PS 3: Ventilation - Properties of Gases and Mechanics of Breathing; Transport of Gases by the Blood
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
What are the seven major components of the Respiratory system?
alveoli
Lungs are make up of small air sacs, ____.
alveoli
The ____ are clusters of thin-walled sacs at the terminal branches of the conducting airways
one cell
The walls of the dense network of pulmonary capillaries surrounding each alveolus are ____ ____ thick.
squamous pulmonary epithelial cells (type 1), septal cells (type 2)
What are the two types of epithelial cells found in the walls of each alveolar?
surfactant (type of phospholipid), facilitating lung expansion
What do the septal cells produce?
alveolar macrophages
Also associated with the alveolar wall are ____ ____ (phagocytic cells), which remove particles of dust and debris from alveolar spaces
respiration
The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells is called ____.
inspiration, expiration, and external respiration
What are the 3 processes involved in respiration?
diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
What are the muscles involved in quiet breathing?
increases
The volume of the thoracic cavity ____ due to contraction of the diaphragm (descends), and by contraction of the external intercostal muscles (raises the ribs)
lungs expand to fill the increases space
What happens as the thoracic cavity enlarges that causes the intro-alveolar pressure to fall slightly?
tidal volume
The amount of air that enters the lungs (500 mL of air)
scalene muscles; sternomastoids
For deeper inspirations, the accessory inspiratory muscles, ____ and ____ further enlarge the thoracic cavity
sternomastoids
These accessory inspiratory muscles raises the sternum
scalene muscles
These accessory inspiratory muscles elevate the first two ribs
passive; it is accomplished by elastic recoil of the lungs following relaxation of the inspiratory muscles
Expiration is normally ____ during quiet breathing, because ____.
intra-alveolar; equal
Outward flow of air during expiration ceases when ____ pressure becomes ____ to atmospheric pressure
active; abdominal wall; diaphragm; internal intercostal muscles
During exercise and voluntary hyperventilation, expiration becomes ____; muscles of the ____ ____ contract and push up the ____, and the ____ ____ ____ contract, pulling the ribs downward and inward, thus decreasing the thoracic volume
compliance
____ refers to how much effort is required to stretch or distend the lungs.
pulmonary surfactant
____ ____, which is mixed with water in the fluid lining the alveoli, increases pulmonary compliance and reduces the work of inflating the lungs
stabilizes them by preventing them from collapsing
What does pulmonary surfactant do for the alveoli?
newborn respiratory distress syndrome
A deficiency of pulmonary surfactant is responsible for ____ ____ ____ ____.
Developing fetal lungs do not synthesize pulmonary surfactant until late in pregnancy, so premature babies require strenuous inspiration to inflate poorly compliant lungs
What is the reasoning behind newborn respiratory distress syndrome?
use of “positive” pressure or surfactant replacement
What is the treatment for newborn respiratory distress syndrome?
5.7L; 4.2L
Total lung capacity in males and females is about ____ and ____, respectively.
moderately
The lungs remain ____ inflated throughout the respiratory cycle.
spirometer
A ____ is used to measure changes in lung volume that occur with different respiratory efforts.
consists of an air-filled drum floating in a water-filled container; as a person breathes air in and out of the drum through a connecting tube, the resultant rise and fall of the drum are recorded as a spirogram. inspiration = upward deflection, expiration = downward deflection
How does a spirometer work?
