Radioactivity
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Particle Theory
Model that helps explain the properties of solids, liquids and gases
What did Dalton discover?
Atoms are small solid spheres
How did Dalton discover atoms shape?
Gas experiments
atomic model of Dalton

Strength of the Dalton model
Simple
Weakness of Dalton's Model
Doesn't show the relative size of particles
What did Thomson discover?
electrons and that they are negatively charged and hardly any mass
How did Thomson discover the Electron?
Electricity gun
Thomson's Model
Plum pudding model
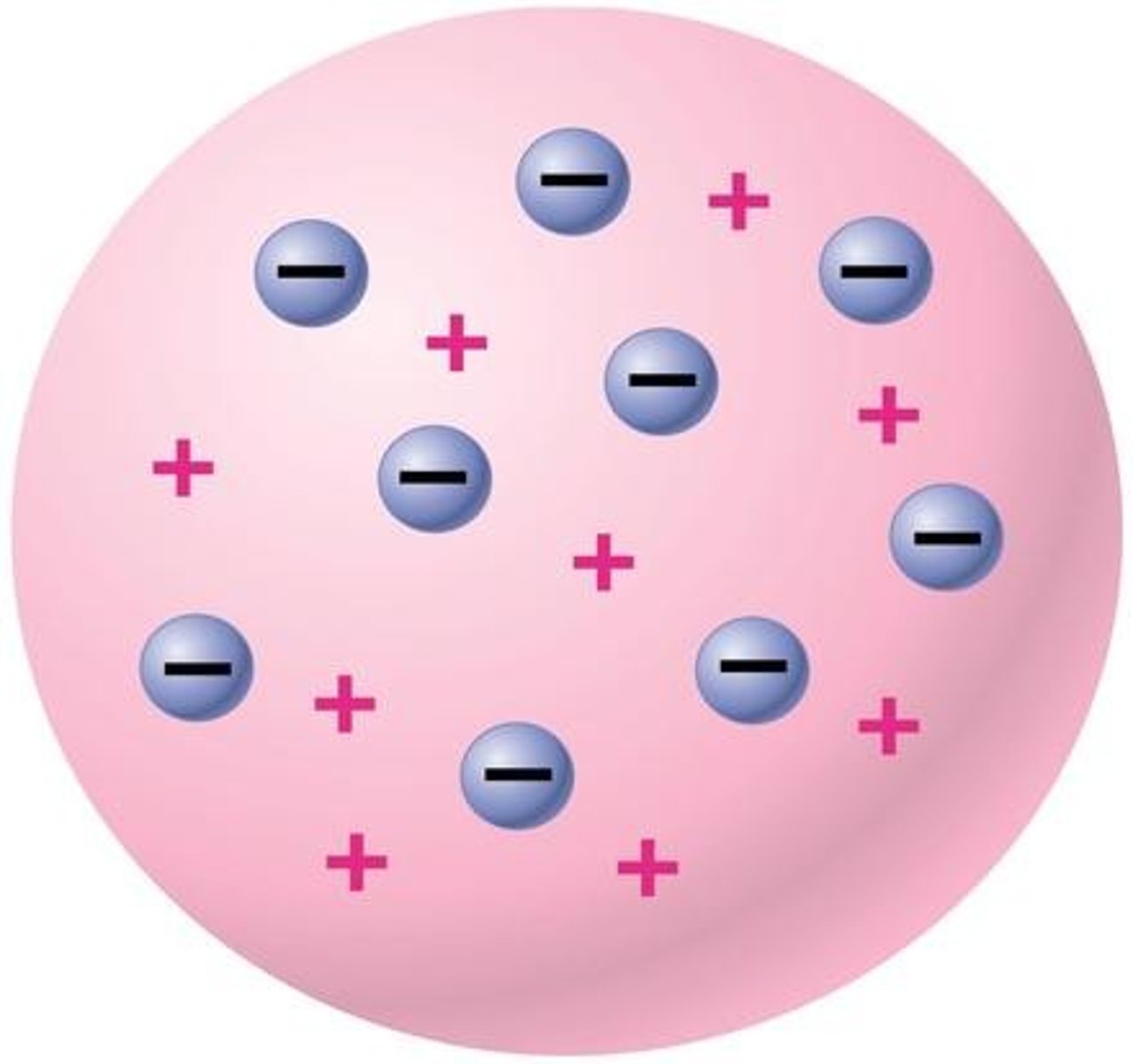
Strength of plum pudding model
Shows electrons
Disadvantage of plum pudding model
Doesn't show neutrons
What did Rutherford discover?
