Understanding Newton's First Law of Motion
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
First Law of Motion
An object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon.
Equilibrium
State where no net force acts on an object.
Force
An interaction that causes a change in motion.
Aristotle's View
Objects at rest require a force to move.
Natural Resting Place
The assumed state of objects without external forces.
Copernicus
Proposed Earth moves around the sun.
Galileo's Contribution
Challenged the need for force to maintain motion.
Friction
Force opposing motion between touching surfaces.
Microscopic Irregularities
Surface imperfections causing friction.
Inclined Plane Experiment
Galileo's test showing motion dynamics on slopes.
Gravity
Force attracting objects toward Earth.
Constant Velocity
Uniform motion without acceleration or deceleration.
Motion Against Gravity
Movement opposing gravitational pull.
Motion with Gravity
Movement in the direction of gravitational pull.
Friction's Role
Necessary to maintain motion in real scenarios.
Height Attainment
Ball reaches similar height on opposing incline.
Distance Traveled
Ball rolls further on longer inclined planes.
Inertia
Resistance of an object to changes in motion.
Natural Tendency
Moving bodies continue in motion unless acted upon.
Horizontal Plane
Surface where only friction affects motion.
Galileo's Conclusion
Without friction, motion continues indefinitely.
Inclined Plane Dynamics
Different angles affect ball's speed and height.
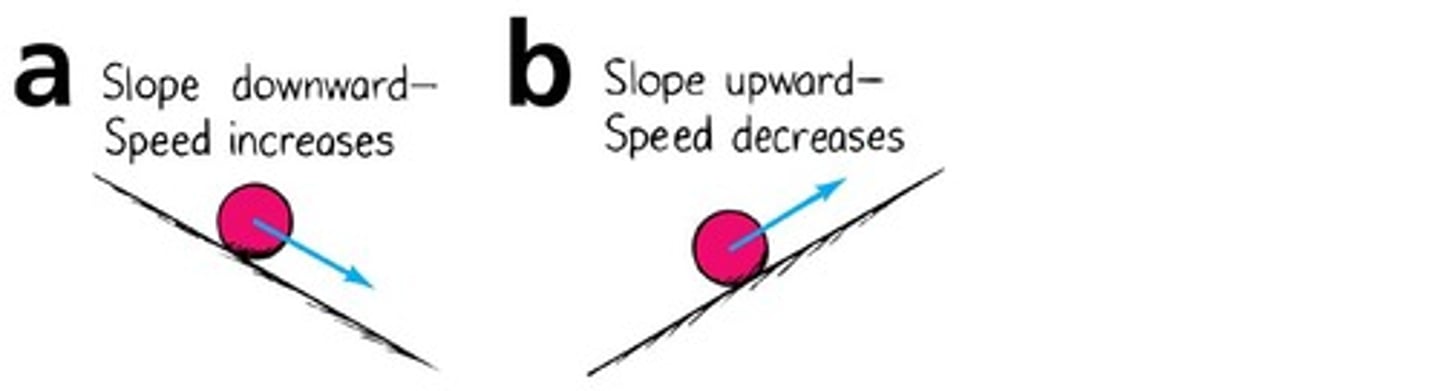
Resting Nature
Objects do not naturally stop moving without friction.
Law of Inertia
Objects resist changes in their state of motion.
Objects at Rest
Remain at rest until acted upon by a force.
Objects in Motion
Continue moving in a straight line indefinitely.
Inertia
Property of objects to resist changes in motion.
Force-Free Environment
Area where no external forces act on objects.
Friction
Force that opposes motion between surfaces.
Mass
Amount of matter in an object, measured in kg.
Acceleration Formula
a = Fnet/m; relates force, mass, and acceleration.
Greater Mass
Requires more force to change motion state.
Volume
Measure of space occupied by an object.
Mass vs Volume
Mass is not the same as volume.
NASA Videos
Educational resources illustrating Newton's laws.
