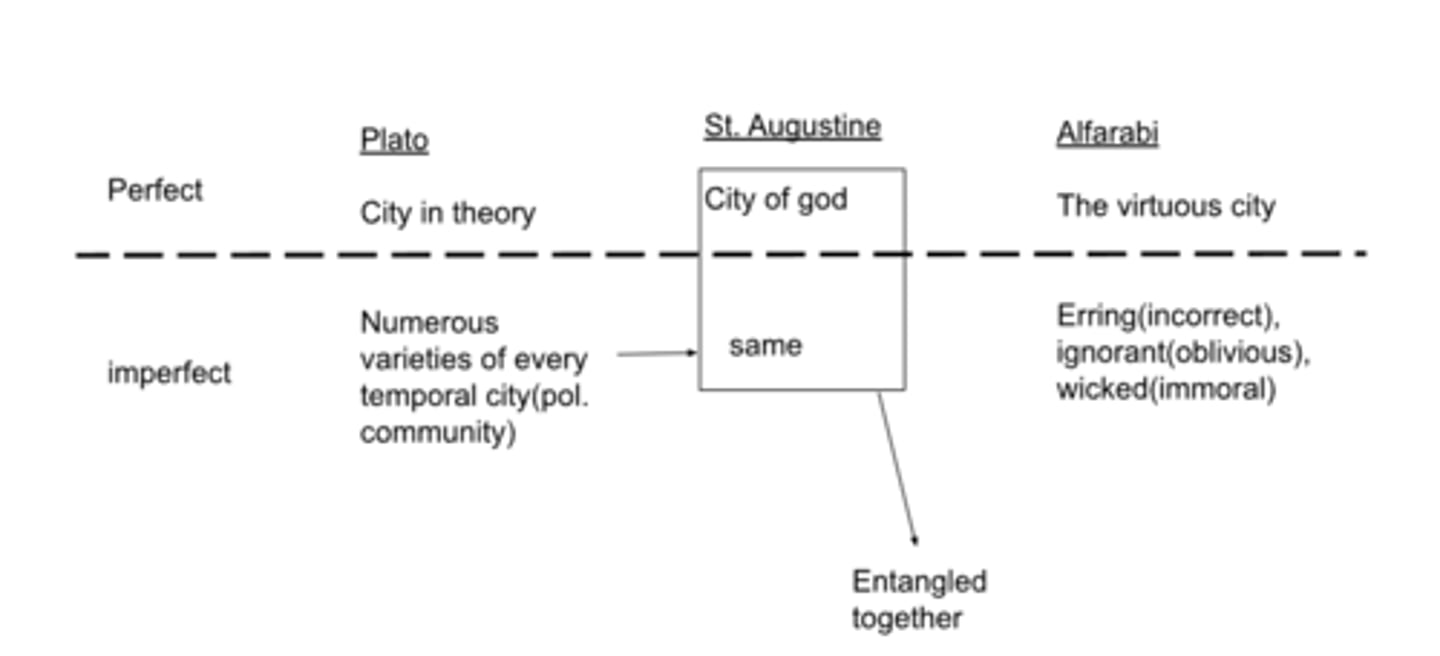
Plato vs Alfarabi
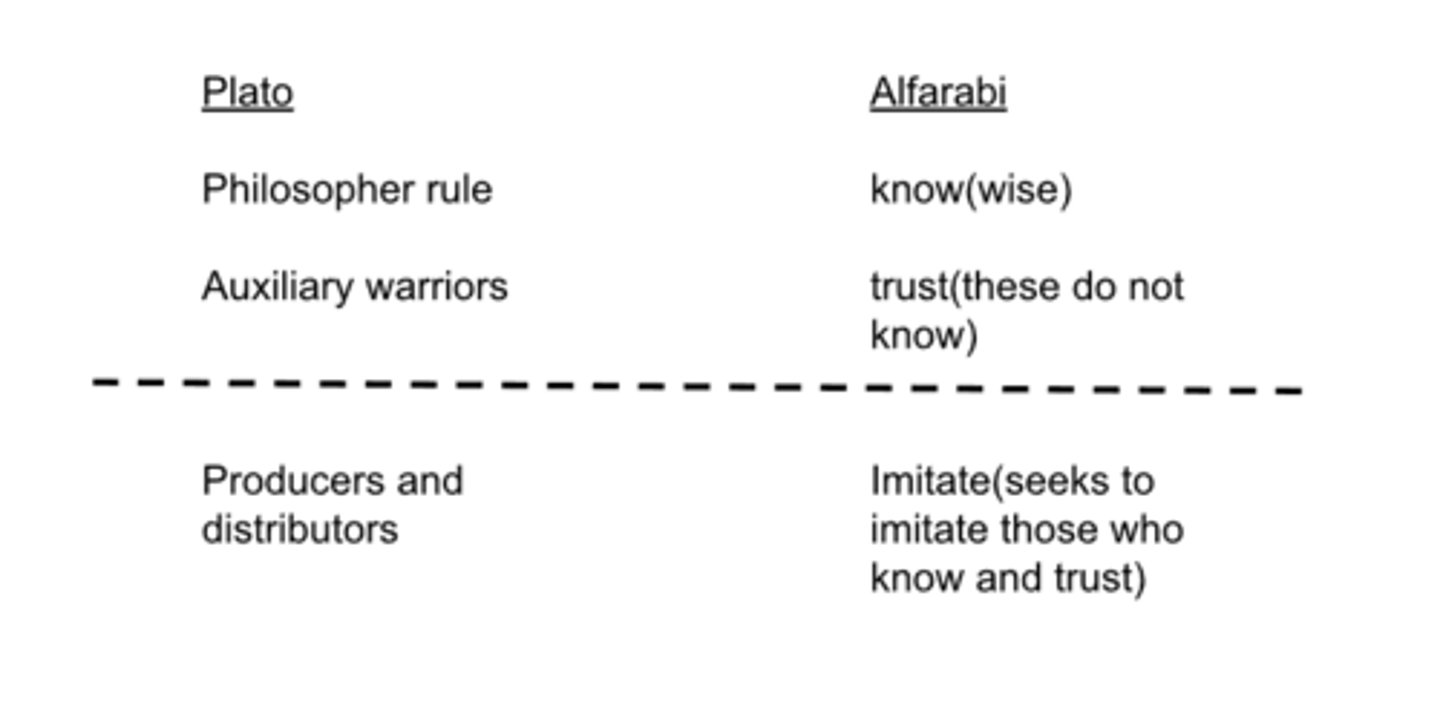
what are the 4 cities for Alfarabi?
-virtuous city(goal is virtue)
-erring(incorrect)(a kind of happiness that is not true happiness is established for, and represented to, them; and actions and opinions are prescribed for them by none of which true happiness can be attained.)
-ignorant(oblivious)(doesn't know, innocent, doesn't know better)
-wicked(immoral)(understands but doesn't care)
what are the goals of the imperfect cities?
-indispensable(necessity)
-vile(like an oligarchy)(goal is wealth)
-base(pleasure)
-timocratic(honor + victory)
-tyranny(power + domination over others)
-corporate association(democracy)(liberty + equality)(includes all types of people)
There are 2 ways to reach a virtuous regime, move toward:
-indispensable
-democracy(mixture of best and worst)
what does St. Thomas Aquinas believe about justice?
