Enzyme Function and Catalysis in Biological Reactions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Self-replication
Ability of organisms to reproduce independently.
Catalysis
Acceleration of chemical reactions by catalysts.
Sucrose
A disaccharide sugar consumed for energy.
Enzymes
Proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions.
Cellulose
Polysaccharide that breaks down into glucose.
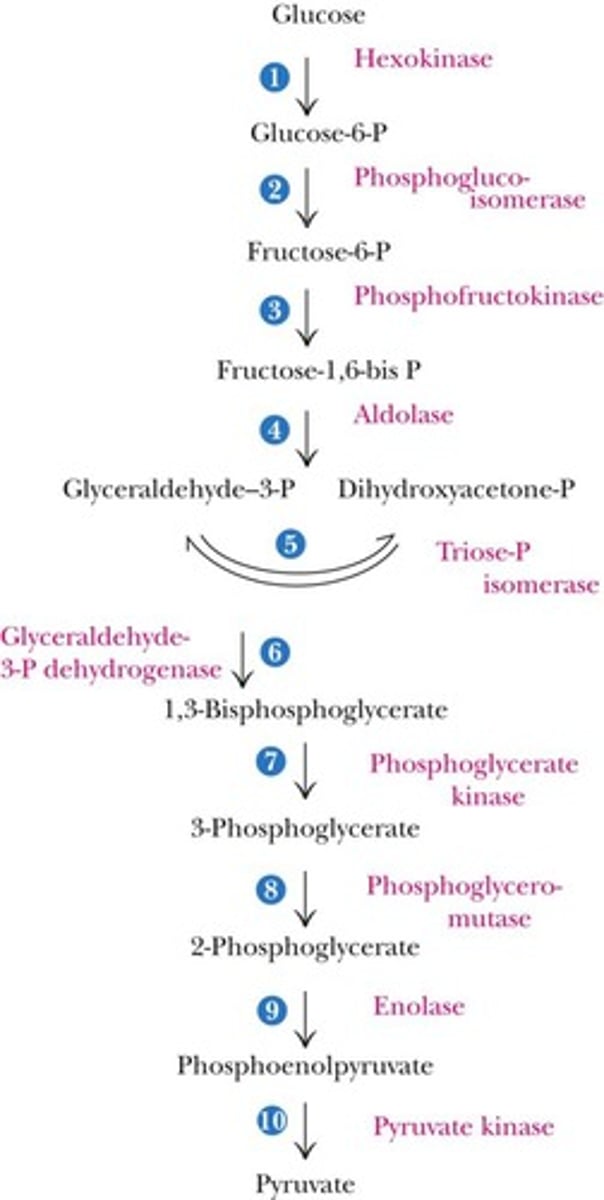
Glycolysis
Metabolic pathway converting glucose to pyruvate.
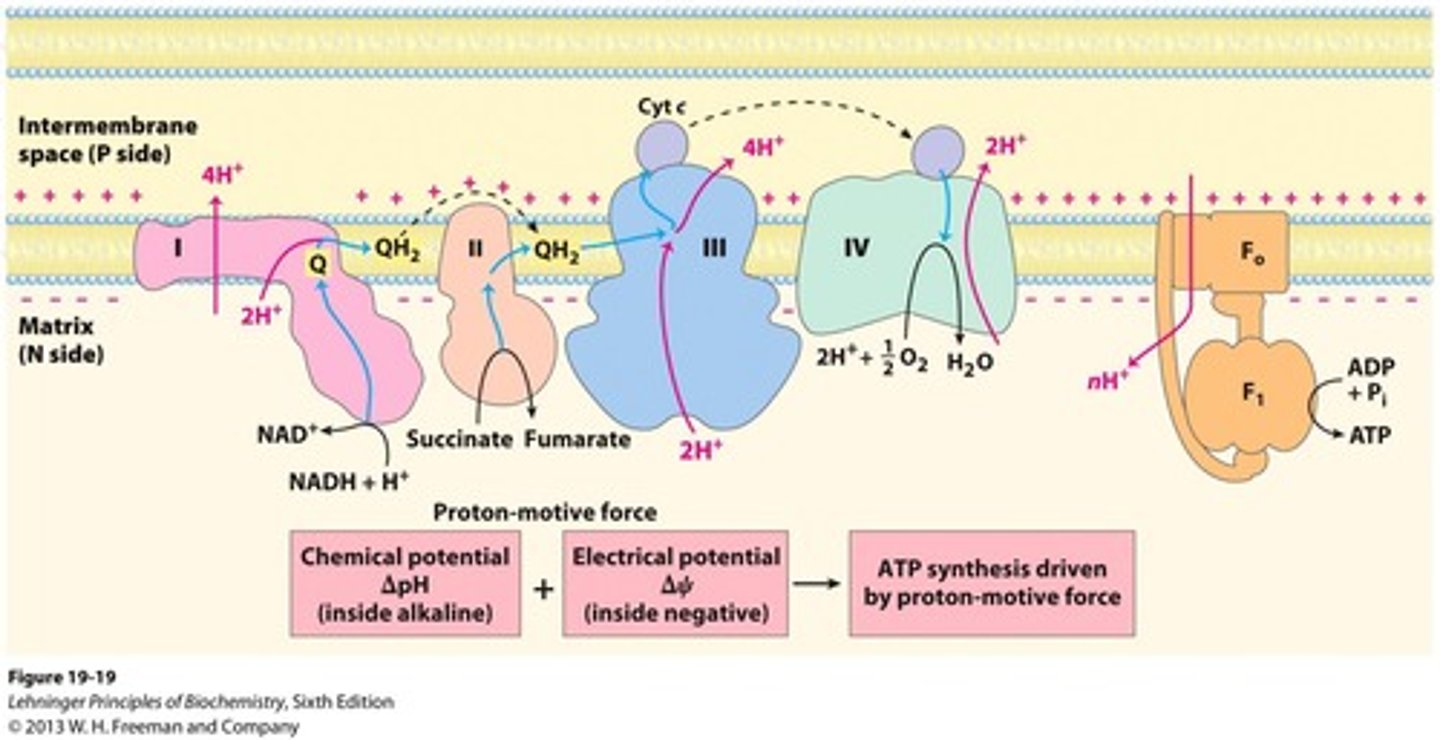
Electron transport chain
Series of protein complexes for ATP production.
