NAT 5 CHEMISTRY
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
4 factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
Temperature, concentration,particle size and use of catalyst
homogeneous catalyst
catalyst is in the same state as the reactants, they are available in all states
heterogeneous catalyst
catalyst is in a different state from the reactants, only available in solid state
atomic number
atomic number of an element tells you how many protons an atom of that element has
3 particles in the atom
electron, neutron and proton
mass of electrons
nearly zero
mass number
number is equal to the number of protons+number of neutrons
what are isotopes?
atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers
what is an ion and how are they formed?
a charged particle and formed when an atom gains or loses an electron
what ions do metals form ?
postive ions (as they lose electrons)
what ions do non-metals form?
negative ions (as they gain electrons)
the _________ ________ have a stable electron arrangement
noble gases
what is a molecule?
a molecule is two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
what is a covalent bond?
the electrostatic force of attraction between the positive nuclei negative shared pair of electrons
a __________ ____________ is made up of molecules that contain two atoms
diatomic molecule
diatomic molecule
fluorine, chlorine, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, bromine and iodine
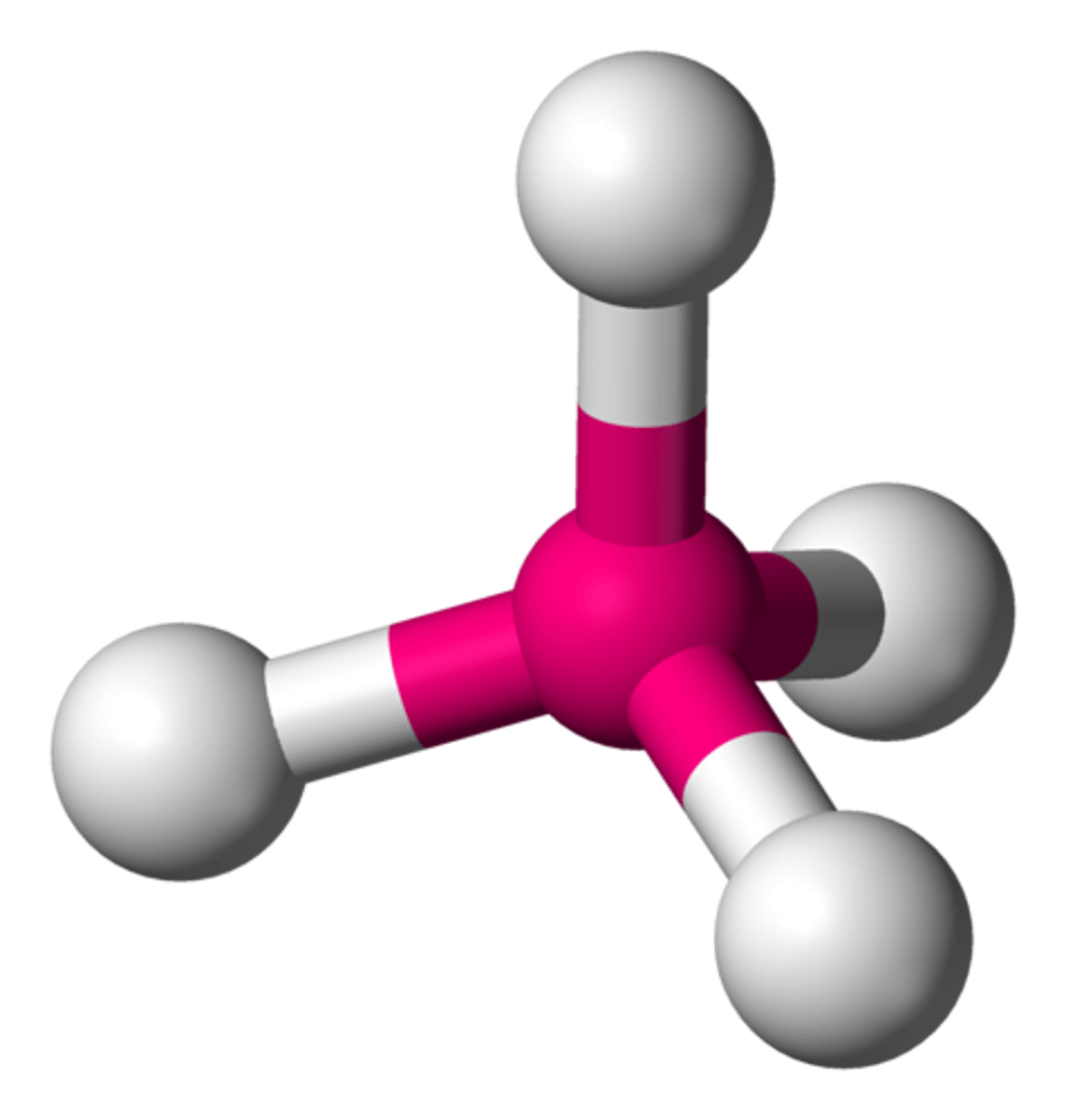
tetrahedral molecule shape
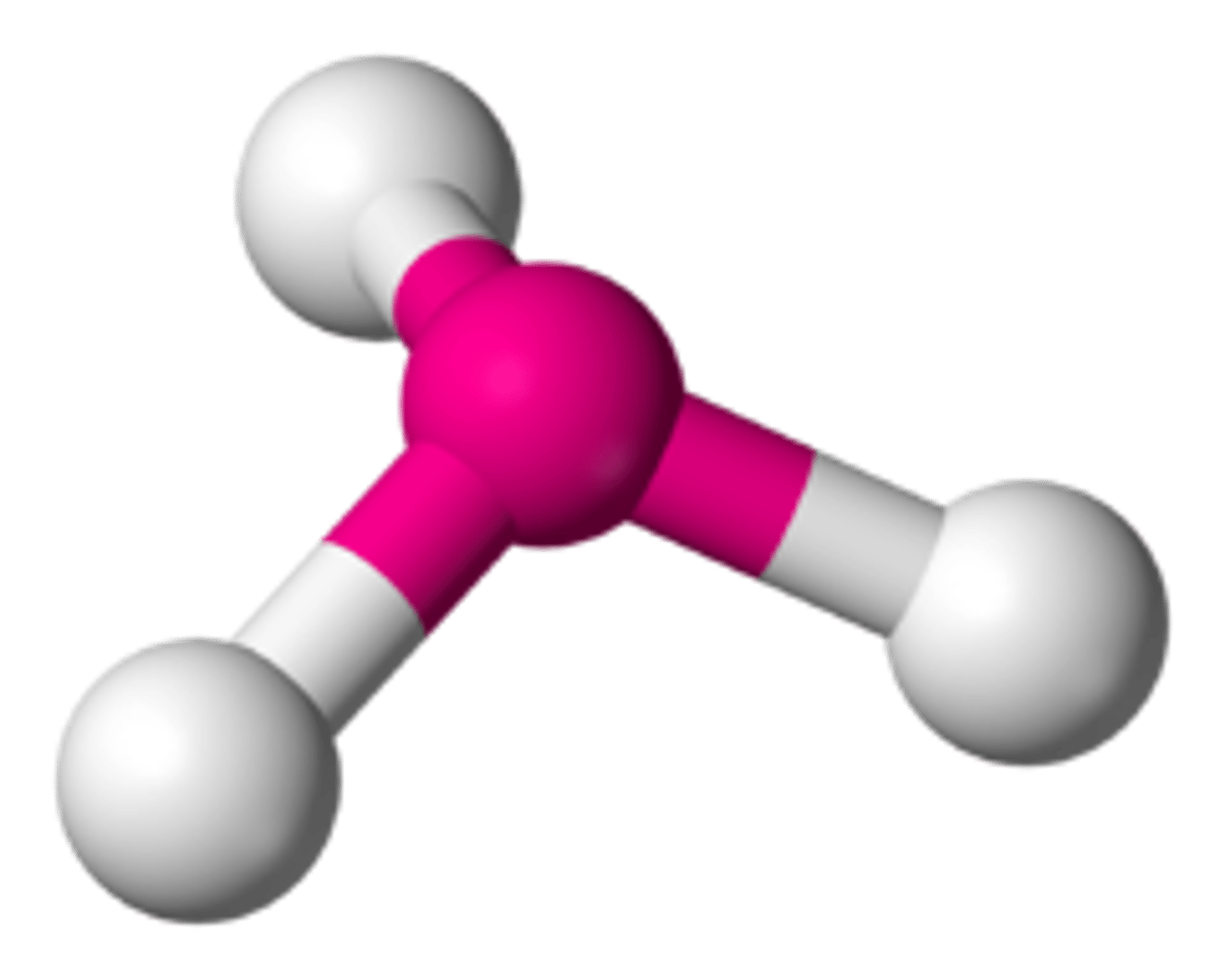
pyramidal molecules
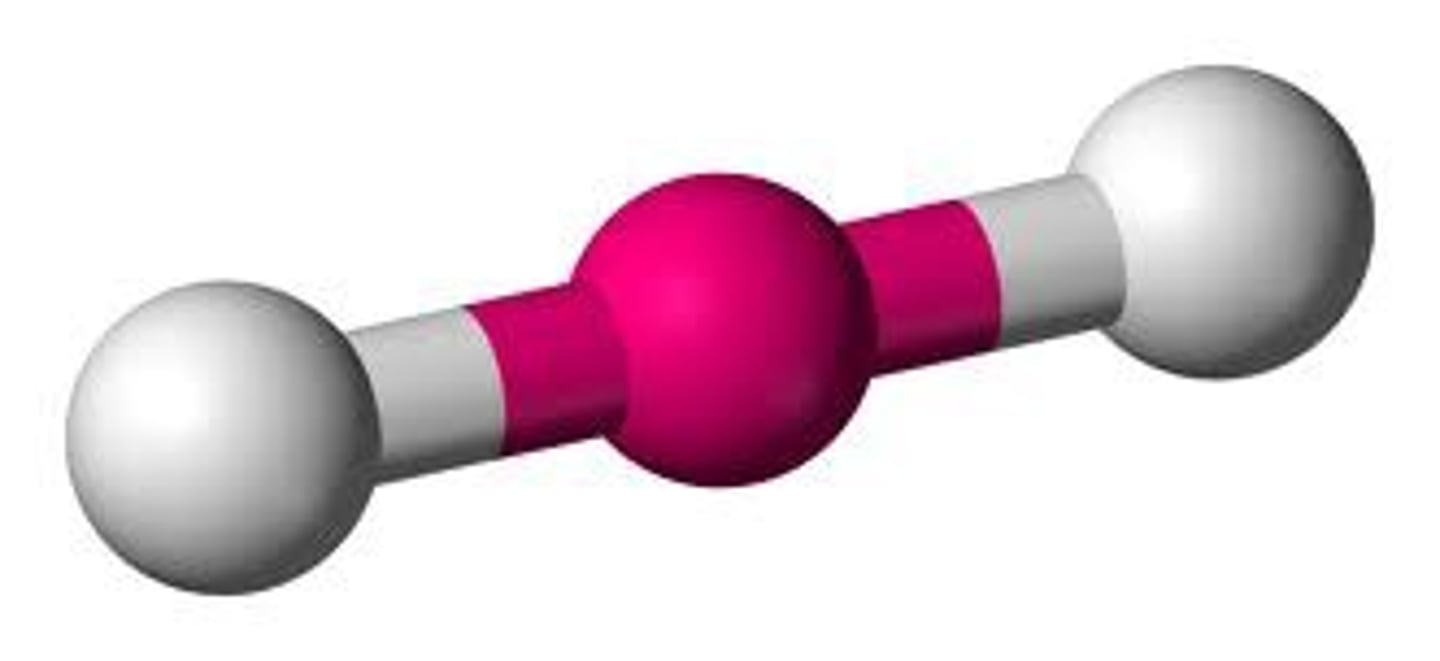
linear molecules
bent molecules
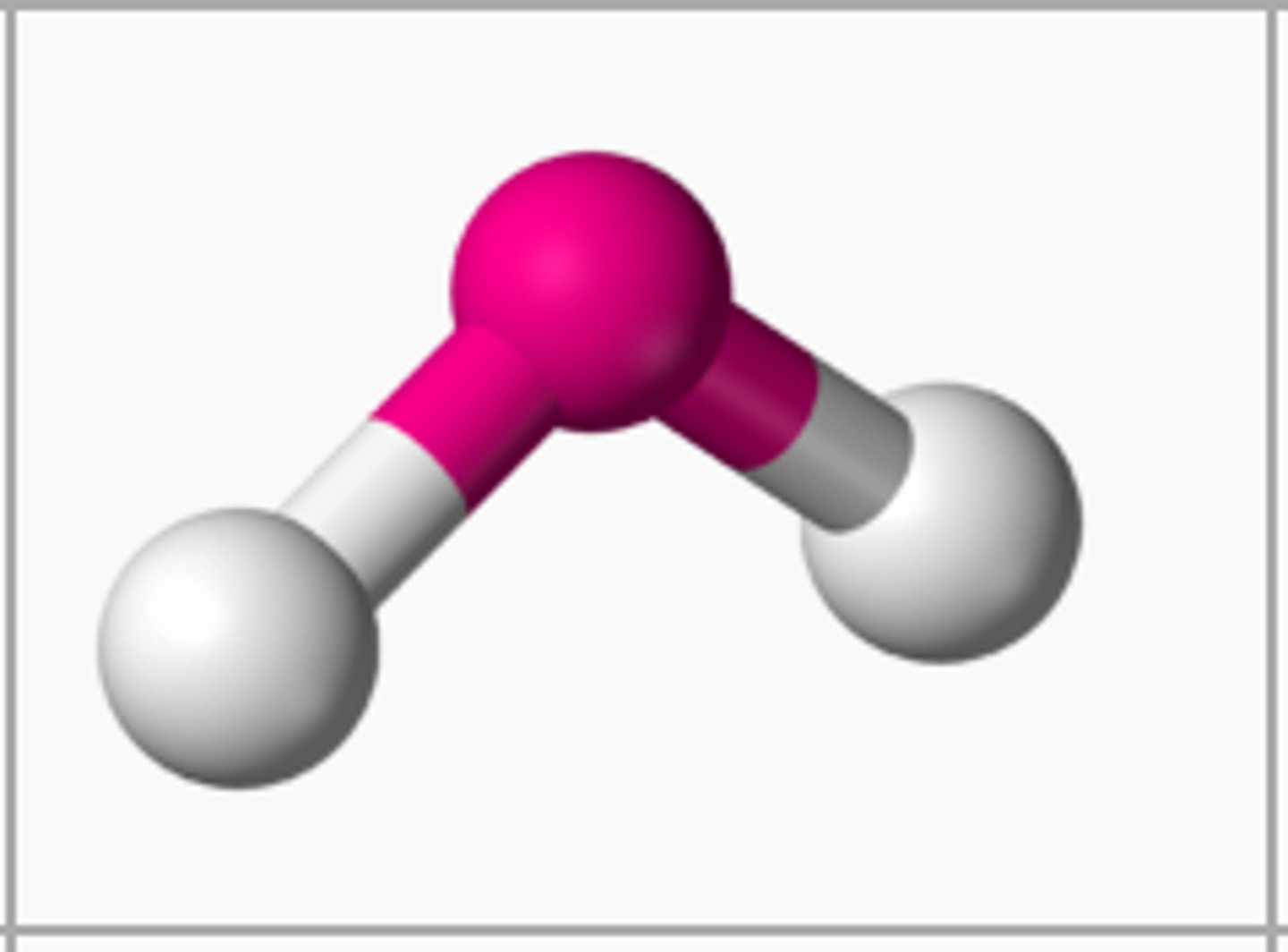
what is an ionic bond?