-influenced by St. Augustine and Aristotle
-each human being contains the light of reason
-human beings by nature are social and political
-the political community community is the perfect community, therefore we can talk about justice in our political communities
-it is possible to have justice in our cities(perfect, not flawless)
St. Thomas Aquinas and laws
-the whole purpose of law is to coerce virtue and lead human beings to virtue
-laws enable us to exercise the habits that will lead us to virtue, laws will not automatically make us virtuous. Gradually over time, it will lead us to virtue
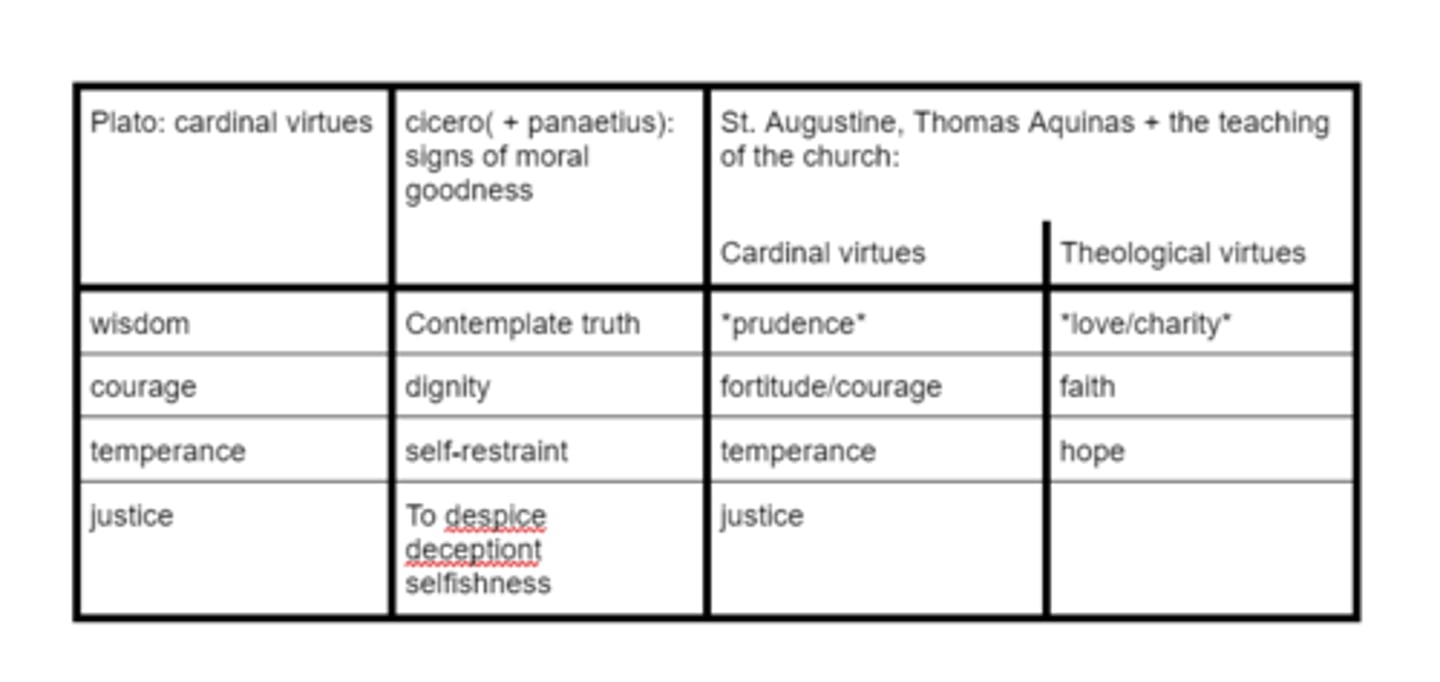
Thinkers and their virtues
*deception
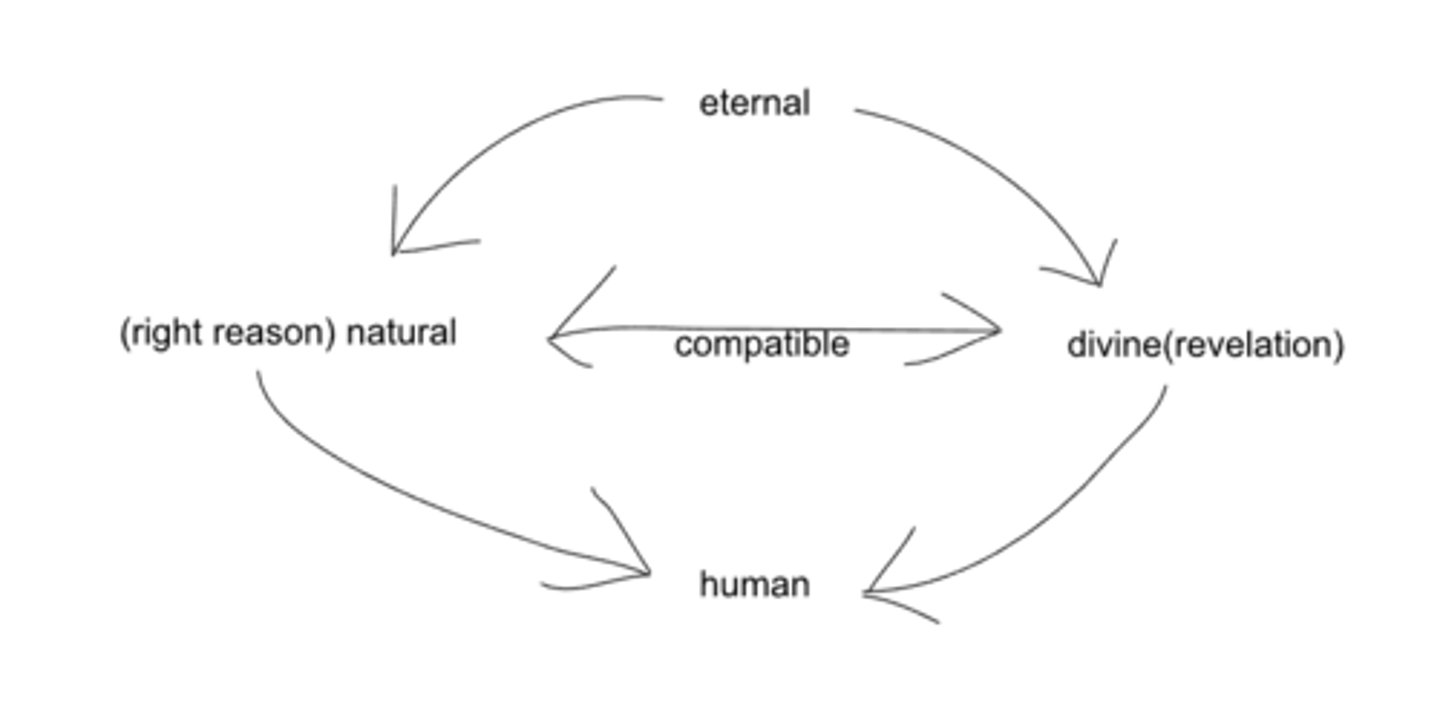
thomas aquinas's 4 kinds of laws
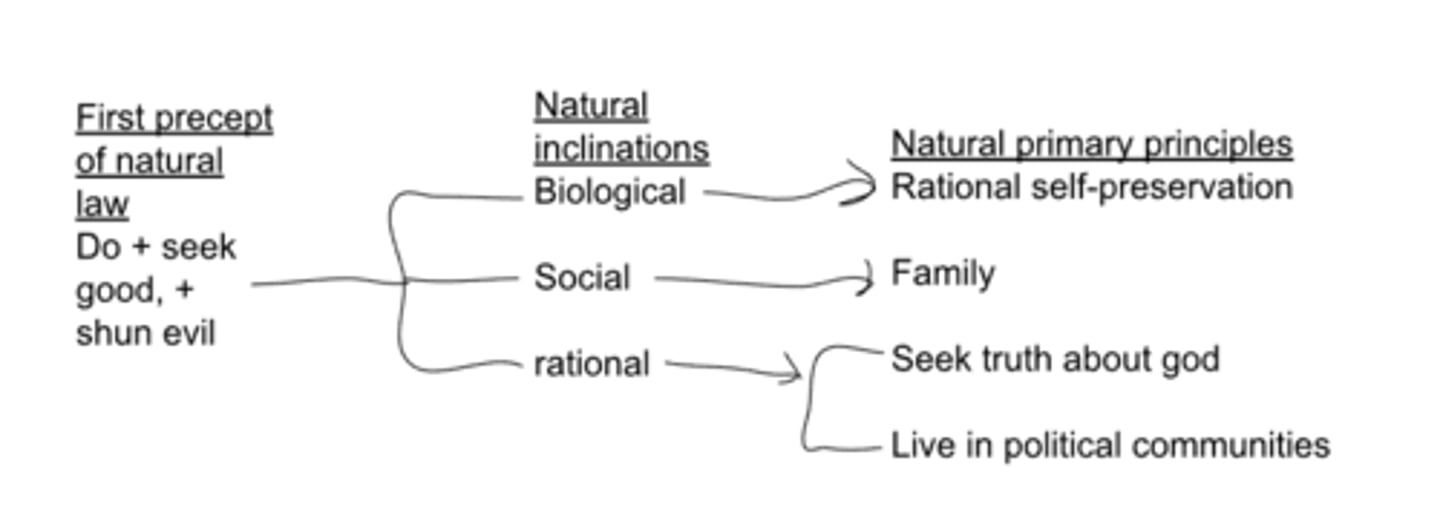
thomas aquinas first precept of natural law, natural inclinations, and natural primary principles
4 ways in which laws are just
-ends(goals)
-authority
-form
-aligned with the higher good(divine good)
When are laws unjust?
