Landscape, Empire, and Social Change - Key Terms (Vocabulary Flashcards)
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards capturing key terms and their definitions from the lecture notes on landscape, empire, and social change.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Landscape
A painter’s representation of natural scenery, and a cultural concept denoting the space humans organize, regulate, and imbue with social meaning; also an instrument of cultural power and imperial dreamwork.
Imagology
The study of images and myths; analyzes how ideology is expressed in narrative forms to create and justify social boundaries and hierarchies.
Myth (in this context)
Ideology presented as narrative;stories used to construct or legitimate social boundaries and power relations.
Ідеологія, представлена як наратив; історії, що використовуються для побудови або легітимізації соціальних меж та владних відносин.
Liberty (17th century)
Shifting meaning of liberty from a property right in medieval times to a broader political-right sense emerging notably during the English Civil War.
Commons
Resources shared by a community (land, water, etc.) governed by rules; not free-for-all, but managed with collective rights.
Norman invasion of England
1066
William the Conqueror led the invasion, resulting in significant cultural and political changes. and haroldGodwinson's defeat at the Battle of Hastings.
Enclosure
The process of converting common land into privately owned property, often leading to displaced rural populations and significant social change (key events: Midland Revolt 1607; Enclosure Acts by 1768; 1549 kett’s rebellion ).
Hides
measurement used in the Domesday survey, reflecting the amount of land needed to support a household.
Domesday Book
The 1086 survey of landholdings, resources, and obligations across England, commissioned by William the Conqueror.
Roman Britain
Period 43–410 CE when Roman rule and cultural influence extended over Britain, including Roman administrative units and infrastructure.
Civitas (Roman Britain)
A tribal city or territorial unit in Roman Britain; a center of administration and governance.
Colonia (Roman Britain)
A Roman settlement established as a city for veterans or colonists; a formal urban center in the empire.
Hadrianic
Relating to Emperor Hadrian; known for building Hadrian’s Wall and consolidating frontiers in Britain.
Flavian
Relating to the Flavian dynasty (Vespasian, Titus, Domitian), a period of consolidation and expansion in the early Empire.
Sutton Hoo
Anglo-Saxon burial site in East Anglia (c. 550 CE), illustrating elite culture and social organization before full Christianization.
Anglo-Saxon settlement
Migration-era process (roughly 5th–7th centuries) where Angles, Jutes, and Saxons populated Britain; mixed with native Britons to form early English identity.
East Anglia (Anglo-Saxon kingdom)
One of the early Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, later integrated into the broader English realm; site of Sutton Hoo.
1066 (Norman invasion of England)
The Norman conquest led by William the Conqueror, culminating in the Battle of Hastings; transformed English governance and culture.
Bayeux Tapestry
A 11th-century embroidered chronicle depicting the Norman conquest of England and the events leading to Hastings.
Battle of Hastings
1066 battle where William the Conqueror defeated Harold II, changing English history and its rulers.
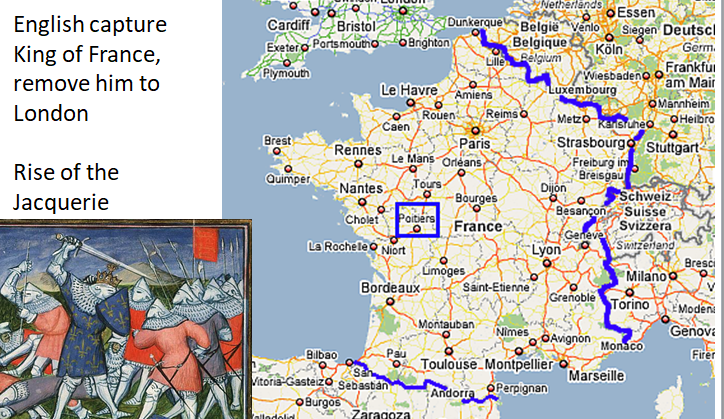
Hundred Years’ War
Conflicted period 1337–1453 between England and France; included major battles (Crécy, Poitiers, Agincourt) and shifts in territorial holdings.
Crécy (1346)
Major English victory during the Hundred Years’ War; demonstrated longbow power and military tactics.
Poitiers (1356) Battle of Poiters
English victory in the Hundred Years’ War; notable for capturing the French king, John II.