the electrostatic force of attraction between a positive metal ion and a negative non-metal ion
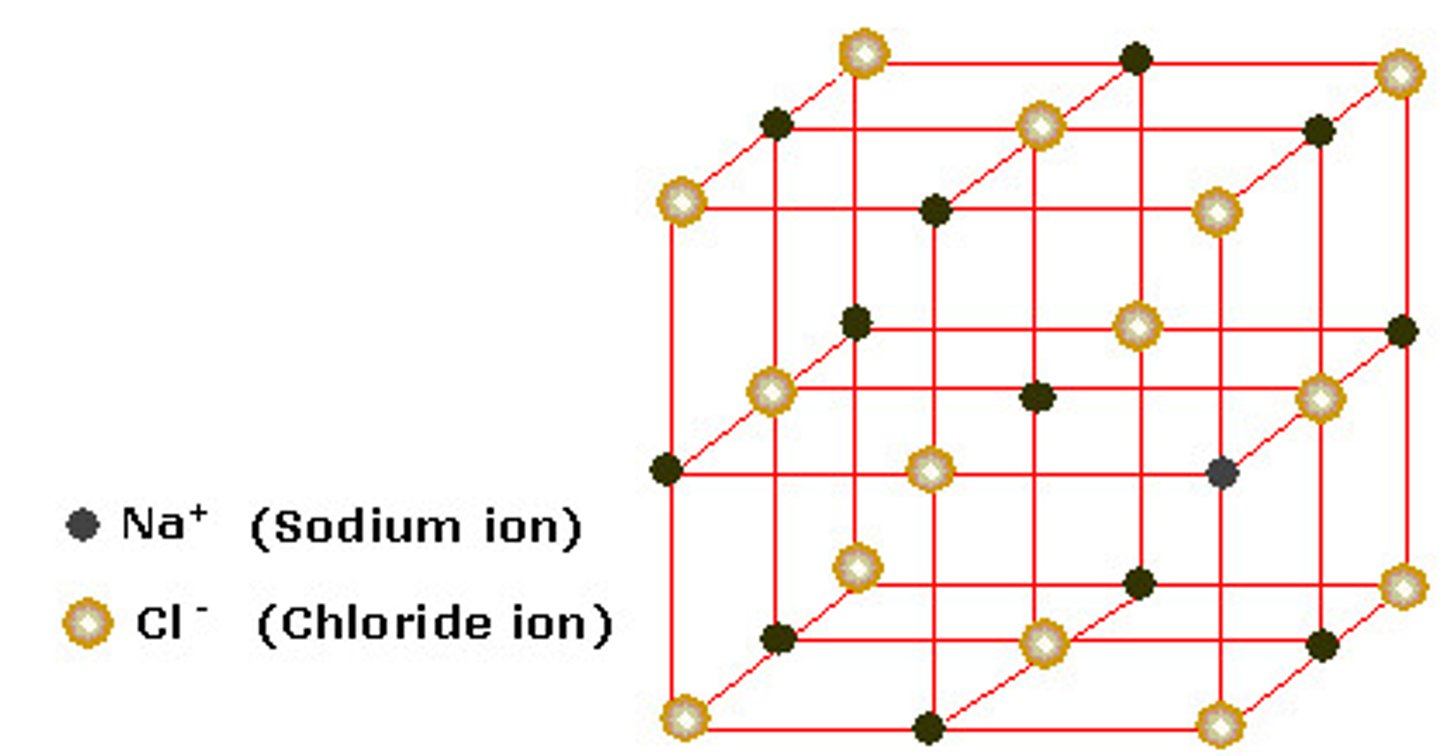
ionic lattice
property of covalent molecular bonded substances
LOW melting and boiling points
properties of ionic substances
HIGH melting and boiling points, conducts never as a solid but only when molten or in solution
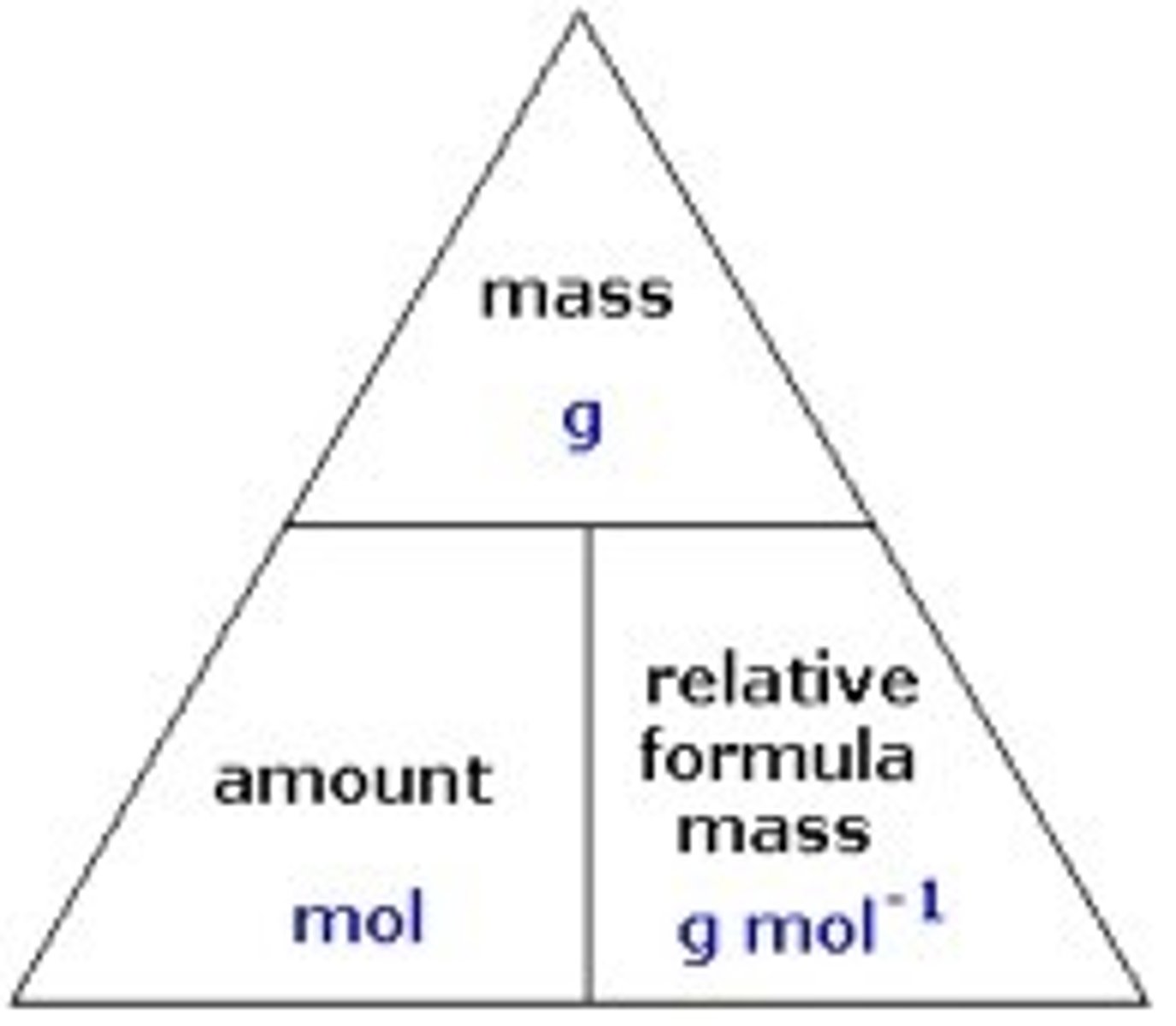
mole calculations formula
acids
have a pH lower than 7, have a greater concentration of H+ ions than OH- ions.
why do acids and alkalis conduct electricity?
they conduct electricity because they have ions that are free to carry the charge
what oxide produces an acidic solution?
