Biology- Lipids and Membranes
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is a lipid?
Macromolecule, not a polymer, hydrophobic, all are made from O, H and C atoms
What is its role in living organisms?
- High energy yield - can act as an important energy source
- Can act as an energy store in plants as lipid droplets and in animals is fat
- Act as an insulating layer - form waxy, cuticle around leaves and stems of plants
What is a triglyceride made of?
Three fatty acids joined by a molecule of glycerol
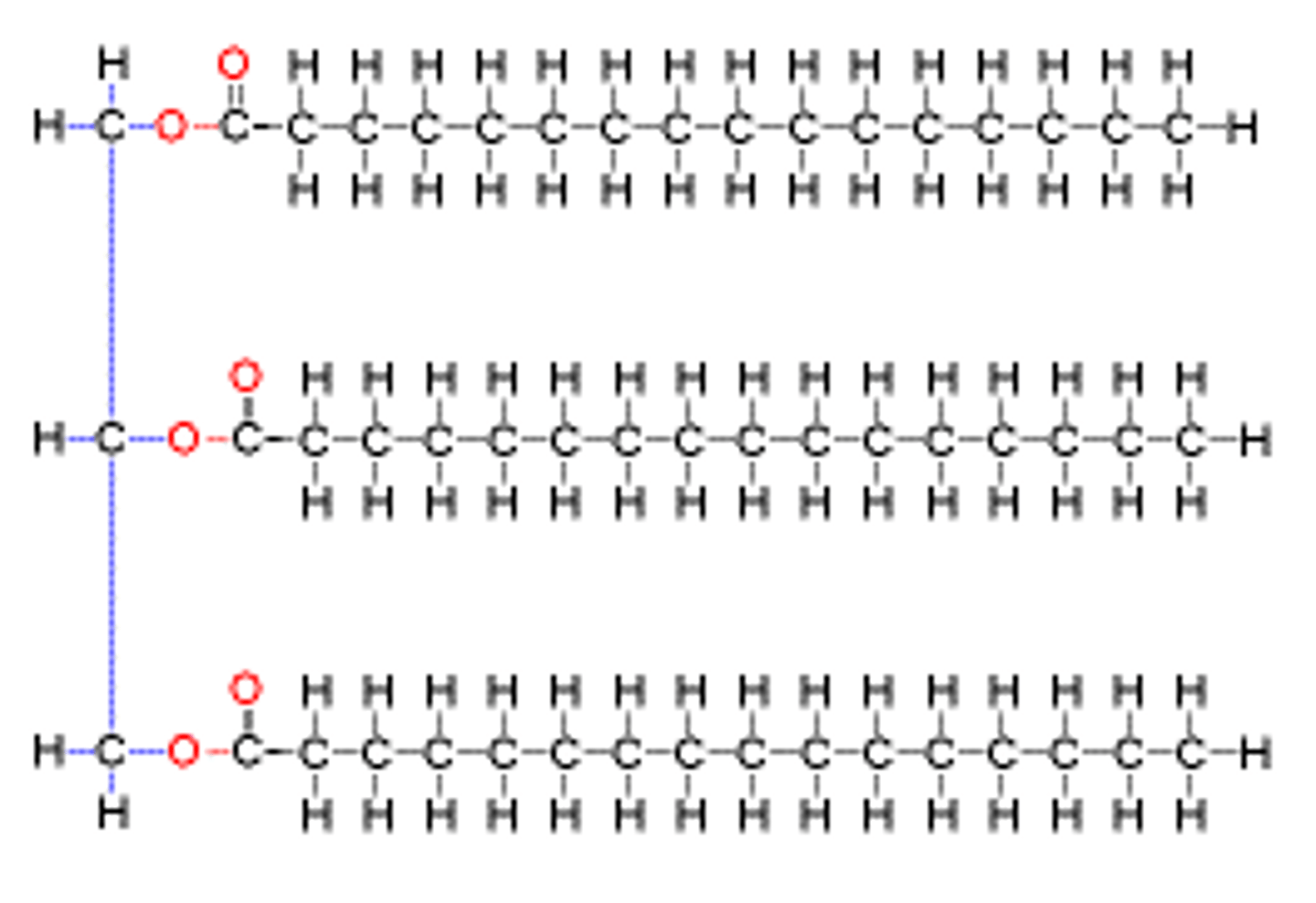
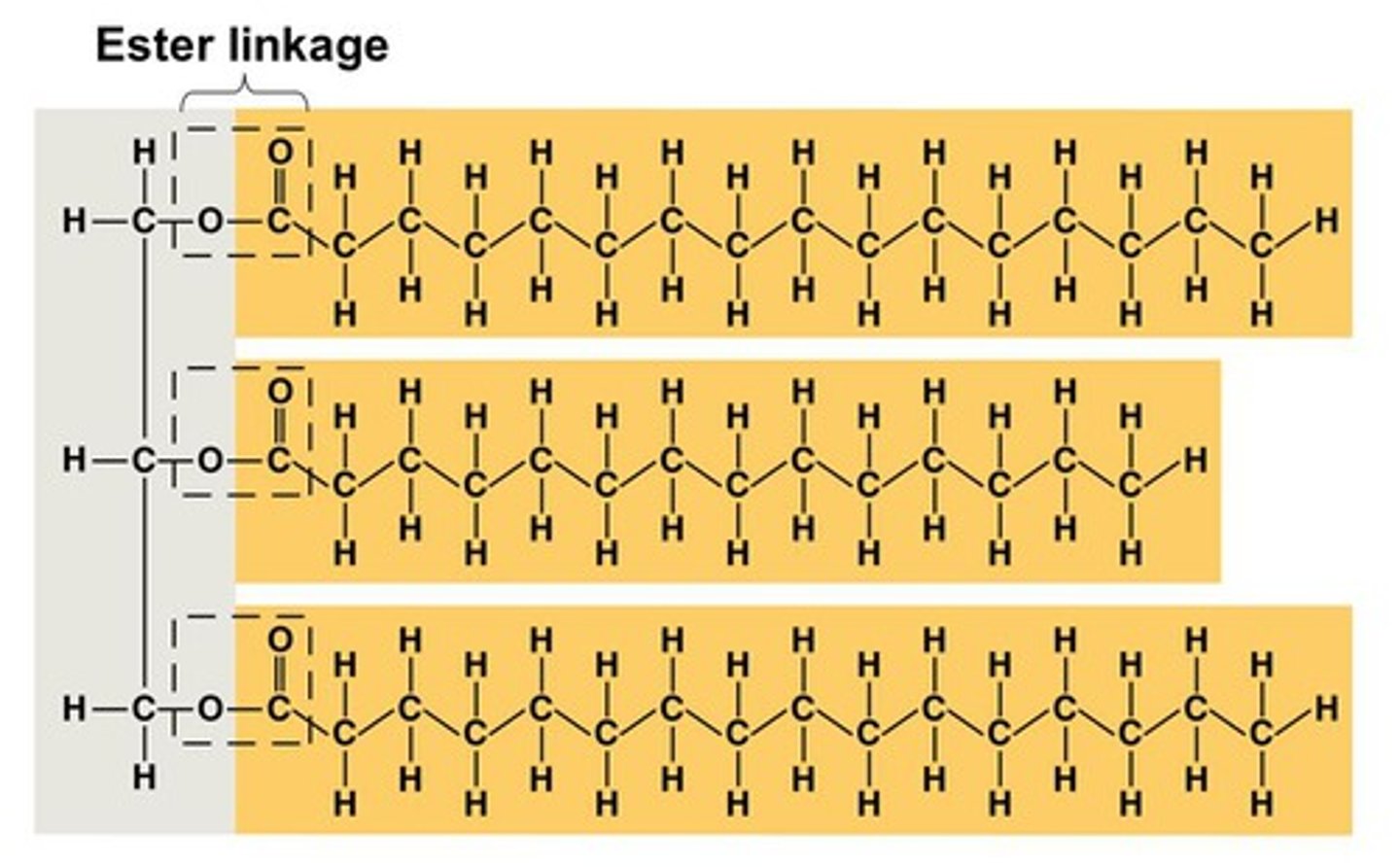
What is a triglyceride?