-laws are unjust if they violate any of the criteria(ends, authority, form, divine good)
-unjust laws don't have obligatory force(we aren't obligated to follow it)
-the primary rule of reason is natural law
-unjust laws aren't even laws
the best regime according to thomas aquinas
-monarchy(says this is the best in one place)
-example we find in nature(god is almighty king)(animals have a king)
-mixed regime(says this is the best in more than one place)
-judicious combination of monarchy, Aristocracy, and democracy(natural law and divine law)
3 problems raise in a Christian polity
-on private property
-on war
-on obedience and rebellion
on private property
-scriptures says people share resources/revenue
-3 ways to justify private property(reality of political world)
1.human beings are more careful for things that are their private property
2.helps human conduct their affairs in an orderly fashion
3.in private property we live in our own peace
on war
-we should seek peace, but sometimes thats not possible
-if you do resort to war, you should engage in war justly
-war should be last resort
-3 criteria to be met for war to be conducted justly
1. have to have legitimate political authority to declare war
2.must be a just cause to wage war(to defend yourself or an ally)
3.the intent must be right
on obedience and rebellion
-rebellion by nature is a mortal sin
-tyranny is unjust(they only seek their own good)
-to resist a tyrant does not count as rebellion
-tyrants insight discontent and rebellion
-the tyrants have rebelled against us, so to rebel against them is ok
what did Machiavelli think of human appetite
-human being are naturally envious
-human appetites are insatiable, but our circumstances only allow us to realize only some of those desires
-men are constantly dissatisfied and wanting more
-he refused to be intimidated by his critics and he believed he is exploring uncharted territories
comparing Machiavelli to the "mirror of princes"
-Christine de Pizan
1.a young prince must be taught by a tutor what is good and virtue
2.a good prince ought to be loved by his people
-john of salisbury
1. a prince performs ministry faithfully
2.a prince doesn't owe his life to himself, but rather to others
3. a prince is father + husband to his subjects
-Machiavelli
1.it is safer to be feared rather than loved. make sure you are not hated (some say Machiavelli is a teacher of evil)
Machiavelli's: the prince central teachings
- a ruler must learn how NOT to be good(to do this they should read Machiavelli's book intelligently)
-a ruler must maintain the appearance of being good
-a ruler's primary concern must be war
-a ruler must lay good foundations for power (good laws/good armies)
-"si guarda al fini"
1.the end justifies the means
2.people judge by the outcomes
Who is Machiavelli's prince examples?