Soluble non-metal oxides
what oxide produces an alkali solution?
soluble metal oxides
what are spectator ions?
ions that are present during the reaction but are unchanged by the reaction
homologous series
a family of compounds with similar chemical and physical properties that can be represented by a general formula
general formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
general formula for alkenes
CnH2n
general formula for cycloalkanes
CnH2n
what are saturated hydrocarbons?
hydrocarbons that only contain single carbon to carbon bonds
what are isomers?
isomers re compounds with he same molecular formula but different structural formula
functional group of alcohols
-OH (hydroxyl)
uses of alcohols
solvents in perfumes, thermometers, fuel
functional group of carboxylic acids
-COOH (carboxyl)
uses of carboxylic acids
manufacture of esters, soaps, medicines and vinegar
alcohol + carboxylic acid ->
ester +water
uses of esters
solvents, perfumes and flavourings
functional group of esters
-COO (ester link)
how are esters formed?
by the condensation reaction known as esterification between and alcohol and a carboxylic acid
combustion
when a substance burns it reacts with oxygen and this is know as combustion
commonly used fuels
carbohydrates, alkanes and alcohols
what are carbohydrates fuels?
carbohydrates such as glucose as used to power our bodies
what is a fuel?
a fuel is a substance that reacts exothermically with oxygen
an _____________ ____________ is one which heat energy is given out
exothermic reaction
what is an endothermic reaction?
a reaction in which heat energy is taken in. this means that the products have more energy than the reactants because energy has been absorbed
formula used to calculate the energy released during combustion:
Eh= c x m x Δt
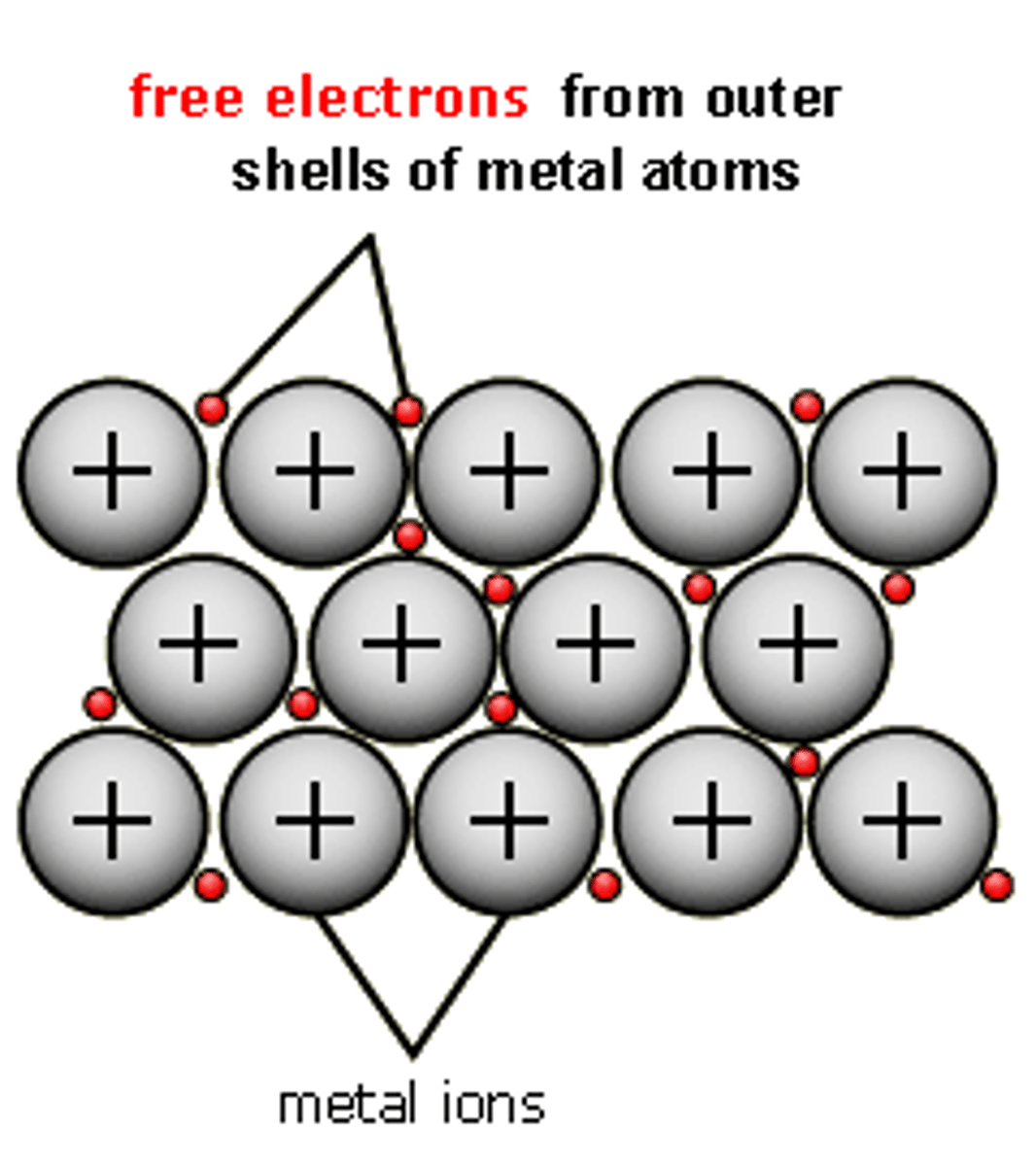
what is metallic bonding?
the electrostatic force of attraction between the positive ions and the negative delocalised electrons between two metals
metallic bonding
metals + water ->
metal hydroxide + hydrogen
metal + acid ->
salt + hydrogen
metal + oxygen ->
metal oxide
what is a cell?
a cell is made up of two different metals connected by an electrolyte
what is an electrolyte?
an ionic solution that is used to complete the circuit
the flow of electrons is produced because of the _____________ in reactivity of the two metals
difference
electrons will flow from the ______ reactive metal to the _______ reactive metal
most (oxidation) , least (reduction)
oxidation is ______ of electrons
Loss
reduction is ______ of electrons
Gain
what is the purpose of an ion bridge?
