exam 2 terms: the heart
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
mediastinum
area within the thoracic cavity where the heart is located
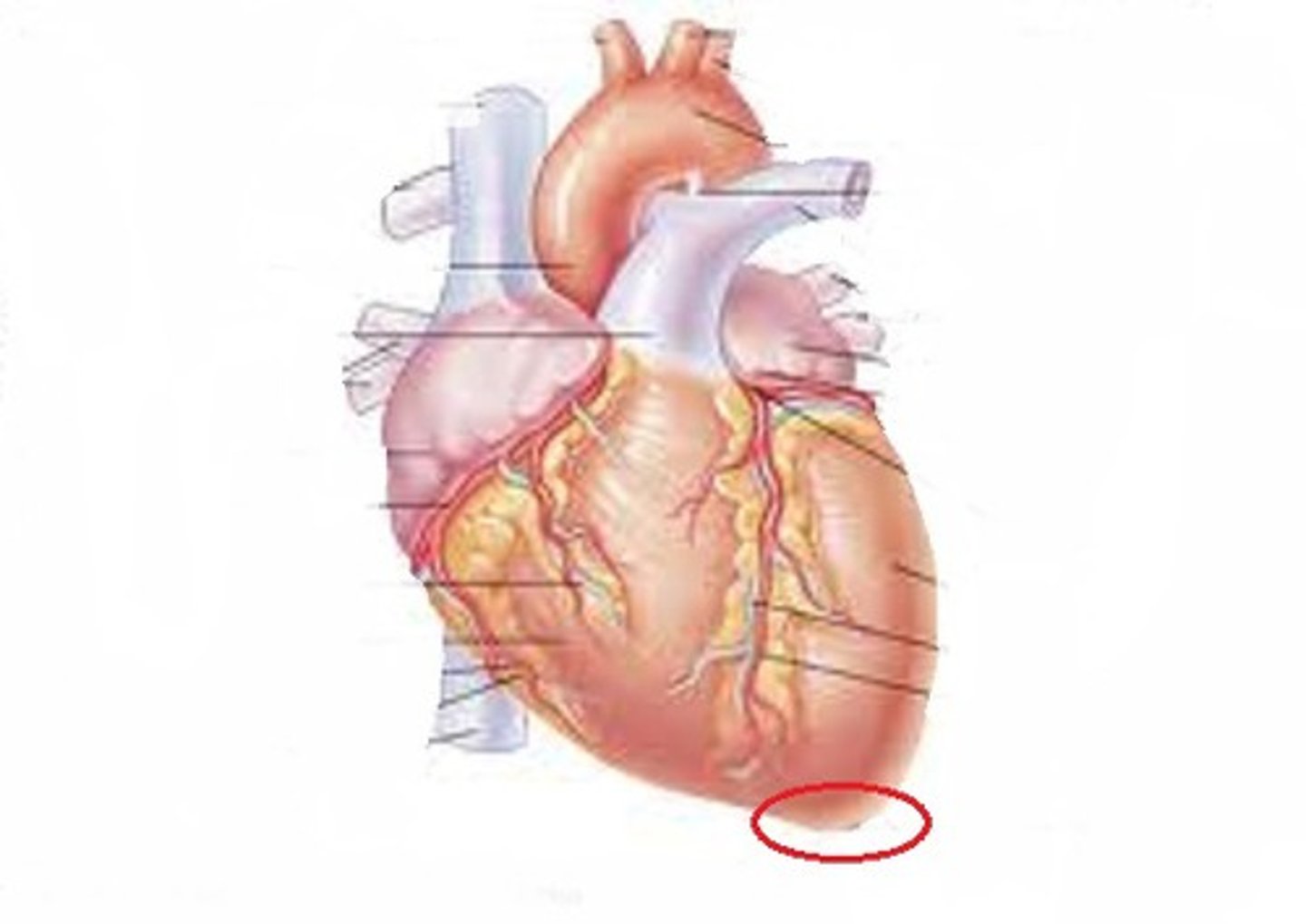
apex
the inferior, pointed end of the heart
base
the superior, rounded end of the heart where the great vessels attach
endocardium
innermost layer of the heart wall composed of simple squamous epithelium
myocardium
the middle layer of the heart wall composed of cardiac muscle
epicardium
the outermost layer of the heart wall. synonymous with the visceral pericardium
annulus fibrosus (fibrous skeleton)
the fibrous connective tissue that supports the cardiac muscle and valves. separates the chambers electrically