Atom has a small positively charged solid nucleus in the centre
Rutherford model of the atom

How did Rutherford discover the nucleus?
Gold foil experiment
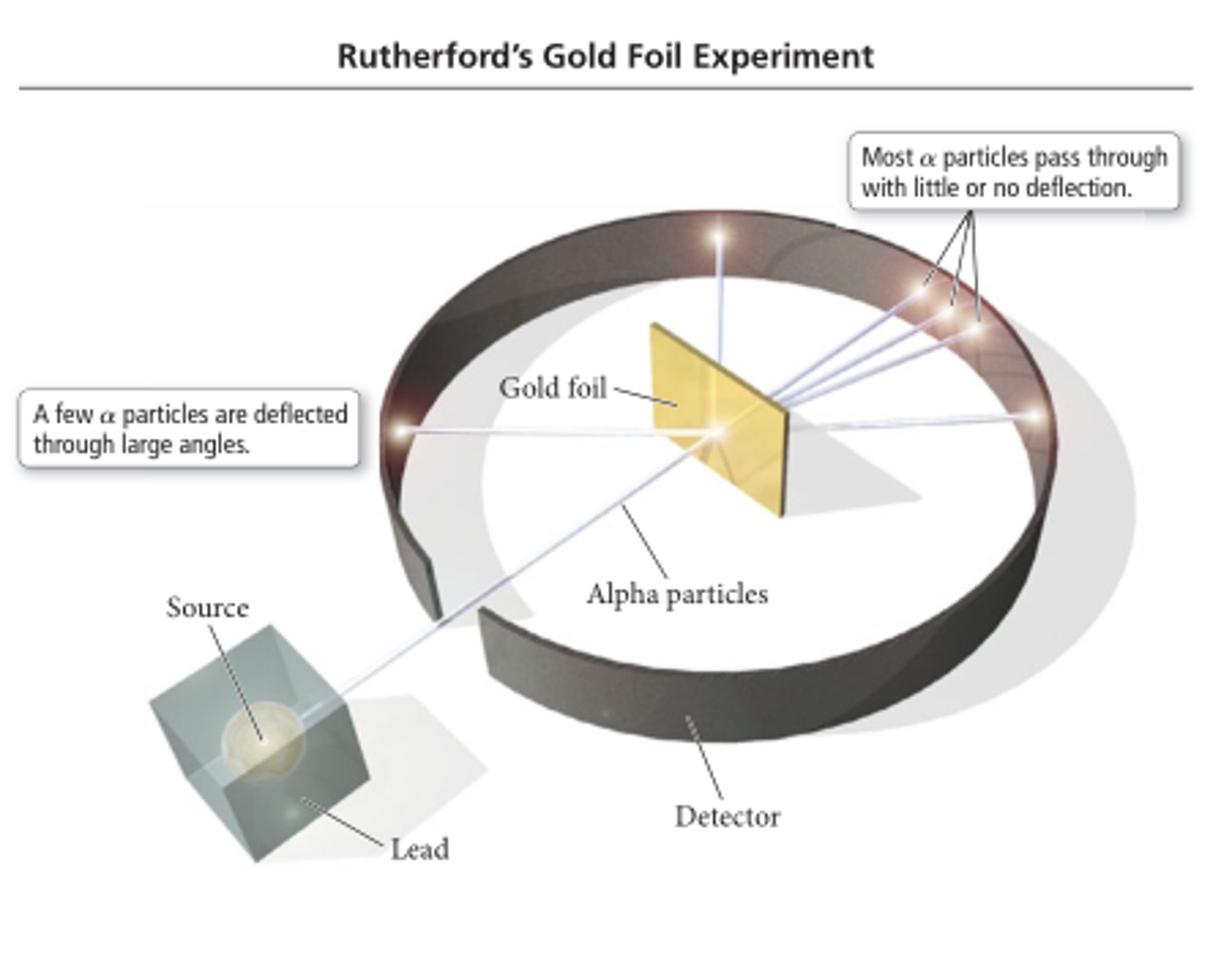
How did the gold foil experiment work?
alphaparticles were shot through very thin gold foil with a detector around the foil. Almost all of the particles went straight through the foil, very few were deflected and an even fewer were bounced straight back.
