AP Psych Units I-7
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/387
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
388 Terms
1
New cards
Empiricism
- The view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should, therefore, rely on observation and experimentation
- Locke
- Tabula Rasa "Blank slate"
- Locke
- Tabula Rasa "Blank slate"
2
New cards
Structuralism
- Early school of thought which used introspection to reveal the structure of the human mind
- Wundt and Titchener
- Wundt and Titchener
3
New cards
Functionalism
- Early school of thought which explored how mental and behavioral processes function
- How they enable the organism to adapt, survive, and flourish
- James and Darwin
- How they enable the organism to adapt, survive, and flourish
- James and Darwin
4
New cards
Experimental Psychology
- The study of behavior and thinking using the experimental method
5
New cards
Behaviorism
- The view that psychology (1) should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes
- Most research psychologists today agree with (1) but not with (2)
- Watson and Rayner
- Most research psychologists today agree with (1) but not with (2)
- Watson and Rayner
6
New cards
Humanistic Psychology
- A historically significant perspective that emphasized the growth potential for healthy people
- Freudian psychology
- Maslow, Skinner, and Freud
- Freudian psychology
- Maslow, Skinner, and Freud
7
New cards
Cognitive Neuroscience
- The interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition
- Including perception, thinking, memory, and language
- Including perception, thinking, memory, and language
8
New cards
Psychology
- The science of behavior and mental processes
9
New cards
Nature-Nurture Issue
- The longstanding controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors
- Today's science sees traits and behaviors arising from the interaction of nature and nurture
- Today's science sees traits and behaviors arising from the interaction of nature and nurture
10
New cards
Natural Selection
- The principle that, among the range of inherited trait variations, those contributing to reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
- Charles Darwin
- Charles Darwin
11
New cards
Levels of Analysis
- The differing complementary views, from biological to psychological to social-cultural, for analyzing any given phenomenon
12
New cards
Biopsychosocial Approach
- An integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
- All lead to behavior or mental processes
- All lead to behavior or mental processes
13
New cards
Behavioral Psychology
- The scientific study of observable behavior, and its explanation by principles of learning
- Attempts to determine aggressive acts
- Attempts to determine aggressive acts
14
New cards
Biological Psychology
- The scientific study of the links between biological and psychological processes
- Neuropsychologists or Behavior Geneticists
- Neuropsychologists or Behavior Geneticists
15
New cards
Cognitive Psychology
- The scientific study of all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
- How our interpretation of a situation affects our anger and how our anger affects our thinking
- How our interpretation of a situation affects our anger and how our anger affects our thinking
16
New cards
Evolutionary Psychology
- The study of evolution of behavior and mind, using principles of natural selection
- Analyze how anger facilitated the survival of our ancestors' genes
- Analyze how anger facilitated the survival of our ancestors' genes
17
New cards
Psychodynamic Psychology
- A branch of psychology that studies how unconscious drives and conflicts influence behavior, and uses that information to treat people with psychological disorders
- Might vies an outburst as an outlet for unconscious hostility
- Might vies an outburst as an outlet for unconscious hostility
18
New cards
Social-Cultural Psychology
- The study of how situations and cultures affect our behavior and thinking
- How expression of anger vary across cultural contexts
- How expression of anger vary across cultural contexts
19
New cards
Psychometrics
- The scientific study of the measurement of human abilities, attitudes, and traits
20
New cards
Basic Research
- Pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base
21
New cards
Developmental Psychology
- A branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span
- Womb to tomb
- Womb to tomb
22
New cards
Educational Psychology
- The study of how psychological processes affect and can enhance teaching and learning
23
New cards
Personality Psychology
- The study of an individual's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting
- Investigating our persistent traits
- Investigating our persistent traits
24
New cards
Social Psychology
- The scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another
25
New cards
Applied Research
- Scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
26
New cards
Industrial-Organizational (I/O) Psychology
- The application of psychological concepts and methods to optimizing human behavior in workplace
- Helps organizations and companies select and train employees
- Helps organizations and companies select and train employees
27
New cards
Human Factors Psychology
- An I/O psychology subfield that explores how people and machines interact and how machines and physical environments can be made safe and easy to use
28
New cards
Counseling Psychology
- A branch of psychology that assists people with problems in living and in achieving greater well-being
- Often related to school, work, or marriage
- Often related to school, work, or marriage
29
New cards
Clinical Psychology
- A branch of psychology that studies, assesses, and treats people with psychological disorders
30
New cards
Psychiatry
- A branch of medicine dealing with psychological disorders
- Practiced by physicians who sometimes provide medical treatments as well as psychological therapy
- Practiced by physicians who sometimes provide medical treatments as well as psychological therapy
31
New cards
Positive Psychology
- The scientific study of human functioning, with the goals of discovering and promoting strengths and virtues that help individuals and communities to thrive
- "Meaningful life"
- "Meaningful life"
32
New cards
Community Psychology
- A branch of psychology that studies how people interact with their social environments and how social institutions affect individuals and groups
- For example, stopping bullying
- For example, stopping bullying
33
New cards
Testing Effect
- Enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information