atria
the 2 upper chambers of the heart (receiving chambers)
ventricles
the 2 lower chambers of the heart (discharging chambers)
fibrous pericardium
the outermost layer of the sac that surrounds the heart. anchors the heart
serous pericardium
the serous membrane that forms the sac around the heart. has a visceral and parietal layer
interatrial septum
the wall that separates the atria
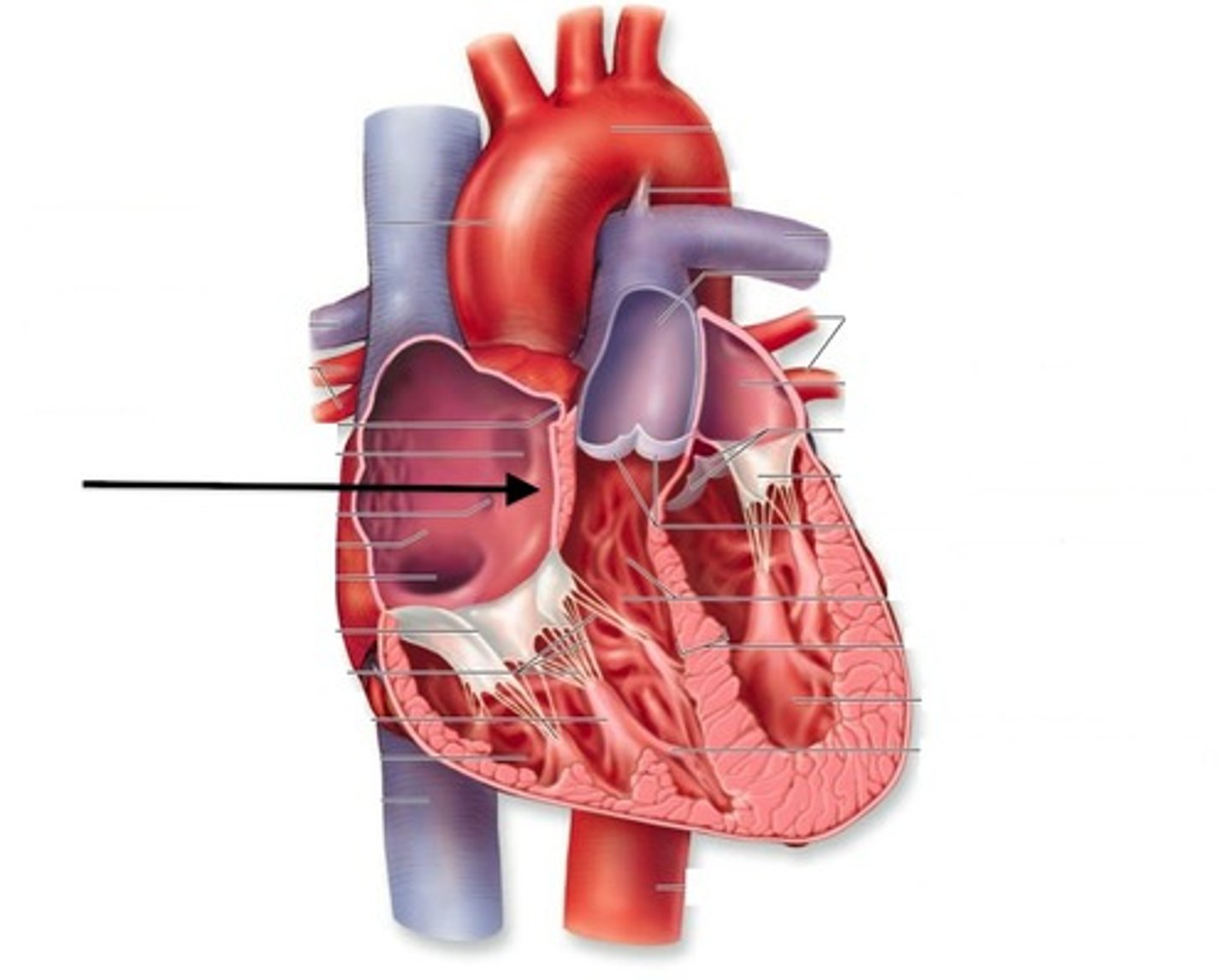
interventricular septum
the wall that separates the ventricles
tricuspid valve
prevents back flow of blood from the right ventricle to the right atrium
mitral/bicuspid valve
prevents the back flow of blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium
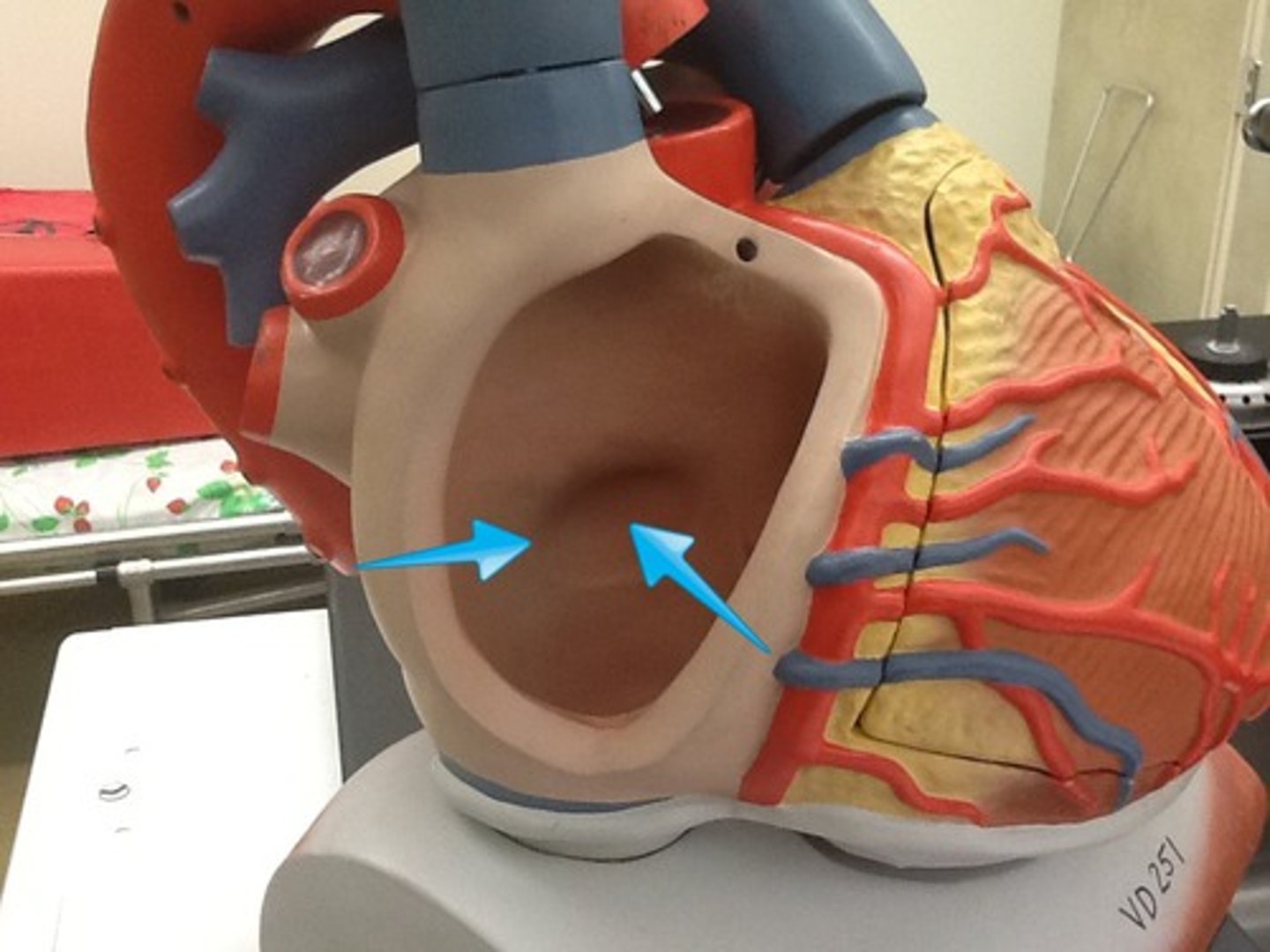
fossa ovalis
depression in the interatrial septum that is a remnant of a hole in the fetal heart
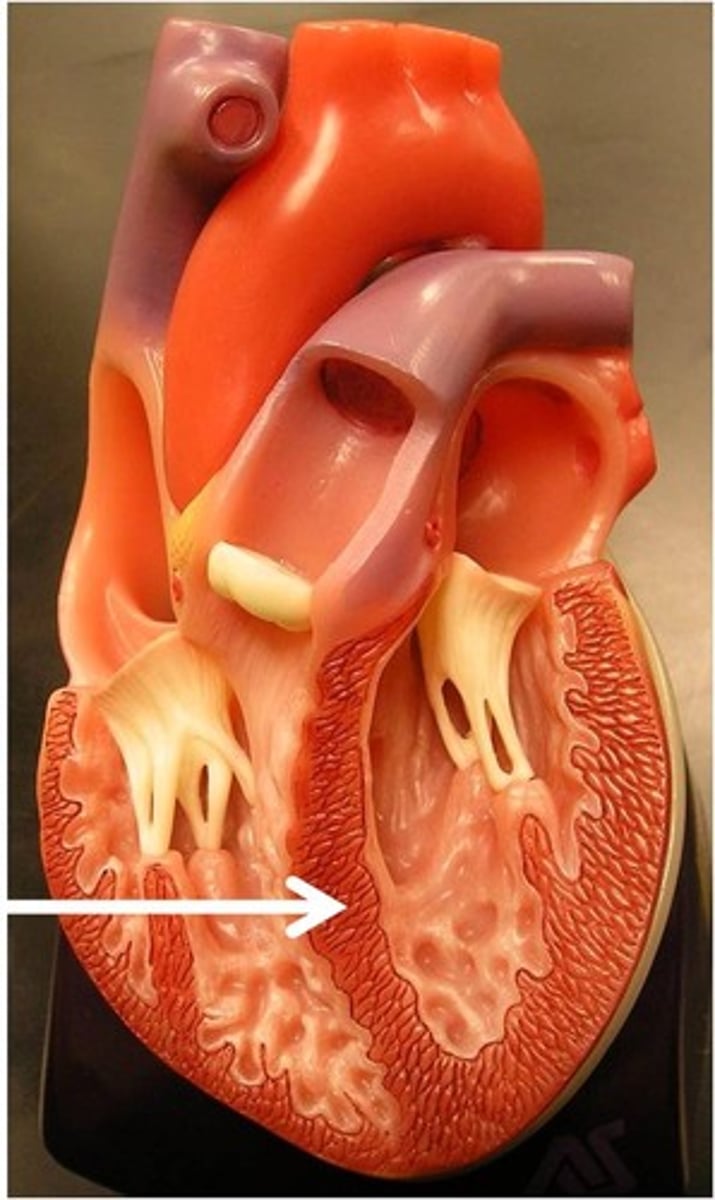
trabeculae carne
the irregular ridges within the myocardium of the ventricles
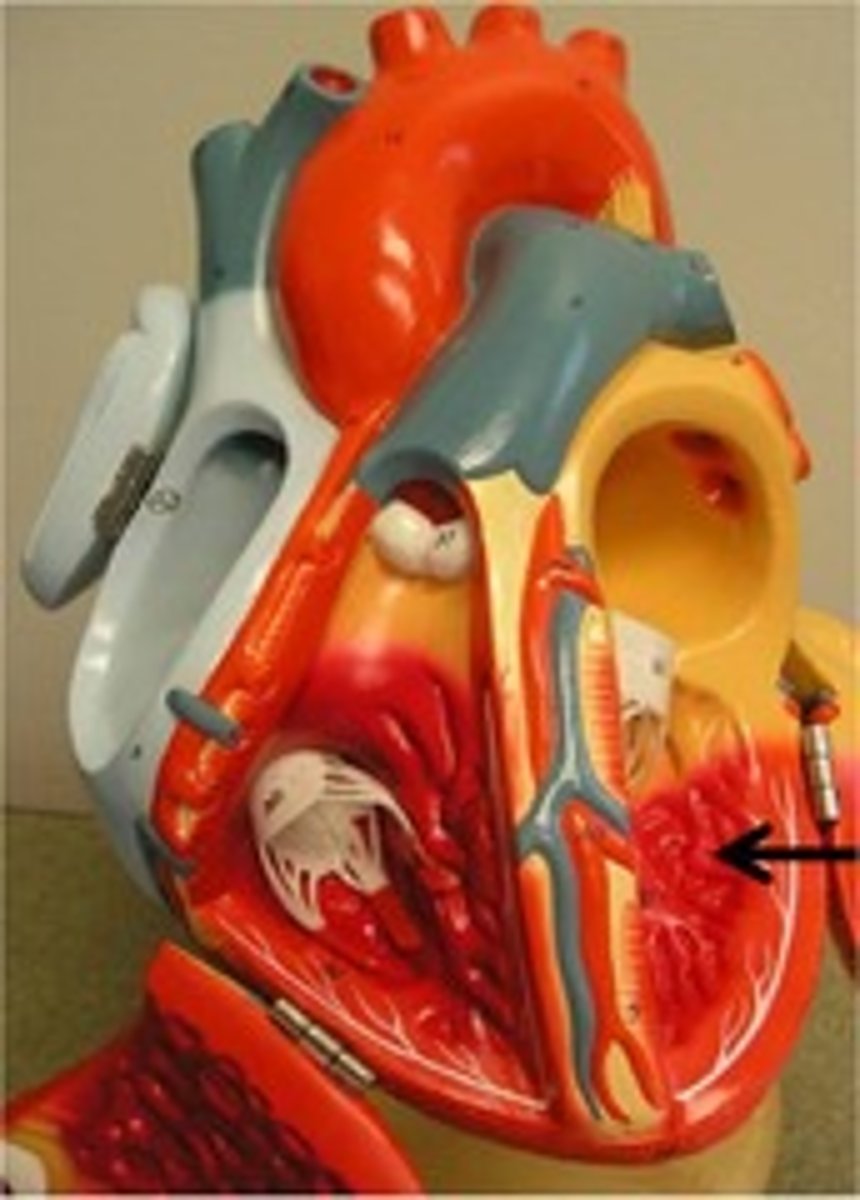
papillary muscles
projections of muscle that the chord tendineae attach to
chordae tendineae
fibrous chords that extend off the flaps of the cuspid valves to attach to the flaps of the heart wall
aortic semilunar valve
prevents the back flow of blood form the aorta to the LEFT ventricle
pulmonary semilunar valve
prevents the back flow of blood from the pulmonary trunk to the RIGHT ventricle