Why did most particles get transmitted in the gold leaf experiment?
Most of the atom is empty space
Why did some particles get deflected in the gold leaf experiment?
The post it I've nucleus deflects the alpha particles
Why did very few particles get reflected in the gold leaf experiment?
The nucleus is very small and very hard, dense
Strength of the Rutherford model?
Shows positive nucleus
What did Chadwick discover?
neutron
How did Chadwick discover the neutron?
Weighed the atom
Where is all of the mass of an atom?
nucleus
Nucleons
protons and neutrons
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
How are atoms neutral?
same number of protons and electrons
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
electromagnetic radiation
When we provide electrons with energy, they absorb the energy and electrons can jump to higher energy levels (electron orbits/shells). After short time, electrons return back to their original shell releasing energy as electromagnetic radiation that we see as colours.
Ionisation
If we give too much energy - electrons escape all together, making the atom a charged particle (ion)
emission spectrum
Each colour emitted from electromagnetic radiation is a different wavelength of light.
background radiation
Low level of radiation to which we are exposed to every day from environment and space
Sources of background radiation
Radon gas, cosmic rays, rocks, building materials, medical x-rays, food, nuclear industry
what is randon gas?
Radioactive gas that has no smell, colour or taste. Produced from the radioactive decay of uranium
How to measure radiation
Dorsimeter, or Geiger-Muller tube
Dorsimeter
Used to be photographic films that would get darker the more radiation it absorbed
Geiger-Müller counter
instruments that detect radiation by counting electric pulses carried by gas ionised by radiation
Decay
When a nucleus emits a particle or a wave.
Why can you not predict when an atom decays?