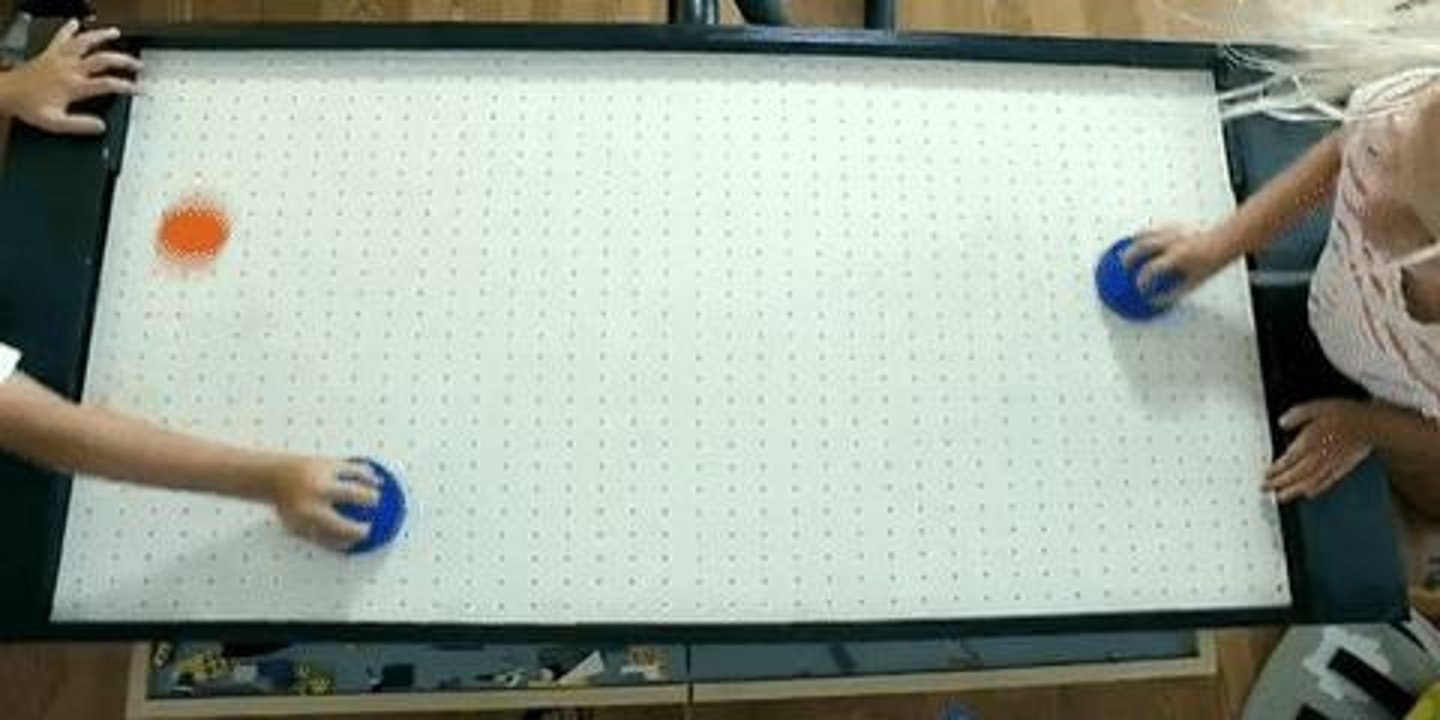
Air Table
Surface providing nearly friction-free conditions.
Hockey Puck Example
Demonstrates effects of friction on motion.

Straight Line Motion
Path of an object without external forces.
Gravity's Role
Keeps planets in orbit around the sun.
Constant Speed
Motion at unchanging velocity in absence of forces.