Fats and oils formed from a condensation reaction between fatty acids and glycerol
What is a fatty acid?
A molecule with a hydrocarbon chain and a carboxyl acid (contains a carboxyl group)
What does a reaction between a fatty acid and glycerol form?
It forms an ester bond
What is an ester bond?
When an organic acid joins to an alcohol by a condensation reaction
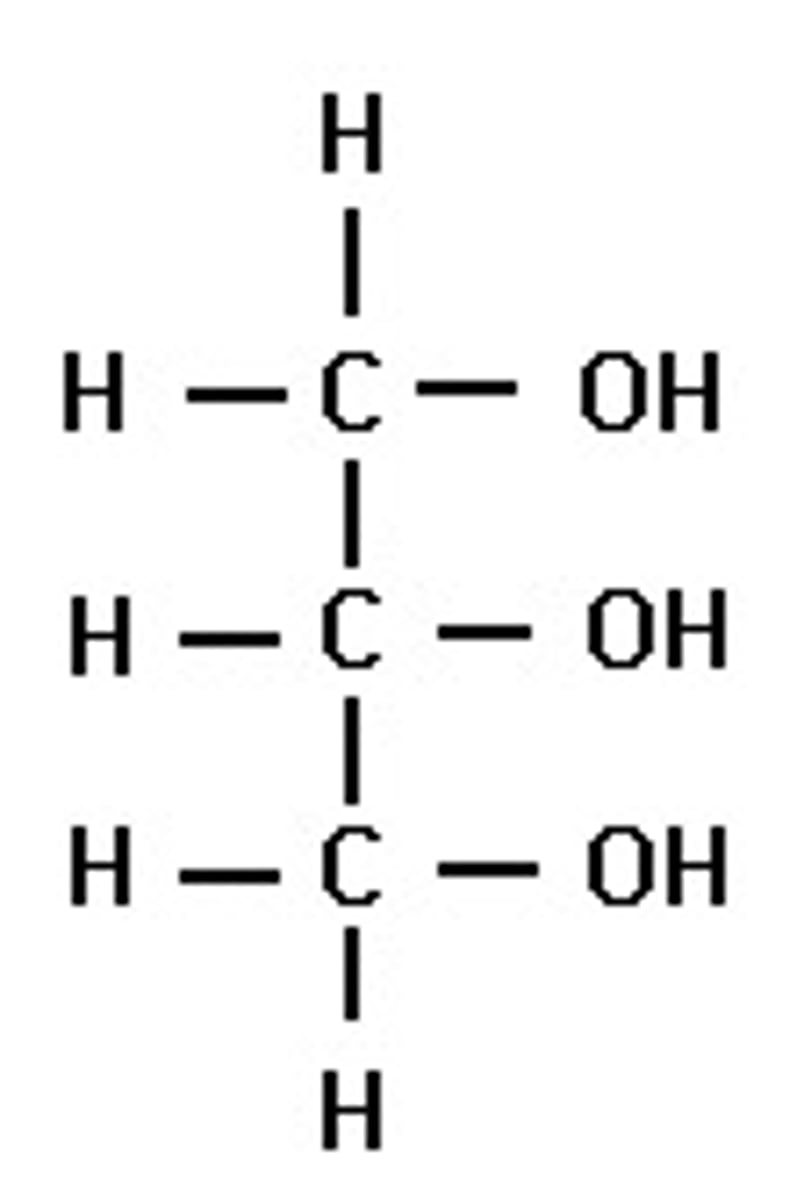
What is a glycerol molecule?