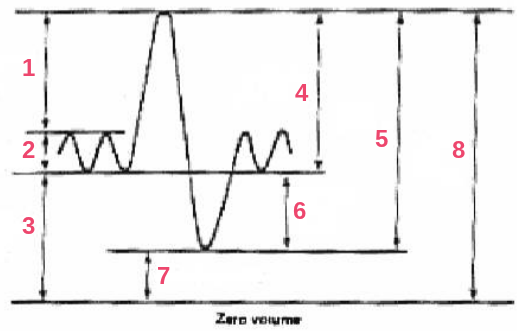
inspiratory reserve volume
tidal volume
functional residual capacity
inspiratory capacity
vital capacity
expiratory reserve volume
residual volume
total lung capacity
What are the respective labels in order?
obstructive lung disease
A disease that affects the airway, such as bronchial asthma, or the lung itself, such as emphysema is called ____.
airway obstruction due to construction of the smaller airways, bronchi and bronchioles; caused by allergy-induced spasm of the smooth muscle in the walls of these airways
What is asthma and what it is caused by?
emptying; filling
A patient with asthma has more difficultly ____ the lungs than ____ them.
normal; functional residual capacity; residual volume; additional air
A person with asthma’s total lung capacity is ____, but the ____ ____ ____ (FRC) and ____ ____ (RV) are elevated due to ____ ____ remaining in the lungs after expiration
wheezing; breathing
Asthma attacks are characterized by ____ (as air is forced through narrowed airways) and difficult ____.
the breakdown of alveolar walls and loss of elasticity due to release of destructive enzymes from alveolar macrophages following chronic exposure to cigarette smoke or other irritants
What is emphysema?
barrel chest
When the lungs remain inflated due to loss of elasticity, the size of chest cage increases leading to a condition called ____ ____.
less; more
Expired air contains ____ oxygen and ____ carbon dioxide compared to inspired air.
partial pressure
The pressure exerted by a gas in a mixture of other gases is called ____ ____.
thin alveolar capillary
Oxygen enters and carbon dioxide leaves the blood in the lungs passively across the ____ ____ ____ membrane.
three
When hemoglobin returns to the lungs, it typically has ____ molecules of O2.
four
The heme portion of hemoglobin contained in red blood cells contains ____ atoms of iron that each binds to a molecule of oxygen
oxyhemoglobin
Oxygen and hemoglobin combine in a readily reversible reaction forming ____.
oxygen
The partial pressure of ____ is the primary factor determining how much oxygen is bound to hemoglobin.
higher; capillaries; cells; blood
The pO2 of blood pumped to the tissues is ____ than the pO2 in the cells, so oxygen diffuses from the ____ to the ____, causing a drop in ____ pO2.
bicarbonate (HCO3-)
70% of carbon dioxide is transported in plasma as ____ ions
plasma; carbaminohemoglobin
7% of carbon dioxide is dissolved in ____ and 23% combines with the globin portion of hemoglobin forming ____.
carbonic anhydrase
The enzyme responsible for conversion of CO2 to carbonic acid intermediate to HCO3- is ____ ____
carbon monoxide
____ ____ binds more tightly to hemoglobin than oxygen.
50
0.1% CO will combine with ____% of hemoglobin in the body
decreases the oxygen-carrying capability of the blood, leading to hypoxia, and resulting in CO poisoning which can be fatal
What does CO do to the human body?
medulla; brain stem
Breathing is an autonomic function generate by neurons in the ____ of the ____ ____ and modulated by higher brain centers.
Respiratory control centers; rhythmic pattern of breathing
____ ____ ____ in the brain stem are responsible for the ____.
phrenic nerve; intercostal nerves
The diaphragm and external intercostal muscles are innervated by the ____ ____ and ____ ____, respectively.
in the spinal cord
The cell bodies for the phrenic nerve and intercostal nerves are located ____.
impulses from the respiratory center terminating on motor neurons
Inspiratory muscles are stimulated by ____
an increase in H+, which is sensed by chemoreceptors located in the medulla leading to reflex increase in ventilation
An increase in arterial blood pCO2 causes ____
hyperventilation
When the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract more forcefully and frequently, this phenomenon is called ____
negative
Hyperventilation is a ____ feedback mechanism
chemoreceptors; breathing rhythm
____ on the ventral surface of the brain stem and in the carotid and aortic bodies on large vessel leaving heart give sensitive feedback for ____ ____.