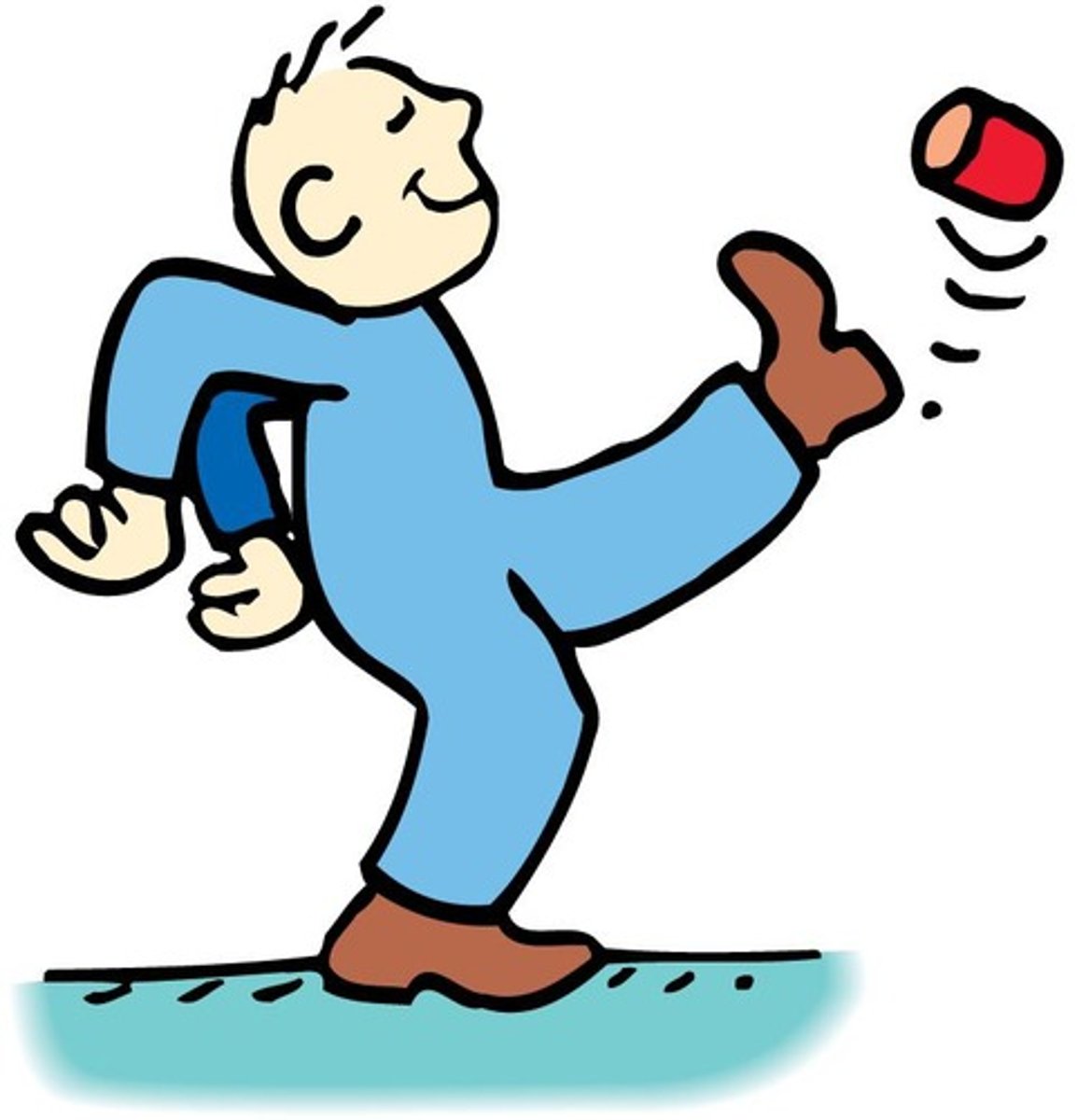
Kick Test
Demonstrates inertia based on mass differences.
Empty Can vs Filled Can
Shows how mass affects motion resistance.

Nonzero Net Force
Required to change an object's state of motion.
Galileo's Idea
Force not needed to maintain motion.
STEMonstrations
Experiments illustrating principles of motion.
Mass
Measure of material in an object.
Weight
Gravitational force acting on an object.
Inertia
Resistance to change in motion.
SI Unit of Force
Newton (N), equivalent to kg•m/s².
Gravitational Acceleration
9.81 m/s² on Earth's surface.
Mass vs Weight
Mass is constant; weight varies with gravity.
Proportional Relationship
Twice the mass equals twice the weight.
Volume
Space occupied by an object.
Density
Mass per unit volume of a substance.
Force-Free Region
Area with negligible gravitational influence.
Newton Definition
Force required to accelerate 1 kg at 1 m/s².
Mass Measurement
Typically measured in kilograms (kg).
Weight Measurement
Typically measured in newtons (N).