Three carbon atoms in a line surrounded by H atoms and on the right side each carbon is attached to an OH group
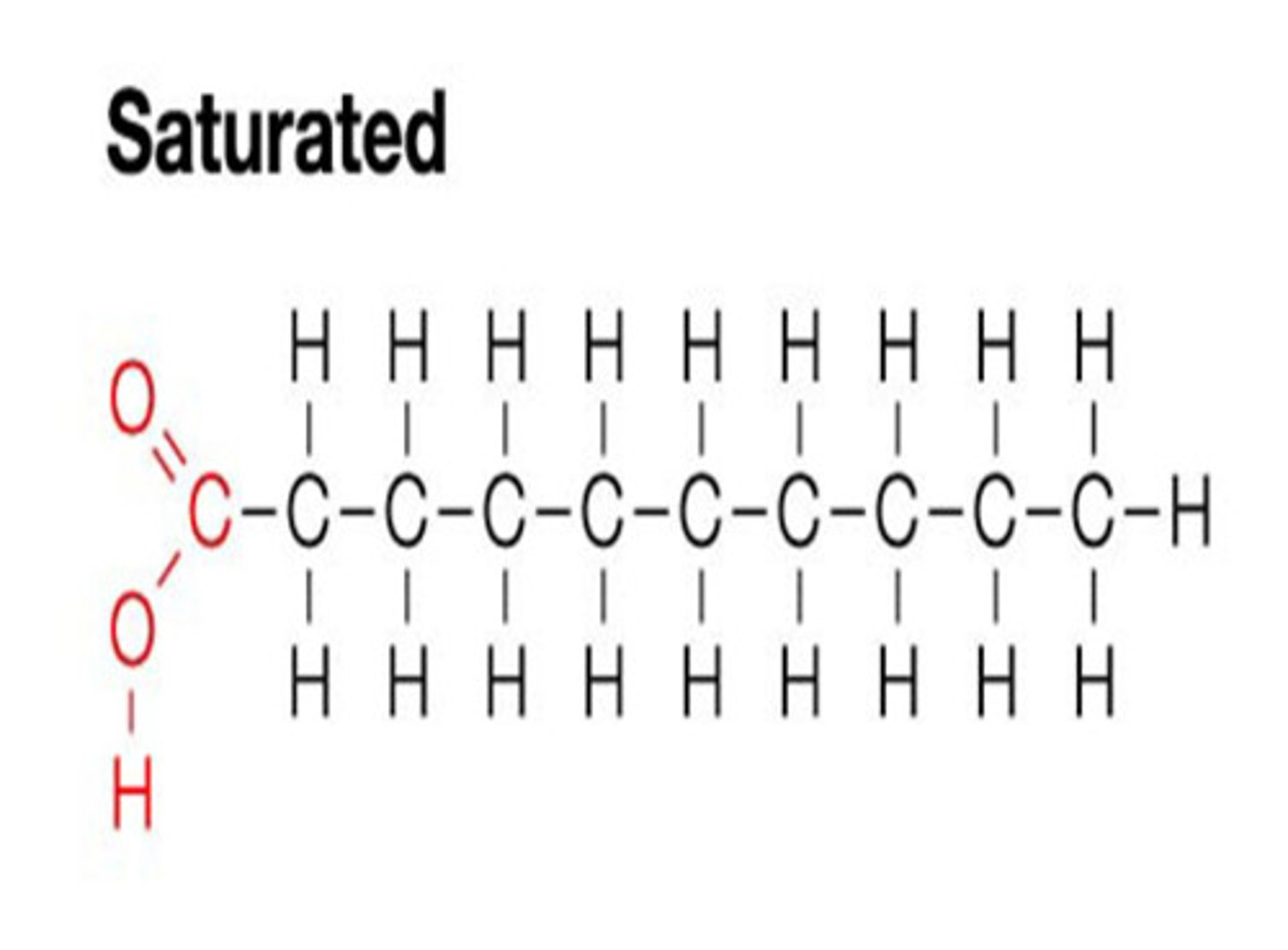
What does a saturated fatty acid mean?