to complete the circuit, simply a piece of filter paper soaked in salt water or some other ionic solution
fuel cells
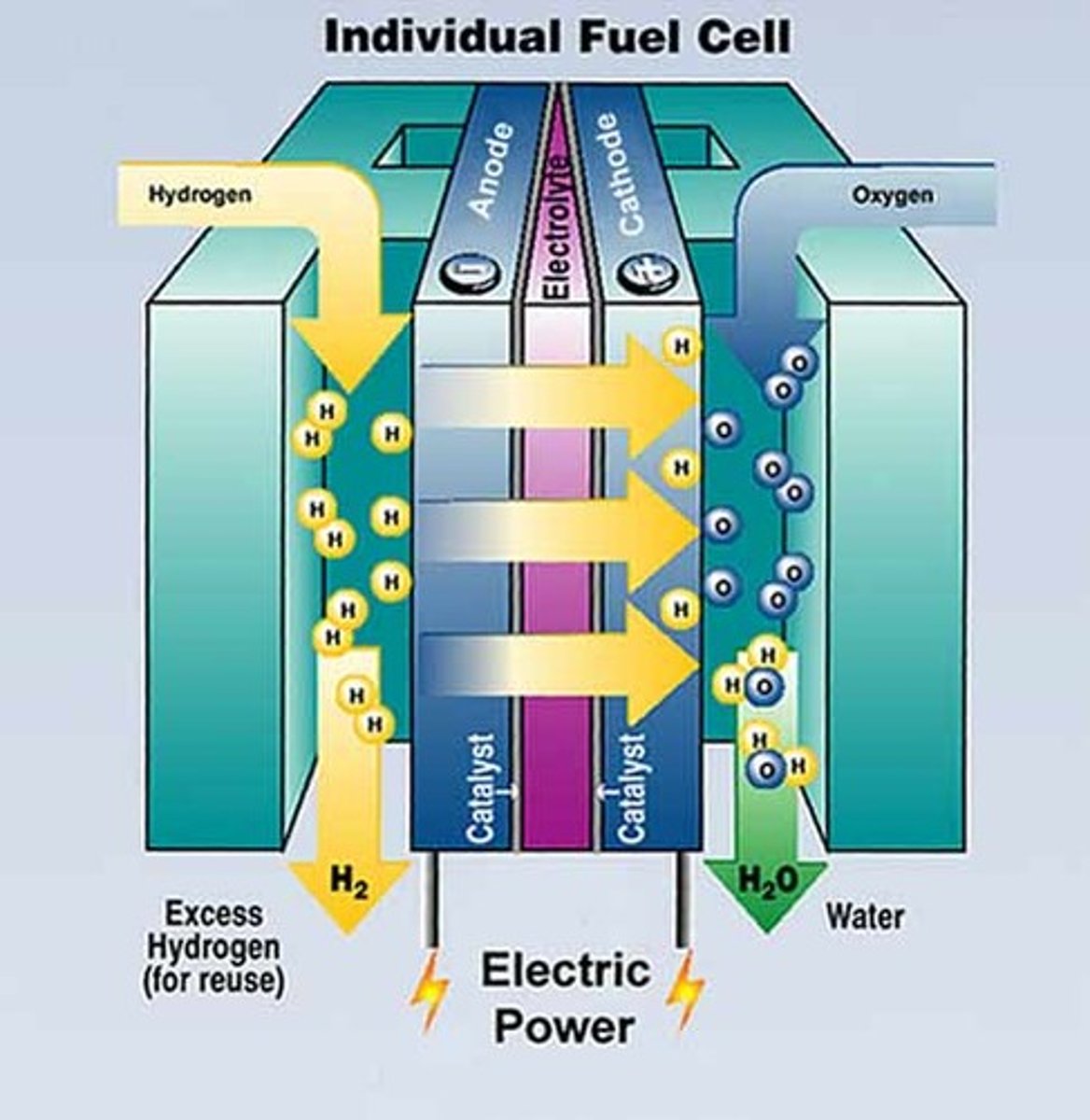
what happens in displacement reactions?
a reactive metal displaces a metal that is less reactive from solution
ores
when metals are found not as a pure metal but as a compound
what is a monomer?
small molecules that combine to form a polymer
what is a polymer?
large molecule formed by combing many monomer molecules
what extra is produced in condensation polymerisation?
water or small molecules such as hydrogen chloride
three main nutrients in fertilisers
-potassium (K)
-nitrogen (N)
-phosphorous (P)
what are the two types of fertilisers?
natural (e.g. manure) and synthetic (man-made)
ammonia
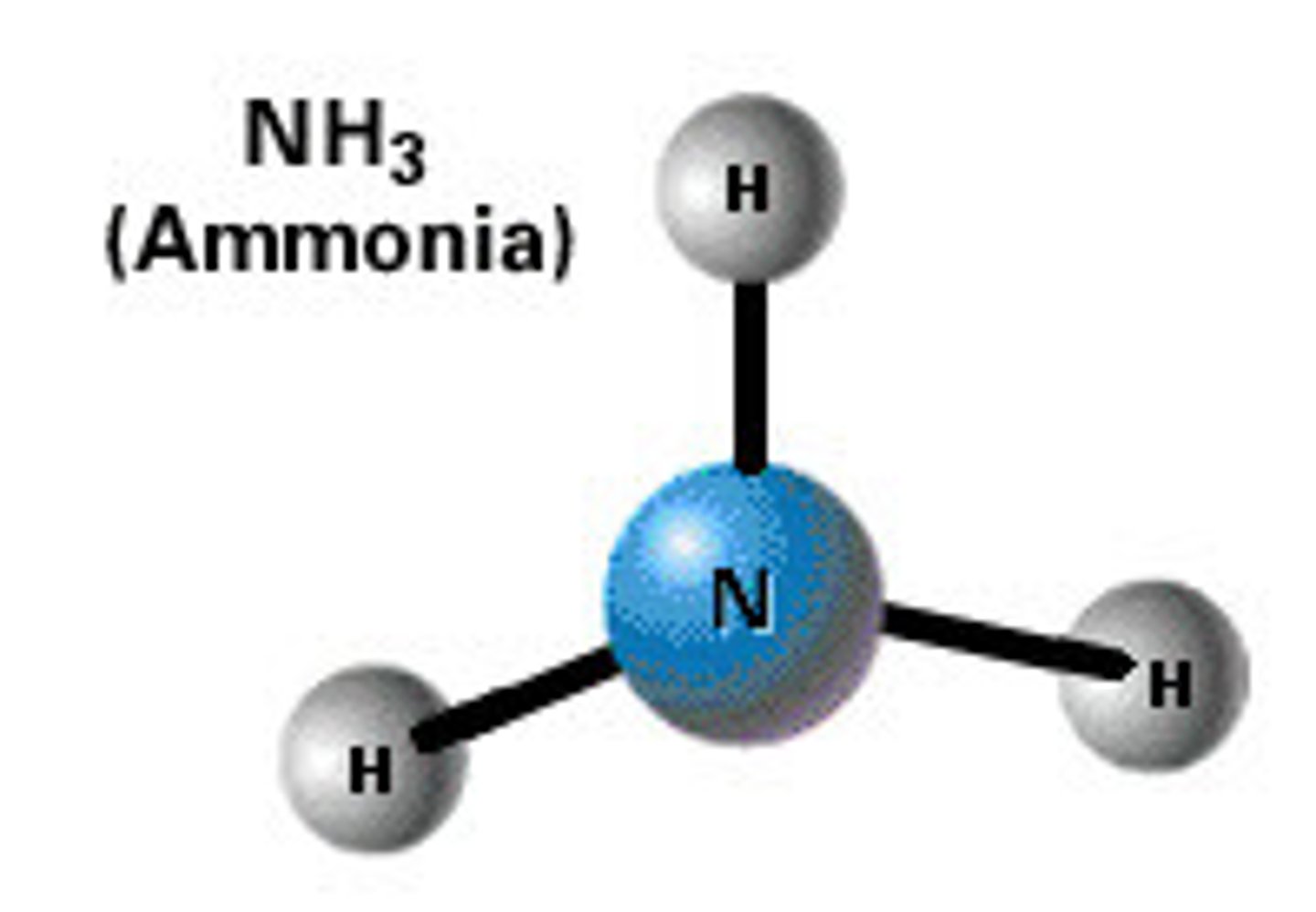
uses of ammonia
can be used to make other fertilisers, explosives, medicines and cleaning products
ammonia is an _______________ _____
alkaline gas
what experiment can be done to test the solubility of ammonia?
'ammonia fountain'
what does the haber process produce?