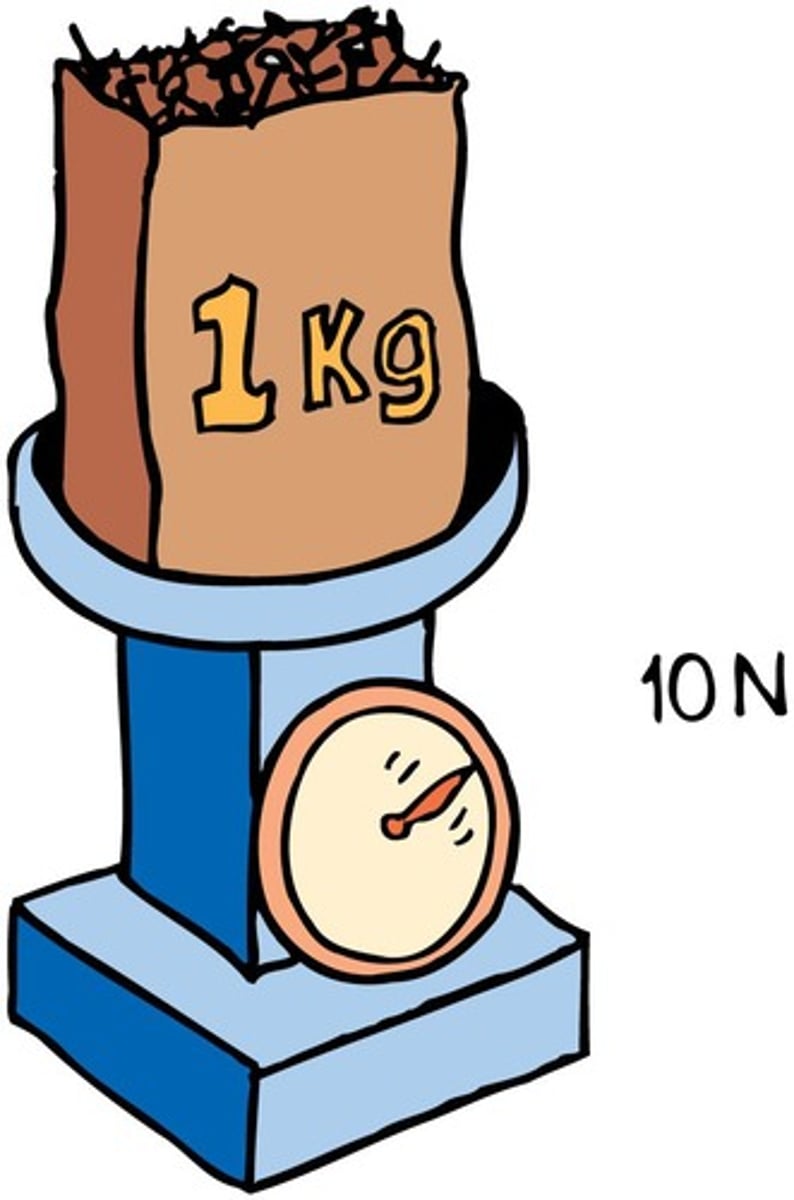
1 kg to N Conversion
1 kg weighs approximately 10 N on Earth.
Bananas vs Bread
2 kg of bananas occupies less volume than 1 kg of bread.
Law of Inertia
Objects remain in motion unless acted upon.
Copernicus' Theory
Proposed a moving Earth in the 16th century.
Inertia and Location
Inertia remains constant regardless of location.
Mass and Inertia Relationship
More mass means more inertia.
Weightlessness
Condition where gravitational force is negligible.
Mass Consistency
Mass remains unchanged in different gravitational fields.
Force Equation
F = mg, where m is mass and g is gravity.
Inertia
Resistance of an object to change its motion.
Copernicus
Challenged the geocentric model of the universe.
Geocentric model
Earth-centered view of the universe.
Vertical motion
Movement in the up or down direction.
30 km/s
Speed of Earth's movement around the sun.
Objects move with Earth
All objects on Earth share its motion.
High-speed vehicle
A car, bus, or plane moving quickly.
Coin flip example
Demonstrates inertia in moving vehicles.
Gravity's effect
Only influences vertical motion of objects.
Perfect circle
Historical belief about Earth's orbital path.
Newton's laws
Fundamental principles governing motion and forces.
Aristotle's belief
Earth is stationary and at universe's center.
Galileo
First to challenge Aristotelian views scientifically.
Weight of matter
Force of gravity acting on an object's mass.
10 N force
Weight of 1 kg of matter on Earth.
Straight-line path
Motion without gravitational influence would be linear.
Air movement
Contributes to perceived motion of objects.
Wall's motion
Remains constant relative to a jumping person.
Natural motion
Historical view that Earth's motion is unnatural.
Center of the universe
Historical belief placing Earth in a central position.
Curved path
Trajectory of Earth if gravity were absent.
Assessment questions
Evaluate understanding of concepts discussed.
Catch a worm
Bird's action demonstrating motion relativity.