Fatty acid with a long hydrocarbon chain when none of the carbons are linked with a double bond
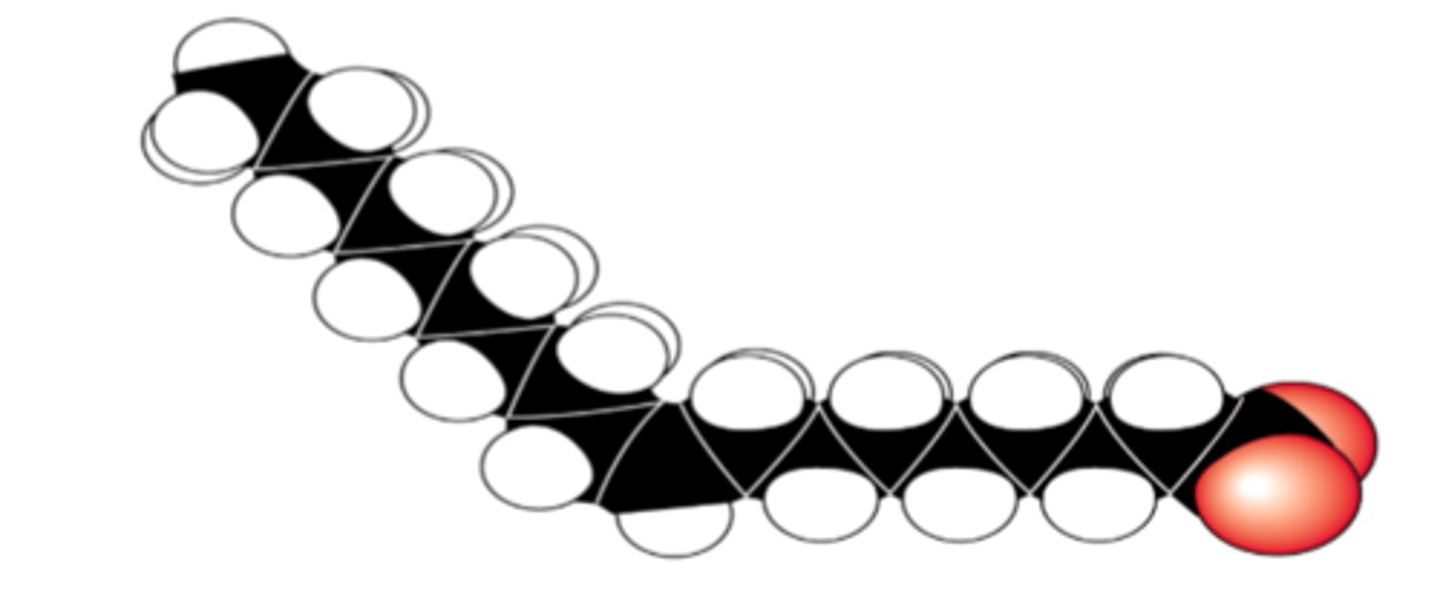
What does an unsaturated fatty acid mean?
Fatty acid with a long hydrocarbon chain where there are double bonds between some of the carbon atoms, where only one hydrogen atom is bonded to each of the carbon atoms on either side of the double bond
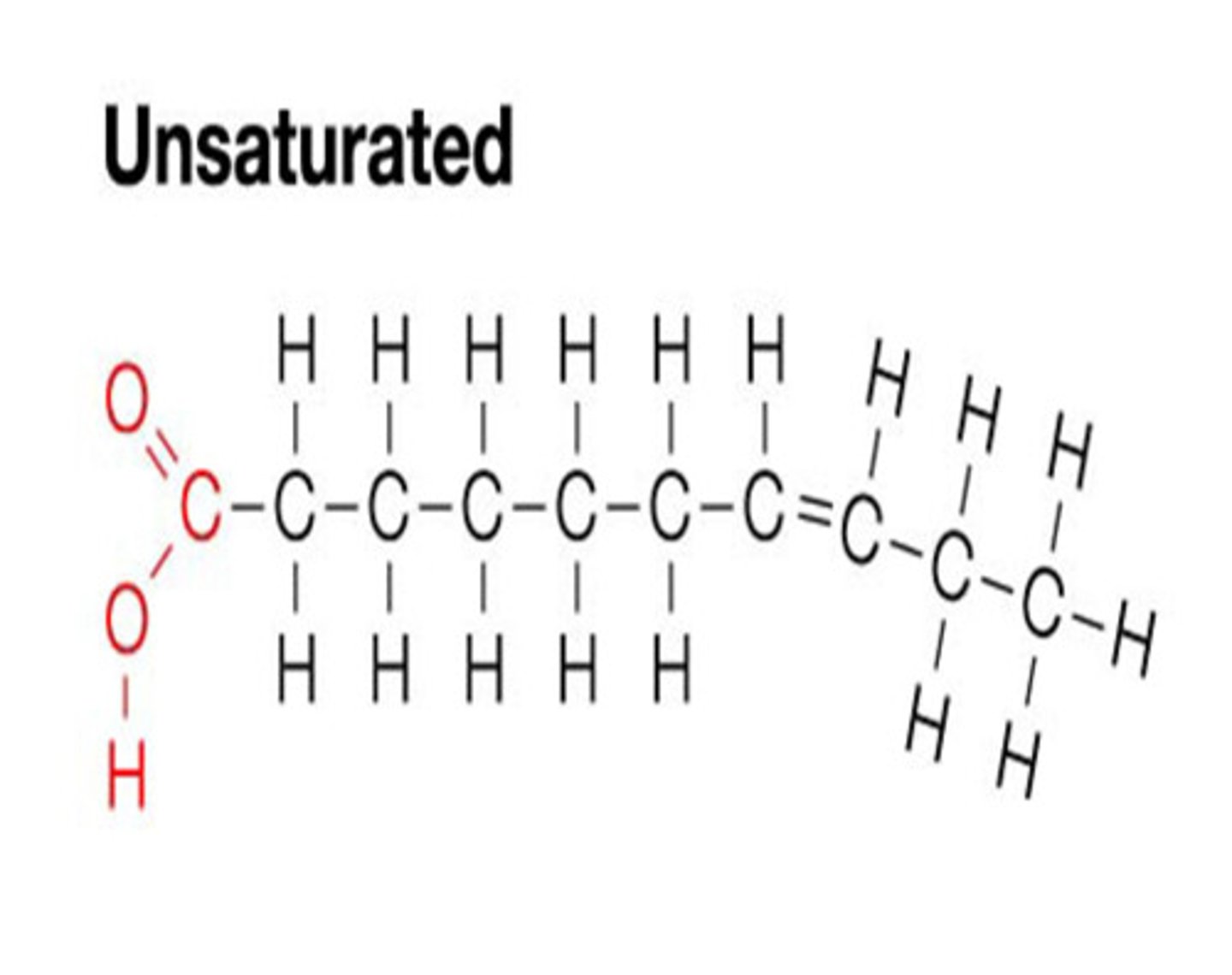
What does a double bond cause?
A kink in the hydrocarbon tail
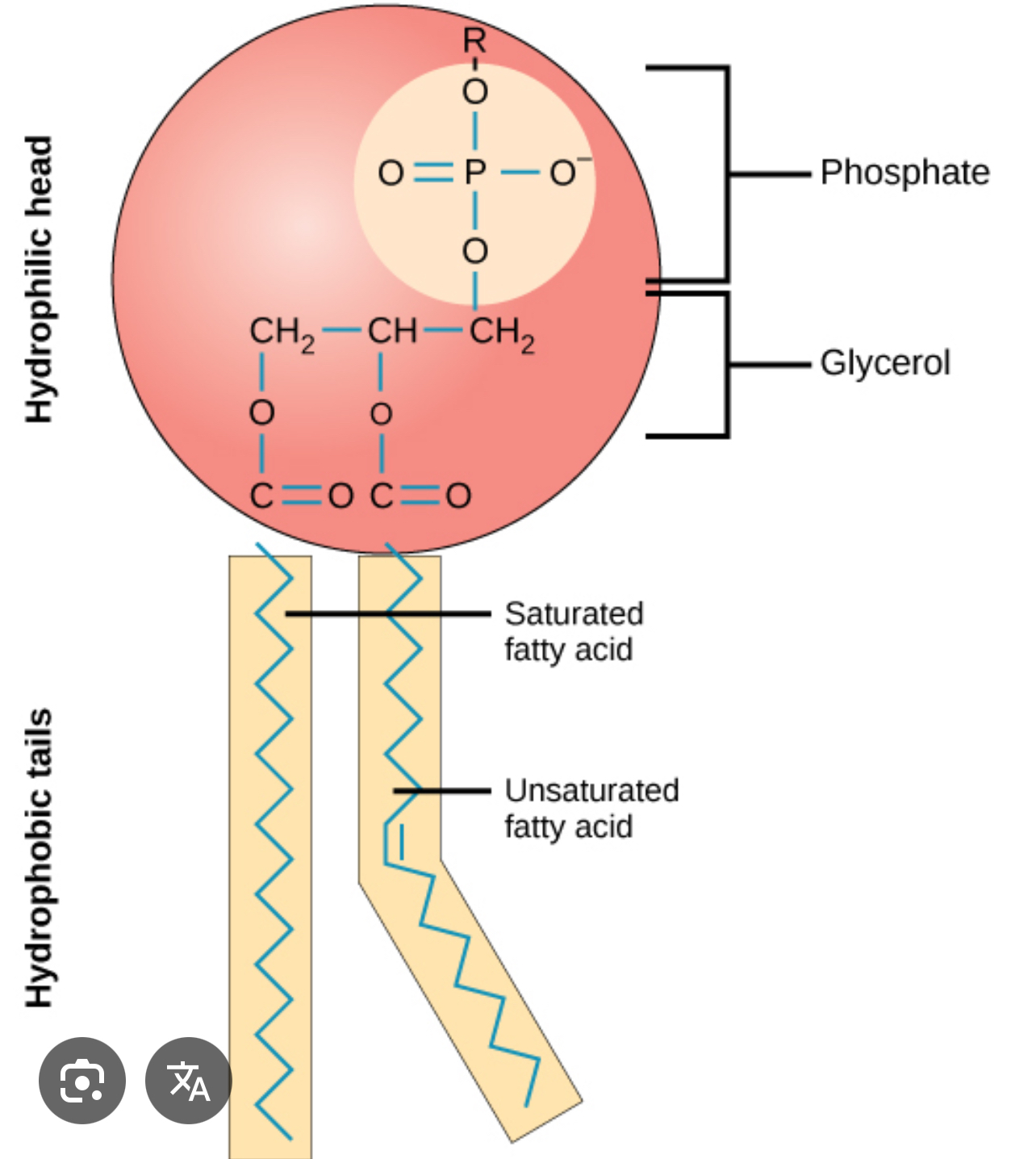
What is a phospholipid?
They are present in all biological membranes, similar to triglycerides but have two fatty acid chains
How are phospholipids formed?
The glycerol molecule connects to the phosphate group to create a head and two fatty acids chains connect to the glycerol
Where are the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions?
The head is hydrophilic and the tail is hydrophobic
What structure does this create?
The hydrophobic cause face away from the watery cytoplasm. This creates a membrane barrier to the cell that prevents certain substances entering and leaving the cell.
What is the function of a triglyceride?
Energy source plus insulating layer
What is the function of a phospholipid?
Actors are barrier to ions and molecules, basis of cell membranes when there are carbohydrate chains attached
What does a phospholipid look like?
What is a fluid mosaic model?
A model of the cell surface
Why is it called a fluid mosaic model?
Fluid because the phospholipids can move around relative to each other.
Mosaic because embedded proteins scatter randomly in the bilayer form a mosaic pattern
What does a protein and a sugar chain make up?
Glycoprotein
What is a glycoprotein?
A protein with a short carbohydrate chain attached to it which protrudes from the cell membrane.
Glycoproteins are important in cell signalling and they form surface antigens
What does a sugar chain and a lipid make up?
A glycolipid
What is a glycolipid?
A lipid with a short carbohydrate chain attached to it they form surface antigens
What is an intrinsic protein?
Protein spans across both sides of the membrane
What are the two types of intrinsic proteins?
Carrier and channel
What is a carrier protein?