English capture King of France, remove him to London
Rise of Jacquerie
Agincourt (1415)
English victory in the Hundred Years’ War under Henry V, emblematic of English military prowess.символ англійської військової доблесті.
Calais (1347)
Capture of Calais by England during the early phase of the Hundred Years’ War; English stronghold on the continent.
Black Death
Black Plague c. 1350
The mid-14th-century plague that decimated Europe’s population (roughly 50%), triggering labor shortages and social upheaval.
Labour shortage meant peasants leveraged (селян залучали до боротьби) for better rights, merchants and rich farmers could buy land cheaply
“Allegiance(відданість) in the 14th century was still given to
a person, not a nation” or Volk
1302
workers’ revolts in Bruges against French nobility; France ennobled wealthy peasants to gain support
Робітничі повстання в Брюгге проти французької знаті; Франція надала шляхетний статус заможним селянам, щоб отримати підтримку
King Richard II (1377-1399)
-Born in Bordeaux; son of Edward of Wales, “The Black Prince”
Peasant Tax revolt (1381) John Ball led a rebellion advocating for social justice and the end of serfdom.
Peasant*s Revolts 1381
A series of uprisings in England, primarily led by dissatisfied peasants protesting against economic hardship and oppressive taxes, most notably the legislation of 1381.
An Archdeacon from Sussex tried collecting upaid poll taxes in Essex. John Ball
It became a war to end serfdom
marched on London because of hight taxes(esp. pool taxes), harsh laws , soc inequality
Wanted: fear treatment, lower taxes ent of serf=dom
John of Gaunt(Ghent)
- Returned from a disastrous campaign in France in 1374 as effective parliamentary administrator of England, under Richard II
-Son of Edward III (younger brother of Edward of Wales), King of Castille, Duke of Acquitaine
-Patron of Chaucer
-Father of Henry IV (Richard II’s successor)
First English poll tax
Impeached reform movement leaders
English Absolutism (1485-1642)
Henry VII (1485-1509) - first Tudor monarch
English Civil War (1642-1651)
“the first bourgeois revolution”
“the first truly capitalist social formation”
period characterized by centralized power and authority in the monarchy, leading to significant political and social changes.
St George's Hill, Weybridge, Surrey, 1649
The Diggers („True Levelers“)
were a group of agrarian communists who sought to establish a communal way of life by reclaiming land for the common people and promoting social equality.
1649 (pamphlet manifesto): "The True Levellers Standard Advanced”
A pamphlet published by the Diggers advocating for land reform, communal ownership, and social equality in post-Civil War England.
Smallpox
(around 90% fatality)contagious disease causing severe illness and often death.
(близько 90% летальності) інфекційне захворювання, що спричиняє важкі перебіги хвороби та часто смерть.
c. 1635, Boston
sympathy in Massachusetts for disestablishment of a national church allows Roger Williams to establish Providence Plantation (Providence, RI)
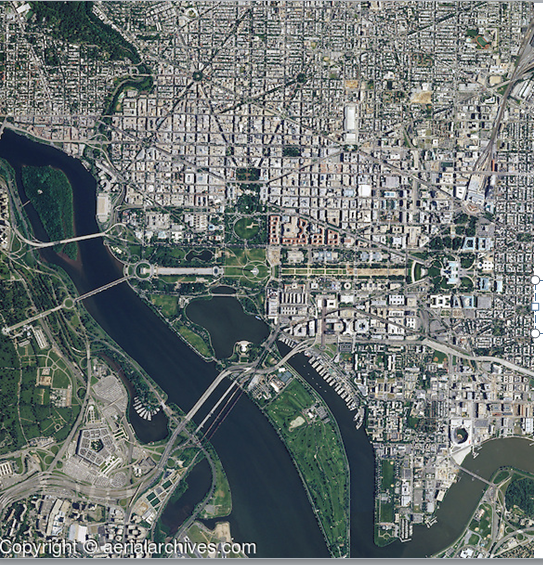
Pierre L'Enfant
1791
designed the layout of Washington D.C., envisioning it as a grand capital with broad avenues and ceremonial spaces.

Yeoman capitalism
A social formation characterized by independent freeholders and private landholding, shaping American colonial development and class structure.
Ramp Hollow (commons vs. private property)
Steven Stoll’s concept describing the transition of common land into private property through enclosure and legal mechanisms.