- Also sometimes referred to as a retrieval practice effort or test-enhanced learning
- Also sometimes referred to as a retrieval practice effort or test-enhanced learning
34
New cards
SQ3R
- A study method incorporating 5 steps
- Survey-Question-Read-Retrieve-Review
- Survey-Question-Read-Retrieve-Review
35
New cards
Hindsight Bias
- The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
- Also known as the I-knew-it-all-along phenomenon
- Also known as the I-knew-it-all-along phenomenon
36
New cards
Critical Thinking
- Thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions
- Rather, it examines assumptions,assesses the source, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
- Rather, it examines assumptions,assesses the source, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
37
New cards
Theory
- An explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
38
New cards
Hypothesis
- A testable prediction often implied by a theory
39
New cards
Operational Definition
- A carefully worded statement of the exact procedures, operations, used in a research study
- For example, human intelligence may be operationally defined as what an intelligence test measures
- For example, human intelligence may be operationally defined as what an intelligence test measures
40
New cards
Replication
- Repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
41
New cards
Case Study
- A descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
42
New cards
Naturalistic Observation
- Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
43
New cards
Survey
- A technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group
44
New cards
Sampling Bias
- A flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample
45
New cards
Population
- All those in a group being studied, from which samples may be drawn
- Except for national studies, this does not refer to a country's whole population
- Except for national studies, this does not refer to a country's whole population
46
New cards
Random Sample
- A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
47
New cards
Correlation
- A measure of the extent to which two variables change together, and thus of how well either variable predicts the other
48
New cards
Correlation Coefficient
- A statistical index of the relationship between two variables
- From -1.0 to +1.0
- From -1.0 to +1.0
49
New cards
Scatterplot
- A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the the values of two variables
- The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables
- The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation
- The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables
- The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation
50
New cards
Illusory Correlation
- The perception of a relationship where none exists
51
New cards
Experiment
- A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process
- By random assignment of participants, the experimenter aims to control other relevant variables
- By random assignment of participants, the experimenter aims to control other relevant variables
52
New cards
Experimental Group
- In an experiment, the group exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable
53
New cards
Control Group
- In an experiment, the group not exposed to the treatment, contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment
54
New cards
Random Assignment
- Assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between the different groups
55
New cards
Double-Blind Procedure
- An experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo
- Commonly used in drug-evaluation studies
- Commonly used in drug-evaluation studies
56
New cards
Placebo Effect
- Experimental results caused by expectations alone
- Any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which the recipient assumes is an active agent
- Any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which the recipient assumes is an active agent
57
New cards
Independent Variable
- The experimental factor that is manipulated
- The variable whose effect is being studied
- The variable whose effect is being studied
58
New cards
Confounding Variable
- A factor other than the independent variable that might produce and effect in an experiment
59
New cards
Dependent Variable
- The outcome factor
- The variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable
- The variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable
60
New cards
Validity
- The extent to which a test or experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to
61
New cards
Descriptive Statistics
- Numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups
- Includes measures of central tendency and measure of variation
- Includes measures of central tendency and measure of variation
62
New cards
History
- A bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
63
New cards
Mode
- The most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution
64
New cards
Mean
- The arithmetic average of a distribution, obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
65
New cards
Median
- The middle score in a distribution
- Half the score are above it and half are below it
- Half the score are above it and half are below it
66
New cards
Skewed Distribution
- A representation of scores that lack symmetry around their average value
67
New cards
Range
- The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
68
New cards
Standard Deviation
- A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
69
New cards
Normal Curve
- A symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data
- Most scores fall near the mean and fewer and fewer near the extremes
- About 68 percent fall within one standard deviation of it
- Most scores fall near the mean and fewer and fewer near the extremes
- About 68 percent fall within one standard deviation of it
70
New cards
Inferential Statistics
- Numerical data that allow one to generalize- to infer from sample data the probability of something being true of a population
71
New cards
Culture
- The enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
72
New cards
Informed Consent
- An ethical principle that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
73
New cards
Debriefing
- The postexperimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions, to its participants
74
New cards
Biological Psychology
- Links between biological and psychological processes
- Behavioral neuroscience
- Introduction to connection of nerve cells and behavior
- Behavioral neuroscience
- Introduction to connection of nerve cells and behavior
75
New cards
Neuron
- Nerve cell which is the building block of the nervous system