superior vena cava
returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium from structures ABOVE the armpits
inferior vena cava
returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium from structures BELOW the armpits
pulmonary trunk
delivers deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle towards the lungs
Aorta
delivers oxygenated blood from the left ventricle towards the body
pulmonary veins
carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
coronary sinus
coronary veins on the posterior heart that collects blood from 3 coronary veins and drains to the right atrium
systole
the term for contraction of the heart muscle
diastole
the term for relaxation of the heart muscle
isovolumetric contraction phase
the brief moment at the beginning of ventricular systole when all valves are closed
isovolumetric relaxation phase
the brief moment at the beginning of ventricular diastole when all valves are closed
lub
heart sound made by closing of cuspid valves at beginning of ventricular systole
dup
heart sound made by closing of semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole
sinoatrial (SA) node
pacemaker of the heart. generates action potential that spreads throughout the atria
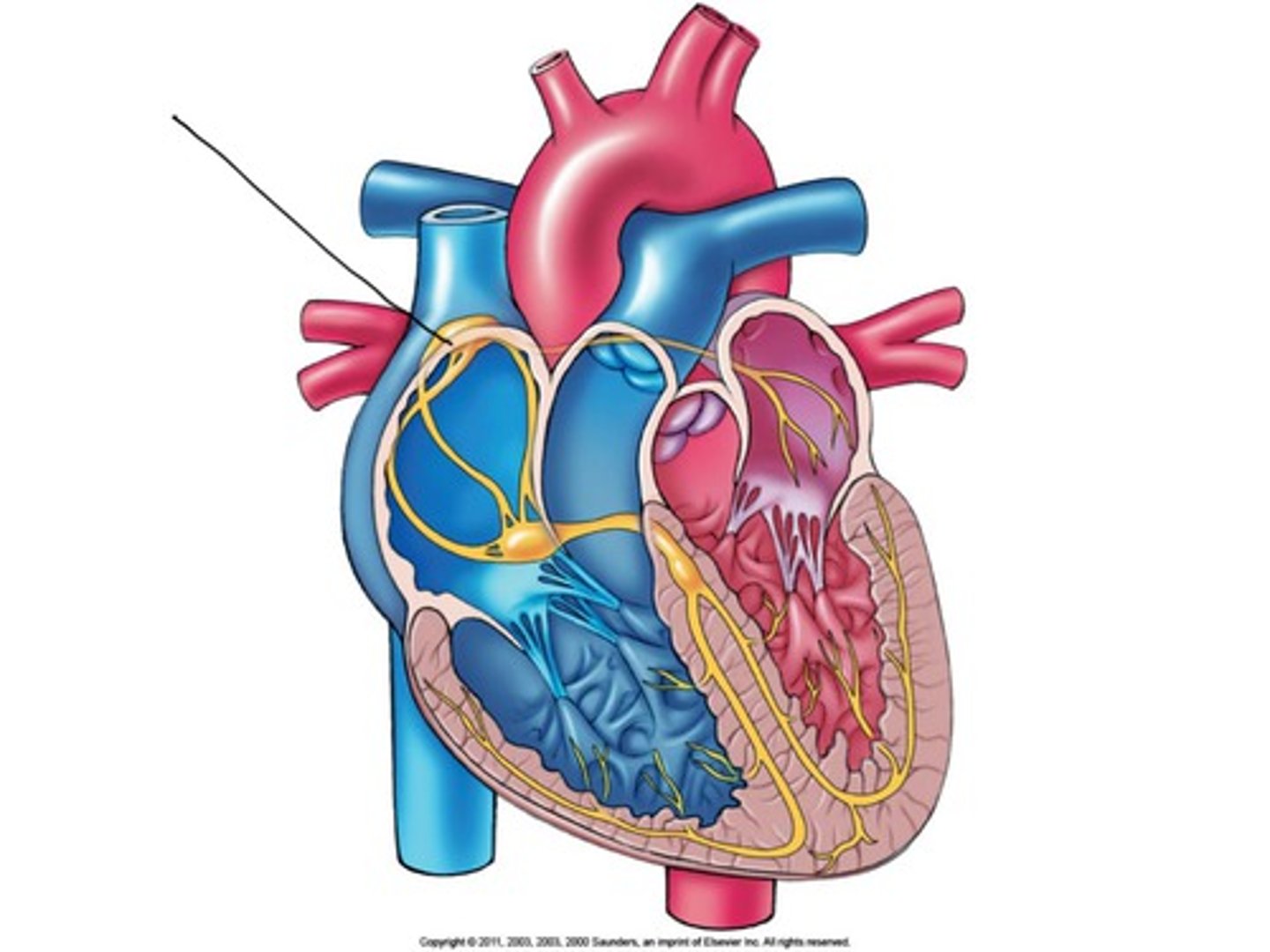
atrioventricular (AV) node