The process is random
What are the types of radiation
alpha, beta, gamma
alpha particle
a type of nuclear radiation consisting of two protons and two neutrons
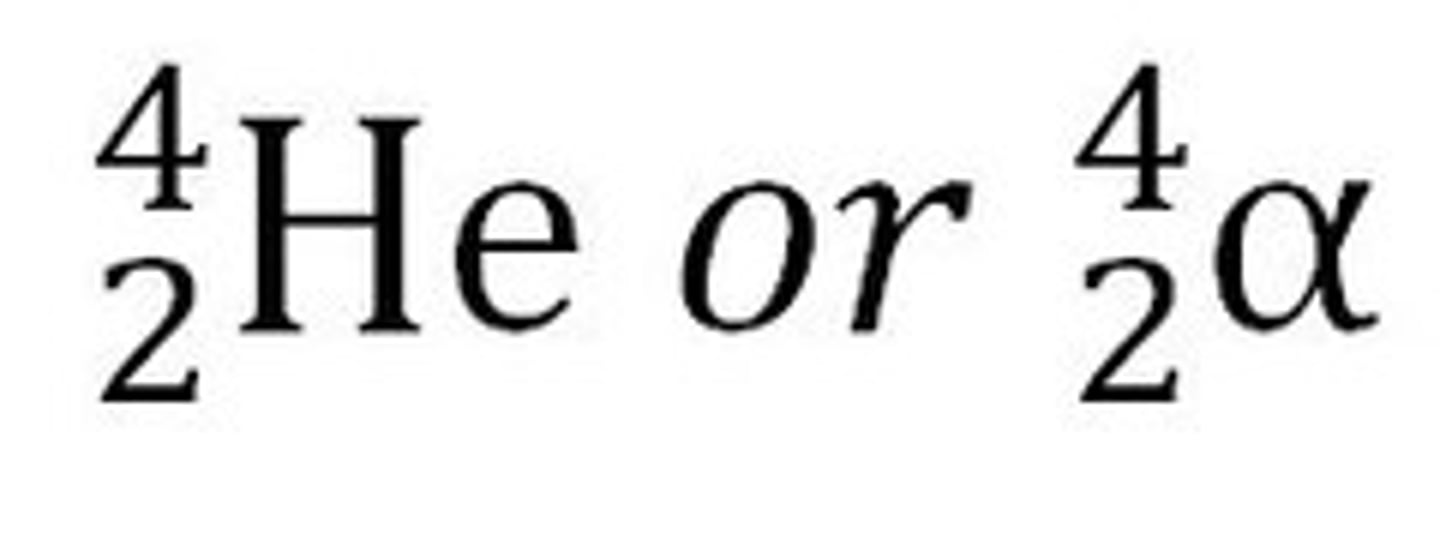
beta particle
a high-speed electron with a 1- charge that is emitted during radioactive decay
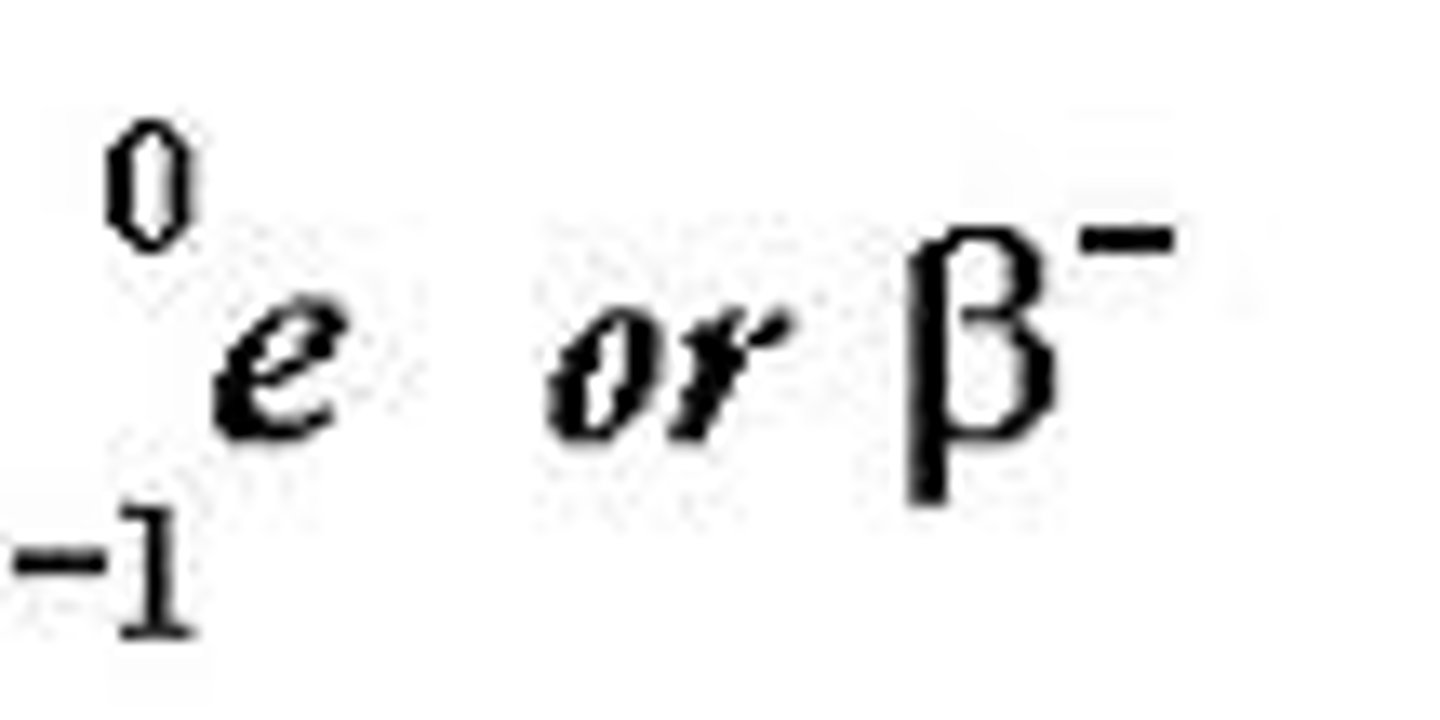
gamma rays
high-energy electromagnetic waves emitted from a nucleus as it decays. They have no charge
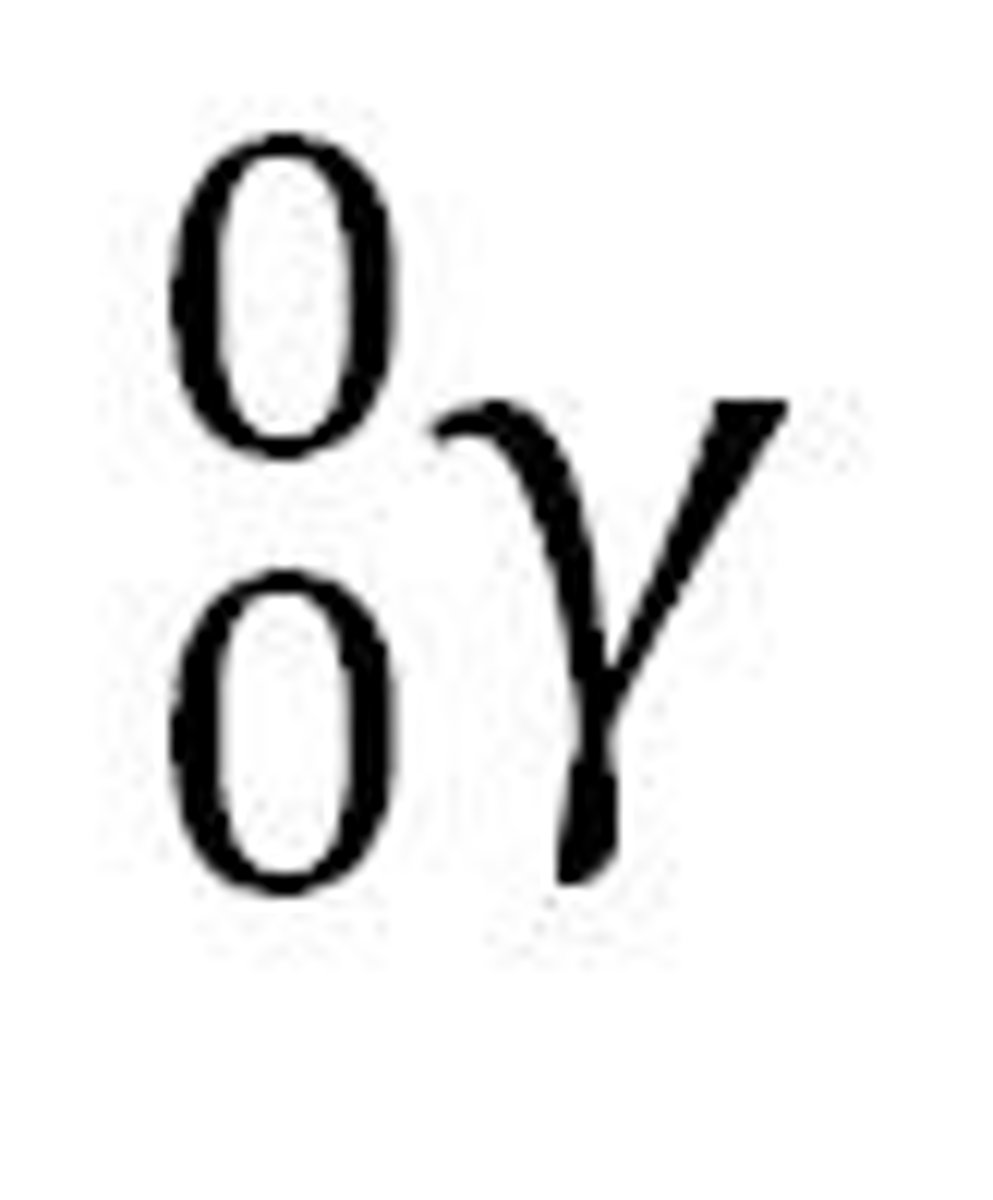
Beta minus decay
The process of a neutron inside a nucleus turning into a proton, and emitting a beta-minus particle (an electron)
Beta plus decay
The process of a proton inside a nucleus turning into a neutron, and emitting a beta-plus particle (a positron)
Ionising radiation
radiation that provides enough energy for an atom to lose an electron and become an ion
radioactive
emits ionising radiation
What is a property of alpha radiation related to ionising power?