They can change shape to move substances from one side to another it can be used down a concentration gradient or against, by facilitated diffusion which uses active transport
What is a channel protein?
They form a passage way through which water and polar substances can pass by diffusion down of concentration gradient
What are the two key features of cholesterol molecule?
Hydroxyl group (HO) is hydrophilic
And the rest of the molecule is hydrophobic
What does this mean?
The cholesterol molecule can insert into cell membranes – hydrophilic hydroxide group can interact with head groups of Phospholipids. While the rest of the cholesterol molecule can interact with the hydrophobic fatty acid tails
What does cholesterol play a key role in?
Controlling fluidity of cell membranes
How is cholesterol used as a starting point for the hormones, testosterone, and oestrogen?
Hydrogen and testosterone are based on cholesterol so these hormones can pass through cell membranes and interact with their receptors inside the cell
How was cholesterol used to make vitamin D?
It takes place in the skin in response to ultraviolet light
Cholesterol is used in the liver to produce bile, what is the function of bile?
Increase the rate of digestion of lipids by the enzyme lipase.
How does temperature affect the membrane structure and permeability?
Temperature rise- increased rate of diffusion.
At 40° many proteins denature- disrupts membrane structure and can no longer act as a barrier.
How does cell signalling work?
Cells communicate with each other through chemical messengers which are produced in a cell and sent to the next one cells that have the correct cell membrane receptors detect the molecule
Where are the plasma membrane receptors?
On the glycoproteins
What is the fusion?
Passive movement of molecules from an area of high water potential to low water potential until equilibrium is reached
What does passive process mean?
Does not require energy
What is simple diffusion?
Happens down the concentration gradient occurs when small molecules or lipids soluble molecules passed through semi permeable membrane without the help of carrier or channel proteins
What molecules can pass through the cell membrane during simple diffusion?
Oxygen, carbon dioxide
What is facilitated diffusion?
Hydrophilic substances cannot pass through the membrane (water is an exception) but hydrophilic substances and necessary for the cell so the membrane uses facilitated diffusion
What happens during facilitated diffusion?
Substances passed a carrier or channel protein down a concentration gradient
What happens with a carrier protein?
When the special chemical binds to the carrier protein structure of the protein changes which brings the chemical to the other side of the membrane to be released
What happens with channel proteins?
The pool contains water, which means hydrophilic substances can pass through. They are selective and some only open in response to a trigger.
What is active transport?
the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane which uses a lot of ATP and is always against the concentration gradient
Why does it require ATP?
Because Carrier proteins need to move substances against the concentration gradient
What substances passed through with active transport?
Na+ / K+
How does it work?
1- molecule attaches to the receptor and carrier protein
2- ATP combines with carrier protein
3- ATP molecule undergoes hydrolysis- produces ADP and one molecular phosphate
4- phosphate attaches to the protein and causes it to change shape
5- shape change causes molecule to be released on other side
What is endocytosis and exocytosis?
They are used to transport larger substances, e.g. antigens and enzymes and it requires ATP
Why is it only large substances?
Because they are too large to be transported by the fusion
What is endocytosis and how does it work?
1- Invaginatio happens (cell surface membrane engulfs the substances
2- the membrane in circles substances to create a vesicle
How does cytosis work?
1- proteins from Golgi apparatus moving vesicles to the plasma membrane
2- vesicles fuse with membrane and protein secreted
What is osmosis?
The net movement of water from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution across a partially permeable membrane
When does it happen?
When water molecules diffuse across a partially permeable membrane
Hypotonic in animal cells
Water potential higher than cell net movement of water into the cell and cell bursts
Hypotonic in plant cells
Water potential higher than cell net water movement into cell cell is turgid
Isotonic in animal cells
Water potential equal to the cell no net movement of water there is equilibrium
Isotonic in plant cells
Water potential equal to cell no net movement of water there is equilibrium
Hypertonic in animal cells
Water potential lower than cell net movement of water out of cell cell shrivels and becomes flaccid
Hypertonic in plant cells
Water potential is lower than cell net movement of water out of cell cell becomes plasmolysed