Ammonia
haber process
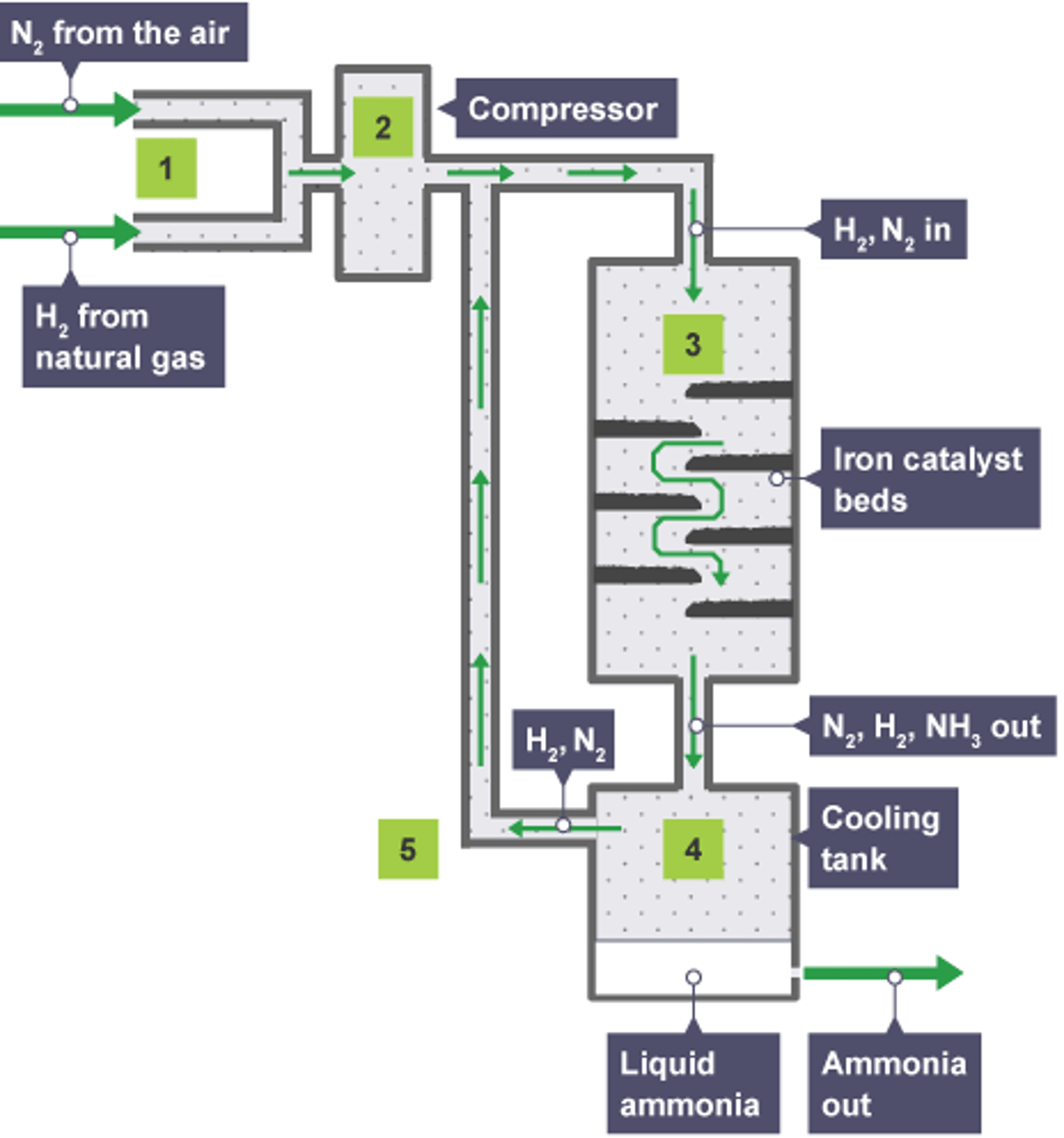
where does the nitrogen and hydrogen come from, that are used in the haber process?
nitrogen(N) from air and hydrogen (H) from steam or methane
what catalyst is used in haber process?
iron catalyst
what temp and pressure is used in the haber process?
400°C and 200 atmospheres
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ->
2NH3 (g)
how does the iron catalyst speed up the reaction (haber process) ?
it is broken down into small pieces to increase its surface area and therefore its effectiveness as a catalyst
what happens to the nitrogen and hydrogen that haven't been converted (haber process)?
put back into the reaction chamber to make the whole process more economic
how is nitric acid produced in an economic way?
ostwald process
what catalyst is used the in the ostwald process?
platinum gauze catalyst at 800°C