High ionising power due to high mass and charge.
What is a property of alpha radiation related to penetrating power?
Low penetrating power with a range of a few cm in air.
What can block alpha radiation?
Skin or a sheet of paper.
What is the ionising power of beta radiation?
Medium ionising power
What is the penetrating power of beta radiation?
Medium penetrating power, with a range of a few meters in air
What material can block beta radiation?
3mm thick aluminium
What is the ionising power of gamma radiation?
Low ionising power
What is the penetrating power of gamma radiation?
High penetrating power
What is the range of gamma radiation in air?
A few kilometers
What material can block gamma radiation?
Many centimetres of lead
nuclear equation
a type of equation that shows the atomic number and mass number of the particles involved
half-life
time taken for half a nuclei to decay
Radioactivity
how many nuclei decai per second
What is radioactivity measured in?
Bequerels (Bq)
How is radiation used in killing microorganisms?
Gamma rays transfer energy to bacteria, killing them and sterilising food. Making it safer to eat and meaning it can be stored for longer without going off
How is radiation used in radioactive detecting?
A gamma source added to water is used to detect leaks in water pipes underground. Where there is a leak, water flows into the surrounding earth, and a Geiger muller tube following the path will detect higher levels of radiation where there is a leak
How is radiation used in smoke alarms?
Americium is used in smoke alarms and it is an alpha emitter.
o This is stopped by a few centimetres of air (as it is weakly penetrating)
o The alpha particles ionise air particles and makes them charged therefore making a current
o If smoke enters the air around the alarm, the current drops in the circuit
▪ Causing the alarm to sound
How is radiation used in checking thickness?
Beta radiation is mildly penetrating, and can just pass through paper
A source and receiver are placed either side of the paper during its production
If there is a drop or rise in received electrons, then that means the thickness of the paper has changed
What are the 2 effects radiation can have on cells?
Kill cells - radiation burns and tissue damage caused by large amounts of radiation
Mutate cells - if cells mutate they can then grow into a tumour, caused by small amounts of radiation over a long time
What is a key requirement for the half-life of medical radiation isotopes?
It must be short enough to minimize the dose of potentially harmful radiation given to the patient.
What is another requirement for the half-life of medical radiation isotopes?
It must be long enough to produce the required image or kill cancer cells.
Irradiation
Exposure to nuclear radiation without becoming radioactive
What is contamination in the context of radiation?
The source of radiation is transferred to an object.
What happens when you touch radioactive material?
Its atoms are now on you.
What does PET stand for in medical imaging?
Positron Emission Tomography
What does a PET scan visualize?
Brain activity
What substance does a PET scan use to detect brain activity?
A radioactive form of glucose
What does a PET scan measure while the brain performs a task?
Where the radioactive form of glucose goes
How does a PET scan work?
1. inject radioactive tracer (glucose)
2. Glucose emits positronn
3. positron reacts with electrons
4. 2 gamma rays are produced going in opposite directions
5. PET scan picks up those gamma rays
internal radiotherapy
Treatment of cancer by putting a radioactive source inside the body.