Концепція Стівена Столла, що описує перехід спільної землі у приватну власність шляхом огородження та правових механізмів.
Roger Williams & Providence Plantations
Early American example of religious tolerance and democratic governance (1635–1651), leading to the First Amendment ideals.
First Amendment (US)
Constitutional provision prohibiting Congress from establishing a state church or restricting free exercise of religion.
Конституційне положення, що забороняє Конгресу створювати державну церкву або обмежувати вільне сповідування релігії.
Royal African Company (1660)
English company established to regulate and profit from the transatlantic slave trade.
Washington, D.C.
The central symbolic landscape of the American republic(accordibg to Cosgrove 180); planned by L'Enfant(1791) to reflect Renaissance urban ideals and republican virtue.
Putney Debates (1647)
Debates within the New Model Army about the constitution and political settlement during the English Civil War.
Diggers (True Levellers)
Commonwealth-era radical group advocating for common ownership of land and more democratic participation; associated with the 1649 pamphlet The True Levellers Standard Advanced.
Peasants’ Revolt (1381)
Mass uprising in England against poll taxes and feudal oppression, highlighting conflicts over labor and rights.
Enclosure Acts (England, 17th–18th c.)
Legislation enabling privatization of common l
legal way for landowners to take the common land
Restoration (1660), London fire of 1666
a period in British history marked by the re-establishment of the monarchy after the Interregnum, leading to significant political and cultural changes.
Massachusetts Body of Liberties (1641–1684)
A colonial legal framework guaranteeing freedoms such as speech, jury trial, and due process in early New England.
Burlington House, 1690: now Royal Academy
An example of 17th-century architecture in London, originally built as a private residence but later became a public gallery for art and culture.
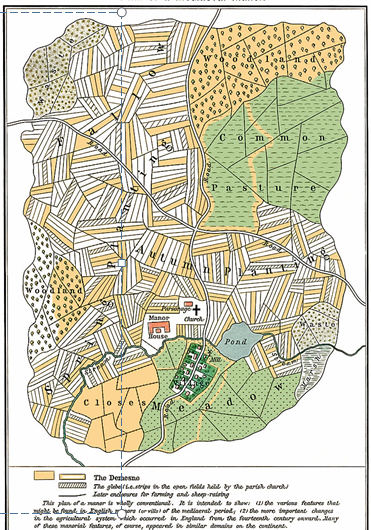
Enclosure
the process of consolidating small landholdings into larger farms, significantly altering agricultural practices and rural society in England.
1607 – Midland Revolt
(Northamptonshire had lost 27,000 acres to enclosure since 1578)
1768 – Act of Enclosure
(England) Previous resistance to earlier enclosure efforts:
1549 – Kett‘s Rebellion
(rebels tear down fences on former common land)
Oliver Goldsmith, „The Deserted Village“
Castle Goring (1797, West Sussex)
Romantic „Carnivalesque Style,“
Built by P.B. Shelley‘s grandfather (b. Newark, New Jersey) sold to a family of Carribean merchants by Mary Shelley in 1845.

Hardwick Hall 1590-
a notable example of Elizabethan architecture designed by Bess of Hardwick, featuring a distinctive style with large windows and materials signifying wealth.

Providence Plantations (Rhode Island)
Colony founded on religious tolerance and democratic governance principles; example of early American pluralism.
Private property as social force
Idea that private land ownership and its legal protections shape social hierarchy and economic power, a key theme in Cosgrove’s analysis.
Ідея про те, що приватна власність на землю та її правовий захист формують соціальну ієрархію та економічну владу, є ключовою темою в аналізі Косгроува.
Landscape as infrastructure/background
how landscape underpins and enables collective living, economic activity, and cultural power.
як ландшафт підтримує та забезпечує колективне життя, економічну діяльність та культурну силу.
Amerigo Cosgrove’s “America as Landscape”
Idea that American settlement reimagines land as a visual and functional landscape, aligning nature with national identity and expansion.
Ідея про те, що американське поселення переосмислює землю як візуальний та функціональний ландшафт, узгоджуючи природу з національною ідентичністю та експансією.
Rambler/Right to Roam movement
The Ramblers: 1932 „mass tresspass“
Contemporary campaigns advocating pedestrian access and public rights to walk across lands and on public pathways.
A pivotal event in the British right to access open land movement, where activists protested against restrictions on walking across the countryside.