ammonia is passed over the platinum catalyst, this produces _________ __________ which combines with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide.
nitrogen monoxide
nitrogen can be easily converted into nitric acid by?
dissolving it in water
the ostwald process is an ______________ __________, so once the reaction is started the heat can be removed and the catalyst will continue to glow red hot.
exothermic reaction
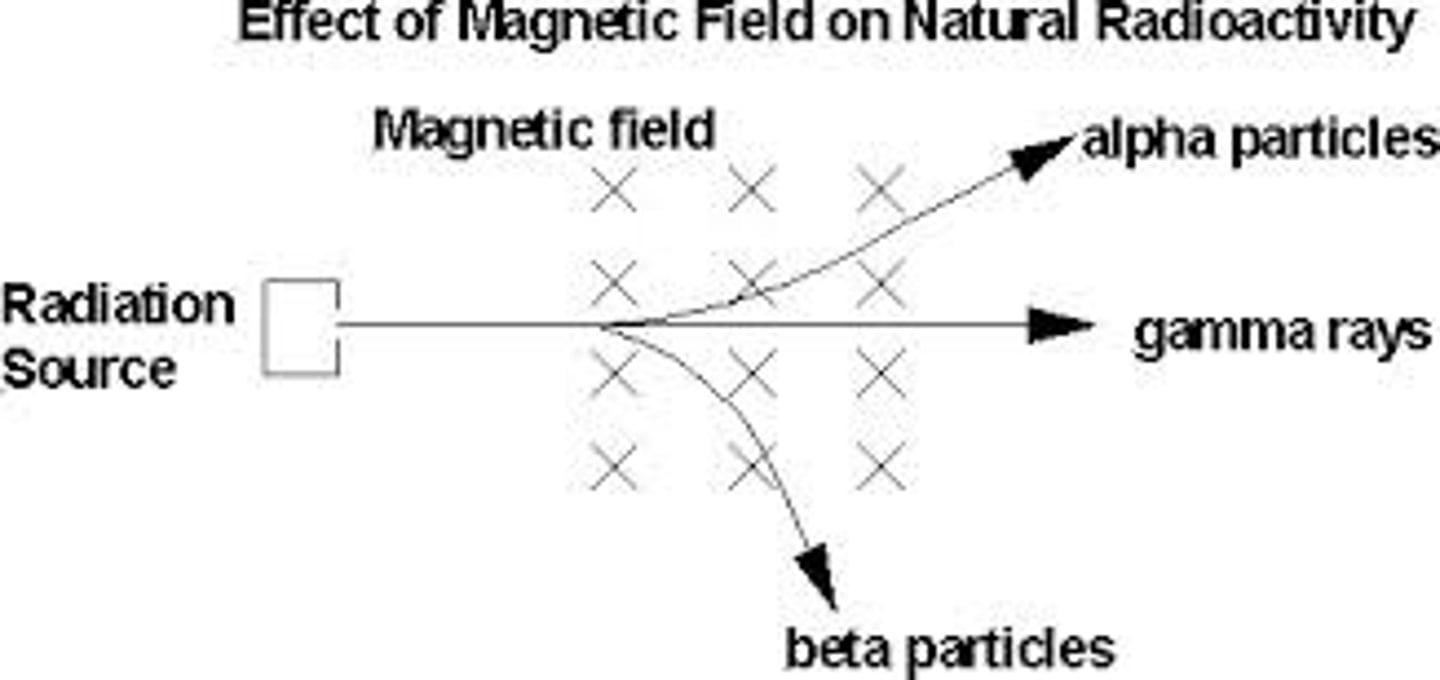
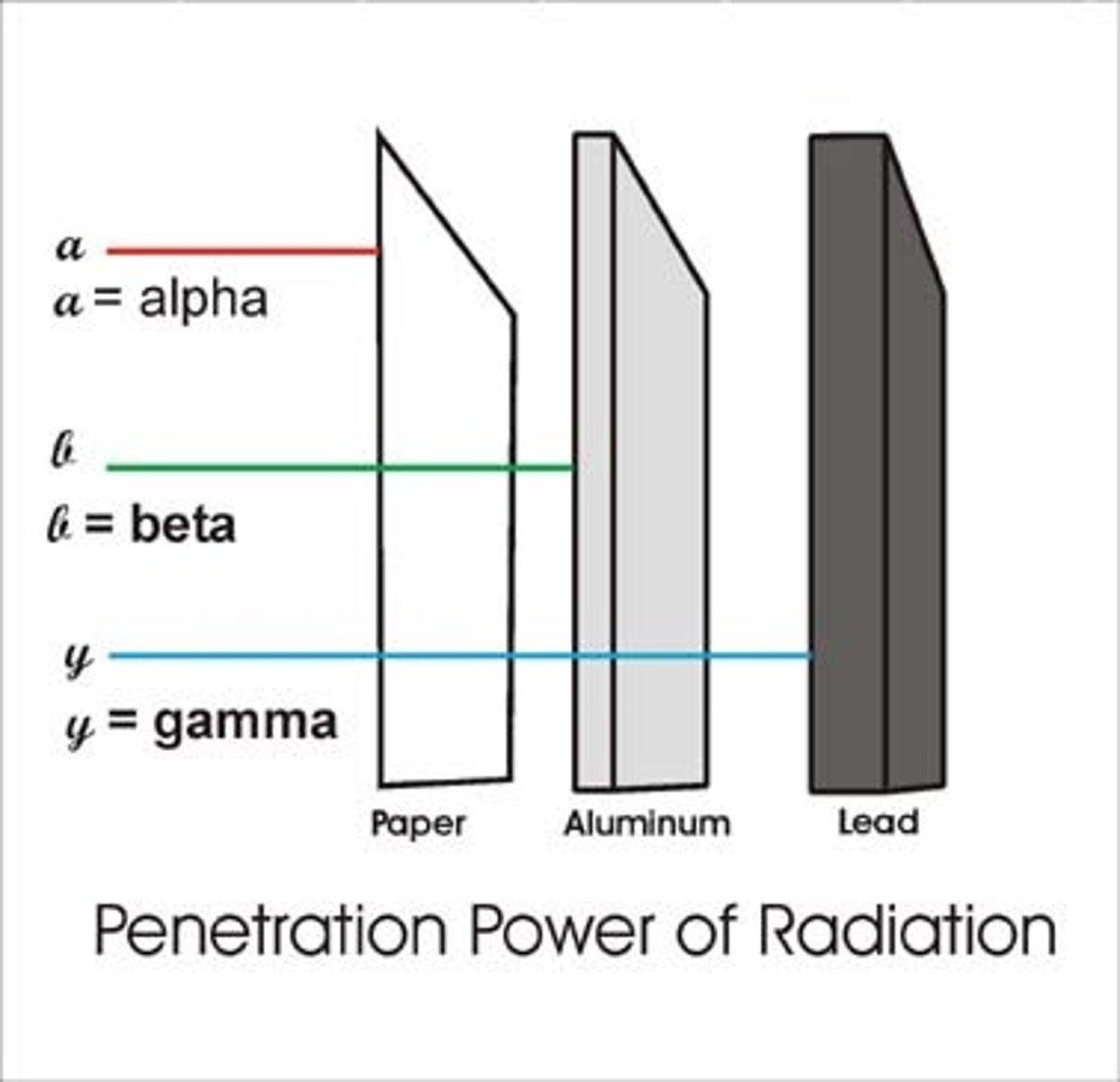
3 types of radiation
alpha , beta and gamma
what is radioactivity?
the result of unstable nuclei emitting energy or a particle to form a more stable nuclei
alpha particle
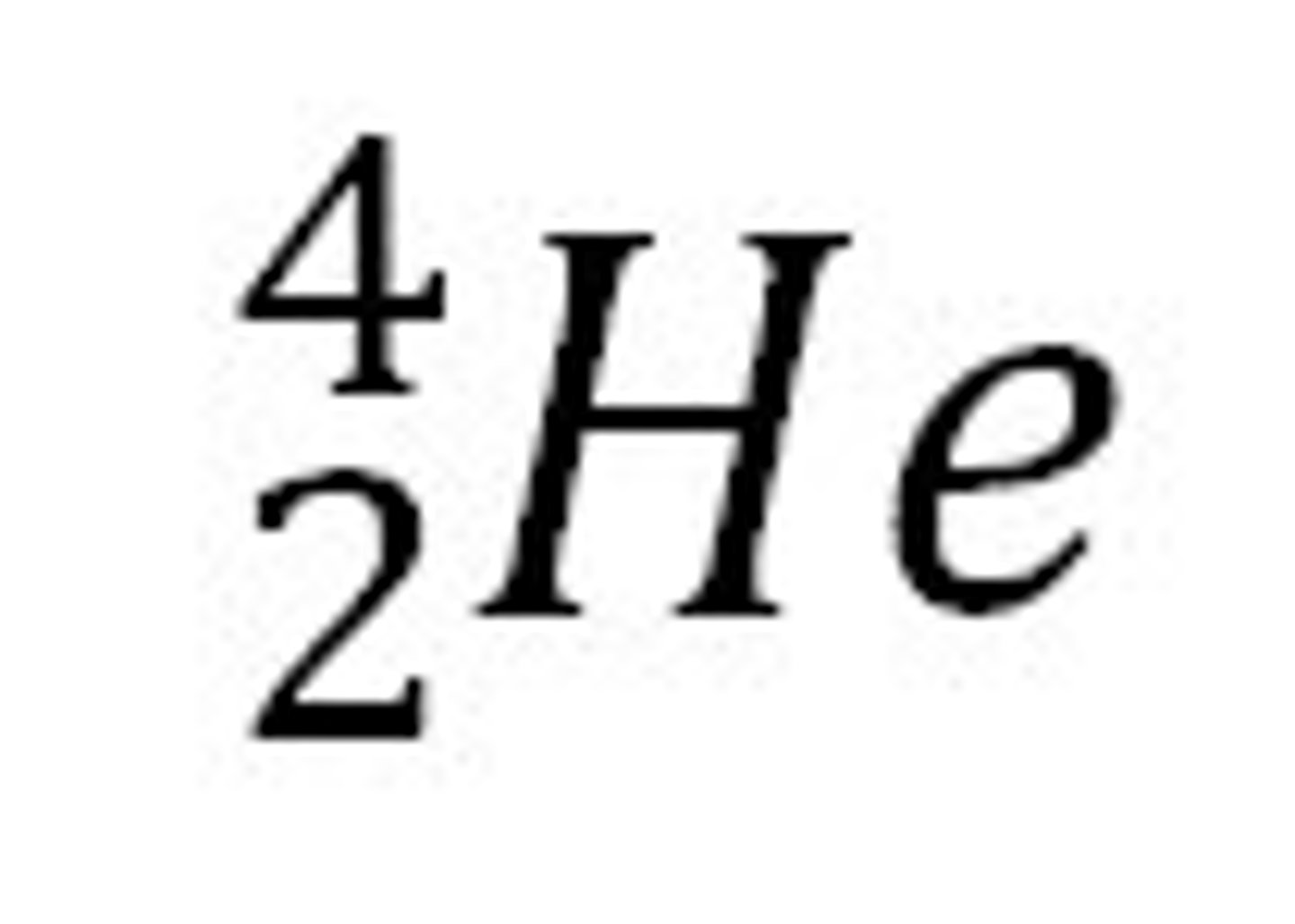
what are alpha particles?
slow moving positively charged particles that come from the nucleus of a radioactive element
what will alpha radiation be stopped by?