Nuclear power
Energy that is harnessed from reactions among radioactive isotopes
advantages of nuclear power
Stores a lot more energy per 1g than other fuels
Produces no polluting gases
Reliable - provides power whatever the weather
disadvantages of nuclear power
Pollution from accidents can contaminate land for decades
Produces radioactive waste that is very difficult and expensive to dispose
Nuclear fission
large nuclei (uranium-235) break up to form smaller nuclei and energy
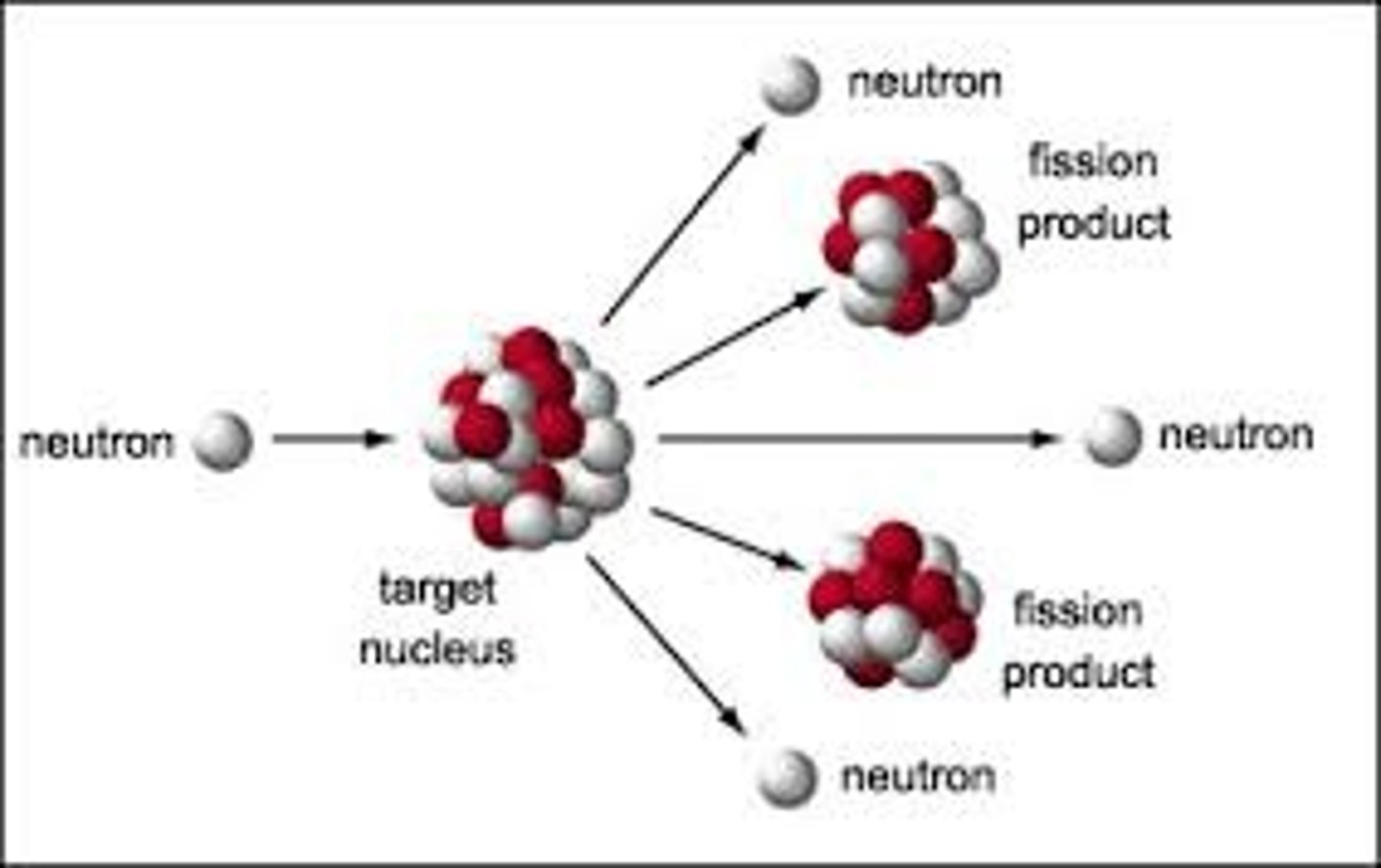
nuclear chain reaction
the continued process of atoms splitting and releasing neutrons that trigger more atoms to split
how to control the chain reaction in nuclear power plants?
By using control rods which slows the reaction down by absorbing more of the neutrons, or moved up so that fewer of the neutrons are absorbed, which means that the reaction remains constant and explosions do not occur.
Control rods
neutron-absorbing rods that help control the reaction by limiting the number of free neutrons
fuel rods
a uranium rod that undergoes fission in a nuclear reactor
moderator
used to slow down the fast neutrons produced by fission
How to generate electricity from a reactor core?
Thermal energy from the core is is used to heat water pumped through the reactor. The heated water is pumped to a heat exchanger where it turns to steam. The steam turns a turbine which turns a generator. The generator transfers kinetic energy to electrical which is then transferred through the national grid
nuclear fusion
2 small nuclei fuse to form a larger nucleus