2.5: Non constant forces/Circular motion
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Which of the following is true for an object in uniform circular motion?
It has constant speed
Which statement best describes Kepler’s 3rd Law of Planetary Motion?
The closer a planet is to the sun, the shorter the orbital period is.
Which statement best describes Kepler’s 2nd Law of Planetary Motion?
Fast & Furious: Close = fast racing, far = slow cruising, but equal areas in equal times.
Which statement best describes Kepler’s 1st Law of Planetary Motion?
Planetary orbits are in the shape of an ellipse
A man weighing 800 Newtons is standing in an elevator. If the elevator rises with an acceleration of 0.5 meters per second2, the force exerted by the elevator on the man will be
1200N
The weight of an object_______as it moves away from the center of Earth
decreases
The force of gravity on the surface of the Moon is about one-sixth the force of gravity on the surface of Earth. Which describes the relationship of mass and weight of an object on the Moon compared to that on Earth?
Mass is the same, but weight is less on the Moon.
If the radius of the string is .3 meters long and the stopper makes 5 revolutions per second, what is the speed of the stopper? (Hint: C=2πr)
9.4 m/s
What object experiences uniform circular motion?
A car traveling around a roundabout at a constant speed
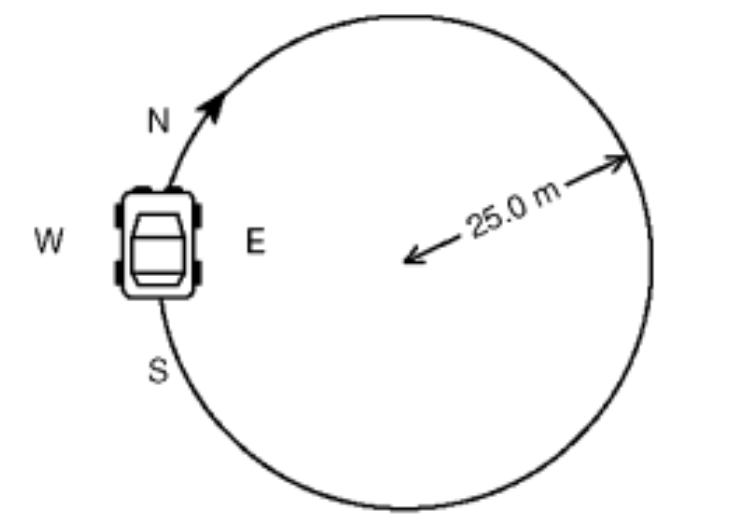
At the instant shown in the diagram, the car's centripetal acceleration is directed-
toward E
What is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal force? Which occurs in a non-rotating frame of reference? Which occurs in a rotating frame of reference?
Centripetal force is real and occurs in a non-rotating frame; centrifugal is fictitious and occurs in a rotating frame.
Centripetal acceleration
Change in velocity direction, points inward, pulls direction toward center (a=v2/ra = v^2/ra=v2/r)
Centripetal force
Real inward force that causes circular motion (F=mv2/rF = mv^2/rF=mv2/r).
Centrifugal force
The “fake” outward force you feel due to inertia when something forces you into circular motion.
Calculate the centripetal force required to make a 5 kg ball move 4 m/s in a circle with a radius of 2 m.
40N
Bruno the bat flies at a speed of 0.5 m/s in circle of radius 1 m. What is his acceleration?
0.25 ms-2
A certain neutron star has a mass of 1.0x10^31 kg packed into a sphere of radius 10000m. What would be the weight of a 100kg person on the star’s surface?
9.8 x 10^12 N
A man standing on a scale in an elevator notices that the scale reads 40 newtons greater than his normal weight. Which type of movement of the elevator could cause this greater-than-normal reading?
accelerating upward
An astronaut has a mass of 100 kg and has a weight of 370 N on Mars. What is the gravitational strength on Mars?
3.7 m/s2
What is the effect of gravitational mass on an object?
It defines the gravitational force between objects
Planets orbit the Sun in a shape called a(n)
ellipse
Captain America and the Avengers follow the Chitauri back to their home planet, Chitauri Prime. If gravity on Chitauri Prime is rumored to be 8.76 m/s2, how much will Captain America weigh there? (Remember, his mass is 86.18 kg)
754.94 N
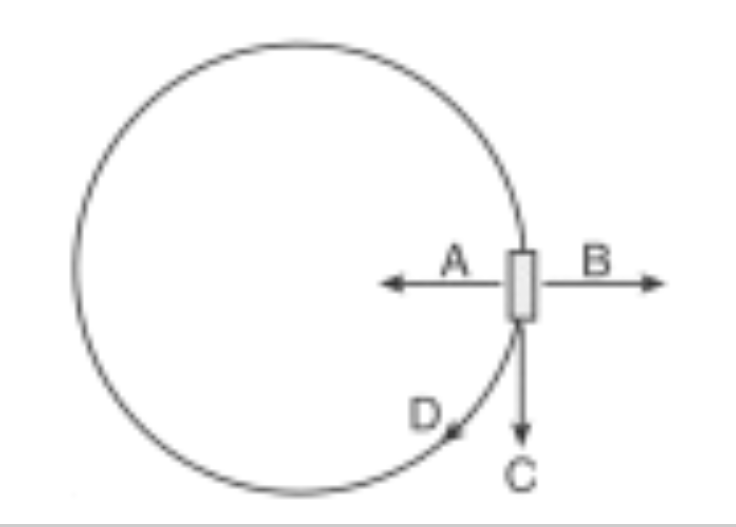
At the position shown in the diagram, which arrow indicates the direction the instantaneous (tangential) velocity of the cart?
C
Elevator accelerating up
fn is greater than objects weight making the person feel heavier (f=ma) (f=fn(up)-fn(rest))
Elevator accelerating down
fn i s smaller, person feels lighter (f=ma)
Uniform circular motion
Constant speed in perfect circle
v and a makes a right angle
Change in direction
v and a make an angle
Causes speed up and change in direction (not uniform circular motion)
Tangential acceleration
It’s how quickly an object speeds up or slows down as it moves along a circle.
It points along the edge (tangent) of the circle, not inward.
👉 Example: A car on a curved racetrack. If the driver hits the gas or brake, that change in speed is tangential acceleration.