a few cm of air or a sheet of paper
beta particle
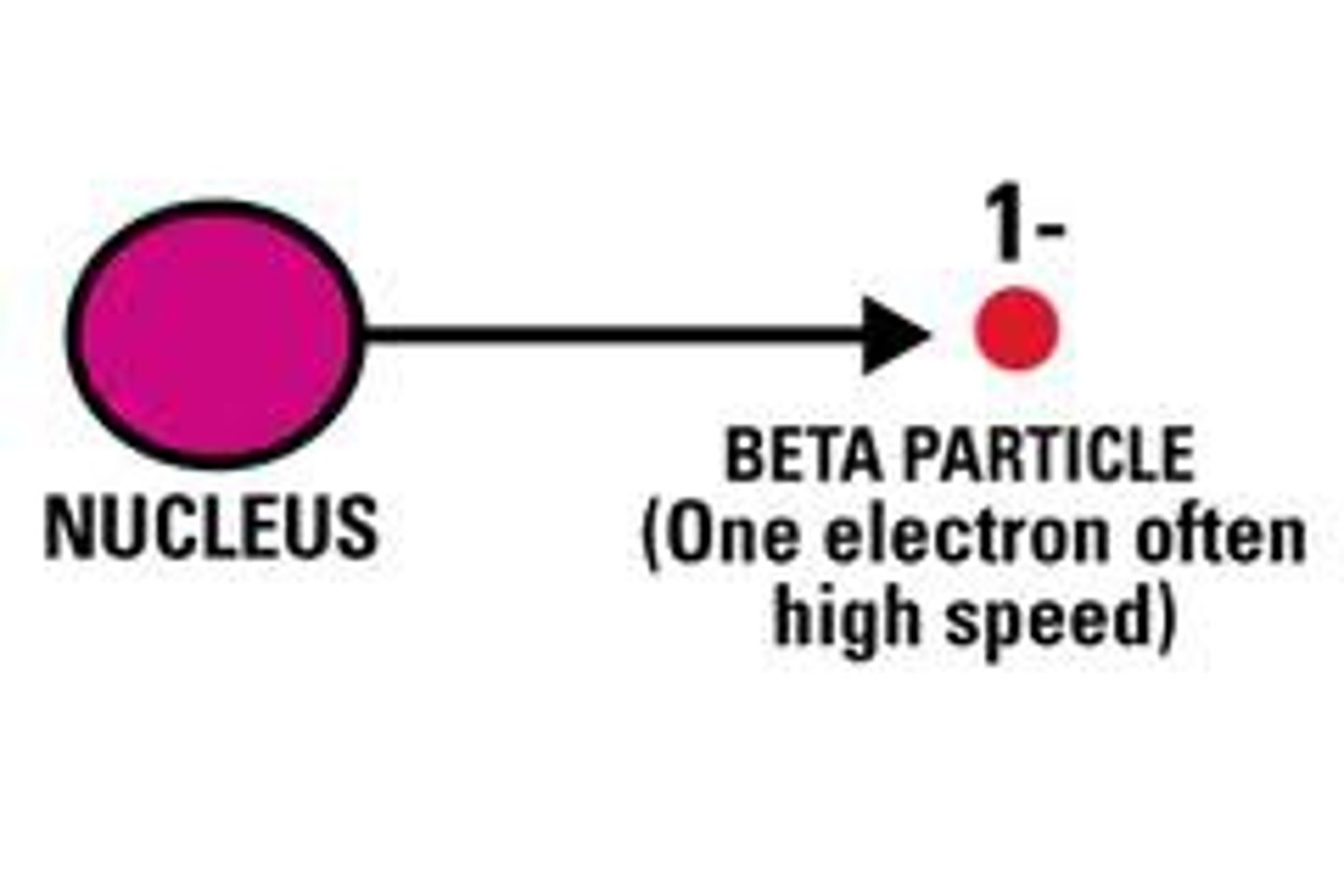
what are beta particles?
fast moving, negatively charged particles that are formed when a neutron from the nucleus splits into a proton and an electron
what will beta radiation is stopped by?
thin metal foil
gamma radiation
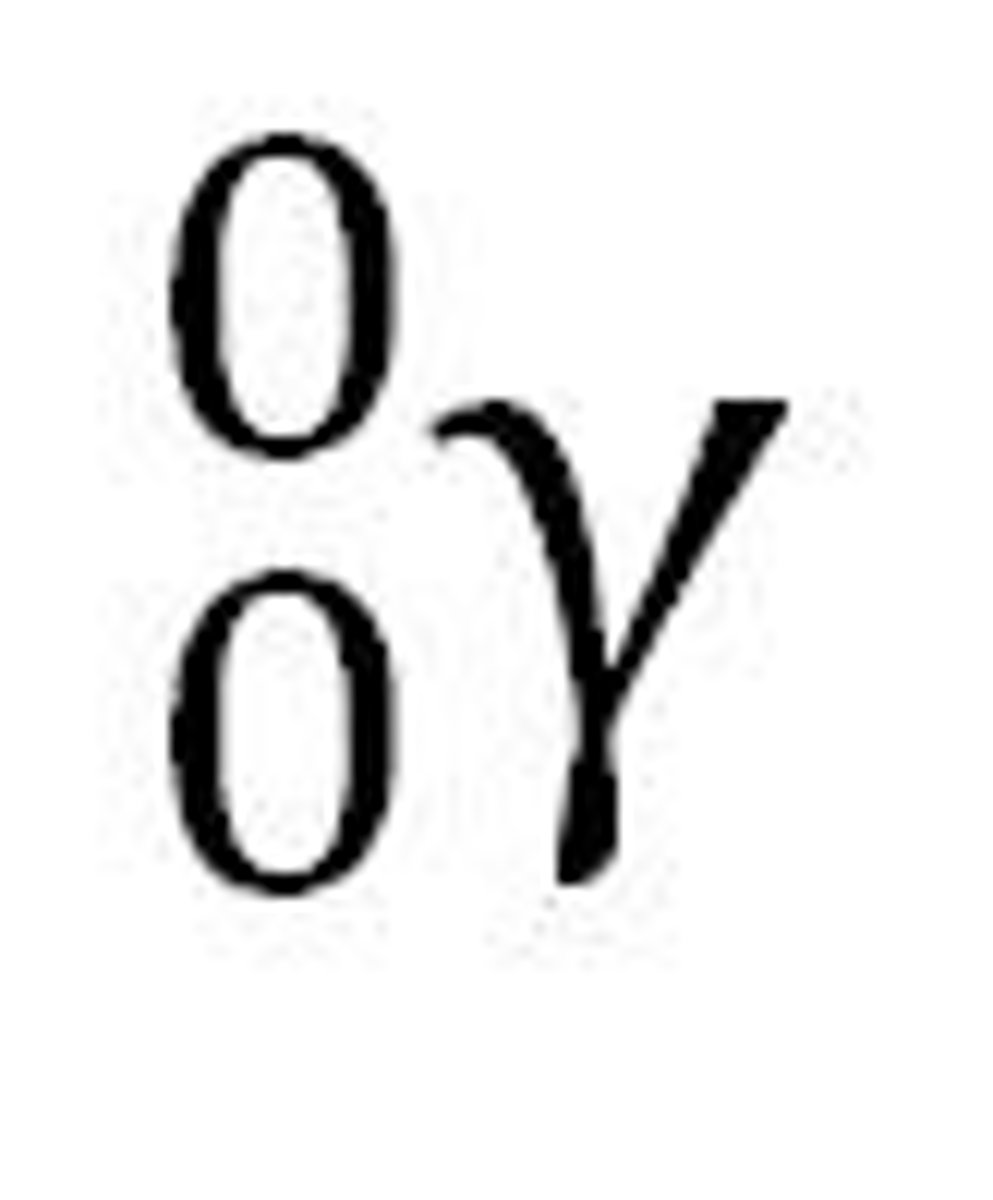
what are gamma waves?
they are non particulate. High energy electromagnetic waves.
penetration of each type of radiation
effect of magnetic field on radioactive elements