Denaturation
Loss of enzyme activity due to structural change.
Cofactor
Inorganic ion required for enzyme activity.
Coenzyme
Organic molecule aiding enzyme function, often from vitamins.
Holoenzyme
Active enzyme with its cofactor or coenzyme.
Apoenzyme
Inactive enzyme without its cofactor or coenzyme.
Oxidoreductases
Enzymes that transfer electrons in redox reactions.
Transferases
Enzymes that transfer functional groups between molecules.
Hydrolases
Enzymes that catalyze hydrolysis reactions.
Lyases
Enzymes that add or remove groups to double bonds.
Isomerases
Enzymes that convert molecules into isomeric forms.
Ligases
Enzymes that form bonds, typically using ATP.
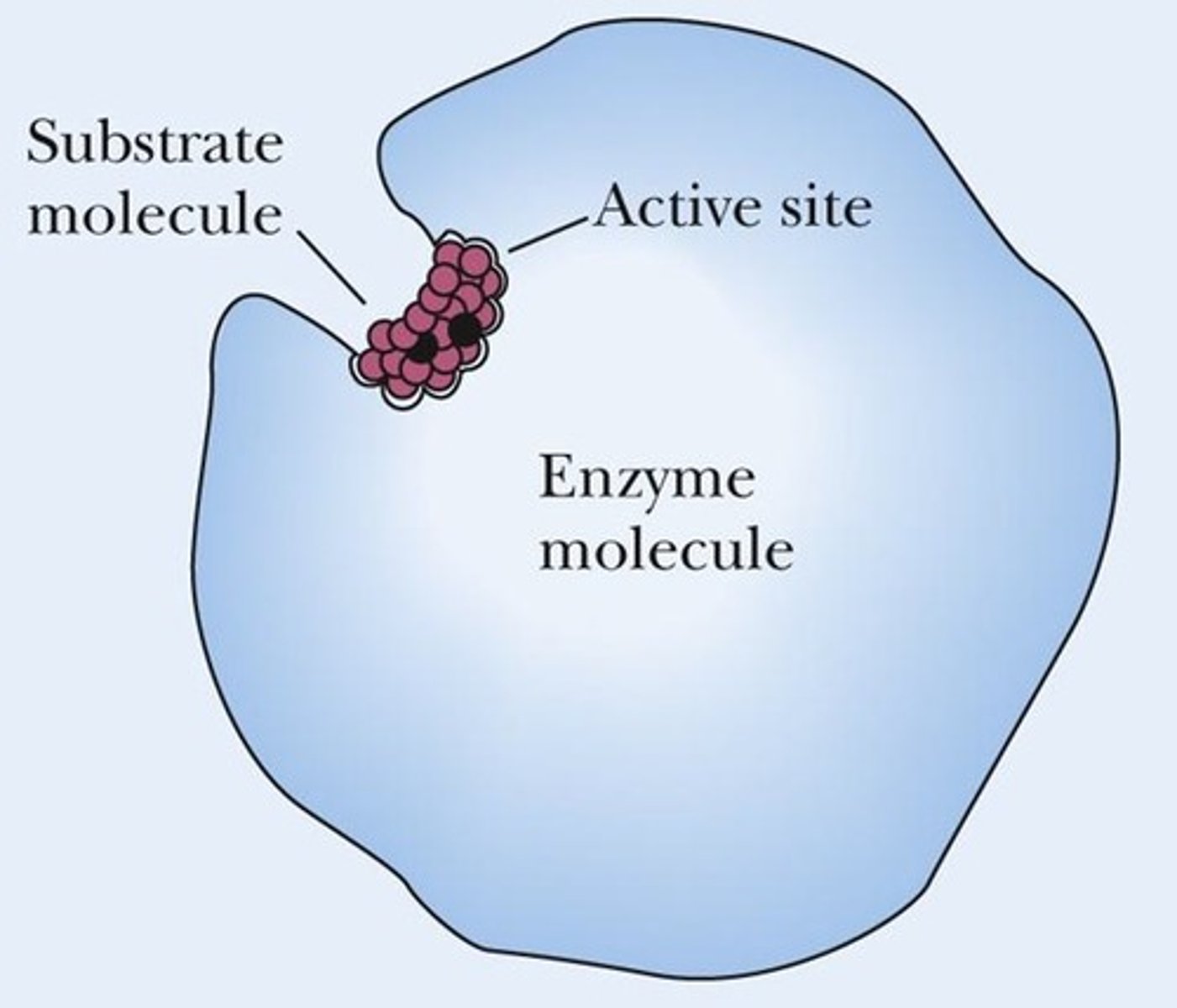
Active site
Region on enzyme where substrate binds.