76
New cards
Dendrites
- Branching extensions that receive messages
- They listen
- They listen

77
New cards
Axon
- Passes messages through branches to other neurons
- They speak
- They speak

78
New cards
Myelin Sheath
- Fatty tissue layer that encases the axons of some neurons

79
New cards
Action Potential
- Neural impulse which is a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon

80
New cards
Refractory Period
- A period of inactive neuron firing
81
New cards
Threshold
- A level of stimulation that triggers a neural impulse
- Excitatory: Neuron accelerating
- Inhibitory: Neuron braking/slowing down
- Excitatory: Neuron accelerating
- Inhibitory: Neuron braking/slowing down
82
New cards
All-or-None Response
- You either get the neuron to fire or not fire with specific actions/behaviors

83
New cards
Synapse
- The junction between the axon tip and cell body of the receiving neuron

84
New cards
Neurotransmitters
- Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons to trigger certain actions/behaviors

85
New cards
Reuptake
- Neurotransmitters reabsorption by the sending neuron
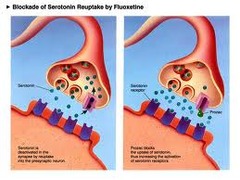
86
New cards
Endorphins
- Natural opiate (pain-killers) to stimulate pleasure
87
New cards
Agonist
-Stimulates a response
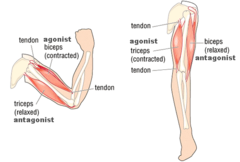
88
New cards
Antagonist
- Blocks/inhibits a response
89
New cards
Nervous System
- Electrochemical communications network
- Controls your nerves and some certain behaviors
- Controls your nerves and some certain behaviors
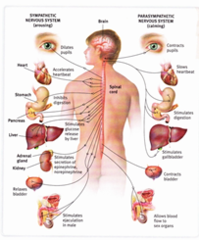
90
New cards
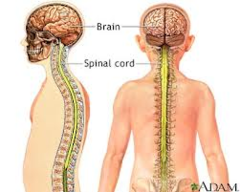
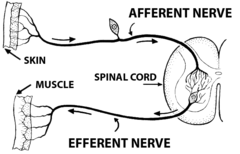
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The brain and the spinal chord which sends back a reaction to a certain sensory nerve or behavior
91
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Sensory and motor neurons
- Responsible for gathering information and transmits central nervous system decisions to other body parts
- Responsible for gathering information and transmits central nervous system decisions to other body parts
92
New cards
Nerves
- Bundled axons that form neural "cables"
- Connects nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs
- Connects nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs
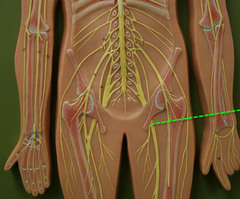
93
New cards
Sensory Association Area
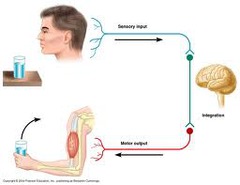
94
New cards
Motor
95
New cards
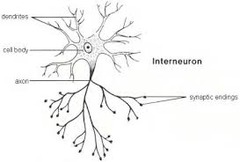
Interneurons
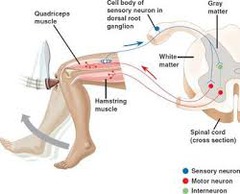
- Neurons within the brain and spinal chord that communicate internally
- Responsible for reflexes
- Intervene with motor and sensory neurons
- Responsible for reflexes
- Intervene with motor and sensory neurons
96
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
- Voluntary control of the skeletal muscles
97
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestions
- Fight or flight
- Fight or flight
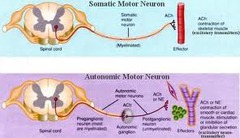
98
New cards
Sympathetic Nervous System
- Arouses the body/excites energy
99
New cards
Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Conserves energy/calms

100
New cards
Reflex
- Automatic response
- Knee-jerk
- Found in the brainstem
- Knee-jerk
- Found in the brainstem