auto rhythmic cells that delay the impulse before relaying it to the Bundle of His
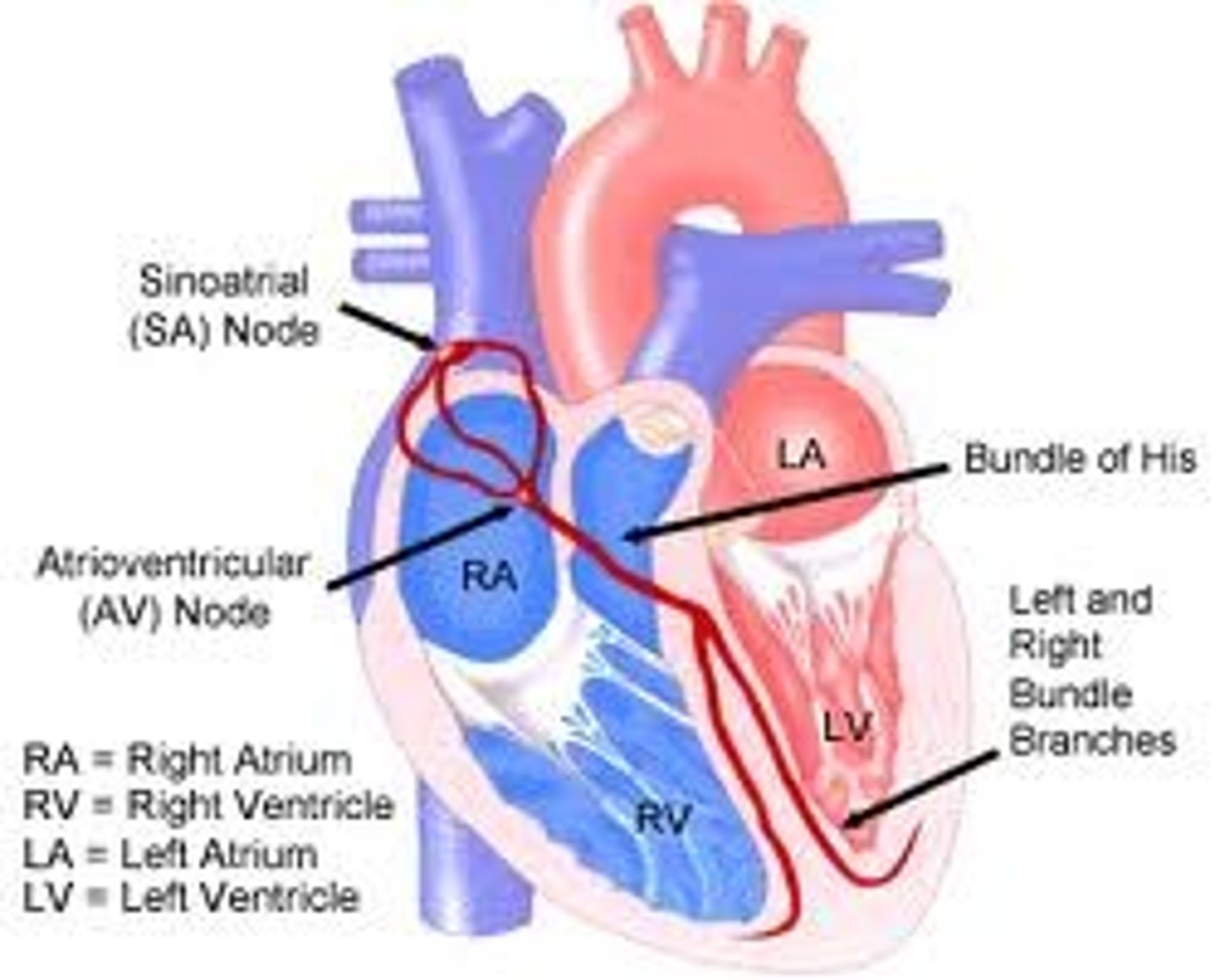
Bundle of His (AV bundle)
continuous with AV node and relay impulse through fibrous skeleton
bundle branches
autorhythmic cells that travel down the inter ventricular septum towards the apex
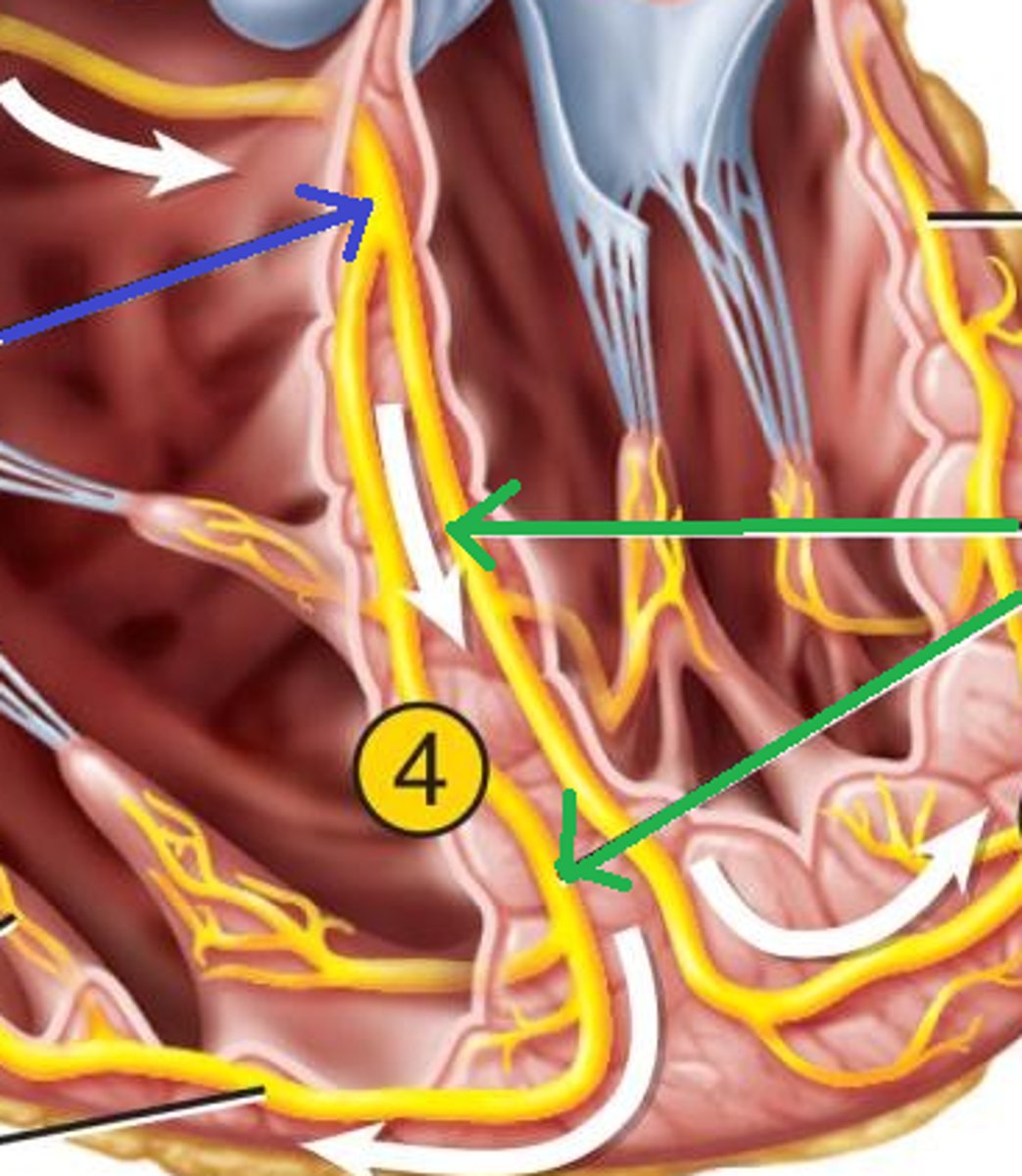
purkinje fibers
autorhythmic cells that branch and supply impulses to the papillary muscles and majority of ventricular wall
vagus nerves
parasympathetic nerve that supplies impulses to the SA node and AV node.
- releases ACH
cardiac nerves
sympathetic nerve that supplies impulse to the SA node, AV node and myocardium
- releases norepinephrine
chronotropic factor
factors that alter heart rate
inotropic factor
factors that alter strength of contraction of the heart
cardiac output
the amount of blood ejected from a ventricle in 1 minute
stroke volume
the amount of blood ejected from a ventricle in 1 contraction
ejection fraction
the %of the blood leaving the heart with each contraction
end diastolic volume (EDV)
the amount of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole
end systolic volume (ESV)
the amount of blood in the ventricle at the end of systole
venous return
the amount of blood returning to the heart in the veins
preload
the amount of ventricular stretch before contraction
afterload
the pressure the heart has to work against to eject the blood
P wave
ECG deflection that represents atrial depolarization
QRS complex
ECG deflection that represents ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
T wave
ECG deflection that represents ventricular repolarization
heart block
a delay in conduction
bradycardia
a resting heart rate below 60 BPM
tachycardia
a heart rate above 100 BPM
fibrillation
an uncoordinated heart beat where patches of myocardium are beating independently
myocardial infarction (MI)
heart attack
beta blockers
medication for high blood pressure that binds beta receptors
calcium channel blockers
medication for high blood pressure that binds calcium channels