Catalyst
Substance that increases reaction rate without changing equilibrium.
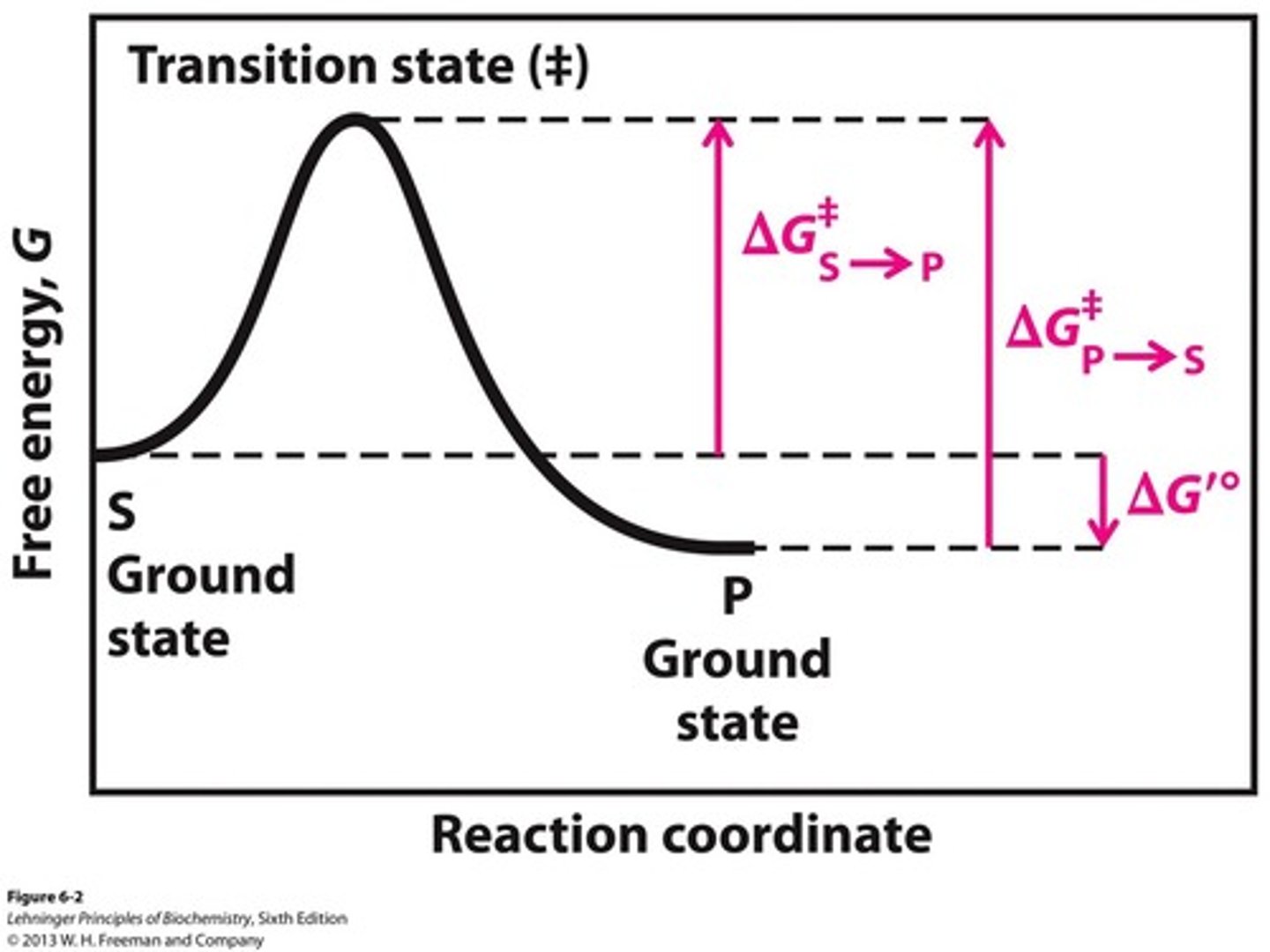
Transition state
High-energy state during a chemical reaction.
Binding energy (ΔGB)
Energy released during enzyme-substrate complex formation.
Induced fit
Enzyme changes shape to better fit substrate.
Thermodynamic potentiality
Energy available for work in biochemical processes.
Energy barriers
Obstacles preventing spontaneous breakdown of compounds.