-cesare borgia
-virtu(ideal ruler)
-NOT julius caesar
-moses, cyrus, Marcus Aurelious
-tutor of Achilles
-a princes needs to be prepared to do vicious things, but appear to be virtuous
-the rational must guide the irrational, but Machiavelli puts the irrational on the same level as rational(and maybe even higher)
Cesare Borgia
-he put one of his liutenits(Remiro d' orco)
-Borgia is the true power, but he steps away and gives d' orco power
- d' orco was cruel and the people hated him(even though Borgia was the one behind him)
-Borgia let d'orco do his dirty work and then Borgia killed him
-Borgia knew the importance of appearance. he knew how not to be good
Machiavelli's prince analogy
-a prince must be a fox and a lion
-detect traps like a fox
-lion has the strength to chase away the wolves
Machiavelli's typology of regimes
-good regimes(monarchy, aristocracy, democracy)
-bad regimes(tyranny, oligarchy, ochlocracy)
-the 3 good ones don't last long and the 3 bad ones are evil
-avoid the simple types and make a mixed regime(it would have checks and balances)
-have a prince or have a republic
-free cities are wealthy and powerful(ex: Rome and Athens)
-not just deposing tyrants but also deposing kings
Machiavelli ideal city
-ideal city is Republican Rome
-a republic is better than a prince
-people participate in republic
-the people could be unstable, but so could the ruler
-people are more prudent, stable, and are better than a prince
-good institutions + good laws will be good or better than a prince
Machiavelli on religion
-religion is good because it's useful( could be used to maintain power), not good because it's true
-Christianity only cares about appearance in the afterlife(he rejects it, he worries about this life)
-he praises savagery(they care about this life)
-says princes can't be christian
-if you are a ruler, how can you be a good christian?
-a ruler can appear to be a good christian, but can't afford to actually be it
-machiavelli focuses on what there is, not what there ought to be
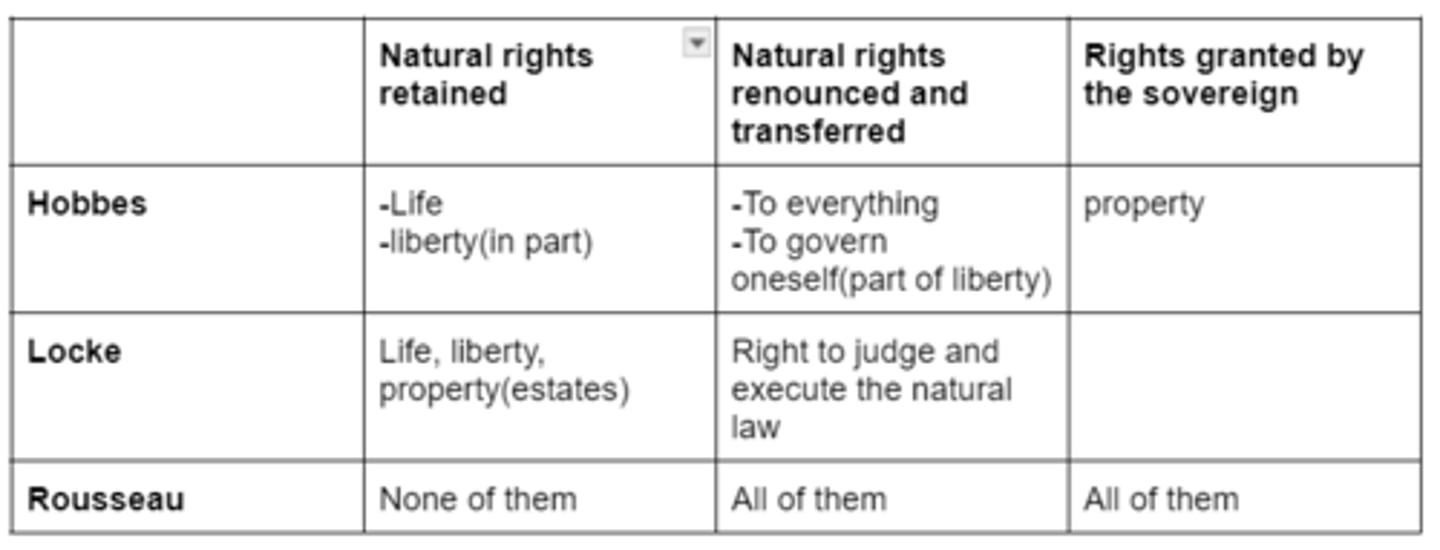
Hobbes vs Locke vs Rousseau on the natural rights retained, natural rights renounced, and rights granted to the sovereign
Who thinks human beings are social and political by nature?
-plato
-aristotle
-cicero
-St. Th. Aquinas
-etc.
who thinks human beings are neither social nor political by nature?
-hobbes
-rousseau